engine DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 812 of 1200
Camshaft Sprocket Remover/Installer Adapter
C-4687-1
Camshaft Seal Installer MD-998713
Installer Crankshaft Damper 6792
Crankshaft Sprocket Remover Insert C-4685-C2
Valve Spring Compressor MD-998772-A
Adapter Spring Compressor 6779
Valve Spring Compressor C-3422-B
Cylinder Bore Indicator C-119
PL2.0L DOHC ENGINE 9 - 99
SPECIAL TOOLS (Continued)
Page 813 of 1200
Front Crankshaft Seal Remover 6771
Front Crankshaft Seal Installer 6780
Crankshaft Sprocket Remover 6793
Crankshaft Sprocket Installer 6792
Rear Crankshaft Seal Guide and Installer 6926-1 and
6926-2
Pressure Gage C-3292
Valve Spring Tester C-647
9 - 100 2.0L DOHC ENGINEPL
SPECIAL TOOLS (Continued)
Page 814 of 1200

ENGINE
CONTENTS
page
1.8L SOHC ENGINE...................... 1
1.8L SOHC ENGINE
INDEX
page
GENERAL INFORMATION
1.8L SOHC ENGINE...................... 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
1.8L SOHC ENGINE
For service of the 1.8L SOHC engine refer to the
2.0L SOHC engine information except for the follow-
ing specifications.
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Type .....................In-Line OHV, SOHC
Bore..............................83.0 mm
Stroke.............................83.0mm
Compression Ratio.....................10.0:1
Displacement......................1.8Liters
Firing Order........................1,3,4,2
Compression (Cranking)
Pressure.......1172-1551 kPa (170 - 225 psi)
Maximum Variation Between Cylinders......25%
Lubrication . . . Pressure Feed - Full Flow Filtration
(Crankshaft Driven Pump)
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON
SPECIFICATIONS CHART
Standard Bore Maximum
Out-of-RoundMaximum
Taper
82.993 - 83.007
mm0.051 mm 0.051 mm
Standard Piston Size
82.974 - 82.956 mm
Piston to Bore Clearance
0.018 - 0.050 mm
Measurements Taken at Piston Size Location
PISTON RING SPECIFICATIONS
Ring Position Ring Gap Wear Limit
Upper Ring 0.23 - 0.38 mm 0.8 mm
Intermediate
Ring0.20 - 0.47 mm 1.0 mm
Oil Control Ring 0.25 -0.64 mm 1.0 mm
Ring Position Groove
ClearanceMaximum
Clearance
Upper Ring 0.03 - 0.07 mm 0.10 mm
Intermediate
Ring0.040 - 0.078
mm0.10 mm
OIL CONTROL RING (THREE PIECE) - OIL RING
SIDE RAILS MUST BE FREE TO ROTATE AFTER
ASSEMBLY
PLENGINE 9 - 1
Page 815 of 1200

ENGINE 1.8L SOHC
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diameter.....82.993 - 83.007 mm
Out-of-Round (Max.)...............0.051 mm
Taper (Max.).....................0.051 mm
Pistons
Clearance from Piston (measured 6.0 mm from
bottom of skirt) to bore.......0.018 - 0.050 mm
Weight.....................296-305grams
Land Clearance (Diametrical) . . 0.753 - 0.799 mm
Piston Length....................54.11 mm
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 1
.........................3.203 - 3.337 mm
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 2
.........................4.406 - 4.272 mm
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 3
.........................3.932 - 3.798 mm
Piston Pins
Clearance in Piston..........0.009 - 0.021 mm
In Rod (Interference).........0.018 - 0.043 mm
Diameter................20.998 - 21.003 mm
End Play............................None
Length....................74.75 - 75.25 mm
Piston Rings
Ring Gap Top Compression Ring . . 0.23 - 0.38 mm
Ring Gap 2nd Compression Ring . . 0.20 - 0.47 mm
Ring Gap Oil Control (Steel
Rails)......................0.25 - 0.64 mm
Ring Side Clearance Compression Ring
Upper.........................0.03 - 0.07
Ring Side Clearance Compression Ring
Lower.....................0.04 - 0.078 mm
Oil Ring (Pack).............0.056 - 0.186 mm
Ring Width Compression Ring
Top ........................1.19 - 1.17 mm
Ring Width Compression Ring
Lower....................1.490 - 1.472 mm
Oil Ring (Pack).............2.984 - 2.854 mm
9 - 2 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 816 of 1200
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
CATALYTIC CONVERTER................... 4
EXHAUST BALL JOINT COUPLING.......... 1
EXHAUST FLEX-JOINT COUPLING (LEV)...... 2
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SYSTEM.............................. 3
EXHAUST SYSTEMS...................... 1
HEAT SHIELDS.......................... 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
EXHAUST MANIFOLD..................... 3
INTAKE MANIFOLD DOHC................. 3
INTAKE MANIFOLD SOHC................. 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EXHAUST SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART...... 4REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EXHAUST MANIFOLD.................... 11
EXHAUST PIPE AND MUFFLER............. 4
INTAKE MANIFOLDÐDOHC ENGINE......... 9
INTAKE MANIFOLDÐSOHC ENGINE......... 6
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
EXHAUST MANIFOLD.................... 12
INTAKE MANIFOLD DOHC................ 12
INTAKE MANIFOLD SOHC................ 12
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART........................ 12
GENERAL INFORMATION
EXHAUST SYSTEMS
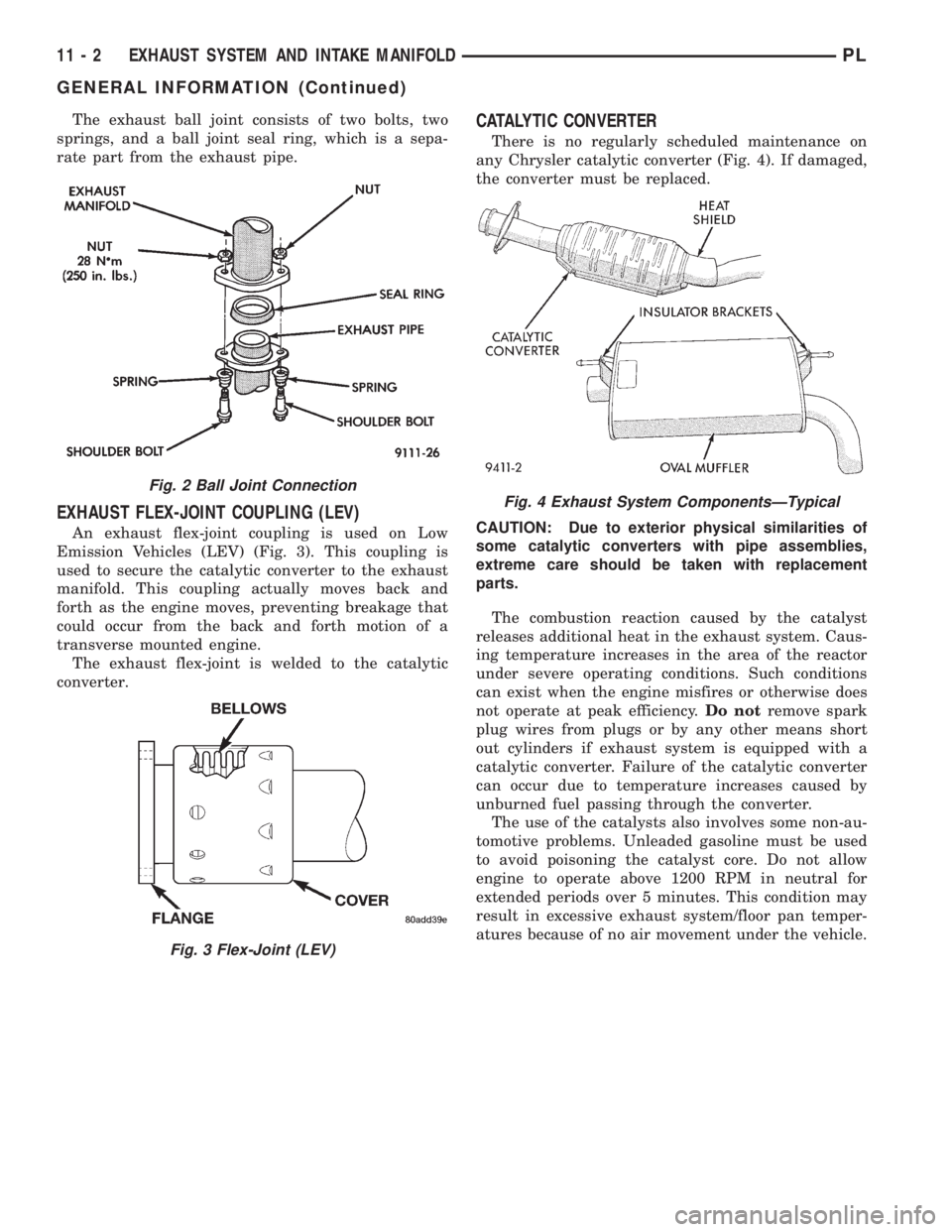
The exhaust system has an underfloor catalytic
converter, tail pipe, and muffler (Fig. 1).
EXHAUST BALL JOINT COUPLING
An exhaust ball joint coupling (Fig. 2) is used to
secure the exhaust pipe to the engine exhaust mani-
fold. This flexible joint moves back and forth as the
engine moves, preventing breakage that could occur
from the back-and-forth motion of a transverse
mounted engine.
Fig. 1 Exhaust System
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11 - 1
Page 817 of 1200
The exhaust ball joint consists of two bolts, two
springs, and a ball joint seal ring, which is a sepa-
rate part from the exhaust pipe.
EXHAUST FLEX-JOINT COUPLING (LEV)
An exhaust flex-joint coupling is used on Low
Emission Vehicles (LEV) (Fig. 3). This coupling is
used to secure the catalytic converter to the exhaust
manifold. This coupling actually moves back and
forth as the engine moves, preventing breakage that
could occur from the back and forth motion of a
transverse mounted engine.
The exhaust flex-joint is welded to the catalytic
converter.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
There is no regularly scheduled maintenance on
any Chrysler catalytic converter (Fig. 4). If damaged,
the converter must be replaced.
CAUTION: Due to exterior physical similarities of
some catalytic converters with pipe assemblies,
extreme care should be taken with replacement
parts.
The combustion reaction caused by the catalyst
releases additional heat in the exhaust system. Caus-
ing temperature increases in the area of the reactor
under severe operating conditions. Such conditions
can exist when the engine misfires or otherwise does
not operate at peak efficiency.Do notremove spark
plug wires from plugs or by any other means short
out cylinders if exhaust system is equipped with a
catalytic converter. Failure of the catalytic converter
can occur due to temperature increases caused by
unburned fuel passing through the converter.
The use of the catalysts also involves some non-au-
tomotive problems. Unleaded gasoline must be used
to avoid poisoning the catalyst core. Do not allow
engine to operate above 1200 RPM in neutral for
extended periods over 5 minutes. This condition may
result in excessive exhaust system/floor pan temper-
atures because of no air movement under the vehicle.
Fig. 2 Ball Joint Connection
Fig. 3 Flex-Joint (LEV)
Fig. 4 Exhaust System ComponentsÐTypical
11 - 2 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLDPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 818 of 1200

HEAT SHIELDS
The heat shield (Fig. 5) is needed to protect both
the car and the environment from the high tempera-
tures developed in the vicinity of the catalytic con-
verter.
CAUTION: Avoid application of rust prevention
compounds or undercoating materials to exhaust
system floor pan heat shield on cars if equipped.
Light over-spray near the edges is permitted. Appli-
cation of coating will greatly reduce the efficiency
of the heat shields resulting in excessive floor pan
temperatures and objectionable fumes.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
To assist in the control of oxides of nitrogen (NOx)
in engine exhaust, some engines are equipped with
an exhaust gas recirculation system. The use of
exhaust gas to dilute incoming air/fuel mixtures low-
ers peak flame temperatures during combustion, thus
limiting the formation of NOx.
Exhaust gases are taken from the number four
exhaust port through a hole in the end of the cylin-
der head. REFER TO GROUP 25, EMISSION SYS-
TEMS FOR A COMPLETE DESCRIPTION,
DIAGNOSIS AND SERVICE PROCEDURES ON
THE EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION SYSTEM
AND COMPONENTS.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTAKE MANIFOLD SOHC
The intake manifold is a molded plastic composi-
tion, attached to the cylinder head with ten fasten-
ers. This long branch design enhances low and
midrange torque. If removing the intake manifold for
any reason, the fasteners can not be reused.
INTAKE MANIFOLD DOHC
The intake manifold is a two piece aluminum cast-
ing, attached to the cylinder head with ten fasteners.
This long branch fan design enhances low and
midrange torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
The exhaust manifold is made of nodular cast iron
for strength and high temperatures. Exhaust gasses
exit through a machined, articulated joint connection
to the exhaust pipe.
Fig. 5 Heat Shield Installation
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 821 of 1200

NOTE: When replacement is required on any com-
ponent of the exhaust system, you must use origi-
nal equipment parts (or their equivalent).
INSTALLATION
When assembling exhaust systemdo nottighten
clamps until components are aligned and clearances
are checked.
(1) Assemble catalytic convertor to exhaust mani-
fold connection. Use a new flange gasket (LEV only)
(Fig. 9) or (Fig. 10).
(2) Assemble exhaust pipe to catalytic convertor
and the support to the underbody
(3) Install the muffler to exhaust pipe and the sup-
ports to the underbody.
(4) Working from the front of system;
(5) Align and tighten the catalytic convertor to
exhaust manifold ball joint bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft.
lbs.) (Fig. 9) or flex-joint attaching nuts (LEV) to 28
N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(6) Align each component to maintain position and
proper clearance with underbody parts (Fig. 11) and
tighten band clamps to specifications (Fig. 12).
CAUTION: Band (Torca) clamps should never be
tighten such that the two sides of the clamps are
bottomed out against the center hourglass shaped
center block. Once this occurs, the clamp has lost
its clamping force and must be replaced.
(7) Connect the downstream heated oxygen sensor
and lower the vehicle.
INTAKE MANIFOLDÐSOHC ENGINE
REMOVAL
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove fuel filler cap.
(3) Remove the fresh air inlet duct from air
cleaner (Fig. 15).
(4) Remove the protective cap from the fuel pres-
sure test port on the fuel rail (Fig. 13).
(5) Place the open end of fuel pressure release
hose, Special Tool C-4799-1, into an approved gaso-
line container. Connect the other end of hose to the
fuel pressure test port (Fig. 14). Fuel pressure will
bleed off through the hose into the gasoline con-
tainer. Fuel gauge C-4799-A contains hose C-4799-1.
(6) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.
(7) Disconnect the fuel supply line quick connect at
the fuel tube assembly.
Fig. 11 Exhaust Clearance
Fig. 12 Band Clamp (Torca)
Fig. 13 Fuel Pressure Test Port
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLDPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 822 of 1200

WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND HOSE
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(8) Remove fuel rail assembly attaching screws
and remove fuel rail assembly from engine. Cover
injector holes with suitable covering.
CAUTION: Do not set fuel injectors on their tips,
damage may occur to the injectors
(9) Remove clean air duct and upper air filter
housing (Fig. 15).
(10) Remove accelerator, kickdown and speed con-
trol cables from throttle lever and bracket. Refer to
Group 14, Fuel System Throttle Body Removal for
procedures.
(11) Disconnect Idle Air Control (IAC) motor and
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) wiring connectors
(Fig. 16).
(12) Disconnect vacuum hoses from throttle body
(Fig. 16).(13) Disconnect Manifold Absolute Pressure/Intake
Air Temperature Sensor (TMAP), electrical connector
(Fig. 17). Disconnect vapor and brake booster hoses.
(14) Disconnect knock sensor electrical connector
(Fig. 18) and disconnect wiring harness from tab
located on the intake manifold.
(15) Disconnect wiring at starter.
(16) Remove transmission to throttle body support
bracket fasteners at the throttle body and loosen the
fasteners at the transmission end.
(17) Remove throttle body.
(18) Remove EGR tube bolts at the valve and at
the intake manifold (Fig. 19). Remove tube from
engine.
(19) Remove the intake manifold to inlet water
tube support fastener (Fig. 20).
(20) Remove 10 intake manifold screws and wash-
ers. Discard the fasteners. Remove intake manifold.
Fig. 14 Releasing Fuel Pressure
Fig. 15 Clean Air Duct to Throttle Body Assembly
Fig. 16 Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor and Throttle
Position Sensor (TPS) Wiring Connectors and
Vacuum Hose Connection
Fig. 17 Intake Manifold Electrical and Vacuum Hose
Connections
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11 - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 823 of 1200

INSTALLATION
Before installing manifold. Clean all mating sur-
faces. Replace all seals, with new seals. All intakemanifold fasteners and washers are to be discarded
andNEWfasteners and washers are to be used.
(1) Install intake manifold onto cylinder head and
tighten fasteners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) in sequence
shown in (Fig. 20).
(2) Install intake manifold to water inlet support.
Tighten fastener (Fig. 20) to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Remove covering from fuel injector holes and
insure the holes are clean. Install fuel rail assembly
to intake manifold. Tighten screws to 23 N´m (200 in.
lbs.).
(4) Connect PCV and brake booster hoses.
(5) Inspect quick connect fittings for damage,
replace if necessary Refer to Group 14, Fuel System
for procedure. Apply a light amount of clean engine
oil to fuel inlet tube. Connect fuel supply hose to fuel
rail assembly. Check connection by pulling on connec-
tor to insure it locked into position.
(6) Install throttle body. Tighten fastener to 22
N´m (200 in. lbs.). Install transmission to throttle
body support bracket and tighten to 11.9 N´m (105
in. lbs.) at the throttle body first. Next tighten the
bracket at the transmission.
(7) Connect Manifold Absolute Pressure/Intake Air
Temperature Sensor (TMAP) wiring connector.
(8) Connect knock sensor connector, and wiring at
starter. Connect wiring harness to intake manifold
tab.
(9) Connect Idle Air Control (IAC) motor and
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) wiring connectors.
(10) Connect vacuum hoses to throttle body.
(11) Install accelerator, kickdown and speed con-
trol cables to their bracket and connect them to the
throttle lever. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System Throt-
tle Body Installation for procedure.
(12) Loose assemble the EGR tube onto valve and
intake manifold finger tight. Tighten tube fasteners
at the EGR valve first to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) then,
tighten the intake manifold side fasteners to 11 N´m
(95 in. lbs.).
(13) Install clean air duct to air filter housing.
Tighten clamp to 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
(14) Connect negative cable to battery.
(15) Install fresh air duct to air cleaner and
tighten wing nut.
(16) With the DRB scan tool use ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize system to check for leaks.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay will remain ener-
gized for 7 minutes or until the ignition switch is
turned to the OFF position, or Stop All Test is
selected.
Fig. 18 Knock Sensor
Fig. 19 EGR Tube Assembly
Fig. 20 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
11 - 8 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLDPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)