Light DODGE DURANGO 1998 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: DURANGO, Model: DODGE DURANGO 1998 1.GPages: 193, PDF Size: 5.65 MB
Page 7 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine OIL PAN
DESCRIPTION
The engine oil pan is made of laminated steel and
has a single plane sealing surface. The sandwich
style oil pan gasket has an integrated windage tray
and steel carrier. The sealing area of the gasket is
molded with rubber and is designed to be reused as
long as the gasket is not cut, torn or ripped.
STRUCTURAL DUST COVER
DESCRIPTION
The structural dust cover is made of die cast alu-
minum and joins the lower half of the transmission
bell housing to the engine bedplate.
OPERATION
The structural cover provides additional power-
train stiffness and reduces noise and vibration.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold is made of a composite mate-
rial and features long runners which maximizes low
end torque. The intake manifold uses single plane
sealing which consist of eight individual press in
place port gaskets to prevent leaks. Eight studs and
two bolts are used to fasten the intake to the head.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The exhaust manifolds are log style with a pat-
ented flow enhancing design to maximize perfor-mance. The exhaust manifolds are made of high
silicon molybdenum cast iron. A perforated core
graphite exhaust manifold gasket is used to improve
sealing to the cylinder head. The exhaust manifolds
are covered by a three layer laminated heat shield
for thermal protection and noise reduction. The heat
shields are fastened with a torque prevailing nut
that is backed off slightly to allow for the thermal
expansion of the exhaust manifold.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐINTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
Refer to the Service DiagnosisÐPerformance chart
and the Service DiagnosisÐMechanical chart for pos-
sible causes and corrections of malfunctions. Refer to
Group 14, Fuel System for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test.
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test.
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis.
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis.
DN4.7L ENGINE 9 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 8 of 193
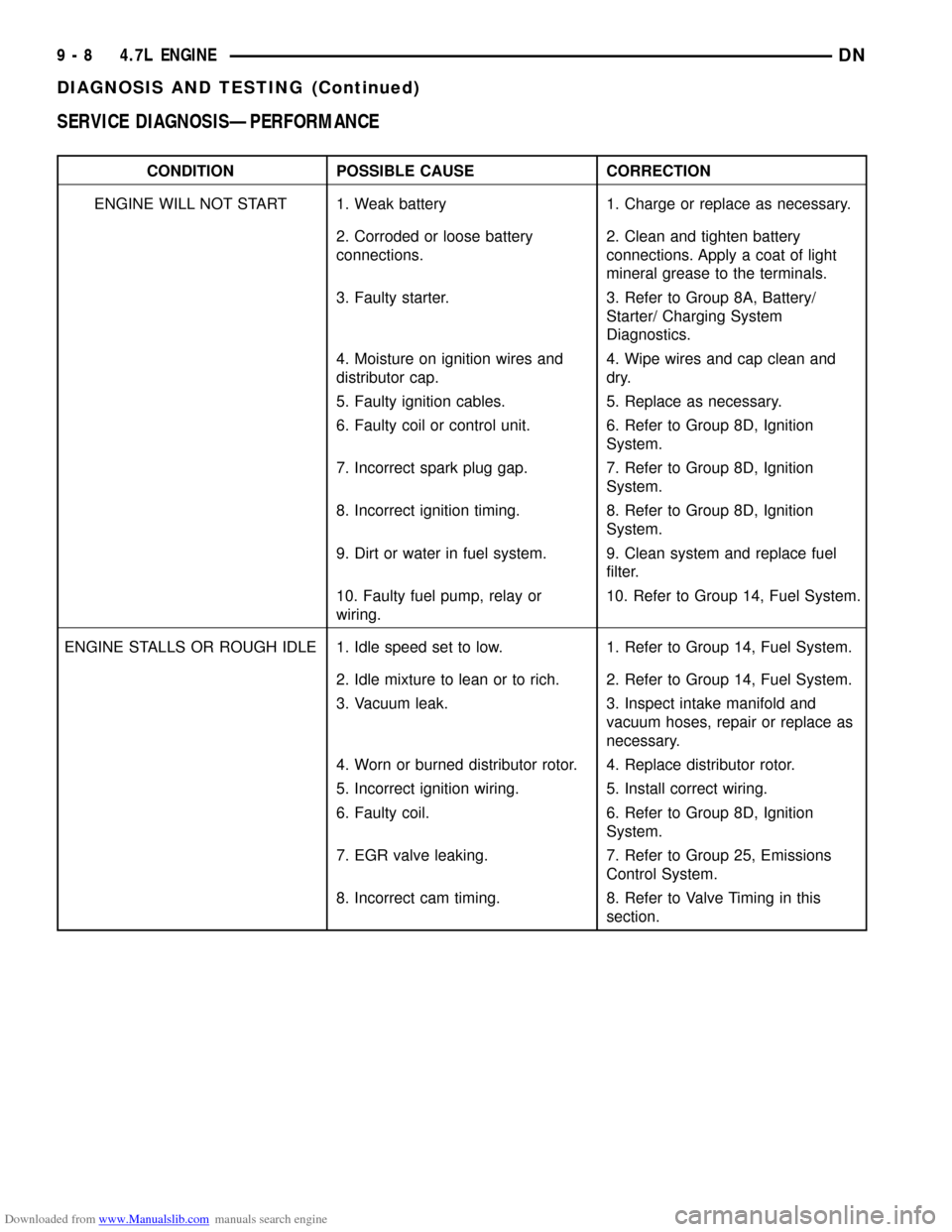
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. Refer to Group 8A, Battery/
Starter/ Charging System
Diagnostics.
4. Moisture on ignition wires and
distributor cap.4. Wipe wires and cap clean and
dry.
5. Faulty ignition cables. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Faulty coil or control unit. 6. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition
System.
7. Incorrect spark plug gap. 7. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition
System.
8. Incorrect ignition timing. 8. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition
System.
9. Dirt or water in fuel system. 9. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
10. Faulty fuel pump, relay or
wiring.10. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Idle speed set to low. 1. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System.
2. Idle mixture to lean or to rich. 2. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System.
3. Vacuum leak. 3. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
4. Worn or burned distributor rotor. 4. Replace distributor rotor.
5. Incorrect ignition wiring. 5. Install correct wiring.
6. Faulty coil. 6. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition
System.
7. EGR valve leaking. 7. Refer to Group 25, Emissions
Control System.
8. Incorrect cam timing. 8. Refer to Valve Timing in this
section.
9 - 8 4.7L ENGINEDN
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 13 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuck or broken piston rings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
ENGINE OIL LEAK INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(4)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method.
Air Leak Detection Test Method
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.(4) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(5) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply
and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
DN4.7L ENGINE 9 - 13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 14 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
REAR SEAL AREA LEAKSÐINSPECTION
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs, oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces. See Group 9, Engines, for
proper repair procedures of these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in the section, Inspection (Engine oil
Leaks in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible thecrankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled. Refer to the service DiagnosisÐMechani-
cal, under the Oil Leak row, for components
inspections on possible causes and corrections.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, Refer to Group
9, EnginesÐCrankshaft Rear Oil Seals, for proper
replacement procedures.
HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER NOISE
DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
9 - 14 4.7L ENGINEDN
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 15 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit (Fig. 3) and
install gauge assembly C-3292.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
(3) Oil Pressure:
²Curb IdleÐ25 Kpa (4 psi) minimum
²3000 rpmÐ170 - 550 KPa (25 - 80 psi)
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle, shut off engine.
Check for a clogged oil pick-up screen or a pressure
relief valve stuck open.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS
There are several places where form-in-place gas-
kets are used on the engine.DO NOT use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Care
must be taken when applying form-in-place gaskets.
Bead size, continuity and location are of great impor-
tance. Too thin a bead can result in leakage while too
much can result in spill-over. A continuous bead of
the proper width is essential to obtain a leak-free
joint.
Two types of form-in-place gasket materials are
used in the engine area (Mopar Silicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant and Mopar Gasket Maker). Eachhave different properties and cannot be used inter-
changeably.
MOPAR SILICONE RUBBER ADHESIVE SEALANT
Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant, normally
black in color, is available in 3 ounce tubes. Moisture
in the air causes the sealant material to cure. This
material is normally used on flexible metal flanges.
It has a shelf life of a year and will not properly cure
if over aged. Always inspect the package for the expi-
ration date before use.
MOPAR GASKET MAKER
Mopar Gasket Maker, normally red in color, is
available in 6 cc tubes. This anaerobic type gasket
material cures in the absence of air when squeezed
between smooth machined metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. DO NOT use
on flexible metal flanges.
SURFACE PREPARATION
Parts assembled with form-in-place gaskets may be
disassembled without unusual effort. In some
instances, it may be necessary to lightly tap the part
with a mallet or other suitable tool to break the seal
between the mating surfaces. A flat gasket scraper
may also be lightly tapped into the joint but care
must be taken not to damage the mating surfaces.
Scrape or wire brush all gasket surfaces to remove
all loose material. Inspect stamped parts to ensure
gasket rails are flat. Flatten rails with a hammer on
a flat plate, if required. Gasket surfaces must be free
of oil and dirt. Make sure the old gasket material is
removed from blind attaching holes.
GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care.
Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant should be
applied in a continuous bead approximately 3 mm
(0.12 inch) in diameter. All mounting holes must be
circled. For corner sealing,a3or6mm(1/8 or 1/4
inch) drop is placed in the center of the gasket con-
tact area. Uncured sealant may be removed with a
shop towel. Components should be torqued in place
while the sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10
minutes). The use of a locating dowel is recom-
mended during assembly to prevent smearing the
material off location.
Mopar Gasket Maker should be applied sparingly
to one gasket surface. The sealant diameter should
be 1.00 mm (0.04 inch) or less. Be certain the mate-
rial surrounds each mounting hole. Excess material
can easily be wiped off. Components should be
torqued in place within 15 minutes. The use of a
Fig. 3 Oil Pressure Sending Unit
1 ± BELT
2 ± OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
3 ± OIL FILTER
4 ± ELEC. CONNECTOR
DN4.7L ENGINE 9 - 15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 17 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
pressure loss or oil foaming can result.
Inspect engine oil level approximately every 800
kilometers (500 miles). Unless the engine has exhib-
ited loss of oil pressure, run the engine for about five
minutes before checking oil level. Checking engine oil
level on a cold engine is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in Maintenance Schedules.
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug if
damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil described in this sec-
tion.
(8) Install oil fill cap.
(9) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(10) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
ENGINE OIL FILTER CHANGE
FILTER SPECIFICATION
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-
flow, disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Cor-
poration recommends a Mopar or equivalent oil filter
be used.OIL FILTER REMOVAL
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise (Fig. 7) to
remove it from the cylinder block oil filter boss.
(4) When filter separates from cylinder block oil
filter boss, tip gasket end upward to minimize oil
spill. Remove filter from vehicle.
(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface of oil and grime.
OIL FILTER INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 8) hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.
(3) Add oil, verify crankcase oil level and start
engine. Inspect for oil leaks.
USED ENGINE OIL DISPOSAL
Care should be exercised when disposing used
engine oil after it has been drained from a vehicle
engine. Refer to the WARNING at beginning of this
section.REPAIR DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Fig. 7 Oil FilterÐ4.7L Engine
1 ± ENGINE OIL FILTER
DN4.7L ENGINE 9 - 17
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 18 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
CYLINDER BOREÐHONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1) Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round, as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60
strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing
oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, available from
major oil distributors.
CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.The hone marks should INTERSECT at 50É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 9).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
HYDROSTATIC LOCK
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(refer to Group 14, Fuel System).
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the plugs from the
engine.
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
Fig. 8 Oil Filter Sealing SurfaceÐTypical
1 ± SEALING SURFACE
2 ± RUBBER GASKET
3 ± OIL FILTER
Fig. 9 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 ± CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 ± INTERSECT ANGLE
9 - 18 4.7L ENGINEDN
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 19 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine (6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (i.e. coolant,
fuel, oil, etc.).
(7) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt engine oil into the cylinders to lubricate
the walls. This will prevent damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil.
(15) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
VALVE SERVICE
REFACING
NOTE: Valve seats that are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise the cylinder head
must be replaced.
NOTE: When refacing valves and valve seats, it is
important that the correct size valve guide pilot be
used for reseating stones. A true and complete sur-
face must be obtained.
(1) Using a suitable dial indicator measure the
center of the valve seat Total run out must not
exceed 0.051 mm (0.002 in).
(2) Apply a small amount of Prussian blue to the
valve seat, insert the valve into the cylinder head,
while applying light pressure on the valve rotate the
valve. Remove the valve and examine the valve face.
If the blue is transferred below the top edge of the
valve face, lower the valve seat using a 15 degree
stone. If the blue is transferred to the bottom edge of
the valve face, raise the valve seat using a 65 degree
stone.
(3) When the seat is properly positioned the width
of the intake seat must be 1.75 ± 2.36 mm (0.0689 ±
0.0928 in.) and the exhaust seat must be 1.71 ± 2.32
mm (0.0673 ± 0.0911 in.).
(4) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat. The installed height for
both intake and exhaust valve springs must not
exceed 41.44 mm (1.6315 in.).
(5) The valve seat and valve face must maintain a
face angle of 44.5 ± 45 degrees angle.
ENGINE TIMINGÐVERIFICATION
CAUTION: The 4.7L is a non free-wheeling design
engine. Therefore, correct engine timing is critical.
NOTE: Components referred to as left hand or right
hand are as viewed from the drivers position inside
the vehicle.
NOTE: The blue link plates on the chains and the
dots on the camshaft drive sprockets may not line
up during the timing verification procedure. The
blue link plates are lined up with the sprocket dots
only when re-timing the complete timing drive.
Once the timing drive is rotated blue link-to-dot
alignment is no longer valid.
Engine base timing can be verified by the following
procedure:
(1) Remove the cylinder head covers. Refer to the
procedure in this section.
(2) Using a mirror, locate the TDC arrow on the
front cover (Fig. 11). Rotate the crankshaft until the
mark on the crankshaft damper is aligned with the
TDC arrow on the front cover. The engine is now at
TDC.
Fig. 10 Valve Assembly Configuration
1 ± VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 ± RETAINER
3 ± VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 ± INTAKE VALVE
5 ± EXHAUST VALVE
6 ± VALVE SPRING
DN4.7L ENGINE 9 - 19
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 22 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine TIMING CHAINÐMEASURING WEAR
NOTE: This procedure must be performed with the
timing chain cover removed.
(1) Remove the timing chain cover. Refer to Timing
Chain Cover in this section for procedure.
(2) To determine if the secondary timing chains
are worn, rotate the engine clockwise until maximum
tensioner piston extension is obtained. Measure the
distance between the secondary timing chain ten-
sioner housing and the step ledge on the piston (Fig.
17). The measurement at point (A) must be less than
15mm (.5906 inches).
(3) If the measurement exceeds the specification
the secondary timing chains are worn and require
replacement. Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets in
this section for procedure.
PISTONSÐFITTING
BORE GAGE METHOD
(1) To correctly select the proper size piston, a cyl-
inder bore gauge, capable of reading in 0.003 mm
(.0001 in.) INCREMENTS is required. If a bore
gauge is not available, do not use an inside microme-
ter.
(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at a point 49.5 mm (1-15/16 inches) below top of
bore. Start perpendicular (across or at 90 degrees) to
the axis of the crankshaft at point A and then takean additional bore reading 90 degrees to that at point
B (Fig. 19).
(3) The coated pistons will be serviced with the
piston pin and connecting rod pre-assembled. Tin
coated pistons should not be used as replacements for
coated pistons.
(4) The coating material is applied to the piston
after the final piston machining process. Measuring
the outside diameter of a coated piston will not pro-
vide accurate results (Fig. 18). Therefore measuring
the inside diameter of the cylinder bore with a dial
Bore Gauge isMANDATORY. To correctly select the
proper size piston, a cylinder bore gauge capable of
reading in 0.003 mm (.0001 in.) increments is
required.
(5) Piston installation into the cylinder bore
requires slightly more pressure than that required
for non-coated pistons. The bonded coating on the
piston will give the appearance of a line-to-line fit
with the cylinder bore.
Fig. 14 Camshaft Dowel To Sprocket Alignment
1 ± ADJUSTABLE PLIERS
2 ± CAMSHAFT DOWEL
Fig. 15 Camshaft Sprocket InstallationÐLeft
Cylinder Head
1 ± TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
3 ± LEFT CYLINDER HEAD
4 ± SPECIAL TOOL 6958 SPANNER WITH ADAPTER PINS 8346
9 - 22 4.7L ENGINEDN
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 32 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ²Throttle Position (TPS) Switch
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Engine Oil Pressure Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs
(31) Disconnect the vacuum lines at the throttle
body and intake manifold.
(32) Release fuel rail pressure then disconnect the
fuel supply quick connect fitting at the fuel rail.
Refer toFUEL SYSTEM for procedure.
(33) Remove power steering pump and position out
of the way.
(34) Install Special Tools 8400 Lifting Studs, into
the cylinder heads.
(35) Install Engine Lifting Fixture Special Tool
8347 (Fig. 47) following these steps.
²Holding the lifting fixture at a slight angle, slide
the large bore in the front plate over the hex portion
of the lifting stud.
²Position the two remaining fixture arms onto
the two Special Tools 8400 Lifting Studs, in the cyl-
inder heads.
²Pull foward and upward on the lifting fixture so
that the lifting stud rest in the slotted area below the
large bore.²Secure the lifting fixture to the three studs
using three 7/16 ± 14 N/C locknuts.
²Make sure the lifting loop in the lifting fixture is
in the last hole (closest to the throttle body) to min-
imize the angle of engine during removal.
(36) Disconnect body ground strap at the right side
cowl (Fig. 48).
(37) Disconnect body ground strap at the left side
cowl (Fig. 49).
NOTE: It will be necessary to support the transmis-
sion in order to remove the engine.
(38) Position a suitable jack under the transmis-
sion.
(39) Remove engine from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position engine in the vehicle.
Position both the left and right side engine mount
brackets and install the through bolts and nuts.
Tighten nuts to4X2 vehicles95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
4X4 vehicles102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 41 Engine Mount Through Bolt and Nut
Removal / InstallationÐ4X4 Vehicles
1 ± ENGINE MOUNT BRACKET (2)
2 ± THROUGH BOLT (2)
3 ± LOCKNUT AND WASHER (2)
4 ± ENGINE ISOLATOR TO ENGINE MOUNT BRACKET STUD (2)
5 ± LOCKNUT (2)
Fig. 42 Axle Isolator Bracket Removal /
InstallationÐ4X4 Vehicles With Automatic
Transmission
1 ± TRANSMISSION
2 ± AXLE ISOLATOR BRACKET
3 ± FRONT AXLE 4X4 VEHICLES
4 ± BOLTS
5 ± ENGINE
9 - 32 4.7L ENGINEDN
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)