Lay down DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 19 of 2643

0B – 12IGENERAL INFORMATION
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
OWNER INSPECTIONS AND SERVICES
WHLE OPERATING THE VEHICLE
Horn Operation
Blow the horn occasionally tomake sure it works. Check
all the button locations.
Brake System Operation
Be alert for abnormal sounds, increased brake pedal trav-
el or repeated pulling to one side when braking. Also, if the
brake warning light goes on, or flashes, something may be
wrong with part of the brake system.
Exhaust System Operation
Be alert to any changes in the sound of the system or the
smell of the fumes. These are signs that the system may
be leaking or overheating. Have the system inspected and
repaired immediately.
Tires,Wheels and Alignment Operation
Be alert to any vibration of the steering wheel or the seats
at normal highway speeds. This may mean a wheel needs
to be balanced. Also, a pull right or left on a straight, level
road may show the need for a tire pressure adjustment or
a wheel alignment.
Steering System Operation
Be alert to changes in the steering action. An inspection
is needed when the steering wheel is hard to turn or has
too much free play, or if unusual sounds are noticed when
turning or parking.
Headlight Aim
Take note of the light pattern occasionally. Adjust the
headlights if the beams seem improperly aimed.
AT EACH FUEL FILL
A fluid loss in any (except windshield washer) system may
indicate a problem. Have the system inspected and re-
paired immediately.
Engine Oil Level
Check the oil level and add oil if necessary. The best time
to check the engine oil level is when the oil is warm.
1. After stopping the engine, wait a few minutes for
the oil to drain back to the oil pan.
2. Pull out the oil level indicator (dip stick).
3. Wipe it clean, and push the oil level indicator back
down all the way.
4. Pull out the oil level indicator and look at the oil lev-
el on it.
5. Add oil, if needed, to keep the oil level above the
MIN line and within the area labeled ”Operating
Range.” Avoid overfilling the engine, since this may
cause engine damage.
6. Push the indicator all the way back down into the
engine after taking the reading.If you check the oil level when the oil is cold, do not run the
engine first. The cold oil will not drain back to the pan fast
enough to give a true oil level reading.
Engine Coolant Level and Condition
Check the coolant level in the coolant reservoir tank and
add coolant if necessary. Inspect the coolant. Replace
dirty or rusty coolant.
Windshield Washer Fluid Level
Check the washer fluid level in the reservoir. Add fluid if
necessary.
AT LEAST MONTHLY
Tire And Wheel Inspection and Pressure
Check
Check the tires for abnormal wear or damage. Also check
for damaged wheels. Check the tire pressure when the
tires are cold (check the spare also, unless it is a stow-
away). Maintain the recommended pressures that are on
the tire placard that is in the glove box.
Light Operation
Check the operation of the license plate light, the head-
lights (including the high beams), the parking lights, the
fog lights, the taillight, the brake lights, the turn signals, the
backup lights and the hazard warning flasher.
Fluid Leak Check
Periodically inspect the surface beneath the vehicle for
water, oil, fuel or other fluids, after the vehicle has been
parked for a while. Water dripping from the air conditioning
system after use is normal. If you notice fuel leaks or
fumes, find the cause and correct it at once.
AT LEAST TWICE A YEAR
Power Steering System Reservoir Level
Check the power steering fluid level. Keep the power
steering fluid at the proper level. Refer to Section 6A, Pow-
er Steering System.
Brake Master Cylinder Reservoir Level
Check the fluid and keep it at the proper level. A low fluid
level can indicate worn disc brake pads which may need
to be serviced. Check the breather hole in the reservoir
cover to be free from dirt and check for an open passage.
Clutch Pedal Free Travel
Check clutch pedal free travel and adjust as necessary.
Measure the distance from the center of the clutch pedal
to the outer edge of the steering wheel with the clutch ped-
al not depressed. Then measure the distance from the
center of the clutch pedal to the outer edge of the steering
wheel with the clutch pedal fully depressed. The difference
between the two values must be greater than 130 mm
(5.19 inches).
Weather–Strip Lubrication
Apply a thin film silicone grease using a clean cloth.
Page 504 of 2643
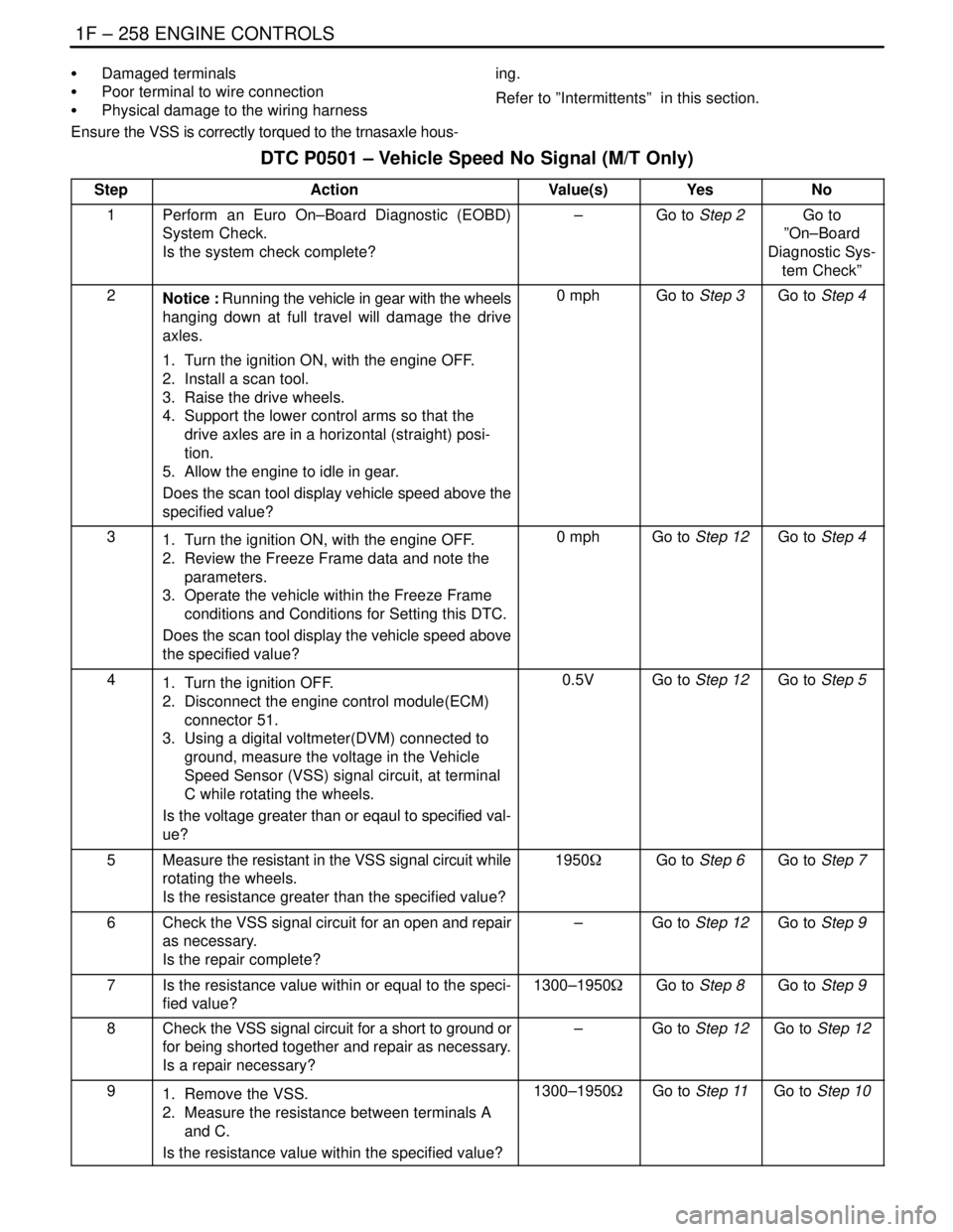
1F – 258IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal to wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Ensure the VSS is correctly torqued to the trnasaxle hous-ing.
Refer to ”Intermittents” in this section.
DTC P0501 – Vehicle Speed No Signal (M/T Only)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Notice : Running the vehicle in gear with the wheels
hanging down at full travel will damage the drive
axles.
1. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Raise the drive wheels.
4. Support the lower control arms so that the
drive axles are in a horizontal (straight) posi-
tion.
5. Allow the engine to idle in gear.
Does the scan tool display vehicle speed above the
specified value?0 mphGo to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Review the Freeze Frame data and note the
parameters.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions and Conditions for Setting this DTC.
Does the scan tool display the vehicle speed above
the specified value?0 mphGo to Step 12Go to Step 4
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the engine control module(ECM)
connector 51.
3. Using a digital voltmeter(DVM) connected to
ground, measure the voltage in the Vehicle
Speed Sensor (VSS) signal circuit, at terminal
C while rotating the wheels.
Is the voltage greater than or eqaul to specified val-
ue?0.5VGo to Step 12Go to Step 5
5Measure the resistant in the VSS signal circuit while
rotating the wheels.
Is the resistance greater than the specified value?1950WGo to Step 6Go to Step 7
6Check the VSS signal circuit for an open and repair
as necessary.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 9
7Is the resistance value within or equal to the speci-
fied value?1300–1950WGo to Step 8Go to Step 9
8Check the VSS signal circuit for a short to ground or
for being shorted together and repair as necessary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 12
91. Remove the VSS.
2. Measure the resistance between terminals A
and C.
Is the resistance value within the specified value?1300–1950WGo to Step 11Go to Step 10
Page 618 of 2643

1F – 372IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0131
FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S1) LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) supplies a voltage of
about 0.45 volts between terminals M12 and M29 (if mea-
sured with a 10 megohm digital voltmeter, this may read
as low as 0.32 volts). The Front Heated Oxygen sensor 1
(HO2S1) varies the voltage within a range of about 1 volt
if the exhaust is rich, down through about 0.10 volts if the
exhaust is lean.
The sensor is like an open circuit and produces no voltage
when it is below 315°C(600°F). An open sensor circuit or
cold sensor causes Open Loop operation.
If the HO2S1 pigtail wiring, connector, or terminal is dam-
aged, the entire HO2S1 assembly must be replaced. Do
not attempt to repair the wiring, connector, or terminals. In
order for the sensor to function properly, it must have a
clean air reference provided to it. This clean air reference
is obtained by way of the HO2S1 wire(s). Any attempt to
repair the wires, connector or terminals could result in the
obstruction of the air reference and degrade the HO2S1
performance. Refer to ”Front Heated Oxygen Sensor” in
this section.Conditions for Setting the DTC
S HO2S1 voltage is less than 0.05 volts.
S Closed loop stoichiometry.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60°C(140°F).
S System voltage is greater than 10 volts.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0351,
P0352, P0402, P0404, P0405, P0406, P0506,
P0507, P1404, and P0443 are not set.
S 3 second delay after conditions are met.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The vehicle will operate in Open Loop.
Page 621 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 375
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0132
FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S1) HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) supplies a voltage of
about 0.45 volts between terminals M12 and M29 (if mea-
sured with a 10 megohm digital voltmeter, this may read
as low as 0.32 volts). The Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) varies the voltage within a range of about 1 volt
if the exhaust is rich, down through about 0.10 volts if the
exhaust is lean.
The sensor is like and open circuit and produces no volt-
age when it is below 315°C (600°F). An open sensor cir-
cuit or cold sensor causes Open Loop operation.
If the HO2S1 pigtail wiring, connector, or terminal is dam-
aged, the entire HO2S1 assembly must be replaced. Do
not attempt to repair the wiring, connector, or terminals. In
order for the sensor to function properly, it must have a
clean air reference provided to it. This clean air reference
is obtained by way of the HO2S1 wire(s). Any attempt to
repair the wires, connector or terminals could result in the
obstruction of the air reference and degrade the HO2S1
performance. Refer to”Front Heated Oxygen Sensor” in
this section.
Conditions for Setting the DTCS HO2S1 voltage is greater than 0.952 volts.
S Closed loop stoichiometry.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60°C(140°F).
S System voltage is greater than 10 volts.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0351,
P0352, P0402, P0404, P0405, P0406, P0506,
P0507, P1404, and P0443 are not set.
S 3 second delay after conditions are met.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The vehicle will operate in Open Loop.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
Page 628 of 2643

1F – 382IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0134
FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S1) NO
ACTIVITY OR OPEN
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) supplies a voltage of
about 0.45 volts between terminals M12 and M29 (if mea-
sured with a 10 megohm digital voltmeter, this may read
as low as 0.32 volts). The Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) varies the voltage within a range of about 1 volt
if the exhaust is rich, down through about 0.10 volts if the
exhaust is lean.
The sensor is like and open circuit and produces no volt-
age when it is below 315 °C (600 °F). An open sensor cir-
cuit or cold sensor causes Open Loop operation.
If the HO2S1 pigtail wiring, connector, or terminal is dam-
aged, the entire HO2S1 assembly must be replaced. Do
not attempt to repair the wiring, connector, or terminals. In
order for the sensor to function properly, it must have a
clean air reference provided to it. This clean air reference
is obtained by way of the HO2S1 wire(s). Any attempt to
repair the wires, connector or terminals could result in the
obstruction of the air reference and degrade the HO2S1
performance. Refer to”Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1)” in this section.Conditions for Setting the DTC
S HO2S1 voltage is between 420 and 480 mV.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60 °C (140 °F)
S System voltage is greater than 10 volts.
S Engine run time is greater than 60 seconds.
S Airflow is greater than 8 g/sec.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0351,
P0352, P0402, P0404, P0405, P0406, P0506,
P0507, P1404, and P0443 are not set.
S 3 second delay after exiting Decel Fuel Cut–off
(DFCO) mode.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The vehicle will operate in Open Loop.
Page 745 of 2643
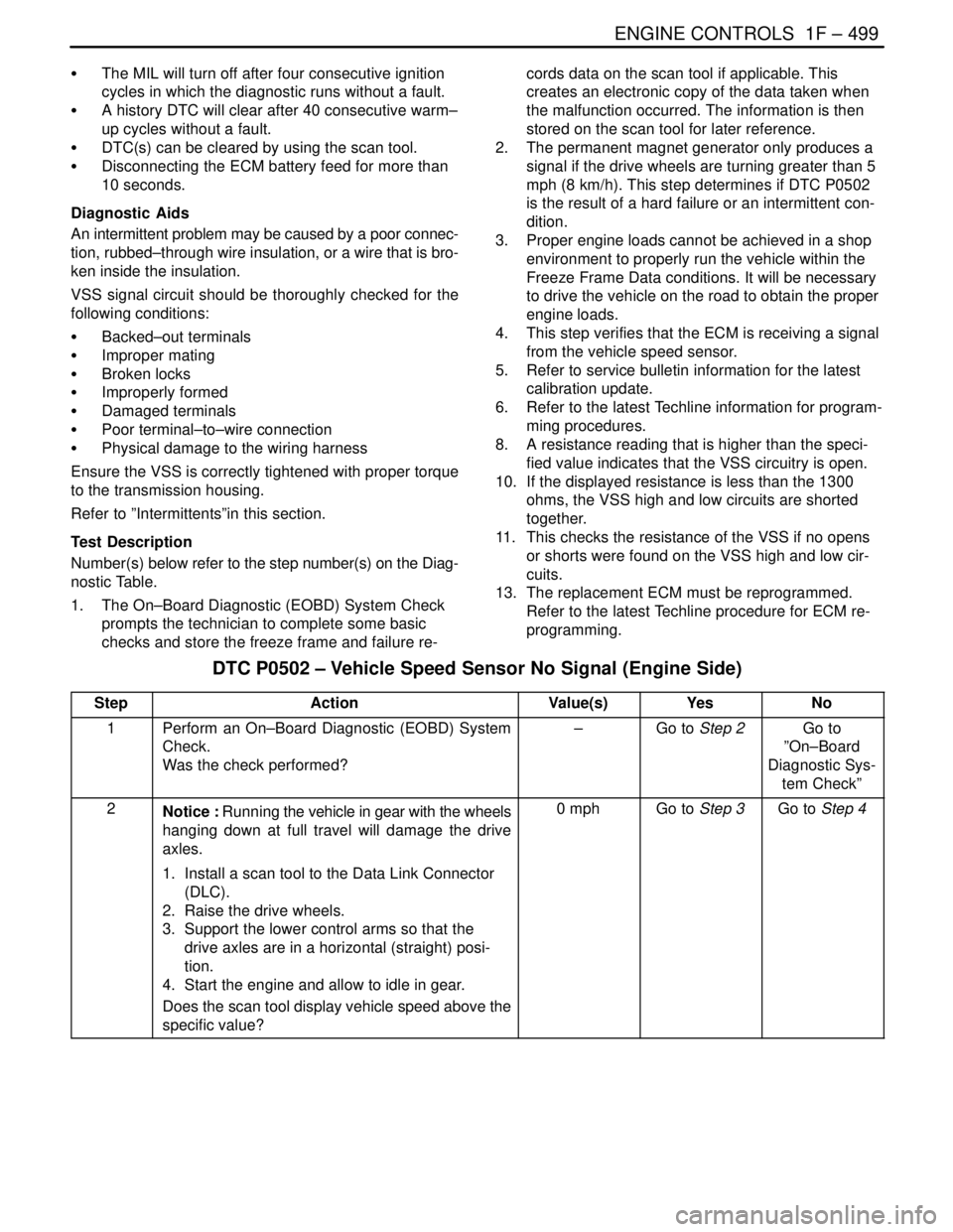
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 499
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire that is bro-
ken inside the insulation.
VSS signal circuit should be thoroughly checked for the
following conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Ensure the VSS is correctly tightened with proper torque
to the transmission housing.
Refer to ”Intermittents”in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. The permanent magnet generator only produces a
signal if the drive wheels are turning greater than 5
mph (8 km/h). This step determines if DTC P0502
is the result of a hard failure or an intermittent con-
dition.
3. Proper engine loads cannot be achieved in a shop
environment to properly run the vehicle within the
Freeze Frame Data conditions. It will be necessary
to drive the vehicle on the road to obtain the proper
engine loads.
4. This step verifies that the ECM is receiving a signal
from the vehicle speed sensor.
5. Refer to service bulletin information for the latest
calibration update.
6. Refer to the latest Techline information for program-
ming procedures.
8. A resistance reading that is higher than the speci-
fied value indicates that the VSS circuitry is open.
10. If the displayed resistance is less than the 1300
ohms, the VSS high and low circuits are shorted
together.
11. This checks the resistance of the VSS if no opens
or shorts were found on the VSS high and low cir-
cuits.
13. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
DTC P0502 – Vehicle Speed Sensor No Signal (Engine Side)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Notice : Running the vehicle in gear with the wheels
hanging down at full travel will damage the drive
axles.
1. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Raise the drive wheels.
3. Support the lower control arms so that the
drive axles are in a horizontal (straight) posi-
tion.
4. Start the engine and allow to idle in gear.
Does the scan tool display vehicle speed above the
specific value?0 mphGo to Step 3Go to Step 4
Page 792 of 2643

1F – 546IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1167
FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S1) RICH IN
DECEL FUEL CUTOFF (DFCO)
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) supplies a voltage of
about 0.45 volts between terminals M12 and M29 (if mea-
sured with a 10 megohm digital voltmeter, this may read
as low as 0.32 volts). The Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) varies the voltage within a range of about 1 volt
if the exhaust is rich, down through about 0.10 volts if the
exhaust is lean.
In internal circuitry of the Engine control Module (ECM)
can identify if the vehicle fuel system is capable of cutoff
amount of the fuel supply during deceleration. When a De-
cel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) mode of operation is requested
during Closed Loop operation, the ECM will cutoff the fuel
supply to the engine. Under these conditions the ECM
should detect a lean condition. If the ECM detect a rich
condition at this time, Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
P1167 will set. Damaged fuel pressure regulator and faulty
injector will be the cause of this DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S HO2S1 voltage is greater than 0.55 volts in Decel
Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) mode.
S System voltage is greater than 10 volts.S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60°C (140°F)
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0351,
P0352, P0402, P0404, P0405, P0406, P0506,
P0507, P1404, and P0443 are not set.
S 3 second delay after in DFCO mode.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The vehicle will operate in Open Loop.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool.
Page 870 of 2643

1F – 624IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the
air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system is called a ”closed
loop” system.
The ECM uses voltage inputs from several sensors to de-
termine how much fuel to provide to the engine. The fuel
is delivered under one of several conditions, called
”modes.”
Starting Mode
When the ignition is turned ON, the ECM turns the fuel
pump relay on for two seconds. The fuel pump then builds
fuel pressure. The ECM also checks the Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor and the Throttle Position (TP)
sensor and determines the proper air/fuel ratio for starting
the engine. This ranges from 1.5 to 1 at –97 °F (–36 °C)
coolant temperature to 14.7 to 1 at 201 °F (94 °C) coolant
temperature. The ECM controls the amount of fuel deliv-
ered in the starting mode by changing how long the fuel in-
jector is turned on and off. This is done by ”pulsing” the fuel
injectors for very short times.
Clear Flood Mode
If the engine floods with excessive fuel, it may be cleared
by pushing the accelerator pedal down all the way. The
ECM will then completely turn off the fuel by eliminating
any fuel injector signal. The ECM holds this injector rate
as long as the throttle stays wide open and the engine is
below approximately 400. If the throttle position becomes
less than approximately 80 percent, the ECM returns to
the starting mode.
Run Mode
The run mode has two conditions called ”open loop” and
”closed loop.”
Open Loop
When the engine is first started and it is above 400 rpm,
the system goes into ”open loop” operation. In ”open loop,”
the ECM ignores the signal from the HO2S and calculates
the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the ECT sensor and
the MAP sensor. The sensor stays in ”open loop” until the
following conditions are met:
S The HO2S sensor has a varying voltage output,
showing that it is hot enough to operate properly.
S The ECT sensor is above a specified temperature.
S A specific amount of time has elapsed after starting
the engine.
Closed Loop
The specific values for the above conditions vary with dif-
ferent engines and are stored in the Electronically Eras-
able Programmable Read–Only Memory (EEPROM).
When these conditions are met, the system goes into
”closed loop” operation. In ”closed loop,” the ECM calcu-
lates the air/fuel ratio (fuel injector on–time) based on the
signal from the oxygen sensor. This allows the air/fuel ratio
to stay very close to 14.7 to 1.Acceleration Mode
The ECM responds to rapid changes in throttle position
and airflow and provides extra fuel.
Deceleration Mode
The ECM responds to changes in throttle position and air-
flow and reduces the amount of fuel. When deceleration
is very fast, the ECM can cut off fuel completely for short
periods of time.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the ECM can compensate for
a weak spark delivered by the ignition module by using the
following methods:
S Increasing the fuel injector pulse width.
S Increasing the idle speed rpm.
S Increasing the ignition dwell time.
Fuel Cut–Off Mode
No fuel is delivered by the fuel injectors when the ignition
is OFF. This prevents dieseling or engine run–on. Also, the
fuel is not delivered if there are no reference pulses re-
ceived from the central power supply. This prevents flood-
ing.
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM OPERATION
The basic Evaporative (EVAP) Emission control system
used is the charcoal canister storage method. This meth-
od transfers fuel vapor from the fuel tank to an activated
carbon (charcoal) storage device (canister) to hold the va-
pors when the vehicle is not operating. When the engine
is running, the fuel vapor is purged from the carbon ele-
ment by intake airflow and consumed in the normal com-
bustion process.
Gasoline vapors from the fuel tank flow into the tube la-
beled TANK. These vapors are absorbed into the carbon.
The canister is purged by the engine control module
(ECM) when the engine has been running for a specified
amount of time. Air is drawn into the canister and mixed
with the vapor. This mixture is then drawn into the intake
manifold.
The ECM supplies a ground to energize the EVAP emis-
sion canister purge solenoid valve. This valve is Pulse
Width Modulated (PWM) or turned on and off several
times a second. The EVAP emission canister purge PWM
duty cycle varies according to operating conditions deter-
mined by mass airflow, fuel trim, and intake air tempera-
ture.
Poor idle, stalling, and poor driveability can be caused by
the following conditions:
S An inoperative EVAP emission canister purge sole-
noid valve.
S A damaged canister.
S Hoses that are split, cracked, or not connected to
the proper tubes.
Page 873 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 627
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
A closed throttle on engine coast down produces a rela-
tively low MAP output. MAP is the opposite of vacuum.
When manifold pressure is high, vacuum is low. The MAP
sensor is also used to measure barometric pressure. This
is performed as part of MAP sensor calculations. With the
ignition ON and the engine not running, the engine control
module (ECM) will read the manifold pressure as baromet-
ric pressure and adjust the air/fuel ratio accordingly. This
compensation for altitude allows the system to maintaindriving performance while holding emissions low. The
barometric function will update periodically during steady
driving or under a wide open throttle condition. In the case
of a fault in the barometric portion of the MAP sensor, the
ECM will set to the default value.
A failure in the MAP sensor circuit sets a diagnostic trouble
code P0107 or P0108.
The following tables show the difference between absolute pressure and vacuum related to MAP sensor output, which
appears as the top row of both tables.
MAP
Volts4.94.43.83.32.72.21.71.10.60.30.3
kPa1009080706050403020100
in. Hg29.626.623.720.717.714.811.88.95.92.90
VACUUM
Volts4.94.43.83.32.72.21.71.10.60.30.3
kPa0102030405060708090100
in. Hg02.95.98.911.814.817..720.723.726.729.6
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
The engine control module (ECM), located inside the pas-
senger kick–panel, is the control center of the fuel injection
system. It constantly looks at the information from various
sensors and controls the systems that affect the vehicle’s
performance. The ECM also performs the diagnostic func-
tions of the system. It can recognize operational problems,
alert the driver through the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL), and store diagnostic trouble code(s) which identify
problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs.
There are no serviceable parts in the ECM. The calibra-
tions are stored in the ECM in the Programmable Read–
Only Memory (PROM).
The ECM supplies either 5 or 12 volts to power the sensors
or switches. This is done through resistances in the ECM
which are so high in value that a test light will not come on
when connected to the circuit. In some cases, even an or-
dinary shop voltmeter will not give an accurate reading be-
cause its resistance is too low. You must use a digital volt-
meter with a 10 megohm input impedance to get accurate
voltage readings. The ECM controls output circuits such
as the fuel injectors, the idle air control valve, the A/C
clutch relay, etc., by controlling the ground circuit through
transistors or a device called a ”quad–driver.”
FUEL INJECTOR
The Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) assembly is a solenoid–
operated device controlled by the engine control module
(ECM). It meters pressurized fuel to a single engine cylin-
der. The ECM energizes the fuel injector or the solenoid
to a normally closed ball or pintle valve. This allows fuel toflow into the top of the injector, past the ball or pintle valve,
and through a recessed flow director plate at the injector
outlet.
The director plate has six machined holes that control the
fuel flow, generating a conical spray pattern of finely atom-
ized fuel at the injector tip. Fuel from the tip is directed at
the intake valve, causing it to become further atomized
and vaporized before entering the combustion chamber.
A fuel injector which is stuck partially open will cause a loss
of fuel pressure after the engine is shut down. Also, an ex-
tended crank time will be noticed on some engines. Diesel-
ing can also occur because some fuel can be delivered to
the engine after the ignition is turned OFF.
KNOCK SENSOR
The knock sensor detects abnormal knocking in the en-
gine. The sensor is mounted in the engine block near the
cylinders. The sensor produces an AC output voltage
which increases with the severity of the knock. This signal
is sent to the engine control module (ECM). The ECM then
adjusts the ignition timing to reduce the spark knock.
ROUGH ROAD SENSOR
The engine control module (ECM) receives rough road in-
formation from the VR sensor. The ECM uses the rough
road information to enable or disable the misfire diagnos-
tic. The misfire diagnostic can be greatly affected by
crankshaft speed variations caused by driving on rough
road surfaces. The VR sensor generates rough road infor-
mation by producing a signal which is proportional to the
movement of a small metal bar inside the sensor.
If a fault occurs which causes the ECM to not receive
rough road information between 30 and 80 mph (50 and
132 km/h), DTC P1391 will set.
Page 879 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 633
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Failed This Ig. (Failed This Ignition)
This message display indicates that the diagnostic test
has failed at least once during the current ignition cycle.
This message will clear when DTCs are cleared or the igni-
tion is cycled.
History
This message display indicates that the DTC has been
stored in memory as a valid fault. A DTC displayed as a
History fault may not mean that the fault is no longer pres-
ent. The history description means that all the conditions
necessary for reporting a fault have been met (maybe
even currently), and the information was stored in the con-
trol module memory.
MIL Requested
This message display indicates that the DTC is currently
causing the MIL to be turned ON. Remember that only
type A and type B DTCs can request the MIL. The MIL re-
quest cannot be used to determine if the DTC fault condi-
tions are currently being experienced. This is because the
diagnostic executive will require up to three trips during
which the diagnostic test passes to turn OFF the MIL.
Not Run Since CI (Not Run Since Cleared)
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has not run since the last time DTCs were cleared.
Therefore, the diagnostic test status (passing or failing) is
unknown. After DTCs are cleared, this message will con-
tinue to be displayed until the diagnostic test runs.
Not Run This Ig. (Not Run This Ignition)
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has not run during this ignition cycle.
Test Ran and Passed
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has done the following:
S Passed the last test.
S Run and passed during this ignition cycle.
S Run and passed since DTCs were last cleared.
If the indicated status of the vehicle is ”Test Ran and
Passed” after a repair verification, the vehicle is ready to
be released to the customer.
If the indicated status of the vehicle is ”Failed This Ignition”
after a repair verification, then the repair is incomplete and
further diagnosis is required.
Prior to repairing a vehicle, status information can be used
to evaluate the state of the diagnostic test, and to help
identify an intermittent problem. The technician can con-
clude that although the MIL is illuminated, the fault condi-
tion that caused the code to set is not present. An intermit-
tent condition must be the cause.
PRIMARY SYSTEM – BASED
DIAGNOSTICS
There are primary system–based diagnostics which eval-
uate system operation and its effect on vehicle emissions.
The primary system–based diagnostics are listed below
with a brief description of the diagnostic function:
Oxygen Sensor Diagnosis
The fuel control Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) is
diagnosed for the following conditions:
S Slow response.
S Response time (time to switch R/L or L/R).
S Inactive signal (output steady at bias voltage
approx. 450 mv).
S Signal fixed high.
S Signal fixed low.
The catalyst monitor Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) is diagnosed for the following conditions:
S Heater performance (time to activity on cold start).
S Signal fixed low during steady state conditions or
power enrichment (hard acceleration when a rich-
mixture should be indicated).
S Signal fixed high during steady state conditions or
deceleration mode (deceleration when a lean mix-
ture should be indicated).
S Inactive sensor (output steady at approximately 438
mv).
If the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector or terminal
are damaged, the entire oxygen sensor assembly must be
replaced. Do not attempt to repair the wiring, connector or
terminals. In order for the sensor to function properly, it
must have clean reference air provided to it. This clean air
reference is obtained by way of the oxygen sensor wire(s).
Any attempt to repair the wires, connector or terminals
could result in the obstruction of the reference air and de-
grade oxygen sensor performance.
Misfire Monitor Diagnostic Operation
The misfire monitor diagnostic is based on crankshaft
rotational velocity (reference period) variations. The en-
gine control module (ECM) determines crankshaft rota-
tional velocity using the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
and the Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor. When a cylinder
misfires, the crankshaft slows down momentarily. By mon-
itoring the CKP and CMP sensor signals, the ECM can cal-
culate when a misfire occurs.
For a non–catalyst damaging misfire, the diagnostic will be
required to monitor a misfire present for between
1000–3200 engine revolutions.
For catalyst–damaging misfire, the diagnostic will respond
to misfire within 200 engine revolutions.
Rough roads may cause false misfire detection. A rough
road will cause torque to be applied to the drive wheels and
drive train. This torque can intermittently decrease the
crankshaft rotational velocity. This may be falsely de-
tected as a misfire.