engine DATSUN 510 1968 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1968, Model line: 510, Model: DATSUN 510 1968Pages: 252, PDF Size: 12.2 MB
Page 106 of 252

ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
101
8
To
separate
the
stator
from
the
dIode
end
housmg
assembly
unsolder
the
three
negatIve
dIodes
from
the
three
co1l1ead
WIres
The
nega
tIve
dIodes
are
marked
WIth
black
figures
and
the
posItIve
ones
With
red
figures
CAUTION
Use
extreme
care
when
unsoldenng
the
diodes
to
prevent
excessive
heat
from
damagmg
thi
m
Use
a
100
to
200
watt
soldermg
Iron
for
no
more
than
two
seconds
at
the
dIOde
Junction
9
Remove
the
brush
cover
by
unscreWIng
the
two
set
screws
10
Unsolder
the
negatIve
terminal
lead
wire
Separate
dIOde
end
from
stator
Figure
33
@
11
Remove
the
heat
smk
and
the
brush
holder
from
the
rear
cover
by
unscrewmg
the
setscrews
as
shown
m
Figure
34
@
12
DIsassemble
the
brush
holder
by
unsolder
ing
the
F
lead
WIre
black
whIte
E
lead
WIre
black
and
the
negatIve
and
pOSItIve
brush
holder
Wires
Figure
35
shows
the
brush
holder
dIsassembled
O
tlII
I
@
13
To
remove
a
dIode
from
the
heat
smk
sup
port
the
heat
SInk
WIth
a
swtable
stand
Figure
36
and
push
out
the
dIode
With
an
arbor
press
Do
not
attempt
removal
WIth
a
hammer
as
the
shock
may
damage
all
the
dIodes
ill
the
heat
SInk
Press
out
so
as
not
to
Injure
the
mounting
bore
01
the
frame
or
the
heat
Sink
14
To
replace
a
dIode
m
the
heat
smk
support
the
heat
SInk
With
a
SUItable
stand
and
press
the
dIode
mto
place
as
shown
m
Figure
37
Inspection
and
Repair
I
InspectIon
of
the
alternator
Includes
electncal
testmg
and
mechanIcal
InspectIon
of
all
parts
for
damage
or
exceSSIve
wear
An
electrIcal
tester
proVIdmg
reSIstance
anI
contmUlty
testlng
IS
requIred
Before
dIsassembly
of
the
alternator
Page 108 of 252
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
103
2
Check
the
lead
Wires
of
the
armature
coil
Includmg
the
neutral
wire
for
ground
as
shown
In
Figure
42
HIgh
reSIStance
no
current
flow
indicates
gqod
condItion
If
not
the
stator
must
be
replaced
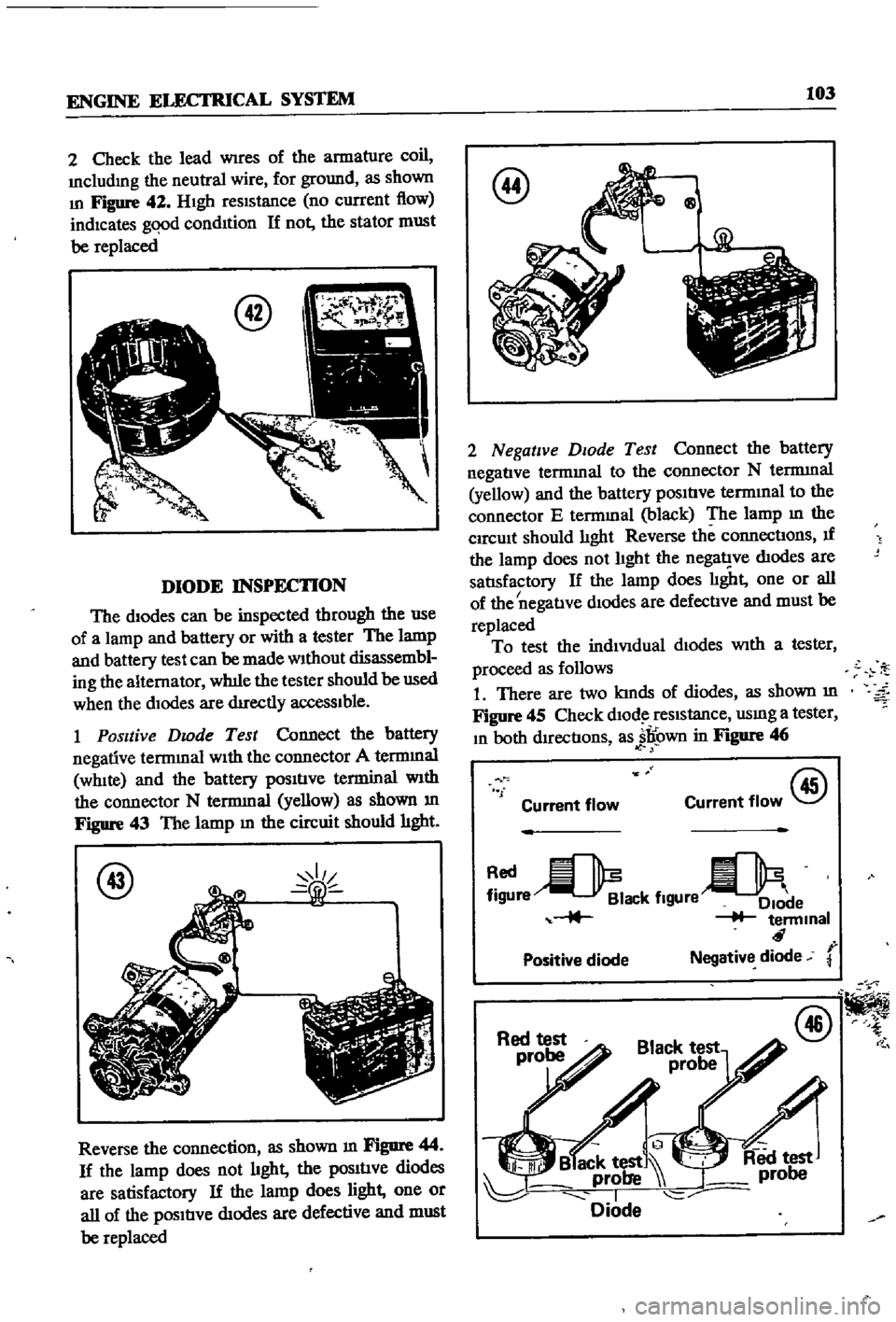
DIODE
INSPECTION
The
diodes
can
be
inspected
through
the
use
of
a
lamp
and
battery
or
with
a
tester
The
lamp
and
battery
test
can
be
made
Without
disassembl
ing
the
alternator
wh1le
the
tester
should
be
used
when
the
dIodes
are
dIrectly
acceSSIble
1
Positive
Dwde
Test
Connect
the
battery
negative
terrmnal
WIth
the
connector
A
terrmnal
WhIte
and
the
battery
pOSItIve
terminal
With
the
connector
N
terrmnal
yellow
as
shown
m
Figure
43
The
lamp
m
the
circuit
should
hght
@
Reverse
the
connection
as
shown
m
Figure
44
If
the
lamp
does
not
hght
the
pOSItIve
diodes
are
satisfactory
If
the
lamp
does
light
one
or
all
of
the
pOSItIve
dIodes
are
defective
and
must
be
replaced
@
Qg
2
Negative
DIOde
Test
Connect
the
battery
negatIve
termmal
to
the
connector
N
terrmnal
yellow
and
the
battery
pOSItIve
termInal
to
the
connector
E
termmal
black
The
lamp
m
the
CIrcUit
should
lIght
Reverse
the
connectIons
If
the
lamp
does
not
lIght
the
nega1
ve
dIodes
are
satlsfactory
If
the
lamp
does
lIght
one
or
all
I
of
the
negatIve
dIodes
are
defectIve
and
must
be
replaced
To
test
the
indiVIdual
dIodes
With
a
tester
proceed
as
follows
1
There
are
two
kInds
of
diodes
as
shown
m
Figure
45
Check
dlOd
reSIstance
usmg
a
tester
In
both
dIrectIons
as
jl
own
in
Figure
46
f
Current
flow
@
Current
flow
re
ack
flgUre
e
terminal
r
Positive
diode
Negative
diode
@
Page 110 of 252
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
105
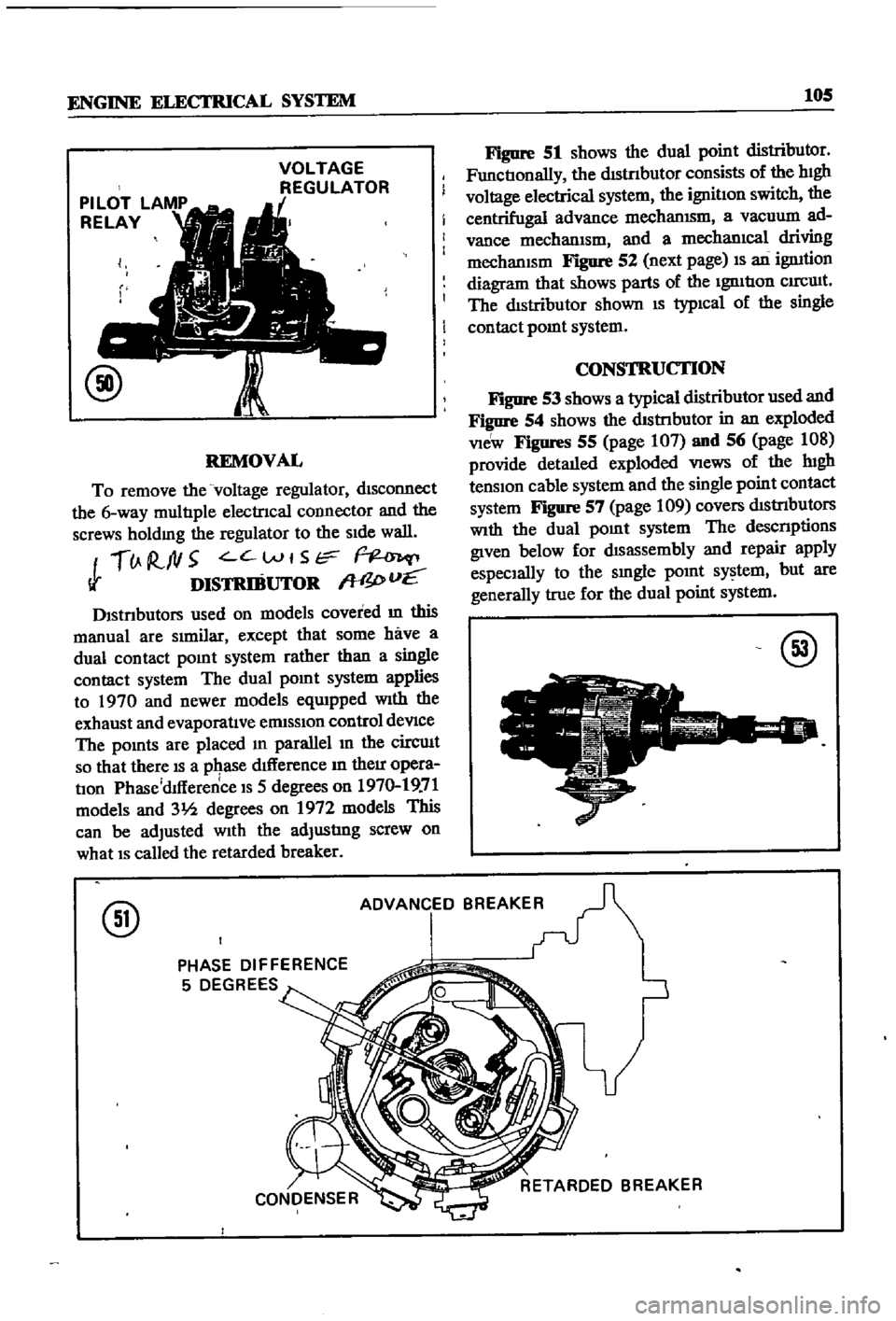
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
REMOVAL
To
remove
the
voltage
regulator
dISconnect
the
6
way
multIple
electrIcal
COlInector
and
the
screws
holdmg
the
regulator
to
the
SIde
wall
lJ
R
ftl5
C
Wt
Str
Ii
DISTRIBUTOR
W
I
vE
Dlstnbutors
used
on
models
covered
m
this
manual
are
SImilar
except
that
some
have
a
dual
contact
pomt
system
rather
than
a
single
contact
system
The
dual
pomt
system
applies
to
1970
and
newer
models
eqUIpped
With
the
exhaust
and
evaporatIve
ermsslOn
control
deVIce
The
pomts
are
placed
m
parallel
In
the
circuIt
so
that
there
IS
a
pqase
dIfference
In
their
opera
tIon
Phase
dlfference
IS
5
degrees
on
1970
19
71
models
and
31h
degrees
on
1972
models
This
can
be
adjusted
With
the
adjustIng
screw
on
what
IS
called
the
retarded
breaker
Figure
51
shows
the
dual
point
distributor
FunctIonally
the
dIStnbutor
consists
of
the
hIgh
voltage
electrical
system
the
ignitIon
switch
the
centrifugal
advance
mechanISm
a
vacuum
ad
vance
mechanIsm
and
a
mechanIcal
driving
mechanISm
Figure
52
next
page
IS
an
ignItion
diagram
that
shows
parts
of
the
IgnItIon
CIrCUIt
The
dIstributor
shown
IS
typIcal
of
the
single
contact
pomt
system
CONSTRUCTION
Figure
53
shows
a
typical
distributor
used
and
Figure
54
shows
the
dIStnbutor
in
an
exploded
VIeW
Figures
55
page
107
and
56
page
108
provide
detaIled
exploded
VIews
of
the
lugh
tenSIon
cable
system
and
the
single
point
contact
system
Figure
57
page
109
covers
dIStrIbutors
With
the
dual
pOInt
system
The
descnptions
given
below
for
dIsassembly
and
repair
apply
espeCIally
to
the
smgle
pOInt
system
but
are
generally
true
for
the
dual
point
system
@
@
ADVANCED
BREAKER
PHASE
DIFFERENCE
5
DEGREES
Page 111 of 252
106
CHAPTER
NINE
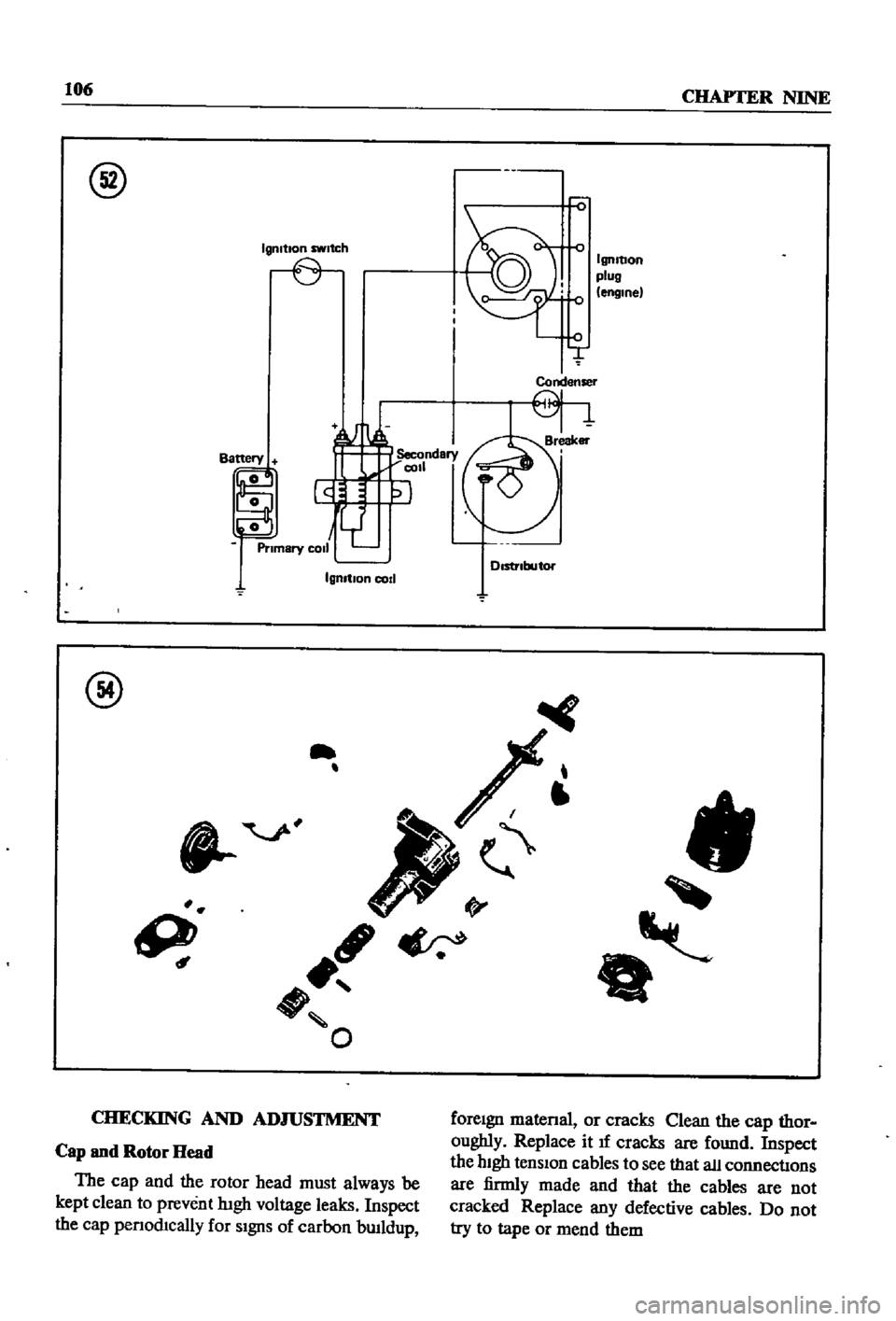
@
Igmtlon
switch
IgnItion
plug
engine
Condenser
IgnItIon
cod
@
II
9
ft
O
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
foreIgn
matenal
or
cracks
Qean
the
cap
thor
oughly
Replace
it
If
cracks
are
found
Inspect
the
hIgh
tensIon
cables
to
see
that
all
connectIons
are
firmly
made
and
that
the
cables
are
not
cracked
Replace
any
defective
cables
Do
not
try
to
tape
or
mend
them
Cap
and
Rotor
Head
The
cap
and
the
rotor
head
must
always
be
kept
clean
to
prevent
lugh
voltage
leaks
Inspect
the
cap
penod1cally
for
SIgnS
of
carbon
bwldup
Page 116 of 252
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
111
@
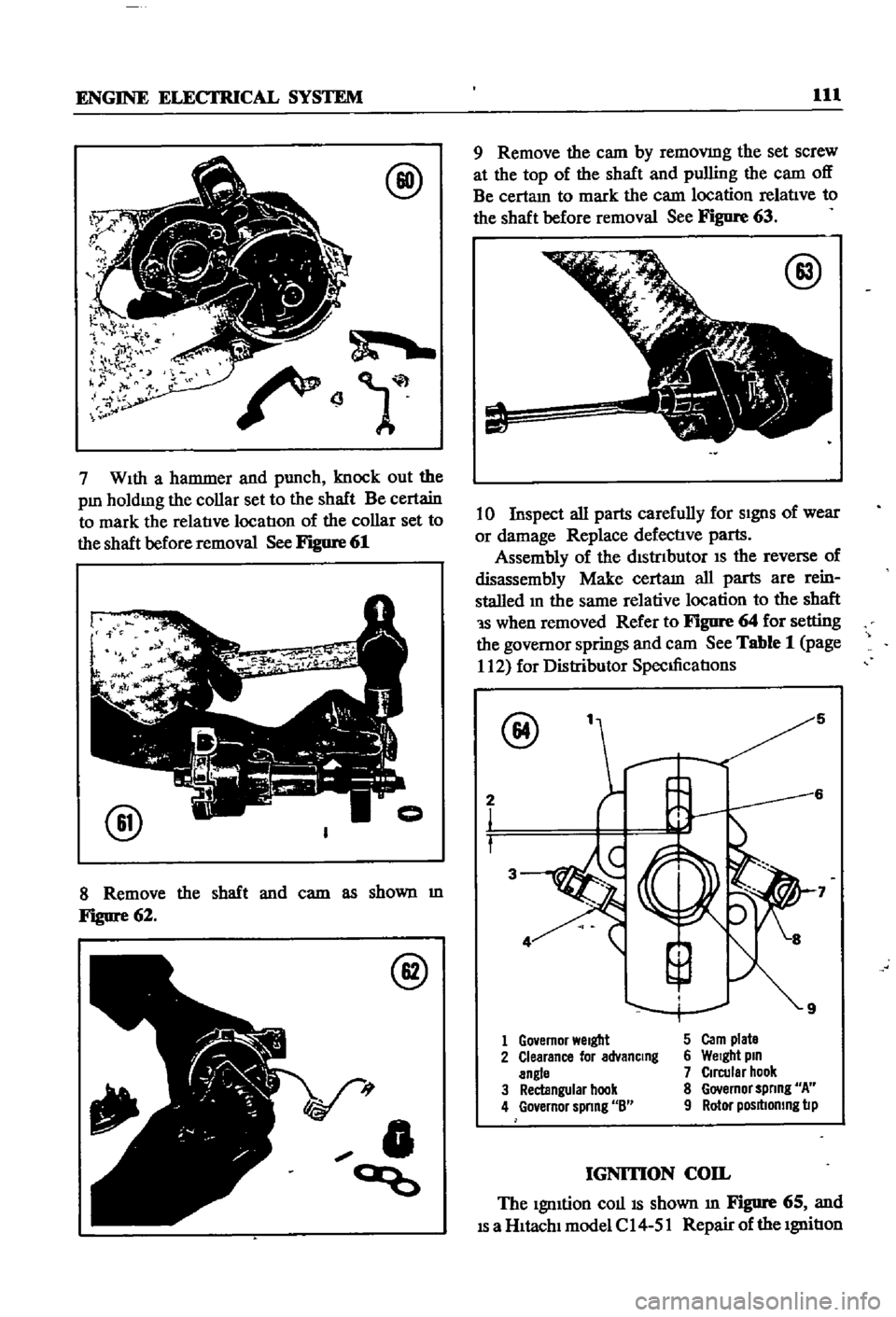
7
WIth
a
hammer
and
punch
knock
out
the
pm
holdmg
the
collar
set
to
the
shaft
Be
certain
to
mark
the
relatIve
locatIon
of
the
collar
set
to
the
shaft
before
removal
See
Figure
61
@
8
Remove
the
shaft
and
cam
as
shown
m
Figure
62
@
V
t
0
ao
9
Remove
the
cam
by
removmg
the
set
screw
at
the
top
of
the
shaft
and
pulling
the
cam
off
Be
certam
to
mark
the
cam
location
relatIve
to
the
shaft
before
removal
See
Figure
63
@
10
Inspect
all
parts
carefully
for
SIgnS
of
wear
or
damage
Replace
defectIve
parts
Assembly
of
the
dIStrIbutor
IS
the
reverse
of
disassembly
Make
certam
all
parts
are
rein
stalled
m
the
same
relative
location
to
the
shaft
1S
when
removed
Refer
to
Figure
64
for
setting
the
governor
springs
and
cam
See
Table
1
page
112
for
Distributor
SpecIficatIons
@
5
2
3
1
Go
emor
Welgbt
5
Carn
plate
2
Clearance
lor
advanCing
6
Welgbt
pin
angle
7
Circular
hook
3
Rectangular
hook
8
Governor
spnng
A
4
Go
ernor
spnng
8
9
Rotor
posltlomng
lip
IGNITION
COIL
The
IgnItion
COllIS
shown
m
Figure
65
and
IS
a
HItachI
model
C
14
51
Repair
of
the
IgnitIon
Page 118 of 252

ENGINE
ELECI
RICAL
SYSTEM
113
i
Normal
plug
appearance
noted
by
the
brown
to
graYlsll
lan
depOSits
and
slight
eleclrode
wear
This
plug
indicates
the
correct
plug
heal
range
and
proper
air
fuel
ratio
jI
Jo
t
Ql
i
Carbon
fouhng
distinguished
by
dry
fluffy
black
carbon
depOSits
which
may
be
caused
by
an
over
rich
alr
lue
mixture
excessive
hand
choking
clogged
air
filler
or
excessl
e
Idling
t
I
j
if
r
l
1
tfc
ji
0
1
fouling
indicated
by
wet
o
ly
depOSits
caused
by
011
pumping
past
worn
rings
or
down
the
Intake
valve
gUIdes
A
hotter
plug
temporanly
reduces
011
depOSits
but
a
plug
that
IS
too
hot
leads
to
pre
Ignition
end
possible
engine
damage
@
Red
brown
yellow
and
white
coatings
caused
by
luel
and
011
addltl
es
These
depOSits
are
not
harm
ful
If
they
remain
In
a
powdery
lorm
pr
11
L
J
J
S
C
ShinY
yellow
glaze
on
Insulalor
cone
IS
caused
when
the
powdery
depOSits
from
fuel
and
011
addltl
es
melt
Melting
occurs
during
hard
acceleration
alter
prolonged
Idling
This
glaze
conducts
electnclty
and
shorts
out
the
plug
e
1
A
I
A
I
7
Overheated
plug
indIcated
by
burned
or
blistered
Insulator
tiP
and
badly
worn
electrodes
ThiS
condl
J
tlon
may
be
caused
by
pre
Ignition
cooling
system
defects
lean
alr
luel
ratiOS
low
octane
luel
or
o
er
advanced
Ignition
timing
Spark
plUI
condition
photos
courtesy
of
AC
SPIr1l
Plug
Olv
s
on
Gene
MolDrs
Corporlllon
Page 119 of 252

CHAPTER
TEN
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
ThIs
chapter
covers
emission
control
and
exhaust
systems
The
emission
devices
used
in
clude
crankcase
ermssion
controls
an
exhaust
ermssion
system
and
evaporative
emission
con
trols
EXHAUST
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
Two
methods
of
exhaust
emission
control
are
used
on
the
Datsun
One
is
an
aIr
injection
system
the
other
consists
of
engine
modifica
tIons
Datsuns
were
equipped
With
the
air
injec
tIon
system
only
through
1970
SInce
then
all
models
have
combined
aIr
mjection
with
engine
modIficatIons
EmisSIon
servicing
IS
complex
and
should
be
left
to
qualIfied
professionals
Figure
1
Illustrates
the
system
used
through
model
year
1969
Figure
2
IS
the
system
used
after
1970
Figures
3
through
7
offer
detaIls
of
various
emission
components
Maintenance
and
Testing
Penodlc
mspection
and
service
should
be
done
every
12
months
or
12
000
miles
The
engine
must
be
in
good
working
order
to
main
tain
a
low
level
of
harmful
emissions
There
fore
perform
a
general
tune
up
as
spec1fied
in
Chapter
Four
before
followmg
the
procedures
below
CRANKCASE
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
The
crankcase
emission
control
system
is
shown
in
FlgDre
8
It
IS
a
closed
system
that
pre
vents
crankcase
gases
from
escaping
to
the
at
mosphere
Blowby
gases
are
dIrected
to
the
intake
manifold
through
the
ventilation
control
valve
Normally
capacity
of
the
valve
is
suffi
cient
to
handle
the
blowby
gas
plus
a
small
amount
of
ventIlating
air
drawn
from
the
air
cleaner
through
a
tube
leading
to
the
crankcase
Under
fun
throttle
condItIons
manifold
vacuum
is
Insufficient
to
draw
the
blowby
through
the
valve
When
this
happens
b10wby
flows
through
the
system
In
the
reverse
dIrection
General
1
Start
the
engine
and
bring
up
to
operating
temperature
2
Check
hoses
and
hose
connections
for
leaks
3
Examine
the
hoses
for
signs
of
cracks
or
de
terioraoon
Replace
as
required
Crankcase
Ventilation
Control
Valve
1
Start
the
engme
2
Remove
the
ventIlator
hose
from
the
crank
case
ventilatIon
control
valve
A
htssmg
nOISe
Page 122 of 252
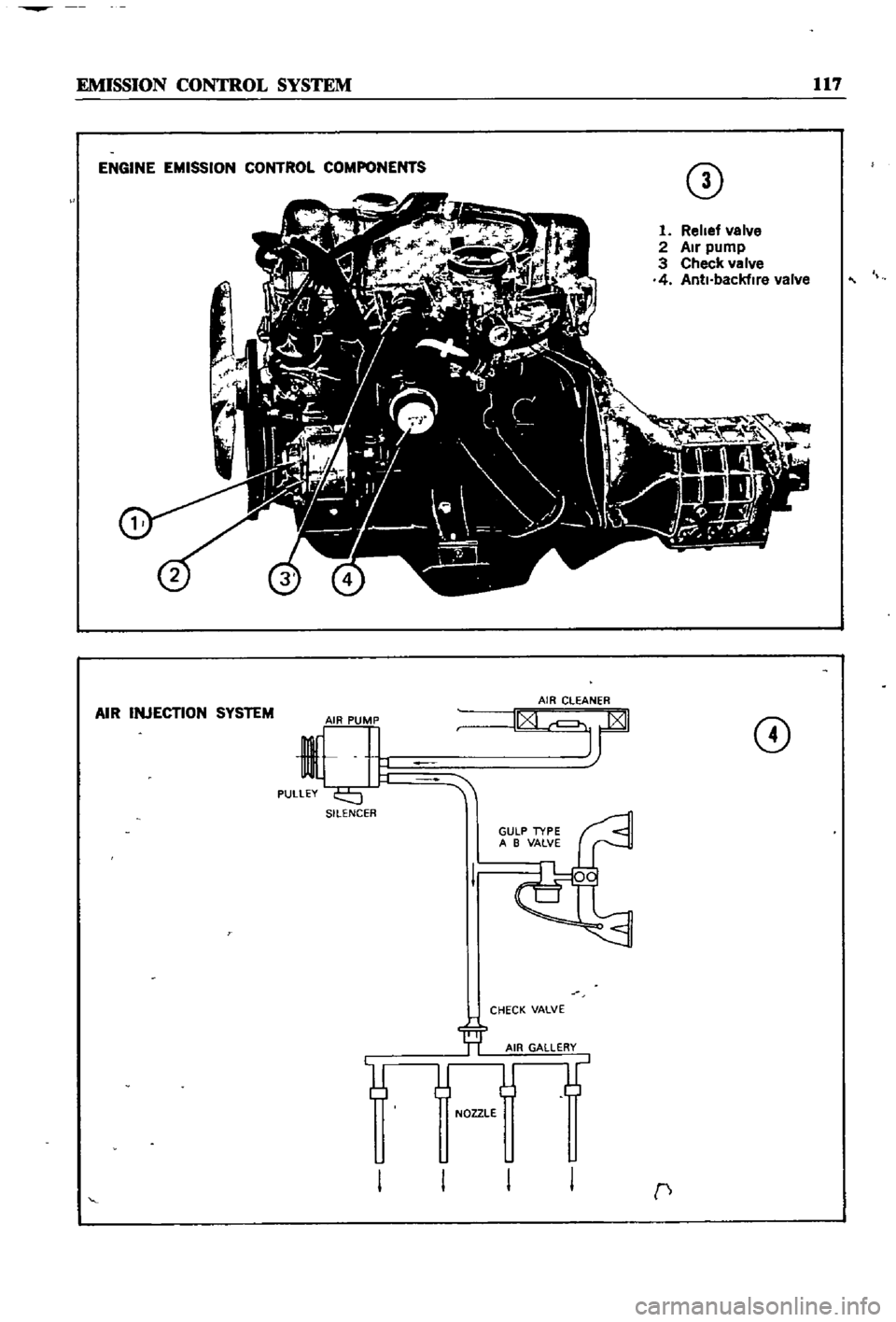
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
117
ENGINE
EMISSION
CONTROL
COMPONENTS
CD
1
Relief
valve
2
Air
pump
3
Check
valve
4
Anti
backfire
valve
AIR
INJECTION
SYSTEM
CD
SILENCER
CHECK
VALVE
NOZZLE
c
Page 127 of 252

122
CHAPTER
TEN
1
Start
the
engIne
and
bnng
It
up
to
normal
operatIng
temperature
2
Inspect
all
hoses
and
connectIons
for
leaks
and
detenoratIon
Shut
off
the
engme
Replace
any
defectIve
hoses
3
Remove
the
hose
attached
to
the
check
valve
4
VIsually
Inspect
the
posItIon
of
the
valve
plate
InsIde
the
valve
body
See
Figure
10
It
should
be
lIghtly
posItIoned
agaInst
the
valve
seat
away
from
the
aIr
dlstnbutor
manifold
5
Insert
a
probe
Into
the
valve
connectIon
on
the
check
valve
Depress
the
valve
plate
It
should
return
freely
agaInst
the
valve
seat
when
released
6
Leave
the
hose
dISconnected
and
start
the
engme
7
Slowly
Increase
engine
speed
to
1
500
rpm
Watch
for
exhaust
gas
leakage
at
the
check
valve
There
should
not
be
any
The
valve
may
flutter
or
VIbrate
at
Idle
speeds
ThIS
IS
normal
Replace
the
valve
u
defecuve
Anti
Backfire
Valve
1
Start
the
engme
and
bnng
to
operating
temperature
2
Inspect
all
hoses
and
hose
connectIons
for
leaks
and
detenoratIon
Replace
as
required
3
DIsconnect
the
hose
at
the
antI
backfire
valve
leading
to
the
Intake
manuold
Insert
a
plug
ill
the
hose
and
fasten
securely
4
Open
and
close
the
throttle
valve
rapidly
See
Figure
11
Place
a
finger
over
the
valve
outlet
to
the
m
take
manuold
If
arr
flow
IS
felt
for
one
to
two
seconds
the
valve
IS
functIonIng
properly
If
there
s
no
aIr
or
If
the
flow
is
felt
for
more
than
two
seconds
the
valve
IS
defectIve
and
must
be
replaced
5
Connect
the
alr
hose
to
the
mtake
manuold
after
remOVIng
the
plug
6
DIsconnect
the
aIr
mlet
hose
from
the
air
pump
at
the
antI
backfire
valve
If
the
engine
Idle
speed
changes
excessIvely
the
valve
is
de
fectIve
and
must
be
replaced
Air
Pump
1
Check
the
atr
InjectIon
pump
belt
tension
DeflectIon
of
the
belt
should
be
0
5
In
when
pushed
In
by
thumb
pressure
Adjust
belt
u
necessary
2
Operate
the
engme
untIl
normal
temperature
IS
reached
3
Inspect
all
hoses
hose
connectIons
and
the
arr
gallery
for
SIgnS
of
leaks
or
detenoratIon
Replace
as
required
4
DIsconnect
the
air
supply
hose
at
the
check
valve
5
Insert
the
open
pipe
end
of
a
pressure
test
gauge
adapter
Into
the
air
supply
hose
See
Fig
ure
12
Clamp
the
adapter
firmly
to
the
hose
Install
the
pressure
test
gauge
to
the
adapter
PosItIon
the
adapter
and
test
gauge
so
that
the
alr
blast
emitted
through
the
dnlled
pipe
plug
Will
be
harmlessly
dislppated
6
Install
a
tachometer
on
the
engme
WIth
the
engIne
speed
set
to
1
500
rpm
observe
the
pres
sure
readmg
AIr
pressure
should
be
0
47
m
Hg
16mm
Hg
Page 128 of 252

EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
123
7
If
the
pressure
does
not
meet
reqwrements
dISconnect
the
aIr
supply
hose
to
the
antI
backfire
valve
Clamp
a
plug
mto
the
hose
and
repeat
the
pressure
test
8
If
the
air
mJection
pump
does
not
meet
the
pressure
specIfication
It
should
be
replaced
NOTE
Repair
of
the
air
injection
pump
is
possible
but
have
the
lob
done
by
your
dealer
9
Close
the
hole
of
the
test
gauge
by
finger
With
the
engme
runnmg
at
1
500
rpm
See
Figure
13
If
a
leakIng
sound
is
heard
or
leakIng
air
is
felt
at
the
relIef
valve
the
relIef
valve
IS
defectIve
RepaIr
or
replace
as
reqUIred
ENGINE
MODIFICATIONS
SYSTEM
Testlng
and
mamtenance
of
the
sWitches
relays
and
solenOIds
comprismg
the
engine
modIficatIons
reqwres
SpecIal
knowledge
and
test
eqUIpment
If
the
mechanic
suspects
that
troubles
eXist
In
these
parts
check
With
a
dealer
Mamtenance
of
the
dIstrIbutor
breaker
points
and
tImmg
of
engines
is
covered
m
Chapter
Four
EVAPORATIVE
EMISSION
y
CONTROL
SYSTEM
f
Detailed
informatIon
on
the
fuel
tank
and
connecting
fuel
lines
IS
given
In
Chapter
Seven
EXHAUST
SYSTEM
Figures
14
next
page
15
page
125
and
16
page
126
are
exploded
VIews
of
the
exhaust
systems
Figure
14
applIes
to
the
sedan
FIgure
15
to
the
wagon
and
FIgure
16
to
the
pIck
up
The
system
in
sedans
and
wagons
consists
of
the
front
tube
pre
muffier
center
tube
rear
tube
mam
muffier
and
tail
pipe
The
pick
up
exhaust
system
mcludes
the
front
tube
muffier
and
rear
tube
Removal
Sedan
and
Wagon
1
Loosen
clamps
at
the
front
tube
center
tube
and
mam
muffier
connectIons
See
Figure
17
2
DIsconnect
front
tube
and
exhaust
manifold
flange
connection
3
Remove
units
from
vehicle