wheel CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 3272 of 4284

2ND GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft second gear is integral to the input shaft,
and is in constant mesh with the intermediate shaft
second speed gear. Because of this constant mesh,
the intermediate shaft second speed gear freewheels
until second gear is selected. As the gearshift lever ismoved to the second gear position, the 1-2 fork moves
the 1-2 synchronizer sleeve towards second gear on
the intermediate shaft. The synchronizer sleeve
engages the second gear clutch teeth, fixing the gear
to the intermediate shaft, and allowing power to
transmit through the intermediate shaft to the differ-
ential (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 2nd Gear Operation
21a - 6 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERG
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3273 of 4284

3RD GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft third speed gear is in constant mesh with
the intermediate shaft 3-4 cluster gear, which is fixed
to the intermediate shaft. Because of this constant
mesh, the input shaft third speed gear freewheelsuntil third gear is selected. As the gearshift lever is
moved to the third gear position, the 3-4 fork moves
the 3-4 synchronizer sleeve towards third gear on the
input shaft. The synchronizer sleeve engages the
third gear clutch teeth, fixing the gear to the input
shaft, and allowing power to transmit through the
intermediate shaft to the differential (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6 3rd Gear Operation
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-7
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3274 of 4284

4TH GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft fourth speed gear is in constant mesh
with the intermediate shaft 3-4 cluster gear, which is
fixed to the intermediate shaft. Because of this con-
stant mesh, the input shaft fourth speed gear free-
wheels until fourth gear is selected. As the gearshiftlever is moved to the fourth gear position, the 3-4
fork moves the 3-4 synchronizer sleeve towards
fourth gear on the input shaft. The synchronizer
sleeve engages the fourth gear clutch teeth, fixing
the gear to the input shaft, and allowing power to
transmit through the intermediate shaft to the differ-
ential (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7 4th Gear Operation
21a - 8 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERG
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3275 of 4284

5TH GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft fifth gear is pressed on to the input shaft,
and is in constant mesh with the intermediate shaft
fifth speed gear. Because of this constant mesh, the
intermediate shaft fifth speed gear freewheels untilfifth gear is selected. As the gearshift lever is moved
to the fifth gear position, the 5-R fork moves the 5-R
synchronizer sleeve towards the intermediate shaft
fifth speed gear. The synchronizer sleeve engages the
fifth gear clutch teeth, fixing the gear to the input
shaft, and allowing power to transmit through the
intermediate shaft to the differential (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8 5th Gear Operation
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-9
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3276 of 4284

REVERSE GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft reverse gear is integral to the input
shaft, and is in constant mesh with the reverse idler
gear. The reverse idler gear, which reverses the rota-
tion of the intermediate shaft, is in constant mesh
with the intermediate shaft reverse gear. Because of
this constant mesh, the intermediate shaft reversegear freewheels until reverse gear is selected. As the
gearshift lever is moved to the reverse gear position,
the 5-R fork moves the 5-R synchronizer sleeve
towards the intermediate shaft reverse gear. The
synchronizer sleeve engages the reverse gear clutch
teeth, fixing the gear to the intermediate shaft, and
allowing power to transmit through the intermediate
shaft to the differential (in reverse) (Fig. 9).
Fig. 9 Reverse Gear Operation
21a - 10 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERG
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3277 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMMON
PROBLEM CAUSES
The majority of transaxle malfunctions are a result
of:
²Insufficient lubrication
²Incorrect lubricant
²Misassembled or damaged internal components
²Improper operation
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting may be caused by a misadjusted
crossover cable. If hard shifting is accompanied by
gear clash, synchronizer clutch and stop rings or gear
teeth may be worn or damaged.
Hard shifting may also be caused by a binding or
broken shift cover mechanism. Remove shift cover
and verify smooth operation. Replace as necessary.
Misassembled synchronizer components also cause
shifting problems. Incorrectly installed synchronizer
sleeves, keys, balls, or springs can cause shift prob-
lems.
NOISY OPERATION
Transaxle noise is most often a result of worn or
damaged components. Chipped, broken gear or syn-
chronizer teeth, and brinnelled, spalled bearings all
cause noise.
Abnormal wear and damage to the internal compo-
nents is frequently the end result of insufficient
lubricant.
SLIPS OUT OF GEAR
Transaxle disengagement may be caused by mis-
aligned or damaged shift components, or worn teeth
on the drive gears or synchronizer components. Incor-
rect assembly also causes gear disengagement. Check
for missing snap rings.
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
Insufficient transaxle lubricant is usually the
result of leaks, or inaccurate fluid level check or refill
method. Leakage is evident by the presence of oil
around the leak point. If leakage is not evident, the
condition is probably the result of an underfill.
If air±powered lubrication equipment is used to fill
a transaxle, be sure the equipment is properly cali-
brated. Equipment out of calibration can lead to an
underfill condition.
CLUTCH PROBLEMS
Worn, damaged, or misaligned clutch components
can cause difficult shifting, gear clash, and noise.
A worn or damaged clutch disc, pressure plate, or
release bearing can cause hard shifting and gear
clash.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L GAS
(1) Raise hood.
(2) Disconnect gearshift cables from shift levers/
cover assembly (Fig. 10).
(3) Remove gearshift cable retaining clips from
mounting bracket (Fig. 10). Remove cables and
secure out of way.
(4) Remove three (3) right engine mount bracket-
to-transaxle bolts (Fig. 11).
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Remove front wheel/tires and halfshafts.
(7) Drain transaxle fluid into suitable container.
(8) Remove cradle plate.
(9) Remove front harness retainer and secure har-
ness out of way.
(10) Remove clutch release access cover.
(11)RHD Models:Using Tool 6638A, disconnect
clutch hydraulic circuit quick connect (located on
slave cylinder tube). Remove clutch slave cylinder by
depressing towards case and rotating counter-clock-
wise 60É, while lifting anti-rotation tab out of case
slot with screwdriver (Fig. 12).LHD Models:
Remove clutch release cable by pulling outward on
cable housing, then forward to allow cable core to
pass through case slot (Fig. 13). Disengage T-end
from release lever and secure cable out of way.
(12) Remove engine left mount bracket.
(13) Remove starter motor (Fig. 14).
Fig. 10 Gearshift Cables at Transaxle
1 - SELECTOR CABLE
2 - CABLE RETAINER
3 - CABLE RETAINER
4 - CROSSOVER CABLE
5 - MOUNT BRACKET
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-11
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3281 of 4284
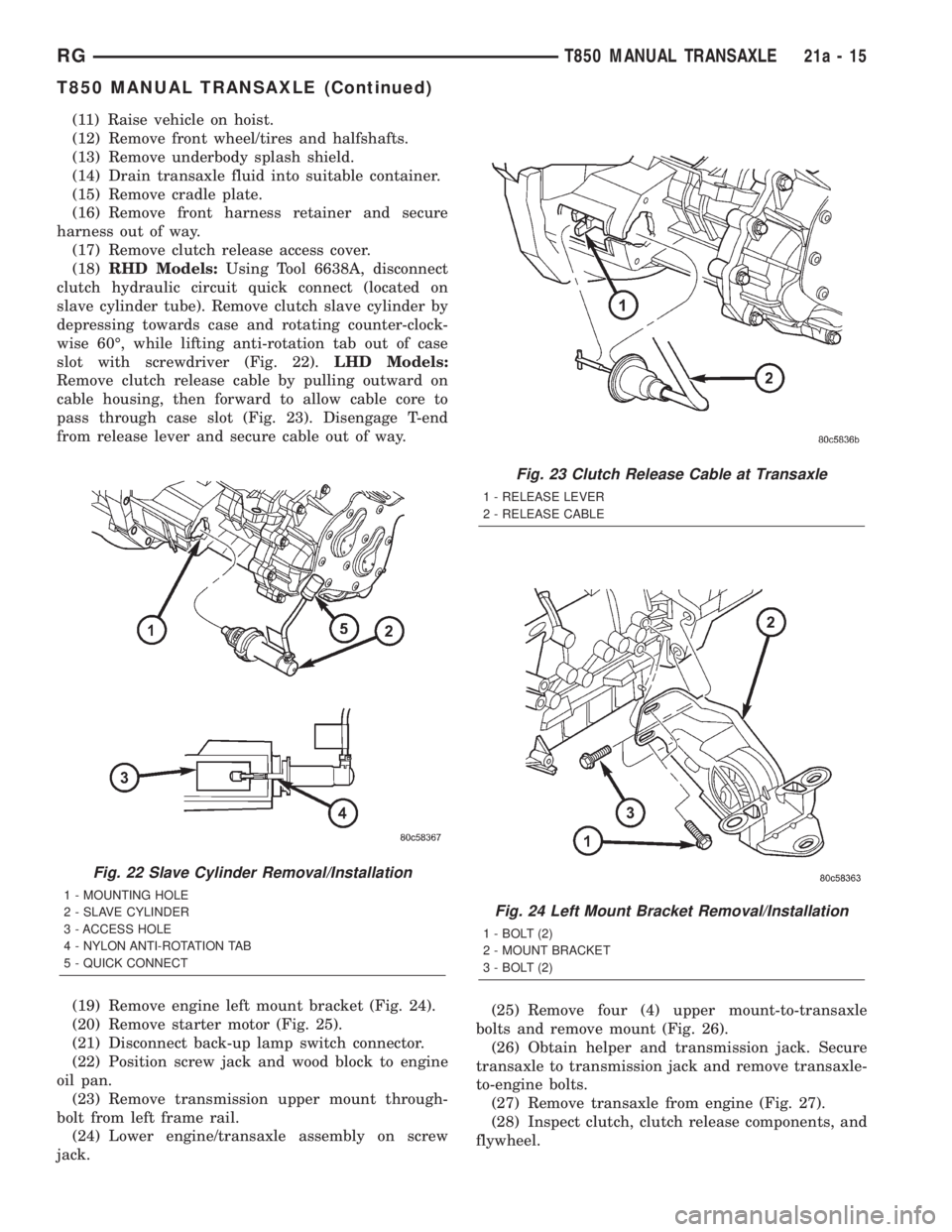
(11) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(12) Remove front wheel/tires and halfshafts.
(13) Remove underbody splash shield.
(14) Drain transaxle fluid into suitable container.
(15) Remove cradle plate.
(16) Remove front harness retainer and secure
harness out of way.
(17) Remove clutch release access cover.
(18)RHD Models:Using Tool 6638A, disconnect
clutch hydraulic circuit quick connect (located on
slave cylinder tube). Remove clutch slave cylinder by
depressing towards case and rotating counter-clock-
wise 60É, while lifting anti-rotation tab out of case
slot with screwdriver (Fig. 22).LHD Models:
Remove clutch release cable by pulling outward on
cable housing, then forward to allow cable core to
pass through case slot (Fig. 23). Disengage T-end
from release lever and secure cable out of way.
(19) Remove engine left mount bracket (Fig. 24).
(20) Remove starter motor (Fig. 25).
(21) Disconnect back-up lamp switch connector.
(22) Position screw jack and wood block to engine
oil pan.
(23) Remove transmission upper mount through-
bolt from left frame rail.
(24) Lower engine/transaxle assembly on screw
jack.(25) Remove four (4) upper mount-to-transaxle
bolts and remove mount (Fig. 26).
(26) Obtain helper and transmission jack. Secure
transaxle to transmission jack and remove transaxle-
to-engine bolts.
(27) Remove transaxle from engine (Fig. 27).
(28) Inspect clutch, clutch release components, and
flywheel.
Fig. 22 Slave Cylinder Removal/Installation
1 - MOUNTING HOLE
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
3 - ACCESS HOLE
4 - NYLON ANTI-ROTATION TAB
5 - QUICK CONNECT
Fig. 23 Clutch Release Cable at Transaxle
1 - RELEASE LEVER
2 - RELEASE CABLE
Fig. 24 Left Mount Bracket Removal/Installation
1 - BOLT (2)
2 - MOUNT BRACKET
3 - BOLT (2)
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-15
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3298 of 4284
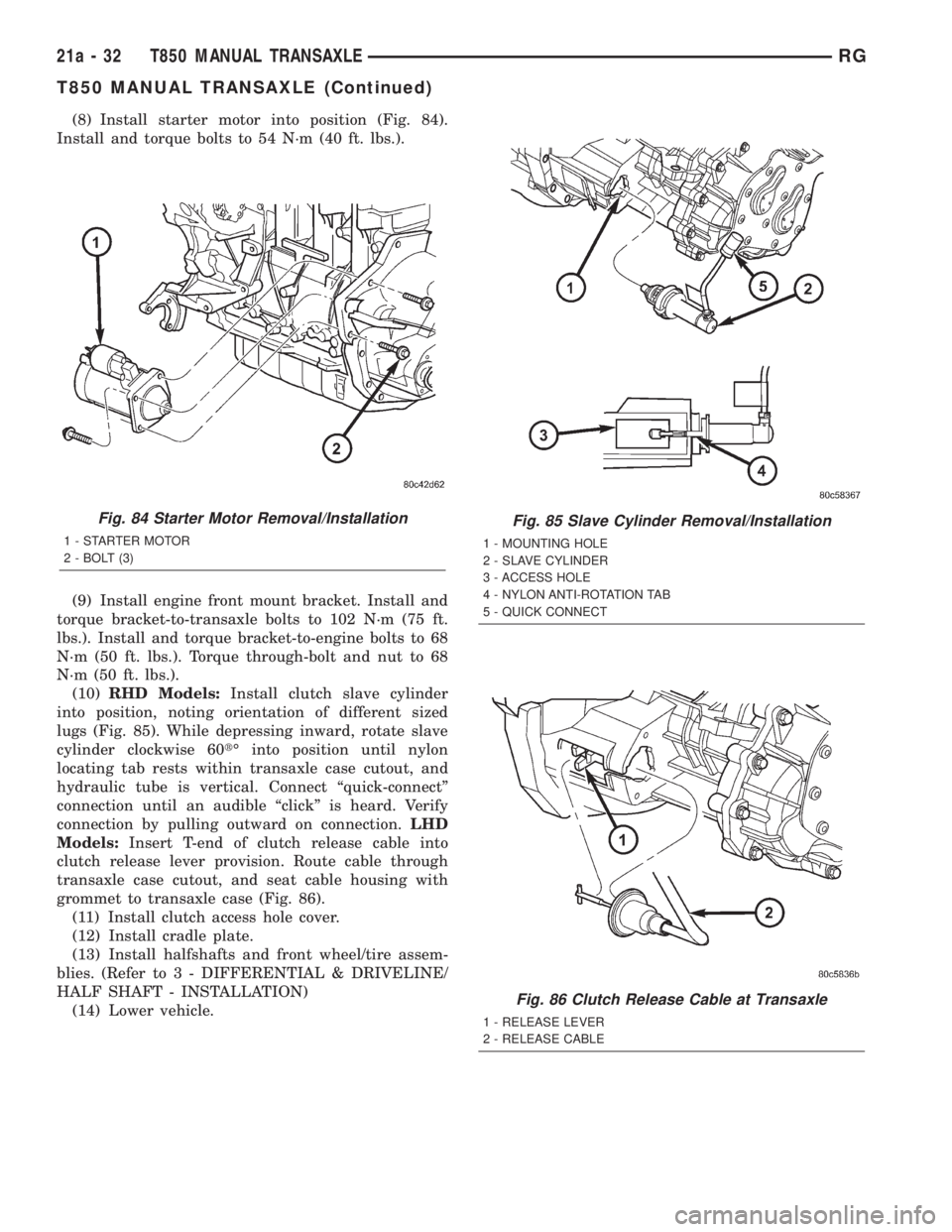
(8) Install starter motor into position (Fig. 84).
Install and torque bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install engine front mount bracket. Install and
torque bracket-to-transaxle bolts to 102 N´m (75 ft.
lbs.). Install and torque bracket-to-engine bolts to 68
N´m (50 ft. lbs.). Torque through-bolt and nut to 68
N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(10)RHD Models:Install clutch slave cylinder
into position, noting orientation of different sized
lugs (Fig. 85). While depressing inward, rotate slave
cylinder clockwise 60tÉ into position until nylon
locating tab rests within transaxle case cutout, and
hydraulic tube is vertical. Connect ªquick-connectº
connection until an audible ªclickº is heard. Verify
connection by pulling outward on connection.LHD
Models:Insert T-end of clutch release cable into
clutch release lever provision. Route cable through
transaxle case cutout, and seat cable housing with
grommet to transaxle case (Fig. 86).
(11) Install clutch access hole cover.
(12) Install cradle plate.
(13) Install halfshafts and front wheel/tire assem-
blies. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/
HALF SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(14) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 84 Starter Motor Removal/Installation
1 - STARTER MOTOR
2 - BOLT (3)
Fig. 85 Slave Cylinder Removal/Installation
1 - MOUNTING HOLE
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
3 - ACCESS HOLE
4 - NYLON ANTI-ROTATION TAB
5 - QUICK CONNECT
Fig. 86 Clutch Release Cable at Transaxle
1 - RELEASE LEVER
2 - RELEASE CABLE
21a - 32 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERG
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3301 of 4284
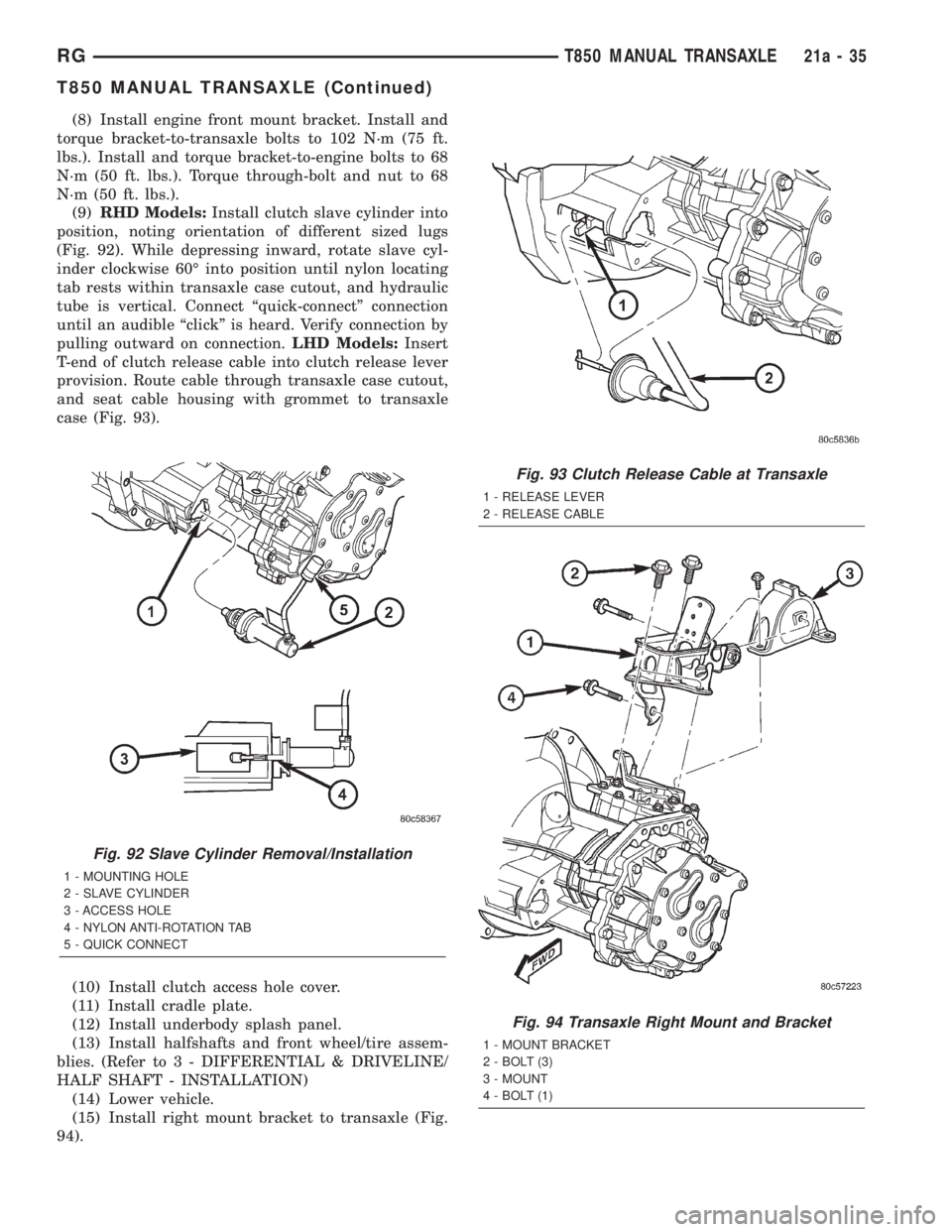
(8) Install engine front mount bracket. Install and
torque bracket-to-transaxle bolts to 102 N´m (75 ft.
lbs.). Install and torque bracket-to-engine bolts to 68
N´m (50 ft. lbs.). Torque through-bolt and nut to 68
N´m (50 ft. lbs.).
(9)RHD Models:Install clutch slave cylinder into
position, noting orientation of different sized lugs
(Fig. 92). While depressing inward, rotate slave cyl-
inder clockwise 60É into position until nylon locating
tab rests within transaxle case cutout, and hydraulic
tube is vertical. Connect ªquick-connectº connection
until an audible ªclickº is heard. Verify connection by
pulling outward on connection.LHD Models:Insert
T-end of clutch release cable into clutch release lever
provision. Route cable through transaxle case cutout,
and seat cable housing with grommet to transaxle
case (Fig. 93).
(10) Install clutch access hole cover.
(11) Install cradle plate.
(12) Install underbody splash panel.
(13) Install halfshafts and front wheel/tire assem-
blies. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/
HALF SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Install right mount bracket to transaxle (Fig.
94).
Fig. 92 Slave Cylinder Removal/Installation
1 - MOUNTING HOLE
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
3 - ACCESS HOLE
4 - NYLON ANTI-ROTATION TAB
5 - QUICK CONNECT
Fig. 93 Clutch Release Cable at Transaxle
1 - RELEASE LEVER
2 - RELEASE CABLE
Fig. 94 Transaxle Right Mount and Bracket
1 - MOUNT BRACKET
2 - BOLT (3)
3 - MOUNT
4 - BOLT (1)
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-35
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3309 of 4284

BACK-UP LAMP SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Disconnect back-up lamp switch connector.
(3) Remove back-up lamp switch (Fig. 103).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install back-up lamp switch (Fig. 103) and
torque to 23 N´m (17 ft. lbs.).
(2) Connect back-up lamp switch connector.
(3) Lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
DESCRIPTION
The T850 differential is a conventional open
design. It consists of a ring gear and a two-piece dif-
ferential case. The differential case contains the pin-
ion and side gears, three floating pinion shafts, and a
pinion shaft retaining ring (Fig. 104). The differential
case is supported in the transaxle by tapered roller
bearings.
OPERATION
The differential assembly is driven by the interme-
diate shaft via the ring gear. The ring gear drives the
differential case, and the case drives the halfshafts
through the differential gears. The differential pinion
and side gears are supported in the case by pinion
shafts and thrust washers. Differential pinion and
side gears make it possible for front wheels to rotate
at different speeds while cornering.
Fig. 103 Back-Up Lamp Switch
1 - BACK-UP LAMP SWITCH
Fig. 104 Differential Assembly
1 - RING GEAR
2 - SUPPORT PLATE
3 - SIDE GEAR (2)
4 - PINION GEAR (4)
5 - BOLT (12)
6 - PINION SHAFT (2-SHORT)
7 - PINION SHAFT (1-LONG)
8 - THRUST WASHER (2)
9 - RETAINING RING
10 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-43