wheel CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 2949 of 4284

SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.
DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER STEERING
PUMP INITIAL OPERATION
CAUTION: The fluid level should be checked with
engine off to prevent injury from moving compo-
nents. Use only MoparTPower Steering Fluid (MS-
5931) or approved equivalent. Do not overfill.
Read the fluid level through the side of the power
steering fluid reservoir. The fluid level should indi-
cateªFILL RANGEºwhen the fluid is at a temper-
ature of approximately 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to 80ÉF).
(1) Wipe the filler cap and area clean, then remove
the cap.
(2) Fill the fluid reservoir to the proper level and
let the fluid settle for at least two (2) minutes.
(3) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds,
then turn the engine off.
(4) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above steps
until the fluid level remains constant after running
the engine.
(5) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(6) Start the engine.
(7) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops.
(8) Add fluid if necessary.
(9) Lower the vehicle, then turn the steering wheel
slowly from lock-to-lock.
(10) Stop the engine. Check the fluid level and
refill as required.
(11) If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the vehi-
cle to stabilize a few minutes, then repeat the above
procedure.
REMOVAL - PUMP (2.4L ENGINE)
(1) Remove the (-) negative battery cable from the
battery and isolate cable.
(2) Remove the cap from the power steering fluid
reservoir.
(3) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(4) Raise the vehicle on jack stands or centered on
a frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrica-
tion and Maintenance.
(5) Disconnect the oxygen sensor wiring harness
from the vehicle wiring harness at the rear engine
mount bracket.
NOTE: The exhaust system needs to be removed
from the engine to allow for an area to remove the
power steering pump from the vehicle.
(6) Remove the four bolts and flag nuts securing
the catalytic converter from the exhaust manifold
(Fig. 3).
(7) Disconnect all the exhaust system isolators/
hangers from the brackets on the exhaust system (2
at the mufflers and 1 at the resonator) (Fig. 4).
(8) Remove the exhaust system by moving it as far
rearward, then lowering the front below the cross-
member and out of the vehicle.
(9) Remove the power steering fluid supply hose
from the fitting on the power steering pump. Drain
off excess power steering fluid from hose.
Fig. 3 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
1 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 - BOLT
3 - GASKET
4 - FLAG NUT
RSPUMP19-25
PUMP (Continued)
Page 2957 of 4284

STEERING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR..................................1PUMP..................................6
GEAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR
REMOVAL...............................1INSTALLATION............................4
GEAR
REMOVAL - RHD GEAR
CAUTION: Positioning the steering column in the
locked position will prevent the clockspring from
being accidentally over-extended when the steering
column is disconnected from the intermediate
steering coupler.
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much fluid as
possible from the power steering fluid reservoir.
(3) With the ignition key in the locked position
turn the steering wheel to the left until the steering
wheel is in the locked position.
(4) With the vehicle on the ground, disconnect the
steering column shaft coupler from the steering gear
intermediate coupler (Fig. 1).
(5) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(6) Remove front wheel and tire assemblies.
(7) If equipped, remove hoses at power steering
cooler and allow fluid to drain.
(8) On both sides of vehicle, remove nut attaching
outer tie rod end to steering knuckle (Fig. 2).
Remove nut by holding tie rod end stud with a
socket while loosening and removing nut with
wrench.
(9) Remove both tie rod ends from steering knuck-
les using Puller, Special Tool C-3894±A (Fig. 3).(10) Remove the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer bolts located on each side of each lower con-
trol arm rear bushing.
NOTE: The bolts fastening the cradle crossmember
reinforcement are of two different thread sizes. Note
the location of the various sizes.
Fig. 1 Steering Column Shaft To Intermediate Shaft
Attachment
1 - STEERING COLUMN SHAFT COUPLER
2 - NUT
3 - SAFETY PIN
4 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
5 - PINCH BOLT
RGSTEERING19a-1
Page 2958 of 4284
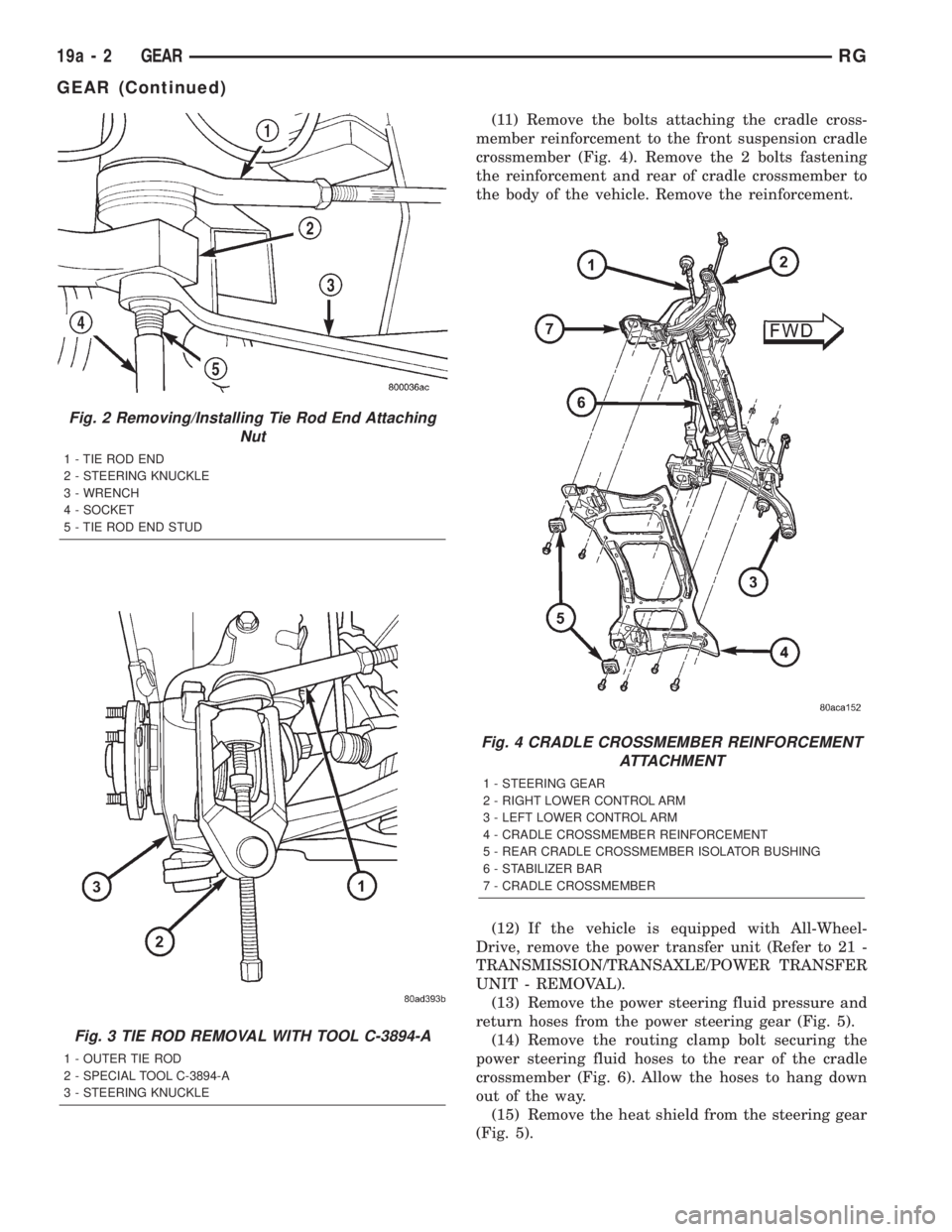
(11) Remove the bolts attaching the cradle cross-
member reinforcement to the front suspension cradle
crossmember (Fig. 4). Remove the 2 bolts fastening
the reinforcement and rear of cradle crossmember to
the body of the vehicle. Remove the reinforcement.
(12) If the vehicle is equipped with All-Wheel-
Drive, remove the power transfer unit (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/POWER TRANSFER
UNIT - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove the power steering fluid pressure and
return hoses from the power steering gear (Fig. 5).
(14) Remove the routing clamp bolt securing the
power steering fluid hoses to the rear of the cradle
crossmember (Fig. 6). Allow the hoses to hang down
out of the way.
(15) Remove the heat shield from the steering gear
(Fig. 5).
Fig. 2 Removing/Installing Tie Rod End Attaching
Nut
1 - TIE ROD END
2 - STEERING KNUCKLE
3 - WRENCH
4 - SOCKET
5 - TIE ROD END STUD
Fig. 3 TIE ROD REMOVAL WITH TOOL C-3894-A
1 - OUTER TIE ROD
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3894-A
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
Fig. 4 CRADLE CROSSMEMBER REINFORCEMENT
ATTACHMENT
1 - STEERING GEAR
2 - RIGHT LOWER CONTROL ARM
3 - LEFT LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER REINFORCEMENT
5 - REAR CRADLE CROSSMEMBER ISOLATOR BUSHING
6 - STABILIZER BAR
7 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER
19a - 2 GEARRG
GEAR (Continued)
Page 2960 of 4284

INSTALLATION - RHD GEAR
(1) Install the steering gear up in the front sus-
pension cradle crossmember, leaving room to install
intermediate coupler.
(2) Start the roll pin into the intermediate coupler
before installing coupler on steering gear shaft. Start
roll pin into coupler, using a hammer and tapping it
into the coupler. Then install the intermediate cou-
pler on the shaft of the steering gear.
(3) Install Remover/Installer Special Tool 6831A
through the center of the roll pin, securing it with
the knurled nut (Fig. 8). Hold threaded rod station-
ary while turning nut. This will pull the roll pin into
the intermediate coupler.
(4) Install power steering gear on the front suspen-
sion cradle. Install the 3 steering gear mounting
bolts and nuts. Tighten the 3 steering gear to sus-
pension cradle mounting bolts to a torque of 183 N´m
(135 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Proper torque on the steering gear to
suspension cradle mounting bolts is very impor-
tant.
(5) Install the heat shield on the steering gear
(Fig. 5).
(6) Attach the power steering fluid pressure and
return hoses to the proper fittings on the steering
gear (Fig. 5). Do not fully tighten the fittings at this
time.
(7) Install the routing clamp with the bolt securing
the power steering fluid hoses to the rear of the cra-
dle crossmember (Fig. 6).(8) Using a crowfoot wrench on a torque wrench,
tighten the power steering fluid hose tube nuts at the
gear to a torque of 31 N´m (275 in. lbs.).
(9) Install tie rod end into steering knuckle. Start
tie rod end to steering knuckle attaching nut onto
stud of tie rod end. While holding stud of tie rod end
stationary using a socket (Fig. 2), tighten tie rod end
to steering knuckle attaching nut. Then using a
crowfoot and socket (Fig. 9), tighten the tie rod end
attaching nut to a torque of 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.).
(10) If the vehicle is equipped with All-Wheel-
Drive, install the power transfer unit (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/POWER TRANSFER
UNIT - INSTALLATION).
CAUTION: Proper torque on the cradle reinforce-
ment to suspension cradle mounting bolts is very
important.
(11) Install the reinforcement on the front suspen-
sion cradle crossmember and install the bolts attach-
ing the reinforcement to the cradle crossmember
(Fig. 4). Tighten the M-14 size bolts to a torque of
163 N´m (120 ft. lbs.). Tighten the M-12 size bolts to
a torque of 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
(12) Install the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer bolts through reinforcement on each side of
each lower control arm rear bushing. Tighten bolts to
a torque of 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the two bolts and bushings attaching
the reinforcement and rear of cradle crossmember to
body of vehicle (Fig. 4). Tighten bolts to a torque of
163 N´m (120 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 8 Installing Roll Pin In Intermediate Coupler
1 - INTERMEDIATE COUPLER
2 - SUSPENSION CRADLE
3 - KNURLED NUT
4 - ROLL PIN
5 - STEERING GEAR
Fig. 9 Torquing Tie Rod End Attaching Nut
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - TIE ROD END
3 - CROWFOOT
4 - SOCKET
5 - TORQUE WRENCH
19a - 4 GEARRG
GEAR (Continued)
Page 2961 of 4284

(14) If equipped, install the power steering cooler
hoses on the cooler inlet and outlet tubes. Install the
clamps.
(15) Install the front tire and wheel assemblies on
vehicle. Install the wheel mounting lug nuts and
tighten to a torque to 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(16) Lower the vehicle to a level were the interior
of vehicle is accessible (keeping tires off the ground).
(17) Using the intermediate coupler, turn the front
wheels of the vehicle to the left until the intermedi-
ate coupler shaft is properly aligned with the steer-
ing column coupler. Assemble the steering columnshaft coupler onto the steering gear intermediate
coupler (Fig. 1). Install steering column coupler to
intermediate shaft retaining pinch bolt. Tighten the
pinch bolt nut to a torque of 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(18) Perform the POWER STEERING PUMP INI-
TIAL OPERATION procedure to properly fill and
bleed the power steering system. (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(19) Inspect for leaks.
(20) Adjust front wheel toe (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
RGGEAR19a-5
GEAR (Continued)
Page 2967 of 4284

OPERATION
The Transfer Unit provides the power to the rear
wheels through a hypoid ring gear and pinion set.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SEAL
IDENTIFICATION
For accurate seal diagnosis, repair seal name and
location is critical. Refer to (Fig. 1), (Fig. 2), (Fig. 3)
and (Fig. 4) for correct seal name and location.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID LEAK
DIAGNOSIS
When diagnosing fluid leaks on the Power Transfer
Unit two weep holes are provided to diagnose certain
seal leaks. These holes are located on the bottom side
of the assembly (Fig. 5).
If fluid leak is detected from either weep hole, seal
replacement is necessary.Do not attempt to repair
the leak by sealing weep holes,they must be kept
clear of sealants for proper seal operation.
If fluid is leaking from weep hole A (Fig. 5) the
type of fluid leaking will determine which seal needs
to be replaced. If the fluid leaking is red in color
1 - PLUG 18 - CASE-PTU 35 - SHIM
2 - WASHER FLAT 19 - PINION-PTU 36 - TAPERED ROLLER BEARING
3 - SEAL RING 20 - O-RING 37 - SHAFT ASSY. FRONT L.H.
4 - SNAP RING 21 - SHIM 38 - SEAL RING
5 - BALL BEARING 22 - TAPERED ROLLER BEARING 39 - OIL WIPER
6 - SEAL RING 23 - COVER-PTU CASE REAR 40 - RETAINER DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
7 - COVER-PTU
CASE END24 - FLANGE TUBE-PTU-OUTPUT ASSY. 41 - SHAFT DIFFERENTIAL PINION
8 - TAPERED ROLLER BEARING 25 - LOCK NUT-HEX FLANGE 42 - PIN
9 - SEAL RING 26 - O- RING 43 - CASE DIFFERENTIAL
10 - SEAL RING 27 - RETAINER PLATE 44 - TAPERED ROLLER BEARING CONE
11 - HEX HEAD SCREW 28 - O-RING 45 - SEAL RING
12 - SHAFT-PTU INPUT 29 - BRACKET 46 - SEAL RING
13 - GEAR-PTU RING 30 - THRUST WASHER 47 - PLUG
14 - TROUGH-PTU (RT.) 31 - SIDE GEAR-DIFFERENTIAL 48 - O-RING
15 - TROUGH-PTU (LT.) 32 - FINAL DRIVE GEAR 49 - SHIM
16 - TAPERED ROLLER BEARING 33 - PINION DIFFERENTIAL 50 - MAGNET
17 - HEX HEAD SCREW 34 - WASHER DIFFERENTIAL PINION 51 - DOWEL
52 - SHAFT ASSY. FRONT R.H.
53 - HEX HEAD SCREW
Fig. 1 Seal
1 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - P.T.U. CASE
3 - MAGNET
4 - INPUT SHAFT END SEAL
5 - OUTPUT SHAFT
6 - RING GEAR
7 - REAR COVER
Fig. 2 Seal Location
1 - REAR COVER
2 - END COVER
3 - OUTER HALFSHAFT SEAL
4 - P.T.U. CASE
5 - P.T.U. OUTPUT SEAL
RSPOWER TRANSFER UNIT21-3
POWER TRANSFER UNIT (Continued)
Page 2969 of 4284
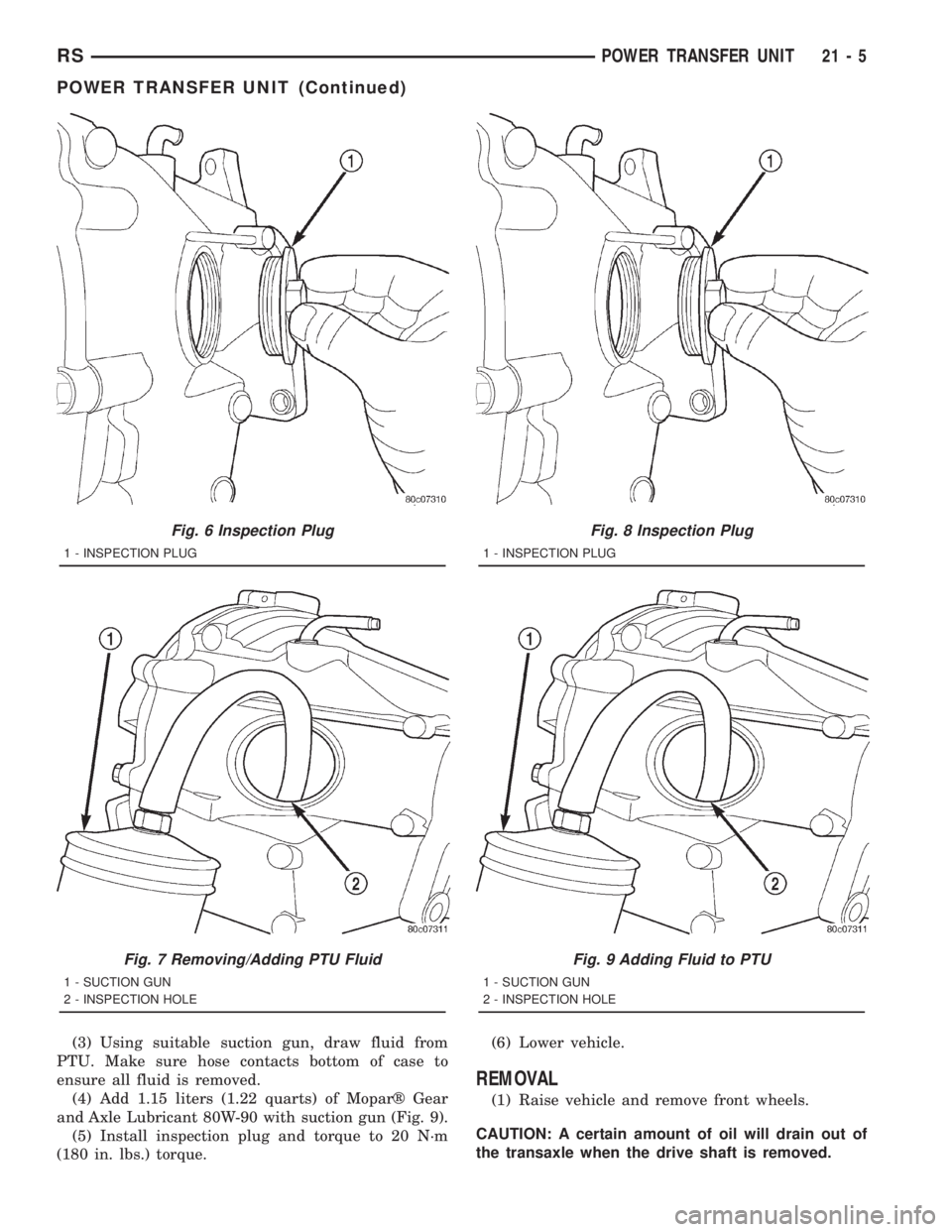
(3) Using suitable suction gun, draw fluid from
PTU. Make sure hose contacts bottom of case to
ensure all fluid is removed.
(4) Add 1.15 liters (1.22 quarts) of Moparž Gear
and Axle Lubricant 80W-90 with suction gun (Fig. 9).
(5) Install inspection plug and torque to 20 N´m
(180 in. lbs.) torque.(6) Lower vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and remove front wheels.
CAUTION: A certain amount of oil will drain out of
the transaxle when the drive shaft is removed.
Fig. 6 Inspection Plug
1 - INSPECTION PLUG
Fig. 7 Removing/Adding PTU Fluid
1 - SUCTION GUN
2 - INSPECTION HOLE
Fig. 8 Inspection Plug
1 - INSPECTION PLUG
Fig. 9 Adding Fluid to PTU
1 - SUCTION GUN
2 - INSPECTION HOLE
RSPOWER TRANSFER UNIT21-5
POWER TRANSFER UNIT (Continued)
Page 2986 of 4284

REMOVAL.............................118
INSTALLATION..........................118
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
REMOVAL.............................118
INSTALLATION..........................118
ADJUSTMENTS.........................120
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION..........................120
OPERATION............................123
REMOVAL.............................125
INSTALLATION..........................125
TRANSFER SYSTEM - OUTPUT SHAFT/GEAR/
BEARING
REMOVAL.............................126
INSTALLATION..........................129
ADJUSTMENTS.........................132TRANSFER SYSTEM - TRANSFER SHAFT/
GEAR/BEARING
REMOVAL.............................134
INSTALLATION..........................137
ADJUSTMENTS.........................142
VALVE BODY
REMOVAL.............................142
DISASSEMBLY..........................145
CLEANING.............................151
INSPECTION...........................152
ASSEMBLY............................152
INSTALLATION..........................155
ADJUSTMENTS.........................157
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR/PINION GEAR
REMOVAL.............................157
INSTALLATION..........................157
AUTOMATIC - 31TH
DESCRIPTION
This transaxle combines torque converter, three
speed transmission, final drive gearing, and differen-
tial into a front wheel drive system.
Within this transaxle, there are three primary
areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor
and parking sprag).
(3) Differential center line.
Center distances between the main rotating parts
in these three areas are held precise to maintain a
low noise level.
The torque converter, transaxle area, and differen-
tial are housed in an integral aluminum die casting.
The differential oil sump is common with the
transaxle sump. Separate filling of the differen-
tial is NOT necessary.
The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through a remote cooler. There are two types of
coolers used. An oil-to-water type cooler located in
the radiator side tank and/or an oil-to-air heat
exchanger. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assembly.Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter and then through the input shaft to multiple-
disc clutches in the transaxle. The power flow
depends on the application of the clutches and bands.
Refer to Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and
Tests section.
The transaxle consists of:
²Two multiple-disc clutches
²An overrunning clutch
²Two servos
²A hydraulic accumulator
²Two bands
²Two planetary gear sets
This provides three forward ratios and a reverse
ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary gear
sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The driving shell is splined to the sun gear and
front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system consists
of an oil pump and a single valve body which con-
tains all of the valves except the governor valves.
The transaxle sump and differential sump are both
vented through the dipstick. Output torque from the
main center line is delivered through helical gears to
the transfer shaft. This gear set is a factor in the
transaxle final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also car-
ries the governor and parking sprag. An integral heli-
cal gear on the transfer shaft drives the differential
ring gear.
21 - 22 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
Page 2996 of 4284

The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit that slips and to confirm proper operation of
good units. Road testing can usually diagnose slip-
ping units, although the actual cause of the problem
may not be detected. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
Therefore, unless the condition is obvious, the
transaxle should never be disassembled until hydrau-
lic pressure tests have been performed.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most transaxle problems.
Before performing pressure tests, check fluid level
and condition, as well as control cable adjustments.
Fluid must be at operating temperature (150-200
degrees F.).
Install an engine tachometer. Raise vehicle on a
hoist that allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read.
Disconnect throttle cable and shift cable from
transaxle levers so they can be controlled from out-
side the vehicle.
Attach 100 psi gauges (C-3292) to ports required
for test being conducted. A 300 psi gauge (C-3293SP)
is required for reverse pressure test at rear servo.
Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Test Port Locations
1 - ACCUMULATOR VENT
2 - MANUAL THROTTLE LEVER SHAFT
3 - MANUAL SHIFT LEVER SHAFT
4 - LOW-REVERSE PRESSURE
5 - GOVERNER PRESSURE (BELOW DIFFERENTIAL COVER
ON RIGHT SIDE)
6 - LINE PRESSURE
7 - KICKDOWN APPLY AT ACCUMULATOR8 - TO COOLER
9 - KICKDOWN RELEASE (FRONT CLUTCH)
10 - KICKDOWN APPLY
11 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CONNECTOR
12 - FROM COOLER
13 - KICKDOWN BAND ADJUSTING SCREW
21 - 32 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
Page 3002 of 4284

(12) Remove front mount and bracket (Fig. 11).
(13) Cut transaxle oil cooler lines flush with fit-
tings. a service kit will be installed upon reintalla-
tion. Plug lines and fittings to prevent debris
intrusion.
(14) Remove structural collar (Fig. 12).
(15) Disconnect vehicle speed sensor connector.
(16) Remove rear mount shield (Fig. 13).
(17) Remove rear mount thru-bolt.
(18) Support engine with screw jack and wood
block.
(19) Remove cradle plate.
(20) Remove torque converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(21) Remove left wheel splash shield.
(22) Remove left upper mount thru-bolt (Fig. 14).
(23) Lower engine/transaxle assembly.
(24) Obtain transmission jack and helper.
(25) Remove remaining transaxle-to-engine bolts
and remove transaxle assembly from vehicle.
Fig. 11 Front Mount and Bracket
1 - BRACKET - FRONT MOUNT
2 - NUT
3 - BOLT
4 - MOUNT - FRONT INSULATOR
5 - BOLT
6 - BOLT
7 - FRONT CROSSMEMBER
Fig. 12 Structural Collar
1 - BOLT - COLLAR TO OIL PAN
2 - BOLT - COLLAR TO TRANSAXLE
3 - STRUCTURAL COLLAR
4 - OIL PAN
Fig. 13 Rear Mount Heat Shield
1 - BOLT - HEAT SHIELD
2 - HEAT SHIELD
3 - CLIP
4 - REAR MOUNT
21 - 38 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)