engine oil DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 783 of 1285

(10) Install connecting rod lower bearing half and
cap. InstallNewbolts and tighten to 27 N´m (20 ft.
lbs.) plus 1/4 turn.
(11) Install cylinder head and oil pan. Refer to pro-
cedures in this section.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP
(1) To remove the relief valve, proceed as follows:
(2) Remove the threaded plug and gasket from the
oil pump (Fig. 116).
CAUTION: Oil pump pressure relief valve must be
installed as shown in (Fig. 116) or serious damage
may occur.
(3) Remove spring and relief valve (Fig. 116).
(4) Remove oil pump cover screws, and lift off
cover.
(5) Remove pump rotors.
(6) Wash all parts in a suitable solvent and inspect
carefully for damage or wear (Fig. 117).
VALVE SERVICE WITH THE CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVED
REMOVAL
(1) With cylinder head removed, compress valve
springs using Special Tool C-3422-B with Adaptor
6526.(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves to insure
installation in original location.
VALVE INSPECTION
(1) Clean valves thoroughly and discard burned,
warped and cracked valves.
(2) Measure valve stems for wear. Measure stem
about 60 mm beneath the valve lock grooves.
(3) If valve stems are worn more than 0.05 mm
(0.002 in.), replace valve.
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(2) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 118). Replace guides if they are not within
specification. For specifications, refer to Engine Spec-
ifications in this section.
(3) Check valve guide height (Fig. 119).
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Whenever valves have been removed for inspec-
tion, reconditioning or replacement, valve springs
should be tested Special Tool C-647. As an example,
the compression length of the spring to be tested is
33.34 mm (1-5/16 in.). Turn tool table until surface is
in line with the 33.34 mm (1-5/16 in.) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device (Fig. 120). Pull on torque
Fig. 116 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
1 ± RETAINER CAP
2 ± GASKET
3 ± OIL PUMP BODY
4 ± RELIEF VALVE
5 ± SPRING
Fig. 117 Oil Pump
1 ± OIL PUMP BODY
2 ± OIL PUMP COVER
3 ± OUTER ROTOR
4 ± INNER ROTOR
9 - 60 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 785 of 1285

then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of the valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15 degrees stone. If the blue is transferred to
the bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a
65 degrees stone.
(6) Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat width
are maintained. The intake valve seat must be ser-
viced when the valve seat width is 2.0 mm (0.079 in.)
or greater. The exhaust valve seat must be serviced
when the valve seat width is 2.5 mm (0.098 in.) or
greater. Otherwise the cylinder head must be
replaced.
(7) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 0.75±1.25 mm
(0.030±0.049 in.) (Fig. 122).
(8) Check valve tip to spring seat dimensions A
after grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve
tip until within specifications. Measure from valve
tip to spring seat when installed in the head (mea-
surement A) (Fig. 123). For specifications, refer to
Engine Specifications in this section. The valve tip
chamfer may need to be reground to prevent seal
damage when the valve is installed.
CLEANING
Clean all valve guides, valves and valve spring
assemblies thoroughly with suitable cleaning solution
before reassembling.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves using
a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 124). The valve stem
seals should be pushed firmly and squarely over
valve guide.CAUTION: If oversize valves are used, there is only
one oversize valve available. The same stem seal is
used on both the standard and oversize valve.
(3) Install valve springs and retainers. Compress
valve springs only enough to install locks, taking
care not to misalign the direction of compression.
Nicked valve stems may result from misalignment of
the valve spring compressor.
CAUTION: When depressing the valve spring
retainers with valve spring compressor the locks
can become dislocated. Check to make sure both
locks are in their correct location after removing
tool.
(4) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat (measurment B) (Fig.
123). Make sure measurements are taken from top of
spring seat to the bottom surface of spring retainer.
If height is greater than 40.18 mm (1.58 in.), install
Fig. 122 Valve Seat Refacing
Fig. 123 Spring Installed Height and Valve Tip to
Spring Seat Dimensions
1 ± GARTER SPRING
2 ± VALVE SPRING SEAT
3 ± CYLINDER HEAD SURFACE
Fig. 124 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
1 ± VALVE SEAL TOOL
2 ± VALVE STEM
9 - 62 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 786 of 1285

a 0.762 mm (0.030 in.) spacer under the valve spring
seat to bring spring height back within specification.
(5) Install rocker arm shafts as previously
described in this section.
(6) Checking dry lash. Dry lash is the amount of
clearance that exists between the base circle of an
installed cam and the rocker arm roller when the
adjuster is drained of oil and completely collapsed.
Specified dry lash is 1.17 mm (0.046 in.) for intake
and 1.28 mm (0.050 in.) for exhaust. After performing
dry lash check, refill adjuster with oil and allow 10
minutes for adjuster(s) to bleed down before rotating
cam.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
INTAKE MANIFOLD
CLEAN AND INSPECT
Check for:
²Inspect manifold for cracks or distortions.
²Check for torn or missing O-rings at the mating
surface of the manifold (Fig. 125).
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
CLEAN AND INSPECT
(1) Discard gasket and clean all gasket surfaces of
manifolds and cylinder head.
(2) Test manifold gasket surfaces for flatness with
straight edge. Surface must be flat within 0.15 mm
per 300 mm (.006 in. per foot) of manifold length.
(3) Inspect manifolds for cracks or distortion.
Replace manifold if necessary.
CYLINDER HEAD AND CAMSHAFT JOURNALS
CLEANING
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head. Be
careful not to gouge or scratch the aluminum head
sealing surface. Clean all engine oil passages.
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
Neveruse the following to clean aluminum gasket
surfaces:
²Metal scraper
²Abrasive pad or paper to clean cylinder block
and head
²High speed power tool with an abrasive pad or a
wire brush (Fig. 126)
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets
require a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:
²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 126)
²Drill motor with 3M RolocyBristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 126)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM can
damage the sealing surfaces. The mild (white, 120
grit) bristle disc is recommended. If necessary, the
medium (yellow, 80 grit) bristle disc may be used
on cast iron surfaces with care.
Fig. 125 Intake Manifold O-Rings
1 ± INTAKE MANIFOLD O-RING GASKETS
Fig. 126 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 ± ABRASIVE PAD
2 ± 3M ROLOCYBRISTLE DISC
3 ± PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 63
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 787 of 1285

INSPECTING CYLINDER HEAD
Check cylinder head for flatness with a straight
edge. Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm
(0.004 in.) (Fig. 127).
INSPECTING CAMSHAFT JOURNALS
Inspect cylinder head camshaft bearings for wear.
Check the camshaft journals for scratches and worn
areas. If light scratches are present, they may be
removed with 400 grit sand paper. If deep scratches
are present, replace the camshaft and check the cyl-
inder head for damage. Replace the cylinder head if
worn or damaged. Check the lobes for pitting and
wear. If the lobes show signs of wear, check the cor-
responding rocker arm roller for wear or damage.
Replace rocker arm/hydraulic lash adjuster if worn or
damaged. If lobes show signs of pitting on the nose,
flank or base circle; replace the camshaft.
OIL PUMP
(1) Clean all parts thoroughly. Mating surface of
the oil pump should be smooth. Replace pump cover
if scratched or grooved.
(2) Lay a straightedge across the pump cover sur-
face (Fig. 128). If a 0.076 mm (0.003 inch.) feeler
gauge can be inserted between cover and straight
edge, cover should be replaced.
(3) Measure thickness and diameter of outer rotor.
If outer rotor thickness measures 7.64 mm (0.301
inch.) or less (Fig. 129), or if the diameter is 79.95
mm (3.148 inches) or less, replace outer rotor.
(4) If inner rotor measures 7.64 mm (0.301 inch) or
less replace inner rotor (Fig. 130).
(5) Slide outer rotor into pump housing, press to
one side with fingers and measure clearance between
rotor and housing (Fig. 131). If measurement is 0.39
Fig. 127 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
2 ± STRAIGHT EDGE
Fig. 128 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
1 ± OIL PUMP BODY
2 ± OIL PUMP COVER
3 ± OUTER ROTOR
4 ± INNER ROTOR
Fig. 129 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
Fig. 130 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
9 - 64 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 788 of 1285

mm (0.015 inch.) or more, replace housing only if
outer rotor is in specification.
(6) Install inner rotor into pump housing. If clear-
ance between inner and outer rotors (Fig. 132) is
0.203 mm (0.008 inch) or more, replace both rotors.(7) Place a straightedge across the face of the
pump housing, between bolt holes. If a feeler gauge
of 0.102 mm (0.004 inch) or more can be inserted
between rotors and the straightedge, replace pump
assembly (Fig. 133).ONLYif rotors are in specs.
(8) Inspect oil pressure relief valve plunger for
scoring and free operation in its bore. Small marks
may be removed with 400-grit wet or dry sandpaper.
(9) The relief valve spring has a free length of
approximately 60.7 mm (2.39 inches) it should test
between 18 and 19 pounds when compressed to 40.5
mm (1.60 inches). Replace spring that fails to meet
specifications.
(10) If oil pressure is low and pump is within spec-
ifications, inspect for worn engine bearings, damaged
or missing oil pick-up tube O-ring, clogged oil pick-up
tube screen, clogged oil filter and stuck open pres-
sure relief valve or other reasons for oil pressure
loss.
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BORE
(1) Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all
core hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
(2) If new core plugs are installed, refer to Engine
Core Plugs in this section.
(3) Examine block and cylinder bores for cracks or
fractures.
Fig. 131 Measuring Outer Rotor Clearance in
Housing
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
2 ± OUTER ROTOR
Fig. 132 Measuring Clearance Between Rotors
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
2 ± INNER ROTOR
3 ± OUTER ROTOR
Fig. 133 Measuring Clearance Over Rotors
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
2 ± STRAIGHT EDGE
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 65
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 791 of 1285

SPECIFICATIONS
2.0L SOHC ENGINE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
General Specification
Type In-Line OHV, SOHC
Number of Cylinders 4
Displacement 2.0 Liters
(122 cu. in.)
Bore 87.5 mm
(3.445 in.)
Stroke 83.0 mm
(3.268 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.8:1
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
Compression Pressure 1172±1551 kPa
(170±225 psi)
Max. Variation Between
Cylinders25%
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diameter 87.4924±87.5076 mm
(3.4446±3.4452 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.) 0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Pistons (Federal Emission)
Piston Diameter 87.463±87.481 mm
(3.4434±3.4441 in.)
Clearance 17.5 mm
(11/16 in.) from bottom of
skirt0.012±0.044 mm
(0.0004±0.0017 in.)
Weight 325±335 grams
(11.47±11.82 oz.)
Land Clearance
(Diametrical)0.734±0.797 mm
(0.029±0.031 in.)
Piston Length 64 mm
(2.520 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 13.989±4.188 mm
(0.157±0.165 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 24.462±4.661 mm
(0.176±0.184 in.)
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 33.847±4.131 mm
(0.151±0.163 in.)
Pistons (Low Emission VehicleÐLEV/ULEV)
Piston Diameter 87.456±87.474 mm
(3.4432±3.4439 in.)
Clearance 10.42 mm
(0.42 in.) from bottom of
skirt0.018±0.50 mm
(0.0008±0.0020 in.)
Weight 320±329 grams
(11.29±11.60 oz.)
Land Clearance
(Diametrical)0.758±0.790 mm
(0.0299±0.0312 in.)
Piston Length 55.8 mm
(2.197 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 13.989±4.188 mm
(0.157±0.165 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 24.462±4.661 mm
(0.176±0.184 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 33.847±4.131 mm
(0.151±0.163 in.)
Piston Pins
Clearance in Piston 0.008±0.015 mm
(0.0003±0.0006 in.)
Clearance in Connecting
RodInterference
Diameter 21.000±21.003 mm
(0.8268±0.8269 in.)
End Play None
Length 74.75±75.25 mm
(2.943±2.963 in.)
Piston Rings
Ring GapÐTop
Compression Ring0.23±0.52 mm
(0.009±0.020 in.)
Wear Limit 0.8 mm
(0.031 in.)
Ring GapÐ2nd
Compression Ring0.49±0.78 mm
(0.019±0.031 in.)
Wear Limit 1.0 mm
(0.039 in.)
Ring GapÐOil Control
Steel Rails0.23±0.66 mm
(0.009±0.026 in.)
9 - 68 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
Page 792 of 1285

DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Wear Limit 1.0 mm
(0.039 in.)
Ring Side ClearanceÐ
Compression Rings0.025±0.065 mm
(0.0010±0.0026 in.)
Wear Limit 0.10 mm
(0.004 in.)
Ring Side ClearanceÐOil
Ring Pack0.004±0.178 mm
(0.0002±0.0070 in.)
Ring WidthÐ
Compression Rings1.17±1.19 mm
(0.046±0.047 in.)
Ring WidthÐOil Ring
Pack2.854±3.008 mm
(0.1124±0.1184 in.)
Connecting Rod
Bearing Clearance 0.026±0.059 mm
(0.001±0.0023 in.)
Wear Limit 0.075 mm
(0.003 in.)
Bore DiameterÐPiston
Pin20.96±20.98 mm
(0.8252±0.8260 in.)
Bore DiameterÐ
Crankshaft End50.991±51.005 mm
(2.0075±2.0081 in.)
Side Clearance 0.13±0.38 mm
(0.005±0.015 in.)
Wear Limit 0.40 mm
(0.016 in.)
WeightÐTotal (Less
Bearing)543 grams
(1.20 lbs.)
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal
Diameter47.9924±48.0076 mm
(1.8894±1.8900 in.)
Main Bearing Journal
Diameter51.9924±52.0076 mm
(2.0469±2.0475 in.)
Journal Out-of-Round
(Max.)0.0035 mm
(0.0001 in.)
Journal Taper (Max.) 0.0038 mm
(0.0001 in.)
End Play 0.09±0.24 mm
(0.0035±0.0094 in.)
Wear Limit 0.37 mm
(0.015 in.)
Main Bearing Diametrical
Clearance0.022±0.062 mm
(0.0008±0.0024 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Rocker Arm Shaft
Rocker Arm Shaft
Diameter19.966±19.984 mm
(0.7861±0.7868 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft Retainers
IntakeÐWidth 28.43±28.49 mm
(1.1193±1.1217 in.)
ExhaustÐWidth1&529.15±29.25 mm
(1.1477±1.1516 in.)
ExhaustÐWidth 2, 3, and
440.40±40.50 mm
(1.5906±1.5945 in.)
Rocker Arm/Hydraulic Lash Adjuster
Rocker Arm Inside
Diameter20.00±20.02 mm
(0.787±0.788 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft
Clearance0.016±0.054 mm
(0.0006±0.0021 in.)
Body Diameter 22.949±22.962 mm
(0.9035±0.9040 in.)
Plunger Travel Minimum
(Dry)2.2 mm
(0.087 in.)
Dry LashÐIntake 1.17 mm
(0.046 in.)
Dry LashÐExhaust 1.28 mm
(0.050 in.)
Rocker Arm Ratio 1.4 to 1
Cylinder Head Camshaft Bearing Diameter
Journal No. 1 41.20±41.221 mm
(1.622±1.6228 in.)
Journal No. 2 41.60±41.62 mm
(1.637±1.638 in.)
Journal No. 3 42.0±42.02 mm
(1.653±1.654 in.)
Journal No. 4 42.4±42.42 mm
(1.669±1.670 in.)
Journal No. 5 42.8±42.82 mm
(1.685±1.6858 in.)
Camshaft
Journal Diameter
No. 1 41.128±41.147 mm
(1.619±1.6199 in.)
No. 2 41.528±41.547 mm
(1.634±1.635 in.)
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 69
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 794 of 1285
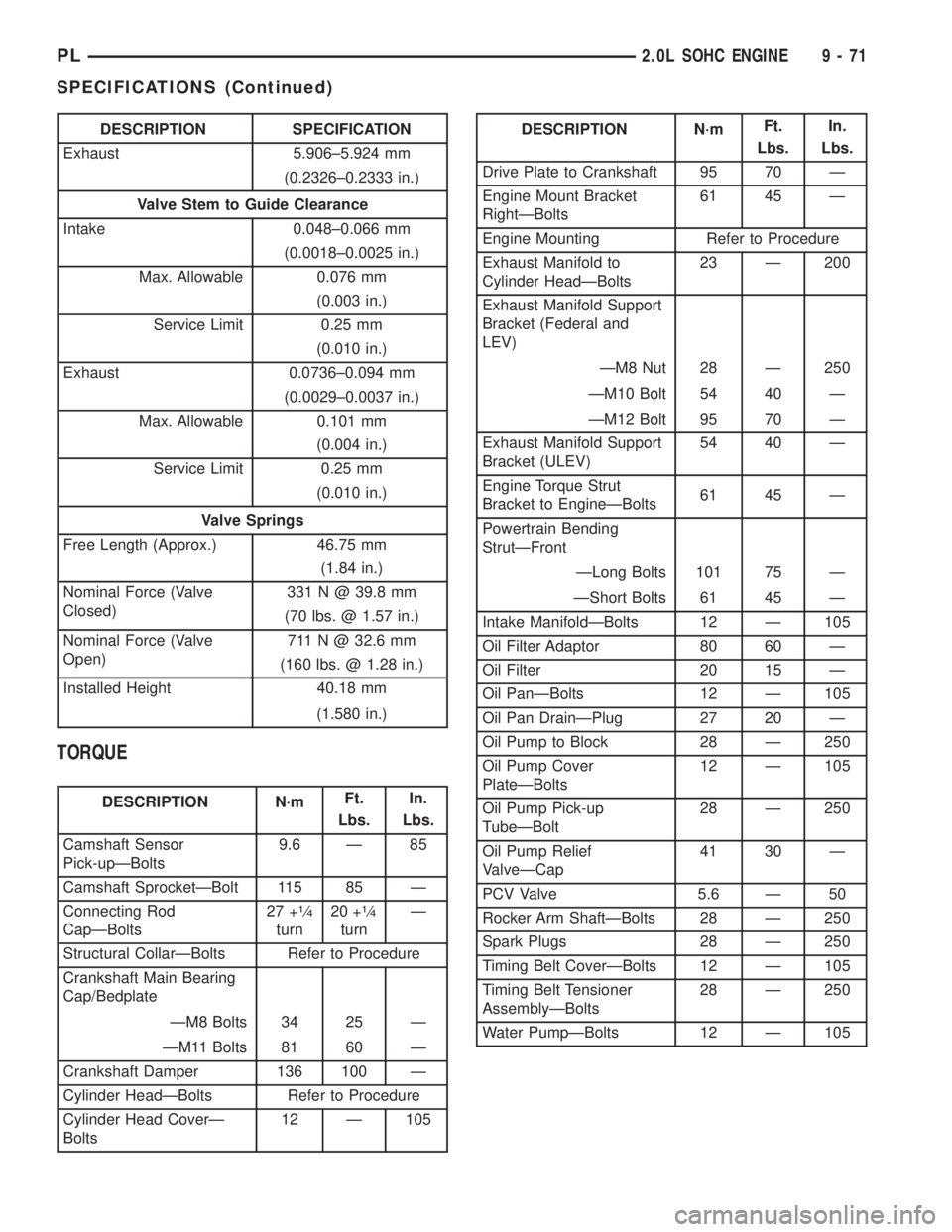
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Exhaust 5.906±5.924 mm
(0.2326±0.2333 in.)
Valve Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake 0.048±0.066 mm
(0.0018±0.0025 in.)
Max. Allowable 0.076 mm
(0.003 in.)
Service Limit 0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)
Exhaust 0.0736±0.094 mm
(0.0029±0.0037 in.)
Max. Allowable 0.101 mm
(0.004 in.)
Service Limit 0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)
Valve Springs
Free Length (Approx.) 46.75 mm
(1.84 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve
Closed)331 N @ 39.8 mm
(70 lbs. @ 1.57 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve
Open)711 N @ 32.6 mm
(160 lbs. @ 1.28 in.)
Installed Height 40.18 mm
(1.580 in.)
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Camshaft Sensor
Pick-upÐBolts9.6 Ð 85
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 115 85 Ð
Connecting Rod
CapÐBolts27 +
1¤4
turn20 +
1¤4
turnÐ
Structural CollarÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Crankshaft Main Bearing
Cap/Bedplate
ÐM8 Bolts 34 25 Ð
ÐM11 Bolts 81 60 Ð
Crankshaft Damper 136 100 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Cylinder Head CoverÐ
Bolts12 Ð 105
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Drive Plate to Crankshaft 95 70 Ð
Engine Mount Bracket
RightÐBolts61 45 Ð
Engine Mounting Refer to Procedure
Exhaust Manifold to
Cylinder HeadÐBolts23 Ð 200
Exhaust Manifold Support
Bracket (Federal and
LEV)
ÐM8 Nut 28 Ð 250
ÐM10 Bolt 54 40 Ð
ÐM12 Bolt 95 70 Ð
Exhaust Manifold Support
Bracket (ULEV)54 40 Ð
Engine Torque Strut
Bracket to EngineÐBolts61 45 Ð
Powertrain Bending
StrutÐFront
ÐLong Bolts 101 75 Ð
ÐShort Bolts 61 45 Ð
Intake ManifoldÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Filter Adaptor 80 60 Ð
Oil Filter 20 15 Ð
Oil PanÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Pan DrainÐPlug 27 20 Ð
Oil Pump to Block 28 Ð 250
Oil Pump Cover
PlateÐBolts12 Ð 105
Oil Pump Pick-up
TubeÐBolt28 Ð 250
Oil Pump Relief
ValveÐCap41 30 Ð
PCV Valve 5.6 Ð 50
Rocker Arm ShaftÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Spark Plugs 28 Ð 250
Timing Belt CoverÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Timing Belt Tensioner
AssemblyÐBolts28 Ð 250
Water PumpÐBolts 12 Ð 105
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 71
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 801 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EXHAUST SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE
EXHAUST NOISE
(UNDER HOOD)1. Exhaust manifold cracked or broken. 1. Replace manifold.
2. Manifold to cylinder head leak. 2. Tighten manifold and/or replace gasket.
3. Exhaust Flex joint to manifold leak. 3. Tighten fasteners or replace gasket.
4. Exhaust flex joint. 4. Replace catalytic converter assembly.
5. Pipe and shell noise from front exhaust
pipe.5. Characteristic of single wall pipes.
EXCESSIVE
EXHAUST NOISE1. Leaks at pipe joints. 1. Tighten or replace clamps at leaking
joints.
2. Burned, blown, or rusted out exhaust
pipe or muffler.2. Replace muffler or exhaust pipes.
3. Restriction in muffler or tailpipe. 3. Remove restriction, if possible or replace
as necessary.
4. Catalytic converter material in muffler. 4. Replace muffler and converter assembly.
Check fuel injection and ignition systems for
proper operation.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EXHAUST PIPE AND MUFFLER
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATING TIME.
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and apply penetrating oil
to band clamp fastener of component being removed.
NOTE: Do not use petroleum-based lubricants
when removing/installing muffler or exhaust pipe
isolators as it may compromise the life of the part.
A suitable substitute is a mixture of liquid dish
soap and water.
(2) Remove exhaust system ground strap.
(3) Loosen band clamp and remove support isola-
tors at muffler. Remove muffler from exhaust pipe
(Fig. 7).(4) Loosen band clamp at the catalytic converter to
intermediate pipe joint (Fig. 7)
(5) Remove intermediate pipe support isolator.
Separate at slip joint and remove intermediate pipe
(Fig. 7).
(6) Clean ends of pipes and muffler to assure mat-
ing of all parts. Discard broken or worn isolators,
rusted or overused clamps, supports, and attaching
parts.
NOTE: When replacement is required on any com-
ponent of the exhaust system, you must use origi-
nal equipment parts (or their equivalent).
INSTALLATION
When assembling exhaust systemdo nottighten
clamps until components are aligned and clearances
are checked.
(1) Assemble intermediate pipe to catalytic con-
verter and the isolator support to the underbody (Fig.
7).
(2) Install the muffler to intermediate pipe and the
isolator supports to the underbody.
(3) Working from the front of system; align each
component to maintain position and proper clearance
with underbody parts (Fig. 9). Tighten band clamps
to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 8).
11 - 4 EXHAUST SYSTEMPL
Page 831 of 1285
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting
without the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean 30 weight engine
oil.
(3) Push the quick-connect fitting over the fuel
tube until theretainer seats and a click is heard.
(4) The plastic quick-connect fitting has windows
in the sides of the casing. When the fitting com-
pletely attaches to the fuel tube, the retainer locking
ears and the fuel tube shoulder are visible in the
windows. If they are not visible, the retainer was not
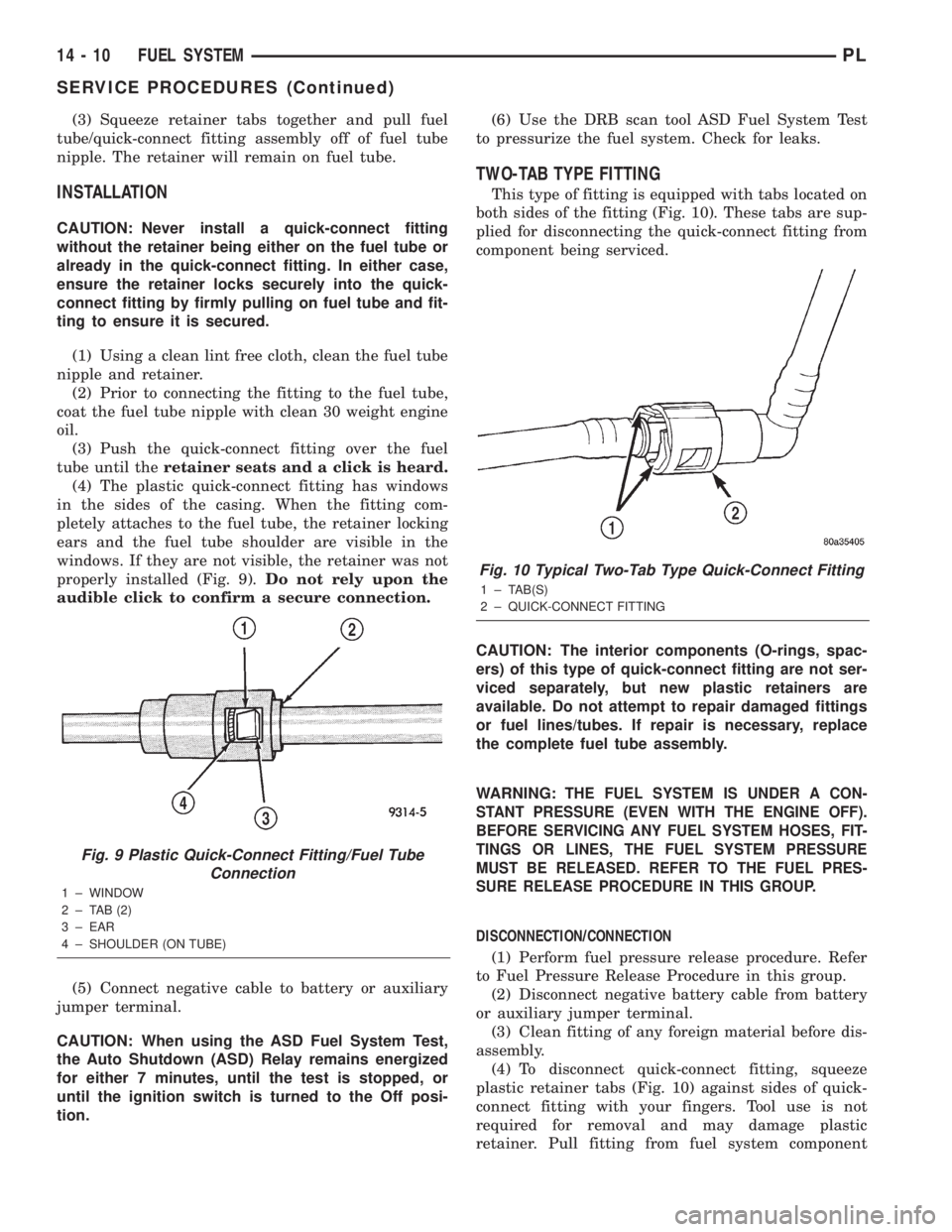
properly installed (Fig. 9).Do not rely upon the
audible click to confirm a secure connection.
(5) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or
until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.(6) Use the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test
to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
TWO-TAB TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting is equipped with tabs located on
both sides of the fitting (Fig. 10). These tabs are sup-
plied for disconnecting the quick-connect fitting from
component being serviced.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers) of this type of quick-connect fitting are not ser-
viced separately, but new plastic retainers are
available. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings
or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace
the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING:
THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES, FIT-
TINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To disconnect quick-connect fitting, squeeze
plastic retainer tabs (Fig. 10) against sides of quick-
connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is not
required for removal and may damage plastic
retainer. Pull fitting from fuel system component
Fig. 9 Plastic Quick-Connect Fitting/Fuel Tube
Connection
1 ± WINDOW
2 ± TAB (2)
3 ± EAR
4 ± SHOULDER (ON TUBE)
Fig. 10 Typical Two-Tab Type Quick-Connect Fitting
1 ± TAB(S)
2 ± QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
14 - 10 FUEL SYSTEMPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)