display DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 155 of 1200

integral part of the rear wheel hub and bearing
assembly. The speed sensor air gap on both applica-
tions is NOT adjustable.
The four Wheel Speed Sensors are serviced individ-
ually. The front Tone Wheels are serviced as an
assembly with the outboard constant velocity joint.
The rear Tone Wheels are serviced as an assembly
with the rear hub and bearing assembly.
Correct ABS system operation is dependent on
accurate wheel speed signals. The vehicle's wheels
and tires must all be the same size and type to gen-
erate accurate signals. Variations in wheel and tire
size can produce inaccurate wheel speed signals.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKES (CAB)
The Controller Antilock Brakes (CAB) is a micro-
processor based device which monitors the ABS sys-
tem during normal braking and controls it when the
vehicle is in an ABS stop. The CAB is mounted to the
bottom of the HCU (Fig. 10). The CAB uses a 25 way
electrical connector on the vehicle wiring harness.
The power source for the CAB is through the ignitionswitch in the Run or On position.THE (CAB) IS ON
THE CCD BUS
The primary functions of the (CAB) are:
(1) Detect wheel locking or wheel slipping tenden-
cies by monitoring the speed of all four wheels of the
vehicle.
(2) Control fluid modulation to the wheel brakes
while the system is in an ABS mode or the traction
control system is activated.
(3) Monitor the system for proper operation.
(4) Provide communication to the DRB Scan Tool
while in diagnostic mode.
(5) Store diagnostic information.
The CAB continuously monitors the speed of each
wheel through the signals generated by the wheel
speed sensors to determine if any wheel is beginning
to lock. When a wheel locking tendency is detected,
the CAB commands the CAB command coils to actu-
ate. The CAB command coils then open and close the
valves in the HCU which modulate brake fluid pres-
sure in some or all of the hydraulic circuits. The CAB
continues to control pressure in individual hydraulic
circuits until a locking tendency is no longer present.
The ABS system is constantly monitored by the
CAB for proper operation. If the CAB detects a fault,
it will turn on the Amber ABS Warning Lamp and
disable the ABS braking system. The normal base
braking system will remain operational.
The CAB contains a self-diagnostic program which
will turn on the Amber ABS Warning Lamp when a
ABS system fault is detected. Faults are then stored
in a diagnostic program memory. There are multiple
fault messages which may be stored in the CAB and
displayed through the DRB Scan Tool. These fault
messages will remain in the CAB memory even after
the ignition has been turned off. The fault messages
can be read and or cleared from the CAB memory by
a technician using the DRB Scan Tool. The fault
occurrence and the fault code will also be automati-
Fig. 8 Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Fig. 9 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor With Disc Brakes
Fig. 10 Controller Antilock Brake (CAB)
5 - 74 BRAKESPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 159 of 1200
ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTC) are kept in the con-
troller's memory until either erased by the technician
using the DRB or erased automatically after 3500
miles or 255 key cycles which ever occurs first. DTC's
are retained by the controller even if the ignition isturned off or the battery is disconnected. More than
one DTC can be stored at a time. The key cycle num-
ber of occurrences and the DTC that was stored is
also displayed. Most functions of the CAB and the
ABS system can be accessed by the technician for
testing and diagnostic purposes by using the DRB.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Some DTC's detected by the CAB are latching; the
DTC is latched and ABS braking is disabled until the
ignition switch is reset. Thus ABS braking is non
operational even if the original DTC has disappeared.
Other DTC's are non-latching; any warning lights
that are turned on, are only turned on as long as the
DTC condition exists. As soon as the condition goes
away, the ABS Warning Light is turned off, although
a DTC will be set in most cases.
INTERMITTENT DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent electrical problems in the ABS system may be
difficult to accurately diagnose.
Most intermittent electrical problems are caused
by faulty electrical connections or wiring. When an
intermittent fault is encountered, check suspect cir-
cuits for:
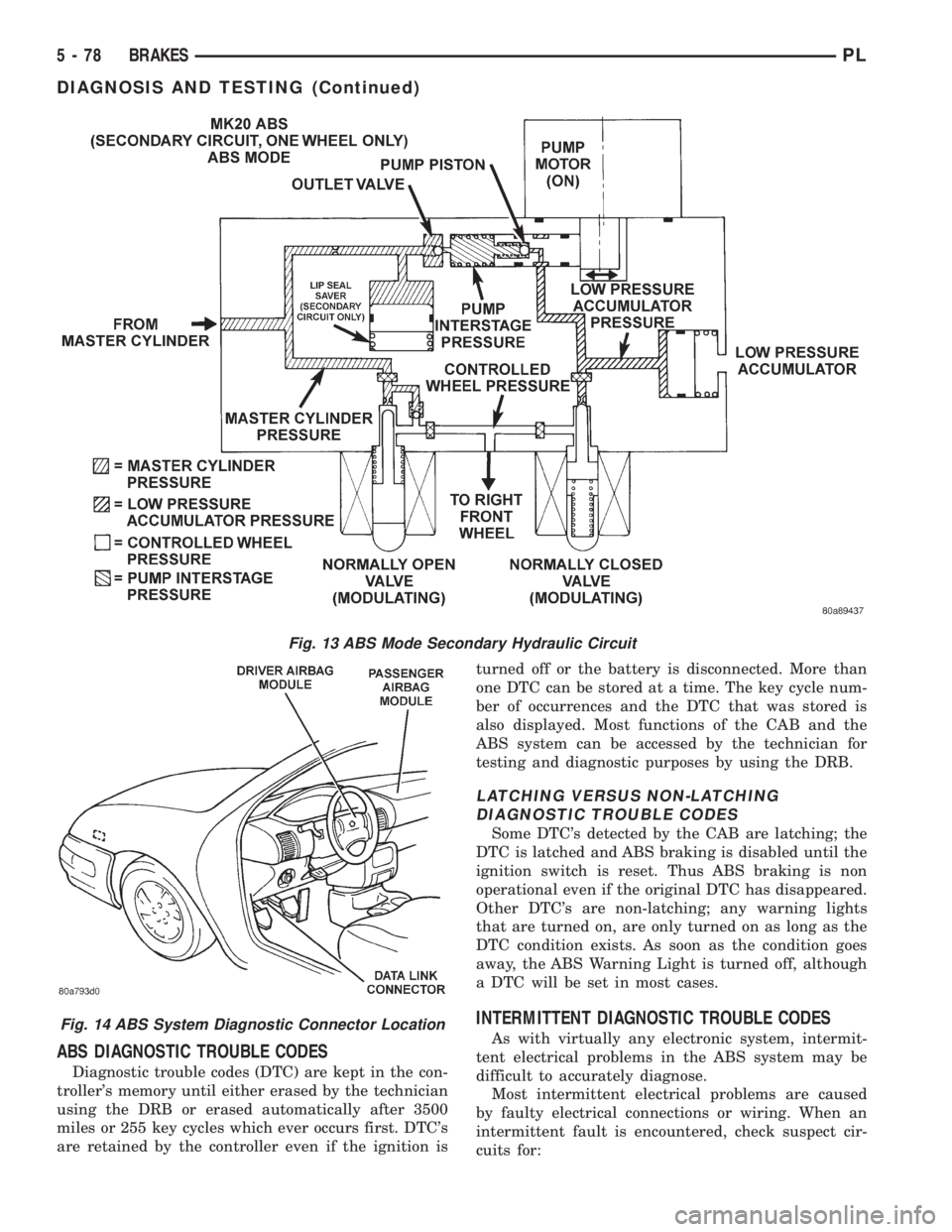
Fig. 13 ABS Mode Secondary Hydraulic Circuit
Fig. 14 ABS System Diagnostic Connector Location
5 - 78 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 243 of 1200

performed at each (- ground) connection in this cir-
cuit to locate the excessive resistance.
(7) Testing (+ positive) circuitry:
(a) Touch the positive lead of voltmeter directly
to battery negativePOST.
(b) Touch the negative lead of voltmeter to the
ground terminal stud on the generator case (not
the terminal mounting nut). Voltage should be no
higher than 0.3 volts. If voltage is higher than 0.3
volts, touch test lead to terminal mounting stud
nut and then to the wiring connector. If voltage is
now below 0.3 volts, look for dirty, loose or poor
connection at this point. A voltage drop test may be
performed at each (+ positive) connection in this
circuit to locate the excessive resistance. This test
can also be performed between the generator case
and the engine. If test voltage is higher than 0.3
volts, check for corrosion at generator mounting
points or loose generator mounting.
CURRENT OUTPUT TEST
The current output test will determine if the
charging system can deliver its minimum test cur-
rent (amperage) output. Refer to the Specifications
section at the end of this group for minimum test
current (amperage) requirements.
The first part of this test will determine the com-
bined amperage output of both the generator and the
Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry.
PREPARATION
(1) Determine if any Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTC) exist. To determine a DTC, refer to On-Board
Diagnostics in this group. For repair, refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures man-
ual.
(2) Before starting test, make sure battery is in
good condition and is fully-charged. See Group 8A,
Battery for more information.
(3) Check condition of battery cables at battery.
Clean if necessary.
(4) Perform the Voltage Drop Test. This will
ensure clean and tight generator/battery electrical
connections.
(5) Be sure the generator drive belt is properly
tensioned. Refer to Group 7, Cooling System for
information.
(6) A volt/amp tester equipped with both a battery
load control (carbon pile rheostat) and an inductive-
type pickup clamp (ammeter probe) will be used for
this test. Refer to operating instructions supplied
with tester. When using a tester equipped with an
inductive-type clamp, removal of wiring at the gener-
ator will not be necessary.
(7) Start the engine and allow it to reach operating
temperature.
(8) Shut engine off.(9) Turn off all electrical accessories and all vehicle
lighting.
(10) Connect the volt/amp tester leads to the bat-
tery. Be sure the carbon pile rheostat control is in the
OPEN or OFF position before connecting leads. See
Load Test in Group 8A, Battery for more information.
Also refer to the operating instructions supplied with
test equipment.
(11) Connect the inductive clamp (ammeter probe).
Refer to the operating instructions supplied with test
equipment.
(12) If volt/amp tester is not equipped with an
engine tachometer, connect a separate tachometer to
the engine.
TEST
(1) Perform the previous test Preparation.
(2) Fully engage the parking brake.
(3) Start engine.
(4) Bring engine speed to 2500 rpm.
(5) With engine speed held at 2500 rpm, slowly
adjust the rheostat control (load) on the tester to
obtain the highest amperage reading. Do not allow
voltage to drop below 12 volts. Record the reading.
This load test must be performed within 15 sec-
onds to prevent damage to test equipment.On
certain brands of test equipment, this load will be
applied automatically. Refer to the operating manual
supplied with test equipment.
(6) The ammeter reading must meet the Minimum
Test Amps specifications as displayed in the Genera-
tor Ratings chart. This can be found in the Specifica-
tions section at the end of this group. A label stating
a part reference number is attached to the generator
case. On some engines this label may be located on
the bottom of the case. Compare this reference num-
ber to the Generator Ratings chart.
(7) Rotate the load control to the OFF position.
(8) Continue holding engine speed at 2500. If EVR
circuitry is OK, amperage should drop below 15±20
amps. With all electrical accessories and vehicle
lighting off, this could take several minutes of engine
operation. If amperage did not drop, refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures man-
ual for testing.
(9) Remove volt/amp tester.
If minimum amperage could not be met, refer to
the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual for testing.
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures manual. To test the sensor only,
refer to the following:
(1) The sensor is located under the battery and is
attached to the battery tray (Fig. 5). A two-wire pig-
8C - 8 CHARGING SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 251 of 1200

The major difference between the two engines is
component location which affects the ignition system
service procedures. There are various sensors that
are in different locations due to a different cylinder
head and intake manifold.
The 2.0L engines use a fixed ignition timing sys-
tem. The distributorless electronic ignition system is
referred to as the Direct Ignition System (DIS).
Basic ignition timing is not adjustable.The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) determines spark
advance. The system's three main components are
the coil pack, crankshaft position sensor, and cam-
shaft position sensor.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) controls the
ignition system (Fig. 1). The PCM supplies battery
voltage to the ignition coil through the Auto Shut-
down (ASD) Relay. The PCM also controls the ground
circuit for the ignition coil. By switching the ground
path for the coil on and off, the PCM adjusts ignition
timing to meet changing engine operating conditions.
During the crank-start period the PCM maintains
spark advance at 9É BTDC. During engine operation
the following inputs determine the amount of spark
advance provided by the PCM.
²Intake air temperature
²Coolant temperature
²Engine RPM
²Intake manifold vacuum
²Knock sensor
The PCM also regulates the fuel injection system.
Refer to the Fuel Injection sections of Group 14.
SPARK PLUGS
The 2.0L engines uses resistor spark plugs. For
spark plug identification and specifications, Refer to
the Specifications section at the end of this group.Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. An iso-
lated plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
Group 0.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective. Refer to the
Spark Plug Condition section of this group. After
cleaning, file the center electrode flat with a small
point file or jewelers file. Adjust the gap between the
electrodes (Fig. 2) to the dimensions specified in the
chart at the end of this section.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion and damage.
Tighten spark plugs to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
SPARK PLUG CABLES
Spark plug cables are sometimes referred to as sec-
ondary ignition wires. The wires transfer electrical
current from the coil pack to individual spark plugs
at each cylinder. The resistor type, nonmetallic spark
plug cables provide suppression of radio frequency
emissions from the ignition system.
Check the spark plug cable connections for good
contact at the coil and spark plugs. Terminals should
be fully seated. The nipples and spark plug covers
should be in good condition. Nipples should fit tightly
on the coil. Spark plug boot should completely cover
the spark plug hole in the cylinder head cover. Install
the boot until the terminal snaps over the spark
plug. A snap must be felt to ensure the spark plug
cable terminal engaged the spark plug.
Loose cable connections will corrode, increase resis-
tance and permit water to enter the coil towers.
These conditions can cause ignition malfunction.
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module
Fig. 2 Setting Spark Plug Electrode Gap
8D - 2 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 253 of 1200

CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The PCM determines what cylinder to fire from the
crankshaft position sensor input and the camshaft
position sensor input. The second crankshaft counter-
weight has machined into it two sets of four timing
reference notches including a 60 degree signature
notch (Fig. 6). From the crankshaft position sensor
input the PCM determines engine speed and crank-
shaft angle (position).
The notches generate pulses from high to low in
the crankshaft position sensor output voltage. When
a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the
crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltage
goes low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns
with the sensor, voltage goes high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the output
voltage switches from low (metal) to high (notch)
then back to low.
If available, an oscilloscope can display the square
wave patterns of each voltage pulse. From the fre-
quency of the output voltage pulses, the PCM calcu-
lates engine speed. The width of the pulses represent
the amount of time the output voltage stays high
before switching back to low. The period of time the
sensor output voltage stays high before switching
back to low is referred to as pulse-width. The faster
the engine is operating, the smaller the pulse-width
on the oscilloscope.
By counting the pulses and referencing the pulse
from the 60 degree signature notch, the PCM calcu-
lates crankshaft angle (position). In each group of
timing reference notches, the first notch represents
69 degrees before top dead center (BTDC). The sec-
ond notch represents 49 degrees BTDC. The third
notch represents 29 degrees. The last notch in eachset represents 9 degrees before top dead center
BTDC.
The timing reference notches are machined at 20É
increments. From the voltage pulse-width the PCM
tells the difference between the timing reference
notches and the 60 degree signature notch. The 60
degree signature notch produces a longer pulse-width
than the smaller timing reference notches. If the
camshaft position sensor input switches from high to
low when the 60 degree signature notch passes under
the crankshaft position sensor, the PCM knows cylin-
der number one is the next cylinder at TDC.
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the generator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 7).
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The PCM determines fuel injection synchronization
and cylinder identification from inputs provided by
Fig. 6 Timing Reference Notches
Fig. 7 Crankshaft Position Sensor
8D - 4 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 270 of 1200

INSTRUMENT PANEL AND SYSTEMS
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
DOME LAMP............................ 1
ELECTRONIC DIGITAL CLOCK.............. 1
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER................... 2
WARNING AND INDICATOR LAMPS......... 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AIRBAG WARNING SYSTEM............... 2
BRAKE SYSTEM WARNING LAMP TEST...... 2
FOG LAMP SWITCH TEST................. 2
FUEL TANK SENDING UNIT TEST........... 3
HEADLAMP SWITCH TEST................. 3
HEATER A/C BLOWER SWITCH TEST........ 3
HEATER BLOWER SWITCH TEST............ 3
INDIVIDUAL GAUGE INOPERATIVE.......... 4
INSTRUMENT PANEL AND COMPONENTS.... 4
LOW OIL PRESSURE WARNING LAMP TEST . . 4
MULTIPLE GAUGE INOPERATIVE TEST....... 4
SEAT BELT REMINDER SYSTEM TEST....... 6
SENDING UNIT......................... 6
SERVICE ENGINE SOON INDICATOR......... 6
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR TEST............. 6
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ASH RECEIVER RETAINER AND LAMP....... 6
CENTER BEZEL.......................... 6
CIGAR LIGHTER RECEPTACLE.............. 6
CLUSTER LAMP......................... 7
CLUSTER PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD........ 7CLUSTER.............................. 7
DOME LENS/LAMP....................... 8
FLOOR CONSOLE........................ 8
GAUGE................................ 8
GLOVE BOX DOOR/BIN................... 8
GLOVE BOX SWITCH/LAMP................ 9
HEADLAMP SWITCH..................... 9
HEATER A/C CONTROL BLOWER SWITCH . . . 10
HEATER A/C CONTROL LAMP............ 10
HEATER A/C CONTROL................... 9
HEATER CONTROL BLOWER SWITCH....... 10
IGNITION KEY LAMP.................... 10
INSTRUMENT PANEL.................... 10
LEFT TRIM PANEL...................... 10
ODOMETER............................ 10
RADIO................................ 12
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER AND/OR FOG
LAMP SWITCH....................... 12
RIGHT TRIM PANEL..................... 12
SHIFTER KNOB......................... 13
STEERING COLUMN COVER LINER......... 13
STEERING COLUMN COVER.............. 13
STEERING COLUMN SHROUDS............ 13
TOP COVER AND CLUSTER BEZEL
REMOVAL........................... 14
TRANSMISSION RANGE INDICATOR LAMP . . 14
TRUNK LAMP/LENS..................... 14
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR................ 14
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
The purpose of the dash gauges and indicator
lamps is to keep the driver informed about the oper-
ating condition of the vehicle. If an abnormal condi-
tion occurs, the driver is informed by indicator lamp.
The driver can seek service before damage occurs.
Indicator lamps use ON/OFF switch functions for
operation, while gauges use a sending unit or sensor.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
DOME LAMP
The Dome Lamp operates when a door is open or
when the headlamp switch is placed in courtesy posi-
tion.
ELECTRONIC DIGITAL CLOCK
The electronic digital clock is in the radio. The
clock and radio each use the display panel built into
the radio. A digital readout indicates the time in
hours and minutes whenever the ignition switch is in
the ON or ACC position.
PLINSTRUMENT PANEL AND SYSTEMS 8E - 1
Page 271 of 1200

When the ignition switch is in the OFF position, or
when the radio frequency is being displayed, time
keeping is accurately maintained.
The procedure for setting the clock varies slightly
with each radio. The correct procedure is described in
the individual radio operating instructions. Refer to
the Owner's Manual supplied with the vehicle.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
There are two conventional instrument cluster
assemblies available. The clusters electronically drive
the speedometer, odometer, and gauges (Fig. 1) and
(Fig. 2).
GAUGES
All gauges in the electronic clusters are the analog
type gauges. When the ignition switch is moved to
the OFF position, the cluster drives each gauge to its
lowest position.
WARNING AND INDICATOR LAMPS
The instrument cluster has warning lamps and
indicators for the following systems:
²Airbag
²Anti-lock Brakes (ABS) if equipped
²Brake warning
²Charging System
²Door Ajar
²High beam indicator
²Low oil pressure
²Malfunction indicator (service engine soon) lamp
²Right and left turn signals.
²Seat belt warning
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AIRBAG WARNING SYSTEM
For testing of this system refer to Group 8M,
Restraint Systems.
BRAKE SYSTEM WARNING LAMP TEST
The brake warning lamp illuminates when the
parking brake is applied with ignition switch turned
to the ON position. The same lamp will also illumi-
nate if one of the two service brake systems fail the
when brake pedal is applied.
To test the system:
²As the ignition switch is turned to the start posi-
tion the lamp should light.
²Turn ignition switch to the ON position and
apply the parking brake. The lamp should light.
If lamp fails to light inspect for:
²A burned out lamp
²Loose, corroded or damaged socket
²A damaged circuit board
²A broken or disconnected wire at the switch
²Defective switch
To test the service brake warning system, refer to
Group 5, Brakes, Hydraulic System Control Valves.
FOG LAMP SWITCH TEST
(1) Remove the fog lamp switch. Refer to the Rear
Window Defogger and/or Fog Lamp Switch Removal.
(2) Using two jumper wires, connect Pin 2 and Pin
4 of the switch to battery voltage.
(3) Using a test lamp, connect the test lamp to Pin
3 as shown in (Fig. 3). Refer to (Fig. 4) for fog lamp
switch circuit.
(4) Push the fog lamp switch button. The test lamp
and the LED indicator on the front of the switch
should illuminate.
(5) If either the LED or the test lamp fails to illu-
minate, replace the switch.Fig. 1 Instrument Cluster Without Tachometer
Fig. 2 Instrument Cluster With Tachometer
Fig. 3 Fog Lamp Switch Test
8E - 2 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 289 of 1200

AUDIO SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
NO AUDIO. 1. FUSE FAULTY.
2. RADIO CONNECTOR
FAULTY.
3. WIRING FAULTY.
4. GROUND FAULTY.
5. RADIO FAULTY.
6. SPEAKERS FAULTY.1. CHECK RADIO FUSES IN FUSEBLOCK MODULE. REPLACE
FUSES, IF REQUIRED.
2. CHECK FOR LOOSE OR CORRODED RADIO CONNECTOR.
REPAIR, IF REQUIRED.
3. CHECK FOR BATTERY VOLTAGE AT RADIO CONNECTOR.
REPAIR WIRING, IF REQUIRED.
4. CHECK FOR CONTINUITY BETWEEN RADIO CHASSIS AND
A KNOWN GOOD GROUND. THERE SHOULD BE
CONTINUITY. REPAIR GROUND, IF REQUIRED.
5. EXCHANGE OR REPLACE RADIO, IF REQUIRED.
6. SEE SPEAKER DIAGNOSIS, IN THIS GROUP.
NO DISPLAY. 1. FUSE FAULTY.
2. RADIO CONNECTOR
FAULTY.
3. WIRING FAULTY.
4. GROUND FAULTY.
5. RADIO FAULTY.1. CHECK RADIO FUSES IN FUSEBLOCK MODULE. REPLACE
FUSES, IF REQUIRED.
2. CHECK FOR LOOSE OR CORRODED RADIO CONNECTOR.
REPAIR, IF REQUIRED.
3. CHECK FOR BATTERY VOLTAGE AT RADIO CONNECTOR.
REPAIR WIRING, IF REQUIRED.
4. CHECK FOR CONTINUITY BETWEEN RADIO CHASSIS AND
A KNOWN GOOD GROUND. THERE SHOULD BE
CONTINUITY. REPAIR GROUND, IF REQUIRED.
5. EXCHANGE OR REPLACE RADIO, IF REQUIRED.
NO MEMORY. 1. FUSE FAULTY.
2. RADIO CONNECTOR
FAULTY.
3. WIRING FAULTY.
4. GROUND FAULTY.
5. RADIO FAULTY.1. CHECK IGNITION-OFF DRAW FUSE. REPLACE FUSE, IF
REQUIRED.
2. CHECK FOR LOOSE OR CORRODED RADIO CONNECTOR.
REPAIR, IF REQUIRED.
3. CHECK FOR BATTERY VOLTAGE AT RADIO CONNECTOR.
REPAIR WIRING, IF REQUIRED.
4. CHECK FOR CONTINUITY BETWEEN RADIO CHASSIS AND
A KNOWN GOOD GROUND. THERE SHOULD BE
CONTINUITY. REPAIR GROUND, IF REQUIRED.
5. EXCHANGE OR REPLACE RADIO, IF REQUIRED.
POOR RADIO
RECEPTION.1. ANTENNA FAULTY.
2. GROUND FAULTY.
3. RADIO FAULTY.1. SEE ANTENNA DIAGNOSIS, IN THIS GROUP. REPAIR OR
REPLACE ANTENNA, IF REQUIRED.
2. CHECK FOR CONTINUITY BETWEEN RADIO CHASSIS AND
A KNOWN GOOD GROUND. THERE SHOULD BE
CONTINUITY. REPAIR GROUND, IF REQUIRED..
3. EXCHANGE OR REPLACE RADIO, IF REQUIRED.
NO/POOR TAPE
OPERATION.1. FAULTY TAPE.
2. FOREIGN OBJECTS
BEHIND TAPE DOOR.
3. DIRTY CASSETTE
TAPE HEAD.
4. FAULTY TAPE DECK.1. INSERT KNOWN GOOD TAPE AND TEST OPERATION.
2. REMOVE FOREIGN OBJECTS AND TEST OPERATION.
3. CLEAN HEAD WITH MOPAR CASSETTE HEAD CLEANER.
4. EXCHANGE OR REPLACE RADIO, IF REQUIRED.
NO COMPACT
DISC
OPERATION1. FAULTY CD.
2. FOREIGN MATERIAL
ON CD.
3. CONDENSATION ON
CD OR OPTICS.
4. FAULTY CD PLAYER.1. INSERT KNOWN GOOD CD AND TEST OPERATION.
2. CLEAN CD AND TEST OPERATION.
3. ALLOW TEMPERATURE OF VEHICLE INTERIOR TO
STABILIZE AND TEST OPERATION.
4. EXCHANGE OR REPLACE RADIO, IF REQUIRED.
8F - 2 AUDIO SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 301 of 1200

CHECKING FOR DIAGNOSTIC CODES
When trying to verify a speed control system elec-
tronic malfunction: Connect a DRB scan tool if avail-
able to the data link connector. The connector is
located at left side of the steering column, and at
lower edge of the panel.
(1) A speed control malfunction may occur without
a diagnostic code being indicated.
Refer to Group 25, for further information and use-
age of the DRB scan tool and a more complete list of
Diagnostic Trouble Code.
SPEED CONTROL SLOWS DOWN BY ITSELF
Test vehicle speed sensor, refer to group 8E. If sen-
sor fails replace sensor, if it passes perform the fol-
lowing test:
(1) Perform the speed control switch test on the
DECEL switch, if it fails replace switch.
(2) If the switch passes, conduct the vacuum sup-
ply test.
(3) If it passes, conduct the servo vacuum test. If it
fails replace servo.
(4) If continuity, replace the PCM.
SPEED CONTROL ELECTRICAL TEST
Electronic speed control systems may be tested
using two different methods. One involves use of aDRB. If this test method is desired, refer to the Pow-
ertrain Diagnostic Test Procedures for charging and
speed control system manual.
The other test method uses a volt/ohm meter. The
volt/ohm meter method is described in the following
tests.
If any information is needed concerning wiring,
refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams (Fig. 4).
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals, or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
When electrical connections are removed, corrosion
should be removed from electrical terminals and a
light coating of Mopar Multi-Purpose Grease, or
equivalent, applied. Inspect connectors for damage
terminals.
A poor connection can cause a complete or inter-
mittent malfunction and is also the only connection
in the circuit, that can not be tested. For this reason,
a loose connection may be misdiagnosed as a compo-
nent malfunction.
SPEED CONTROL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Hex Code DRB Scan Tool Display Description of Diagnostic Trouble Code
23No Vehicle Speed Sensor
SignalNo vehicle distance (speed) sensor signal detected during
road load conditions.
OFSpeed Control Solenoid
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Speed Control
vacuum or vent solenoid circuits.
56MUX S/C Switch High Speed Control switch input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
57MUX S/C Switch Low Speed Control switch input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
52S/C Power Relay Or 12V
Driver CircuitMalfunction detected with power feed to speed control servo
solnoids.
Check Engine Lamp will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
8H - 4 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 867 of 1200

CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The PCM determines what cylinder to fire from the
crankshaft position sensor input and the camshaft
position sensor input. The second crankshaft counter-
weight has two sets of four timing reference notches
including a 60 degree signature notch (Fig. 7). From
the crankshaft position sensor input the PCM deter-
mines engine speed and crankshaft angle (position).
The notches generate pulses from high to low in
the crankshaft position sensor output voltage. When
a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the
crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltage
goes low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns
with the sensor, voltage goes high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the outputvoltage switches from low (metal) to high (notch)
then back to low.
If available, an oscilloscope can display the square
wave patterns of each voltage pulses. From the width
of the output voltage pulses, the PCM calculates
engine speed. The width of the pulses represent the
amount of time the output voltage stays high before
switching back to low. The period of time the sensor
output voltage stays high before switching back to
low is referred to as pulse width. The faster the
engine is operating, the smaller the pulse width on
the oscilloscope.
By counting the pulses and referencing the pulse
from the 60 degree signature notch, the PCM calcu-
lates crankshaft angle (position). In each group of
timing reference notches, the first notch represents
69 degrees before top dead center (BTDC). The sec-
ond notch represents 49 degrees BTDC. The third
notch represents 29 degrees. The last notch in each
set represents 9 degrees before top dead center
(TDC).
The timing reference notches are machined at 20É
increments. From the voltage pulse width the PCM
tells the difference between the timing reference
notches and the 60 degree signature notch. The 60
degree signature notch produces a longer pulse width
than the smaller timing reference notches. If the
camshaft position sensor input switches from high to
low when the 60 degree signature notch passes under
the crankshaft position sensor, the PCM knows cylin-
der number one is the next cylinder at TDC.
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the alternator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 8).
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The combination coolant temperature sensor has
two elements. One element supplies coolant temper-
ature signal to the PCM. The other element supplies
coolant temperature signal to the instrument panel
gauge cluster. The PCM determines engine coolant
temperature from the coolant temperature sensor.
As coolant temperature varies the coolant temper-
ature sensors resistance changes resulting in a differ-
ent input voltage to the PCM and the instrument
panel gauge cluster.
When the engine is cold, the PCM will provide
slightly richer air- fuel mixtures and higher idle
speeds until normal operating temperatures are
reached.
SOHC
The coolant sensor threads into the rear of the cyl-
inder head, next to the camshaft position sensor (Fig.
9). New sensors have sealant applied to the threads.
Fig. 5 Target MagnetÐTypical
Fig. 6 Target Magnet Polarity
14 - 26 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)