radiator DODGE NEON 1999 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 680 of 1200
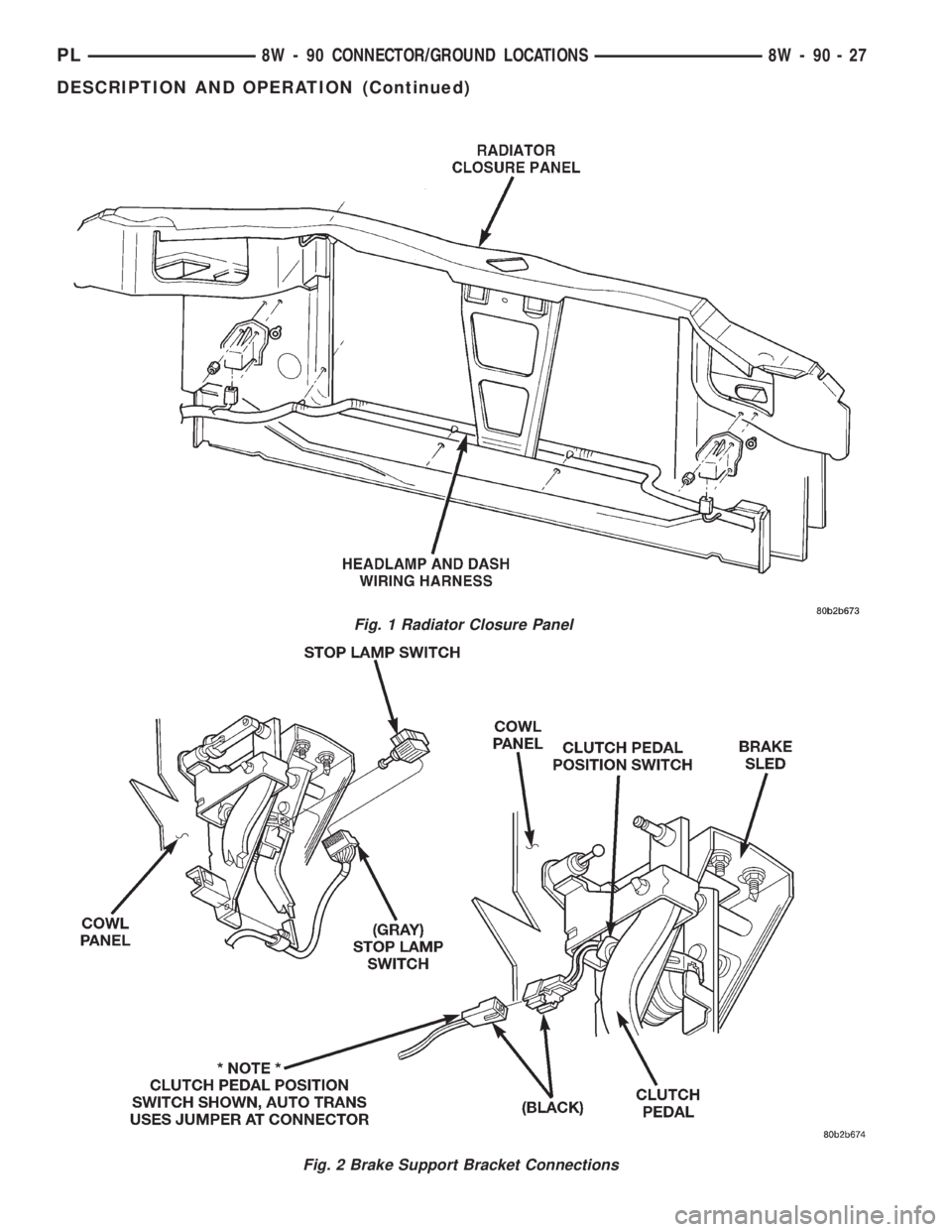
Fig. 1 Radiator Closure Panel
Fig. 2 Brake Support Bracket Connections
PL8W - 90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONS 8W - 90 - 27
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 694 of 1200
8W-95 SPLICE LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
This section provides illustrations identifying the
general location of the splices in this vehicle. A splice
index is provided. Use the wiring diagrams in each
section for splice number identification. Refer to the
index for proper splice number.
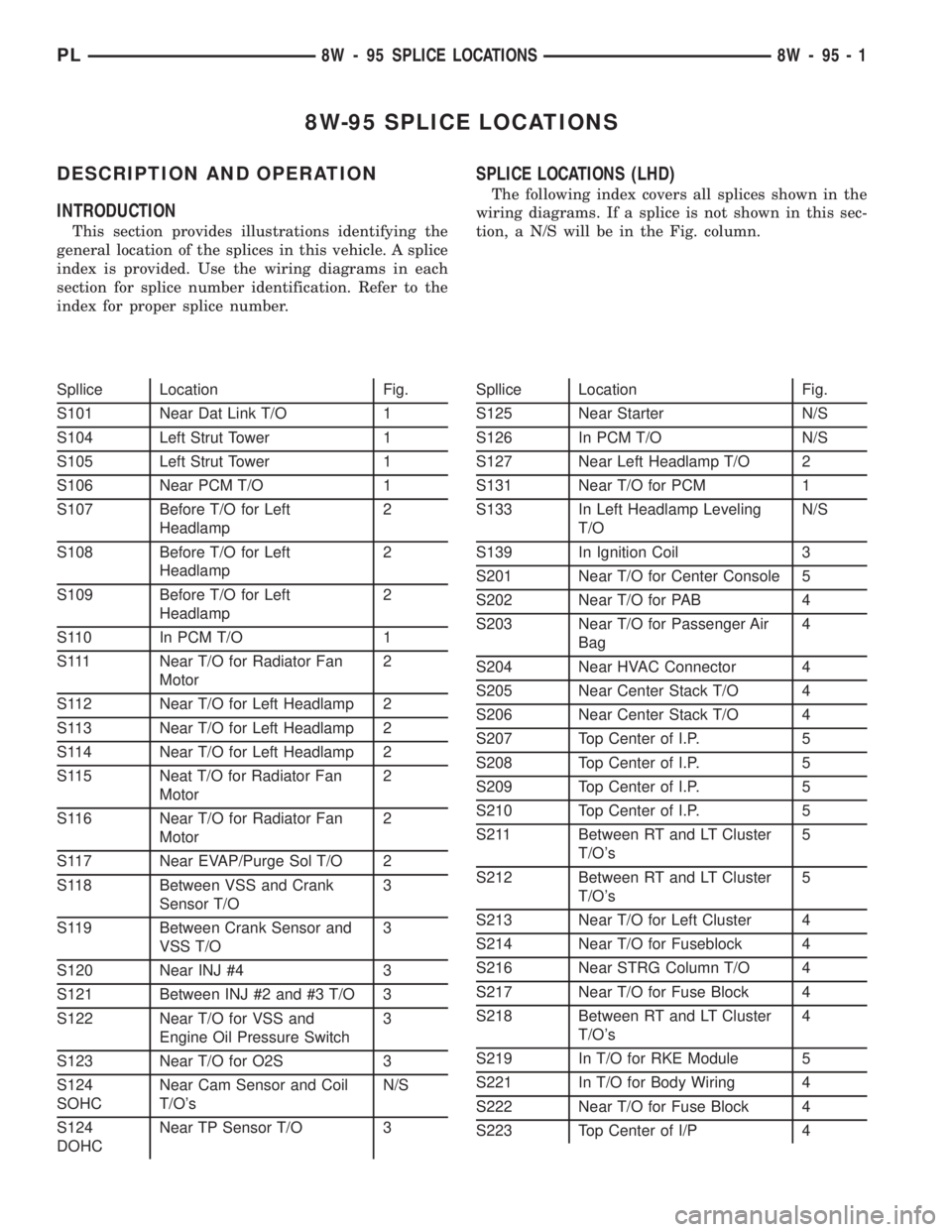
SPLICE LOCATIONS (LHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S101 Near Dat Link T/O 1
S104 Left Strut Tower 1
S105 Left Strut Tower 1
S106 Near PCM T/O 1
S107 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S108 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S109 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S110 In PCM T/O 1
S111 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S112 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S113 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S114 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S115 Neat T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S116 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S117 Near EVAP/Purge Sol T/O 2
S118 Between VSS and Crank
Sensor T/O3
S119 Between Crank Sensor and
VSS T/O3
S120 Near INJ #4 3
S121 Between INJ #2 and #3 T/O 3
S122 Near T/O for VSS and
Engine Oil Pressure Switch3
S123 Near T/O for O2S 3
S124
SOHCNear Cam Sensor and Coil
T/O'sN/S
S124
DOHCNear TP Sensor T/O 3Spllice Location Fig.
S125 Near Starter N/S
S126 In PCM T/O N/S
S127 Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S131 Near T/O for PCM 1
S133 In Left Headlamp Leveling
T/ON/S
S139 In Ignition Coil 3
S201 Near T/O for Center Console 5
S202 Near T/O for PAB 4
S203 Near T/O for Passenger Air
Bag4
S204 Near HVAC Connector 4
S205 Near Center Stack T/O 4
S206 Near Center Stack T/O 4
S207 Top Center of I.P. 5
S208 Top Center of I.P. 5
S209 Top Center of I.P. 5
S210 Top Center of I.P. 5
S211 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's5
S212 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's5
S213 Near T/O for Left Cluster 4
S214 Near T/O for Fuseblock 4
S216 Near STRG Column T/O 4
S217 Near T/O for Fuse Block 4
S218 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S219 In T/O for RKE Module 5
S221 In T/O for Body Wiring 4
S222 Near T/O for Fuse Block 4
S223 Top Center of I/P 4
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 1
Page 704 of 1200
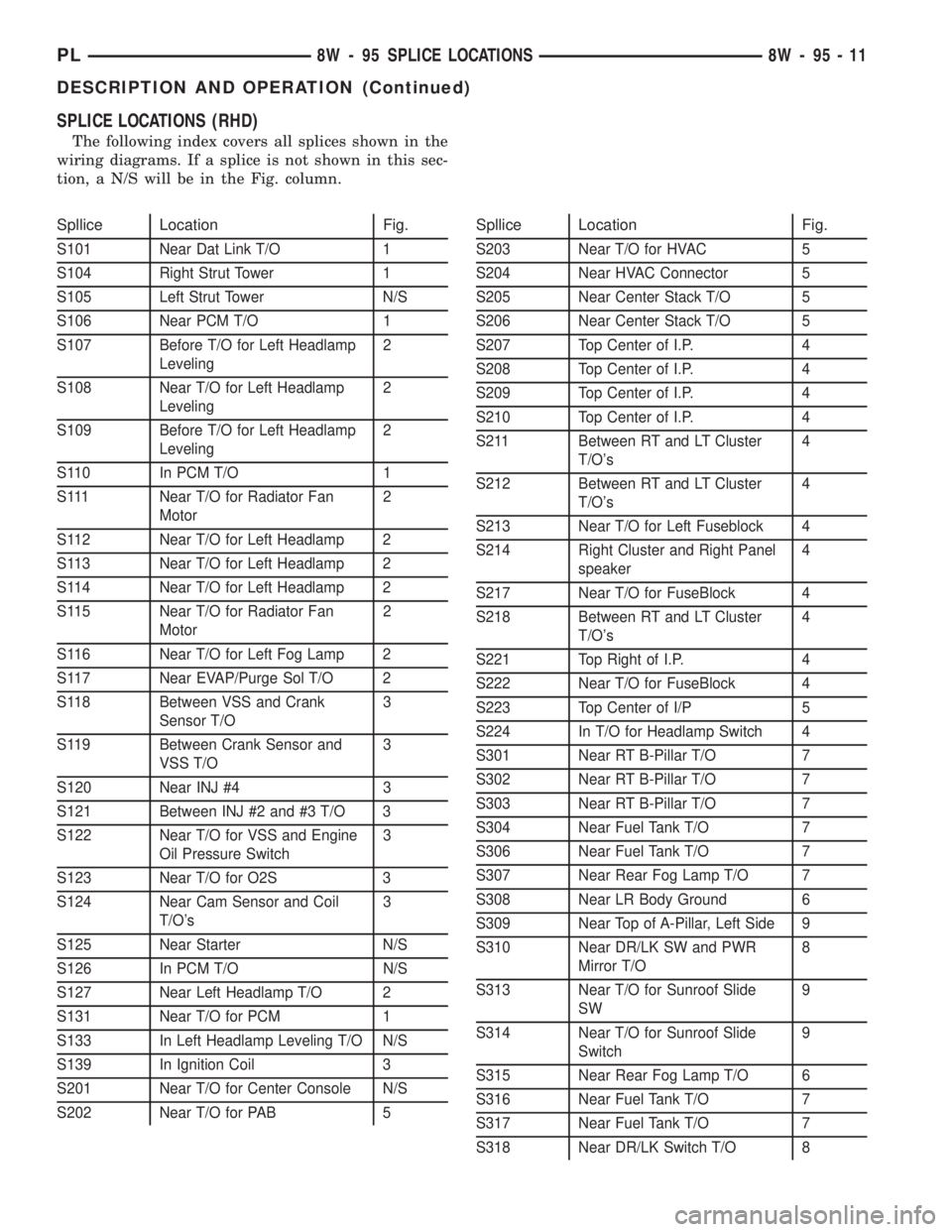
SPLICE LOCATIONS (RHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S101 Near Dat Link T/O 1
S104 Right Strut Tower 1
S105 Left Strut Tower N/S
S106 Near PCM T/O 1
S107 Before T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S108 Near T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S109 Before T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S110 In PCM T/O 1
S111 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S112 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S113 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S114 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S115 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S116 Near T/O for Left Fog Lamp 2
S117 Near EVAP/Purge Sol T/O 2
S118 Between VSS and Crank
Sensor T/O3
S119 Between Crank Sensor and
VSS T/O3
S120 Near INJ #4 3
S121 Between INJ #2 and #3 T/O 3
S122 Near T/O for VSS and Engine
Oil Pressure Switch3
S123 Near T/O for O2S 3
S124 Near Cam Sensor and Coil
T/O's3
S125 Near Starter N/S
S126 In PCM T/O N/S
S127 Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S131 Near T/O for PCM 1
S133 In Left Headlamp Leveling T/O N/S
S139 In Ignition Coil 3
S201 Near T/O for Center Console N/S
S202 Near T/O for PAB 5
Spllice Location Fig.
S203 Near T/O for HVAC 5
S204 Near HVAC Connector 5
S205 Near Center Stack T/O 5
S206 Near Center Stack T/O 5
S207 Top Center of I.P. 4
S208 Top Center of I.P. 4
S209 Top Center of I.P. 4
S210 Top Center of I.P. 4
S211 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S212 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S213 Near T/O for Left Fuseblock 4
S214 Right Cluster and Right Panel
speaker4
S217 Near T/O for FuseBlock 4
S218 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S221 Top Right of I.P. 4
S222 Near T/O for FuseBlock 4
S223 Top Center of I/P 5
S224 In T/O for Headlamp Switch 4
S301 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S302 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S303 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S304 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S306 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S307 Near Rear Fog Lamp T/O 7
S308 Near LR Body Ground 6
S309 Near Top of A-Pillar, Left Side 9
S310 Near DR/LK SW and PWR
Mirror T/O8
S313 Near T/O for Sunroof Slide
SW9
S314 Near T/O for Sunroof Slide
Switch9
S315 Near Rear Fog Lamp T/O 6
S316 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S317 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S318 Near DR/LK Switch T/O 8
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 721 of 1200

cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
(11) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary
and adjust gap as specified in Group 8, Electrical.
Tighten to specifications.
(12) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System Secondary Cir-
cuit Inspection.
(13) Test coil output voltage, primary and second-
ary resistance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System.
(14) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and differ-
ent RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(15) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance,.
(16) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(17) Inspect and adjust accessory belt drives refer-
ring to Group 7, Cooling System, Accessory Drive
Belts for proper adjustments.
(18) Road test vehicle as a final test.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1 379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor pressed into the vertical oil
passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected rocker arms (sohc) or lash
adjuster (dohc) and replace.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
9 - 8 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 727 of 1200

MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to connecting
rod journals.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up into the cylin-
der head. The rocker shafts route oil to the rocker
arms/hydraulic lash adjuster assemblies.
SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
B LY:A partial open deck is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4 mm. The bedplate
incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFT:A nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket trans-
mits crankshaft movement, via timing belt to the
camshaft sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONS:The SOHC EngineDOES NOThave
provision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hex
head cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly. Pistons And Connecting
rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGS:The piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package consist of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADÐSOHC:It features a Single
Over Head Camshaft, four-valves per cylinder cross
flow design. The valves are arranged in two inlinebanks, with the two intake per cylinder facing
toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFTÐSOHC:The nodular iron camshaft
has five bearing journals and 3 cam lobes per cylin-
der. Provision for cam position sensor on the cam at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVESÐSOHC:Four valves per cylinder are
actuated by roller rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjust-
ers assemblies which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All
valves have 6 mm diameter chrome plated valve
stems. The valve train has 33 mm (1.299 inch) diam-
eter intake valves and 28 mm (1.10 inch) diameter
exhaust valves. Viton rubber valve stem seals are
integral with spring seats. Valve springs, spring
retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The intake manifold is a
molded plastic composition, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch design
enhances low and mid-range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD:The exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 3). The cylin-
der bore out-of-round is 0.050 mm (.002 inch)
maximum and cylinder bore taper is 0.051 mm (0.002
9 - 14 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 731 of 1200

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ENGINE MOUNTÐFRONT
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Support the engine and transmission assembly
with a floor jack so it will not rotate.
(3) Remove the front engine mount thru-bolt from
the insulator and engine mount bracket (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove the mass damper. Remove the front
mount nuts and remove insulator assembly.
(5) Remove the engine mount bracket, if necessary.
(6) Reverse removal procedure for installation and
tighten fasteners in this order.
a. If engine mount bracket was removed, tighten
bolt 1 to 3 N´m (20 in. lbs.) and bolts 2, 3 and 4 to
108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 10).
b. If engine mount bracket was removed, tighten
bolts 5 and 1 to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
c. Tighten engine mount bracket to insulator
assembly thru-bolt to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
d. Tighten insulator assembly nuts to the lower
radiator crossmember torque to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
e. Install mass damper and tighten to 54 N´m (40
ft. lbs.).
ENGINE MOUNTÐLEFT
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and remove left front
wheel.
(2) Remove the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
on manual transaxle model, from battery tray mount
and lay aside.
(3) Support the transmission with a transmission
jack.(4) Remove the thru-bolt access hole cover. Remove
the insulator thru-bolt from the mount (Fig. 11).
(5) Remove the transmission mount fasteners and
remove mount.
(6) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
Tighten fasteners in this order (Fig. 11):
²55 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
²108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.)
ENGINE MOUNTÐRIGHT
(1) Remove the purge duty solenoid from engine
mount bracket.
(2) Remove the right engine mount insulator verti-
cal fasteners from frame rail (Fig. 12).
(3) Remove the load on the engine mounts by care-
fully supporting the engine and transmission assem-
bly with a floor jack.
(4) Remove the thru-bolt access hole cover. Remove
the thru-bolt from the insulator assembly (Fig. 12).
Remove insulator.
(5) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
Tighten engine mount to rail fasteners to 54 N´m (40
ft. lbs.), then tighten engine mount to engine bracket
thru-bolt to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
POWER HOP DAMPER
NOTE: Power hop damper is used on manual trans-
mission vehicle only.
(1) Remove the thru-bolt and nut from the front
suspension crossmember (Fig. 13).
(2) Remove the damper nut and grommets.
Remove the damper.
Fig. 10 Engine MountingÐFront
Fig. 11 Engine MountingÐLeft
9 - 18 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
Page 732 of 1200
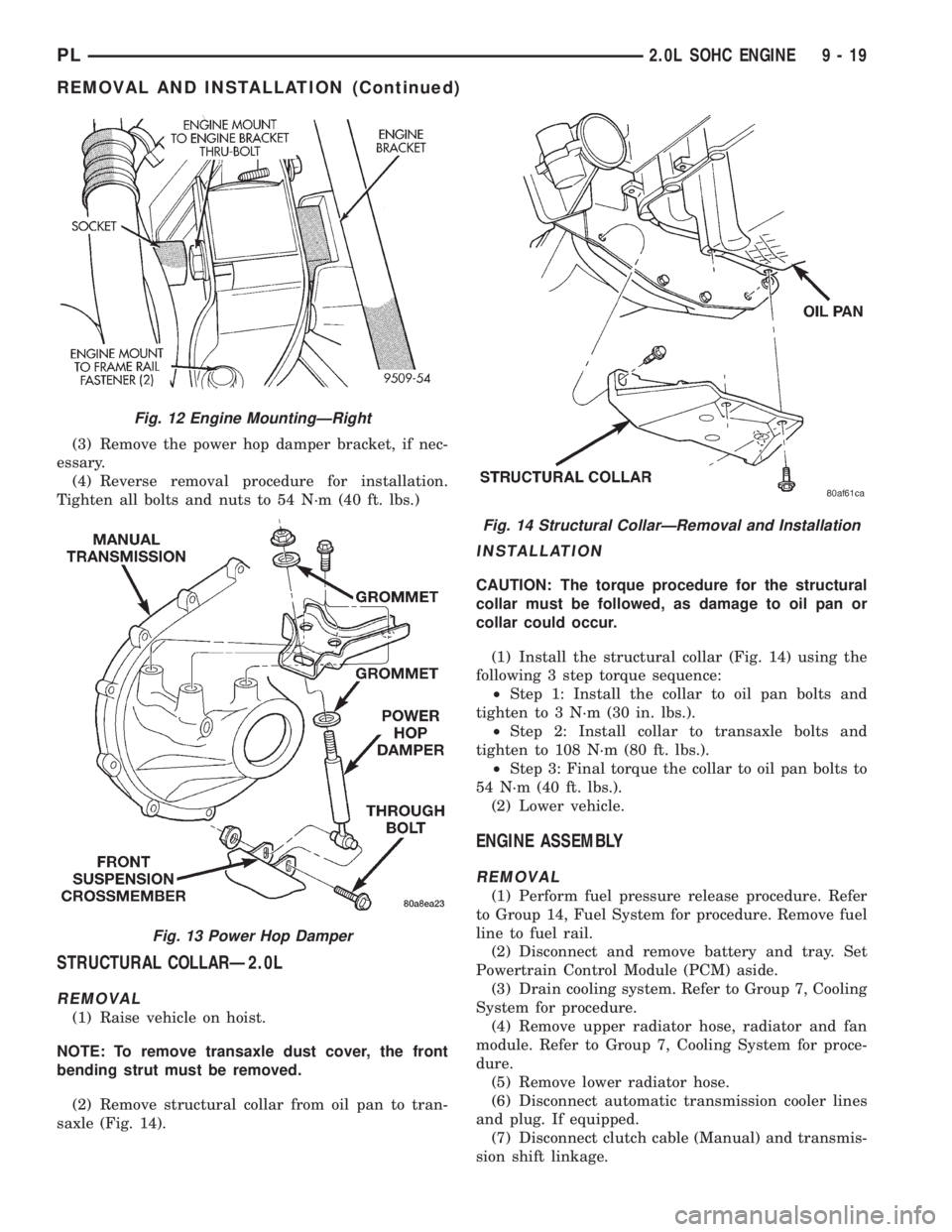
(3) Remove the power hop damper bracket, if nec-
essary.
(4) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
Tighten all bolts and nuts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
STRUCTURAL COLLARÐ2.0L
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
NOTE: To remove transaxle dust cover, the front
bending strut must be removed.
(2) Remove structural collar from oil pan to tran-
saxle (Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The torque procedure for the structural
collar must be followed, as damage to oil pan or
collar could occur.
(1) Install the structural collar (Fig. 14) using the
following 3 step torque sequence:
²Step 1: Install the collar to oil pan bolts and
tighten to 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
²Step 2: Install collar to transaxle bolts and
tighten to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
²Step 3: Final torque the collar to oil pan bolts to
54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(2) Lower vehicle.
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Group 14, Fuel System for procedure. Remove fuel
line to fuel rail.
(2) Disconnect and remove battery and tray. Set
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) aside.
(3) Drain cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System for procedure.
(4) Remove upper radiator hose, radiator and fan
module. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System for proce-
dure.
(5) Remove lower radiator hose.
(6) Disconnect automatic transmission cooler lines
and plug. If equipped.
(7) Disconnect clutch cable (Manual) and transmis-
sion shift linkage.
Fig. 12 Engine MountingÐRight
Fig. 13 Power Hop Damper
Fig. 14 Structural CollarÐRemoval and Installation
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 734 of 1200

(8) Install A/C compressor and hoses. Refer to
Group 24, Heater and Air Conditioning for procedure.
(9) Install accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System Accessory Drive Section for belt ten-
sion adjustment.
(10) Install front engine mount. Refer to this sec-
tion for procedure.
(11) Manual transmission: Install power hop
damper.
(12) Install inner splash shield. Install wheels and
tires.
(13)Manual Transmission:Connect clutch cable
and linkages. Refer to Group 6, Manual Transaxle
Clutch.
(14)Automatic Transmission:Connect shifter
and kickdown linkage. Refer to Group 21, Transaxle
for procedures.
(15) Connect fuel line and heater hoses.
(16) Install ground straps. Connect engine and
throttle body connections and harnesses. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical for procedure.
(17) Connect throttle body linkage. Refer to Group
14, Fuel System for procedure.
(18) Install radiator and shroud assembly. Install
radiator hoses. Fill cooling system. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for filling procedure.
(19) Install battery tray and battery. Set Power-
train Control Module (PCM) into place.
(20) Install air cleaner and hoses.
(21) Install oil filter. Fill engine crankcase with
proper oil to correct level.
(22) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
(23) Start engine and run until operating temper-
ature is reached.
(24) Adjust transmission linkage, if necessary.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner inlet duct (Fig. 17)
(2) Remove ignition coil pack (Fig. 18).
(3) Remove the cylinder head cover bolts.
(4) Remove cylinder head cover from cylinder
head.
INSTALLATION
Before installation, clean cylinder head and cover
mating surfaces. Make certain the cylinder head
cover mating surface is flat.
(1) Install new cylinder head cover gasket.
CAUTION: Do not allow oil or solvents to contact
the timing belt as they can deteriorate the rubber
and cause tooth skipping.
(2) Install cover assembly to head and tighten fas-
teners to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Install ignition coil pack. Tighten fasteners to
23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
SPARK PLUG TUBE
(1) Remove cylinder head cover. Refer to procedure
outlined in this section.
(2) Using locking pliers remove the tube from the
cylinder head (Fig. 19). Discard old tube.
(3) Clean area around spark plug with Mopart
parts cleaner or equivalent.
Fig. 17 Inlet Duct Removal
Fig. 18 Ignition Coil Pack
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 21
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 773 of 1200

incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFTA nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket pro-
vides motive power; via timing belt to the camshaft
sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONSThe DOHC EngineDO NOThave pro-
vision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hex
head cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly.
PISTON RINGSThe piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package contains of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADFeatures a Dual Over Head
Camshaft (DOHC), 4 valves per cylinder cross flow
design. The valves are arranged in two in-line banks,
with the ports of the bank of two intake valves per
cylinder facing toward the radiator side of engine
and ports of the bank of two exhaust valves per cyl-
inder facing toward the dash panel. Incorporates
powder metal valve guides and seats. Integral oil gal-
leys within the cylinder head supplies oil to the
hydraulic lash adjusters, camshaft and valve mecha-
nisms.
CAMSHAFTSThe nodular iron camshafts have
six bearing journals and 2 cam lobes per cylinder.
Flanges at the rear journals control camshaft end
play. Provision for cam position sensor is located on
the intake camshaft at the rear of cylinder head. A
hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control at the
front of the camshaft.
VA LV E SFour valves per cylinder are actuated by
roller cam followers which pivot on stationary
hydraulic lash adjusters. All valves have 6 mm diam-
eter chrome plated valve stems. The valve sizes are
34.8 mm (1.370 inch.) diameter intake valves and
30.5 mm (1.20 inch.) diameter exhaust valves. Viton
rubber valve stem seals are integral with the springseats. Valve springs, spring retainers, and locks are
conventional.
INTAKE MANIFOLDThe intake manifold is a
two piece aluminum casting, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch fan design
enhances low and mid-speed torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDThe exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
If any of the following parts have been changed or
replaced:
²Camshaft
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Camshaft Position Sensor Target Magnet
²Cylinder Block
²Cylinder Head
²Water Pump
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Timing Belt and Timing Belt Tensioner
The camshaft and crankshaft timing relearn proce-
dure must be performed. Refer to the component
Removal and Installation procedure outlined in this
Group.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 4). The cylin-
der bore out-of-round is 0.050 mm (.002 inch)
maximum and cylinder bore taper is 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) maximum. If the cylinder walls are badly
scuffed or scored, the cylinder block should be
rebored and honed, and new pistons and rings fitted.
Whatever type of boring equipment is used, boring
and honing operation should be closely coordinated
9 - 60 2.0L DOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 776 of 1200

CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
DIAL INDICATOR METHOD
(1) Mount a dial indicator to front of engine, locat-
ing probe on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 10).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move crankshaft all the way to the front and
read the dial indicator. Refer to Crankshaft Specifi-
cation Chart for specifications.
FEELER GAGE METHOD
(1) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel using a lever inserted between a main bearing
cap and a crankshaft cheek, using care not to dam-
age any bearing surface. Donotloosen main bearing
cap.
(2) Use a feeler gauge between number three
thrust bearing and machined crankshaft surface to
determine end play.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ENGINE MOUNTÐFRONT
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Support the engine and transmission assembly
with a floor jack so it will not rotate.
(3) Remove the front engine mount thru-bolt from
the insulator and engine mount bracket (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove the mass damper. Remove the front
mount nuts and remove insulator assembly.
(5) Remove the engine mount bracket, if necessary.
(6) Reverse removal procedure for installation and
tighten fasteners in this order.
a. If engine mount bracket was removed, tighten
bolt 1 to 3 N´m (20 in. lbs.) and bolts 2, 3 and 4 to
108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 11).
b. If engine mount bracket was removed, tighten
bolts 5 and 1 to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
c. Tighten engine mount bracket to insulator
assembly thru-bolt to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
d. Tighten insulator assembly nuts to the lower
radiator crossmember torque to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
e. Install mass damper and tighten to 54 N´m (40
ft. lbs.)
ENGINE MOUNTÐLEFT
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and remove left front
wheel.
(2) Remove the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
on manual transaxle model, from battery tray mount
and lay aside.
(3) Support the transmission with a transmission
jack.
(4) Remove the thru-bolt access hole cover. Remove
the insulator thru-bolt from the mount (Fig. 12).
(5) Remove the transmission mount fasteners and
remove mount.
(6) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
Tighten fasteners in this order (Fig. 12):
²55 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
²108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.)
CRANKSHAFT SPECIFICATION CHART
Crankshaft End-PlayNew Part: 0.09 - 0.24 mm (0.0035 - 0.0094 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.37 mm (0.015 in.)
Main Bearing ClearanceNew Part: 0.022 - 0.062 mm (0.0008 - 0.0024 in.)
Connecting Rod Bearing
ClearanceNew Part: 0.026 - 0.059 mm (0.001 - 0.0023 in.)
Wear Limit: 0.075 mm (0.003 in.)
Main Bearing Journal DiameterStandard: 52.00060.008 mm (2.047260.0003 in.)
1st Undersize: 51.98360.008 mm (2.046660.0003 in.)
Connecting Rod Journal
DiameterStandard: 48.00060.008 mm (1.889760.0003 in.)
1st Undersize: 47.98360.008 mm (1.889160.0003 in.)
Fig. 10 Checking Crankshaft End PlayÐ Dial
Indicator
PL2.0L DOHC ENGINE 9 - 63
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)