gas type DATSUN 210 1979 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 128 of 548

Remove
snap
ring
CD
and
lock
bolt
@
and
the
following
parts
can
be
detached
from
heat
control
valve
shaft
Key
ID
Counterweight
@
Thermostat
spring
@
Coil
spring
@
Note
As
previously
descnbed
heat
control
valve
j
is
welded
to
valve
shaft
@
at
exhaust
manifold
and
cannot
be
disassembled
To
install
reverse
the
removal
procedure
INSPECTION
1
With
engine
stopped
visually
check
the
quick
heat
manifold
system
for
the
following
items
I
Check
heat
control
valve
for
malfunction
due
to
break
of
key
that
locates
counterweight
to
valve
shaft
2
Rotate
heat
control
valve
shaft
with
fingers
and
check
for
binding
between
shaft
and
bushing
in
closing
and
opening
operation
of
heat
control
valve
If
any
binding
is
felt
in
rotating
operation
move
valve
shaft
in
the
rotation
direction
several
times
If
this
operation
does
not
correct
binding
condition
it
is
due
to
seizure
between
shaft
and
bushing
and
exhaust
mani
fold
should
be
replaced
as
an
assem
bly
Emission
Control
System
Counterweight
Heat
control
valve
Stopper
pin
EC249
Fig
EC
IO
Checking
Heat
Control
Valve
Movement
2
Run
engine
and
visually
check
counterweight
to
see
if
it
operates
properly
I
When
engine
speed
is
increased
discharge
pressure
of
exhaust
gases
causes
counterweight
to
move
down
ward
clockwise
2
For
some
time
after
starting
engine
in
cold
weather
counterweight
turns
counterclockwise
until
it
comes
into
contact
with
stopper
pin
installed
to
exhaust
manifold
EC
9
Counterweight
gradually
moves
down
clockwise
as
engine
warms
up
and
ambient
temperature
goes
higher
around
exhaust
manifold
If
it
does
not
move
at
all
check
and
replace
thermostat
spring
AIR
INJECTION
SYSTEM
A
I
S
DESCRIPTION
The
Air
Injection
System
A
I
S
is
adopted
on
U
S
A
models
except
FU
models
and
injects
compressed
air
secondary
air
coming
from
the
air
pump
into
the
exhaust
port
of
the
cylinder
head
to
reduce
hydrocarbons
He
and
carbon
monoxide
CO
in
exhaust
gas
through
recombustion
There
are
two
types
of
Air
Injection
System
Fresh
outside
air
is
drawn
by
the
air
pump
through
the
air
pump
air
cleaner
Compressed
air
is
injected
into
the
exhaust
manifold
through
the
check
valve
The
A
B
valve
supplies
air
from
the
carburetor
air
cleaner
to
the
intake
manifold
so
as
to
prevent
after
fire
during
deceleration
The
amount
of
injected
air
is
con
trolled
by
C
A
C
valve
California
models
or
air
relief
valve
Non
California
models
Page 137 of 548
Note
When
tho
vaCUUm
hose
is
dis
connected
plug
it
up
or
engine
will
stumble
EC
47A
FiJ
Fig
EC
49
Disconnecting
Vacuum
Hose
from
C
A
C
Valve
5
Connect
hand
operated
vacuum
pump
in
place
and
manipulate
it
in
order
to
apply
a
pressure
of
2oo
to
250
mmHg
7
87
to
9
84
inHg
to
C
A
C
valve
Increase
engine
speed
to
3
000
rpm
and
confIrm
that
no
air
leaks
from
C
J
C
valve
Fig
EC
50
Checking
C
A
C
Valve
1
6
With
the
above
condition
discon
nect
air
hose
at
check
valve
and
plug
it
up
At
this
point
confirm
the
air
leaks
from
C
A
C
valve
ECl48A
Fig
EC
51
Checking
C
A
C
Volve
2
Emission
Control
System
7
If
teshesults
satisfy
3
4
5
and
6
the
C
A
C
valve
is
properly
function
ing
AIR
INDUCTION
SYSTEM
A
I
S
DESCRIPTION
The
air
induction
system
A
1
s
is
adopted
on
the
FU
model
and
Canada
models
and
is
designed
to
send
see
ondary
air
to
the
exhaust
tube
utiliz
ing
a
vacuum
caused
by
exhaust
pulsa
tion
in
the
exhaust
tube
Air
inductIon
valve
A
reed
valve
type
check
valve
is
installed
in
the
air
cleaner
When
the
exhaust
pressure
is
below
atmospheric
pressure
negative
pressure
secondary
air
is
sent
to
the
exhaust
manifold
When
the
exhaust
pressure
is
above
atmospheric
pressure
the
reed
valve
prevents
secondary
air
from
being
sent
back
to
the
air
cleaner
EC
t8
The
exhaust
pressure
in
the
exhaust
tube
usually
pulsates
in
response
to
the
opening
and
closing
of
the
exhaust
valve
and
it
decreases
below
atmos
pheric
pressure
periodically
If
a
secondary
air
intake
is
opened
to
the
atmosphere
under
vacuum
con
ditions
secondary
air
can
be
drawn
into
the
exhaust
tube
in
proportion
to
the
vacuum
Therefore
the
air
induction
system
A
I
s
reduces
CO
and
HC
emissions
in
exhaust
gases
operatiug
the
same
as
the
air
injection
system
A
I
s
The
system
cpnsistsof
an
air
in
tJctio
valve
a
filter
an
A
B
valve
and
hoses
fl
V
t
5
1
Air
ind9ction
valve
2
Air
c
eancr
3
Carburetor
4
Exhaust
manifold
5
Anti
obRcldlre
valve
EC919
Fig
EC
52
Ai
Induction
SYltem
1
Reed
valvo
2
Stopper
EC920
Fig
EC
53
Air
Induction
Val
Page 140 of 548

Emission
Control
System
EXHAUST
GAS
RECIRCULATION
E
G
R
CONTROL
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
to
lower
the
spark
flame
temperature
during
combustion
This
results
in
a
reduction
of
the
nitrogen
oxide
NOx
content
in
the
exhaust
gas
When
the
E
G
R
control
valve
is
open
some
of
the
exhaust
gas
is
led
from
the
exhaust
manifold
to
the
E
G
R
chamber
through
the
E
G
R
passage
The
exhaust
gas
is
then
con
trolled
in
quantity
by
the
E
G
R
valve
and
is
introduced
into
the
intake
manifold
In
the
exhaust
gas
recirculation
system
a
part
of
the
exhaust
gas
is
returned
to
the
combustion
chamber
U
S
A
models
c
r
i
From
carburetor
EC309A
1
E
G
R
thermal
vacuum
valve
2
E
G
R
control
valve
3
Carburetor
4
E
G
R
passage
5
Intake
manifold
6
Exhaust
manifold
7
E
G
R
tube
8
Orifice
9
B
P
T
tube
10
B
P
T
valve
Canada
models
CD
o
1
Thermal
vacuum
valve
2
E
C
R
control
valve
3
Carburetor
4
E
C
R
passage
5
Intake
manifold
6
Exhaust
manifold
7
E
G
R
tube
Thermal
vacuum
valve
3
port
type
T
V
V
Thermal
vacuum
valve
2
port
type
T
V
V
for
FU
model
E
G
R
tube
E
G
R
control
valve
4
Thermal
vacuum
valve
2
port
type
T
V
v
E
G
R
tube
EC155A
Fig
EC
63
E
G
R
System
EC
21
Page 141 of 548
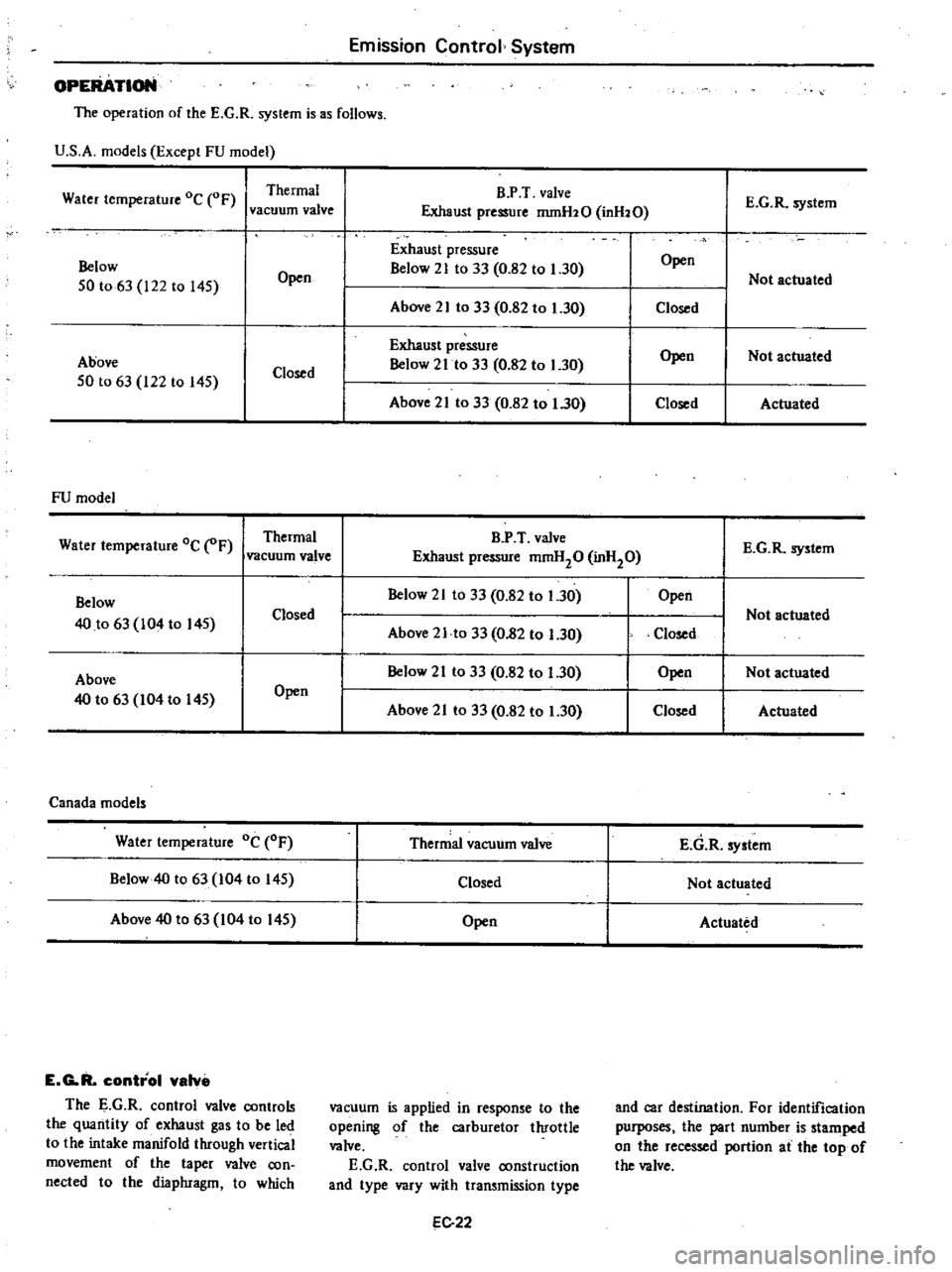
Emission
Control
System
ATloN
The
operation
of
the
E
G
R
system
is
as
follows
U
S
A
models
Except
FU
model
Thermal
Water
temperature
Oc
OF
vacuum
valve
B
P
T
valve
Exhaust
pressure
mmH20
inH20
E
G
R
system
Below
SO
to
63
I22
to
145
Open
Exhaust
pressure
Below
21
to
33
0
82
to
1
30
Open
Not
actuated
Above
21
to
33
0
82
to
1
30
Closed
Exhaust
pressure
Open
Not
actuated
Aliove
Closed
Below
21
to
33
0
82
to
1
30
SO
to
63
I
22
to
145
Above
21
to
33
0
82
to
130
Closed
Actuated
FU
model
Water
temperature
Oc
F
Thermal
B
P
T
valve
E
G
R
system
vacuum
valve
Exhaust
pressure
mmH20
inH2O
Below
Below
21
to
33
0
82
to
1
30
Open
Closed
Not
actuated
40
to
63
104
to
145
Above
2
to
33
0
82
to
1
30
Closed
Above
Below
21
to
33
0
82
to
1
30
Open
Not
actuated
40
to
63
104
to
145
Open
Above
21
to
33
0
82
to
1
30
Closed
Actuated
Canada
models
Water
temperature
Oc
OF
Thermal
vacuum
valve
E
G
R
system
Below
40
to
63
I04
to
145
Closed
Not
actuated
Above
40
to
63
I04
to
145
Open
Actuated
E
G
R
control
valve
The
E
G
R
control
valve
controls
the
quantity
of
exhaust
gas
to
be
led
to
the
intake
manifold
through
vertical
movement
of
the
taper
valve
con
nected
to
the
diaphragm
to
which
vacuum
is
applied
in
response
to
the
opening
of
the
carburetor
throttle
valve
E
G
R
control
valve
construction
and
type
vary
with
transmission
type
and
car
destination
For
identification
purposes
the
part
number
is
stamped
on
the
recessed
portion
at
the
top
of
the
valve
EC22
Page 142 of 548
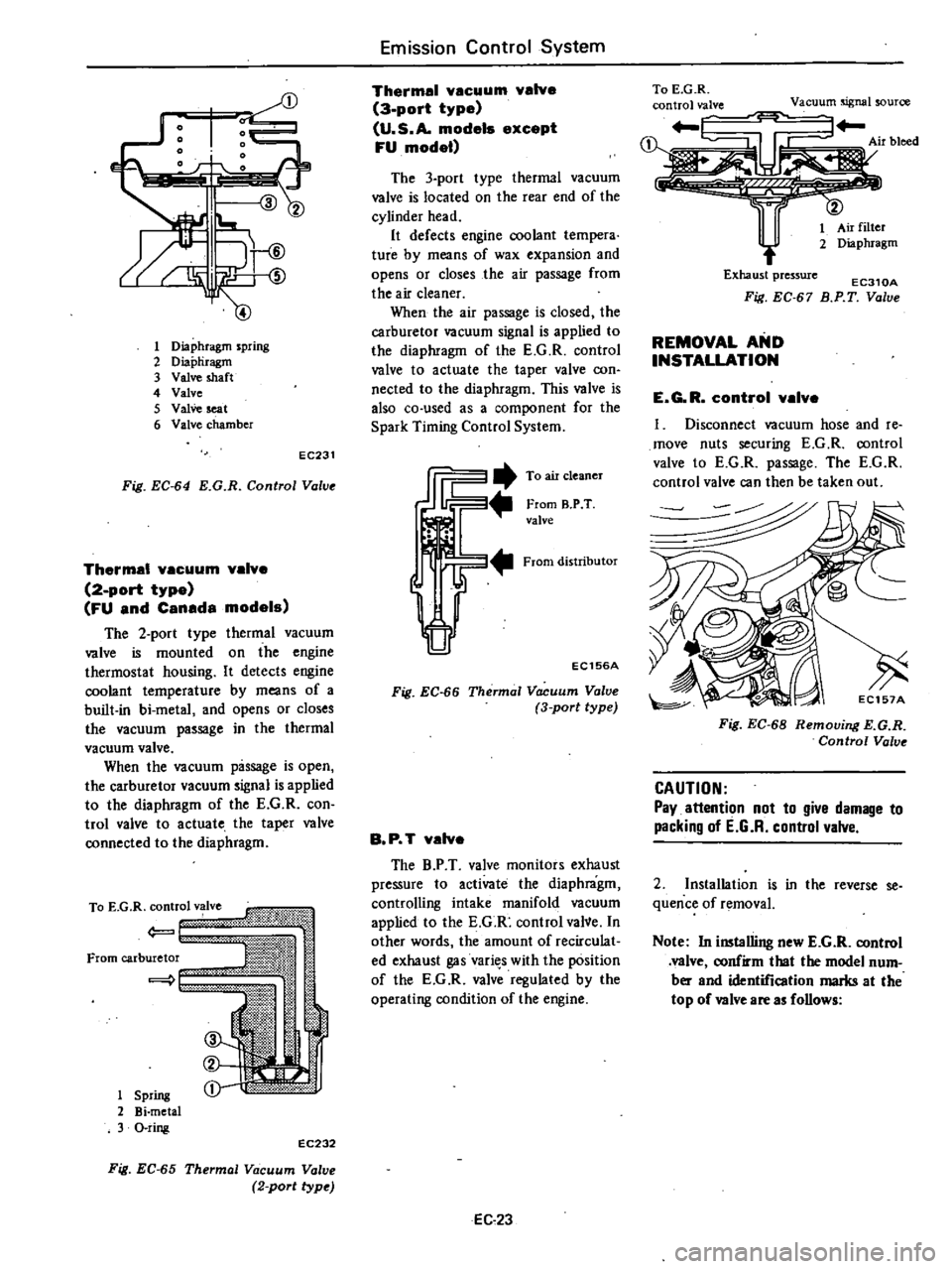
1l
I
I
1J
1
Diaphragm
spring
2
Diapliragm
3
Valve
shaft
4
Valve
5
ValVe
seat
6
Valve
chamber
EC231
Fig
EC
64
E
G
R
Control
Value
Thermal
vacuum
valve
2
port
type
FU
and
Canada
models
The
2
port
type
thermal
vacuum
valve
is
mounted
on
the
engine
thermostat
housing
It
detects
engine
coolant
temperature
by
means
of
a
built
in
bi
metal
and
opens
or
closes
the
vacuum
passage
in
the
thermal
vacuum
valve
When
the
vacuum
passage
is
open
the
carburetor
vacuum
signal
is
applied
to
the
diaphragm
of
the
E
G
R
con
trol
valve
to
actuate
the
taper
valve
connected
to
the
diaphragm
1
Spring
2
Bi
metal
3
O
ring
EC232
Fig
EC
65
Thermal
Vacuum
Valve
2
port
type
Emission
Control
System
Thermal
vacuum
valve
3
port
type
U
S
A
models
except
FU
model
The
3
port
type
thermal
vacuum
valve
is
located
on
the
rear
end
of
the
cylinder
head
It
defects
engine
coolant
tempera
ture
by
means
of
wax
expansion
and
opens
or
closes
the
air
passage
from
the
air
cleaner
When
the
air
passage
is
closed
the
carburetor
vacuum
signal
is
applied
to
the
diaphragm
of
the
E
G
R
control
valve
to
actuate
the
taper
valve
con
nected
to
the
diaphragm
This
valve
is
also
co
used
as
a
component
for
the
Spark
Timing
Control
System
JiI2
To
air
cleaner
From
B
P
T
valve
From
distributor
EC156A
Fig
EC
66
Thermal
Vacuum
Valve
3
port
type
B
P
T
valve
The
B
P
T
valve
monitors
exhaust
pressure
to
activate
the
diaphragm
controlling
intake
manifold
vacuum
applied
to
the
E
G
R
control
vaNe
In
other
words
the
amount
of
recirculat
ed
exhaust
gas
vari
s
with
the
position
of
the
E
G
R
valve
regulated
by
the
operating
condition
of
the
engine
EC
23
To
E
G
R
control
valve
Vacuum
nal
Curce
Air
bleed
1
Exhaust
pressure
EC310A
Fig
EC
67
B
P
T
Value
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
E
G
R
control
valve
I
Disconnect
vacuum
hose
and
re
move
nuts
securing
E
G
R
control
valve
to
E
G
R
passage
The
E
G
R
control
valve
can
then
be
taken
out
Fig
EC
68
Remouing
E
G
R
Control
Valve
CAUTION
Pay
attention
not
to
give
damage
to
packing
of
E
G
R
control
valve
2
Installation
is
in
the
reverse
se
quence
of
removal
Note
In
installing
new
E
G
R
control
valve
confirm
that
the
model
num
ber
and
identification
marks
at
the
top
of
valve
are
as
follows
Page 143 of 548
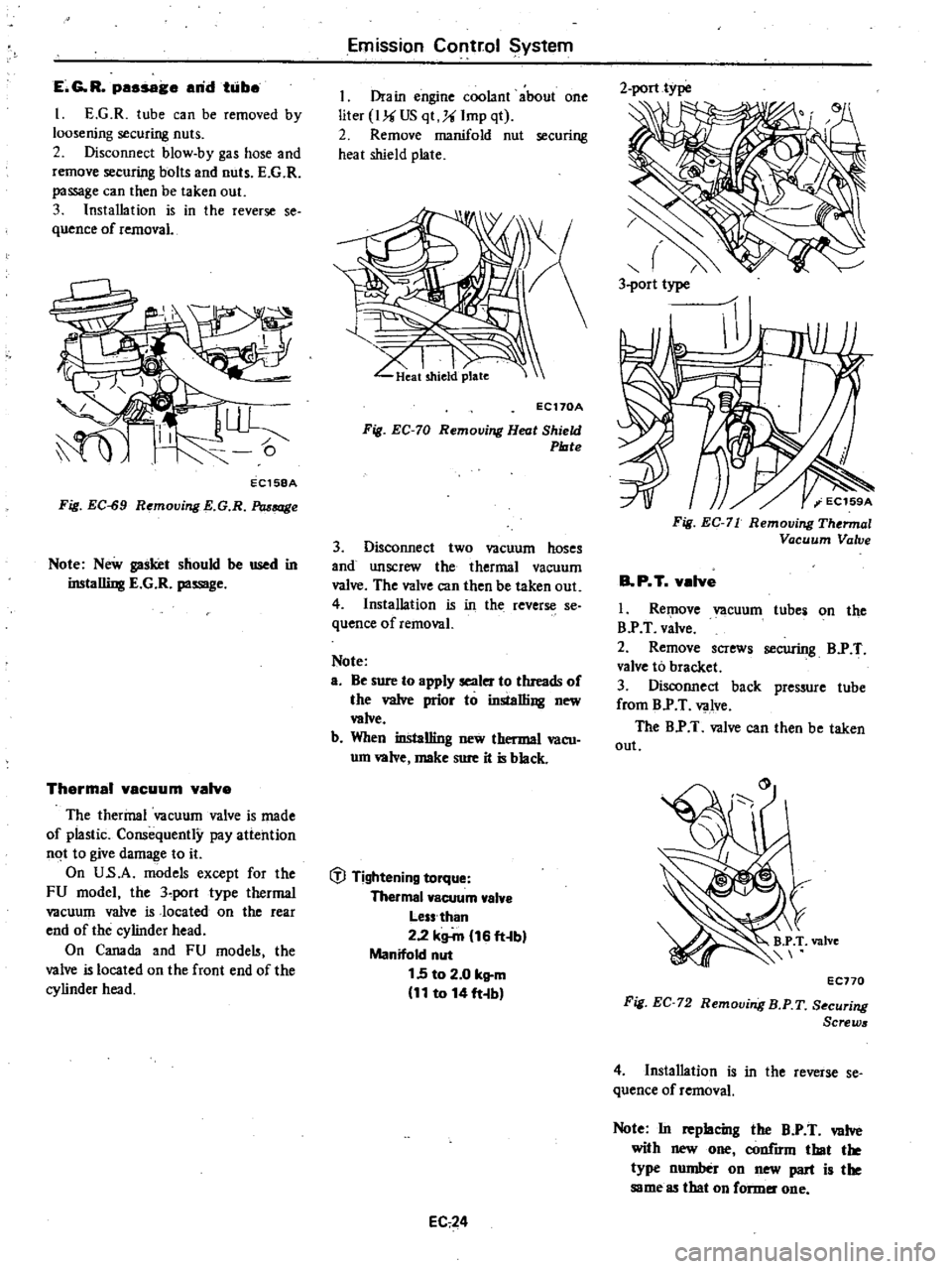
E
G
R
passage
arid
taibe
I
E
G
R
tube
can
be
removed
by
loosening
securing
nuts
2
Disconnect
blow
by
gas
hose
and
remove
securing
bolts
and
nuts
E
G
R
passage
can
then
be
taken
out
3
Installation
is
in
the
reverse
se
quence
of
removal
EC158A
Fig
EC
S9
Removing
E
G
R
Passage
Note
New
gasket
should
be
used
in
installing
E
G
R
passage
Thermal
vacuum
valve
The
thermal
vacuum
valve
is
made
of
plastic
Consequently
pay
attention
not
to
give
damage
to
it
On
U
s
A
models
except
for
the
FU
model
the
3
port
type
thermal
vacuum
valve
is
located
on
the
rear
end
of
the
cylinder
head
On
Canada
and
FU
mode
the
valve
is
located
on
the
front
end
of
the
cylinder
head
Emission
Corltr
ol
System
I
Drain
engine
coolant
about
one
liter
I
US
qt
Imp
qt
2
Remove
manifold
nut
securing
heat
shield
plate
I
I
LIkat
shield
plate
EC170A
Fig
EC
70
Removing
Heat
Shield
Plate
3
Disconnect
two
vacuum
hoses
and
unscrew
the
thermal
vacuum
valve
The
valve
can
then
be
taken
out
4
Installation
is
in
the
reverse
se
quence
of
removal
Note
a
Be
sure
to
apply
sealer
to
threads
of
the
valve
prior
to
installing
new
wive
b
When
installing
new
thermal
vacu
um
wive
make
sure
it
is
black
t
J
Tightening
torque
Thermal
vacuum
valve
Less
than
2
2
kg
m
16
ft
b
Manifold
nut
1
5
to
2
0
kg
m
11
to
14
ft
b
EC
24
2
port
type
3
port
type
Fig
EC
71
Removing
Thermal
Vacuum
Valve
B
P
T
valve
I
Remove
vacuum
tube
on
the
B
P
T
valve
2
Remove
screws
securing
B
P
T
valve
to
bracket
3
Disconnect
back
pressure
tube
from
B
P
T
valve
The
B
P
T
valve
can
then
be
taken
out
EC770
Fig
EC
72
Removing
B
P
T
S
curing
Screws
4
Installation
is
in
the
reverse
se
quence
of
removal
Note
In
replacing
the
B
P
T
valve
with
new
one
h
that
the
type
number
on
new
part
is
the
same
85
that
on
former
one
Page 347 of 548

I
AA552
Fig
RA
18
Shock
A
bllOrber
Upper
End
2
Remove
bolt
securing
shock
ab
sorber
lower
end
and
remove
shock
absorber
Note
When
removing
shock
ebsorber
lower
end
from
bracket
Iueeze
shock
absorber
end
lift
it
out
right
aJ
o
J
to
accommodate
emb
ss
ment
inside
bracket
c
RA486
Fig
RA
19
Shock
Absorber
Lower
End
Brocket
Inspection
I
Test
shock
absorber
and
compare
with
specification
given
in
Service
Data
and
Specifications
Replace
if
nece
ry
2
Check
for
cracks
Also
check
pis
ton
rod
for
straightness
3
Check
all
rubber
parts
for
wear
cracks
damage
or
deformation
Re
place
if
necessary
Installation
Install
shock
absorber
in
the
reverse
order
of
removal
Note
Tighten
shock
absorber
upper
end
nut
to
specification
until
it
is
fully
tightened
to
thread
end
of
pis
ton
rod
Then
securely
tighten
lock
nut
Rear
Axle
Rear
Suspension
@
Tightening
tonlU1l
Shock
absorber
upper
end
nut
1
5
to
2
0
kg
m
11
to
14
ft
b
Shock
absorber
lower
end
n1
t
7
0
to
8
0
k
l
m
51
to
58
ft
bl
CAUTION
I
Be
careful
not
to
damage
or
bend
piston
rod
during
operation
b
Do
not
open
or
heat
gas
filled
type
shock
absorbers
COIL
SPRING
Removal
Block
front
wheels
with
chocks
2
Raise
rear
of
car
high
enough
to
permit
working
underneath
and
place
stands
solidly
under
body
member
on
both
sides
3
Support
under
center
of
dif
ferential
carrier
with
a
garage
jack
4
Remove
rear
wheels
5
Remove
bolts
securing
shock
absorber
lower
ends
on
each
side
C
J
1
v
I
JJJ
RA485
Fig
RA
20
RemoviTIII
Bolt
Securing
Shock
Abwrber
Lower
End
6
Lower
jack
slowly
and
remove
coil
springs
on
each
side
after
they
are
fully
extended
RA546
Fig
RA
21
Removing
Coil
Spring
RA
6
Inspection
1
Check
coil
spring
for
yield
defor
mation
or
cracks
2
Test
spring
and
compare
with
specifications
given
in
Service
Data
and
Specifications
3
Check
all
rubber
parts
for
wear
cracks
damage
or
deformation
Re
place
if
necessary
InsteDatlon
Install
coil
spring
in
the
reverse
order
ofremoval
CAUTION
Correctly
fit
open
end
on
spring
seat
CD
Tightening
torque
Shock
absorber
lowel
end
nut
7
010
8
0
kg
51
to
58
ft
b
LINK
ASSEMBLY
Removal
It
is
possible
to
remove
one
link
assembly
alone
When
removing
more
than
two
link
assemblies
remove
axle
assembly
first
Refer
to
Rear
Axle
Assembly
for
removal
Remove
upper
link
or
lower
link
alone
by
removing
bolt
on
each
end
Fig
RA
22
Removing
Upper
Link
RA553
Fig
RA
23
Remouing
Lower
Link
Page 416 of 548

DESCRIPTION
The
front
and
rear
bumpers
consist
essentially
of
a
center
bumper
two
side
bumpers
and
two
shock
absorbers
The
bumper
is
attached
to
the
side
member
through
a
gas
filled
strut
type
shock
absorber
at
each
end
to
effectively
absorb
the
energy
of
a
collision
upon
ilnpact
The
side
bumper
is
constructed
with
a
steel
insert
panel
and
porous
urethane
rubber
The
urethane
rubber
FRONT
BUMPER
I
I
Body
BUMPER
section
reduces
to
a
nummum
the
possibility
of
damaging
the
car
body
when
the
bumper
is
involved
in
a
collision
CAUTION
The
shock
ebsorber
is
filled
with
a
high
pressure
gn
and
should
not
be
disassembled
drilled
or
exposed
to
In
open
flame
CAUTION
LABEL
Pasted
on
shock
absorbers
x
DANGER
i
t
e
e
e
t
I
Contents
under
pressure
Don
t
take
apart
puncture
apply
heat
or
fira
3S
mm
1
38
in
BF
5
1
Front
center
bumper
2
Over
rider
3
Side
bumper
4
Bumper
mounting
bracket
5
Center
bumper
brace
6
Bumper
rainforce
7
Sight
shield
8
Shock
absorber
9
Bumper
attaching
bolt
BF738B
Fig
BF
5
Front
Bumper
Page 515 of 548

4
Wfefrlgerant
charging
speed
slows
down
charge
it
while
running
the
compressor
for
ease
of
charging
After
having
taken
the
steps
up
to
3
above
proceed
with
charging
in
the
following
order
1
Shut
off
high
pressure
valve
of
manifold
gauge
2
Run
the
engine
at
idling
speeds
below
1
500
rpm
3
Set
the
Temperature
lever
and
Fan
switch
at
maximum
cool
and
maximum
speed
respectively
To
Lpw
pressure
service
valve
t
Air
Conditioning
4
Charge
efiigerani
while
con
trolling
low
pressure
gauge
reading
at
2
8
kg
cm2
40
psi
or
less
by
turning
in
or
out
low
pressure
valve
of
mani
fold
gauge
See
Fig
A
20
WARNING
Never
charge
refrigerant
through
high
pressure
side
discharge
side
of
system
since
this
will
force
re
frigerant
back
into
refrigerant
can
and
can
may
explode
To
High
pressure
service
valve
A
5
When
refrigerant
can
is
empty
fully
close
both
valves
of
manifold
gauge
and
replace
refrigerant
can
with
a
new
ot
e
Before
opening
manifold
gauge
valve
to
charge
refrigerant
from
new
can
be
sure
to
purge
air
from
inside
charging
hose
6
Charge
the
specified
amount
of
refrigerant
into
system
by
weighing
charged
refrigerant
with
scale
Over
charging
wiU
cause
discharge
pressure
to
rise
AC380A
Fig
AC
20
Charging
Refrigeront
Measure
the
amount
of
charged
refrigerant
with
a
scale
Make
a
note
of
the
amount
charged
from
can
AC252
Fig
AC
21
Chorging
Refrigeront
Refrigerant
capacity
Unit
kg
lb
Refrigerarit
Minimum
Maximum
R
12
0
8
1
8
1
0
2
2
AC14
Note
The
p
Ce
of
btibble
hi
sight
glass
of
receiver
drier
is
an
unsuitable
method
of
checking
the
amount
of
refrigerant
charged
in
system
The
state
of
the
bubbles
iJt
sight
glass
should
only
be
used
ior
checking
whether
the
amount
of
charged
refrigerant
is
small
or
not
The
amount
of
charged
refrigerani
can
be
correcdy
judged
by
means
of
discharge
pressure
Refer
to
Re
frigerant
Level
Check
7
After
the
specified
amount
of
refrigerant
has
been
charged
intosys
tern
close
manifold
gauge
valves
Then
detach
charging
hoses
from
service
valves
of
system
Be
sure
to
install
valve
cap
to
service
valve
8
Confirm
that
there
are
no
leaks
in
system
by
checking
with
a
leak
detec
tor
Refer
to
Checking
for
Leaks
Note
Conducting
8
performance
test
prior
to
removing
manifold
gauge
is
8
good
service
operation
Refer
to
Performance
Test
CHECKING
FOR
LEAKS
Conduct
a
leak
t
st
whenever
leak
age
of
refrigerant
is
suspected
and
when
conducting
service
operations
which
are
accompanied
by
disassembly
or
loosening
of
connection
fittings
Refrigerant
is
a
colorless
odorless
gas
and
leakage
from
system
is
diffi
cult
to
detect
Accordingly
the
use
of
a
leak
detector
facilitates
check
for
leaks
Two
methods
of
checking
are
available
one
employs
a
halide
leak
detector
which
bums
propane
gas
or
butane
gas
and
the
other
is
an
electric
type
leak
detector
If
any
trace
of
oil
is
noted
at
and
around
connection
fittings
it
is
a
sure
indication
that
refrigerant
is
leaking
This
condition
can
be
corrected
easily
by
retightening
the
joints
If
any
joint
on
line
is
suspected
of
small
amount
of
leakage
use
a
leak
detector
to
locate
leaking
points
Page 516 of 548

HALIDE
LEAK
DETECTOR
Since
the
propane
leak
detector
and
butane
leak
detector
are
the
same
in
respect
to
their
operation
this
section
describes
the
operation
of
the
propane
leak
detector
The
copper
screen
is
heated
by
the
Air
Conditioning
burning
of
propane
Refrigerant
gas
decomposes
to
color
the
flame
when
it
contacts
the
heated
screen
The
gas
to
be
checked
is
drawn
into
the
sampling
tube
and
sent
out
to
the
burner
A
refrigerant
leak
can
clearly
be
detected
by
variations
in
the
color
of
the
flame
1
Copper
reaction
plate
2
Flame
adjusting
lines
3
Burner
4
Sampling
tube
5
Strainer
6
Gas
bomb
7
Flame
adjuster
AC010
Fig
AC
22
Checking
for
Leaks
4
The
flame
will
be
almost
colorless
when
there
is
no
refrigerant
gas
being
burned
When
there
is
a
small
refriger
ant
gas
leak
the
flame
will
be
green
or
yellowgreen
When
refrigerant
gas
leak
age
is
large
the
flame
will
be
brilliant
blue
or
purple
Since
the
color
of
the
flame
will
be
yellow
when
dust
is
being
burned
or
there
is
aging
scale
on
copper
reaction
plate
always
keep
the
strainer
of
sampling
tube
and
reaction
plate
clean
5
Major
check
points
l
Compressor
Compressor
shaft
seal
rotate
the
compressor
by
hand
Flexible
hose
connections
Front
and
rear
head
gaskets
Service
valve
2
Condenser
Condenser
pipe
fitting
Condenser
inlet
and
outlet
pipe
connections
3
Refrigerant
lines
Flared
section
of
high
pressure
and
low
pressure
flexible
hoses
Une
connections
4
Evaporator
housing
Inlet
and
outlet
line
connections
Expansion
valve
Propane
type
Butane
type
ELECTRIC
LEAK
DETECTOR
NO
LEAK
Greenish
blue
Pale
blue
For
the
operational
procedures
SMALL
LEAK
Yellow
Bright
blue
refer
to
the
instructions
furnished
with
LARGE
LEAK
Purple
Vivid
green
each
electric
leak
detector
Discharge
refrigerant
in
one
or
two
seconds
to
ascertain
that
system
has
a
sufficient
pressure
needed
for
leak
detection
Charge
with
0
4
kg
0
9
Ib
of
refrigeranl
if
necessary
2
Light
leak
detector
Adjust
the
height
of
the
flame
between
flame
adjusting
lines
at
the
top
and
bottom
of
combustion
tube
A
reaction
plate
will
immediately
become
red
hot
3
Place
the
end
of
sampling
tube
near
the
point
of
the
suspected
leak
in
system
Note
a
Since
refrigerant
gas
is
heavier
than
air
small
leaks
can
be
easily
detect
ed
by
placing
sampling
tube
direct
ly
below
the
check
point
b
Suitable
ventilation
is
required
If
refrigerant
gas
is
mixed
with
the
surrounding
air
leak
detector
will
always
indicate
a
response
and
detection
of
the
actual
leak
will
be
difficult
c
Never
hold
leak
detector
at
an
angle
WARNING
a
Never
inhale
the
fumes
produced
by
combustion
of
refrigerant
gas
since
they
are
toxic
b
Never
use
halide
torch
in
a
place
where
combustible
or
explosive
gas
is
present
AC
15
REFRIGERANT
LEVEL
CHECK
SIGHT
GLASS
Sight
glass
is
provided
at
the
top
of
receiver
drier
One
guide
for
whether
there
is
enough
refrigerant
in
syst
m
is
given
by
observing
refrigerant
flow
through
sight
glass
However
this
method
is
unsuitable
for
judging
the
aJTlount
of
refrigerant
The
correct
refrigeranl
level
can
be
judged
by
measuring
the
system
pressures
in
ac
cordance
with
the
procedures
as
de
scribed
in
Performance
Test
1
Start
the
engine
and
hold
engine
speed
al
1
500
rpm
2
Set
AIR
lever
to
AlC
position