service CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1099 of 1938

PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
REMOVAL
NOTE: Cylinder Head must be removed before Pis-
tons and Rods. Refer to Cylinder Head Removal in
this section.
(1) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a reli-
able ridge reamer before removing pistons from cyl-inder block.Be sure to keep tops of pistons
covered during this operation. Mark piston with
matching cylinder number (Fig. 90).
(2) Remove oil pan. Scribe the cylinder number on
the side of the rod and cap (Fig. 91) for identification.
(3) Pistons have a directional stamping in the
front half of the piston facing towards thefrontof
engine.
(4) Pistons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. Rotate crankshaft so that
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
(5) Remove Balance Shaft Assembly. Refer to Bal-
ance Shaft Removal in this section.
(6) Remove connecting rod cap bolts. Push each
piston and rod assembly out of cylinder bore.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(7) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod.
(8) Piston and Rods are serviced as an assembly.INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, be sure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap.
Fig. 88 Front Crankshaft SealÐInstallation
Fig. 89 Crankshaft SprocketÐInstallation
Fig. 90 Piston Markings
Fig. 91 Identify Connecting Rod to Cylinder
NS2.4L ENGINE 9 - 49
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1101 of 1938

(4) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and
inspect carefully for damage or wear.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Assemble pump, using new parts as required.
Install the inner rotor with chamfer facing the
cast iron oil pump cover.
(2) Prime oil pump before installation by filling
rotor cavity with engine oil.
(3) Install cover and tighten screws to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.).
CAUTION: Oil pump pressure relief valve must be
installed as shown in (Fig. 95) or serious damage
may occur.
(4) Install relief valve, spring, gasket and cap as
shown in (Fig. 95). Tighten cap to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.)
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER HEAD
CLEANING
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block. Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
INSPECTION
(1) Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm
(0.004 inch) (Fig. 96).
(2) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for scoring.
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(2) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 97). Refer to Valve Guide SpecificationChart. Replace guides if they are not within specifi-
cation.
(3) Check valve guide height (Fig. 98).
VALVE AND VALVE SPRING
VALVES
(1) Clean valves thoroughly and discard burned,
warped and cracked valves.
(2) Measure valve stems for wear. Measure stem
about 60 mm beneath the valve lock grooves.
Fig. 96 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
Fig. 97 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
VALVE GUIDE SPECIFICATION CHART
Valve Guide Diameter
Intake and
Exhaust Valve:5.975 - 6.000 mm
(0.2352 - 0.2362 in.)
Valve Guide Clearance
New Service
Limit
Intake Valve: 0.048 - 0.066 mm
(0.0018 - 0.0025 in.)
0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)
Exhaust Valve: 0.0736 - 0.094 mm
(0.0029 - 0.0037 in.)
Fig. 98 Valve Guide Height
NS2.4L ENGINE 9 - 51
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1111 of 1938

3.0L ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE COMPONENTS.................. 61
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER......... 61
ENGINE LUBRICATION................... 61
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE......... 62
SERVICE PROCEDURES
AUTO LASH ADJUSTER................... 62
CHECKING CRANKSHAFT END PLAY........ 65
FITTING CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS...... 63
FITTING MAIN BEARING.................. 63
VALVE SERVICE RECONDITION............ 66
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT SEAL....................... 72
CAMSHAFT............................ 71
CRANKSHAFT.......................... 81
CYLINDER HEAD COVER................. 70
CYLINDER HEAD........................ 73
ENGINE ASSEMBLY...................... 69
ENGINE MOUNTS....................... 68
FRONT CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL............ 83OIL FILTER AND ADAPTOR................ 84
OILPAN ............................... 77
OIL PUMP............................. 84
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD........... 78
REAR CRANKSHAFT SEAL................ 83
ROCKER ARMS......................... 72
TIMING BELT........................... 75
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFTS.............. 85
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER BORE........................ 87
CYLINDER HEAD........................ 86
OIL PUMP............................. 87
TIMING BELT........................... 86
ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE MOUNTS....................... 88
SPECIFICATIONS
3.0L ENGINE........................... 89
TORQUE CHART 3.0L.................... 90
SPECIAL TOOLS
3.0L ENGINE........................... 91
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block just below the cylinder
head (Fig. 1).
ENGINE LUBRICATION
System is a full flow filtration, pressure feed type.
The oil pump is mounted behind the timing belt
cover. The pump inner rotor is driven by the crank-
shaft. The engine oil pan contains a baffle plate to
control oil level fluctuation during engine operation.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
BLOCK:The cylinder block is a light weight
design created by reducing thickness in many parts
and a short 10 mm (3/8 in.) block skirt. High rigidity
is provided with ribs cast in the outer wall, a full
length water jacket, and a mono-block or beam type,
main bearing cap. This single unit four bearing cap
is designed to control vibration of the cylinder block
partition walls.
CRANKSHAFT:A six throw, five weight crank-
shaft is supported by four main bearings with num-
ber three being the thrust bearing. The six separate
connecting rod throws pins reduce torque fluctua-tions while a torsional vibration damper is used to
control torsion caused vibration of the crankshaft.
Rubber lipped seals are used at front and rear. The
Fig. 1 Engine Identification
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 61
Page 1112 of 1938

front seal is retained in the oil pump case and the
rear is retained in a block-mounted housing.
PISTONS:Are aluminum alloy with a steel strut,
short height, and thin wall so as to be autothermic
and light weight. The piston head with valve
recesses, in combination with the cylinder head,
forms a compact spherical head with clearance for
total valve lift with pistons at top dead center. The
piston skirt, top and second ring lands are finished to
a tapered roughness for oil retention and high resis-
tance to scuffing. Piston pins, pressed into place, join
the pistons to the connecting rods.
CYLINDER HEAD:The alloy cylinder heads fea-
ture cross-flow type intake and exhaust ports. Valve
guides and inserts are hardened cast iron. Valves of
heat resistance steel are arranged in a V with each
camshaft on center. To improve combustion speed the
chambers are a compact spherical design with a
squish area of approximately 30 percent of the piston
top area. The cylinder heads are common to either
cylinder bank by reversing the direction of installa-
tion.
CAMSHAFTS:Two overhead camshafts provide
valve actuation, one front (radiator side of cylinder
bank) and one rear. The front camshaft is provided
with a distributor drive and is longer. Both cam-
shafts are supported by four bearing journals, thrust
for the front camshaft is taken at journal two and
the rear at journal three. Front and rear camshaft
driving sprockets are interchangeable. The sprockets
and the engine water pump are driven by a single
notched timing belt.
ROCKER ARM SHAFTS:The shafts are retained
by the camshaft bearing journal caps. Four shafts are
used, one for each intake and exhaust rocker arm
assembly on each cylinder head. The hollow shafts
provide a duct for lubricating oil flow from the cylin-
der head to the valve mechanisms.
ROCKER ARMS:Are of light weight die-cast with
roller type follower operating against the cam shaft.
The valve actuating end of the rocker arms are
machined to retain hydraulic lash adjusters, elimi-
nating valve lash adjustment.
VALVES:Are made of heat resistant steel, valve
springs are especially designed to be short. The valve
spring wire cross-section is oval shaped and provides
the same spring tension as longer springs. Valve
spring retainers, locks and seals are conventional.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The aluminum alloy mani-
fold is a cross type with long runners to improve
inertia. The runners, attaching below at the cylinder
head, also attach above and support an air plenum.
The air plenum chamber absorbs air pulsations cre-
ated during the suction phase of each cylinder.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS:Both manifolds are a
log style made of ductile cast iron. Exhaust gasses,collected from the front cylinder bank, leave the front
manifold through an end outlet and are fed through
an upper crossover tube to the rear manifold. The
collected exhaust from both manifolds are combined,
and exit to the exhaust pipe through an articulated
joint.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
Check oil pressure using gauge at oil pressure
switch location. Oil pressure should be 41 kPa ( 6
psi.) at idle or 241 to 517 kPa (35 to 75 psi.) at 3000
RPM.
(1) Remove pressure sending unit and install oil
pressure gauge. (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not Run
engine at 3000 RPM.
(2) Warm engine at high idle until thermostat
opens.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
AUTO LASH ADJUSTER
The automatic lash adjusters are precision units
installed in machined openings in the valve actuating
ends of the rocker arms. Do not disassemble the auto
lash adjuster.
FUNCTION CHECK
Check auto adjusters for free play by inserting a
small wire through the air bleed hole in the rocker
arm andvery lightlypushing the auto adjuster ball
check down (Fig. 3). While lightly holding the check
ball down move the rocker up and down to check for
free play. If there is no play replace the adjuster.
Fig. 2 Checking Engine Oil Pressure
9 - 62 3.0L ENGINENS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1113 of 1938

FITTING CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
CONNECTING ROD CLEARANCE
(1) Following procedures specified in the Standard
Service Procedures Section for Measuring Main Bear-
ing Clearance and Connecting Rod Bearing Clear-
ance (Fig. 4). Refer to Connecting Rod Specification
Chart.
(2) Tighten nuts to 52 N´m (38 ft. lbs.).
(3) Remove connecting rod cap and measure Plas-
tigage (Fig. 4).
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft or the Plasti-
gage may be smeared.
CONNECTING ROD SIDE CLEARANCE
Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 5). Refer to Connecting Rod Specifica-
tion Chart.
FITTING MAIN BEARING
INSPECTION
Visually check the main and connecting rod bear-
ing journals for wear, scuffs or scoring and replace if
necessary.
CRANKSHAFT OIL CLEARANCEÐ
MECHANICAL MEASUREMENT
Measure the journal outside diameter and the
main bearing inside diameter (Fig. 6) & (Fig. 7). If
the clearance exceeds the specifications limit, replace
the main bearing(s) and if necessary replace the
crankshaft. Refer to Crankshaft Clearance Specifica-
tion Chart.
PLASTIGAGE MEASUREMENT
(1) Remove oil from journal and bearing shell.
(2) Install crankshaft.
(3) Cut plastigage to same length as width of the
bearing and place it in parallel with the journal axis
(Fig. 8).
Fig. 3 Auto Lash AdjusterÐFunction Check
Fig. 4 Connecting RodÐChecking Bearing
Clearance
Fig. 5 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance
CONNECTING ROD SPECIFICATION CHART
Connecting Rod Bearing Oil Clearance
New Part: 0.018 - 0.036 mm
(0.0007 - 0.0014 in.)
Connecting Rod Side Clearance
New Part: 0.10 - 0.25 mm
(0.004 - 0.010 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.4 mm (0.015 in.)
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 63
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1114 of 1938

CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft or the plasti-
gage will be smeared.
(4) Install the main bearing cap carefully and
tighten the bolts to specified torque.(5) Carefully remove the bearing cap and measure
the width of the plastigage at the widest part using
the scale on the plastigage package (Fig. 9). Refer to
Crankshaft Clearance Specification Chart for proper
clearances. Also see Measuring Main and Connecting
Rod Bearing Clearance in Standard Service Proce-
dures.
CRANKSHAFT BEARING INSTALLATION
When the bearings need replacing, select and
install the proper bearing by the following procedure.
(1) Measure the crankshaft journal diameter and
confirm its classification from the following. In the
case of a bearing supplied as a service part, its iden-
tification color is painted at the position show in (Fig.
10).
NOTE: Service replacement parts have identifica-
tion marks, but factory-assembled parts have no
identification marks. Service crankshaft identifica-
tion may have marks or paint at counterweights.
Refer to Crankshaft Size Classification Chart.
Fig. 6 Measure Crankshaft Journal O.D.
Fig. 7 Measure Main Bearing I.D.
CRANKSHAFT SPECIFICATION CHART
Crankshaft End-Play
New Part: 0.05 - 0.25 mm
(0.002 - 0.001 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.30 mm (0.012 in.)
Main Bearing Oil Clearance
New Part: 0.018 - 0.036 mm
(0.0007 - 0.0014 in.)
Wear Part: 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
Crankshaft Main Bearing Journal
Standard Diameter: 59.980 mm (2.361 in.)
Crankshaft Connecting Rod Journal
Standard Diameter: 50.00 mm (1.968 in.)
Fig. 8 Measure Oil Clearance with Plastigage
Fig. 9 Measuring Clearance
9 - 64 3.0L ENGINENS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1115 of 1938

CHECKING CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
(1) Mount a dial indicator to front of engine, locat-
ing probe on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 11).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move crankshaft all the way to the front and
read the dial indicator. Refer to Crankshaft Specifi-
cation Chart.
CRANKSHAFT SIZE CLASSIFICATION CHART
SIZE NEW CURRENT
MAIN JOURNAL
59.982 - 59.988 mm
(2.3615 - 2.3617 in.)2 WHITE
ENAMEL
59.988 - 59.994 mm
(2.3617 - 2.3620 in.)1 NONE
59.994 - 60.000 mm
(2.3620 - 2.3622 in.)0 YELLOW
ENAMEL
CONNECTING ROD JOURNAL
49.980 - 49.985 mm
(1.9677 - 1.9679 in.)III WHITE
ENAMEL
49.985 - 49.995 mm
(1.9679 - 1.9683 in.)II NONE
49.995 - 50.000 mm
(1.9683 - 1.9685 in.)I YELLOW
ENAMEL
Fig. 10 Bearing Identification
Fig. 11 Checking Crankshaft End Play
CRANKSHAFT SPECIFICATION CHART
Crankshaft End-Play
New Part: 0.05 - 0.25 mm
0.002 - 0.001 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.30 mm (0.012 in.)
Main Bearing Oil Clearance
New Part: 0.018 - 0.036 mm
(0.0007 - 0.0014 in.)
Wear Part: 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
Crankshaft Main Bearing Journal
Standard Diameter: 59.980 mm (2.361 in.)
Crankshaft Connecting Rod Journal
Standard Diameter: 50.00 mm (1.968 in.)
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 65
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1116 of 1938

VALVE SERVICE RECONDITION
(1) With suitable valve spring compressor, remove
spring retainer locks, retainer, valve spring, spring
seat and valve (Fig. 12).
(2) Remove valve stem seals with suitable tool
(Fig. 13). Do not reuse valve stem seals.
VALVES
(1) Check valve stem tip for pitting or depression
at point A (Fig. 14).
(2) Check for wear and ridge wear at Point B.
(3) Check for even contact (at face center) with
valve seat, Point C.
(4) Check margin (Fig. 14). Replace valve if mar-
gin is out of specification. Refer to Valve Specification
Chart.
(5) Check valve guide height (Fig. 15).
(6) Measure valve stem to guide clearance. Refer
to Valve Specification Chart.
(7) Measure Valve spring free length and square-
ness (Fig. 16). Refer to Valve Specification Chart.
Fig. 12 Remove Valves
Fig. 13 Remove Valve Stem Seals
Fig. 14 Valve Inspection
Fig. 15 Valve Guide Height
9 - 66 3.0L ENGINENS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1117 of 1938
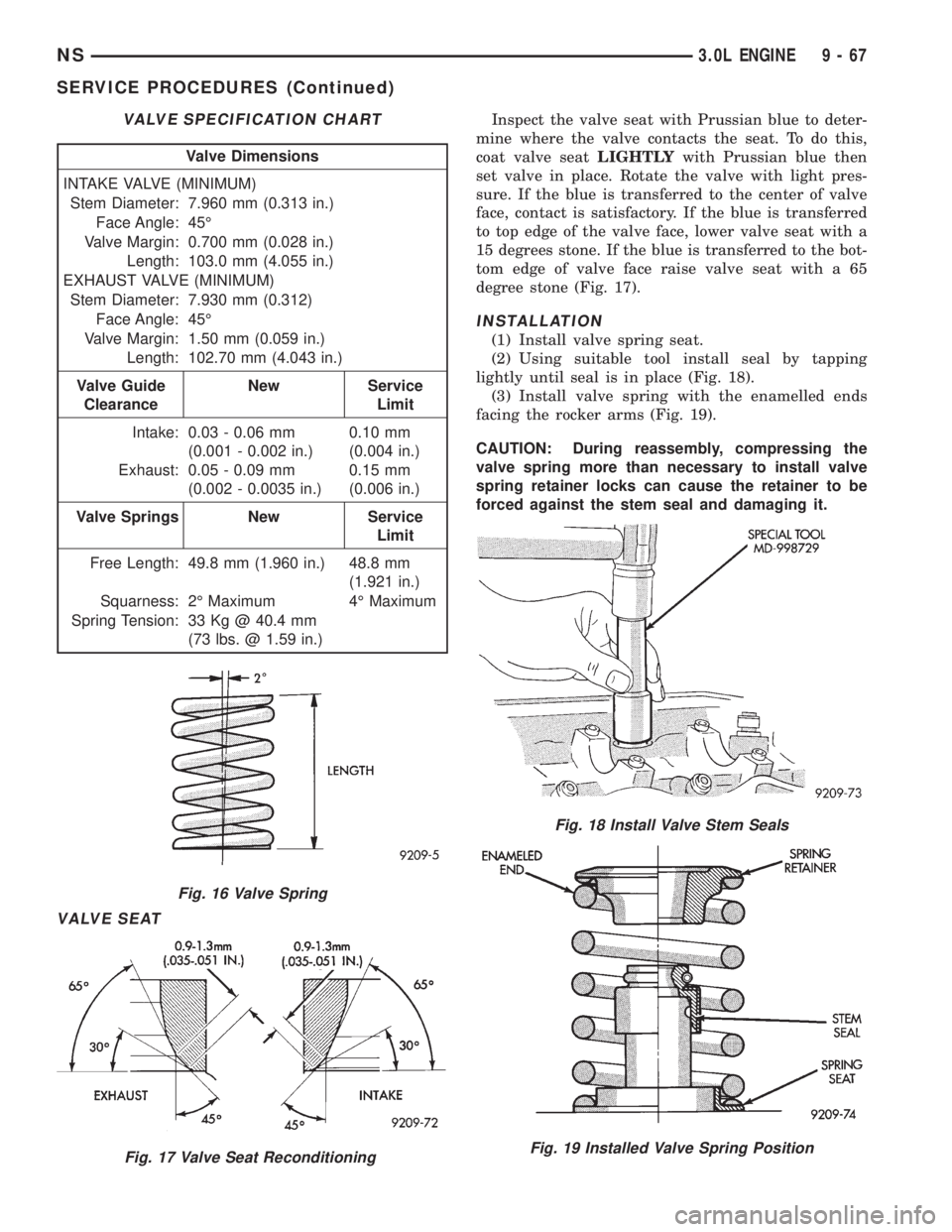
VALVE SEAT
Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to deter-
mine where the valve contacts the seat. To do this,
coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue then
set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light pres-
sure. If the blue is transferred to the center of valve
face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is transferred
to top edge of the valve face, lower valve seat with a
15 degrees stone. If the blue is transferred to the bot-
tom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 65
degree stone (Fig. 17).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install valve spring seat.
(2) Using suitable tool install seal by tapping
lightly until seal is in place (Fig. 18).
(3) Install valve spring with the enamelled ends
facing the rocker arms (Fig. 19).
CAUTION: During reassembly, compressing the
valve spring more than necessary to install valve
spring retainer locks can cause the retainer to be
forced against the stem seal and damaging it.
VALVE SPECIFICATION CHART
Valve Dimensions
INTAKE VALVE (MINIMUM)
Stem Diameter: 7.960 mm (0.313 in.)
Face Angle: 45É
Valve Margin: 0.700 mm (0.028 in.)
Length: 103.0 mm (4.055 in.)
EXHAUST VALVE (MINIMUM)
Stem Diameter: 7.930 mm (0.312)
Face Angle: 45É
Valve Margin: 1.50 mm (0.059 in.)
Length: 102.70 mm (4.043 in.)
Valve Guide
ClearanceNew Service
Limit
Intake: 0.03 - 0.06 mm
(0.001 - 0.002 in.)0.10 mm
(0.004 in.)
Exhaust: 0.05 - 0.09 mm
(0.002 - 0.0035 in.)0.15 mm
(0.006 in.)
Valve Springs New Service
Limit
Free Length: 49.8 mm (1.960 in.) 48.8 mm
(1.921 in.)
Squarness: 2É Maximum 4É Maximum
Spring Tension: 33 Kg @ 40.4 mm
(73 lbs. @ 1.59 in.)
Fig. 16 Valve Spring
Fig. 17 Valve Seat Reconditioning
Fig. 18 Install Valve Stem Seals
Fig. 19 Installed Valve Spring Position
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 67
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1118 of 1938

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ENGINE MOUNTS
RIGHT SIDE MOUNT
REMOVAL
NOTE: Right mount should only be serviced as an
assembly to prevent noise, vibration and harshness
concerns.
(1) Remove the purge duty solenoid and wiring
harness from engine mount.
(2) Remove the two right engine mount insulator
vertical fasteners and loosen the horizontal fastener.
Do Not remove the large nut on the end of the
core from the frame rail (Fig. 20).
(3) Remove the load on the engine motor mounts
by carefully supporting the engine and transmission
assembly with a floor jack.
(4) Remove the vertical and horizontal fasteners
from the engine side bracket. Remove the engine
mount assembly
INSTALLATION
(1) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
Tighten assembly in the following order:
(a) Engine mount to rail fasteners to 68 N´m (50
ft. lbs.).
(b) The vertical engine fastener to 102 N´m (75
ft. lbs.).
(c) The horizontal fastener to 150 N´m (111 ft.
lbs.).
(2) Install the purge duty solenoid and wiring har-
ness to the engine mount.
(3) Engine mount adjustment, Refer to Engine
Mount Insulator Adjustment.
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL
(1) Support the engine and transmission assembly
with a floor jack so it will not rotate.
(2) Remove the front engine mount through bolt
from the insulator and front crossmember mounting
bracket (Fig. 21).
(3) Remove six screws from air dam to allow
access to the front mount screws.
(4) Remove the front engine mount screws and
remove the insulator assembly.
(5) Remove the front mounting bracket, if neces-
sary (Fig. 21).
INSTALLATION
(1) Reverse removal procedure for installation and
tighten fasteners in this order:
(a) Tighten bolts 2, 3, and 4 to 108 N´m (80 ft.
lbs.).
(b) Tighten bolts 1 and 5 to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(2) Engine mount adjustment. Refer to Engine
Mount Insulator Adjustment of this section.
(3) Install six screws to air dam and tighten to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.).
LEFT SIDE MOUNT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and remove left front
wheel.
(2) Support the transmission with a transmission
jack.
(3) Remove the insulator through bolt from the
mount.
(4) Remove the transmission mount fasteners and
remove mount.
INSTALLATION
(1) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
Fig. 20 Engine MountÐRight
Fig. 21 Engine MountÐFront
9 - 68 3.0L ENGINENS