engine oil CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1209 of 1938

Total runout should not exceed. 0.051 mm (0.002
inch.) (total indicator reading).
(5) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of the valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15 degrees stone. If the blue is transferred to
the bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a
65 degrees stone.
²Intake valve seat diameter is 33 mm (1.299 in.)
²Exhaust valve seat diameter is 28 mm (1.102
in.)
(6) Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat width
are maintained. The intake valve seat must be ser-
viced when the valve seat width is 2.0 mm (0.079 in.)
or greater. The exhaust valve seat must be serviced
when the valve seat width is 2.5 mm (0.098 in.) or
greater. Otherwise the cylinder head must be
replaced.
(7) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 0.75 to 1.25 mm
(0.030 to 0.049 in.) (Fig. 91).
(8) Check valve tip to spring seat dimensions A
after grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve
tip to 43.51 - 44.57 mm (1.71 - 1.75 in.) for exhaust
valve and 45.01 - 46.07 mm (1.77 - 1.81 in.) for
intake valve over spring seat when installed in the
head (Fig. 92). The valve tip chamfer may need to be
reground to prevent seal damage when the valve is
installed.
CLEANING
Clean all valve guides, valves and valve spring
assemblies thoroughly with suitable cleaning solution
before reassembling.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves using
a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 93). The valve stem seals
should be pushed firmly and squarely over valve
guide.
CAUTION: If oversize valves are used, there is only
one oversize valve available. The same stem seal is
used on both the standard and oversize valve.
(3) Install valve springs and retainers. Compress
valve springs only enough to install locks, taking
care not to misalign the direction of compression.
Nicked valve stems may result from misalignment of
the valve spring compressor.
VALVE SPECIFICATION CHART
Face Angle
Intake and
Exhaust:45 - 45 1/2É
Head Diameter
Intake: 33.12 - 33.37 mm (1.303 - 1.313 in.)
Exhaust: 28.57 - 28.83 mm (1.124 - 1.135 in.)
Length (Overall)
Intake: 114.69 - 115.19 mm (4.515 - 4.535 in.)
Exhaust: 116.94 - 117.44 mm (4.603 - 4.623 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake: 5.934 - 5.952 mm (0.2337 - 0.2344 in.)
Exhaust: 5.906 - 5.924 mm (0.2326 - 0.2333 in.)
Valve Margin
Intake: 1.15 - 1.48 mm (0.0452 - 0.0582 in.)
Exhaust: 1.475 - 1.805 mm (0.0580 - 0.0710 in.)
Fig. 91 Valve Seat Refacing
Fig. 92 Spring Installed Height and Valve Tip to
Spring Seat Dimensions
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 31
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1210 of 1938

CAUTION: When depressing the valve spring
retainers with valve spring compressor the locks
can become dislocated. Check to make sure both
locks are in their correct location after removing
tool.
(4) Check the valve spring installed height B after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 92). Make sure mea-
surements are taken from top of spring seat to the
bottom surface of spring retainer. If height is greater
than 40.18 mm (1.58 in.), install a 0.762 mm (0.030
in.) spacer under the valve spring seat to bring
spring height back within specification.
(5) Install rocker arm shafts as previously
described in this section.
(6) Checking dry lash. Dry lash is the amount of
clearance that exists between the base circle of an
installed cam and the rocker arm roller when the
adjuster is drained of oil and completely collapsed.
Specified dry lash is 1.17 mm (0.046 in.) for intake
and 1.28 mm (0.050 in.) for exhaust. After performing
dry lash check, refill adjuster with oil and allow 10
minutes for adjuster/s to bleed down before rotating
cam.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER HEAD AND CAMSHAFT JOURNALS
INSPECTING CYLINDER HEAD
Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm (0.004
inch) (Fig. 94).
Inspect cylinder head camshaft bearings for wear.
Check camshaft journals for scratches and worn
areas. If light scratches are present, they may be
removed with 400 grit sand paper. If deep scratches
are present, replace the camshaft and check the cyl-
inder head for damage. Replace the cylinder head if
worn or damaged. Check the lobes for pitting and
wear. If the lobes show signs of wear, check the cor-
responding rocker arm roller for wear or damage.Replace rocker arm/hydraulic lash adjuster if worn or
damaged. If lobes show signs of pitting on the nose,
flank or base circle; replace the camshaft.
CLEANING
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block. Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
OIL PUMP
(1) Clean all parts thoroughly. Mating surface of
the oil pump should be smooth. Replace pump cover
if scratched or grooved.
(2) Lay a straightedge across the pump cover sur-
face (Fig. 95). If a 0.076 mm (0.003 inch.) feeler
gauge can be inserted between cover and straight
edge, cover should be replaced.
(3) Measure thickness and diameter of outer rotor.
If outer rotor thickness measures 7.64 mm (0.301
inch.) or less (Fig. 96), or if the diameter is 79.95 mm
(3.148 inches) or less, replace outer rotor.
Fig. 93 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
Fig. 94 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
Fig. 95 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
9 - 32 ENGINENS/GS
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1211 of 1938
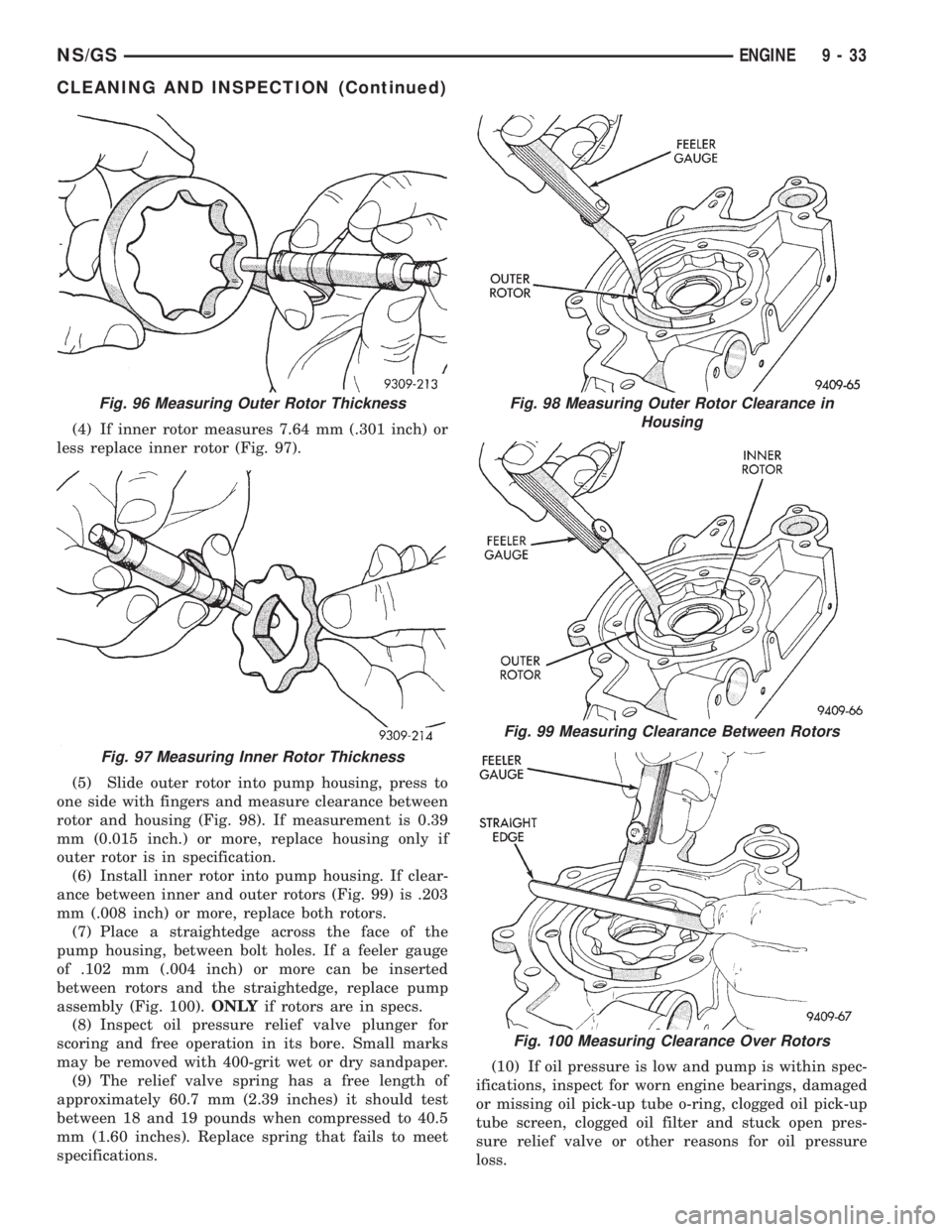
(4) If inner rotor measures 7.64 mm (.301 inch) or
less replace inner rotor (Fig. 97).
(5) Slide outer rotor into pump housing, press to
one side with fingers and measure clearance between
rotor and housing (Fig. 98). If measurement is 0.39
mm (0.015 inch.) or more, replace housing only if
outer rotor is in specification.
(6) Install inner rotor into pump housing. If clear-
ance between inner and outer rotors (Fig. 99) is .203
mm (.008 inch) or more, replace both rotors.
(7) Place a straightedge across the face of the
pump housing, between bolt holes. If a feeler gauge
of .102 mm (.004 inch) or more can be inserted
between rotors and the straightedge, replace pump
assembly (Fig. 100).ONLYif rotors are in specs.
(8) Inspect oil pressure relief valve plunger for
scoring and free operation in its bore. Small marks
may be removed with 400-grit wet or dry sandpaper.
(9) The relief valve spring has a free length of
approximately 60.7 mm (2.39 inches) it should test
between 18 and 19 pounds when compressed to 40.5
mm (1.60 inches). Replace spring that fails to meet
specifications.(10) If oil pressure is low and pump is within spec-
ifications, inspect for worn engine bearings, damaged
or missing oil pick-up tube o-ring, clogged oil pick-up
tube screen, clogged oil filter and stuck open pres-
sure relief valve or other reasons for oil pressure
loss.
Fig. 96 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
Fig. 97 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
Fig. 98 Measuring Outer Rotor Clearance in
Housing
Fig. 99 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
Fig. 100 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 33
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 1213 of 1938

Cylinder Block
Diameter................20.998 - 21.003 mm
(0.8267 - 0.8269 in.)
End Play............................None
Length.....74.75 - 75.25 mm (2.943 - 2.963 in.)
Piston Rings
Ring Gap Top Compression Ring . . 0.23 - 0.52 mm
(0.009 - 0.020 in.)
Ring Gap 2nd Compression Ring . . 0.49 - 0.78 mm
(0.019 - 0.031 in.)
Ring Gap Oil Control
(Steel Rails) . . . 0.23 - 0.66 mm (0.009 - 0.026 in.)
Ring Side Clearance Both Compression
Rings....0.025 - 0.065 mm (0.0010 - 0.0026 in.)
Oil Ring (Pack).............0.004 - 0.178 mm
(0.0002 - 0.0070 in.)
Ring Width Compression Rings . . . 1.17 - 1.19 mm
(0.046 - 0.047 in.)
Oil Ring (Pack).............2.854 - 3.008 mm
(0.1124 - 0.1184 in.)
Connecting Rod
Bearing Clearance...........0.026 - 0.059 mm
(0.001 - 0.0023 in.)
Piston Pin Bore Diameter.....20.96 - 20.98 mm
(0.8252 - 0.8260 in.)
Large End Bore Diameter . . . 50.991 - 51.005 mm
(2.0075 - 2.0081 in.)
Side Clearance . 0.13 - 0.38 mm (0.005 - 0.015 in.)
Total Weight (Less Bearing) . 543 grams (1.20 lbs.)
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal
Diameter . .
47.9924 - 48.0076 mm (1.8894 - 1.8900 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.).....0.0035 mm (0.0001 in.)
Taper (Max.)...........0.0038 mm (0.0001 in.)
Main Bearing Diametrical Clearance
No.1-5 ..0.022 - 0.062 mm (0.0008 - 0.0024 in.)
End Play....0.09 - 0.24 mm (0.0035 - 0.0094 in.)
Main Bearing Journals
Diameter..............51.9924 - 52.0076 mm
(2.0469 - 2.0475 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.).....0.0035 mm (0.0001 in.)
Taper (Max.)...........0.0038 mm (0.0001 in.)
ENGINE 2.0L SOHC
Rocker Arm Shaft
Rocker Arm Shaft Diameter . . 19.996 ± 19.984mm
(0.786 ± 0.7867 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft Retainers (Width)
Intake (All)...............28.46 mm (1.12 in.)
Exhaust.............1&529.20 mm (1.14in.)
2, 3, and 4 - 40.45 mm (1.59 in.)
Rocker Arm/Hydraulic Lash Adjuster *
Rocker Arm Inside Diameter . . 20.00 ± 20.02 mm
(0.787 ± 0.788 in.)Rocker Arm Shaft Clearance . . . 0.016 ± 0.054 mm
(0.0006 ± 0.0021 in.)
Body Diameter...........22.949 ± 22.962 mm
(0.9035 ± 0.9040 in.)
Plunger Travel Minimum (Dry).........2.2mm
(0.087 in.)
Rocker Arm Ratio...................1.4to1
Cylinder Head Camshaft Bearing Diameter
No.1 ....41.20 ± 41.221 mm (1.622 ± 1.6228 in.)
No.2 ......41.6 ± 41.621 mm (1.637 ± 1.638 in.)
No.3 ......42.0 ± 42.021 mm (1.653 ± 1.654 in.)
No.4 ......42.4 ± 42.421 mm (1.669 ± 1.670 in.)
No.5 .....42.8 ± 42.821 mm (1.685 ± 1.6858 in.)
Camshaft Journal Diameter
No. 1 . . . 41.128 ± 41.147 mm (1.619 ± 1.6199 in.)
No.2 ....41.528 ± 41.547 mm (1.634 ± 1.635 in.)
No.3 ....41.928 ± 41.947 mm (1.650 ± 1.651 in.)
No.4 ....42.328 ± 42.374 mm (1.666 ± 1.668 in.)
No. 5 . . . 42.728 ± 42.747 mm (1.682 ± 1.6829 in.)
Diametrical Bearing Clearance . 0.053 ± 0.093 mm
(0.0027 ± 0.003 in.)
Max. Allowable...........0.12 mm (0.0047 in.)
End Play..........0.05 ± 0.39 mm (0.0059 in.)
Lift (Zero Lash )
Intake...................7.2mm(0.283 in.)
Exhaust.................7.03 mm (0.277 in.)
Valve Timing Exhaust Valve**
Closes (ATDC)........................5.4É
Opens (BBDC).......................43.7É
Duration...........................229.1É
Valve Timing Intake Valve **
Closes (ABDC).......................41.1É
Opens (ATDC)........................13.9É
Duration...........................207.2É
Valve Overlap..........................0É
Cylinder Head
Material....................Cast Aluminum
Gasket Thickness (Compressed).......1.15 mm
(0.045 in.)
Valve Seat
Angle................................45É
Runout (Max.)..............0.050 mm (0.002)
Width (Finish) Intake and
Exhaust.....0.75 ± 1.25 mm (0.030 ± 0.049 in.)
Valve Guide Finished
Diameter I.D. . 5.975 ± 6.000 mm (.235 ± .236 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter (Std.).....11.0±11.02 mm
(0.4330 ± 0.4338 in.)
Valves
Face Angle Intake and Exhaust.....45±45-1/2É
Head Diameter Intake.......32.12 ± 33.37 mm
(1.303 ± 1.313 in.)
Head Diameter Exhaust......28.57 ± 28.83 mm
(1.124 ± 1.135 in.)
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 35
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 1214 of 1938

Valve Margin
Intake.....1.15 ± 1.48 mm (0.0452 ± 0.0582 in.)
Exhaust....1.475 ± 1.805 mm (0.058 ± 0.071 in.)
Valve Length (Overall)
Intake....114.69 ± 115.19 mm (4.515 ± 4.535 in.)
Exhaust . . 109.59 ± 110.09 mm (4.603 ± 4.623 in.)
Valve Stem Tip Height
Intake.......45.01 ± 46.07 mm (1.77 ± 1.81 in.)
Exhaust......43.51 ± 44.57 mm (1.71 ± 1.75 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake.....5.934 ± 5.952 mm (0.234 ± 0.234 in.)
Exhaust....5.906 ± 5.924 mm (0.233 ± 0.233 in.)
Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake . . . 0.048 ± 0.066 mm (0.0018 ± 0.0025 in.)
Exhaust . 0.0736 ± 0.094 mm (0.0029 ± 0.0037 in.)
Max. Allowable Intake.....0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Max. Allowable Exhaust....0.101 mm (0.004 in.)
Valve Springs
Free Length (Approx.)......44.4 mm (1.747 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve closed) . 91 N´m @ 39.8 mm
(67 ft. lbs. @ 1.57 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve open) . 239 N´m @ 32.6 mm
(176 lbs. @ 1.28 in.)
Installed Height..........40.18 mm (1.580 in.)
* SERVICE AS AN ASSEMBLY WITH ROCKER
ARM.
** ALL READINGS IN CRANKSHAFT DEGREES,
AT 0.5 mm (0.019 in.) OF VALVE LIFT.
TORQUE CHART 2.0L SOHC
DESCRIPTION...................TORQUE
Camshaft Sensor Pick Up
Bolts...................9.6N´m(85in.lbs.)
Camshaft Sprocket
Bolt....................115N´m(85ft.lbs.)
Connecting Rod Cap
Bolts.........27N´m(20ft.lbs.) Plus 1/4 Turn
CollarÐOil Pan to Transaxle
Step 1: Collar to Oil Pan Bolts . 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.)
Step 2: Collar to Transaxle
Bolts...................108N´m(80ft.lbs.)
Step 3: Collar to Oil Pan
Bolts....................54N´m(40ft.lbs.)
Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap/Bedplate
M8 Bedplate Bolts..........30N´m(22ft.lbs.)
M11 Main Cap Bolts........81N´m(60ft.lbs.)
Crankshaft Damper
Bolt...................142N´m(105 ft. lbs.)
Cylinder Head
Bolts.......Refer To Cylinder Head Installation
Cylinder Head Cover
Bolts...................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Engine Mount BracketÐRight
Bolts....................61N´m(45ft.lbs.)DESCRIPTION...................TORQUE
Engine Mounting
Bolts.......Refer to Engine Mount Installation
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder Head
Bolts...................23N´m(200 in. lbs.)
Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield
Bolts...................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Intake Manifold
Bolts...................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Oil Filter Adapter
Fastener.................80N´m(60ft.lbs.)
Oil Filter.................20N´m(15ft.lbs.)
Oil Pan
Bolts...................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Drain Plug...............27N´m(20ft.lbs.)
Oil Pump Attaching
Bolts...................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Cover Fastener . . . 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Pick-up Tube Bolt . 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Relief Valve Cap . . . 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.)
Rocker Arm Shaft
Bolts...................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Spark Plugs...............28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
Thermostat Housing
Bolts...................23N´m(200 in lbs.)
Timing Belt Cover
Bolts M6................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Timing Belt Mechanical Tensioner Assembly
Bolts...................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Timing Belt Hydraulic Tensioner
Pulley Bolt...............68N´m(50ft.lbs.)
Pivot Bracket Bolt..........31N´m(23ft.lbs.)
Tensioner Bolts............31N´m(23ft.lbs.)
Water Pump Mounting
Bolts...................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
SPECIAL TOOLS
ENGINE 2.0L SOHC
Puller 1026
9 - 36 ENGINENS/GS
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 1218 of 1938

2.5L VM DIESEL
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION................ 41
GENERAL SPECIFICATION............... 40
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
LUBRICATION SYSTEM.................. 41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL....... 44
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE..... 43
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS................... 47
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CHANGING ENGINE OIL AND FILTER....... 47
CHECKING OIL LEVEL................... 47
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY................ 50
FITTING PISTON RING.................. 50
TIMING PROCEDURE................... 49
VALVE AND SEAT REFACING............. 49
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT........................... 62
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS.................. 63
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS........... 63
CRANKSHAFTÐREMOVAL............... 72
CYLINDER HEAD....................... 55
CYLINDER HEAD COVER................ 54
CYLINDER LINER...................... 72
ENGINE ASSEMBLY..................... 53
ENGINE MOUNTÐFRONT................ 51
ENGINE MOUNTÐREAR................. 52
ENGINE MOUNTÐRIGHT................ 51
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS................... 60
INJECTION PUMP...................... 61
MOUNTÐLEFT SIDE.................... 51
OIL FILTER ADAPTER AND OIL COOLER.... 68
OILPAN .............................. 66OIL PUMP............................ 67
OIL PUMP PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE...... 67
PISTONS AND CONNECTING ROD......... 68
REAR CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL............ 72
ROCKER ARMS AND PUSH RODS......... 54
TIMING GEAR COVER................... 61
TIMING GEAR COVER OIL SEAL........... 61
VACUUM PUMP........................ 68
VALVE SPRINGSÐCYLINDER HEAD NOT
REMOVED.......................... 55
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGSÐHEAD OFF . . 60
VIBRATION DAMPER.................... 61
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS................... 73
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CRANKSHAFT......................... 77
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING............ 77
CYLINDER HEAD....................... 75
CYLINDER HEAD COVERS............... 74
CYLINDER LINER...................... 78
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS................... 76
OILPAN .............................. 78
OIL PUMP............................ 76
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD.......... 76
ROCKER ARMS AND PUSH RODS......... 74
TIMING GEAR COVER................... 75
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS............ 76
SPECIFICATIONS
2.5L VM DIESEL........................ 78
TORQUE............................. 80
SPECIAL TOOLS
2.5L VM DIESEL........................ 81
GENERAL INFORMATION
GENERAL SPECIFICATION
Type ........................425CLIEE (36B)
Displacement...................2.5L (2499 cc)
Bore.............................92.00 mm
Stroke............................94.00 mm
Compression Ratio....................20.95:1
Vacuum at Idle..........600mm/Hg (23.6 In/Hg)
Thermostat Opening................80ÉC62ÉC
Generator Rating............Bosch 50/120 Amp
Cooling System Capacity..............9.5Liter
Power Steering Capacity.............0.75 LiterType ........................425CLIEE (36B)
Engine Oil Capacity.....6.5Liters With Oil Filter
Change
Timing System . Pushrod Operated Overhead valves,
With Gear-Driven Camshaft.
Air Intake........................DryFilter
Fuel Feed...........Vacuum Pump Incorporated
in Injection Pump.
Fuel System.............Indirect Fuel Injection
(Precombustion Chamber)
Combustion Cycle....................4Stroke
Cooling System..................Water Cooled
Injection Pump.......Rotary Pump Electronically
Controlled.
9 - 40 ENGINENS/GS
Page 1219 of 1938

Type ........................425CLIEE (36B)
Lubrication . Pressure Lubrication by Rotary Pump,
Full-Flow Filtration
Engine Rotation....Clockwise Viewed From Front
Cover
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
The engine model code (3-digit number/letter code)
and serial number are stamped on the forward facing
side of the engine block (Fig. 1).
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
LUBRICATION SYSTEM
The pressurized system (Fig. 2) uses a rotary pump
(3) located in the front of the engine block, driven by
a gear which meshes directly with the crankshaft
gear. All the oil sent to every lubricated part is fil-
tered. The pump sends the oil through a pressure
relief valve (2) to the filter (7) and through galleries
in the crankcase to the crankshaft bearings (8), cam-
shaft bearings (11) and turbocharger (10). The piston
pins, connecting rod small ends and insides of the
pistons are lubricated and cooled by oil sprayed out
from jets (9) in the crankshaft mounting blocks. The
lubricating oil is sent to the rockers (12) through anexternal pipe (Fig. 3). A valve in the filter cartridge
enables the oil to be circulated even when the car-
tridge is clogged.
Sump inlet (1). Pressure relief valve (2). Oil pump
(3). Oil cooler (6). Filter cartridge (7). Crankshaft
bearings (8). Jet valve (9). Turbocharger bearings
(10). Camshaft bearings (11). Rockers (12).
Fig. 2 Lubrication System
Fig. 1 Engine Code Location
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 41
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1222 of 1938
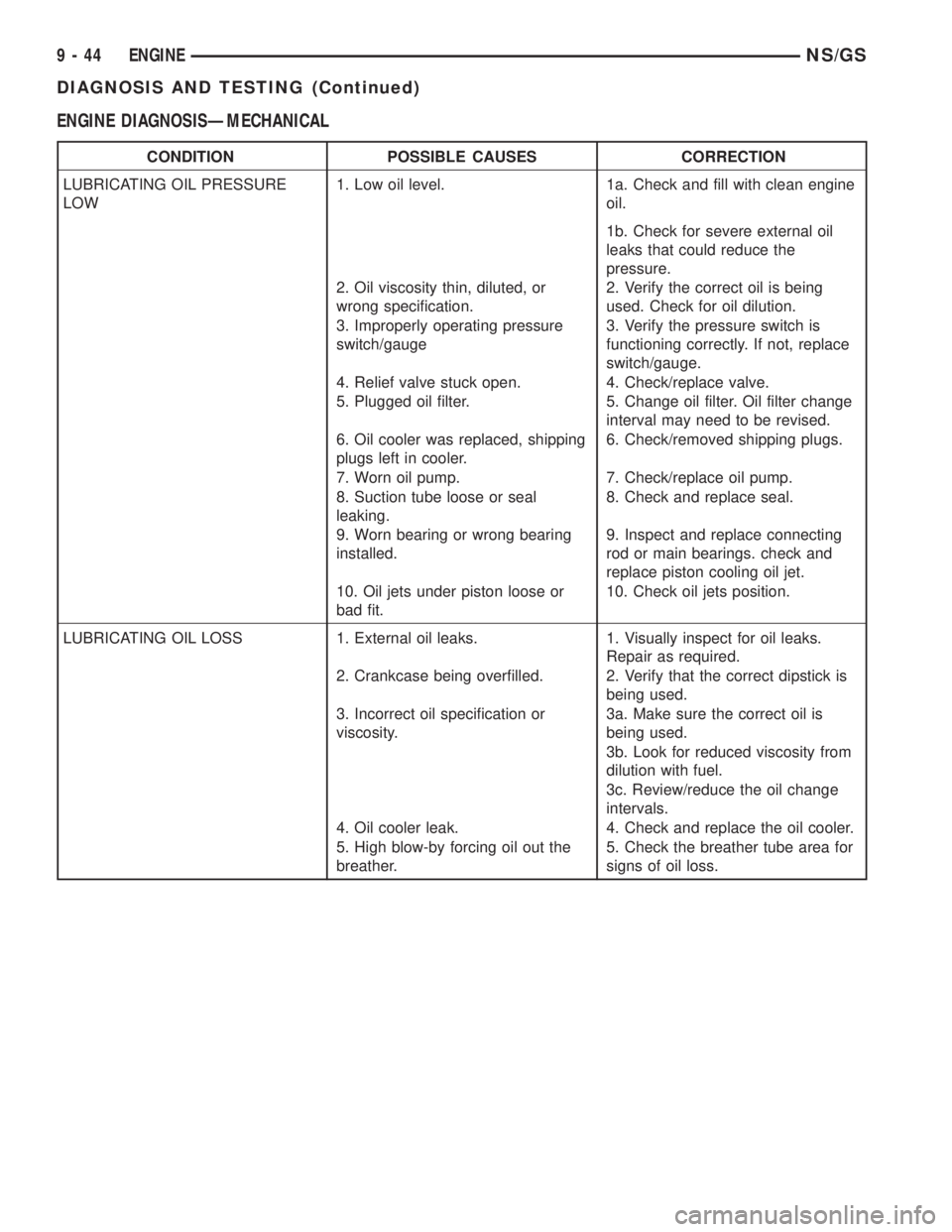
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LUBRICATING OIL PRESSURE
LOW1. Low oil level. 1a. Check and fill with clean engine
oil.
1b. Check for severe external oil
leaks that could reduce the
pressure.
2. Oil viscosity thin, diluted, or
wrong specification.2. Verify the correct oil is being
used. Check for oil dilution.
3. Improperly operating pressure
switch/gauge3. Verify the pressure switch is
functioning correctly. If not, replace
switch/gauge.
4. Relief valve stuck open. 4. Check/replace valve.
5. Plugged oil filter. 5. Change oil filter. Oil filter change
interval may need to be revised.
6. Oil cooler was replaced, shipping
plugs left in cooler.6. Check/removed shipping plugs.
7. Worn oil pump. 7. Check/replace oil pump.
8. Suction tube loose or seal
leaking.8. Check and replace seal.
9. Worn bearing or wrong bearing
installed.9. Inspect and replace connecting
rod or main bearings. check and
replace piston cooling oil jet.
10. Oil jets under piston loose or
bad fit.10. Check oil jets position.
LUBRICATING OIL LOSS 1. External oil leaks. 1. Visually inspect for oil leaks.
Repair as required.
2. Crankcase being overfilled. 2. Verify that the correct dipstick is
being used.
3. Incorrect oil specification or
viscosity.3a. Make sure the correct oil is
being used.
3b. Look for reduced viscosity from
dilution with fuel.
3c. Review/reduce the oil change
intervals.
4. Oil cooler leak. 4. Check and replace the oil cooler.
5. High blow-by forcing oil out the
breather.5. Check the breather tube area for
signs of oil loss.
9 - 44 ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1223 of 1938
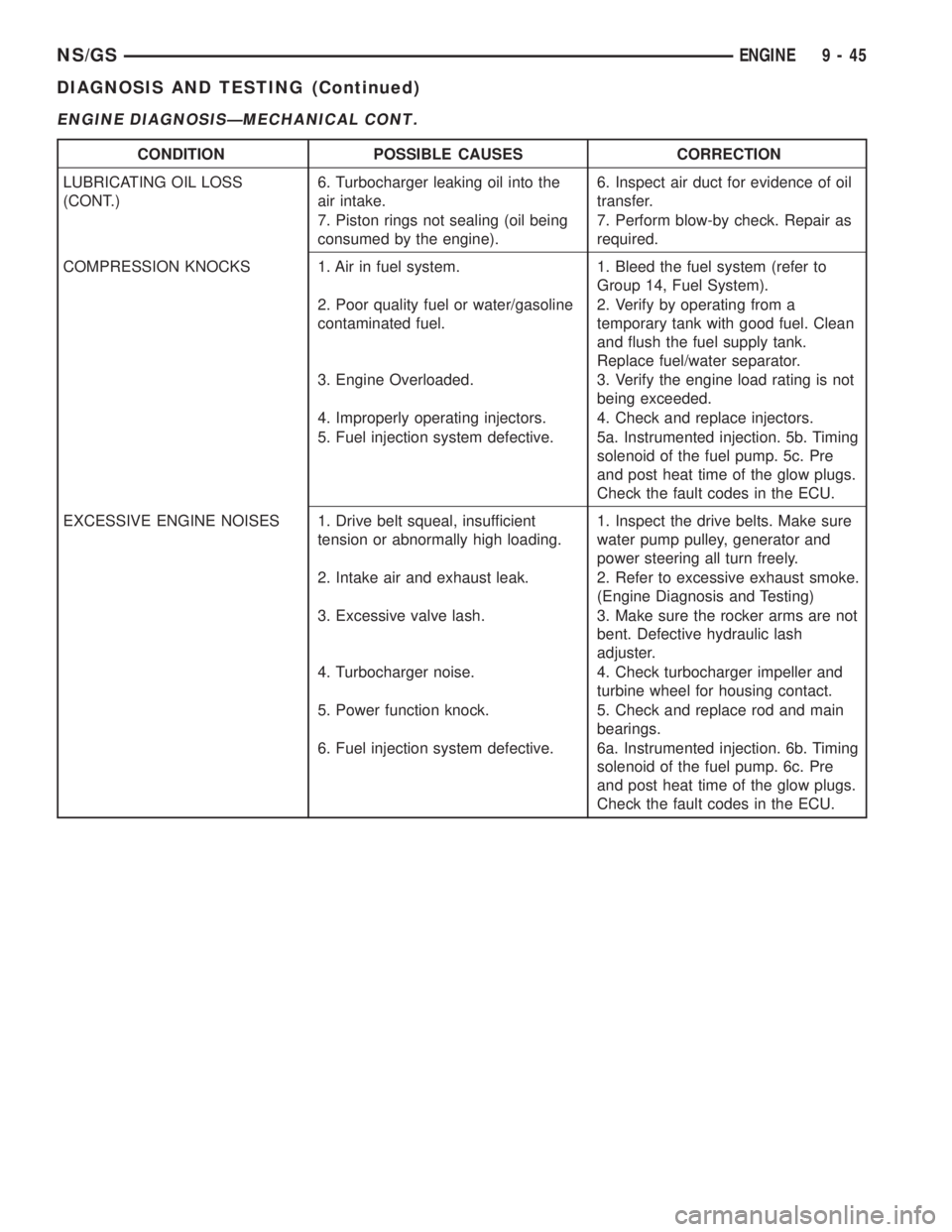
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL CONT.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LUBRICATING OIL LOSS
(CONT.)6. Turbocharger leaking oil into the
air intake.6. Inspect air duct for evidence of oil
transfer.
7. Piston rings not sealing (oil being
consumed by the engine).7. Perform blow-by check. Repair as
required.
COMPRESSION KNOCKS 1. Air in fuel system. 1. Bleed the fuel system (refer to
Group 14, Fuel System).
2. Poor quality fuel or water/gasoline
contaminated fuel.2. Verify by operating from a
temporary tank with good fuel. Clean
and flush the fuel supply tank.
Replace fuel/water separator.
3. Engine Overloaded. 3. Verify the engine load rating is not
being exceeded.
4. Improperly operating injectors. 4. Check and replace injectors.
5. Fuel injection system defective. 5a. Instrumented injection. 5b. Timing
solenoid of the fuel pump. 5c. Pre
and post heat time of the glow plugs.
Check the fault codes in the ECU.
EXCESSIVE ENGINE NOISES 1. Drive belt squeal, insufficient
tension or abnormally high loading.1. Inspect the drive belts. Make sure
water pump pulley, generator and
power steering all turn freely.
2. Intake air and exhaust leak. 2. Refer to excessive exhaust smoke.
(Engine Diagnosis and Testing)
3. Excessive valve lash. 3. Make sure the rocker arms are not
bent. Defective hydraulic lash
adjuster.
4. Turbocharger noise. 4. Check turbocharger impeller and
turbine wheel for housing contact.
5. Power function knock. 5. Check and replace rod and main
bearings.
6. Fuel injection system defective. 6a. Instrumented injection. 6b. Timing
solenoid of the fuel pump. 6c. Pre
and post heat time of the glow plugs.
Check the fault codes in the ECU.
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 45
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1225 of 1938

HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending unit. The pressure should be
between 3.5 bars to 5.0 bars at 4000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these 2 condi-
tions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length which
allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake side
of oil pump through which air can be drawn will cre-
ate the same tappet action. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the pump cover,
including the relief valve retainer cap. When tappet
noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent or
constant, and usually more than 1 tappet will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
operate the engine at fast idle. Run engine for a suf-
ficient time to allow all of the air inside the tappets
to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3) Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak down around the unit plunger or by the
plunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder.
The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click iscaused by a tappet check valve not seating or by for-
eign particles becoming wedged between the plunger
and the tappet body. This will cause the plunger to
stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the
valve stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either
case, tappet assembly should be removed for inspec-
tion and cleaning.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
ing the noise. In general, if more than one tappet
seems to be noisy, its probably not the tappets.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CHECKING OIL LEVEL
To assure proper engine lubrication, the engine oil
must be maintained at the correct level. Check the
oil level at regular intervals, such as every fuel stop.
The best time to check the oil level is about 5 min-
utes after a fully warmed-up engine is shut off, or
before starting the vehicle after it has sat overnight.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground, will improve the accuracy of the oil level
readings (Fig. 4).
CHANGING ENGINE OIL AND FILTER
Change engine oil and filter at mileage and time
intervals described in the Maintenance Schedule.
Fig. 4 Checking Engine Oil
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 47
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)