fuel tank removal DATSUN B110 1973 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 182 of 513
ENGINE
CONTROL
FUEL
EXHAUST
SYSTEM
R
H
drive
L
H
drive
KICK
DOWN
SWITCH
STRIKER
Pedal
free
play
mrn
in
2
0
0787
2
0
0787
Pedal
stroke
mm
in
48
1
890
50
1
969
Pedal
depressing
force
when
fully
open
3
8
8
4
3
3
7
3
kg
lb
Fig
FE
6
FUEL
AND
EXHAUST
PIPING
CONTENTS
EXHAUST
PIPE
AND
MUF
LER
Description
Precautions
for
removal
and
installation
FE
3
FE
4
FUEL
TANK
AND
PIPINGS
Description
Replacement
I
nspection
and
repair
FE
4
FE
4
FE
5
FE
S
FE
4
EXHAUST
PIPE
AND
MUFFLER
i
@
@
@
Fig
FE
Exhaust
system
FE
3
Page 183 of 513
CHASSIS
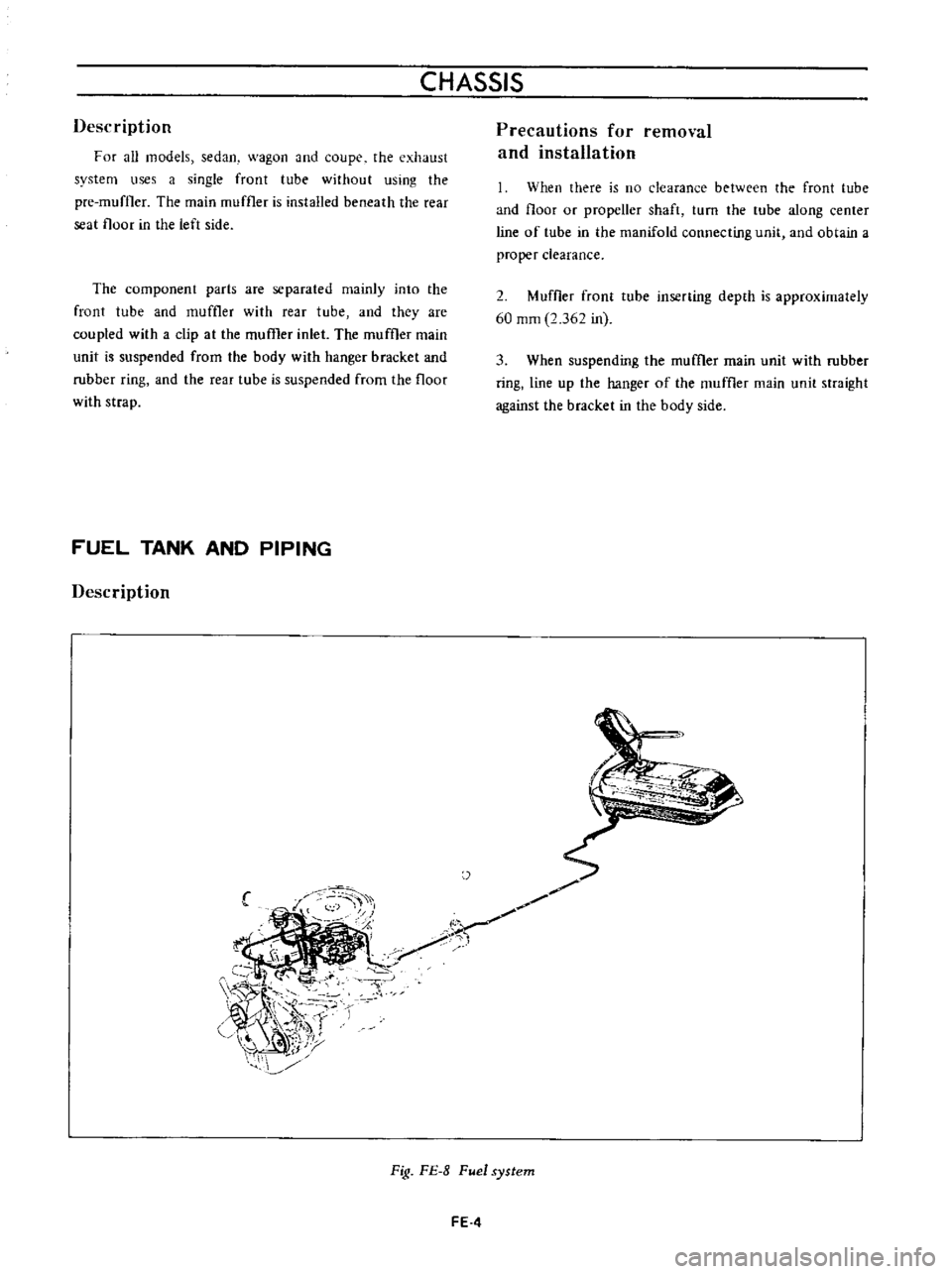
Description
F
Of
aU
models
sedan
wagon
and
coupe
the
exhaust
system
uses
a
single
front
tube
without
using
the
pre
muffler
The
main
muffler
is
installed
beneath
the
rear
seat
floor
in
the
left
side
The
component
parts
are
separated
mainly
into
the
front
tube
and
muffler
with
rear
tube
and
they
are
coupled
with
a
dip
at
the
muffler
inlet
The
rnuffler
main
unit
is
suspended
from
the
body
with
hanger
bracket
and
rubber
ring
and
the
rear
tube
is
suspended
from
the
floor
with
strap
FUEL
TANK
AND
PIPING
Description
Precautions
for
removal
and
installation
When
there
is
no
clearance
between
the
front
tube
and
floor
or
propeller
shaft
turn
the
tube
along
center
line
of
tube
in
the
manifold
connecting
unil
and
obtain
a
proper
clearance
2
Muffler
front
tube
inserting
depth
is
approximately
60
mm
2
362
in
3
When
suspending
the
muffler
rnain
unit
with
rubber
ring
line
up
the
hanger
of
the
muffler
main
unit
straight
against
the
bracket
in
the
body
side
OJ
f
r
ii
7
0
i
i
c
5t
r
t5j
n
jJ
I
L
Fig
FE
8
Fuel
system
FE
4
Page 254 of 513

BODY
ELECTRICAL
SPEEDOMETER
The
speedometer
is
equipped
with
a
total
odometer
which
records
travelled
distance
Replacement
1
When
removing
the
speedometer
remove
the
cluster
lid
first
Separate
the
combination
meter
housing
from
the
cluster
lid
after
removing
four
screws
and
remove
the
trip
recorder
reset
knob
if
any
2
Unscrew
two
screws
and
remove
the
speedometer
from
the
combination
meter
housing
3
Reinstall
a
new
speedometer
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
Fig
BE
36
Removing
combination
meter
o
Fig
BE
37
Removing
sp
edometer
FUEL
GAUGE
AND
TEMPE
RATURE
GAUGE
Description
The
fuel
gauge
consists
of
a
tank
unit
located
in
the
fuel
tank
and
fuel
meter
The
tank
unit
detects
fuel
level
with
its
float
converts
fuel
level
variation
to
a
resistance
of
slide
resistor
installed
on
the
float
base
and
thus
controls
current
flowing
to
the
fuel
meter
The
temperature
gauge
consists
of
a
thermorneter
and
thermal
transmitter
located
in
the
engine
block
The
thermal
transmitter
is
equipped
with
a
thermistor
element
which
converts
cooling
water
temperature
variation
to
a
resistance
and
thus
the
thermal
transmitter
controls
current
flowing
to
the
thermometer
The
fuel
rneter
and
thermometer
are
provided
with
bimetal
a
and
heater
coil
When
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
current
flows
to
the
heat
coil
and
the
heat
coil
is
heated
With
this
heat
the
bimetal
arm
is
bent
and
thus
the
pointer
connected
to
the
bimetal
ann
is
operated
The
characteristics
ot
both
meters
are
same
A
tolerance
may
occur
on
the
thermometer
or
fuel
gauge
due
to
source
voltage
fluctuation
The
voltage
regulator
is
used
to
supply
a
constant
voltage
so
that
the
therrnorneter
and
fuel
gauge
operate
correctly
The
voltage
regulator
is
built
in
the
thermometer
The
operating
part
of
the
regulator
consists
of
a
bimetal
arm
and
a
heater
coil
When
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
the
birnetal
arm
is
heated
and
bent
by
the
coil
opening
the
contact
Consequently
current
to
the
coil
is
interrupted
As
the
bimetal
cools
the
contact
closes
The
repetition
of
this
operation
produces
a
pulsating
voltage
of
8V
which
is
applied
to
the
ternperature
and
fuel
gauges
If
both
thermometer
and
fuel
meters
become
defective
at
the
same
time
this
may
be
attributable
to
trouble
in
the
voltage
regulator
BE
19
Page 255 of 513
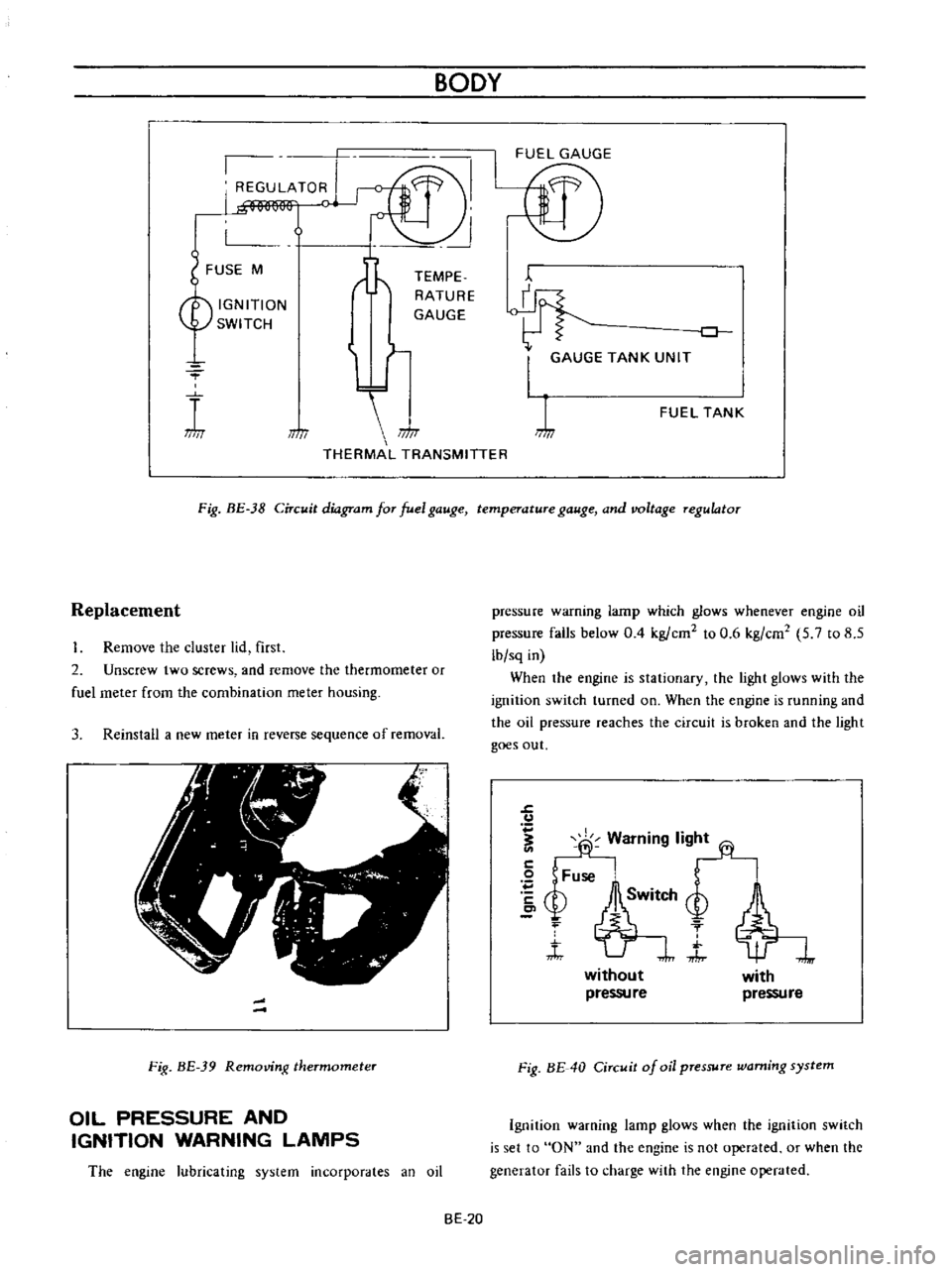
BODY
REGULATOR
FUSE
M
TEMPE
RATURE
GAUGE
IGNITION
SWITCH
Lf
I
iT
Ji
1M
THERMAL
TRANSMITTER
I
J
0
I
GAUGE
TANK
UNIT
FUEL
TANK
Fig
BE
38
Circuit
diagram
for
fuel
gauge
temperature
gauge
and
voltage
regulator
Replacement
Remove
the
cluster
lid
first
2
Unscrew
two
screws
and
remove
the
thermometer
or
fuel
meter
from
the
combination
meter
housing
3
Reinstall
a
new
meter
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
Fig
BE
39
Removing
thermometer
OIL
PRESSURE
AND
IGNITION
WARNING
LAMPS
The
engine
lubricating
system
incorporates
an
oil
pressure
warning
lamp
which
glows
whenever
engine
oil
pressure
falls
below
0
4
kg
ern
to
0
6
kg
em
5
7
to
8
5
lb
sq
in
When
the
engine
is
stationary
the
light
glows
with
the
ignition
switch
turned
on
When
the
engine
is
running
and
the
oil
pressure
reaches
the
circuit
is
broken
and
the
light
goes
out
J
u
fj
Warning
lig
2
Fuse
bSM
Q
f
t
J
without
pressu
re
with
pressure
Fig
BE
40
Circuit
of
oil
pressure
warning
system
Ignition
warning
lamp
glows
when
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
and
the
engine
is
not
operated
or
when
the
generator
fails
to
charge
with
the
engine
operated
BE
20
Page 396 of 513
FUEl
SYSTEM
FUEL
STRAINER
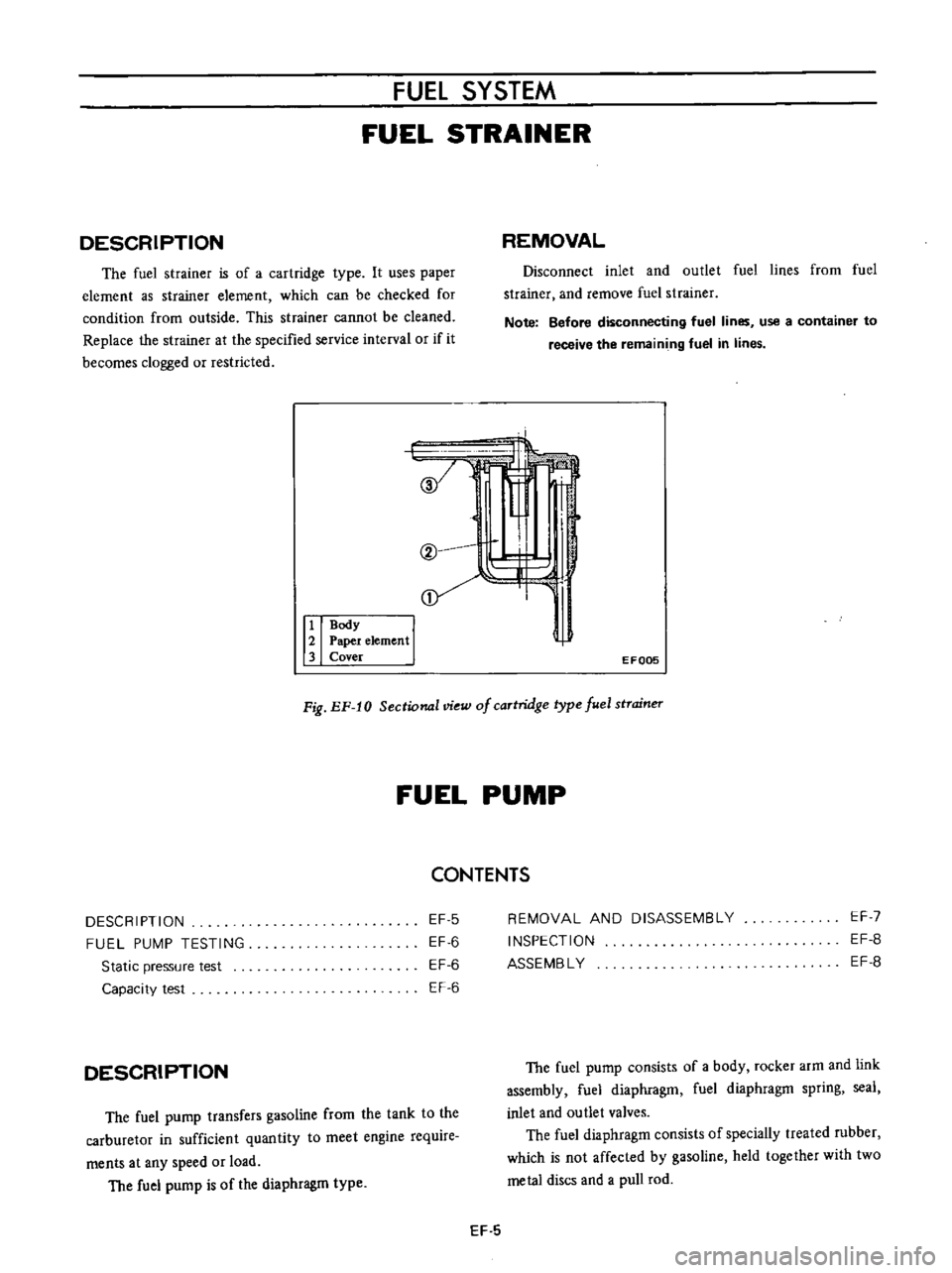
DESCRIPTION
The
fuel
strainer
is
of
a
cartridge
type
It
uses
paper
element
as
strainer
element
which
can
be
checked
for
condition
from
outside
This
strainer
cannot
be
cleaned
Replace
the
strainer
at
the
specified
service
interval
or
if
it
becomes
clogged
or
restricted
REMOVAL
Disconnect
inlet
and
outlet
fuel
lines
from
fuel
strainer
and
remove
fuel
strainer
Note
Before
disconnecting
fuel
lines
use
a
container
to
receive
the
remaining
fuel
in
lines
r
@
I
I
Il
QY
I
I
I
elementl
3
Cover
@
EF005
Fig
EF
10
Sectional
view
of
caTtridge
type
fuel
stTaineT
FUEL
PUMP
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
FUEL
PUMP
TESTING
Static
pressure
test
Capacity
test
EF
5
EF
6
EF
6
EF
6
DESCRIPTION
The
fuel
pump
transfers
gasoline
from
the
tank
to
the
carburetor
in
sufficient
quantity
to
meet
engine
require
ments
at
any
speed
or
load
The
fuel
pump
is
of
the
diaphragm
type
REMOVAL
AND
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
ASSEMBLY
EF
7
EF
B
EF
B
The
fuel
pump
consists
of
a
body
rocker
arm
and
link
assembly
fuel
diaphragm
fuel
diaphragm
spring
seal
inlet
and
outlet
valves
The
fuel
diaphragm
consists
of
specially
treated
rubber
which
is
not
affected
by
gasoline
held
together
with
two
metal
discs
and
a
pull
rod
EF
5
Page 397 of 513
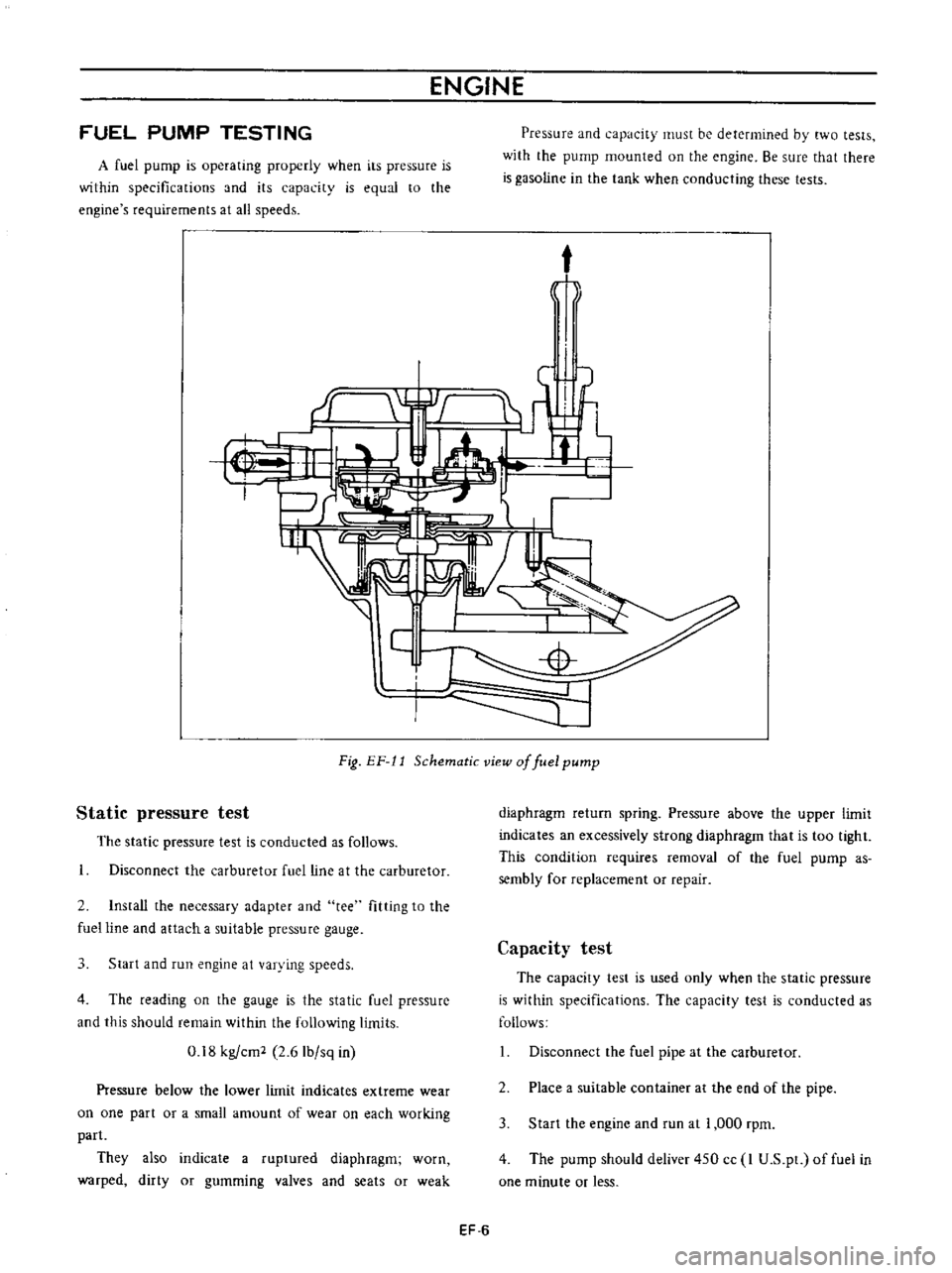
ENGINE
FUEL
PUMP
TESTING
A
fuel
pump
is
operating
properly
when
its
pressure
is
within
specifications
and
its
capacity
is
equal
to
the
engine
5
requirements
at
all
speeds
Pressure
and
cap
lcity
must
be
determined
by
two
tests
with
the
pump
mounted
on
the
engine
Be
sure
that
there
is
gasoline
in
the
tank
when
conducting
these
tests
Fig
EF
11
Schematic
view
of
fuel
pump
Static
pressure
test
The
static
pressure
test
is
conducted
as
follows
Disconnect
the
carburetor
fuel
line
at
the
carburetor
2
Install
the
necessary
adapter
and
tee
fitting
to
the
fuel
line
and
attach
a
suitable
pressure
gauge
Start
and
run
engine
at
varying
speeds
4
The
reading
on
the
gauge
is
the
static
fuel
pressure
and
this
should
remain
within
the
following
limits
0
18
kgJcm2
2
61b
sq
in
Pressure
below
the
lower
limit
indicates
extreme
wear
on
one
part
or
a
small
amount
of
wear
on
each
working
part
They
also
indicate
a
ruptured
diaphragm
worn
warped
dirty
or
gumming
valves
and
seats
or
weak
diaphragm
return
spring
Pressure
above
the
upper
limit
indicates
an
excessively
strong
diaphragm
that
is
too
tight
This
condition
requires
removal
of
the
fuel
pump
as
sembly
for
replacement
or
repair
Capacity
test
The
capacity
test
is
used
only
when
the
static
pressure
is
within
specifications
The
capacity
test
is
conducted
as
follows
1
Disconnect
the
fuel
pipe
at
the
carburetor
2
Place
a
suitable
container
at
the
end
of
the
pipe
3
Start
the
engine
and
run
at
1
000
rpm
4
The
pump
should
deliver
450
cc
I
V
S
p
of
fuel
in
one
minute
or
less
EF
6
Page 398 of 513
FUEL
SYSTEM
If
no
gasoline
or
only
a
little
flows
from
open
end
of
pipe
the
fuel
pipe
is
clogged
or
the
pump
is
malfunction
ing
Before
removing
the
pump
remove
the
gas
tank
cap
disconnect
both
inlet
and
outlet
pipes
and
blow
through
them
with
an
air
hose
to
make
sure
that
they
are
clear
This
will
eliminate
possible
clogged
gas
strainer
in
the
fuel
tank
Reconnect
the
pipes
to
the
pump
and
retest
flow
REMOVAL
AND
DISASSEMBLY
Remove
the
fuel
pump
assembly
by
unscrewing
two
mounting
nuts
and
disassemble
in
the
following
order
1
Separate
the
upper
body
and
the
lower
body
by
unscrewing
the
body
set
screws
2
Take
off
the
cap
and
the
cap
gasket
by
removing
the
cap
screw
3
Unscrew
the
elbow
and
the
connector
4
Take
off
the
valve
retainer
by
unscrewing
two
valve
retainer
screws
Two
valves
are
easily
removed
@
@
GS
5
To
remove
the
diaphragm
diaphragm
spring
lower
body
seal
washer
and
lower
body
seal
from
the
lower
body
press
down
the
diaphragm
counter
to
the
force
of
the
diaphragm
spring
and
while
doing
this
cant
the
diaphragm
so
that
the
rectangular
part
in
the
lower
end
of
the
pull
rod
is
unhooked
from
the
rocker
arm
link
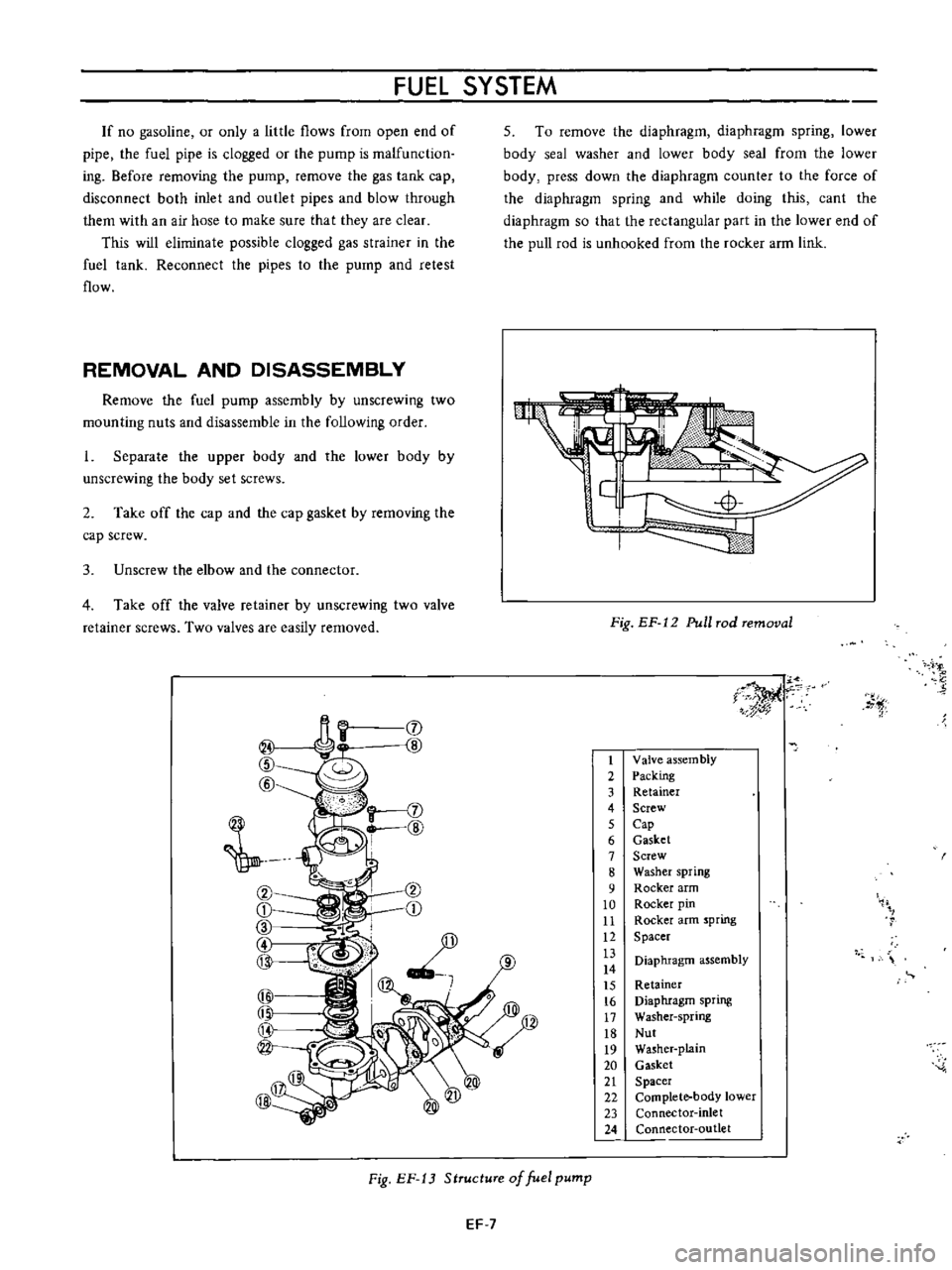
Fig
EF
jJ
StructuTe
of
fuel
pump
EF
7
j
i
I
of
4
Fig
EF
12
Pull
Tad
Temoval
r1
r
f
i
t
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
B
9
10
tt
t2
t3
t4
15
t6
t7
tB
t9
20
2t
22
23
24
Valve
assem
bly
Packing
Retainer
Screw
Cap
Gasket
Screw
Washer
spring
Rocker
arm
Rocker
pin
Rocker
arm
spring
Spacer
Diaphragm
assembly
Retainer
Diaphragm
spring
Washer
spring
Nut
Washer
plain
Gasket
Spacer
Complete
body
lower
Connector
inlet
Connector
outlet