torque DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 199 of 2643
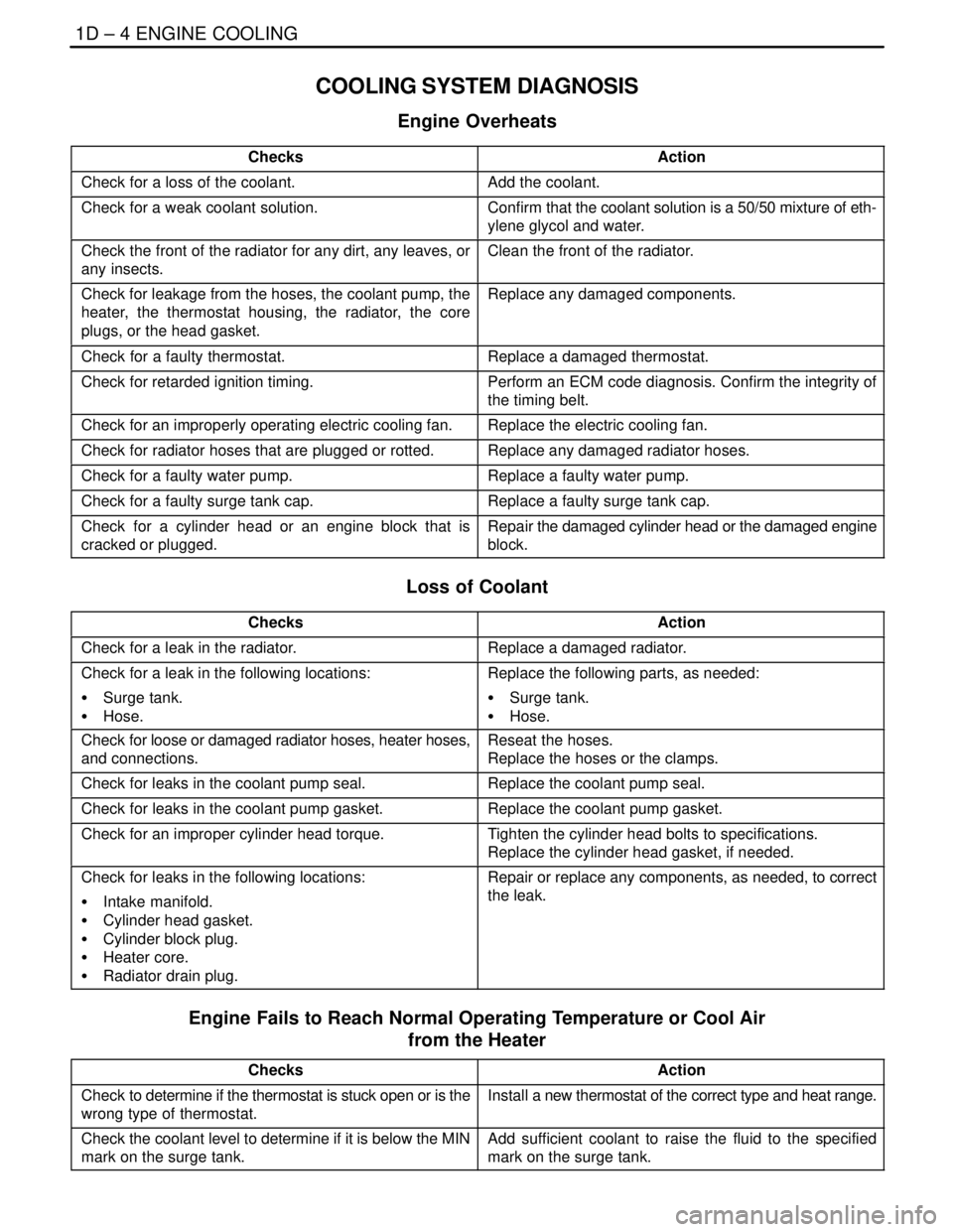
1D – 4IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Engine Overheats
ChecksAction
Check for a loss of the coolant.Add the coolant.
Check for a weak coolant solution.Confirm that the coolant solution is a 50/50 mixture of eth-
ylene glycol and water.
Check the front of the radiator for any dirt, any leaves, or
any insects.Clean the front of the radiator.
Check for leakage from the hoses, the coolant pump, the
heater, the thermostat housing, the radiator, the core
plugs, or the head gasket.Replace any damaged components.
Check for a faulty thermostat.Replace a damaged thermostat.
Check for retarded ignition timing.Perform an ECM code diagnosis. Confirm the integrity of
the timing belt.
Check for an improperly operating electric cooling fan.Replace the electric cooling fan.
Check for radiator hoses that are plugged or rotted.Replace any damaged radiator hoses.
Check for a faulty water pump.Replace a faulty water pump.
Check for a faulty surge tank cap.Replace a faulty surge tank cap.
Check for a cylinder head or an engine block that is
cracked or plugged.Repair the damaged cylinder head or the damaged engine
block.
Loss of Coolant
ChecksAction
Check for a leak in the radiator.Replace a damaged radiator.
Check for a leak in the following locations:
S Surge tank.
S Hose.Replace the following parts, as needed:
S Surge tank.
S Hose.
Check for loose or damaged radiator hoses, heater hoses,
and connections.Reseat the hoses.
Replace the hoses or the clamps.
Check for leaks in the coolant pump seal.Replace the coolant pump seal.
Check for leaks in the coolant pump gasket.Replace the coolant pump gasket.
Check for an improper cylinder head torque.Tighten the cylinder head bolts to specifications.
Replace the cylinder head gasket, if needed.
Check for leaks in the following locations:
S Intake manifold.
S Cylinder head gasket.
S Cylinder block plug.
S Heater core.
S Radiator drain plug.Repair or replace any components, as needed, to correct
the leak.
Engine Fails to Reach Normal Operating Temperature or Cool Air
from the Heater
ChecksAction
Check to determine if the thermostat is stuck open or is the
wrong type of thermostat.Install a new thermostat of the correct type and heat range.
Check the coolant level to determine if it is below the MIN
mark on the surge tank.Add sufficient coolant to raise the fluid to the specified
mark on the surge tank.
Page 240 of 2643

1E – 26IENGINE ELECTRICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
9. Retest by connecting the ohmmeter terminals in
reverse.
10. Replace the rectifier bridge, if each reading is the
same.
11. Test the remaining two diodes after the above pro-
cedure.
Notice : Some kinds of digital ohmmeters are not suited
for the test of the bridge diode. In this case, consult the
manufacturer regarding the test capacity.
12. Test the diodes by connecting the ohmmeter termi-
nals to the bridge terminal and the base plate. If the
reading is the same, the rectifier bridge should be
replaced.
13. Remove the generator through – bolts.
Important : The fastening torque of this nut is 81 NSm (60
lb–ft) and may not normally be unfastened using hand
strength.
14. Move to the drive end of the generator and remove
the drive end bearing nut.
15. Remove the pulley and the collars.
Page 255 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Spark Advance
This is a display of the spark advance Ignition Coil (IC) cal-
culation which the ECM is programming in the ignition sys-
tem. It computes the desired spark advance using data
such as engine temperature, rpm, engine load, vehicle
speed and operating mode.
TCC Engaged
When the brake pedal is applied, the Torque Converter
Clutch (TCC) brake switch sends a signal to the ECM to
disengage the TCC and disable the cruise control.
Total Misfire Current Counter
Indicates the total number of misfires that have been de-tected in all the cylinders after 100 engine cycles. One
cycle equals one complete 4 stroke cycle. The total misfire
only increments during the steady state cruise conditions.
TP Sensor
The ECM uses the TP Sensor in order to determine the
amount of the throttle demanded by the vehicle’s operator.
The TP Sensor reads between 0.36–0.96 volts at idle to
above 4 volts at WOT.
Vehicle Speed
The vehicle speed sensor signal is converted into mph or
km/h for display. The vehicle speed output from the ECM
is 4000 pulses per mile. The scan tool uses the KWP 2000
serial data from the ECM to obtain vehicle speed, while the
Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC), cruise control module and
the chime alarm module use the 4000 ppm output.
Page 504 of 2643
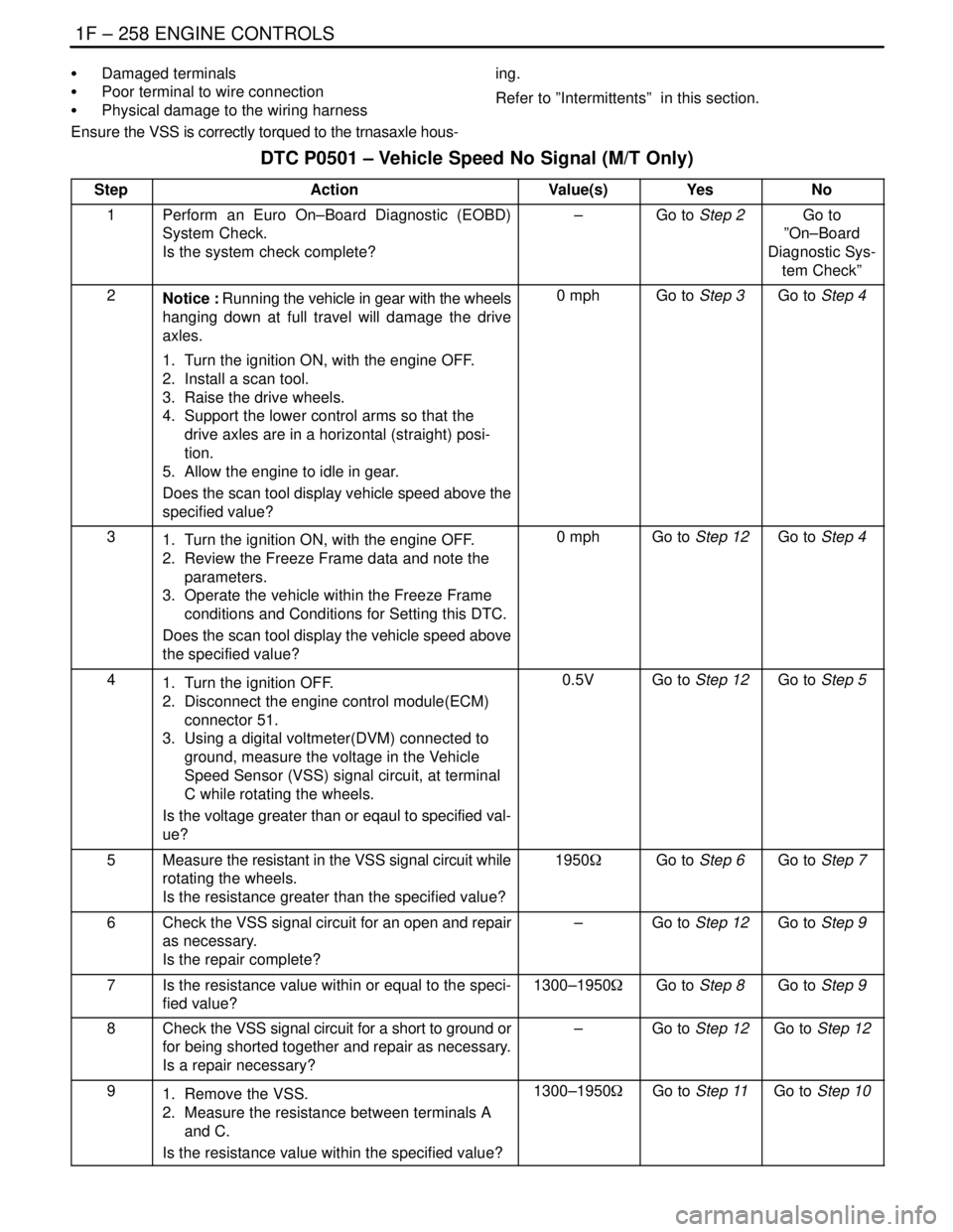
1F – 258IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal to wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Ensure the VSS is correctly torqued to the trnasaxle hous-ing.
Refer to ”Intermittents” in this section.
DTC P0501 – Vehicle Speed No Signal (M/T Only)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Notice : Running the vehicle in gear with the wheels
hanging down at full travel will damage the drive
axles.
1. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Raise the drive wheels.
4. Support the lower control arms so that the
drive axles are in a horizontal (straight) posi-
tion.
5. Allow the engine to idle in gear.
Does the scan tool display vehicle speed above the
specified value?0 mphGo to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Review the Freeze Frame data and note the
parameters.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions and Conditions for Setting this DTC.
Does the scan tool display the vehicle speed above
the specified value?0 mphGo to Step 12Go to Step 4
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the engine control module(ECM)
connector 51.
3. Using a digital voltmeter(DVM) connected to
ground, measure the voltage in the Vehicle
Speed Sensor (VSS) signal circuit, at terminal
C while rotating the wheels.
Is the voltage greater than or eqaul to specified val-
ue?0.5VGo to Step 12Go to Step 5
5Measure the resistant in the VSS signal circuit while
rotating the wheels.
Is the resistance greater than the specified value?1950WGo to Step 6Go to Step 7
6Check the VSS signal circuit for an open and repair
as necessary.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 9
7Is the resistance value within or equal to the speci-
fied value?1300–1950WGo to Step 8Go to Step 9
8Check the VSS signal circuit for a short to ground or
for being shorted together and repair as necessary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 12
91. Remove the VSS.
2. Measure the resistance between terminals A
and C.
Is the resistance value within the specified value?1300–1950WGo to Step 11Go to Step 10
Page 506 of 2643

1F – 260IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0510
THROTTLE POSITION SWITCH CIRCUIT FAULT
(1.4L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA(Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (05, 195). The charac-
teristics of the air flow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TP sensor is lower for small
angles that permits to be more precise during the idle
speed control. Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated
mechanically by a classical bowdencable.
This switch indicates throttle plate in idle position when
contact closed. This switch is fixed at the DC–motor drive
and the throttle plate closes the contact in dependence to
the actual motor drive position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The engine stopped and ignition switch turned ON.
S DTCs P0122, P0123, P0222 and P0223 are not
set.
S MTIA output signal is highter than throttle position +
2.5° and throttle position is open at least 0.2 sec-
onds.
Or
S DTCs P0122, P0123, P0222, and P0223 are not
set.
S The throttle position output signal is greater than
30° and throttle position is closed at least 2 sec-
onds.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An Intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed through wire insulation, or wire that is broken
inside the insulation.
VSS signal circuit should be thoroughly checked for the
following conditions
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal to wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Ensure the VSS is correctly torqued to the trnasaxle hous-
ing.
Refer to ”Intermittents” in this section.
Page 508 of 2643

1F – 262IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0510
THROTTLE POSITION SWITCH CIRCUIT FAULT
(1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA(Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (05, 195). The charac-
teristics of the air flow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TP sensor is lower for small
angles that permits to be more precise during the idle
speed control. Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated
mechanically by a classical bowdencable.
This switch indicates throttle plate in idle position when
contact closed. This switch is fixed at the DC–motor drive
and the throttle plate closes the contact in dependence to
the actual motor drive position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The engine stopped and ignition switch turned ON.
S DTCs P0122, P0123, P0222 and P0223 are not
set.
S MTIA output signal is highter than throttle position +
2.5° and throttle position is open at least 0.2 sec-
onds.
Or
S DTCs P0122, P0123, P0222, and P0223 are not
set.
S The throttle position output signal is greater than
30° and throttle position is closed at least 2 sec-
onds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S Coolant fan turns on.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S Using the scan tool can clear DTC(s).
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
An Intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed through wire insulation, or wire that is broken
inside the insulation.
VSS signal circuit should be thoroughly checked for the
following conditions
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal to wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Ensure the VSS is correctly torqued to the trnasaxle hous-
ing.
Refer to ”Intermittents” in this section.
Page 593 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 347
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0106
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE RATIONALITY
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) uses the Manifold Ab-
solute Pressure (MAP) sensor to control the fuel delivery
and the ignition timing. The MAP sensor measures the
changes in the intake manifold pressure which results
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and the rpm
changes, and it converts these into voltage outputs. The
ECM can detect if the MAP sensor is not responding to the
Throttle Position (TP) changes by comparing the actual
MAP change to a predicted MAP change based on the
amount of TP change that occurs. If the ECM does not see
the expected MAP change or more, DTC P0106 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Altitude compensated MAP reading is higher than
high threshold or lower than low threshold table
based on rpm and TP signal.
S DTCs P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118, P0122,
P0123, P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P0300,
P0351, P0352, P0402, P0404, P1404, P0405,
P0406, P0506, P0507 are not set.
S Engine running.
S Valid Barometric Pressure (BARO) update.
S Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) steady (A/T).
S A/C steady state.
S No TP sensor fail conditions present.
S No MAP fail conditions present.
S Change in Idle Air Control (IAC) is less than 5%.
S Coolant temperature is greater than –10°C (14°F).
S Change in rpm is less than 200.
S Change in TP sensor is less than 3%.
S Change in Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) value
is less than 6%.
S The rpm is between 1300 and 4500.
S All of the above are stabilized for 1.5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The ECM will substitute a fixed MAP value and use
TP sensor to control the fuel delivery. (The scan
tool will not show defaulted value.)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine stopped, the manifold
pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure and the signal
voltage will be high. This information is used by the ECM
as an indication of vehicle altitude. Comparison of this
reading with a known good vehicle with the same sensor
is a good way to check the accuracy of a suspect sensor.
Readings should be the same +0.4 volt.
The MAP sensor vacuum source should be thoroughly
checked for restrictions at the intake manifold.
Test Description
Numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnos-
tic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the occurred. The information is then stored on the
scan tool for later reference.
2. A sensor that displays an ignition ON, engine OFF
BARO value that does not appear normal for the
altitude the vehicle is in should be considered to be
malfunctioning.
3. While starting the engine, the MAP sensor should
detect any changes in the manifold pressure. This
test is to determine if the sensor is stuck at a value.
4. A normal MAP sensor will react as quickly to the
throttle changes as they can be made. A sensor
should not appear to be lazy or catch up with the
throttle movements.
5. This step checks if the reason for no MAP change
was due to a faulty sensor or vacuum source to the
sensor.
6. The MAP sensor vacuum source should be thor-
oughly checked for restrictions. A drill bit can be
used to clean out any casting flash that may exist in
the vacuum port.
7. The MAP sensor vacuum source should be thor-
oughly checked for restrictions. A drill bit can be
used to clean out any casting flash that may exist in
the vacuum port.
9. The MAP Sensor System Performance diagnostic
may have to complete several tests before deter-
mining if the diagnostic has passed or failed the last
test. Operate the vehicle in the Conditions for Set-
ting the DTC several times to ensure that the diag-
nostic runs enough tests to pass or fail.
10. If no faults have been found at this point and no
additional DTCs were set, refer to ”Diagnostic
Aids”in this section for additional checks and infor-
mation.
Page 667 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 421
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0300
MULTIPLE CYLINDER MISFIRE DETECTED
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to ”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label. Check thoroughly for any type
of leak or restriction.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
misfire. Depending on the engine load, the condi-
tions may have to be maintained for up to 20 sec-
onds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to
increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire
counter will store the number of misfires that have
occurred until the DTC is cleared.
Page 672 of 2643

1F – 426IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0301
CYLINDER 1 MISFURE
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to ”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label.
S Check thoroughly for any type of leak or restric-
tion.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
Page 677 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 431
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0302
CYLINDER 2 MISFIRE
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label. Check thoroughly for any type
of leak or restriction.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
misfire. Depending on the engine load, the condi-
tions may have to be maintained for up to 20 sec-
onds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to
increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire
counter will store the number of misfires that have
occurred until the DTC is cleared.