automatic transmission CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 14 of 1938

DIGITS 16, 17, AND 18
Vehicle Shell Car Line
²GSYH = Voyager/Grand Voyager SE FWD
²GSYP = Voyager/Grand Voyager LE FWD
²GSYS = Voyager LX FWD
²GSCP = Voyager/Grand Voyager LE AWD
²GSCS = Voyager LX AWD
DIGIT 19
Price Class
²H = High Line
²P = Premium
²S = Special/SportDIGITS 20 AND 21
Body Type
²52 = Short Wheel Base
²53 = Long Wheel Base
BODY CODE PLATEÐLINE 2
DIGITS 1,2, AND 3
Paint Procedure
DIGIT 4
Open Space
VIN DECODING INFORMATION
POSITION INTERPRETATION CODE = DESCRIPTION
1 Country of origin 1 = United States or Austria
2 = Canada
2 Make C = Chrysler
D = Dodge
3 Vehicle Type 4 = Multipurpose Pass. Veh.
4 Gross Vehicle Weight Rating G = 2268-2721 kg (5001-6000 lbs)
5 Car Line C = Voyager/Grand Voyager AWD
Y = Voyager/Grand Voyager FWD
6 Series 4 = Voyager/Grand Voyager SE FWD
5 = Voyager/Grand Voyager LE FWD/AWD
6 = Voyager LX FWD/AWD
N = 5-Speed Manual Transmission
B = 4-Speed Automatic Transmission
7 Body Style 2 = Short Wheelbase 4-Door
3 = Short Wheelbase 3-Door
4 = Long Wheelbase Premium 4-Door
5 = Long Wheelbase Highline 4-door
7 = Short Wheelbase Commercial Van
8 Engine B = 2.4 L 4cyl. MPI 16-Valve DOHC
C = 2.0L 4cyl. MPI 16-Valve SOHC
M = 2.5L 4cyl Turbo Diesel (Intercooler)
R = 3.3 L 6 cyl. gas MPI
L = 3.8 L 6 cyl. gas MPI
9 Check Digit See explanation in this section.
10 Model Year W = 1998
11 Assembly Plant B = St. Louis South, U.S.A.
R = Windsor, Canada
U = Graz, Austria
12 Build Sequence 6 Digit number assigned by assembly plant
2 INTRODUCTIONNS/GS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 19 of 1938

MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 3
SCHEDULE ± A.......................... 3SCHEDULE ± B.......................... 4
UNSCHEDULED INSPECTION............... 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
Service and maintenance procedures for compo-
nents and systems listed in Schedule ± A or B can be
found by using the Group Tab Locator index at the
front of this manual. If it is not clear which group
contains the information needed, refer to the index at
the back of this manual.
There are two maintenance schedules that show
proper service based on the conditions that the vehi-
cle is subjected to.
Schedule ±A, lists scheduled maintenance to be
performed when the vehicle is used for general trans-
portation.
Schedule ±B, lists maintenance intervals for vehi-
cles that are operated under the conditions listed at
the beginning of the Maintenance Schedule section.
Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions.
Where time and mileage are listed, follow the
interval that occurs first.
UNSCHEDULED INSPECTION
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check engine oil level, add as required.
²Check windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Inspect battery and clean and tighten terminals
as required.
²Check fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transaxle and
add as needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
²Check rubber seals on each side of the radiator
for proper fit.
At Each Oil Change
²Inspect exhaust system.
²Inspect brake hoses
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown on Schedule ± A (7,500 miles) or every other
interval shown on Schedule ± B (6,000 miles).
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²If your mileage is less than 7,500 miles (12 000
km) yearly, replace the engine oil filter at each oil
change.
²Replace engine oil filter on 2.4L engines.
SCHEDULE ± A
7,500 Miles (12 000 km) or at 6 months
²Change engine oil.
15,000 Miles (24 000 km) or at 12 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
22,500 Miles (36 000 km) or at 18 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
30,000 Miles (48 000 km) or at 24 months
²Change engine oil.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
37,500 Miles (60 000 km) or at 30 months
²Change engine oil.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km) or at 36 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect brake linings.
²Flush and replace engine coolant at 36 months,
regardless of mileage.
NSLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 3
Page 20 of 1938

52,500 Miles (84 000 km) or at 42 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if not done at
36 months.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km) or at 48 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Check PCV valve and replace, if necessary.
*
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
67,500 Miles (108 000 km) or at 54 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km) or at 60 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
82,500 Miles (132 000 km) or at 66 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km) or at 72 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Check PCV valve and replace, if necessary.
Not required if previously changed. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
²Inspect brake linings.
97,500 Miles (156 000 km) or at 78 months
²Change engine oil.
100,000 Miles (160,000 km)
²Replace spark plugs on 3.3L and 3.8L
engines.
²Replace ignition cables on 3.3L and 3.8L
engines.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km) or at 84 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
112,500 Miles (180 000 km) or at 90 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
120,000 Miles (192 000 km) or at 96 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace automatic transmission fluid.
²Replace engine air cleaner element.
²Check and replace PCV valve, if necessary.
*
²Inspect serpentine drive belt. Not required if
replaced at 75,000, 90,000 or 105,000 miles.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
* This maintenance is recommended by Chrysler to
the owner but is not required to maintain the war-
ranty on the PCV valve.
** If California vehicle, this maintenance is recom-
mended by Chrysler to the owner but is not required
to maintain the warranty of the timing belt.
SCHEDULE ± B
3,000 Miles (5 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
6,000 Miles (10 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
9,000 Miles (14 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
12,000 Miles (19 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
15,000 Miles (24 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect air cleaner element. Replace as
necessary.
0 - 4 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 21 of 1938

²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See
note)
²Change AWD powertransfer fluid unit.
18,000 Miles (29 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect brake linings.
21,000 Miles (34 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Check AWD overrunning clutch and rear carrier
fluid.
24,000 Miles (38 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
27,000 Miles (43 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
30,000 Miles (48 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Inspect PCV valve. Replace as necessary. *
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See
note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
33,000 Miles (53 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
36,000 Miles (58 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect brake linings.
39,000 Miles (62 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
42,000 Miles (67 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Change AWD overrunning clutch and rear car-
rier fluid.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect air cleaner element. Replace as
necessary.²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See
note)
²Inspect brake linings.
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
48,000 Miles (77 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
51,000 Miles (82 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
54,000 Miles (86 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect brake linings.
57,000 Miles (91 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Inspect PCV valve, replace if necessary. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See
note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
63,000 Miles (101 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Change AWD overrunning clutch and rear car-
rier fluid.
²Inspect brake linings.
66,000 Miles (106 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
69,000 Miles (110 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
72,000 Miles (115 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect air cleaner element. Replace as
necessary.
NSLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 22 of 1938

²Replace spark plugs.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transaxle fluid and
replace filter. Adjust band, if so equipped. (See note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
78,000 Miles (125 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
81,000 Miles (130 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
84,000 Miles (134 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Change AWD overrunning clutch and rear car-
rier fluid.
87,000 Miles (139 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Check PCV valve and replace if necessary.
Not required if previously changed. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See
note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
²Inspect brake linings.
93,000 Miles (149 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
96,000 Miles (154 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
99,000 Miles (158 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
102,000 Miles (163 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect air cleaner element. Replace as
necessary.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Change AWD overrunning clutch and rear car-
rier fluid.
108,000 Miles (173 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect brake linings.
111,000 Miles (178 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
114,000 Miles (182 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
117,000 Miles (187 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
120,000 Miles (192 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Inspect PCV valve. Replace as necessary. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt. Not required if
replaced at 75,000, 90,000 or 105,000 miles.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped.
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
* This maintenance is recommended by Chrysler to
the owner but is not required to maintain the war-
ranty on the PCV valve.
** If California vehicle, this maintenance is recom-
mended by Chrysler to the owner but is not required
to maintain the warranty of the timing belt.
NOTE: Operating vehicle more than 50% in heavy
traffic during hot weather, above 90ÉF (32ÉC), using
vehicle for police, taxi, limousine type operation or
trailer towing require the more frequent transaxle
service noted in Schedule ± B. Perform these ser-
vices if vehicle is usually operated under these con-
ditions.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
0 - 6 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 23 of 1938

JUMP STARTING, HOISTING AND TOWING
INDEX
page page
SERVICE PROCEDURES
HOISTING RECOMMENDATIONS............ 9JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE.............. 7
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS.............. 8
SERVICE PROCEDURES
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN GROUP 8A, BATTERY/START-
ING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS. DO NOT
JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY, PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT JUMP START WHEN
MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERY INDICATOR DOT IS
YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR. DO NOT JUMP
START A VEHICLE WHEN THE BATTERY FLUID IS
BELOW THE TOP OF LEAD PLATES. DO NOT
ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO TOUCH
EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A BOOSTER
SOURCE. DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY. REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON
HANDS OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCI-
DENTAL ARCING OF BATTERY CURRENT. WHEN
USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING DEVICE, DO
NOT ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO EXCEED 16
VOLTS. REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED
WITH DEVICE BEING USED.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually
inspect engine compartment for:
²Battery cable clamp condition, clean if necessary.
²Frozen battery.
²Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
²Low battery fluid level.
²Generator drive belt condition and tension.
²Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, park the booster vehicle within cable reach.
Turn off all accessories, set the parking brake, placethe automatic transmission in PARK or the manual
transmission in NEUTRAL and turn the ignition
OFF.
(3) On disabled vehicle, place gear selector in park
or neutral and set park brake. Turn off all accesso-
ries.
(4) Connect jumper cables to booster battery. RED
clamp to positive terminal (+). BLACK clamp to neg-
ative terminal (-). DO NOT allow clamps at opposite
end of cables to touch, electrical arc will result.
Review all warnings in this procedure.
(5) On disabled vehicle, connect RED jumper cable
clamp to positive (+) terminal. Connect BLACK
jumper cable clamp to engine ground as close to the
ground cable attaching point as possible (Fig. 1).
(6) Start the engine in the vehicle which has the
booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes,
then start the engine in the vehicle with the dis-
charged battery.
CAUTION: Do not crank starter motor on disabled
vehicle for more than 15 seconds, starter will over-
heat and could fail.
(7) Allow battery in disabled vehicle to charge to
at least 12.4 volts (75% charge) before attempting to
start engine. If engine does not start within 15 sec-
onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 min.), before cranking again.
Fig. 1 Jumper Cable Clamp Connections
NSLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
Page 215 of 1938

COOLING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS................ 1
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLERÐ
2.4L................................. 3
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)....... 3
COOLANT.............................. 3
COOLING SYSTEM....................... 2
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER.................. 5
ENGINE THERMOSTAT.................... 3
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP................ 4
RADIATOR............................. 3
WATER PUMPS......................... 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COOLANT PERFORMANCE................. 6
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS........... 6
WATER PIPESÐ3.0L ENGINE.............. 6
WATER PUMPÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES.......... 7
WATER PUMPÐ2.4L ENGINE.............. 6
WATER PUMPÐ3.0L ENGINE.............. 6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT.................. 7
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS............. 8
DEAERATION.......................... 16
ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR TEST.............. 14
LOW COOLANT LEVEL AERATION.......... 15
PRESSURE TESTING RADIATOR CAP....... 15
RADIATOR CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL
PRESSURE RELIEF CHECK.............. 15
RADIATOR COOLANT FLOW TEST.......... 14
RADIATOR FAN CONTROL................ 14
TEMPERATURE GAUGE INDICATION........ 16
TESTING COOLING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS.... 14
SERVICE PROCEDURES
COOLANT LEVEL CHECKÐROUTINE........ 16
COOLANT LEVEL SERVICE................ 16COOLANTÐADDING ADDITIONAL.......... 16
COOLING SYSTEMÐDRAINING............ 16
COOLING SYSTEMÐREFILLING........... 16
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTSÐ2.4L.......... 23
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTSÐ3.0L.......... 24
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTÐ3.3/3.8L........ 24
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER................. 23
FAN MODULE.......................... 22
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK.................. 21
RADIATOR............................ 21
THERMOSTATÐ2.4L ENGINE............. 19
THERMOSTATÐ3.0L ENGINE............. 20
THERMOSTATÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES......... 20
WATER PUMP INLET TUBEÐ2.4L ENGINE . . . 17
WATER PUMPÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES......... 19
WATER PUMPÐ2.4L ENGINE............ 17
WATER PUMPÐ3.0L ENGINE............. 18
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT................. 25
CHEMICAL CLEANING................... 25
COOLING SYSTEM CLEANING............. 25
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP............... 25
REVERSE FLUSHING THE ENGINE......... 25
REVERSE FLUSHING THE RADIATOR....... 25
WATER PUMP......................... 24
ADJUSTMENTS
BELT TENSION CHART................... 26
BELT TENSION GAUGE METHOD........... 26
PROPER BELT TENSION................. 25
SPECIFICATIONS
COOLING SYSTEM CAPACITY............. 26
TORQUE CHART........................ 26
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING............................. 26
GENERAL INFORMATION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS
The accessory drive system utilizes two different
style of drive belts. The conventional V-belt and the
Poly-V belt are used to drive the generator, air con-
ditioning compressor, power steering pump and waterpump. Satisfactory performance of these belts
depends on belt condition and proper belt tension.
Belt tensioning should be performed with the aid of a
Burroughs gauge Special Tool C-4162. Because of
space limitations in the engine compartment, the use
of the gauge may be restricted. Raise the vehicle on a
hoist and then remove the splash shield to gain
access to the drive belts.
NSCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 1
Page 216 of 1938
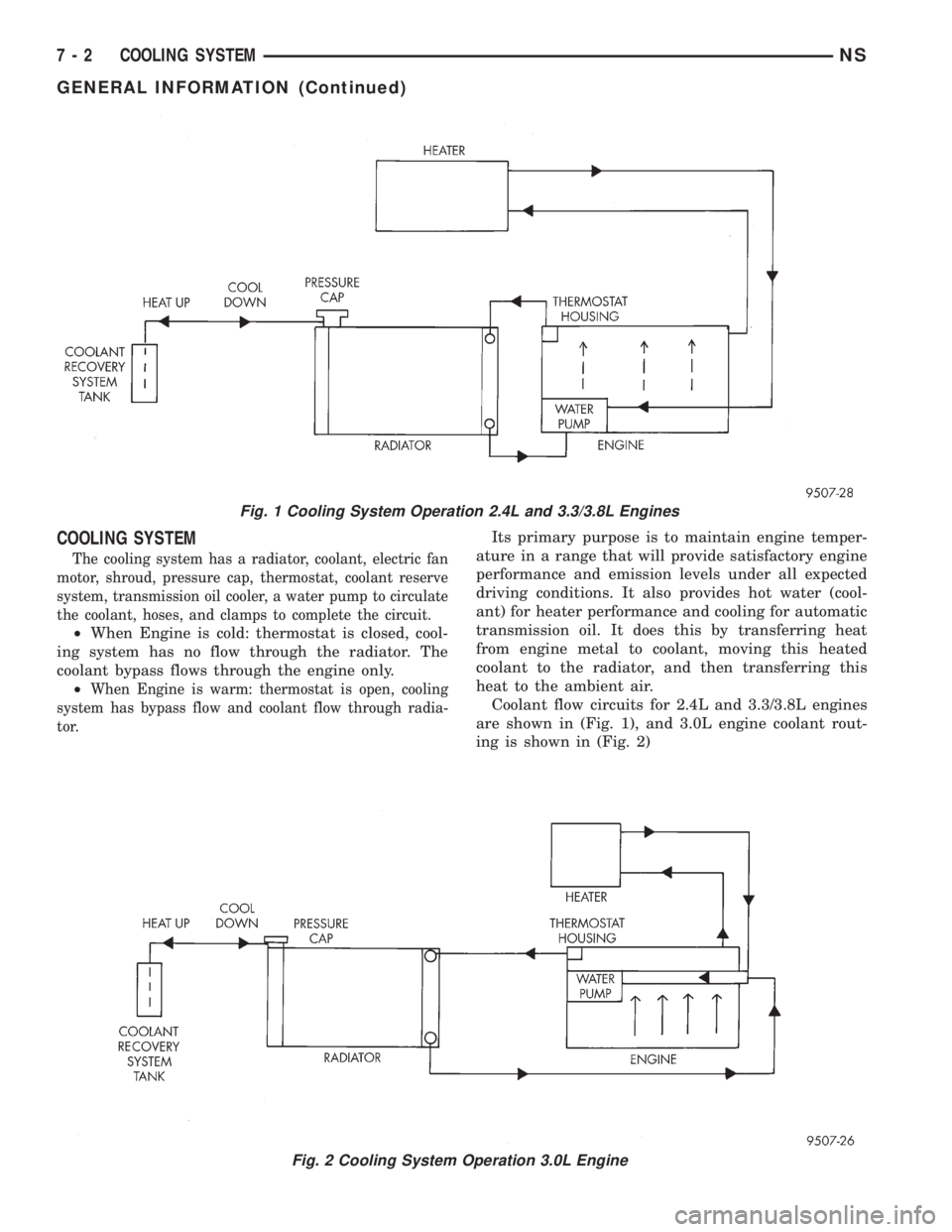
COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system has a radiator, coolant, electric fan
motor, shroud, pressure cap, thermostat, coolant reserve
system, transmission oil cooler, a water pump to circulate
the coolant, hoses, and clamps to complete the circuit.
²When Engine is cold: thermostat is closed, cool-
ing system has no flow through the radiator. The
coolant bypass flows through the engine only.
²
When Engine is warm: thermostat is open, cooling
system has bypass flow and coolant flow through radia-
tor.
Its primary purpose is to maintain engine temper-
ature in a range that will provide satisfactory engine
performance and emission levels under all expected
driving conditions. It also provides hot water (cool-
ant) for heater performance and cooling for automatic
transmission oil. It does this by transferring heat
from engine metal to coolant, moving this heated
coolant to the radiator, and then transferring this
heat to the ambient air.
Coolant flow circuits for 2.4L and 3.3/3.8L engines
are shown in (Fig. 1), and 3.0L engine coolant rout-
ing is shown in (Fig. 2)
Fig. 1 Cooling System Operation 2.4L and 3.3/3.8L Engines
Fig. 2 Cooling System Operation 3.0L Engine
7 - 2 COOLING SYSTEMNS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 217 of 1938

COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)
This system works with the radiator pressure cap
to use thermal expansion and contraction of the cool-
ant to keep the coolant free of trapped air. Provides a
convenient and safe method for checking coolant
level and adjusting level at atmospheric pressure
without removing the radiator pressure cap. It also
provides some reserve coolant to cover deaeration
and evaporation or boiling losses. All vehicles are
equipped with this system and take various shapes
and forms. (Fig. 3) shows a typical system in the typ-
ical location.
See Coolant Level Service, and Deaeration, and
Pressure Cap sections for operation and service.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLERÐ2.4L
Oil cooler is internal oil to coolant type, mounted
in the radiator left tank (Fig. 4). Rubber oil lines feed
the oil cooler and the automatic transmission. Use
only approved transmission oil cooler hose. Since
these are molded to fit space available, molded hoses
are recommended.
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
The engine cooling thermostats are a wax pellet
driven, reverse poppet choke type. They are designed
to provide the fastest warm up possible by prevent-
ing leakage through them and to guarantee a mini-
mum engine operating temperature of 88 to 93ÉC
(192 to 199ÉF). They also automatically reach wide
open so they do not restrict flow to the radiator as
temperature of the coolant rises in hot weather to
around 104ÉC (220ÉF). Above this temperature the
coolant temperature is controlled by the fan, the
radiator, and the ambient temperature, not the ther-
mostat.
WATER PUMPS
A quick test to tell whether the pump is working is
to see if the heater warms properly. A defective pump
can not circulate heated coolant through the long
heater hose.The water pump on all models can
be replaced without discharging the air condi-
tioning system.
COOLANT
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine metal, in
the cylinder head area near the exhaust valves. Cool-
ant then carries this heat to the radiator, where the
tube/fin assemblies of these components can give it
up to the air.
The use of aluminum cylinder heads, intake mani-
folds, and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent is
recommended for best engine cooling without corro-
sion, when mixed only to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it loses color or becomes
contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with fresh
properly mixed solution.
CAUTION: Do not use well water, or suspect water
supply in cooling system. A 50/50 ethylene glycol
and distilled water mix is recommended.
RADIATOR
The radiators are cross-flow types (horizontal
tubes) with design features that provide greater
strength along with sufficient heat transfer capabili-
Fig. 3 Coolant Recovery System
Fig. 4 Automatic Transmission Oil Cooler
NSCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 235 of 1938

INSTALLATION
(1) Place a new gasket (dipped in water) on the
thermostat housing surface, center thermostat into
opening in the intake manifold water box.
(2) Place housing and gasket over the thermostat,
making sure thermostat is in the recess provided
(Fig. 28).
(3) Bolt housing to intake manifold, tighten bolts
to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(4) Refill the cooling system to the proper level.
Refer to Cooling System Refilling outlined in this sec-
tion for procedure.
RADIATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK PLUG OR THE RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
(2) Drain cooling system. Refer to Draining Cool-
ing System of this section.
(3) Remove air intake resonator.
(4) Remove coolant reserve system tank to filler
neck tube hose.
(5) Disconnect fans from the connector located on
the left side of the fan module.
(6) Remove the Coolant Recovery System (CRS)
tank retaining screw from the upper radiator closure
panel crossmember.
(7) Disconnect the upper radiator mounting
screws from the crossmember. Disconnect the engine
block heater wire if equipped.
(8) Remove the upper radiator closure panel
crossmember. Refer to Group 23 Body for procedure.
(9) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(10) Disconnect automatic transmission oil cooler
lines at radiator and plug.
(11) Disconnect inlet and outlet hoses from the
radiator. Remove the lower hose clip from the fan
module.
(12) Remove A/C condenser fasteners and sepa-
rate the condenser from the radiator (Fig. 29). Verify
the condenser is supported in position.
(13) Remove A/C filter/dryer mounting bracket, 2
bolts to the fan module, and 2 nuts to the filter/dryer.
(14) Radiator can now be lifted free from engine
compartment.Care should be taken not to dam-
age radiator cooling fins or water tubes during
removal.INSTALLATION
(1)Be sure the air seals are in position before
radiator is installed.Slide radiator down into posi-
tion behind closure panel. Seat the radiator with the
rubber isolators into the mounting holes provided,
with a 10 lbs. force.
(2) Install A/C filter/dryer and mounting bracket
onto fan module.
(3) Install Air Conditioning Condenser onto the
radiator (Fig. 29).
(4) Unplug and connect automatic transmission
oil cooler lines to radiator.
(5) Install inlet and outlet radiator hoses (includ-
ing coolant reserve hose) and connect the fan motor
electrical connection.
(6) Install air cleaner assembly.
(7) Install the upper radiator closure panel cross-
member. Refer to Group 23 Body for procedure.
(8) Install the upper radiator mounting screws.
Tighten radiator mounting bolts to 12 N´m (105 in.
lbs.). Connect the engine block heater wire if
equipped.
(9) Install the Coolant Recovery System (CRS)
tank retaining screw to the upper radiator closure
panel crossmember.
(10) Install air intake resonator.
(11) Fill cooling system. Refer to Cooling System
Filling in this section.
(12) Connect negative cable to battery.
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Use of pliers on draincock is not rec-
ommended. Damage may occur to part. Draincock
should not be removed unless leakage observed.
(1) Turn the draincock stem counterclockwise to
unscrew the stem. When the stem is unscrewed to
Fig. 29 Air Conditioning Condenser Mounting
Fasteners
NSCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 21
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)