seats CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1152 of 1938

NOTE: Valve seats which are worn or burned can
be reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise cylinder head must
be replaced.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.75 to 2.25 mm (0.69 to 0.088
in.) The width of the exhaust seats should be 1.50 to
2.00 mm (0.059 to 0.078 in.) (Fig. 19).
(5) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 22).
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested (Fig. 21).As an example;the compression
length of the spring to be tested is 33.34 mm (1-5/16
inches). Turn table of Tool C-647 until surface is in
line with the 33.34 mm (1-5/16 inch) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by two. This will give
the spring load at test length. Fractional measure-
ments are indicated on the table for finer adjust-
ments. Refer to specifications to obtain specified
height and allowable tensions. Discard the springs
that do not meet specifications.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WIPER UNIT
When performing work on the upper engine.
Refer to Section 8K, Windshield Wipers and
Washers for removal of the Wiper Unit.
ENGINE MOUNTS
RIGHT SIDE MOUNT
REMOVAL
NOTE: Right mount should only be serviced as an
assembly to prevent noise, vibration and harshness
concerns.
(1) Remove the purge duty solenoid and wiring
harness from engine mount.
(2) Remove the two right engine mount insulator
vertical fasteners and loosen the horizontal fastener,
Do Notremove the large nut on the end of the core
from frame rail (Fig. 23).
(3) Remove the load on the engine motor mounts
by carefully supporting the engine and transmission
assembly with a floor jack.
Fig. 20 Refacing Valve SeatsFig. 21 Testing Valve Springs
Fig. 22 Checking Valve Installed Height
ITEM DESCRIPTION
A Valve Stem Height
B Valve Installed Height
9 - 102 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1160 of 1938
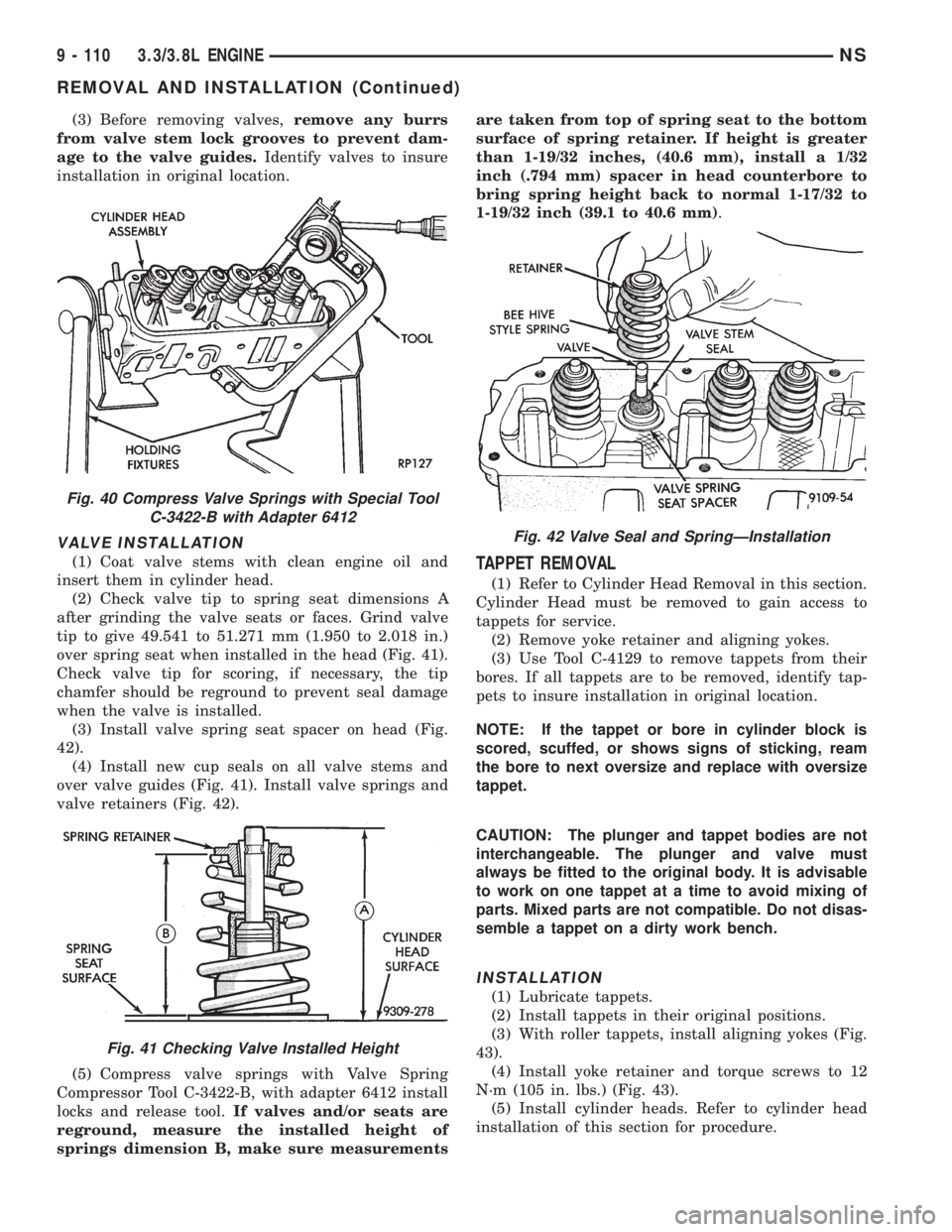
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves to insure
installation in original location.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert them in cylinder head.
(2) Check valve tip to spring seat dimensions A
after grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve
tip to give 49.541 to 51.271 mm (1.950 to 2.018 in.)
over spring seat when installed in the head (Fig. 41).
Check valve tip for scoring, if necessary, the tip
chamfer should be reground to prevent seal damage
when the valve is installed.
(3) Install valve spring seat spacer on head (Fig.
42).
(4) Install new cup seals on all valve stems and
over valve guides (Fig. 41). Install valve springs and
valve retainers (Fig. 42).
(5) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool C-3422-B, with adapter 6412 install
locks and release tool.If valves and/or seats are
reground, measure the installed height of
springs dimension B, make sure measurementsare taken from top of spring seat to the bottom
surface of spring retainer. If height is greater
than 1-19/32 inches, (40.6 mm), install a 1/32
inch (.794 mm) spacer in head counterbore to
bring spring height back to normal 1-17/32 to
1-19/32 inch (39.1 to 40.6 mm).TAPPET REMOVAL
(1) Refer to Cylinder Head Removal in this section.
Cylinder Head must be removed to gain access to
tappets for service.
(2) Remove yoke retainer and aligning yokes.
(3) Use Tool C-4129 to remove tappets from their
bores. If all tappets are to be removed, identify tap-
pets to insure installation in original location.
NOTE: If the tappet or bore in cylinder block is
scored, scuffed, or shows signs of sticking, ream
the bore to next oversize and replace with oversize
tappet.
CAUTION: The plunger and tappet bodies are not
interchangeable. The plunger and valve must
always be fitted to the original body. It is advisable
to work on one tappet at a time to avoid mixing of
parts. Mixed parts are not compatible. Do not disas-
semble a tappet on a dirty work bench.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate tappets.
(2) Install tappets in their original positions.
(3) With roller tappets, install aligning yokes (Fig.
43).
(4) Install yoke retainer and torque screws to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 43).
(5) Install cylinder heads. Refer to cylinder head
installation of this section for procedure.
Fig. 40 Compress Valve Springs with Special Tool
C-3422-B with Adapter 6412
Fig. 41 Checking Valve Installed Height
Fig. 42 Valve Seal and SpringÐInstallation
9 - 110 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1181 of 1938

SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
B LY:A partial open deck is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4 mm. The bedplate
incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFT:A nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket trans-
mits crankshaft movement, via timing belt to the
camshaft sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONS:The SOHC EngineDOES NOThave
provision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hexhead cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly. Pistons And Connecting
rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGS:The piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package consist of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADÐSOHC:It features a Single
Over Head Camshaft, four-valves per cylinder cross
flow design. The valves are arranged in two inline
banks, with the two intake per cylinder facing
toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFTÐSOHC:The nodular iron camshaft
has five bearing journals and 3 cam lobes per cylin-
der. Provision for cam position sensor on the cam at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVESÐSOHC:Four valves per cylinder are
actuated by roller rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjust-
ers assemblies which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All
valves have 6 mm diameter chrome plated valve
stems. The valve train has 33 mm (1.299 inch) diam-
eter intake valves and 28 mm (1.10 inch) diameter
exhaust valves. Viton rubber valve stem seals are
integral with spring seats. Valve springs, spring
retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The intake manifold is a
molded plastic composition, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch design
enhances low and mid-range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD:The exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
Fig. 2 Engine Lubrication SystemÐ SOHC
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1208 of 1938
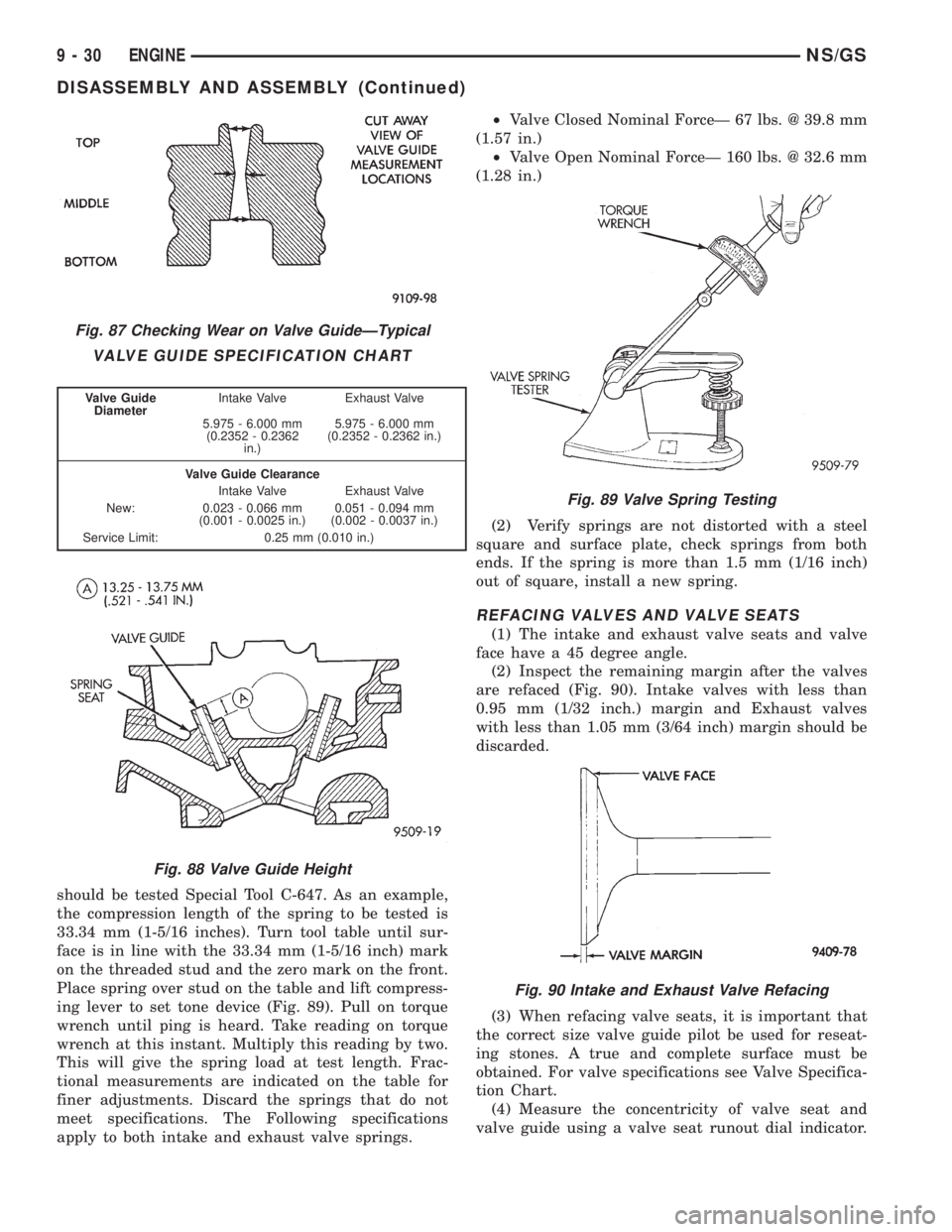
should be tested Special Tool C-647. As an example,
the compression length of the spring to be tested is
33.34 mm (1-5/16 inches). Turn tool table until sur-
face is in line with the 33.34 mm (1-5/16 inch) mark
on the threaded stud and the zero mark on the front.
Place spring over stud on the table and lift compress-
ing lever to set tone device (Fig. 89). Pull on torque
wrench until ping is heard. Take reading on torque
wrench at this instant. Multiply this reading by two.
This will give the spring load at test length. Frac-
tional measurements are indicated on the table for
finer adjustments. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications. The Following specifications
apply to both intake and exhaust valve springs.²Valve Closed Nominal ForceÐ 67 lbs. @ 39.8 mm
(1.57 in.)
²Valve Open Nominal ForceÐ 160 lbs. @ 32.6 mm
(1.28 in.)
(2) Verify springs are not distorted with a steel
square and surface plate, check springs from both
ends. If the spring is more than 1.5 mm (1/16 inch)
out of square, install a new spring.
REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
(1) The intake and exhaust valve seats and valve
face have a 45 degree angle.
(2) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced (Fig. 90). Intake valves with less than
0.95 mm (1/32 inch.) margin and Exhaust valves
with less than 1.05 mm (3/64 inch) margin should be
discarded.
(3) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained. For valve specifications see Valve Specifica-
tion Chart.
(4) Measure the concentricity of valve seat and
valve guide using a valve seat runout dial indicator.
Fig. 87 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
VALVE GUIDE SPECIFICATION CHART
Valve Guide
DiameterIntake Valve Exhaust Valve
5.975 - 6.000 mm
(0.2352 - 0.2362
in.)5.975 - 6.000 mm
(0.2352 - 0.2362 in.)
Valve Guide Clearance
Intake Valve Exhaust Valve
New: 0.023 - 0.066 mm
(0.001 - 0.0025 in.)0.051 - 0.094 mm
(0.002 - 0.0037 in.)
Service Limit: 0.25 mm (0.010 in.)
Fig. 88 Valve Guide Height
Fig. 89 Valve Spring Testing
Fig. 90 Intake and Exhaust Valve Refacing
9 - 30 ENGINENS/GS
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1209 of 1938

Total runout should not exceed. 0.051 mm (0.002
inch.) (total indicator reading).
(5) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of the valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15 degrees stone. If the blue is transferred to
the bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a
65 degrees stone.
²Intake valve seat diameter is 33 mm (1.299 in.)
²Exhaust valve seat diameter is 28 mm (1.102
in.)
(6) Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat width
are maintained. The intake valve seat must be ser-
viced when the valve seat width is 2.0 mm (0.079 in.)
or greater. The exhaust valve seat must be serviced
when the valve seat width is 2.5 mm (0.098 in.) or
greater. Otherwise the cylinder head must be
replaced.
(7) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 0.75 to 1.25 mm
(0.030 to 0.049 in.) (Fig. 91).
(8) Check valve tip to spring seat dimensions A
after grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve
tip to 43.51 - 44.57 mm (1.71 - 1.75 in.) for exhaust
valve and 45.01 - 46.07 mm (1.77 - 1.81 in.) for
intake valve over spring seat when installed in the
head (Fig. 92). The valve tip chamfer may need to be
reground to prevent seal damage when the valve is
installed.
CLEANING
Clean all valve guides, valves and valve spring
assemblies thoroughly with suitable cleaning solution
before reassembling.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves using
a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 93). The valve stem seals
should be pushed firmly and squarely over valve
guide.
CAUTION: If oversize valves are used, there is only
one oversize valve available. The same stem seal is
used on both the standard and oversize valve.
(3) Install valve springs and retainers. Compress
valve springs only enough to install locks, taking
care not to misalign the direction of compression.
Nicked valve stems may result from misalignment of
the valve spring compressor.
VALVE SPECIFICATION CHART
Face Angle
Intake and
Exhaust:45 - 45 1/2É
Head Diameter
Intake: 33.12 - 33.37 mm (1.303 - 1.313 in.)
Exhaust: 28.57 - 28.83 mm (1.124 - 1.135 in.)
Length (Overall)
Intake: 114.69 - 115.19 mm (4.515 - 4.535 in.)
Exhaust: 116.94 - 117.44 mm (4.603 - 4.623 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake: 5.934 - 5.952 mm (0.2337 - 0.2344 in.)
Exhaust: 5.906 - 5.924 mm (0.2326 - 0.2333 in.)
Valve Margin
Intake: 1.15 - 1.48 mm (0.0452 - 0.0582 in.)
Exhaust: 1.475 - 1.805 mm (0.0580 - 0.0710 in.)
Fig. 91 Valve Seat Refacing
Fig. 92 Spring Installed Height and Valve Tip to
Spring Seat Dimensions
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 31
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1233 of 1938

(3) Install cylinder head cover, torque nuts to 14.7
N´m (132 in. lbs.).
(4) Install coolant pressure tank.
(5) Install breather hose.
(6) Install generator bracket, tighten bolts to 7
N´m (4 ft. lbs.).
(7) Connect the service valves to the A/C compres-
sor ports, if equipped with air conditioning.
(8) Connect battery cable.
VALVE SPRINGSÐCYLINDER HEAD NOT
REMOVED
This procedure can be done with the engine cylin-
der head installed on the block.
REMOVAL
Each valve spring is held in place by a retainer
and a set of conical valve locks. The locks can be
removed only by compressing the valve spring.
(1) Remove the engine cylinder head cover, refer to
cylinder head cover removal in this section.
(2) Remove rocker arms assemblies for access to
each valve spring to be removed.
(3) Remove push rods. Retain the push rods, and
rocker arms assemblies in the same order and posi-
tion as removed.
(4) Inspect the springs and retainer for cracks and
possible signs of weakening.
(5) Install an air hose adaptor in the fuel injector
hole.
(6) Connect an air hose to the adapter and apply
air pressure slowly. Maintain at least 621 kPa (90psi) of air pressure in the cylinder to hold the valves
against their seats.
(7) Tap the retainer or tip with a rawhide hammer
to loosen the lock from the retainer. Use Valve Spring
Compressor Tool to compress the spring and remove
the locks.
(8) Remove valve spring and retainer.
Inspect the valve stems, especially the grooves. An
Arkansas smooth stone should be used to remove
nicks and high spots.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install valve spring and retainer.
(2) Compress the valve spring with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool and insert the valve locks. Release
the spring tension and remove the tool. Tap the
spring from side-to-side to ensure that the spring is
seated properly on the engine cylinder head.
(3) Disconnect the air hose. Remove the adaptor
from the fuel injector hole and install the fuel injec-
tor.
(4) Repeat the procedures for each remaining valve
spring to be removed.
(5) Install the push rods. Ensure the bottom end of
each rod is centered in the plunger cap seat of the
hydraulic valve tappet.
(6) Install the rocker arm assemblies, at their orig-
inal location.
(7) Tighten the rocker arm assembly nut to 106
N´m (78 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install the engine cylinder head cover, refer to
cylinder head cover installation in this section.
CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery cable.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAIN COCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE
COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
(2) Drain the cooling system. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling.
(3) Remove wiper module. Refer to Group 8K,
Windshield Wiper Unit Removal for procedure.
(4) Remove coolant pressure bottle.
(5) Remove intercooler hose at intake manifold
(Fig. 23).
(6) Remove intercooler hose at turbocharger inter-
cooler tube.
(7) Remove the upper radiator hose.
(8) Remove water manifold.
(9) Disconnect the heater hoses and coolant pres-
sure bottle hoses.
Fig. 22 Rocker Arm Retaining Nut
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 55
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1238 of 1938

(36) Operate the engine with the radiator cap off.
Inspect for leaks and continue operating the engine
until the thermostat opens. Add coolant, if required.
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGSÐHEAD OFF
This procedure is done with the engine cylinder
head removed from the block.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the engine cylinder head from the cyl-
inder block. Refer to cylinder head removal in this
section.
(2) Use Valve Spring Compressor Tool and com-
press each valve spring.
(3) Remove the valve locks, retainers, and springs.
(4) Use an Arkansas smooth stone or a jewelers
file to remove any burrs on the top of the valve stem,
especially around the groove for the locks.
(5) Remove the valves, and place them in a rack in
the same order as removed.
INSTALLATION
(1) Fit each valve to its respective valve guide.
NOTE: If valves and valve seats have been refaced
refer to Service Procedures in this section. Follow
The Valve Stand Down procedure.
(2) Install lower, washer and spring.
(3) Install upper spring collar, and compress valve
spring with spring compressor tool. Install split cone
retainers.
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove coolant pressure bottle.
(2) Remove cylinder head cover. Refer to cylinder
head cover removal in this section.
(3) Remove rocker assembly and push rods. Iden-
tify push rods to ensure installation in original loca-
tion (Fig. 34).
(4) Remove cylinder head, intake manifold, and
exhaust manifold. Refer to cylinder head removal in
this section.
(5) Remove yoke retainer and aligning yokes (Fig.
35).
(6) Slide Hydraulic Tappet Remover/Installer Tool
through opening in block and seat tool firmly in the
head of tappet.
(7) Pull tappet out of bore with a twisting motion.
If all tappets are to be removed, identify tappets to
ensure installation in original location.
(8) If the tappet or bore in cylinder block is scored,
scuffed, or shows signs of sticking, ream the bore to
next oversize. Replace with oversize tappet.CAUTION: The plunger and tappet bodies are not
interchangeable. The plunger and valve must
always be fitted to the original body. It is advisable
to work on one tappet at a time to avoid mixing of
parts. Mixed parts are not compatible. DO NOT dis-
assemble a tappet on a dirty work bench.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate tappets.
(2) Install tappets and yoke retainers in their orig-
inal positions. Ensure that the oil feed hole in the
side of the tappet body faces up (away from the
crankshaft).
Fig. 34 Tappet and Rocker Arm Assembly
Fig. 35 Tappet and Yoke
9 - 60 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1306 of 1938

(9) Momentarily touch the other end of this
jumper wire to the negative terminal of the battery
for no more than 4 seconds.
(10) Place a rag or towel below the fuel line at the
quick connect to the rail.
(11) Disconnect the quick connect fitting to the
rail. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings in this section.
(12) Return the fuel pump relay to the PDC.
(13) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in the PCM memory due to the
fuel pump relay removal. The DRB scan tool must be
used to erase a DTC. Refer to group 25, On-Board
Diagnostics.
HOSES AND CLAMPS
Inspect all hose connections (clamps and quick con-
nect fittings) for completeness and leaks. Replace
cracked, scuffed, or swelled hoses. Replace hoses that
rub against other vehicle components or show sign of
wear.
Fuel injected vehicles use specially constructed
hoses. When replacing hoses, only use hoses marked
EFM/EFI.
When installing hoses, ensure that they are routed
away from contact with other vehicle components
that could rub against them and cause failure. Avoid
contact with clamps or other components that cause
abrasions or scuffing. Ensure that rubber hoses are
properly routed and avoid heat sources.
The hose clamps have rolled edges to prevent the
clamp from cutting into the hose. Only use clamps
that are original equipment or equivalent. Other
types of clamps may cut into the hoses and cause
high pressure fuel leaks. Tighten hose clamps to 1
N´m (10 in. lbs.) torque.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting
without the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean 30 weight engine
oil.
(3) Push the quick-connect fitting over the fuel
tube until theretainer seats and a click is heard.
(4) The plastic quick-connect fitting has windows
in the sides of the casing. When the fitting com-
pletely attaches to the fuel tube, the retainer locking
ears and the fuel tube shoulder are visible in the
windows. If they are not visible, the retainer was not
properly installed (Fig. 12).Do not rely upon the
audible click to confirm a secure connection.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or
until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.
(5) Use the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test
to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
FUEL FILTER
The fuel filter mounts to the top of the fuel tank.
The inlet and outlet tubes are permanently attached
to the filter (Fig. 13).
Fig. 12 Plastic Quick-Connect Fitting/Fuel Tube
Connection
14 - 12 FUEL SYSTEMNS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1380 of 1938

FUEL HEATER RELAY TEST
The fuel heater relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC). Refer to RelaysÐOperation/
Testing in Fuel Ingection System section of this
group for test procedures.
FUEL INJECTOR TEST
The fuel injection nozzels, located on the engine
cylinder head, spray fuel under high pressure into
the individual combustion chambers. Pressurized
fuel, delivered by the fuel injection pump, unseats a
spring-loaded needle valve inside the injector, and
the fuel is atomized as it escapes through the injector
opening into the engine's combustion chamber. If the
fuel injector does not operate properly, the engine
may misfire, or cause other driveability problems.
A leak in the injection pump±to±injector high±pres-
sure fuel line can cause many of the same symptoms
as a malfunctioning injector. Inspect for a leak in the
high±pressure lines before checking for a malfunc-
tioning fuel injector.
WARNING: THE INJECTION PUMP SUPPLIES HIGH-
±PRESSURE FUEL OF UP TO APPROXIMATELY
45,000 KPA (6526 PSI) TO EACH INDIVIDUAL INJEC-
TOR THROUGH THE HIGH±PRESSURE LINES. FUEL
UNDER THIS AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN PENE-
TRATE THE SKIN AND CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY.
WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES AND ADEQUATE PRO-
TECTIVE CLOTHING. AVOID CONTACT WITH FUEL
SPRAY WHEN BLEEDING HIGH±PRESSURE FUEL
LINES.
WARNING: DO NOT BLEED AIR FROM THE FUEL
SYSTEM OF A HOT ENGINE. DO NOT ALLOW FUEL
TO SPRAY ONTO THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD WHEN
BLEEDING AIR FROM THE FUEL SYSTEM.
To determine which fuel injector is malfunctioning,
run the engine and loosen the high±pressure fuel line
nut at the injector (Fig. 21). Listen for a change in
engine speed. If engine speed drops, the injector was
operating normally. If engine speed remains the
same, the injector may be malfunctioning. After test-
ing, tighten the line nut to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.)
torque. Test all injectors in the same manner one at
a time.
Once an injector has been found to be malfunction-
ing, remove it from the engine and test it. Refer to
the Removal/Installation section of this group for pro-
cedures.
After the injector has been removed, install it to a
bench±mount injector tester. Refer to operating
instructions supplied with tester for procedures.
The opening pressure or ªpopº pressure should be
15,000±15,800 kPa (2175±2291 psi). If the fuel injec-tor needle valve is opening (ªpoppingº) to early or to
late, replace the injector.
FUEL INJECTOR SENSOR TEST
The fuel injector sensor is used only on the fuel
injector for the number±1 cylinder (Fig. 22). It is not
used on the injectors for cylinders number 2, 3, or 4.
To test the sensor, unplug the sensor connector
(Fig. 22) from the engine wiring harness. Check
resistance across terminals. Resistance should be 110
ohms610 ohms at 20ÉC (68ÉF). Replace sensor if
specification cannot be met.
FUEL INJECTION PUMP TEST
The injection pump is not to be serviced or
the warranty may be voided. If the injection
pump requires service, the complete assembly
must be replaced.
Incorrect injection pump timing (mechanical or
electrical) can cause poor performance, excessive
smoke and emissions and poor fuel economy.
Fig. 21 Typical Inspection of Fuel Injector
Fig. 22 Fuel Injector Sensor Location
14 - 12 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1729 of 1938

SERVICE PROCEDURES
WHEEL INSTALLATION
To install the wheel, first position it properly on
the mounting surface of the hub using the hub pilot
as a guide. All wheel nuts should be lightly tightened
before progressively tightening them in the proper
sequence (Fig. 7). Then fully tighten the wheel nuts
in the proper sequence (Fig. 7) to a torque of 135
N´m (100 ft. lbs.). Never use oil or grease on studs or
nuts.
TIRE AND WHEEL BALANCE
Balancing need is indicated by vibration of seats,
floor pan, or steering wheel. The vibration will be
noticed mostly when driving over 90 km/h (55 mph)
on a smooth road.
It is recommended that a two plane dynamic bal-
ancer be used when a wheel and tire assembly
require balancing. Static balancing should be used
only when a two plane balancer is not available.
Off-vehicle tire and wheel balancing is recom-
mended to be used on this vehicle.
NOTE: If on vehicle equipment is being used to bal-
ance the tire /wheel assemblies, remove the oppo-
site tire/wheel from the vehicle.
For static balancing, find the location of heavy spot
on tire/wheel causing the imbalance. Counter balance
wheel directly opposite the heavy spot. Determine
weight required to counterbalance the area of imbal-
ance. Place half of this weight on theinnerrim
flange and the other half on theouterrim flange
(Fig. 8).
For dynamic balancing, the balancing equipment is
designed to indicate the location and amount of
weight to be applied to both the inner and outer rim
flanges (Fig. 9).
Fig. 5 Checking Wheel Radial Run Out
Fig. 6 Checking Wheel Lateral Run Out
Fig. 7 Tightening Wheel Nuts
NSTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)