acc DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 1950 of 2643

POWER STEERING GEAR 6C – 33
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
POWER RACK AND PINION
The power rack and pinion steering system has a rotary
control valve that directs hydraulic fluid coming from the
hydraulic pump to one side or the other side of the rack pis-
ton. The integral rack piston is attached to the rack. The
rack piston converts hydraulic pressure to a linear force
that moves the rack left or right. That force is then trans-
mitted through the tie rods to the steering knuckles, which
turn the wheels.
If power rack and pinion steering is not available, manual
rack and pinion control is used; however, with this system,
more steering effort is required. The movement of the
steering wheel is transferred to the pinion. The rotary
movement of the pinion is then transferred through the pin-
ion threads, which mesh with teeth on the rack, thereby
causing the rack to move in a linear direction.
A vane–type of hydraulic pump provides hydraulic pres-
sure for both steering systems.
SPEED SENSITIVE POWER
STEERING SYSTEM
The speed sensitive power steering (SSPS) system varies
the driver effort required to steer as the vehicle speed
changes. At low speeds, the system provides maximum
power assist for easy turning and parking maneuvers. At
higher speeds, the steering power is reduced to provide
the driver with firmer steering and directional stability. The
SSPS system accomplishes this by reducing the amount
of power steering fluid flow from the power steering pump
to the power steering gear as the vehicle speed increases.
When the vehicle is stationary, the SSPS system provides
maximum fluid flow to the steering gear. As the vehicle
speed increases, the fluid flow to the steering gear is de-
creased.
Control Module
The SSPS control module processes the vehicle speed in-
formation from the engine control module (ECM) and uses
the steering wheel rotation sensor to provide a control sig-
nal to the electronic variable orifice (EVO) actuator located
on the power steering pump.
Electronic Variable Orifice (EVO) Actuator
The electronic variable orifice (EVO) actuator is located on
the power steering pump and contains a solenoid– oper-
ated pintle valve. Fluid leaving the pump passes through
an orifice in the actuator tip. When the EVO actuator is
powered by the SSPS control module, the pintle moves
into the orifice and reduces the power steering fluid flow.As the vehicle speed increases, current from the SSPS
control module increases, and the pintle blocks more and
more of the orifice.
Steering Wheel Rotation Sensor
The steering wheel rotation sensor is located at the end of
the steering column housing and is used to send a signal
to the controller when abrupt or evasive steering maneu-
vers are needed.
Power Steering Pressure Hose
SSPS vehicles have a specific pressure hose assembly
which includes an in–line check valve in the rack and pin-
ion assembly. This reduces the amount of steering wheel
”kick” when driving over irregular road surfaces while oper-
ating at speeds with reduced flow rate and pressure.
Power Rack and Pinion
Except for differences in valve machining, the design of
the SSPS power rack and pinion assembly is the same as
for the a non–SSPS system. The steering wheel move-
ment is transferred to the pinion via the intermediate shaft.
The pinion moves the rack left or right through meshing the
pinion and the rack teeth. The force is then transmitted
through the tie rods and steering knuckle to steer the
wheels.
The power rack and pinion steering system has a rotary
control valve which directs the hydraulic fluid from the
power steering pump to one side or the other side of the
rack piston. The piston is attached to the rack and uses hy-
draulic pressure to move the rack left or right. The rotary
control valve regulates the degree of assist by responding
to the driver’s torque input.
If hydraulic assist is not available, manual control is main-
tained. However, under this condition, more steering effort
is required.
Power Steering Pump
The standard vane–type pump, which provides hydraulic
pressure for the system, incorporates a special discharge
fitting to hold the EVO actuator.
System Operation
System operation originates with input from the vehicle
speed sensor via the engine control module to the SSPS
control module. The SSPS control module sends a signal
to the SSPS actuator to vary the rate of fluid flow output
by the power steering pump.
Circuit Operation
The SSPS system uses inputs from the speed sensor and
steering wheel rotation sensor to the SSPS controller to
determine the desired amount of power steering assist.
The SSPS control module constantly compares the
amount of current flowing through the EVO actuator to the
desired current it has calculated. The EVO actuator has a
pintle that moves in and out of an orifice, regulating power
Page 1951 of 2643
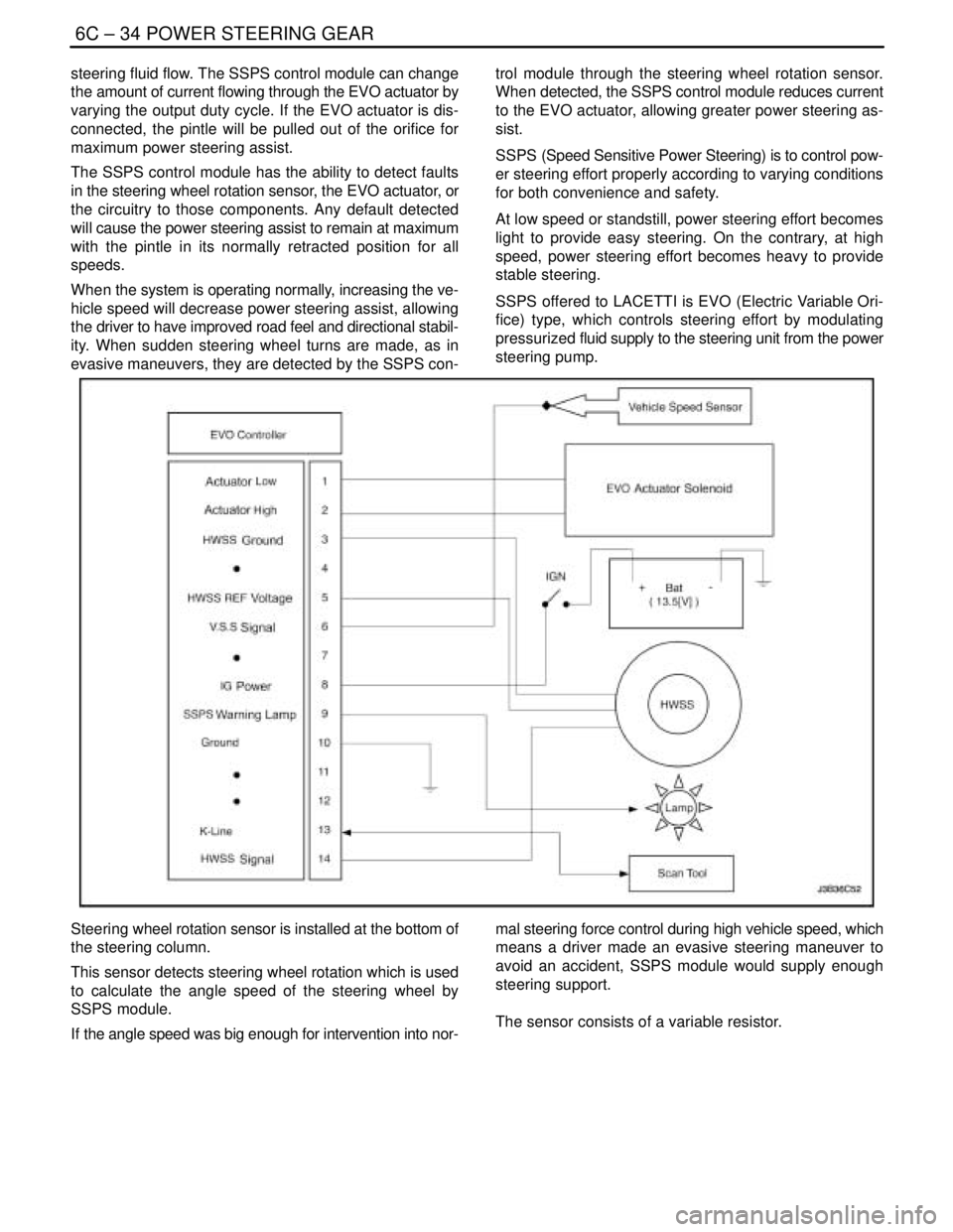
6C – 34IPOWER STEERING GEAR
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
steering fluid flow. The SSPS control module can change
the amount of current flowing through the EVO actuator by
varying the output duty cycle. If the EVO actuator is dis-
connected, the pintle will be pulled out of the orifice for
maximum power steering assist.
The SSPS control module has the ability to detect faults
in the steering wheel rotation sensor, the EVO actuator, or
the circuitry to those components. Any default detected
will cause the power steering assist to remain at maximum
with the pintle in its normally retracted position for all
speeds.
When the system is operating normally, increasing the ve-
hicle speed will decrease power steering assist, allowing
the driver to have improved road feel and directional stabil-
ity. When sudden steering wheel turns are made, as in
evasive maneuvers, they are detected by the SSPS con-trol module through the steering wheel rotation sensor.
When detected, the SSPS control module reduces current
to the EVO actuator, allowing greater power steering as-
sist.
SSPS (Speed Sensitive Power Steering) is to control pow-
er steering effort properly according to varying conditions
for both convenience and safety.
At low speed or standstill, power steering effort becomes
light to provide easy steering. On the contrary, at high
speed, power steering effort becomes heavy to provide
stable steering.
SSPS offered to LACETTI is EVO (Electric Variable Ori-
fice) type, which controls steering effort by modulating
pressurized fluid supply to the steering unit from the power
steering pump.
Steering wheel rotation sensor is installed at the bottom of
the steering column.
This sensor detects steering wheel rotation which is used
to calculate the angle speed of the steering wheel by
SSPS module.
If the angle speed was big enough for intervention into nor-mal steering force control during high vehicle speed, which
means a driver made an evasive steering maneuver to
avoid an accident, SSPS module would supply enough
steering support.
The sensor consists of a variable resistor.
Page 1954 of 2643
![DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual POWER STEERING GEAR 6C – 37
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
[Vehicle Speed – Actuator Current Relation]
SOLENOID RESISTANCE
13 W
The control module is installed on the right side of the au-
dio and can be acc DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual POWER STEERING GEAR 6C – 37
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
[Vehicle Speed – Actuator Current Relation]
SOLENOID RESISTANCE
13 W
The control module is installed on the right side of the au-
dio and can be acc](/img/54/56877/w960_56877-1953.png)
POWER STEERING GEAR 6C – 37
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
[Vehicle Speed – Actuator Current Relation]
SOLENOID RESISTANCE
13 W
The control module is installed on the right side of the au-
dio and can be accessible after the glove box is removed.
It receives signals from the vehicle speed sensor and the
steering wheel rotation sensor and processes them to de-
cide proper fluid flow through the actuator.
It also has a self–diagnosis. If it detects any malfunction,
it starts default mode, which is basically actuator full open
for light steering effort.
TERMINALCOLORFUNCTION
1SBActuator Low
2VActuator High
3BWSteering Wheel Sensor Ground
4–Not used
5GrSteering Wheel Sensor 5V ref.
6GWVSS
7–Not Used
8PIGN ON
9BrWarning Lamp
10BWGround
11–Not Used
12–Not Used
13LDiagnosis
14SBSteering Wheel Sensor Signal
Page 1965 of 2643

STEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN 6E – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
2. Install the intermediate shaft onto the steering col-
umn. Refer to ”Steering Column” in this section.
3. Connect the steering wheel rotation sensor electri-
cal connector.
4. Install the upper and the lower instrument trim pan-
els. Refer to Section 9E, Instrumentation/Driver
Information.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
STEERING WHEEL WITHOUT SIR
Tools Required
KM–210–A Steering Wheel Puller
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Rotate the steering wheel to allow access to the
steering wheel horn cap screw. Remove the horn
cap screw.
3. Rotate the steering wheel to allow access to the
other steering wheel horn cap screw. Remove the
horn cap screw.
4. Remove the steering wheel horn cap and discon-
nect the horn leads.
5. Remove the steering wheel nut and the retaining
clip.
Page 1966 of 2643
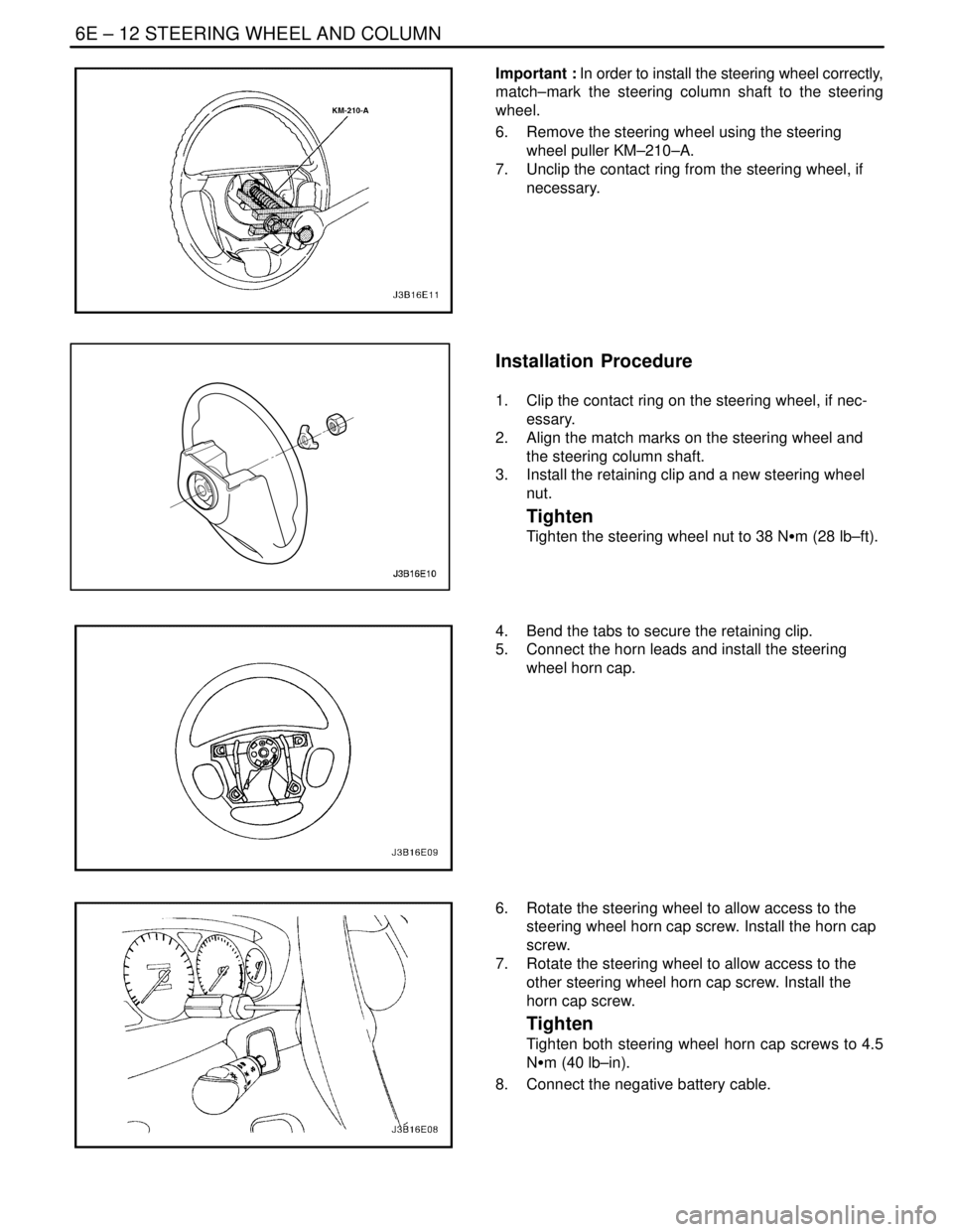
6E – 12ISTEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Important : In order to install the steering wheel correctly,
match–mark the steering column shaft to the steering
wheel.
6. Remove the steering wheel using the steering
wheel puller KM–210–A.
7. Unclip the contact ring from the steering wheel, if
necessary.
Installation Procedure
1. Clip the contact ring on the steering wheel, if nec-
essary.
2. Align the match marks on the steering wheel and
the steering column shaft.
3. Install the retaining clip and a new steering wheel
nut.
Tighten
Tighten the steering wheel nut to 38 NSm (28 lb–ft).
4. Bend the tabs to secure the retaining clip.
5. Connect the horn leads and install the steering
wheel horn cap.
6. Rotate the steering wheel to allow access to the
steering wheel horn cap screw. Install the horn cap
screw.
7. Rotate the steering wheel to allow access to the
other steering wheel horn cap screw. Install the
horn cap screw.
Tighten
Tighten both steering wheel horn cap screws to 4.5
NSm (40 lb–in).
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 1968 of 2643
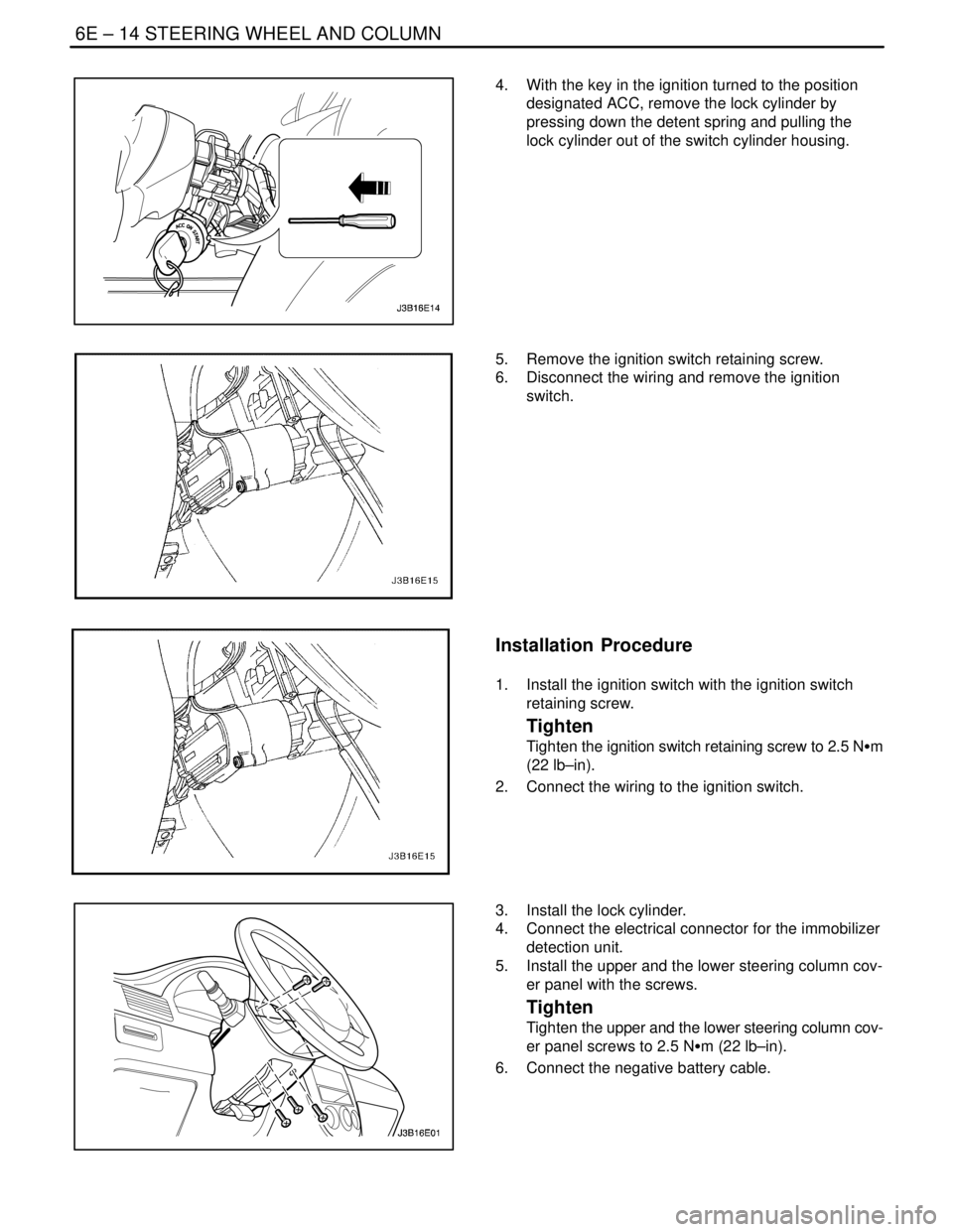
6E – 14ISTEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. With the key in the ignition turned to the position
designated ACC, remove the lock cylinder by
pressing down the detent spring and pulling the
lock cylinder out of the switch cylinder housing.
5. Remove the ignition switch retaining screw.
6. Disconnect the wiring and remove the ignition
switch.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the ignition switch with the ignition switch
retaining screw.
Tighten
Tighten the ignition switch retaining screw to 2.5 NSm
(22 lb–in).
2. Connect the wiring to the ignition switch.
3. Install the lock cylinder.
4. Connect the electrical connector for the immobilizer
detection unit.
5. Install the upper and the lower steering column cov-
er panel with the screws.
Tighten
Tighten the upper and the lower steering column cov-
er panel screws to 2.5 NSm (22 lb–in).
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 1981 of 2643
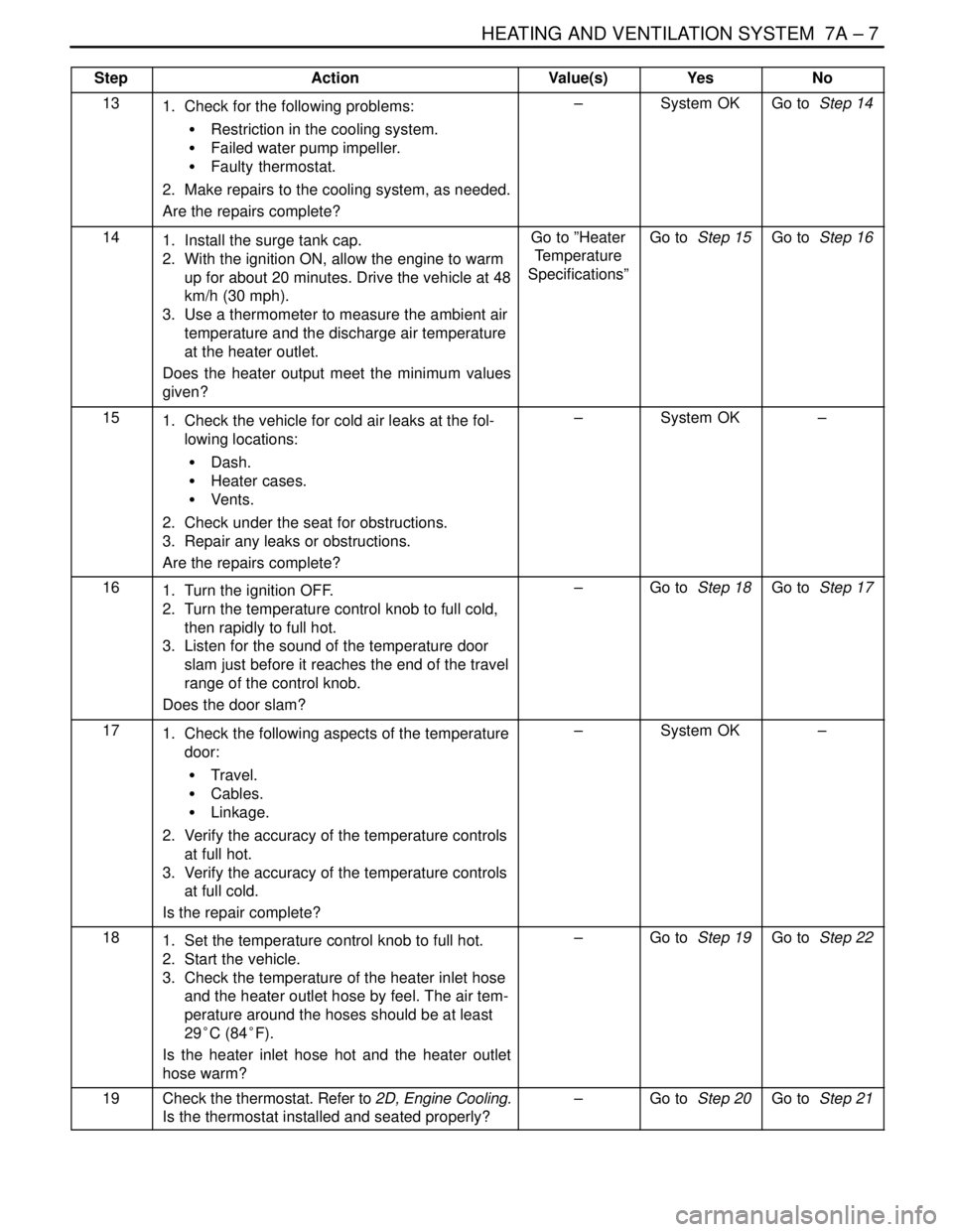
HEATING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM 7A – 7
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
131. Check for the following problems:
S Restriction in the cooling system.
S Failed water pump impeller.
S Faulty thermostat.
2. Make repairs to the cooling system, as needed.
Are the repairs complete?–System OKGo to Step 14
141. Install the surge tank cap.
2. With the ignition ON, allow the engine to warm
up for about 20 minutes. Drive the vehicle at 48
km/h (30 mph).
3. Use a thermometer to measure the ambient air
temperature and the discharge air temperature
at the heater outlet.
Does the heater output meet the minimum values
given?Go to ”Heater
Temperature
Specifications”Go to Step 15Go to Step 16
151. Check the vehicle for cold air leaks at the fol-
lowing locations:
S Dash.
S Heater cases.
S Vents.
2. Check under the seat for obstructions.
3. Repair any leaks or obstructions.
Are the repairs complete?–System OK–
161. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Turn the temperature control knob to full cold,
then rapidly to full hot.
3. Listen for the sound of the temperature door
slam just before it reaches the end of the travel
range of the control knob.
Does the door slam?–Go to Step 18Go to Step 17
171. Check the following aspects of the temperature
door:
S Travel.
S Cables.
S Linkage.
2. Verify the accuracy of the temperature controls
at full hot.
3. Verify the accuracy of the temperature controls
at full cold.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
181. Set the temperature control knob to full hot.
2. Start the vehicle.
3. Check the temperature of the heater inlet hose
and the heater outlet hose by feel. The air tem-
perature around the hoses should be at least
29°C (84°F).
Is the heater inlet hose hot and the heater outlet
hose warm?–Go to Step 19Go to Step 22
19Check the thermostat. Refer to 2D, Engine Cooling.
Is the thermostat installed and seated properly?–Go to Step 20Go to Step 21
Page 1983 of 2643
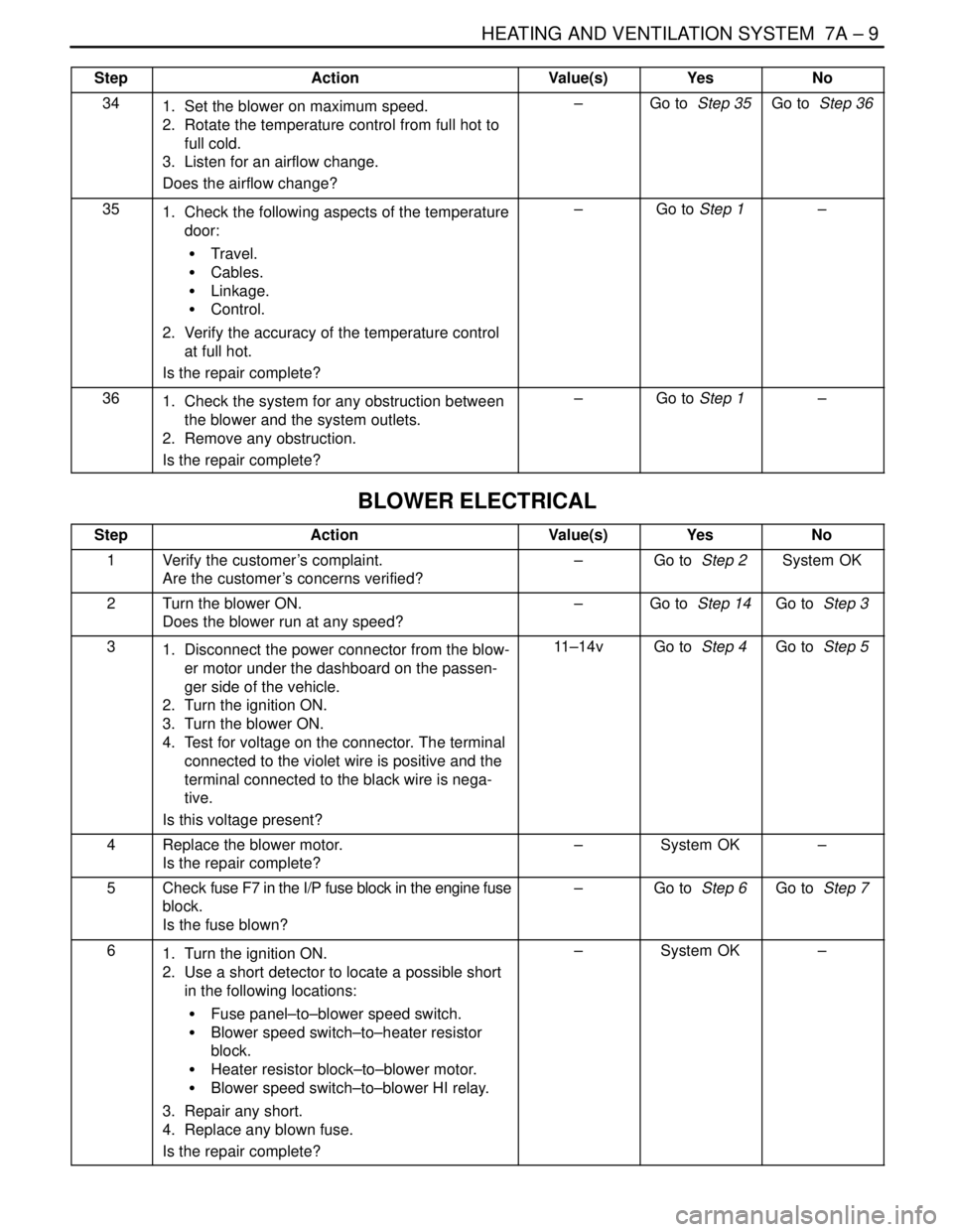
HEATING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM 7A – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
341. Set the blower on maximum speed.
2. Rotate the temperature control from full hot to
full cold.
3. Listen for an airflow change.
Does the airflow change?–Go to Step 35Go to Step 36
351. Check the following aspects of the temperature
door:
S Travel.
S Cables.
S Linkage.
S Control.
2. Verify the accuracy of the temperature control
at full hot.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 1–
361. Check the system for any obstruction between
the blower and the system outlets.
2. Remove any obstruction.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 1–
BLOWER ELECTRICAL
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Verify the customer’s complaint.
Are the customer’s concerns verified?–Go to Step 2System OK
2Turn the blower ON.
Does the blower run at any speed?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 3
31. Disconnect the power connector from the blow-
er motor under the dashboard on the passen-
ger side of the vehicle.
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Turn the blower ON.
4. Test for voltage on the connector. The terminal
connected to the violet wire is positive and the
terminal connected to the black wire is nega-
tive.
Is this voltage present?11–14vGo to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Replace the blower motor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
5Check fuse F7 in the I/P fuse block in the engine fuse
block.
Is the fuse blown?–Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
61. Turn the ignition ON.
2. Use a short detector to locate a possible short
in the following locations:
S Fuse panel–to–blower speed switch.
S Blower speed switch–to–heater resistor
block.
S Heater resistor block–to–blower motor.
S Blower speed switch–to–blower HI relay.
3. Repair any short.
4. Replace any blown fuse.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 2013 of 2643

MANUAL CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM 7B – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
LEAK TESTING REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM
Test for leaks whenever you suspect a refrigerant leak in
the system. You should also test for leaks whenever you
perform a service operation which results in disturbing the
lines or the connections. Leaks are commonly found at the
refrigerant fittings or at the connections. Leaks are com-
monly caused by the following problems:
S Improper torque.
S Damaged O–ring seals.
S Dirt or lint on the O–ring seals.
Liquid Leak Detectors
Use a liquid leak detector solution on locations such as fit-
tings. Apply the solution to the area in question with the
swab that is supplied with the solution. Look for bubbles
to appear. This will indicate the existence and the location
of any leak.
For areas where this is not practical, such as sections of
the evaporator and the condenser, an electronic leak de-
tector is more useful.
Electronic Leak Detectors
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration, op-
eration, and maintenance of an electronic leak detector.
Battery condition is especially important to the accuracy
of a portable model. Set the detector to R–134a before be-
ginning the test.
Notice : Electronic leak detectors are sensitive to wind-
shield washing solutions, solvents and cleaners, and cer-
tain vehicle adhesives. Surfaces must be clean to prevent
false readings. Make sure that all surfaces are dry to pre-
vent damage to the detector.
General Testing Instructions
1. Follow the entire path of the refrigerant system.
2. Completely circle each joint at 25 to 50 mm (1 to 2
inches) per second.
3. Hold the probe tip within 6 mm (1/4 inch) of the sur-
face.4. Do not block the air intake.
5. The audible tone changes from 1 to 2 clicks per
second into a solid alarm if there is a leak. Adjust
the balance control to maintain 1 to 2 clicks per
second.
6. Test all of the following areas, even after one leak
has been confirmed:
S Evaporator inlet and outlet.
S Receiver–drier inlet and outlet.
S Condenser inlet and outlet.
S Brazed and welded areas.
S Damaged areas.
S Hose couplings.
S Compressor rear head.
S All fittings and joints.
Testing Service Ports/Access Valves
The sealing caps provide protection for the service ports.
Make sure that these caps are not missing or loose. Al-
ways use the correct cap for each port.
Testing the Evaporator Core
Leaks in the evaporator core are difficult to find. Test the
evaporator core using the following procedure:
1. Run the blower fan at the maximum speed setting
for at least 15 minutes.
2. Turn the blower OFF.
3. Wait for 10 minutes.
4. Remove the blower motor resistor. Refer to Section
7A, Heating and Ventilation System.
5. Insert the leak detector probe as close as possible
to the evaporator core. The detector will indicate a
leak with a solid alarm.
6. Use a flashlight to search for refrigerant oil on the
core surface.
Testing the Compressor Shaft Seal
1. Blow shop air behind and in front of the compressor
clutch/pulley for at least 15 seconds.
2. Wait 1 to 2 minutes.
3. Probe the area in front of the pulley. If the detector
emits a solid alarm, there is a leak.
Page 2014 of 2643
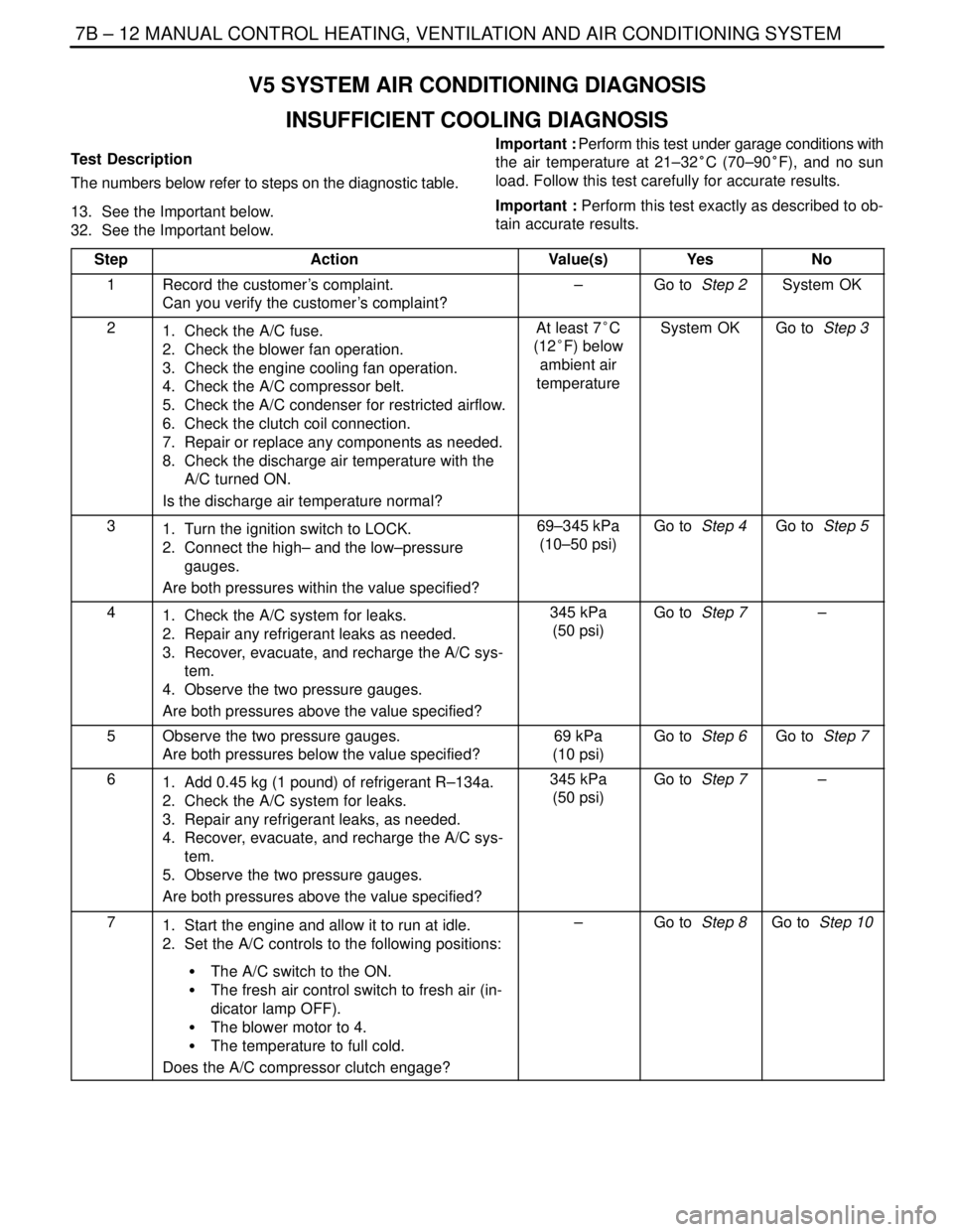
7B – 12IMANUAL CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
V5 SYSTEM AIR CONDITIONING DIAGNOSIS
INSUFFICIENT COOLING DIAGNOSIS
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps on the diagnostic table.
13. See the Important below.
32. See the Important below.Important : Perform this test under garage conditions with
the air temperature at 21–32°C (70–90°F), and no sun
load. Follow this test carefully for accurate results.
Important : Perform this test exactly as described to ob-
tain accurate results.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Record the customer’s complaint.
Can you verify the customer’s complaint?–Go to Step 2System OK
21. Check the A/C fuse.
2. Check the blower fan operation.
3. Check the engine cooling fan operation.
4. Check the A/C compressor belt.
5. Check the A/C condenser for restricted airflow.
6. Check the clutch coil connection.
7. Repair or replace any components as needed.
8. Check the discharge air temperature with the
A/C turned ON.
Is the discharge air temperature normal?At least 7°C
(12°F) below
ambient air
temperatureSystem OKGo to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Connect the high– and the low–pressure
gauges.
Are both pressures within the value specified?69–345 kPa
(10–50 psi)Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Check the A/C system for leaks.
2. Repair any refrigerant leaks as needed.
3. Recover, evacuate, and recharge the A/C sys-
tem.
4. Observe the two pressure gauges.
Are both pressures above the value specified?345 kPa
(50 psi)Go to Step 7–
5Observe the two pressure gauges.
Are both pressures below the value specified?69 kPa
(10 psi)Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
61. Add 0.45 kg (1 pound) of refrigerant R–134a.
2. Check the A/C system for leaks.
3. Repair any refrigerant leaks, as needed.
4. Recover, evacuate, and recharge the A/C sys-
tem.
5. Observe the two pressure gauges.
Are both pressures above the value specified?345 kPa
(50 psi)Go to Step 7–
71. Start the engine and allow it to run at idle.
2. Set the A/C controls to the following positions:
S The A/C switch to the ON.
S The fresh air control switch to fresh air (in-
dicator lamp OFF).
S The blower motor to 4.
S The temperature to full cold.
Does the A/C compressor clutch engage?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 10