torque specification DODGE DURANGO 1999 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DURANGO, Model: DODGE DURANGO 1999 1.GPages: 193, PDF Size: 5.65 MB
Page 92 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Scrape or wire brush all gasket surfaces to remove
all loose material. Inspect stamped parts to ensure
gasket rails are flat. Flatten rails with a hammer on
a flat plate, if required. Gasket surfaces must be free
of oil and dirt. Make sure the old gasket material is
removed from blind attaching holes.
GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care.
Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant should be
applied in a continuous bead approximately 3 mm
(0.12 inch) in diameter. All mounting holes must be
circled. For corner sealing,a3or6mm(1/8 or 1/4
inch) drop is placed in the center of the gasket con-
tact area. Uncured sealant may be removed with a
shop towel. Components should be torqued in place
while the sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10
minutes). The use of a locating dowel is recom-
mended during assembly to prevent smearing the
material off location.
Mopar Gasket Maker should be applied sparingly
to one gasket surface. The sealant diameter should
be 1.00 mm (0.04 inch) or less. Be certain the mate-
rial surrounds each mounting hole. Excess material
can easily be wiped off. Components should be
torqued in place within 15 minutes. The use of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing the material off location.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and the lowest emission levels. If vehicle is not oper-
ating to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis
outlined in this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Electri-
cal Group 8B, Cold Cranking Test.
(2) Check intake manifold bolt torque.
(3) Perform cylinder compression test. Refer to
Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in the Engine
Diagnosis area of this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Electrical Group 8D.
Tighten to specifications.
(5) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Electrical Group 8D, Spark Plug Cables.
(6) Inspect the primary wires. Test coil output volt-
age and primary resistance. Replace parts as neces-
sary. Refer to Electrical Group 8D, for specifications.
(7) Test fuel pump for pressure. Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System Specifications.
(8) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Lubrication and Maintenance, Group 0.(9) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(10) Road test vehicle as a final test.
ENGINE OIL
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
In gasoline engines, use an engine oil that is API
Service Grade Certified (Fig. 11). Standard engine oil
identification notations have been adopted to aid in
the proper selection of engine oil. The identifying
notations are located on the label of engine oil plastic
bottles and the top of engine oil cans. MOPAR only
provides engine oil that conforms to this certification.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. SAE 10W-30 specifies a multiple
viscosity engine oil. These are specified with a dual
SAE viscosity grade which indicates the cold-to-hot
temperature viscosity range. When choosing an
engine oil, consider the range of temperatures the
vehicle will be operated in before the next oil change.
Select an engine oil that is best suited to your area's
Fig. 11 Engine Oil Container Standard Notations
9 - 92 5.2L ENGINEDN
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 97 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine (3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
inch). The width of the exhaust seats should be
1.524-2.032 mm (0.060-0.080 inch).
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 inch. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 inch mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 22). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN STRETCH
NOTE: To access timing chain Refer to Timing
Chain Cover in Removal and Installation Section.
(1) Place a scale next to the timing chain so that
any movement of the chain may be measured.
(2) Place a torque wrench and socket over cam-
shaft sprocket attaching bolt. Apply torque in the
direction of crankshaft rotation to take up slack; 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque with cylinder head installed
or 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque with cylinder head
removed. With a torque applied to the camshaft
Fig. 20 Intake and Exhaust Valves
1 ± MARGIN
2 ± VALVE SPRING RETAINER LOCK GROOVE
3 ± STEM
4±FACE
Fig. 21 Refacing Valve Seats
1±STONE
2 ± PILOT
3 ± VALVE SEAT
4 ± SHROUD
Fig. 22 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
Length
1 ± TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± VALVE SPRING TESTER
DN5.2L ENGINE 9 - 97
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 108 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine (15) Remove intake manifold and throttle body as
an assembly. Discard the flange side gaskets and the
front and rear cross-over gaskets.
(16) Remove exhaust manifolds.
(17) Remove rocker arm assemblies and push rods.
Identify to ensure installation in original locations.
(18) Remove the head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads. Discard the cylin-
der head gasket.
(19) Remove spark plugs.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the new cylinder head gaskets onto
the cylinder block.
(2) Position the cylinder heads onto head gaskets
and cylinder block.
(3) Starting at top center, tighten all cylinder head
bolts, in sequence, to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig.
45). Repeat procedure, tighten all cylinder head bolts
to 143 N´m (105 ft. lbs.) torque. Repeat procedure to
confirm that all bolts are at 143 N´m (105 ft. lbs.)
torque.
CAUTION: When tightening the rocker arm bolts,
make sure the piston in that cylinder is NOT at
TDC. Contact between the valves and piston could
occur.
(4) Install push rods and rocker arm assemblies in
their original position. Tighten the bolts to 28 N´m
(21 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install the intake manifold and throttle body
assembly.
(6) Install exhaust manifolds. Tighten the bolts
and nuts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Adjust spark plugs to specifications. Refer to
IGNITION SYSTEM. Install the plugs and tighten to
41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install coil wires.
(9) Connect heat indicator sending unit wire.(10) Connect the heater hoses and bypass hose.
(11) Install distributor cap and wires.
(12) Connect the accelerator linkage and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(13) Install the fuel supply line.
(14) Install the generator and drive belt. Tighten
generator mounting bolt to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(15) Install the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Tighten the bolts.
(16) Place the cylinder head cover gaskets in posi-
tion and install cylinder head covers. Tighten the
bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(17) Install closed crankcase ventilation system.
(18) Connect the evaporation control system.
(19) Install the air cleaner assembly and air inlet
hose.
(20) Install the heat shields. Tighten the bolts to
41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(21) Fill cooling system.
(22) Connect the battery negative cable.
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head. Refer to Cylinder
Head in this section for correct procedure.
(2) Compress valve springs using Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD- 998772A and adapter 6716A.
(3) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(4) Before removing valves, remove any burrs from
valve stem lock grooves to prevent damage to the
valve guides. Identify valves to ensure installation in
original location.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean valves thoroughly. Discard burned,
warped and cracked valves.
(2) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(3) Measure valve stems for wear. If wear exceeds
0.051 mm (0.002 inch), replace the valve.
(4) Coat valve stems with lubrication oil and insert
them in cylinder head.
(5) If valves or seats are reground, check valve
stem height. If valve is too long, replace cylinder
head.
(6) Install new seals on all valve guides. Install
valve springs and valve retainers.
(7) Compress valve springs with Valve Spring
Compressor Tool MD-998772A and adapter 6716A,
install locks and release tool. If valves and/or seats
are ground, measure the installed height of springs.
Make sure the measurement is taken from bottom ofFig. 45 Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening Sequence
9 - 108 5.2L ENGINEDN
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 124 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine (2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using a
dial indicator. Total runout should not exceed 0.051
mm (0.002 inch) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seat LIGHTLY with Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to the top edge of valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15É stone. If the blue is transferred to bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 60É stone.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.016-1.524 mm (0.040-0.060
inch). The width of the exhaust seats should be
1.524-2.032 mm (0.060-0.080 inch).
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 inch. Turn table of
Universals Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is
in line with the 1-5/16 inch mark on the threaded
stud. Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 80).
Place spring over stud on the table and lift compress-
ing lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench
until ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench
at this instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will
give the spring load at test length. Fractional mea-
surements are indicated on the table for finer adjust-
ments. Refer to specifications to obtain specified
height and allowable tensions. Discard the springs
that do not meet specifications.
OIL PUMP
DISASSEMBLE
(1) Remove the relief valve as follows:
(a) Remove cotter pin. Drill a 3.175 mm (1/8
inch) hole into the relief valve retainer cap and
insert a self-threading sheet metal screw.
(b) Clamp screw into a vise and while support-
ing oil pump, remove cap by tapping pump body
using a soft hammer. Discard retainer cap and
remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 81).
(2) Remove oil pump cover (Fig. 82).
(3) Remove pump outer rotor and inner rotor with
shaft (Fig. 82).
(4) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear.
ASSEMBLE
(1) Install pump rotors and shaft, using new parts
as required.
(2) Position the oil pump cover onto the pump
body. Tighten cover bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Install the relief valve and spring. Insert the
cotter pin.
(4) Tap on a new retainer cap.
(5) Prime oil pump before installation by filling
rotor cavity with engine oil.
Fig. 80 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
Length
1 ± TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± VALVE SPRING TESTER
Fig. 81 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
1 ± OIL PUMP ASSEMBLY
2 ± COTTER PIN
3 ± RELIEF VALVE
4 ± RETAINER CAP
5 ± SPRING
DN5.2L ENGINE 9 - 123
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 133 of 193
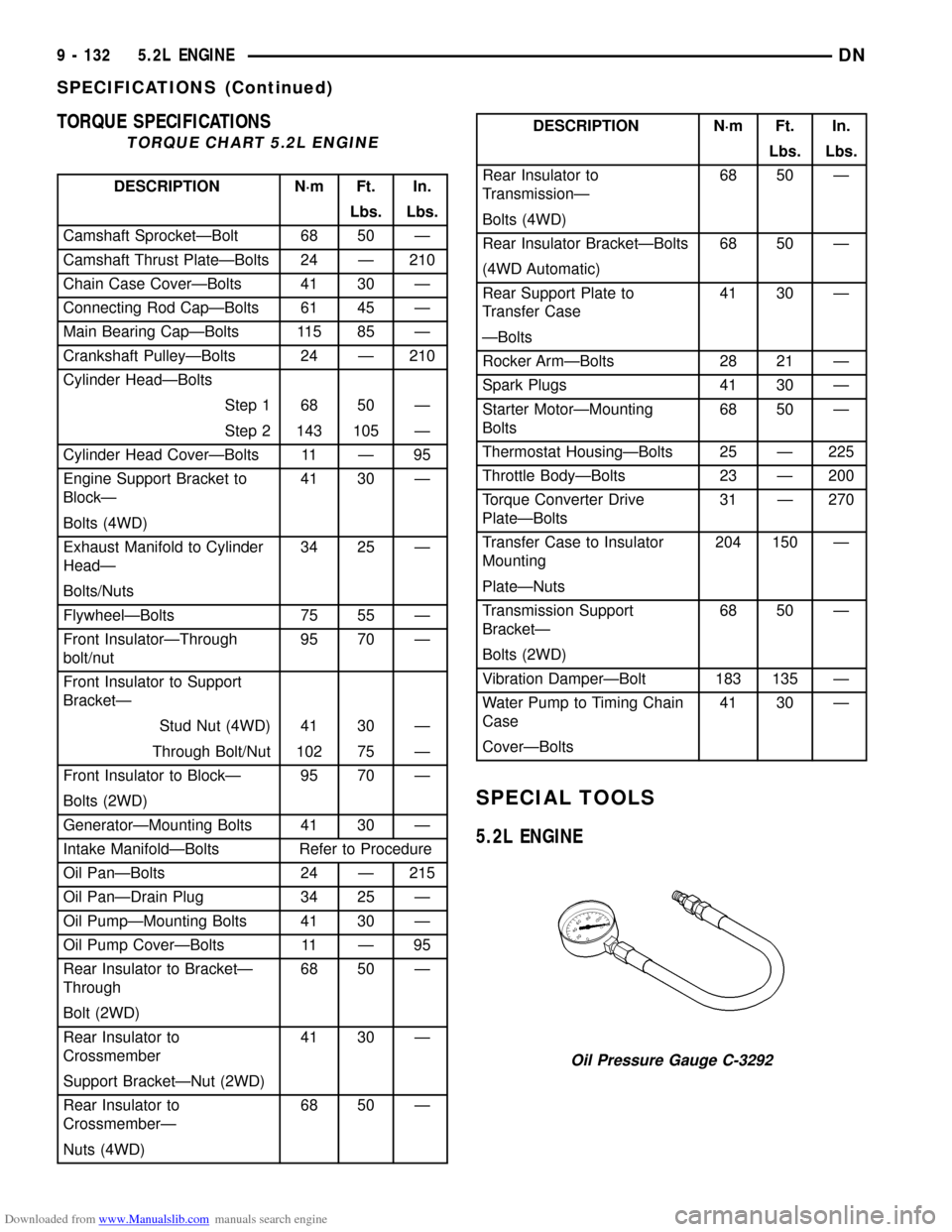
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART 5.2L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 68 50 Ð
Camshaft Thrust PlateÐBolts 24 Ð 210
Chain Case CoverÐBolts 41 30 Ð
Connecting Rod CapÐBolts 61 45 Ð
Main Bearing CapÐBolts 115 85 Ð
Crankshaft PulleyÐBolts 24 Ð 210
Cylinder HeadÐBolts
Step 1 68 50 Ð
Step 2 143 105 Ð
Cylinder Head CoverÐBolts 11 Ð 95
Engine Support Bracket to
BlockÐ41 30 Ð
Bolts (4WD)
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder
HeadÐ34 25 Ð
Bolts/Nuts
FlywheelÐBolts 75 55 Ð
Front InsulatorÐThrough
bolt/nut95 70 Ð
Front Insulator to Support
BracketÐ
Stud Nut (4WD) 41 30 Ð
Through Bolt/Nut 102 75 Ð
Front Insulator to BlockÐ 95 70 Ð
Bolts (2WD)
GeneratorÐMounting Bolts 41 30 Ð
Intake ManifoldÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Oil PanÐBolts 24 Ð 215
Oil PanÐDrain Plug 34 25 Ð
Oil PumpÐMounting Bolts 41 30 Ð
Oil Pump CoverÐBolts 11 Ð 95
Rear Insulator to BracketÐ
Through68 50 Ð
Bolt (2WD)
Rear Insulator to
Crossmember41 30 Ð
Support BracketÐNut (2WD)
Rear Insulator to
CrossmemberÐ68 50 Ð
Nuts (4WD)
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Rear Insulator to
TransmissionÐ68 50 Ð
Bolts (4WD)
Rear Insulator BracketÐBolts 68 50 Ð
(4WD Automatic)
Rear Support Plate to
Transfer Case41 30 Ð
ÐBolts
Rocker ArmÐBolts 28 21 Ð
Spark Plugs 41 30 Ð
Starter MotorÐMounting
Bolts68 50 Ð
Thermostat HousingÐBolts 25 Ð 225
Throttle BodyÐBolts 23 Ð 200
Torque Converter Drive
PlateÐBolts31 Ð 270
Transfer Case to Insulator
Mounting204 150 Ð
PlateÐNuts
Transmission Support
BracketÐ68 50 Ð
Bolts (2WD)
Vibration DamperÐBolt 183 135 Ð
Water Pump to Timing Chain
Case41 30 Ð
CoverÐBolts
SPECIAL TOOLS
5.2L ENGINE
Oil Pressure Gauge C-3292
9 - 132 5.2L ENGINEDN
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 145 of 193
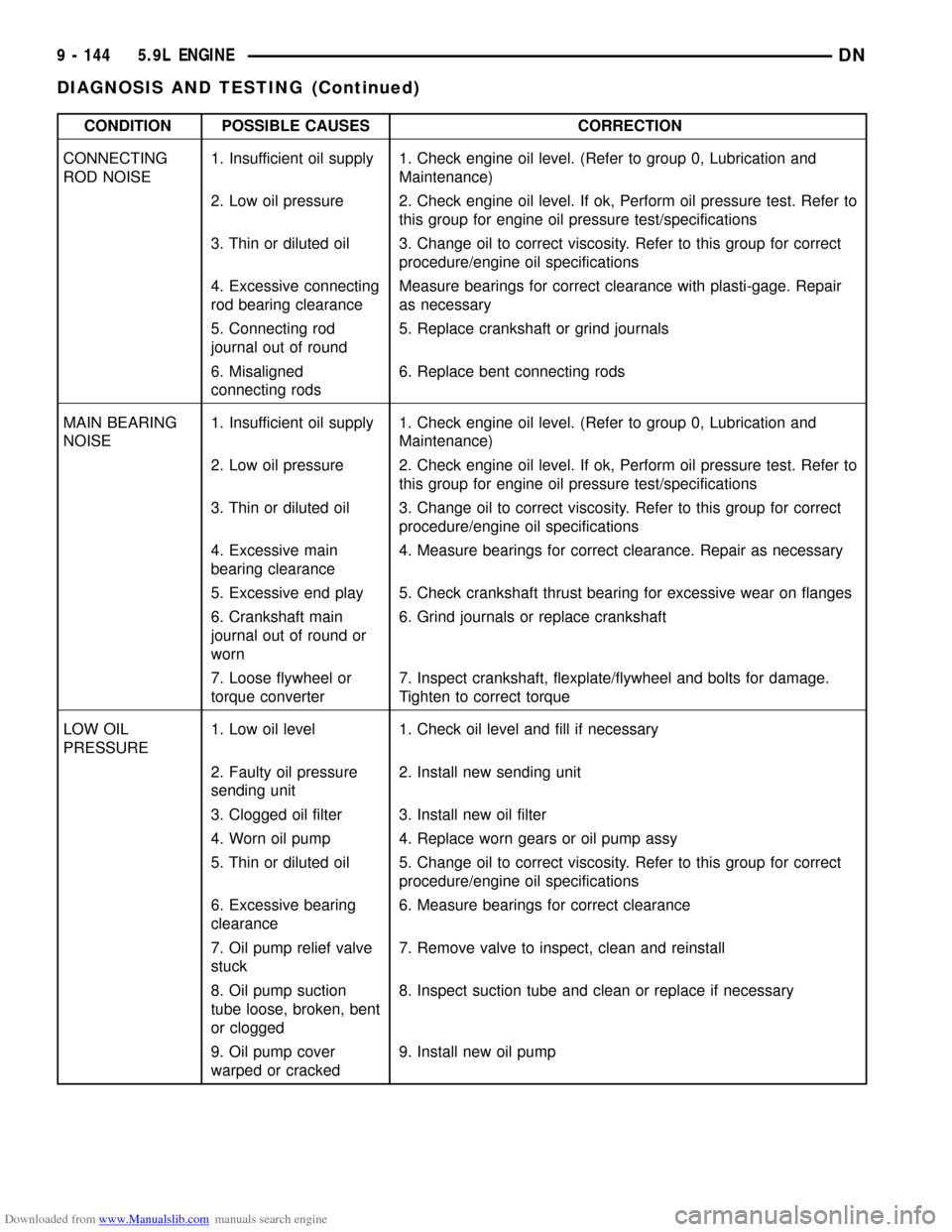
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CONNECTING
ROD NOISE1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level. (Refer to group 0, Lubrication and
Maintenance)
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok, Perform oil pressure test. Refer to
this group for engine oil pressure test/specifications
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity. Refer to this group for correct
procedure/engine oil specifications
4. Excessive connecting
rod bearing clearanceMeasure bearings for correct clearance with plasti-gage. Repair
as necessary
5. Connecting rod
journal out of round5. Replace crankshaft or grind journals
6. Misaligned
connecting rods6. Replace bent connecting rods
MAIN BEARING
NOISE1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level. (Refer to group 0, Lubrication and
Maintenance)
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok, Perform oil pressure test. Refer to
this group for engine oil pressure test/specifications
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity. Refer to this group for correct
procedure/engine oil specifications
4. Excessive main
bearing clearance4. Measure bearings for correct clearance. Repair as necessary
5. Excessive end play 5. Check crankshaft thrust bearing for excessive wear on flanges
6. Crankshaft main
journal out of round or
worn6. Grind journals or replace crankshaft
7. Loose flywheel or
torque converter7. Inspect crankshaft, flexplate/flywheel and bolts for damage.
Tighten to correct torque
LOW OIL
PRESSURE1. Low oil level 1. Check oil level and fill if necessary
2. Faulty oil pressure
sending unit2. Install new sending unit
3. Clogged oil filter 3. Install new oil filter
4. Worn oil pump 4. Replace worn gears or oil pump assy
5. Thin or diluted oil 5. Change oil to correct viscosity. Refer to this group for correct
procedure/engine oil specifications
6. Excessive bearing
clearance6. Measure bearings for correct clearance
7. Oil pump relief valve
stuck7. Remove valve to inspect, clean and reinstall
8. Oil pump suction
tube loose, broken, bent
or clogged8. Inspect suction tube and clean or replace if necessary
9. Oil pump cover
warped or cracked9. Install new oil pump
9 - 144 5.9L ENGINEDN
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 150 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine (2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292. Start engine and record pressure. Refer to
Oil Pressure in Engine Specifications for the proper
pressures.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS
There are several places where form-in-place gas-
kets are used on the engine.DO NOT use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Care
must be taken when applying form-in-place gaskets.
Bead size, continuity and location are of great impor-
tance. Too thin a bead can result in leakage while too
much can result in spill-over. A continuous bead of
the proper width is essential to obtain a leak-free
joint.
Two types of form-in-place gasket materials are
used in the engine area (Mopar Silicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant and Mopar Gasket Maker). Each
have different properties and cannot be used inter-
changeably.
MOPAR SILICONE RUBBER ADHESIVE SEALANT
Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant, normally
black in color, is available in 3 ounce tubes. Moisture
in the air causes the sealant material to cure. This
material is normally used on flexible metal flanges.
It has a shelf life of a year and will not properly cure
if over aged. Always inspect the package for the expi-
ration date before use.
MOPAR GASKET MAKER
Mopar Gasket Maker, normally red in color, is
available in 6 cc tubes. This anaerobic type gasket
material cures in the absence of air when squeezed
between smooth machined metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. DO NOT use
on flexible metal flanges.
SURFACE PREPARATION
Parts assembled with form-in-place gaskets may be
disassembled without unusual effort. In some
instances, it may be necessary to lightly tap the part
with a mallet or other suitable tool to break the seal
between the mating surfaces. A flat gasket scraper
may also be lightly tapped into the joint but care
must be taken not to damage the mating surfaces.
Scrape or wire brush all gasket surfaces to remove
all loose material. Inspect stamped parts to ensure
gasket rails are flat. Flatten rails with a hammer on
a flat plate, if required. Gasket surfaces must be free
of oil and dirt. Make sure the old gasket material is
removed from blind attaching holes.
GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care.
Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant should be
applied in a continuous bead approximately 3 mm
(0.12 inch) in diameter. All mounting holes must be
circled. For corner sealing,a3or6mm(1/8 or 1/4
inch) drop is placed in the center of the gasket con-
tact area. Uncured sealant may be removed with a
shop towel. Components should be torqued in place
while the sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10
minutes). The use of a locating dowel is recom-
mended during assembly to prevent smearing the
material off location.
Mopar Gasket Maker should be applied sparingly
to one gasket surface. The sealant diameter should
be 1.00 mm (0.04 inch) or less. Be certain the mate-
rial surrounds each mounting hole. Excess material
can easily be wiped off. Components should be
torqued in place within 15 minutes. The use of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing the material off location.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and the lowest emission levels. If vehicle is not oper-
ating to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis
outlined in this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Electri-
cal Group 8B, Cold Cranking Test.
Fig. 11 Leak-Down Tester
1 ± POINTER
2 ± WEIGHTED ARM
3 ± RAM
4 ± CUP
5 ± HANDLE
6 ± PUSH ROD
DN5.9L ENGINE 9 - 149
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 151 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine (2) Check intake manifold bolt torque.
(3) Perform cylinder compression test. Refer to
Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in the Engine
Diagnosis area of this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Electrical Group 8D.
Tighten to specifications.
(5) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Electrical Group 8D, Spark Plug Cables.
(6) Inspect the primary wires. Test coil output volt-
age and primary resistance. Replace parts as neces-
sary. Refer to Electrical Group 8D, for specifications.
(7) Test fuel pump for pressure. Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System Specifications.
(8) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Lubrication and Maintenance, Group 0.
(9) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(10) Road test vehicle as a final test.
ENGINE OIL
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
In gasoline engines, use an engine oil that is API
Service Grade Certified (Fig. 12). Standard engine oil
identification notations have been adopted to aid in
the proper selection of engine oil. The identifying
notations are located on the label of engine oil plastic
bottles and the top of engine oil cans. MOPAR only
provides engine oil that conforms to this certification.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. SAE 10W-30 specifies a multiple
viscosity engine oil. These are specified with a dualSAE viscosity grade which indicates the cold-to-hot
temperature viscosity range. When choosing an
engine oil, consider the range of temperatures the
vehicle will be operated in before the next oil change.
Select an engine oil that is best suited to your area's
particular ambient temperature range and variation
(Fig. 13).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. The designation of ENERGY CON-
SERVING is located on the label of an engine oil con-
tainer.
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located at the right
front of the engine, left of the generator on 5.9L
engines (Fig. 14).
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
Fig. 12 Engine Oil Container Standard Notations
Fig. 13 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity
Recommendation
9 - 150 5.9L ENGINEDN
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 156 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine inch). The width of the exhaust seats should be
1.524-2.032 mm (0.060-0.080 inch).
VALVE SPRING INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested. As an example the compression length of
the spring to be tested is 1-5/16 inch. Turn table of
Universal Valve Spring Tester Tool until surface is in
line with the 1-5/16 inch mark on the threaded stud.
Be sure the zero mark is to the front (Fig. 23). Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by 2. This will give the
spring load at test length. Fractional measurements
are indicated on the table for finer adjustments.
Refer to specifications to obtain specified height and
allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN STRETCH
NOTE: To access timing chain Refer to Timing
Chain Cover in Removal and Installation Section.
(1) Place a scale next to the timing chain so that
any movement of the chain may be measured.
(2) Place a torque wrench and socket over cam-
shaft sprocket attaching bolt. Apply torque in the
direction of crankshaft rotation to take up slack; 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque with cylinder head installed
or 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque with cylinder head
removed. With a torque applied to the camshaftsprocket bolt, crankshaft should not be permitted to
move. It may be necessary to block the crankshaft to
prevent rotation.
(3) Hold a scale with dimensional reading even
with the edge of a chain link. With cylinder heads
installed, apply 14 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque in the
reverse direction. With the cylinder heads removed,
apply 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque in the reverse direc-
tion. Note the amount of chain movement (Fig. 24).
(4) Install a new timing chain, if its movement
exceeds 3.175 mm (1/8 inch).
(5) If chain is not satisfactory, remove camshaft
sprocket attaching bolt and remove timing chain with
crankshaft and camshaft sprockets.
(6) Place both camshaft sprocket and crankshaft
sprocket on the bench with timing marks on exact
imaginary center line through both camshaft and
crankshaft bores.
Fig. 22 Refacing Valve Seats
1±STONE
2 ± PILOT
3 ± VALVE SEAT
4 ± SHROUD
Fig. 23 Testing Valve Spring for Compressed
Length
1 ± TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± VALVE SPRING TESTER
Fig. 24 Measuring Timing Chain Wear and Stretch
1 ± TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± 3.175 MM
(0.125 IN.)
DN5.9L ENGINE 9 - 155
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 159 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Upper and lower No.3 bearing halves are flanged
to carry the crankshaft thrust loads. They are NOT
interchangeable with any other bearing halves in the
engine (Fig. 31). Bearing shells are available in stan-
dard and the following undersizes: 0.25 mm (0.001
inch), 0.051 mm (0.002 inch), 0.076 mm (0.003 inch),
0.254 mm (0.010 inch) and 0.305 mm (0.012 inch).
Never install an undersize bearing that will reduce
clearance below specifications.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ENGINE FRONT MOUNTS
REMOVALÐ2WD
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise hood and position fan to assure clearance
for radiator top tank and hose.
CAUTION: DO NOT lift the engine by the intake
manifold.
(3) Install engine lifting fixture.
(4) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(5) Remove the insulator through bolt (Fig. 32)
(Fig. 33).
(6) Raise engine with lifting fixture SLIGHTLY.
Remove insulator retaining bolts and remove the
insulator assembly.
(7) Remove insulator heat shield and transfer to
new insulator.
INSTALLATIONÐ2WD
(1) With the engine raised SLIGHTLY, position
insulator assembly onto the engine block and install
bolts (Fig. 32) (Fig. 33). Tighten the bolts to 41 N´m
(30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Lower engine with lifting fixture while guiding
insulator assembly into the engine insulator bracket
(Fig. 34).
(3) Install insulator to bracket thru-bolt. Tighten
the thru-bolt nut to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Remove lifting fixture.
(5) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
Fig. 29 Compression Ring Chamfer Location
(Typical)
1 ± CHAMFER
2 ± TOP COMPRESSION RING
3 ± SECOND COMPRESSION RING
4 ± PISTON
5 ± CHAMFER
Fig. 30 Proper Ring Installation
1 ± OIL RING SPACER GAP
2 ± SECOND COMPRESSION RING GAP OIL RING RAIL GAP
(TOP)
3 ± OIL RING RAIL GAP (BOTTOM)
4 ± TOP COMPRESSION RING GAP
Fig. 31 Main Bearing Identification
9 - 158 5.9L ENGINEDN
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)