ECU CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1859 of 1938

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
When diagnosing electrical problems in the auxil-
iary rear heater or rear A/C system, refer to Group
8W, Wiring Diagrams.
When diagnosing problems in the auxiliary sys-
tems, refer to diagnostic sections for front heater A/C.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AIR DISTRIBUTION DUCT-A/C
REMOVAL
(1) Remove quarter trim panel, D-pillar, and head-
liner (Fig. 8). Refer to Group 23, Body.
(2) Remove screws securing D-pillar duct to quar-
ter panel. Pull duct up and away from unit.
(3) Remove screws securing duct to rear header
(Fig. 9).
(4) Remove screws securing duct to right and left
rails (Fig. 10).
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
AIR DISTRIBUTION DUCT-HEATER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove quarter trim panel and D-pillar (Fig.
8) and (Fig. 11). Refer to Group 23, Body.
(2) Remove screws securing lower heat duct to
housing.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Fig. 7 Rear Blower Switch
Fig. 8 Quarter Trim Panel
Fig. 9 Rear Crossover Duct
Fig. 10 Upper A/C Duct
NSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 43
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1861 of 1938

CAUTION: Do not damage the evaporator insulation
liner during installation.
(3) Carefully install the evaporator and expansion
valve straight into the unit. Do not scratch the seal-
ing surfaces with the plumbing extension tube pilots.
(4) Determine the amount of old refrigerant oil
drained from the evaporator. Add this amount (of
clean refrigerant oil) back into the system.
(5) Carefully align the expansion valve onto the
pilot tubes of the plumbing extension (do not scratch
the sealing surface). Install the bolt through the
plumbing plate into the unit sealing plate. Tighten
bolts to 2363 N´m (200630 inch pounds) torque.
(6) Install evaporator cover and blower scroll.
(7) Install quarter trim panel, evacuate/charge sys-
tem, and perform the performance test.
REAR AIR CONDITIONING LINES
WARNING: THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM MUST
BE COMPLETELY EMPTY BEFORE PROCEEDING
WITH THIS OPERATION.
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist vehicle
(2) Remove compression fittings to the suction and
liquid lines located on the right, outboard side of the
underbody, rearward of the front crossmember. (Fig.
2)
(3) remove (1) bolt securing a/c lines to block
located on the right, outboard side of the underbody,
rearward of the rear wheel and tire. (Fig. 5)
(4) Remove (3) straps securing underbody lines.
(Fig. 1)
(5) Separate and remove a/c lines from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installation, replace all O-rings and gas-
kets. Coat all sealing surfaces with approved wax-
free refrigerant oil. Then, reverse the above
procedures.
(2) Evacuate and recharge system.
REAR HEATER A/C AIR OUTLETS
REMOVAL
Separate barrel from bezel by pulling outward.
INSTALLATION
For installation, push the outlet firmly into the
opening until it locks into place.
REAR HEATER-A/C AUXILIARY CONDENSER
If vehicle is equipped with a 3.3L or 3.8L engine
with rear heater and air conditioning, it will be
equipped with an auxiliary condenser. The auxiliarycondenser is mounted on the primary condenser in
front of the radiator. Both condenser must be
removed as an assembly and then separated.
WARNING: THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM MUST
BE COMPLETELY EMPTY BEFORE PROCEEDING
WITH THIS OPERATION.
NOTE: Special effort must be used to keep all
R-134a system components moisture-free. Moisture
in the oil is very difficult to remove and will cause a
reliability problem with the compressor.
The condenser assembly must first be removed
from vehicle. Refer to CONDENSER ASSEMBLY
removal and installation in this section for service
procedures.
REMOVAL
(1) After condenser assembly removal, place on
bench for disassembly.
(2) Remove (1) bolt to liquid line on auxiliary con-
denser.
(3) Remove (4) attaching bolts and separate auxil-
iary from primary condenser. (Fig. 15)
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installation, replace all O-rings and gas-
kets. Coat all sealing surfaces with approved wax-
free refrigerant oil. Then, reverse the above
procedures.
(2) Evacuate and recharge system.
Fig. 15 3.3L/3.8L REAR HEAT-A/C AUXILIARY
CONDENSER
NSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 45
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1862 of 1938
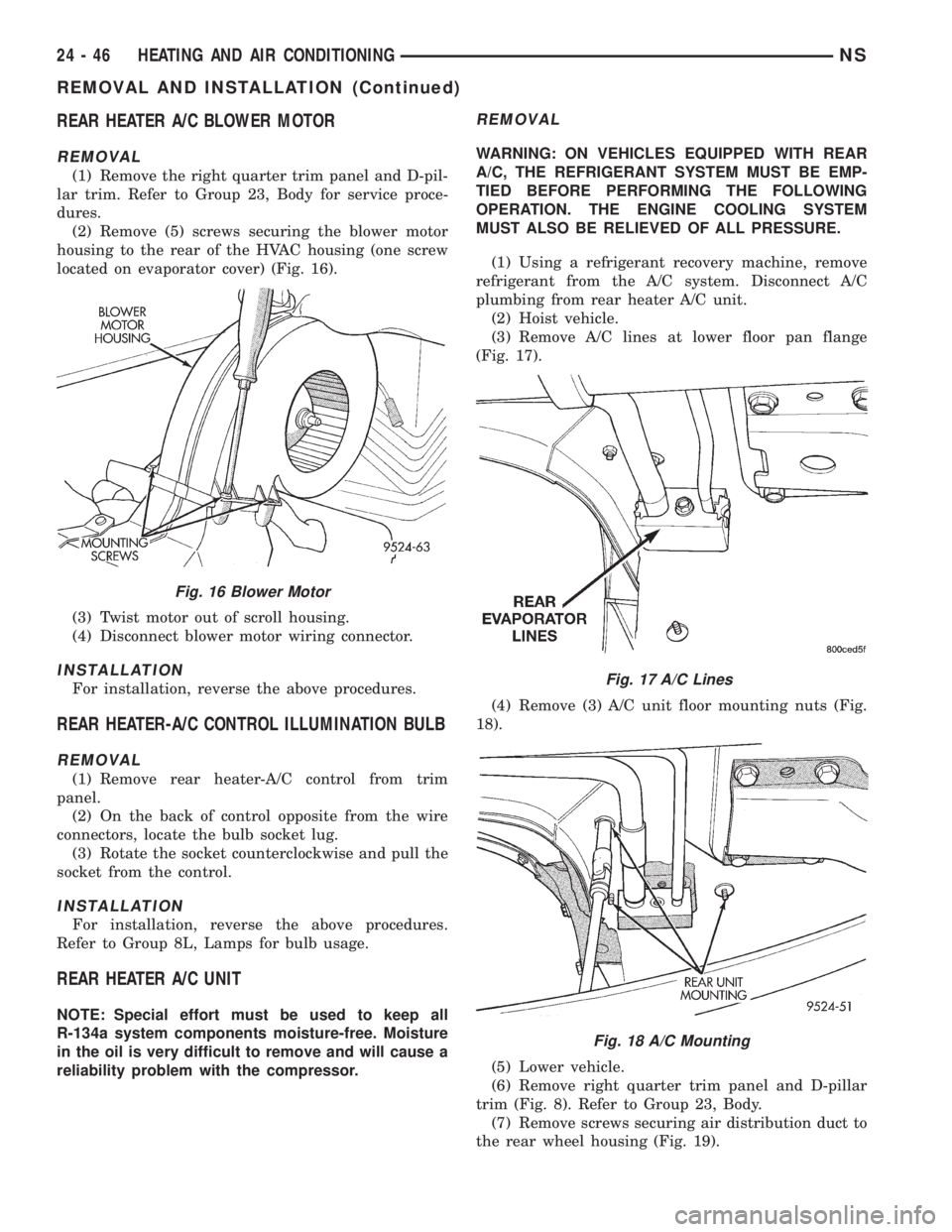
REAR HEATER A/C BLOWER MOTOR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the right quarter trim panel and D-pil-
lar trim. Refer to Group 23, Body for service proce-
dures.
(2) Remove (5) screws securing the blower motor
housing to the rear of the HVAC housing (one screw
located on evaporator cover) (Fig. 16).
(3) Twist motor out of scroll housing.
(4) Disconnect blower motor wiring connector.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
REAR HEATER-A/C CONTROL ILLUMINATION BULB
REMOVAL
(1) Remove rear heater-A/C control from trim
panel.
(2) On the back of control opposite from the wire
connectors, locate the bulb socket lug.
(3) Rotate the socket counterclockwise and pull the
socket from the control.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Refer to Group 8L, Lamps for bulb usage.
REAR HEATER A/C UNIT
NOTE: Special effort must be used to keep all
R-134a system components moisture-free. Moisture
in the oil is very difficult to remove and will cause a
reliability problem with the compressor.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH REAR
A/C, THE REFRIGERANT SYSTEM MUST BE EMP-
TIED BEFORE PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING
OPERATION. THE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
MUST ALSO BE RELIEVED OF ALL PRESSURE.
(1) Using a refrigerant recovery machine, remove
refrigerant from the A/C system. Disconnect A/C
plumbing from rear heater A/C unit.
(2) Hoist vehicle.
(3) Remove A/C lines at lower floor pan flange
(Fig. 17).
(4) Remove (3) A/C unit floor mounting nuts (Fig.
18).
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Remove right quarter trim panel and D-pillar
trim (Fig. 8). Refer to Group 23, Body.
(7) Remove screws securing air distribution duct to
the rear wheel housing (Fig. 19).
Fig. 16 Blower Motor
Fig. 17 A/C Lines
Fig. 18 A/C Mounting
24 - 46 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1865 of 1938

NOTE: If the heater core was emptied and was not
prefilled, it is necessary to thermal cycle the vehicle
TWICE. The heater core is positioned higher than
the radiator fill cap. Therefore the heater core will
not gravity fill to level. To thermal cycle the vehicle,
it must be operated till the thermostat opens, then
turned off and allowed to cool. In order to verify
that the auxiliary unit is filled completely, the follow-
ing procedure can be used:
²Vehicle at room temperature.
²Engine is brought up to operating temperature.
²Front unit is OFF, temperature slides are at full
HEAT position.
²Engine is at idle.
²With rear blower motor ON HIGH
²Discharge air temperature, measured at the
dual register located on the C-pillar base, is between
57ÉC to 62ÉC (135É and 145É F).
REAR HEATER LINES
REMOVAL
NOTE: Review Safety Precautions and Warnings
before proceeding with this operation.
(1) Partially drain engine cooling system. Refer to
Group 7, Engine Cooling.
(2) Loosen clamp at the front end of the hose
located at the right, outboard side of the underbody,
rearward of the front crossmember. (Fig. 2)
(3) Carefully rotate hose back and forth while tug-
ging slightly away from connector nipple. If the hose
will not come off, slice the hose at the connector nip-
ple and peel off heater hose. This method will require
heater hose replacement.
CAUTION: When removing hoses from outlet nip-
ples, do not use excessive force. Outlet nipples
may become damaged and leak engine coolant.
(4) Compress insert in rear heater hose quick con-
nection and pull downward on hose. (Fig. 4)(5) Remove (3) straps securing underbody lines.
(Fig. 1)
(6) Separate and remove rear heater lines from
vehicle.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
MODE DOOR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove A/C unit.
(2) Place unit on bench.
(3) Remove heater core.
(4) Remove blower scroll.
(5) Remove evaporator cover.
(6) Remove A/C line to expansion valve mounting
nut.
(7) Carefully pull evaporator out of housing.
(8) Remove mode door actuator and gear exten-
sion.
(9) Remove Heater-A/C housing clips and screws.
(10) Separate housing halves.
(11) Remove mode door.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove A/C unit.
(2) Place unit on bench.
(3) Remove mode door actuator connector.
(4) Remove mode door actuator mounting screws
and remove actuator.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
NSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 49
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1891 of 1938
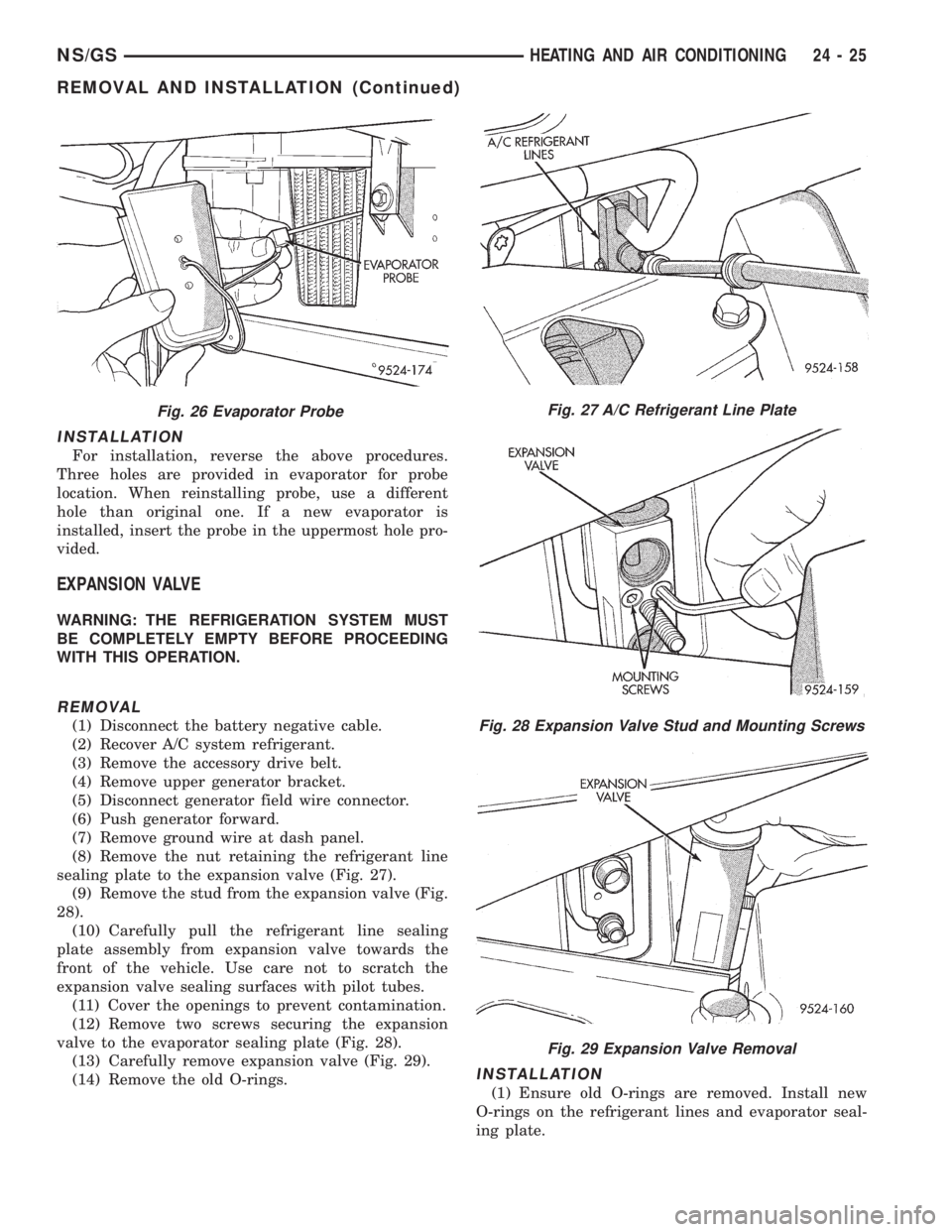
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Three holes are provided in evaporator for probe
location. When reinstalling probe, use a different
hole than original one. If a new evaporator is
installed, insert the probe in the uppermost hole pro-
vided.
EXPANSION VALVE
WARNING: THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM MUST
BE COMPLETELY EMPTY BEFORE PROCEEDING
WITH THIS OPERATION.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Recover A/C system refrigerant.
(3) Remove the accessory drive belt.
(4) Remove upper generator bracket.
(5) Disconnect generator field wire connector.
(6) Push generator forward.
(7) Remove ground wire at dash panel.
(8) Remove the nut retaining the refrigerant line
sealing plate to the expansion valve (Fig. 27).
(9) Remove the stud from the expansion valve (Fig.
28).
(10) Carefully pull the refrigerant line sealing
plate assembly from expansion valve towards the
front of the vehicle. Use care not to scratch the
expansion valve sealing surfaces with pilot tubes.
(11) Cover the openings to prevent contamination.
(12) Remove two screws securing the expansion
valve to the evaporator sealing plate (Fig. 28).
(13) Carefully remove expansion valve (Fig. 29).
(14) Remove the old O-rings.
INSTALLATION
(1) Ensure old O-rings are removed. Install new
O-rings on the refrigerant lines and evaporator seal-
ing plate.
Fig. 26 Evaporator ProbeFig. 27 A/C Refrigerant Line Plate
Fig. 28 Expansion Valve Stud and Mounting Screws
Fig. 29 Expansion Valve Removal
NS/GSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 25
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1892 of 1938

(2) Hand-start the stud into the expansion valve
and torque to7-11N´m(64-96in.lbs.).
(3) Carefully install the expansion valve to the
sealing plate. Install the two screws and tighten 8 to
14 N´m (70 to 130 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Carefully install the refrigerant lines and seal-
ing plate to the expansion valve. Install the nut and
tighten 20 to 26 N´m (170 to 230 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install the ground wire at dash panel.
(6) Pull generator back into the proper position for
bracket mounting.
(7) Install generator field wire connector.
(8) Install the upper generator bracket.
(9) Install accessory drive belt.
(10) Evacuate and recharge system.
(11) After expansion valve is installed, the system
is charged, and leaks have checked repeat the A/C
performance check.
FILTER-DRIER ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM MUST
BE COMPLETELY EMPTY BEFORE PROCEEDING
WITH THIS OPERATION.
(1) Recover A/C system refrigerant.
(2) Remove liquid line at filter-drier (Fig. 21).
(3) Remove the (2) bolts holding filter-drier bracket
to radiator fan module bracket.
(4) Remove the lower liquid line at condenser.
(5) Remove the upper radiator crossmember.
(6) Pull up on radiator and slide filter-drier from
the mounting location.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installation, replace both refrigerant
line O-rings. Then reverse the above procedures.
(2) Evacuate and recharge system.
HEATER A/C UNIT HOUSING
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF EQUIPPED WITH AIR CONDITIONING,
THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM MUST BE COM-
PLETELY EMPTY BEFORE PROCEEDING.
(1) Set parking brake.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Using a refrigerant recovery machine, remove
refrigerant from the A/C system.
(4) Remove wiper module. Refer to Group 8K,
Windshield Wipers and Washers.
(5) Drain engine coolant. Remove heater hoses at
the heater core, refer to Heater Hoses Removal and
Installation procedures. Plug coolant lines.(6) Remove suction and liquid lines at the expan-
sion valve (Fig. 27).
(7) Remove the Instrument Panel Assembly. Refer
to Group 8E, Instrument Panel and Systems.
(8) Remove heater ducts.
(9) Disconnect the two upper mounts from the
upper reinforcement and the lower mount from the
tunnel.
(10) Remove the (3) nuts (in the engine compart-
ment) securing the unit to the dash panel (Fig. 30).
(11) Disconnect the HVAC housing wiring harness.
(12) Pull the entire unit rearward until the studs
on the unit clear the dash panel. Drop the unit down.
Pull it rearward to remove it from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) For installation of the assembly, reverse the
above procedures. Install new O-rings on plumbing
inlets
(2) Evacuate and recharge the A/C system.
(3) Perform HVAC control Calibration Diagnostic
and Cooldown test.
HEATER CORE
REMOVAL
(1) Drain coolant system.
(2) Remove left side lower column cover.
(3) Remove steering column assembly. Refer to
Group 19, Steering for service procedure.
(4) Remove ABS module, bracket and wiring (Fig.
31).
(5) Remove I/P to body harness interconnect and
bracket (Fig. 32).
(6) Remove lower silencer boot at base of steering
shaft (Fig. 33)
(7) Pinch off heater lines under the hood.
Fig. 30 HVAC Bolt-Up
24 - 26 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGNS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1906 of 1938

cranking. Whenever the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) sets a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that
affects vehicle emissions, it illuminates the MIL. If a
problem is detected, the PCM sends a message over
the CCD Bus to the instrument cluster to illuminate
the lamp. The PCM illuminates the MIL only for
DTC's that affect vehicle emissions. The MIL stays
on continuously when the PCM has entered a
Limp-In mode or identified a failed emission compo-
nent or system. The MIL remains on until the DTC
is erased. Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Code
charts in this group for emission related codes.
Also, the MIL either flashes or illuminates contin-
uously when the PCM detects active engine misfire.
Refer to Misfire Monitoring in this section.
Additionally, the PCM may reset (turn off) the MIL
when one of the following occur:
²PCM does not detect the malfunction for 3 con-
secutive trips (except misfire and fuel system moni-
tors).
²PCM does not detect a malfunction while per-
forming three successive engine misfire or fuel sys-
tem tests. The PCM performs these tests while the
engine is operating within6375 RPM of and within
10 % of the load of the operating condition at which
the malfunction was first detected.
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. From
the state display screen, access either State Display
Inputs and Outputs or State Display Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link connec-
tor and access the State Display screen. Then access
Inputs and Outputs. The following list contains the
PCM system functions accessible through the Inputs
and Outputs screen.
Park/Neutral Switch
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
S/C Vent Solenoid
Actual S/C Vent Sol.
S/C Vacuum Solenoid
Actual S/C Vacuum Sol.
S/C Cancel
S/C Last Cutout
S/C Working Status
S/C Denied Status
A/C Clutch Relay
Actual A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Actual EGR Sol.
Automatic Shutdown Relay
Actual Automatic Shutdown Relay
Automatic Shutdown Relay Sense
Radiator Fan Control Module
Actual Radiator Fan Control Module
Duty Cycle EVAP Purge Solenoid
Actual EVAP Purge Sol.
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
Power Steering Switch
Closed Loop State
Current CMP Edge
Current CKP State
Current Sync State
Fuel Pump Relay
Actual Fuel Pump Relay
Ignition Sense (A21)
Malfunction Lamp
Limp-in Reason
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRB scan tool to the vehicle and
access the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following list contains the PCM system
functions accessible through the Sensor Display
screen.
Battery Temperature
Engine Coolant Temperature
Engine Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position Volts
Minimum Throttle
Knock Sensor Volts
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Fig. 1 Data Link (Diagnostic) Connector
25 - 2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1914 of 1938

The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º H20.
The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid as the
system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .020º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pumpdiaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
TRIP DEFINITION
A ªTripº means vehicle operation (following an
engine-off period) of duration and driving mode such
that all components and systems are monitored at
least once by the diagnostic system. The monitors
must successfully pass before the PCM can verify
that a previously malfunctioning component is meet-
ing the normal operating conditions of that compo-
nent. For misfire or fuel system malfunction, the
MIL may be extinguished if the fault does not recur
when monitored during three subsequent sequential
driving cycles in which conditions are similar to
those under which the malfunction was first deter-
mined.
Anytime the MIL is illuminated, a DTC is stored.
The DTC can self erase only when the MIL has been
extinguished. Once the MIL is extinguished, the
PCM must pass the diagnostic test for the most
recent DTC for 40 warm-up cycles (80 warm-up
cycles for the Fuel System Monitor and the Misfire
Monitor). A warm-up cycle can best be described by
the following:
²The engine must be running
²A rise of 40ÉF in engine temperature must occur
from the time when the engine was started
²Engine coolant temperature must reach at least
160ÉF
²A ªdriving cycleº that consists of engine start up
and engine shut off.
Once the above conditions occur, the PCM is con-
sidered to have passed a warm-up cycle. Due to the
conditions required to extinguish the MIL and erase
the DTC, it is most important that after a repair has
been made, all DTC's be erased and the repair veri-
fied.
COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
25 - 10 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1923 of 1938

the amount of EGR supplied to the engine. This pro-
vides the correct amount of exhaust gas recirculation
for different operating conditions.
This system does not allow EGR at idle. The EGR
systems can operate at all coolant temperatures
above 60ÉF as long as the battery ambient tempera-
ture is above 7ÉF.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EGR SYSTEM ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The PCM performs an on-board diagnostic check of
the EGR system. The diagnostic system uses the
electronic EGR transducer for the system tests.
The diagnostic check activates only during selected
engine/driving conditions. When the conditions are
met, the PCM energizes the transducer solenoid to
disable the EGR. The PCM checks for a change in
the heated oxygen sensor signal. If the air-fuel mix-
ture goes lean, the PCM will attempt to enrichen the
mixture. The PCM registers a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) if the EGR system is not operating cor-
rectly. After registering a DTC, the PCM turns on the
malfunction indicator (Check Engine) lamp after 2
consecutive trips. There are 2 types of failures sensed
by the PCM. The first is a short or open in the elec-
trical solenoid circuit. The second is a mechanical
failure or loss of vacuum. The Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) indicates the need for service.
If a problem is indicated by the MIL and a DTC for
the EGR system is set, check for proper operation of
the EGR system. Use the System Test, EGR Gas
Flow Test. If the EGR system tests properly, check
the system using the DRB scan tool. Refer to
On-Board Diagnosis sections in this Group. Also,
refer to the DRB scan tool and the appropriate Pow-
ertrain Diagnostics Procedure manual.
EGR SYSTEM TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE TESTING THE EGR SYS-
TEM.
(1) Check the condition of all EGR system hoses
and tubes for leaks, cracks, kinks and hardening of
rubber hoses. Repair and correct these conditions
before performing any tests.
(2) Be sure the hoses at both the EGR valve and
EGR valve control are connected to the proper fit-
tings (Fig. 4).
(3) Be sure the electrical connector is firmly con-
nected at the valve control.
(4) To check EGR system operation, connect the
DRB scan tool to the 16±way data link connector.
The data link connector is located on the lower edge
of the instrument panel near the steering column.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Pro-
cedures service manual for operation of the DRB
scan tool when diagnosing the EGR system.
(5) After checking the system with the DRB scan
tool, proceed to the following EGR Valve Leakage and
EGR Valve Control Tests and repair as necessary.
Fig. 3 Electric EGR Transducer Assembly
Fig. 4 EGR Value and EGR Value ÐTypical
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 19
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)