Vacuum DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 693 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 447
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0325
KNOCK SENSOR INTERNAL MALFUNCTION
System Description
The Knock Sensor (KS) system is used to detect engine
detonation, allowing the Engine Control Module (ECM) to
retard the ignition control spark timing based on the KS
signal being received. The KS produces an AC signal so
that under a no–knock condition the signal on the KS cir-
cuit measures about 0.007 volts AC. The KS signal’s am-
plitude and frequency depend upon the amount of knock
being experienced. The ECM contains a nonreplaceable
knock filter module called a Digitally Controlled Signal–to–
Noise Enhancement Filter (DSNEF) module. This filter
module in the ECM determines whether or not knock is oc-
curring by comparing the signal level on the KS circuit with
the voltage level on the noise channel. The noise channel
allows the ECM to reject any false knock signal by knowing
the amount of normal engine mechanical noise present.
Normal engine noise varies depending on engine speed
and load. When the ECM determines that an abnormally
low noise channel voltage level is being experienced,
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0325 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S DSNEF A/D reading is less than 1.0% or greater
than 80% any of the 4 cylinders.
S Vacuum is less than the predetermined value (10 to
50 kPa, based on rpm).
S The rpm is greater than 1600.
S DTC(s) P0106, P0107, P0108 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Failure Records buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTCS A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before us-
ing the diagnostic table.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the complaint,
should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. If the conditions for the test as described above are
met, a DTC P0325 will set and MIL will illuminate.
4. If the engine has an internal knock or audible noise
that causes a knocking type noise on the engine
block, the knock sensor may be responding to the
noise.
6. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
DTC P0325 – Knock Sensor Internal Malfunction
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
3. Start the engine.
4. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
Setting the DTC as noted.
Is the DTC set again.–Go to Step 3Go to Step 6
Page 695 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 449
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0327
KNOCK SENSOR CIRCUIT FAULT
System Description
The Knock Sensor (KS) system is used to detect engine
detonation, allowing the Engine Control Module (ECM) to
retard the ignition control spark timing based on the KS
signal being received. The KS produces an AC signal so
that under a no–knock condition the signal on the KS cir-
cuit measures about 0.007 volts AC. The KS signal’s am-
plitude and frequency depend upon the amount of knock
being experienced. The ECM monitors the KS signal and
can diagnose the KS and circuitry.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Minimum difference between cylinders is greater
than 0.4%.
S Vacuum is less than the predetermined value (10 to
50 kPa, based on rpm).
S The rpm is greater than 1600.
S DTC(s) P0106, P0107, P0108 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Failure Records buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.Diagnostic Aids
Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before us-
ing the diagnostic table.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the complaint,
should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. If the conditions for the test as described above are
met, a DTC P0327 will set and MIL will illuminate.
3. If the engine has an internal knock or audible noise
that causes a knocking type noise on the engine
block, the KS may be responding to the noise.
5. Checking the internal resistance of the KS or the
wiring to the KS is OK.
6. Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the com-
plaint, should be thoroughly checked for backed–
out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, im-
Page 714 of 2643

1F – 468IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0401
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION INSUFFICIENT FLOW
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with an En-
gine Control Module (ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM
controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle
Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sors. The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the De-
sired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-
back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
Position.
This diagnostic will determine if there is a reduction in EGR
flow.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204,
P0351, P0352, P0402, P0404, P1404, P0405,
P0406 and P0502 are not set.
S Test in Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) mode.
S Barometric Pressure (BARO) is greater than 72
kPa (10.4 psi).
S Vehicle speed is greater than 18 km/h (11.2
mph).
S A/C clutch/transmission clutch are unchanged.
S Rpm is between 1400 and 3000 for manual
transaxle.
S Rpm is between 1300 and 2900 for automatic
transaxle.
S Compensated MAP is with 10.3 to 32 kpa (1.5 to
4.6 psi) range.
S Start test
S Throttle position (TP) sensor is less then 1%.
S EGR is less than 1%.
S Change in MAP is less than 1.0 kpa (0.15 psi)Note : Test will be aborted when:
S Change in vehicle speed is greater than 5km/h (3.1
mph).
S Rpm is increased more than 75.
S EGR opened less than 90% commanded position.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC set as Failure Records data only.
This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
S EGR is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
The EGR Decel Filter value can be a great aid in determin-
ing if a problem exists and to verify repairs. The EGR De-
cel Filter is an average of the difference in the expected
MAP change and the actual MAP change caused by open-
ing the EGR valve during a deceleration, and is used to de-
termine when the MIL is illuminated. By driving the vehicle
up to approximately 97 km/h (60 mph) and decelerating to
32 km/h (20 mph), it can be determined if the EGR system
is OK, partially restricted, or fully restricted.
A more negative number (less than –3) indicates that the
system is working normally, whereas a positive number in-
dicates that the system is being restricted and that the ex-
pected amount of EGR flow is was not seen. A number
that falls between negative 3 and positive 2 indicates that
the system is partially restricted but not restricted enough
to cause an emissions impact.
The EGR Decel Filter value should always be at –3 or low-
er. If the EGR Decel Filter number becomes more positive
(towards 0 or more), then the EGR system is becoming re-
stricted. Look for possible damage to the EGR pipe or for
a restriction caused by carbon deposits in the EGR pas-
sages or on the EGR valve.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
Page 716 of 2643

1F – 470IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0402
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION EXCESSIVE FLOW
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with an En-
gine Control Module (ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM
controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle
Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sors. The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the De-
sired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-
back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
Position.
This Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will detect an EGR
open to a large valve during crank. Crank time may be ex-
cessive with an open EGR valve.Conditions for Setting the DTC
S EGR position is greater than 70% for more than 3
seconds during cranking.
S Engine cranking (not running).
S Ignition voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
S EGR is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turns off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Due to moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in cold weather at times.
After the vehicle is brought into a warm shop for repairs,
the valve warms and the problem disappears. By watching
the Actual EGR and Desired EGR Positions on a cold ve-
hicle with a scan tool, the fault can be easily verified.
Check the freeze frame data to determine if the DTC set
when the vehicle was cold by viewing the Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT).
Page 720 of 2643

1F – 474IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0404
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION OPEN VALVE POSITION
ERROR
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with an En-
gine Control Module (ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM
controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle
Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sors. The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the De-
sired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-
back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
Position.
This Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will detect an open
valve position.
Conditions for Setting the DTCS Difference between current and commended posi-
tion is greater than 15%.
S Desired EGR position is greater than 0.
S Change in Desired EGR is less than 3%.
S Engine is running.
S Ignition voltage is between 11.7 and 16 volts.
S Air temperature is greater than 3°C.
S DTCs P0112, P0113 P0405, P0406, and P0502 are
not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate, after three concecutive ignition cycle with a
fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
S EGR is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turns off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Due to moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in cold weather at times.
After the vehicle is brought into a warm shop for repairs,
the valve warms and the problem disappears. By watching
Page 724 of 2643

1F – 478IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0405
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION PINTLE POSITION LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with an En-
gine Control Module (ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM
controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle
Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sors. The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the De-
sired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-
back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
Position. This diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will detect
an open or short circuit.Conditions for Setting the DTC
S EGR position signal is less than 2%.
S Ignition voltage is between 11.7 and 16 volts.
S Fail condition last more than 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
S EGR is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turns off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Due to moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in cold weather at times.
After the vehicle is brought into a warm shop for repairs,
the valve warms and the problem disappears. By watching
the Actual EGR and Desired EGR Positions on a cold ve-
hicle with a scan tool, the fault can be easily verified.
Check the freeze frame data to determine if the DTC set
when the vehicle was cold by viewing the Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT).
Page 727 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 481
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0406
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION PINTLE POSITION HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with an En-
gine Control Module (ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM
controls the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle
Position (TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sors. The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the De-
sired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-
back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR Position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
Position. This diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will detect
short circuit.Conditions for Setting the DTC
S EGR position signal is greater than 98%.
S Ignition voltage is between 11.7 and 16 volts.
S Fail condition last more than 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
S EGR is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turns off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Due to moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in cold weather at times.
After the vehicle is brought into a warm shop for repairs,
the valve warms and the problem disappears. By watching
the Actual EGR and Desired EGR Positions on a cold ve-
hicle with a scan tool, the fault can be easily verified.
Check the freeze frame data to determine if the DTC set
when the vehicle was cold by viewing the Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT).
Page 768 of 2643

1F – 522IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1106
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE INTERMITTENT HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
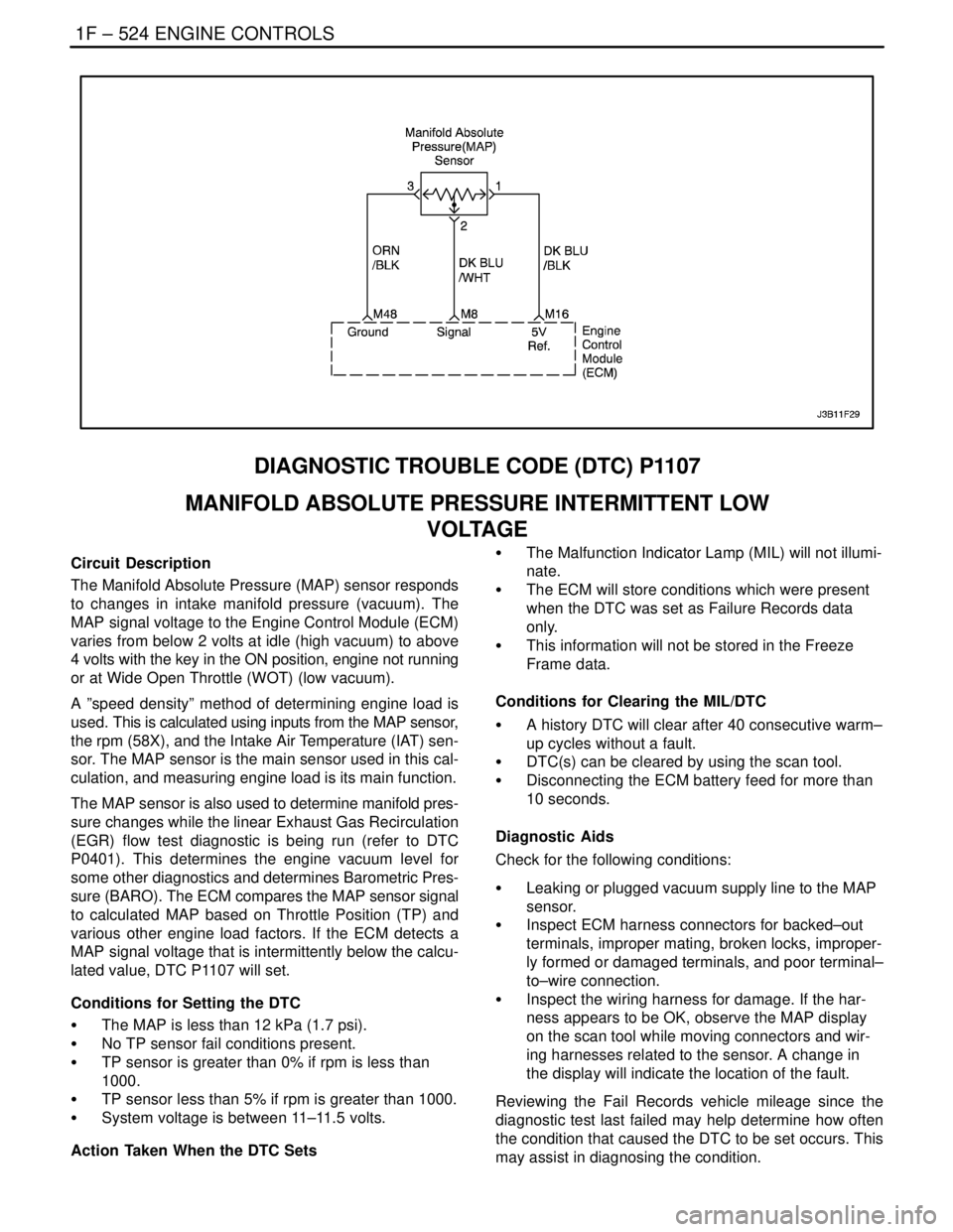
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP signal voltage to the Engine Control Module (ECM)
varies from below 2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above
4 volts with the key in the ON position, engine not running
or at Wide Open Throttle (WOT) (low vacuum).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used. This is calculated using inputs from the MAP sensor,
the rpm (58X), and the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sen-
sor. The MAP sensor is the main sensor used in this cal-
culation, and measuring engine load is its main function.
The MAP sensor is also used to determine manifold pres-
sure changes while the linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) flow test diagnostic is being run (refer to DTC
P0401). This determines the engine vacuum level for
some other diagnostics and determines Barometric Pres-
sure (BARO). The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal
to calculated MAP based on Throttle Position (TP) and
various other engine load factors. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is intermittently above the calcu-
lated value, DTC P1106 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The MAP is greater than 103 kPa (15 psi).
S No TP sensor fail conditions present.
S Engine running more than 10 seconds
S TP sensor is less than 15 % if rpm is less than
2500.
S TP sensor less than 35% if rpm is greater than
2500.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
S Leaking or plugged vacuum supply line to the MAP
sensor.
S Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed–out
terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improper-
ly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal–
towire connection.
S Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the har-
ness appears to be OK, observe the MAP display
on the scan tool while moving connectors and wir-
ing harnesses related to the sensor. A change in
the display will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Page 770 of 2643
1F – 524IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1107
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE INTERMITTENT LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP signal voltage to the Engine Control Module (ECM)
varies from below 2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above
4 volts with the key in the ON position, engine not running
or at Wide Open Throttle (WOT) (low vacuum).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used. This is calculated using inputs from the MAP sensor,
the rpm (58X), and the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sen-
sor. The MAP sensor is the main sensor used in this cal-
culation, and measuring engine load is its main function.
The MAP sensor is also used to determine manifold pres-
sure changes while the linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) flow test diagnostic is being run (refer to DTC
P0401). This determines the engine vacuum level for
some other diagnostics and determines Barometric Pres-
sure (BARO). The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal
to calculated MAP based on Throttle Position (TP) and
various other engine load factors. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is intermittently below the calcu-
lated value, DTC P1107 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The MAP is less than 12 kPa (1.7 psi).
S No TP sensor fail conditions present.
S TP sensor is greater than 0% if rpm is less than
1000.
S TP sensor less than 5% if rpm is greater than 1000.
S System voltage is between 11–11.5 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
S Leaking or plugged vacuum supply line to the MAP
sensor.
S Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed–out
terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improper-
ly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal–
to–wire connection.
S Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the har-
ness appears to be OK, observe the MAP display
on the scan tool while moving connectors and wir-
ing harnesses related to the sensor. A change in
the display will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Page 786 of 2643
1F – 540IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P1133 is most likely caused by one of the following
items:
S Fuel Pressure – The system will go rich if the fuel
pressure is too high. The ECM can compensate for
some increase. However, if it gets too high, a DTC
P1133 may set. Refer to ”Fuel System Diagnosis”
in this section.
S Leaking injector – A leaking or malfunctioning injec-
tor can cause the system to go rich.
S Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor – An
output that causes the ECM to sense a higher than
normal manifold pressure (low vacuum) can cause
the system to go rich. Disconnecting the MAP sen-
sor will allow the ECM to set a fixed value for the
MAP sensor. Substitute a different MAP sensor if
the rich condition is gone while the sensor is dis-
connected.
S Pressure regulator – Check for a leaking fuel pres-
sure regulator diaphragm by checking for the pres-
ence of liquid fuel in the vacuum line to the pres-
sure regulator.
S Throttle Position (TP) sensor – An intermittent TP
sensor output can cause the system to go rich due
to a false indication of the engine accelerating.S HO2S1 contamination – Inspect the HO2S1 for sili-
cone contamination from fuel or improper use of
Room Temperature Vulcanizing (RTV) sealant. The
sensor may have a white powdery coating and re-
sult in a high but false voltage signal (rich exhaust
indication). The ECM will then reduce the amount
of fuel delivered to the engine causing a severe
surge or driveability problem.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Chart.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
14. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
16. If no malfunctions have been found at this point and
no additional DTCs are set, refer to ”Diagnostic
Aids” in this section for additional checks and infor-
mation.
DTC P1133 – Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) Too Few
Transition
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
Are any additional Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTCs) set?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableGo to Step 3
31. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
2. Operate the vehicle within the specified param-
eter under the Conditions For Setting the DTC.
3. Monitor the lean–to–rich transition and rich–to–
lean transition and note the number of
switches.
Does the parameter show fewer transitions than the
specified value within 90 seconds.15Go to Step 4Go to Step 18