battery DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 4 of 1200

MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 3
SCHEDULE ± A.......................... 3SCHEDULE ± B.......................... 4
UNSCHEDULED INSPECTION............... 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
Service and maintenance procedures for compo-
nents and systems listed in Schedule ± A or B can be
found by using the Group Tab Locator index at the
front of this manual. If it is not clear which group
contains the information needed, refer to the index at
the back of this manual.
There are two maintenance schedules that show
proper service based on the conditions that the vehi-
cle is subjected to. Use the schedule that best
describes these conditions.
Schedule ±A, lists maintenance recommended for
vehicles used for general transportation.
Schedule ±B, lists maintenance recommended for
vehicles used under the following conditions:
²Frequent short trip driving less than 5 miles (8
km)
²Frequent driving in dusty conditions
²Frequent trailer towing
²Extensive idling
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 90ÉF (32ÉC)
Where time and mileage are listed, follow the
interval that occurs first.
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
The scheduled emission maintenance listed inbold
typeon the Maintenance Schedules, must be done at
the mileage specified to assure the continued proper
functioning of the emission control system. These,
and all other maintenance services included in this
manual, should be done to provide the best vehicle
performance and reliability. More frequent mainte-
nance may be needed for vehicles in severe operating
conditions such as dusty areas and very short trip
driving.
UNSCHEDULED INSPECTION
At Each Stop For Fuel
²Check engine oil level, add as required.
²Check windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once A Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Inspect battery, clean, and tighten terminals as
required.
²Check fluid levels of coolant reservoir, power
steering and automatic transmission and add as
required.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
²Inspect exhaust system.
²Inspect brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents.
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown on Schedule ± A (7,500 miles) or every other
interval shown on schedule ± B (6,000 miles).
²Check coolant level, hoses and clamps.
²Check the manual transaxle fluid level.
²If the mileage is less than 7,500 miles (12 000
km) yearly, replace the engine oil filter at each oil
change.
SCHEDULE ± A
7,500 Miles (12 000 km) or at 6 months
²Change engine oil.
15,000 Miles (24 000 km) or at 12 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
22,500 Miles (36 000 km) or at 18 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
30,000 Miles (48 000 km) or at 24 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate front suspension ball joints.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
PLLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 3
Page 8 of 1200

JUMP STARTING, TOWING AND HOISTING
INDEX
page page
SERVICE PROCEDURES
HOISTING RECOMMENDATIONS............ 9JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE.............. 7
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS.............. 8
SERVICE PROCEDURES
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN GROUP 8A, BATTERY/START-
ING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS. DO NOT
JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY, PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT JUMP START WHEN
MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERY INDICATOR DOT IS
YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR. DO NOT JUMP
START A VEHICLE WHEN THE BATTERY FLUID IS
BELOW THE TOP OF LEAD PLATES. DO NOT
ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO TOUCH
EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A BOOSTER
SOURCE. DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY. REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON
HANDS OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCI-
DENTAL ARCING OF BATTERY CURRENT. WHEN
USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING DEVICE, DO
NOT ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO EXCEED 16
VOLTS. REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED
WITH DEVICE BEING USED.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually
inspect engine compartment for:
²Battery cable clamp condition, clean if necessary.
²Frozen battery.
²Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
²Low battery fluid level.
²Generator drive belt condition and tension.
²Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, park the booster vehicle within cable reach.
Turn off all accessories, set the parking brake, placethe automatic transmission in PARK or the manual
transmission in NEUTRAL and turn the ignition
OFF.
(3) On disabled vehicle, place gear selector in park
or neutral and set park brake. Turn off all accesso-
ries.
(4) Connect jumper cables to booster battery. RED
clamp to positive terminal (+). BLACK clamp to neg-
ative terminal (-). DO NOT allow clamps at opposite
end of cables to touch, electrical arc will result.
Review all warnings in this procedure.
(5) On disabled vehicle, connect RED jumper cable
clamp to positive (+) terminal. Connect BLACK
jumper cable clamp to engine ground as close to the
ground cable attaching point as possible (Fig. 1).
(6) Start the engine in the vehicle which has the
booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes,
then start the engine in the vehicle with the dis-
charged battery.
CAUTION: Do not crank starter motor on disabled
vehicle for more than 15 seconds, starter will over-
heat and could fail.
(7) Allow battery in disabled vehicle to charge to
at least 12.4 volts (75% charge) before attempting to
start engine. If engine does not start within 15 sec-
onds, stop cranking engine and allow starter to cool
(15 min.), before cranking again.
Fig. 1 Jumper Cable Clamp Connections
PLLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
Page 9 of 1200

DISCONNECT CABLE CLAMPS AS FOLLOWS:
²Disconnect BLACK cable clamp from engine
ground on disabled vehicle.
²When using a Booster vehicle, disconnect
BLACK cable clamp from battery negative terminal.
Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery positive
terminal.
²Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery posi-
tive terminal on disabled vehicle.
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW TOWING ATTACH-
MENT DEVICES TO CONTACT THE FUEL TANK OR
LINES, FUEL LEAK CAN RESULT. DO NOT LIFT OR
TOW VEHICLE BY FRONT OR REAR BUMPER, OR
BUMPER ENERGY ABSORBER UNITS. DO NOT
VENTURE UNDER A LIFTED VEHICLE IF NOT SUP-
PORTED PROPERLY ON SAFETY STANDS. DO NOT
ALLOW PASSENGERS TO RIDE IN A TOWED VEHI-
CLE. USE A SAFETY CHAIN THAT IS INDEPENDENT
FROM THE TOWING ATTACHMENT DEVICE.
CAUTION: Do not damage brake lines, exhaust
system, shock absorbers, sway bars, or any other
under vehicle components when attaching towing
device to vehicle. Do not attach towing device to
front or rear suspension components. Do not
secure vehicle to towing device by the use of front
or rear suspension or steering components.
Remove or secure loose or protruding objects from
a damaged vehicle before towing. Refer to state and
local rules and regulations before towing a vehicle.
Do not allow weight of towed vehicle to bear on
lower fascia, air dams, or spoilers.
RECOMMENDED TOWING EQUIPMENT
To avoid damage to bumper fascia and air dams
use of a wheel lift or flat bed towing device (Fig. 2) is
recommended. When using a wheel lift towing device,
be sure the unlifted end of disabled vehicle has at
least 100 mm (4 in.) ground clearance. If minimum
ground clearance cannot be reached, use a towing
dolly. If a flat bed device is used, the approach angle
should not exceed 15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels
removed, install lug nuts to retain brake drums or
rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until lifted wheels
are a minimum 100 mm (4 in) from the ground. Be
sure there is adequate ground clearance at the oppo-
site end of the vehicle, especially when towing overrough terrain or steep rises in the road. If necessary,
remove the wheels from the lifted end of the vehicle
and lower the vehicle closer to the ground, to
increase the ground clearance at the opposite end of
the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching studs
to retain brake drums or rotors.
LOCKED VEHICLE TOWING
When a locked vehicle must be towed with the
front wheels on the ground, use a towing dolly or flat
bed hauler.
FLAT TOWING WITH TOW BAR
²3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
not more than 25 km (15 miles). The steering column
must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
²5-speed manual transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at any legal highway speed for extended dis-
tances. The gear selector must be in the neutral posi-
tion.
TOWINGÐFRONT WHEEL LIFT
Chrysler Corporation recommends that a vehicle be
towed with the front end lifted, whenever possible.
TOWINGÐREAR WHEEL LIFT
If a vehicle cannot be towed with the front wheels
lifted, the rear wheels can be lifted provided the fol-
lowing guide lines are observed.
CAUTION: Do not use steering column lock to
secure steering wheel during towing operation.
²Unlock steering column and secure steering
wheel in straight ahead position with a clamp device
designed for towing.
²Verify that front drive line and steering compo-
nents are in good condition.
²5-speed manual transaxle vehicles can be towed
at any legal highway speed for extended distances.
The gear selector must be in the neutral position.
²3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
Fig. 2 Recommended Towing Devices
0 - 8 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 89 of 1200

either through the park brake switch, the fluid level
sensor in the master cylinder reservoir, or the igni-
tion switch in the crank position.
The Brake Fluid Level sensor is located in the
brake fluid reservoir of the master cylinder assembly
(Fig. 18). The purpose of the sensor is to provide the
driver with an early warning that the brake fluid
level in the master cylinder reservoir has dropped to
below normal. This may indicate an abnormal loss of
brake fluid in the master cylinder fluid reservoir
resulting from a leak in the hydraulic system.
As the fluid drops below the minimum level, the
fluid level sensor closes the brake warning light cir-
cuit. This will turn on the red brake warning light.
At this time, master cylinder fluid reservoir shouldbe checked and filled to the full mark with DOT 3
brake fluid.If brake fluid level has dropped in
master cylinder fluid reservoir, the entire
brake hydraulic system should be checked for
evidence of a leak.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
The stop lamp switch controls operation of the
vehicles stop lamps. Also, if the vehicle is equipped
with speed control, the stop lamp switch will deacti-
vate speed control when the brake pedal is
depressed.
The stop lamp switch controls operation of the
right and left tail, stop and turn signal lamp and
CHMSL lamp, by supplying battery current to these
lamps.
The stop lamp switch controls the lamp operation
by opening and closing the electrical circuit to the
stop lamps.
REAR WHEEL HUB/BEARING
CAUTION: If a vehicle is equipped with antilock
brakes the tone wheels for the rear wheel speed
sensors are pressed onto the hub. The tone wheels
used on this vehicle equipped with the Teves Mark
20 Antilock Brake System are different then those
used on past models of this vehicle equipped with
antilock brakes. Reduced braking performance will
result if this part is used on earlier model vehicles
and an accident could result. Do not use on
pre-1998 model year vehicles.
All vehicles are equipped with permanently lubri-
cated and sealed for life rear wheel bearings. There
is no periodic lubrication or maintenance recom-
mended for these units. However, if servicing of a
rear wheel bearing is required, refer to procedures in
the diagnosis and testing section and the removal
and installation section in this group of the service
manual for the inspection and replacement of the
rear wheel bearing.Fig. 17 Power Brake Booster Assembly
Fig. 18 Master Cylinder Fluid Level Sensor
5 - 8 BRAKESPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 154 of 1200

ABS FUSES
The fuse for the ABS pump motor and the ABS
system are located in the power distribution center
(PDC) (Fig. 5). Refer to the sticker on the inside of
the PDC cover for the location of the ABS pump
motor and the ABS system fuse in the PDC. The
PDC is located on the drivers side of the engine com-
partment between the back of the battery and the
strut tower (Fig. 5).
ABS RELAYS
On this vehicle three relays are used to control the
Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake System. The three
relays are the pump motor relay, the system relay,
and the ABS yellow warning lamp relay. The pump
motor relay and the system relay are located in the
CAB and the ABS yellow warning lamp relay is
located in the PDC. If either the pump motor relay or
the system relay is diagnosed as not functioning
properly the CAB will need to be replaced. Refer to
Controller Antilock Brakes in the Removal And
Installation Section in this group of the service man-
ual for the procedure. If the ABS yellow warning
lamp relay is diagnosed as not functioning properly it
can be replaced as a seperated relay in the PDC.
PROPORTIONING VALVE
There are two proportioning valves (Fig. 6) used in
the Teves Mark 20 ABS system. One proportioning
valve is located in the chassis brake line of each rear
wheel brake hydraulic circuit (Fig. 7). The propor-
tioning valves function the same as in a standard
brake system. The proportioning valve can be identi-
fied by the bar code label and stamp on the propor-
tioning valve. Be sure replacement proportioning
valve have the same stamp as the proportioning
valve being replaced.
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
CAUTION: The tone wheels used on this vehicle
equipped with the Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake
System are different then the tone wheels used on
past models of this vehicle equipped with antilock
brakes. Reduced braking performance will result if
this part is used on earlier model vehicles and an
accident could result. Do not use on pre-1998
model year vehicles.
One Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS) is located at each
wheel (Fig. 8) and (Fig. 9), and sends a small AC sig-
nal to the control module (CAB). This signal is gen-
erated by magnetic induction created when a toothed
sensor ring (tone wheel) (Fig. 8) and (Fig. 9) passes
the stationary magnetic Wheel Speed Sensor. The
(CAB) converts the AC signal generated at each
wheel into a digital signal. If a wheel locking ten-
dency is detected by the CAB, it will then modulate
hydraulic pressure via the HCU to prevent the
wheel(s) from locking.
The front Wheel Speed Sensor is attached to a boss
in the steering knuckle (Fig. 8). The tone wheel is
part of the outboard constant velocity joint (Fig. 8).
The rear Wheel Speed Sensor on rear disc brake
applications is mounted to the rear disc brake
adapter (Fig. 9) and the rear tone wheel is also an
Fig. 5 Power Distribution Center
Fig. 6 Proportioning Valve
Fig. 7 Proportioning Valve Location In Vehicle
PLBRAKES 5 - 73
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 157 of 1200
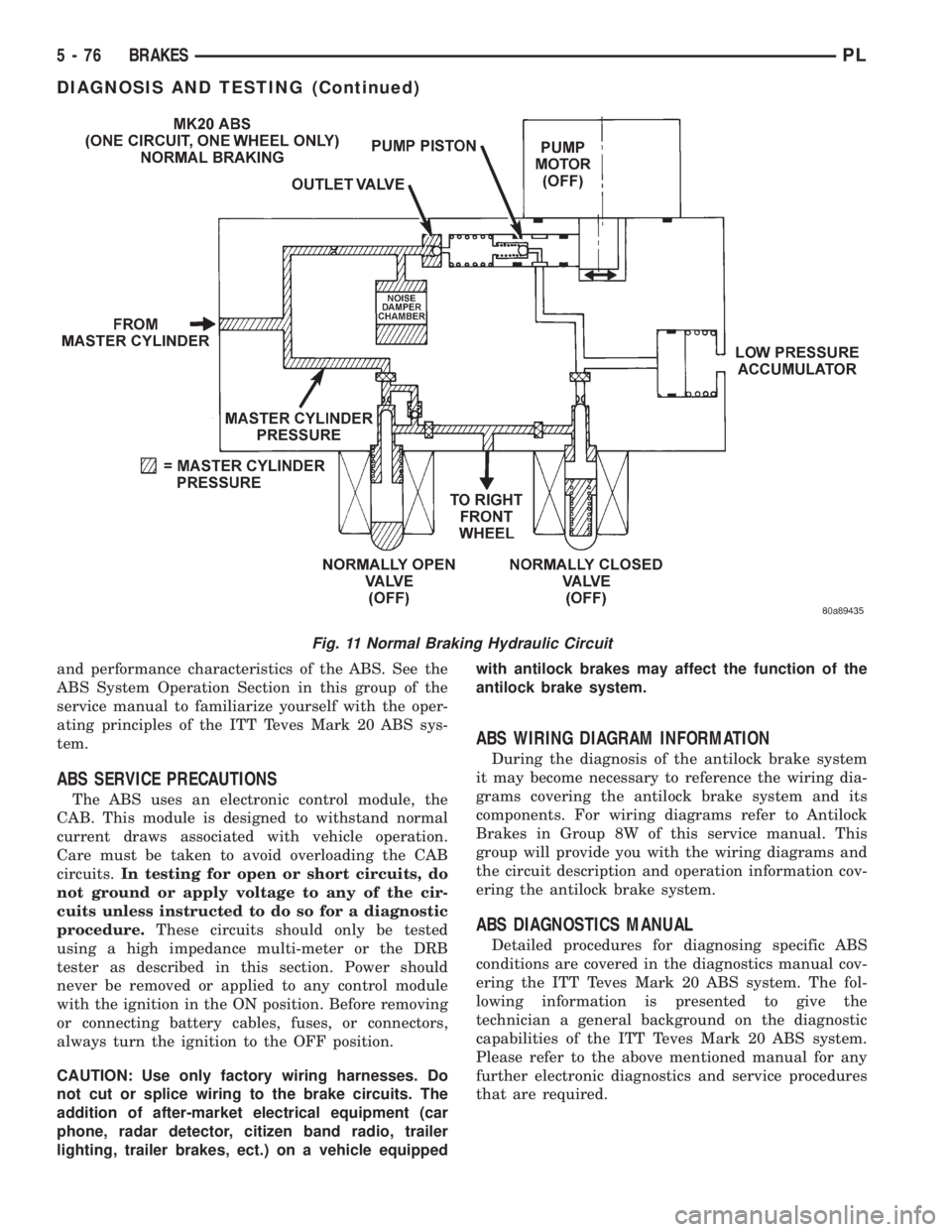
and performance characteristics of the ABS. See the
ABS System Operation Section in this group of the
service manual to familiarize yourself with the oper-
ating principles of the ITT Teves Mark 20 ABS sys-
tem.
ABS SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The ABS uses an electronic control module, the
CAB. This module is designed to withstand normal
current draws associated with vehicle operation.
Care must be taken to avoid overloading the CAB
circuits.In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the cir-
cuits unless instructed to do so for a diagnostic
procedure.These circuits should only be tested
using a high impedance multi-meter or the DRB
tester as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module
with the ignition in the ON position. Before removing
or connecting battery cables, fuses, or connectors,
always turn the ignition to the OFF position.
CAUTION: Use only factory wiring harnesses. Do
not cut or splice wiring to the brake circuits. The
addition of after-market electrical equipment (car
phone, radar detector, citizen band radio, trailer
lighting, trailer brakes, ect.) on a vehicle equippedwith antilock brakes may affect the function of the
antilock brake system.
ABS WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION
During the diagnosis of the antilock brake system
it may become necessary to reference the wiring dia-
grams covering the antilock brake system and its
components. For wiring diagrams refer to Antilock
Brakes in Group 8W of this service manual. This
group will provide you with the wiring diagrams and
the circuit description and operation information cov-
ering the antilock brake system.
ABS DIAGNOSTICS MANUAL
Detailed procedures for diagnosing specific ABS
conditions are covered in the diagnostics manual cov-
ering the ITT Teves Mark 20 ABS system. The fol-
lowing information is presented to give the
technician a general background on the diagnostic
capabilities of the ITT Teves Mark 20 ABS system.
Please refer to the above mentioned manual for any
further electronic diagnostics and service procedures
that are required.
Fig. 11 Normal Braking Hydraulic Circuit
5 - 76 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 159 of 1200
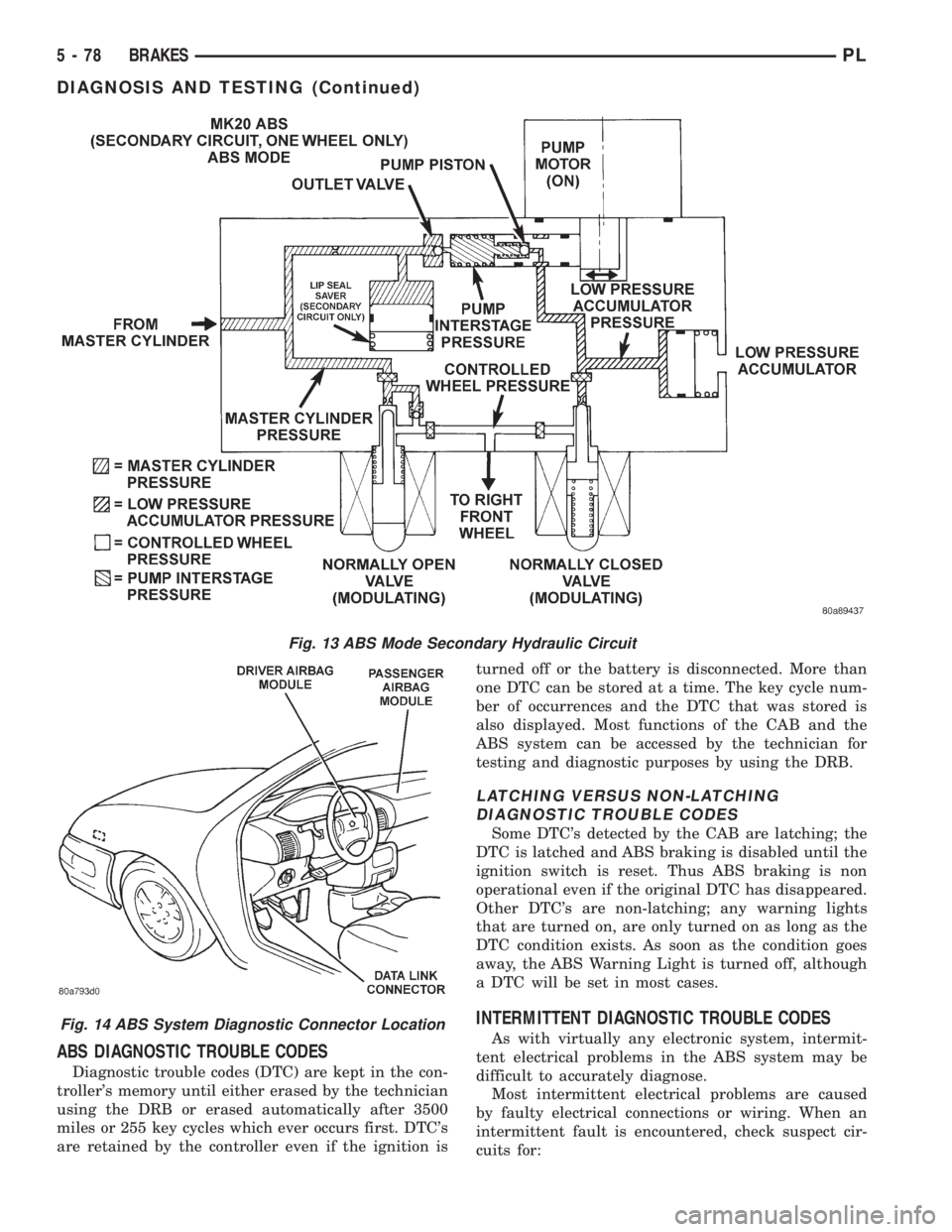
ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTC) are kept in the con-
troller's memory until either erased by the technician
using the DRB or erased automatically after 3500
miles or 255 key cycles which ever occurs first. DTC's
are retained by the controller even if the ignition isturned off or the battery is disconnected. More than
one DTC can be stored at a time. The key cycle num-
ber of occurrences and the DTC that was stored is
also displayed. Most functions of the CAB and the
ABS system can be accessed by the technician for
testing and diagnostic purposes by using the DRB.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Some DTC's detected by the CAB are latching; the
DTC is latched and ABS braking is disabled until the
ignition switch is reset. Thus ABS braking is non
operational even if the original DTC has disappeared.
Other DTC's are non-latching; any warning lights
that are turned on, are only turned on as long as the
DTC condition exists. As soon as the condition goes
away, the ABS Warning Light is turned off, although
a DTC will be set in most cases.
INTERMITTENT DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent electrical problems in the ABS system may be
difficult to accurately diagnose.
Most intermittent electrical problems are caused
by faulty electrical connections or wiring. When an
intermittent fault is encountered, check suspect cir-
cuits for:
Fig. 13 ABS Mode Secondary Hydraulic Circuit
Fig. 14 ABS System Diagnostic Connector Location
5 - 78 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 160 of 1200

A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or mis-
routed wires should be done before attempting to
diagnose or service the ITT Teves Mark 20 antilock
brake system. A visual inspection will eliminate
unnecessary testing and diagnostics time. A thorough
visual inspection will include the following compo-
nents and areas of the vehicle.
(1) Inspect fuses in the power distribution center
(PDC) and the wiring junction block. Verify that all
fuses are fully inserted into the PDC and wring junc-
tion block. A label on the underside of the PDC cover
identifies the locations of the ABS fuses in the PDC.
(2) Inspect the 25-way electrical connector at the
CAB for damage, spread or backed-out wiring termi-
nals. Verify that the 25-way connector is fully
inserted in the socket on the CAB. Be sure that wires
are not stretched tight or pulled out of the connector.
(3) Verify that all the wheel speed sensor connec-
tions are secure.
(4) Poor mating of connector halves or terminals
not fully seated in the connector body.
(5) Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All
connector terminals in a suspect circuit should be
carefully reformed to increase contact tension.
(6) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to
inspect.
(7) Pin presence in the connector assembly
(8) Proper ground connections. Check all ground
connections for signs of corrosion, tight fasteners, or
other potential defects. Refer to wiring diagram man-
ual for ground locations.
(9) Problems with main power sources of the vehi-
cle. Inspect battery, generator, ignition circuits and
other related relays and fuses.
(10) If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record the trouble code.
(11) Most failures of the ABS system will disable
ABS function for the entire ignition cycle even if the
fault clears before key-off. There are some failure
conditions, however, which will allow ABS operation
to resume during the ignition cycle in which a failure
occurred if the failure conditions are no longer
present. The following conditions may result in inter-
mittent illumination of the ABS Warning Lamp. All
other failures will cause the lamp to remain on until
the ignition switch is turned off. Circuits involving
these inputs to the CAB should be investigated if a
complaint of intermittent warning system operation
is encountered.
(12) Low system voltage. If Low System Voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the ABS
Warning Lamp until normal system voltage is
achieved. Once normal voltage is seen at the CAB,
normal operation resumes.(13) High system voltage. If high system voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the
Amber ABS Warning Lamp until normal system volt-
age is achieved. Once normal voltage is again
detected by the CAB, normal ABS operation resumes.
(14) Additionally, any condition which results in
interruption of electrical current to the CAB or mod-
ulator assembly may cause the ABS Warning Lamp
to turn on intermittently.
(15) The body controller can turn on the (yellow)
ABS warning lamp if CCD communication between
the body controller and the CAB is interupted.
TONEWHEEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: The tone wheels used on this vehicle
equipped with the Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake
System are different then those used on past mod-
els of this vehicle equipped with antilock brakes.
Reduced braking performance will result if this part
is used on earlier model vehicles and an accident
could result. Do not use on pre-1998 model year
vehicles.
Carefully inspect tonewheel at the suspected faulty
wheel speed sensor for missing, chipped or broken
teeth, this can cause erratic speed sensor signals.
Tonewheels should show no evidence of contact
with the wheel speed sensors. If contact was made,
determine cause and correct before replacing the
wheel speed sensor.
Excessive runout of the tonewheel can cause
erratic wheel speed sensor signals. Refer to Tone-
wheel Runout in the Specification Section in this sec-
tion of the service manual for the tonewheel runout
specification. Replace drive shaft assembly or rear
hub/bearing assembly if tonewheel runout exceeds
the specification.
Inspect tonewheels for looseness on their mounting
surfaces. Tonewheels are pressed onto their mounting
surfaces and should not rotate independently from
the mounting surface.
Check the wheel speed sensor head alignment to
the tone wheel. Also check the gap between the speed
sensor head and the tone wheel to ensure it is at
specification. Refer to Wheel Speed Sensor Clearance
in the Specification Section in this section of the ser-
vice manual.
PROPORTIONING VALVE
CAUTION: Proportioning valves should never be
disassembled.
If premature rear wheel skid occurs on a hard
brake application, it could be an indication that a
PLBRAKES 5 - 79
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 163 of 1200

CAUTION: Certain components of the ABS System
are not intended to be serviced individually.
Attempting to remove or disconnect certain system
components may result in improper system opera-
tion. Only those components with approved
removal and installation procedures in this manual
should be serviced.
CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage painted sur-
faces. If brake fluid is spilled on any painted sur-
faces, wash off with water immediately.
CAUTION: When performing any service procedure
on a vehicle equipped with ABS do not apply a 12
volt power source to the ground circuit of the pump
motor in the HCU. Doing this will damage the pump
motor and will require replacement of the entire
HCU.
The following are general cautions which should be
observed when servicing the ABS system and/or
other vehicle systems. Failure to observe these pre-
cautions may result in ABS System component dam-
age.
If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle,
using an electric arc welder, the CAB connector
should be disconnected during the welding operation.
The CAB 25 way connector connector should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition switch
in the ON position.
Many components of the ABS System are not ser-
viceable and must be replaced as an assembly. Do not
disassemble any component which is not designed to
be serviced.
ABS HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT
REMOVE
(1) Disconnect negative (ground) cable from the
battery and isolate cable.
(2) Remove the power distribution center (PDC)
(Fig. 17) from the battery thermogaurd. PDC is
removed by unlatching the two retaining clips hold-
ing it to the thermogaurd and then pulling it straight
up off of the thermogaurd.
(3) Remove vacuum supply hose from speed control
servo (Fig. 18).
(4) Remove the 2 bolts (Fig. 18) mounting the
bracket for the speed control servo to the body.
(5) Remove the wiring harness connector (Fig. 19)
from the speed control servo. Then remove the rout-
ing clip for the speed control servo wiring harness
from the speed control servo mounting bracket.
(6) Lay the speed control servo, with the speed
control cable attached, on top of the engine.(7) Disconnect wiring harness connector from the
brake fluid level sensor on master cylinder reservoir.
Fig. 17 PDC Attachment To Thermogaurd
Fig. 18 Speed Control Servo Bracket Mounting
Fig. 19 Wiring Harness Connection To Speed
Control Servo
5 - 82 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 167 of 1200

(18) Install the wiring harness connector (Fig. 19)
on the speed control servo. Then install the routing
clip for the speed control servo wiring harness on the
speed control servo mounting bracket.
Install speed control servo mounting bracket on
body.
(19) Install and securely tighten the 2 bolts (Fig.
18) mounting the bracket for the speed control servo
to the body.
(20) Install the vacuum supply hose on the speed
control servo (Fig. 18).
(21) Install the power distribution center (PDC)
(Fig. 17) on the battery thermogaurd. PDC is install
by pushing straight down on it until the two retain-
ing clips holding it to the thermogaurd are latched to
the thermogaurd.
(22) Connect the negative (ground) cable on the
battery.
(23) Bleed the base brakes and the ABS brakes
hydraulic systems. Refer to Bleeding Base Brake
Hydraulic System in Service Procedures of the Base
Brake Section and Antilock Brakes Hydraulic System
Bleeding Procedure in Service Procedures of the
Antilock Brake Section for the required procedures.
(24) Fill the master cylinder to the proper fill
level.
(25) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation
of the base and ABS brake systems.
PROPORTIONING VALVES
CAUTION: Proportioning valves should never be
disassembled.
REMOVE
(1) Remove the chassis brake tube nuts (Fig. 32)
from the proportioning valve controlling the rear
wheel of the vehicle which has premature wheel skid.
(2) Remove the proportioning valve from the chas-
sis brake tube (Fig. 32).
INSTALL
(1) Install the proportioning valve in the chassis
brake tube (Fig. 32).
(2) Tighten the 2 chassis brake tube nuts to a
torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Bleed the affected brake line. See Bleeding
Brake System in the Service Procedures section of
the manual for proper bleeding procedure.
MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
If the Master Cylinder or the Power Booster need
to be serviced or replaced, refer to Master Cylinder
or Power Brake Booster in the Removal And Instal-
lation Section in the Base Brake Section of this ser-
vice manual.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKES (CAB)
REMOVE
NOTE: To replace the controller antilock brakes
(CAB) on this vehicle, the integrated control unit
(ICU) and CAB need to be removed from the vehicle
as a unit. The CAB can then be separated from the
HCU. Do not attempt to replace the CAB with the
ICU mounted in the vehicle.
(1) Remove the ICU from the vehicle. Refer to ABS
Integrated Control Unit in the Removal And Instal-
lation Section in this group of the service manual for
the removal procedure.
Fig. 31 Torquing Brake Tube Nuts At Master
Cylinder
Fig. 32 Proportioning Valve Location
5 - 86 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)