engine DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 852 of 1200

The hose clamps have rolled edges to prevent the
clamp from cutting into the hose. Only use clamps
that are original equipment or equivalent. Other
types of clamps may cut into the hoses and cause
high pressure fuel leaks. Tighten hose clamps to 1
N´m (10 in. lbs.) torque.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting
without the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean 30 weight engine
oil.
(3) Push the quick-connect fitting over the fuel
tube until theretainer seats and a click is heard.
(4) The plastic quick-connect fitting has windows
in the sides of the casing. When the fitting com-
pletely attaches to the fuel tube, the retainer locking
ears and the fuel tube shoulder are visible in the
windows. If they are not visible, the retainer was not
properly installed (Fig. 14).Do not rely upon the
audible click to confirm a secure connection.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or
until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.
(5) Use the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test
to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) (Fig. 15). The PDC is located next to the
battery in the engine compartment. For the location
of the relay within the PDC, refer to the PDC cover
for location. Check electrical terminals for corrosion
and repair as necessary.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
REMOVAL
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Drain the fuel. Refer to Draining Fuel Tank in
the Fuel Tank section of this group.
Fig. 14 Plastic Quick-Connect Fitting/Fuel Tube
Connection
Fig. 15 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 11
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 853 of 1200
WARNING: THE FUEL RESERVOIR OF THE FUEL
PUMP MODULE DOES NOT EMPTY OUT WHEN THE
TANK IS DRAINED. THE FUEL IN THE RESERVOIR
WILL SPILL OUT WHEN THE MODULE IS
REMOVED.
(2) Disconnect fuel line from fuel pump module by
depressing quick connect retainers with thumb and
fore finger.
(3) Slide fuel pump module electrical connecter
lock to unlock.
(4) Disconnect the electrical connection from the
fuel pump module, by pushing down on connector
retainer and pulling connector off of module.
(5) Use a transmission jack to support the fuel
tank. remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(6) Lower tank slightly.
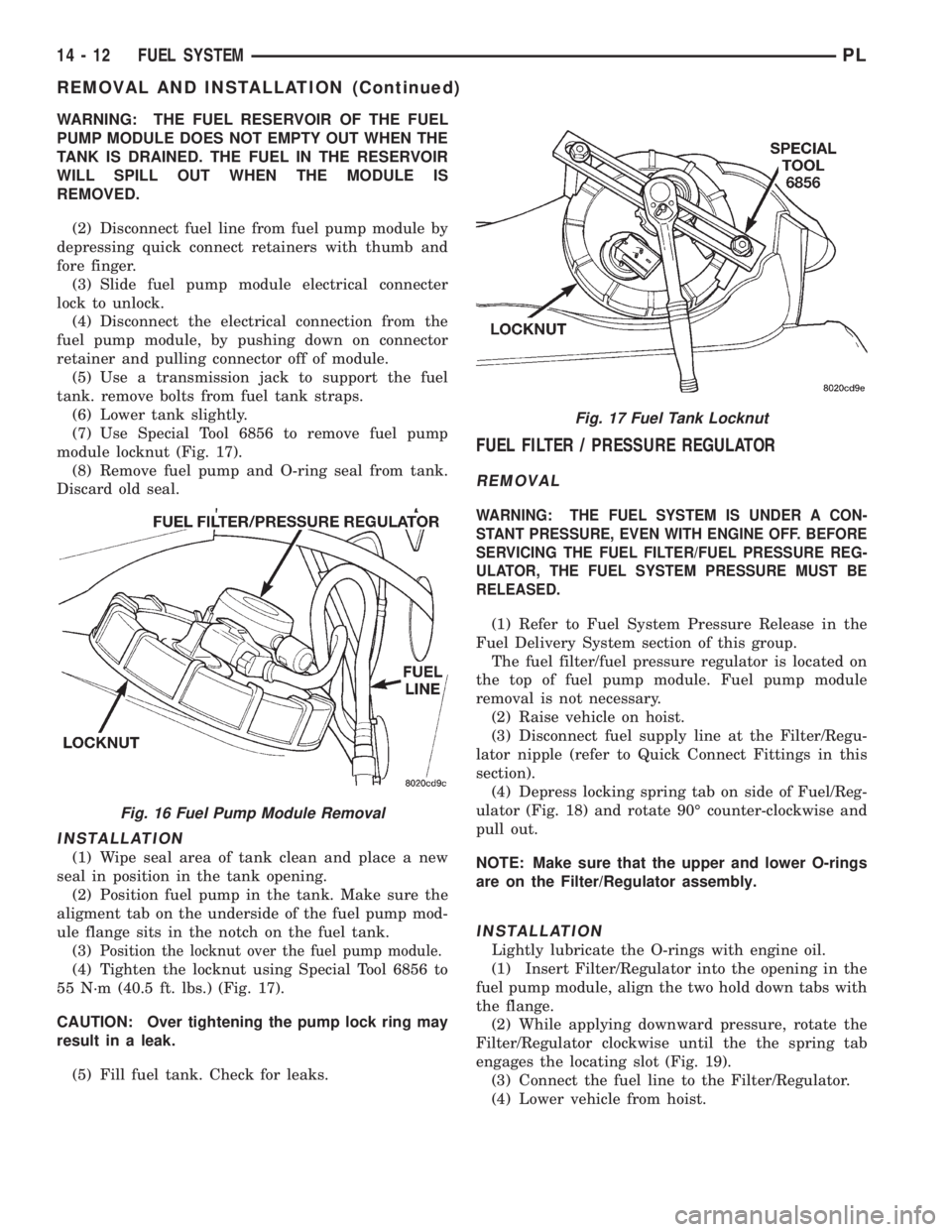
(7) Use Special Tool 6856 to remove fuel pump
module locknut (Fig. 17).
(8) Remove fuel pump and O-ring seal from tank.
Discard old seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Wipe seal area of tank clean and place a new
seal in position in the tank opening.
(2) Position fuel pump in the tank. Make sure the
aligment tab on the underside of the fuel pump mod-
ule flange sits in the notch on the fuel tank.
(3)
Position the locknut over the fuel pump module.
(4) Tighten the locknut using Special Tool 6856 to
55 N´m (40.5 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 17).
CAUTION: Over tightening the pump lock ring may
result in a leak.
(5) Fill fuel tank. Check for leaks.
FUEL FILTER / PRESSURE REGULATOR
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE, EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF. BEFORE
SERVICING THE FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REG-
ULATOR, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED.
(1) Refer to Fuel System Pressure Release in the
Fuel Delivery System section of this group.
The fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator is located on
the top of fuel pump module. Fuel pump module
removal is not necessary.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Disconnect fuel supply line at the Filter/Regu-
lator nipple (refer to Quick Connect Fittings in this
section).
(4) Depress locking spring tab on side of Fuel/Reg-
ulator (Fig. 18) and rotate 90É counter-clockwise and
pull out.
NOTE: Make sure that the upper and lower O-rings
are on the Filter/Regulator assembly.
INSTALLATION
Lightly lubricate the O-rings with engine oil.
(1) Insert Filter/Regulator into the opening in the
fuel pump module, align the two hold down tabs with
the flange.
(2) While applying downward pressure, rotate the
Filter/Regulator clockwise until the the spring tab
engages the locating slot (Fig. 19).
(3) Connect the fuel line to the Filter/Regulator.
(4) Lower vehicle from hoist.
Fig. 16 Fuel Pump Module Removal
Fig. 17 Fuel Tank Locknut
14 - 12 FUEL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 854 of 1200

FUEL PUMP INLET STRAINER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal in this section.
(2) Using a thin straight blade screwdriver, pry
back the locking tabs on fuel pump reservoir and
remove the strainer (Fig. 20).
(3) Remove strainer O-ring from the fuel pump
reservoir body.
(4) Remove any contaminants in the fuel tank by
washing the inside of the fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the strainer O-ring with clean engine
oil.
(2) Insert strainer O-ring into outlet of strainer so
that it sits evenly on the step inside the outlet.
(3) P
ush strainer onto the inlet of the fuel pump
reservoir body. Make sure the locking tabs on the res-
ervoir body lock over the locking tangs on the strainer.
(4) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Installation in this section.
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR
REMOVAL
Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module in this section.
(1) Depress retaining tab and remove the fuel
pump/level sensor connector from the bottom of the
fuel pump module electrical connector (Fig. 21).
(2) Pull off blue locking wedge (Fig. 22).
(3) Using a small screwdriver lift locking finger
away from terminal and push terminal out of connec-
tor (Fig. 23).
(4) Push level sensor signal and ground terminals
out of the connector (Fig. 24).
(5) Insert a screwdriver between the fuel pump
module and the top of the level sensor housing (Fig.
25). Push level sensor down slightly.
Fig. 18 Locking Spring Tab
Fig. 19 Spring Tab In Locating Slot
Fig. 20 Inlet Strainer Removal
Fig. 21 Fuel Pump/Level Sensor Electrical
Connector
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 13
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 856 of 1200

(5) Remove fuel rail mounting screws.
(6) Lift rail off of intake manifold. Cover the fuel
injector openings in the intake manifold.
(7) Remove fuel injector retainer (Fig. 28).
(8) Pull injector out of fuel rail. Replace fuel injec-
tor O-rings (Fig. 29).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of clean engine oil to the
upper O-ring.(2) Install injector in cup on fuel rail.
(3) Install retaining clip.
(4) Apply a light coating of clean engine oil to the
O-ring on the nozzle end of each injector.
(5) Insert fuel injector nozzles into openings in
intake manifold. Seat the injectors in place. Tighten
fuel rail mounting screws to 22.5 N´m63 N´m
(200630 in. lbs.).
(6) Attach electrical connectors to fuel injectors.
(7) Connect fuel supply tube to fuel rail. Refer to
Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery Section
of this Group.
FUEL TANK
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release.
(2) Drain fuel tank. Refer to Draining Fuel Tank
in this section (Fig. 30).
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND
HOSES TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(4) Disconnect fuel pump module electrical connec-
tor (Fig. 31).
(5) Disconnect the fuel tube from Fuel Filter/Reg-
ulator. Refer to Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel
Delivery section of this group.
(6) Support tank with transmission jack. Loosen
tank mounting straps and lower tank slightly.
(7) Disconnect fuel filler tube and filler vent tube
from filler hose at fuel tank (Fig. 32).
(8) Disconnect fuel filler vapor relief tube from tee
connecting it to the tank vapor relief tube and EVAP
canister tube.
(9) Disconnect vapor line from Evap canister tube.
(10) Remove tank mounting straps and lower tank.Fig. 27 Fuel Rail and Injectors
Fig. 28 Fuel Injector Retainer
Fig. 29 Fuel Injector O-Rings
Fig. 30 Fuel Tank
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 15
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 858 of 1200

(2) Disconnect vapor tube from rollover valve.
(3) Using a straight screwdriver, pry the valve out
of the grommet in the fuel filler tube.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of power steering fluid to
the grommet.
(2) Install valve in grommet.
(3) Attach vapor tube to valve.
(4) Install fuel filler tube cap.
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
CAUTION: When servicing the accelerator pedal,
throttle cable or speed control cable, do not dam-
age or kink the core wire inside the cable sheath-
ing.
REMOVAL
(1) Working from the engine compartment, remove
the throttle control shield.
(2) Hold the throttle body throttle lever in the
wide open position. Remove the throttle cable from
the throttle body cam.
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
remove the cable retainer and throttle cable from the
upper end of the pedal shaft (Fig. 35) and (Fig. 36).
(4) Working from the engine compartment, remove
nuts from accelerator pedal attaching studs (Fig. 35).
Remove assembly from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position accelerator pedal assembly on dash
panel. Install retaining nuts. Tighten retaining nuts
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.(2) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
install the throttle cable and cable retainer in the
upper end of the pedal shaft.
(3) From the engine compartment, hold the throt-
tle body lever in the wide open position and install
the throttle cable. Install the throttle control shield.
THROTTLE CABLEÐMANUAL TRANSMISSION
REMOVAL
(1) Remove throttle control shield (Fig. 37).
(2) Working from the engine compartment, remove
the throttle cable from the throttle body lever (Fig.
38) and (Fig. 39).
Fig. 35 Accelerator Pedal and Throttle CableÐFront
View
Fig. 36 Accelerator Pedal and Throttle CableÐRear
View
Fig. 37 Throttle Control Shield
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 859 of 1200

(3) Compress the retaining tabs on the cable and
slide cable out of bracket.
(4) From inside the vehicle, hold the accelerator
pedal up and remove the cable retainer and cable
from upper end of pedal shaft (Fig. 35) and (Fig. 36).
(5) Remove retainer clip from throttle cable and
grommet at the dash panel.
(6) From the engine compartment, pull the throttle
cable out of the dash panel grommet. The grommet
should remain in the dash panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) From the engine compartment, push the hous-
ing end fitting into the dash panel grommet.
(2) Install cable housing (throttle body end) into
the cable mounting bracket on the engine.
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up pedal and feed
throttle cable core wire through hole in upper end of
the pedal shaft. Install cable retainer.
(4) Install cable retainer clip.(5) From the engine compartment, rotate the
throttle lever forward to the wide open position and
install cable clasp (Fig. 39).
(6) Install throttle control shield (Fig. 37). Tighten
screw to 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
THROTTLE CABLEÐAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
REMOVAL
(1) Remove throttle control shield (Fig. 37).
(2) Working from the engine compartment, remove
throttle cable from throttle body cam (Fig. 40) and
(Fig. 41).
(3) Compress the retaining tabs on the cable and
slide cable out of bracket.
(4) From inside the vehicle, hold the throttle pedal
up and remove the cable retainer and cable from
upper end of pedal shaft (Fig. 35) and (Fig. 36).
(5) Remove retainer clip from throttle cable and
grommet at the dash panel.
Fig. 38 Throttle Cable Attachment to Throttle Body
Fig. 39 Disconnecting Throttle Cable
Fig. 40 Throttle Body Cables Attachment to Throttle
Body
Fig. 41 Disconnecting Throttle Cable
14 - 18 FUEL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 860 of 1200

(6) From the engine compartment, pull the throttle
cable out of the dash panel grommet. The grommet
should remain in the dash panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) From the engine compartment, push the hous-
ing end fitting into the dash panel grommet.
(2) Install cable housing (throttle body end) into
the cable mounting bracket on the engine.
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up pedal and feed
throttle cable core wire through hole in upper end of
the pedal shaft. Install cable retainer (Fig. 36).
(4) Install cable retainer clip.
(5) From the engine compartment, rotate the
throttle lever forward to the wide open position and
install cable clasp (Fig. 41).
(6) Install throttle control shield (Fig. 37). Tighten
to 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Accelerator Pedal to Dash Nuts...........12N´m
(105 in. lbs.)
Fuel Pump Module Locknut.....55N´m(40ft.lbs.)
Fuel Tank Strap Bolts.......22.5 N´m (200 in. lbs.)
Fuel Rail Bolts..............23N´m(195 in. lbs.)
Ignition Coil Mounting Bolts....11N´m(95in.lbs.)
Intake Manifold Bolts..........11N´m(95in.lbs.)
Throttle Control Shield........5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.)
FUEL TANK CAPACITY
Vehicle Liters U.S. Gallons
PL 47 12.5
Nominal refill capacities are shown. A variation may be
observed from vehicle to vehicle due to manufacturing
tolerance and refill procedure.
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 861 of 1200

FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 21
MODES OF OPERATION.................. 21
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
AIR CONDITIONING CLUTCH RELAYÐ
PCM OUTPUT......................... 31
AIR CONDITIONING PRESSURE
TRANSDUCERÐPCM INPUT............. 25
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) SENSEÐ
PCM INPUT........................... 25
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAYÐ
PCM OUTPUT......................... 32
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSORÐ
PCM INPUT........................... 25
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT........... 25
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT.............. 25
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT . 25
CHARGING SYSTEM INDICATOR LAMPÐ
PCM OUTPUT......................... 32
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐ
PCM INPUT........................... 26
DATA LINK CONNECTOR.................. 33
DUTY CYCLE EVAP PURGE SOLENOIDÐ
PCM OUTPUT......................... 32
ELECTRIC EGR TRANSDUCERÐ
PCM OUTPUT......................... 32
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐ
PCM INPUT........................... 26
FUEL INJECTORSÐPCM OUTPUT.......... 34
FUEL LEVEL SENSORÐPCM INPUT......... 27
FUEL PUMP RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT......... 32
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT......... 33
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S SENSOR)Ð
PCM INPUT........................... 27
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT . . 33
IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSEÐPCM INPUT..... 28
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT............. 34
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSORÐ
PCM INPUT........................... 28
KNOCK SENSORÐPCM INPUT............. 29
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE)
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT.................. 34
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSORÐPCM INPUT.................. 29
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCHÐ
PCM INPUT........................... 30
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER........... 23
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCHÐ
PCM INPUT........................... 30
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE.......... 24SCI RECEIVEÐPCM INPUT................ 30
SCI RECEIVEÐPCM OUTPUT.............. 35
SENSOR RETURNÐPCM INPUT............ 30
SOLID STATE FAN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT.... 35
SPEED CONTROL SERVOSÐPCM OUTPUT . . . 30
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUT............ 35
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS..................... 23
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT............. 35
THROTTLE POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT . 30
TORQUE CONVERTOR CLUTCH SOLENOIDÐ
PCM OUTPUT......................... 35
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT..... 30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ASD AND FUEL PUMP RELAYS............. 46
CAMSHAFT AND CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR............................. 47
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR . . 47
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR............... 47
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) MOTOR TEST...... 47
KNOCK SENSOR........................ 47
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSOR............................. 48
THROTTLE BODY MINIMUM AIR FLOW....... 48
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR............ 48
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR................ 49
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐDOHC.............. 40
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐSOHC.............. 35
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT.................. 55
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR............ 54
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR.......... 54
DOWNSTREAM HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR . . . 55
DUTY CYCLE EVAP PURGE SOLENOID VALVE . 53
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR . . 56
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR............... 52
KNOCK SENSOR........................ 57
MAP/IAT SENSORÐDOHC................. 53
MAP/IAT SENSORÐSOHC................. 53
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM).... 54
THROTTLE BODYÐAUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION....................... 50
THROTTLE BODYÐMANUAL TRANSMISSION . 50
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)....... 52
UPSTREAM HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR...... 54
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR................ 56
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE.............................. 57
VECI LABEL............................ 57
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL................................. 57
14 - 20 FUEL SYSTEMPL
Page 862 of 1200

GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygen
sensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35É the PCM will wait 44
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait
11 seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than .745
volts or less than .1 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 21
Page 863 of 1200

ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay. The following
actions occur when the starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays. If
the PCM does not receive both signals within approx-
imately one second, it will not energize the ASD
relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel pump
relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump, fuel
injectors, ignition coil and heated oxygen sensors.
²The PCM energizes all four injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within664 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode. If
the PCM does not detect a minimum difference
between the two values, it sets a MAP diagnostic
trouble code into memory.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine RPM
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch
²Battery voltage²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²Both O2 sensors
²All diagnostics
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²A/C control positions
²Power steering pressure switch
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor
²Purge system monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to Group 25 for
On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)