engine DODGE NEON 1999 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 88 of 1200

boosters differ at the interface to the master cylinder.
If the power brake booster requires replacement be
sure it is replaced with the correct part.
The power brake booster can be identified by the
tag attached to the body of the booster assembly (Fig.
16). This tag contains the following information: The
production part number of the power booster assem-
bly, the date it was built, who manufactured it, and
brake sales code.
NOTE: The power brake booster assembly is not a
repairable part and must be replaced as a complete
unit if it is found to be faulty in any way. The power
booster vacuum check valve is not repairable but
can be replaced as an assembly.The power brake booster reduces the amount of
force required by the driver to obtain the necessary
hydraulic pressure to stop vehicle.
The power brake booster is vacuum operated. The
vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the
engine through the power brake booster check valve
(Fig. 16).
As the brake pedal is depressed, the power booster
input rod moves forward (Fig. 17). This opens and
closes valves in the power booster, allowing atmo-
spheric pressure to enter on one side of a diaphragm.
Engine vacuum is always present on the other side.
This difference in pressure forces the output rod of
the power booster (Fig. 17) out against the primary
piston of the master cylinder. As the pistons in the
master cylinder move forward this creates the
hydraulic pressure in the brake system.
Different engine options available for this vehicle
require that different vacuum hose routings be used.
The power brake vacuum booster assembly mounts
on the engine side of the dash panel. It is connected
to the brake pedal by the input push rod (Fig. 17). A
vacuum line connects the power booster to the intake
manifold. The master cylinder is bolted to the front
of the power brake vacuum booster assembly.
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP
The red Brake warning lamp is located in the
instrument panel cluster and is used to indicate a
low brake fluid condition or that the parking brake is
applied. In addition, the brake warning lamp is
turned on as a bulb check by the ignition switch
when the ignition switch is placed in the crank posi-
tion. Problems with this system will generally be of
the type where the warning lamp fails to turn on
when it should, or remains on when it should not.
The warning lamp bulb is supplied a 12 volt igni-
tion feed anytime the ignition switch is on. The bulb
is then illuminated by completing the ground circuit
Fig. 14 Master Cylinder For Antilock Brake
Equipped Vehicles
Fig. 15 Non-ABS Master Cylinder Primary And
Secondary Ports
Fig. 16 Power Brake Booster Identification
PLBRAKES 5 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 90 of 1200
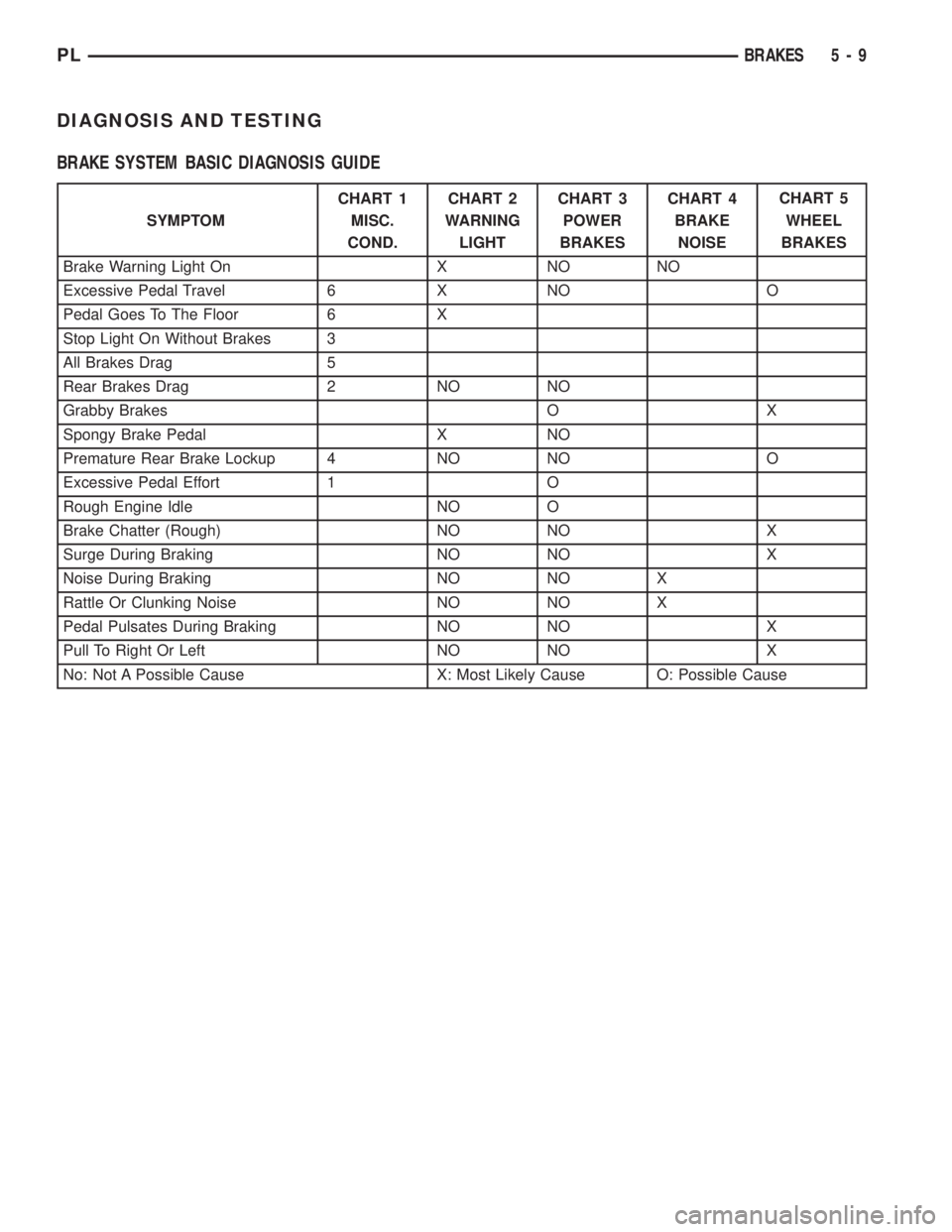
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BRAKE SYSTEM BASIC DIAGNOSIS GUIDE
SYMPTOMCHART 1
MISC.
COND.CHART 2
WARNING
LIGHTCHART 3
POWER
BRAKESCHART 4
BRAKE
NOISECHART 5
WHEEL
BRAKES
Brake Warning Light On X NO NO
Excessive Pedal Travel 6 X NO O
Pedal Goes To The Floor 6 X
Stop Light On Without Brakes 3
All Brakes Drag 5
Rear Brakes Drag 2 NO NO
Grabby Brakes O X
Spongy Brake Pedal X NO
Premature Rear Brake Lockup 4 NO NO O
Excessive Pedal Effort 1 O
Rough Engine Idle NO O
Brake Chatter (Rough) NO NO X
Surge During Braking NO NO X
Noise During Braking NO NO X
Rattle Or Clunking Noise NO NO X
Pedal Pulsates During Braking NO NO X
Pull To Right Or Left NO NO X
No: Not A Possible Cause X: Most Likely Cause O: Possible Cause
PLBRAKES 5 - 9
Page 122 of 1200

MASTER CYLINDER
REMOVE
CAUTION: On ABS equipped vehicles, vacuum in
power booster must be pumped down before
removing master cylinder to prevent booster from
sucking in any contamination. This can be done
simply by pumping the brake pedal until a firm
pedal is achieved, with the ignition off.
(1) On ABS equipped vehicles, be sure engine is
not running, and pump the brake pedal until a firm
pedal is achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Remove vehicle wiring harness connector, from
brake fluid level sensor, in master cylinder brake
fluid reservoir (Fig. 103).
(3) Disconnect the primary and secondary brake
tubes from the master cylinder (Fig. 104) and (Fig.
105). Install plugs at all open brake tube outlets on
master cylinder assembly.(4) On vehicles equipped with ABS, clean area
where master cylinder attaches to booster using a
suitable brake cleaner product such as Mopar Brake
Parts Cleaner or an equivalent.
(5) Remove the 2 nuts (Fig. 106) attaching master
cylinder housing to power brake vacuum booster.
(6) Slide master cylinder assembly straight out of
the power brake vacuum booster.
CAUTION: On vehicles equipped with ABS, the
master cylinder is used to create the seal for hold-
ing vacuum in the power brake vacuum booster.
The vacuum seal in the front of the power brake
vacuum booster (Fig. 107) MUST be replaced when-
ever the master cylinder is removed from the power
brake vacuum booster.
(7) If vehicle is equipped with ABS, remove vac-
uum seal (Fig. 107) located in the front of the power
brake vacuum booster. Vacuum seal is removed by
Fig. 102 Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
Fig. 103 Master Cylinder Fluid Level Sensor
Fig. 104 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes W/O
ABS Brakes
Fig. 105 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes With
ABS Brakes
PLBRAKES 5 - 41
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 125 of 1200

VACUUM BOOSTER
REMOVE
CAUTION: On ABS equipped vehicles, vacuum in
power booster must be pumped down before
removing master cylinder to prevent booster from
sucking in any contamination. This can be done
simply by pumping the brake pedal until a firm
pedal is achieved, with the ignition off.
(1) On ABS equipped vehicles, with engine not
running, pump the brake pedal until a firm pedal is
achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Remove vehicle wiring harness connector from
brake fluid level sensor located in master cylinder
brake fluid reservoir (Fig. 114).
(3) Disconnect the primary and secondary brake
tubes from the master cylinder (Fig. 115) and (Fig.
116). Install plugs at all open brake tube outlets on
master cylinder assembly.(4) On vehicles equipped with ABS, clean area
where master cylinder attaches to booster using a
suitable brake cleaner such as Mopar Brake Parts
Cleaner or an equivalent.
(5) Remove the 2 nuts (Fig. 117) attaching master
cylinder housing to power brake vacuum booster.
(6) Slide master cylinder assembly straight out of
the power brake vacuum booster.
CAUTION: On vehicles equipped with ABS, the
master cylinder is used to create the seal for hold-
ing vacuum in the power brake vacuum booster.
The vacuum seal in the front of the power brake
vacuum booster (Fig. 118) MUST be replaced when-
ever the master cylinder is removed from the power
brake vacuum booster.
(7) If vehicle is equipped with ABS, remove vac-
uum seal (Fig. 118) located in the front of the power
Fig. 114 Master Cylinder Fluid Level Sensor
Fig. 115 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes W/O
ABS Brakes
Fig. 116 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes With
ABS Brakes
Fig. 117 Master Cylinder Mounting To Vacuum
Booster
5 - 44 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 146 of 1200

If old brake shoe return or hold down springs have
overheated or are damaged, replace. Overheating
indications are paint discoloration or distorted end
coils.
REAR DRUM BRAKE WHEEL CYLINDER
With brake drums removed, inspect the wheel cyl-
inder boots for evidence of a brake fluid leak. Visu-
ally check the boots for cuts, tears, or heat cracks. If
any of these conditions exist, the wheel cylinders
should be completely cleaned, inspected and new
parts installed.
If a wheel cylinder is leaking and the brake lining
material is saturated with brake fluid, the brake
shoes must be replaced.
CHASSIS TUBES AND HOSES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front and rear
brakes. Inspection of brake hoses should be per-
formed whenever the brake system is serviced and
every 7,500 miles or 12 months, whichever comes
first (every engine oil change). Inspect hydraulic
brake hoses for severe surface cracking, scuffing,
worn spots or physical damage. If the fabric casing of
the rubber hose becomes exposed due to cracks or
abrasions in the rubber hose cover, the hose should
be replaced immediately. Eventual deterioration of
the hose can take place with possible burst failure.
Faulty installation can cause twisting, resulting in
wheel, tire, or chassis interference.
The steel brake tubing should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of corrosion, physical damage or con-
tact with moving or hot components of the vehicle.
REAR WHEEL HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
The rear hub and bearing assembly is designed for
the life of the vehicle and should require no mainte-
nance. The following procedure may be used for eval-
uation of bearing condition.
With wheel and brake drum removed, rotate
flanged outer ring of hub. Excessive roughness, lat-
eral play or resistance to rotation may indicate dirt
intrusion or bearing failure. If the rear wheel bear-
ings exhibit these conditions during inspection, the
hub and bearing assembly should be replaced.Damaged bearing seals and resulting excessive
grease loss may also require bearing replacement.
Moderate grease loss from bearing is considered nor-
mal and should not require replacement of the hub
and bearing assembly.
ADJUSTMENTS
STOP LAMP SWITCH
(1) Remove stop lamp switch from its bracket by
rotating it approximately 30É in a counter-clockwise
direction.
(2) Disconnect wiring harness connector from stop
lamp switch.
(3) Hold stop lamp switch firmly in one hand.
Then using other hand, pull outward on the plunger
of the stop lamp switch until it has ratcheted out to
its fully extended position.
(4) Install the stop lamp switch into the bracket
using the following procedure. Depress the brake
pedal as far down as possible. Then while keeping
the brake pedal depressed, install the stop lamp
switch into the bracket by aligning index key on
switch with slot at top of square hole in mounting
bracket. When switch is fully installed in the square
hole of the bracket, rotate switch clockwise approxi-
mately 30É to lock the switch into the bracket.
CAUTION: Do not use excessive force when pulling
back on brake pedal to adjust the stop lamp switch.
If too much force is used, damage to the vacuum
booster, stop lamp switch or striker (Fig. 185) can
result.
(5) Connect the wiring harness connector to the
stop lamp switch.
(6) Gently pull back on brake pedal until the pedal
stops moving. This will cause the switch plunger
(Fig. 185) to ratchet backward to the correct position.
REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOE ADJUSTMENT
NOTE: Normally, self adjusting drum brakes will
not require manual brake shoe adjustment.
Although in the event of a brake reline it is advis-
able to make the initial adjustment manually to
speed up the adjusting time.
(1) Raise the vehicle so all wheels are free to turn.
See Hoisting Recommendations in the Lubrication
And Maintenance Section at the front of this service
manual.
(2) Remove rear brake adjusting hole rubber plug
(Fig. 186) from the rear brake shoe support plate.
Fig. 184 Adjuster Screw And Lever (Typical)
PLBRAKES 5 - 65
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 148 of 1200

(3) Remove the rubber plug from the adjusting
hole in the brake shoe backing plate on both sides of
the vehicle.
(4)Driver (left) side park brake shoe adjust-
ment procedure.Insert a medium size screwdriver
through adjustment hole in backing plate. Position
the srewdriver against the starwheel on the park
brake shoe adjuster mechanism. Using the screw-
driver rotate the starwheeldownwarduntil a slight
drag is felt when turning the rear tire and wheel.
Then, using the screwdriver rotate the starwheel
upwardjust until the rear tire and wheel can be
rotated with no park brake shoe drag. From the
point where there is no more park brake drag rotate
the starwheelupwarda maximum of two additional
clicks. The park brake shoe to drum clearance is
know properly adjusted.
(5)Passenger (right) side park brake shoe
adjustment procedure.Insert a medium size
screwdriver through adjustment hole in backing
plate. Position the srewdriver against the starwheel
on the park brake shoe adjuster mechanism. Using
the screwdriver rotate the starwheelupwarduntil a
slight drag is felt when turning the rear tire and
wheel. Then, using the screwdriver rotate the star-
wheeldownwardjust until the rear tire and wheel
can be rotated with no park brake shoe drag. From
the point where there is no more park brake drag
rotate the starwheeldownwarda maximum of two
additional clicks. The park brake shoe to drum clear-
ance is know properly adjusted.
(6) Install the rubber plug in the adjusting hole on
the brake shoe backing plate on both sides of the
vehicle.
(7) Lower vehicle far enough to allow access the
park brake lever. The rear tires must not be on the
ground.
(8) Fully apply and release the park brakes two
times after adjusting the park brake shoes. Then
rotate both rear wheels to ensure that the park
brake shoes do not drag on the brake drum following
the application and release of the park brakes.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications and SAE J1703 standards.
No other type of brake fluid is recommended or
approved for usage in the vehicle brake system. Use
only Mopar brake fluid or an equivalent from a
tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. Anopen container will absorb moisture from the air
and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-
based fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of
such type fluids will result in seal damage of the
vehicle brake hydraulic system causing a failure of
the vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids
would be items such as engine oil, transmission
fluid, power steering fluid ect.
BRAKE ACTUATION SYSTEM
ACTUATION:
Vacuum Operated Power Brakes.........Standard
Hydraulic System...........Dual-Diagonally Split
MASTER CYLINDER ASSEMBLY:
Type ...........................Dual Tandem
Body Material...............Anodized Aluminum
Reservoir Material................Polypropelene
MASTER CYLINDER BORE / STROKE
AND SPLIT:
NonABS ....21mmx32.6 mm (.875 in. x 1.28 in.)
ABS........21mmx32.7 mm (.874 in. x 1.29 in.)
Displacement Split.....................50/50
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID OUTLET PORTS:
ABS ..........Primary 3/8±24 Secondary 7/16±24
Non ABS . . .Primary Inboard And Outboard 7/16±24
Non ABS . . .Secondary Inboard And Outboard 3/8±23
Outlet Fitting Type.......SAE 45 É Inverted Flare
ABS HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT:
Hydraulic Tube Fitting Type.SAE 45 É Inverted Flare
BOOSTER:
Make/Type.........Bendix Vacuum W/&W/O ABS
Mounting Studs.....................M8x1.25
Type ..........................230 mm Single
Boost At 20 inches Of Manifold Vacuum. . . .4690 All
PROPORTIONING VALVE:
Material...........................Aluminum
Function........Hydraulic Pressure Proportioning
BRAKE PEDAL
Pedal Ratio.............................3.28
BRAKE FASTENER TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
BRAKE TUBES:
Tube Nuts To Fittings And
Components Except HCU. . . . 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.)
From Master Cylinder To
HCU At HCU Ports........21N´m(185 in. lbs.)
BRAKE HOSE:
To Caliper Banjo Bolt..........48N´m(35ft.lbs.)
Intermediate Bracket.........12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
PLBRAKES 5 - 67
ADJUSTMENTS (Continued)
Page 154 of 1200

ABS FUSES
The fuse for the ABS pump motor and the ABS
system are located in the power distribution center
(PDC) (Fig. 5). Refer to the sticker on the inside of
the PDC cover for the location of the ABS pump
motor and the ABS system fuse in the PDC. The
PDC is located on the drivers side of the engine com-
partment between the back of the battery and the
strut tower (Fig. 5).
ABS RELAYS
On this vehicle three relays are used to control the
Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake System. The three
relays are the pump motor relay, the system relay,
and the ABS yellow warning lamp relay. The pump
motor relay and the system relay are located in the
CAB and the ABS yellow warning lamp relay is
located in the PDC. If either the pump motor relay or
the system relay is diagnosed as not functioning
properly the CAB will need to be replaced. Refer to
Controller Antilock Brakes in the Removal And
Installation Section in this group of the service man-
ual for the procedure. If the ABS yellow warning
lamp relay is diagnosed as not functioning properly it
can be replaced as a seperated relay in the PDC.
PROPORTIONING VALVE
There are two proportioning valves (Fig. 6) used in
the Teves Mark 20 ABS system. One proportioning
valve is located in the chassis brake line of each rear
wheel brake hydraulic circuit (Fig. 7). The propor-
tioning valves function the same as in a standard
brake system. The proportioning valve can be identi-
fied by the bar code label and stamp on the propor-
tioning valve. Be sure replacement proportioning
valve have the same stamp as the proportioning
valve being replaced.
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
CAUTION: The tone wheels used on this vehicle
equipped with the Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake
System are different then the tone wheels used on
past models of this vehicle equipped with antilock
brakes. Reduced braking performance will result if
this part is used on earlier model vehicles and an
accident could result. Do not use on pre-1998
model year vehicles.
One Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS) is located at each
wheel (Fig. 8) and (Fig. 9), and sends a small AC sig-
nal to the control module (CAB). This signal is gen-
erated by magnetic induction created when a toothed
sensor ring (tone wheel) (Fig. 8) and (Fig. 9) passes
the stationary magnetic Wheel Speed Sensor. The
(CAB) converts the AC signal generated at each
wheel into a digital signal. If a wheel locking ten-
dency is detected by the CAB, it will then modulate
hydraulic pressure via the HCU to prevent the
wheel(s) from locking.
The front Wheel Speed Sensor is attached to a boss
in the steering knuckle (Fig. 8). The tone wheel is
part of the outboard constant velocity joint (Fig. 8).
The rear Wheel Speed Sensor on rear disc brake
applications is mounted to the rear disc brake
adapter (Fig. 9) and the rear tone wheel is also an
Fig. 5 Power Distribution Center
Fig. 6 Proportioning Valve
Fig. 7 Proportioning Valve Location In Vehicle
PLBRAKES 5 - 73
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 163 of 1200

CAUTION: Certain components of the ABS System
are not intended to be serviced individually.
Attempting to remove or disconnect certain system
components may result in improper system opera-
tion. Only those components with approved
removal and installation procedures in this manual
should be serviced.
CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage painted sur-
faces. If brake fluid is spilled on any painted sur-
faces, wash off with water immediately.
CAUTION: When performing any service procedure
on a vehicle equipped with ABS do not apply a 12
volt power source to the ground circuit of the pump
motor in the HCU. Doing this will damage the pump
motor and will require replacement of the entire
HCU.
The following are general cautions which should be
observed when servicing the ABS system and/or
other vehicle systems. Failure to observe these pre-
cautions may result in ABS System component dam-
age.
If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle,
using an electric arc welder, the CAB connector
should be disconnected during the welding operation.
The CAB 25 way connector connector should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition switch
in the ON position.
Many components of the ABS System are not ser-
viceable and must be replaced as an assembly. Do not
disassemble any component which is not designed to
be serviced.
ABS HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT
REMOVE
(1) Disconnect negative (ground) cable from the
battery and isolate cable.
(2) Remove the power distribution center (PDC)
(Fig. 17) from the battery thermogaurd. PDC is
removed by unlatching the two retaining clips hold-
ing it to the thermogaurd and then pulling it straight
up off of the thermogaurd.
(3) Remove vacuum supply hose from speed control
servo (Fig. 18).
(4) Remove the 2 bolts (Fig. 18) mounting the
bracket for the speed control servo to the body.
(5) Remove the wiring harness connector (Fig. 19)
from the speed control servo. Then remove the rout-
ing clip for the speed control servo wiring harness
from the speed control servo mounting bracket.
(6) Lay the speed control servo, with the speed
control cable attached, on top of the engine.(7) Disconnect wiring harness connector from the
brake fluid level sensor on master cylinder reservoir.
Fig. 17 PDC Attachment To Thermogaurd
Fig. 18 Speed Control Servo Bracket Mounting
Fig. 19 Wiring Harness Connection To Speed
Control Servo
5 - 82 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 164 of 1200

(8) Disconnect primary and secondary brake tubes
from master cylinder (Fig. 20). Install plugs at brake
tube outlets of master cylinder assembly.
(9) Clean the area where the master cylinder
attaches to the vacuum booster using a suitable
brake cleaner such as Mopar Brake Parts Cleaner or
an equivalent.
CAUTION: On ABS equipped vehicles, vacuum in
power booster must be pumped down before
removing master cylinder to prevent the booster
from sucking in any contamination. This can be
done simply by pumping the brake pedal, with the
engine not running, until a firm brake pedal is
achieved.
(10) Remove the 2 nuts (Fig. 21) attaching master
cylinder to power brake booster unit.(11) Slide the master cylinder straight out of the
vacuum booster unit.
(12) Remove the primary and secondary master
cylinder brake tubes (Fig. 22) from the inlet ports of
the HCU.
(13) Remove the 4 chassis brake tubes from the
outlet ports of the (HCU) (Fig. 23).
CAUTION: Do not apply a 12 volt power source to
any terminals of the 25 HCU connector when dis-
connected from the CAB.
(14) Disconnect the 25 way wiring harness connec-
tor from the CAB using the following procedure.
Grasp the lock on the 25 way connector and pull it
out from the connector as far as possible (Fig. 24).
This will unlock and raise the 25 way connector out
of the socket on the CAB.
(15) Remove the 3 bolts attaching the CAB and
HCU to the mounting bracket. (Fig. 25).
(16) Remove the ICU as a unit from the vehicle.
Fig. 20 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes With
ABS Brakes
Fig. 21 Master Cylinder Mounting
Fig. 22 Primary And Secondary Brake Tubes From
Master Cylinder To HCU
Fig. 23 Chassis Brake Tube Connections To HCU
PLBRAKES 5 - 83
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 173 of 1200

The clutch cable has a unique self-adjuster mecha-
nism built into the cable which compensates for
clutch disc wear. The cable requires no maintenance
or lubrication. There are no serviceable components
on the cable assembly.
The clutch pedal is connected to the cable through
a plastic spacer. The upper end of the clutch pedal
pivots in the pedal bracket on two nylon bushings
and a shaft. These bushings are greased at assembly
and do not require periodic lubrication.
CLUTCH DISC AND COVER APPLICATION
The 2.0 single overhead cam engine uses a 216 mm
(8.5 in.) clutch disc. The manual transaxle is avail-
able only with the 2.0 liter engine.
CLUTCH REPLACEMENT
The transaxle must be removed to service the
clutch disc, pressure plate, flywheel/drive plate,
and/or clutch release bearing and lever.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CLUTCH CABLE
The manual transaxle clutch release system has a
unique self-adjusting mechanism to compensate for
clutch disc wear. This adjuster mechanism is located
within the clutch cable assembly. The preload spring
maintains tension on the cable. This tension keeps
the clutch release bearing continuously loaded
against the fingers of the clutch cover assembly.
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
The clutch pedal position switch functions as a
safety interlock device. It prevents possible engine
cranking with the clutch engaged.
The clutch pedal position switch is wired in series
between the starter relay coil and the ignition
switch.
The clutch pedal position switch is mounted to a
bracket located behind the clutch pedal. The switch
is held in place by four plastic wing tabs.The clutch pedal position switch IS NOT adjust-
able. The pedal blade contacts the switch in the down
position (Fig. 1).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION
SWITCH±ELECTRICAL TEST
Disconnect clutch pedal position switch harness
from instrument panel wiring harness. Using an
ohmmeter, check for continuity between the two ter-
minals in the connector on the switch harness. There
should be no continuity between the terminals when
the switch is in its normal (fully extended) position.
When the switch is depressed more than 1.25 mm
(0.050), the ohmmeter should show continuity (zero
ohms).
If ohmmeter readings do not fall within these
ranges, the switch is defective, and must be replaced.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS±CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ENGINE WON'T CRANK
WHEN CLUTCH PEDAL IS
PRESSED TO THE FLOORSwitch does not have continuity
when plunger is depressed 1.25
mmDefective switch. Replace switch.
Switch plunger is not depressed
when clutch pedal is pushed to the
floorFloor mat interferes with clutch pedal
movement. Move floor mat out of the way.
Problem is related to other
components in the starting circuitCheck other components in the starting
circuit. Refer to Section 8A, Battery/Starting/
Charging System.
Fig. 1 Clutch Pedal Position Switch and
Components
6 - 2 CLUTCHPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)