motor DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 682 of 1285
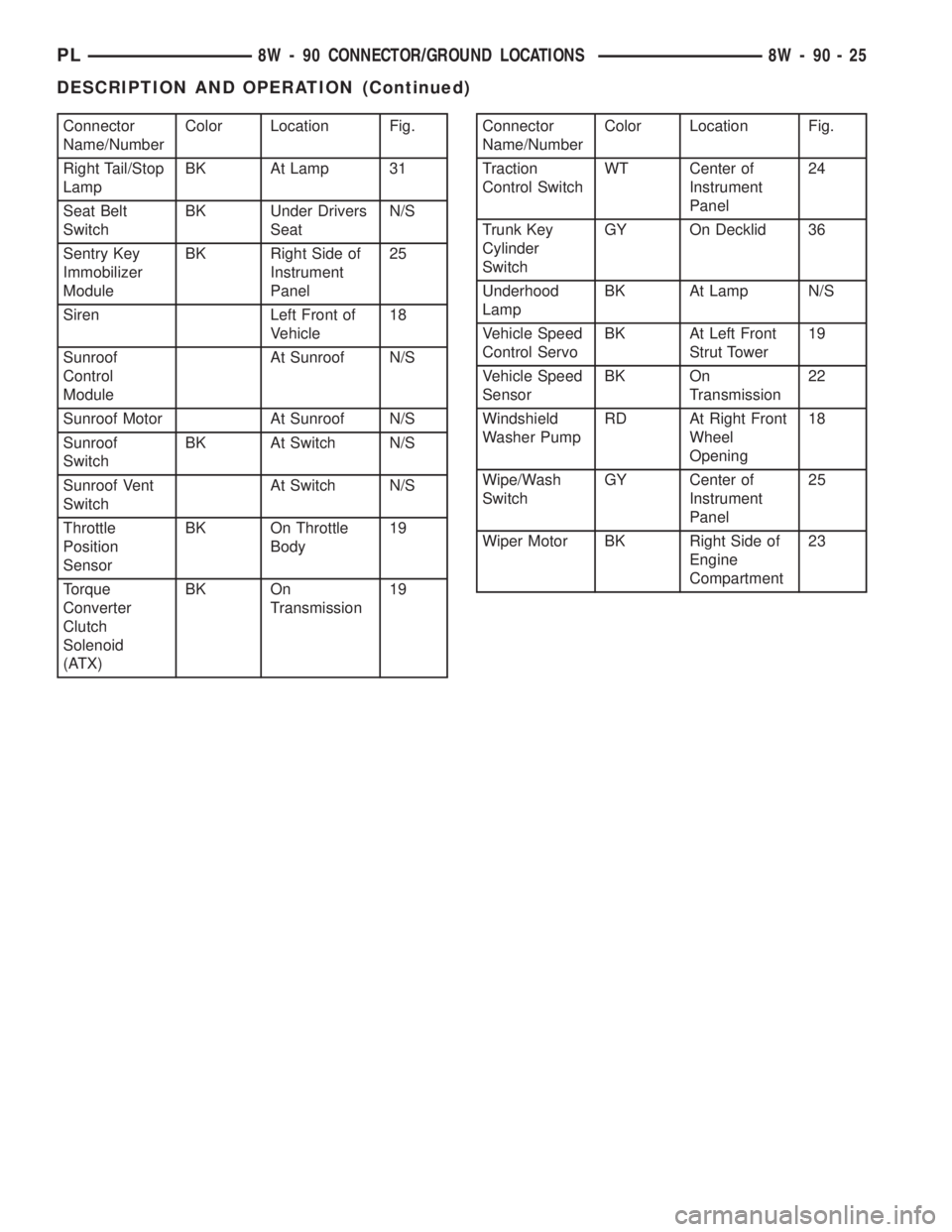
Connector
Name/NumberColor Location Fig.
Right Tail/Stop
LampBK At Lamp 31
Seat Belt
SwitchBK Under Drivers
SeatN/S
Sentry Key
Immobilizer
ModuleBK Right Side of
Instrument
Panel25
Siren Left Front of
Vehicle18
Sunroof
Control
ModuleAt Sunroof N/S
Sunroof Motor At Sunroof N/S
Sunroof
SwitchBK At Switch N/S
Sunroof Vent
SwitchAt Switch N/S
Throttle
Position
SensorBK On Throttle
Body19
Torque
Converter
Clutch
Solenoid
(ATX)BK On
Transmission19Connector
Name/NumberColor Location Fig.
Traction
Control SwitchWT Center of
Instrument
Panel24
Trunk Key
Cylinder
SwitchGY On Decklid 36
Underhood
LampBK At Lamp N/S
Vehicle Speed
Control ServoBK At Left Front
Strut Tower19
Vehicle Speed
SensorBK On
Transmission22
Windshield
Washer PumpRD At Right Front
Wheel
Opening18
Wipe/Wash
SwitchGY Center of
Instrument
Panel25
Wiper Motor BK Right Side of
Engine
Compartment23
PL8W - 90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONS 8W - 90 - 25
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 698 of 1285
8W-95 SPLICE LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
This section provides illustrations identifying the
general location of the splices in this vehicle. A splice
index is provided. Use the wiring diagrams in each
section for splice number identification. Refer to the
index for proper splice number.
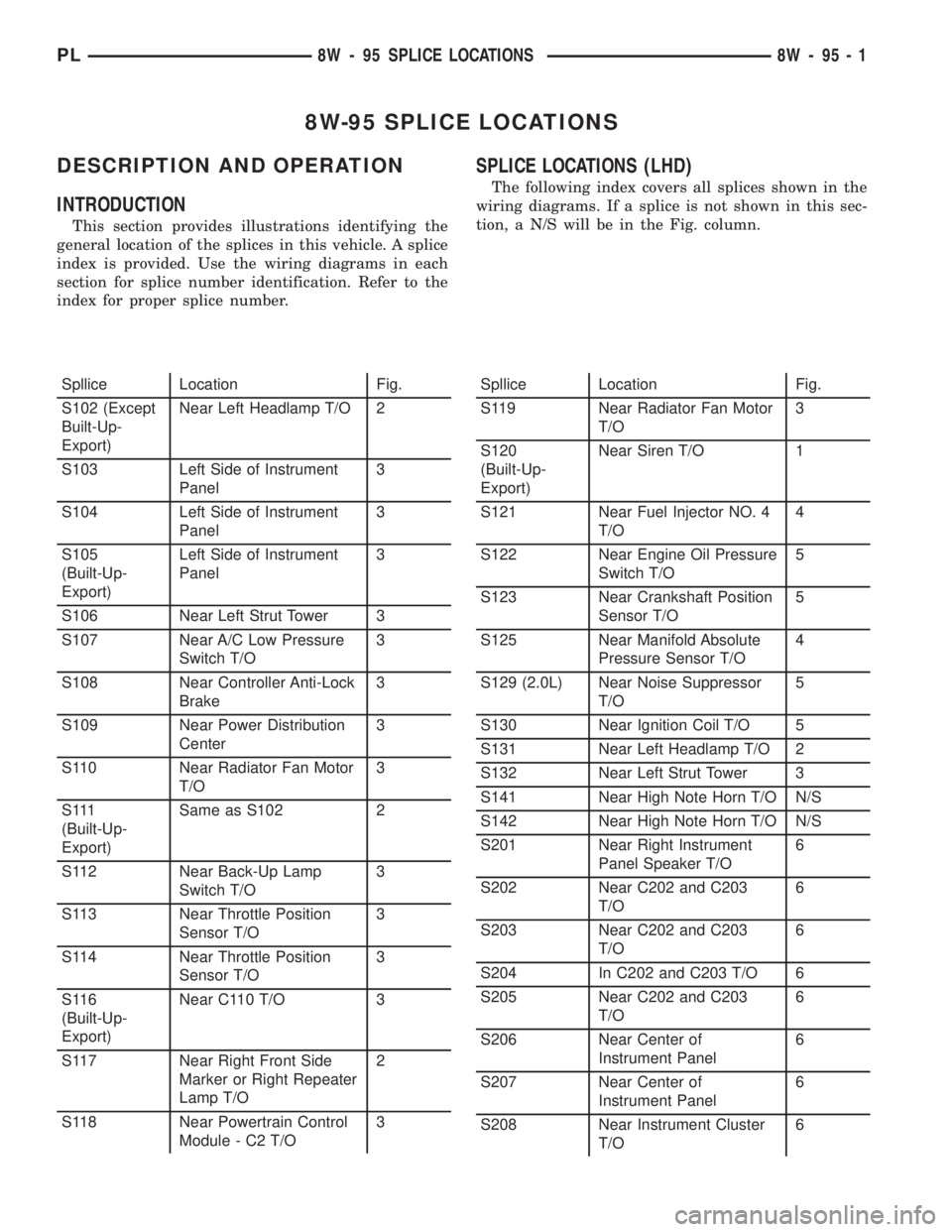
SPLICE LOCATIONS (LHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S102 (Except
Built-Up-
Export)Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S103 Left Side of Instrument
Panel3
S104 Left Side of Instrument
Panel3
S105
(Built-Up-
Export)Left Side of Instrument
Panel3
S106 Near Left Strut Tower 3
S107 Near A/C Low Pressure
Switch T/O3
S108 Near Controller Anti-Lock
Brake3
S109 Near Power Distribution
Center3
S110 Near Radiator Fan Motor
T/O3
S 111
(Built-Up-
Export)Same as S102 2
S112 Near Back-Up Lamp
Switch T/O3
S113 Near Throttle Position
Sensor T/O3
S114 Near Throttle Position
Sensor T/O3
S116
(Built-Up-
Export)Near C110 T/O 3
S117 Near Right Front Side
Marker or Right Repeater
Lamp T/O2
S118 Near Powertrain Control
Module - C2 T/O3Spllice Location Fig.
S119 Near Radiator Fan Motor
T/O3
S120
(Built-Up-
Export)Near Siren T/O 1
S121 Near Fuel Injector NO. 4
T/O4
S122 Near Engine Oil Pressure
Switch T/O5
S123 Near Crankshaft Position
Sensor T/O5
S125 Near Manifold Absolute
Pressure Sensor T/O4
S129 (2.0L) Near Noise Suppressor
T/O5
S130 Near Ignition Coil T/O 5
S131 Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S132 Near Left Strut Tower 3
S141 Near High Note Horn T/O N/S
S142 Near High Note Horn T/O N/S
S201 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O6
S202 Near C202 and C203
T/O6
S203 Near C202 and C203
T/O6
S204 In C202 and C203 T/O 6
S205 Near C202 and C203
T/O6
S206 Near Center of
Instrument Panel6
S207 Near Center of
Instrument Panel6
S208 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O6
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 1
Page 699 of 1285
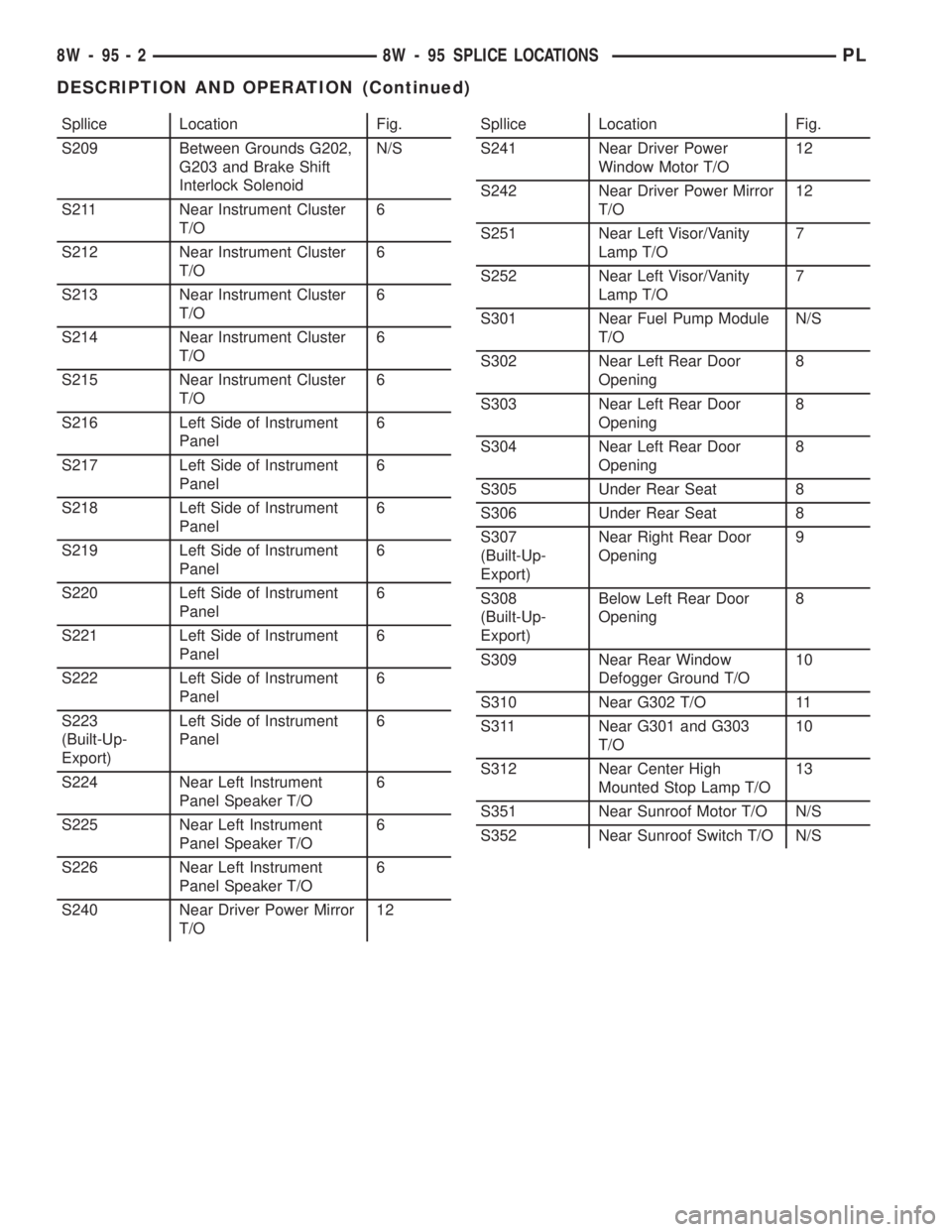
Spllice Location Fig.
S209 Between Grounds G202,
G203 and Brake Shift
Interlock SolenoidN/S
S211 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O6
S212 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O6
S213 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O6
S214 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O6
S215 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O6
S216 Left Side of Instrument
Panel6
S217 Left Side of Instrument
Panel6
S218 Left Side of Instrument
Panel6
S219 Left Side of Instrument
Panel6
S220 Left Side of Instrument
Panel6
S221 Left Side of Instrument
Panel6
S222 Left Side of Instrument
Panel6
S223
(Built-Up-
Export)Left Side of Instrument
Panel6
S224 Near Left Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O6
S225 Near Left Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O6
S226 Near Left Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O6
S240 Near Driver Power Mirror
T/O12Spllice Location Fig.
S241 Near Driver Power
Window Motor T/O12
S242 Near Driver Power Mirror
T/O12
S251 Near Left Visor/Vanity
Lamp T/O7
S252 Near Left Visor/Vanity
Lamp T/O7
S301 Near Fuel Pump Module
T/ON/S
S302 Near Left Rear Door
Opening8
S303 Near Left Rear Door
Opening8
S304 Near Left Rear Door
Opening8
S305 Under Rear Seat 8
S306 Under Rear Seat 8
S307
(Built-Up-
Export)Near Right Rear Door
Opening9
S308
(Built-Up-
Export)Below Left Rear Door
Opening8
S309 Near Rear Window
Defogger Ground T/O10
S310 Near G302 T/O 11
S311 Near G301 and G303
T/O10
S312 Near Center High
Mounted Stop Lamp T/O13
S351 Near Sunroof Motor T/O N/S
S352 Near Sunroof Switch T/O N/S
8W - 95 - 2 8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 710 of 1285
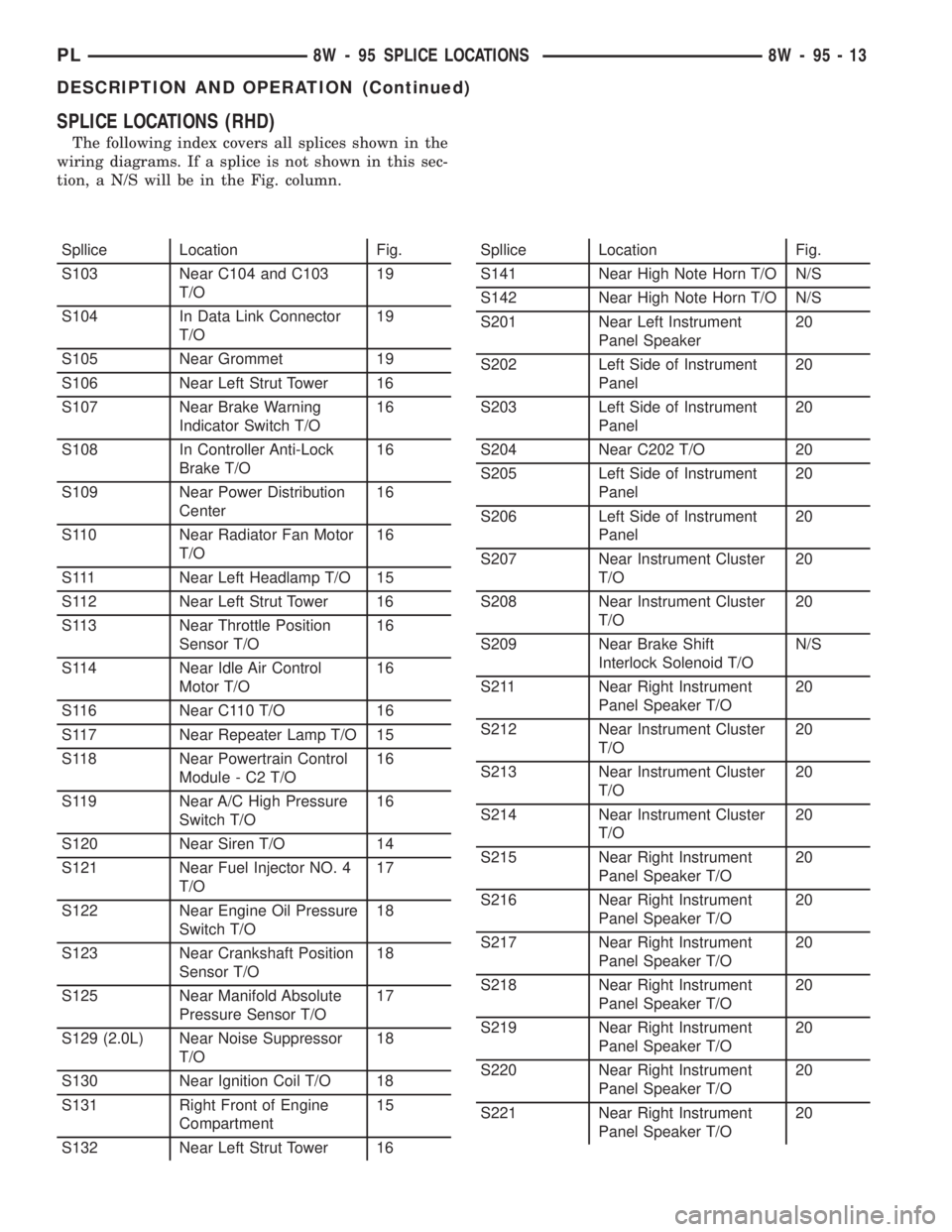
SPLICE LOCATIONS (RHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S103 Near C104 and C103
T/O19
S104 In Data Link Connector
T/O19
S105 Near Grommet 19
S106 Near Left Strut Tower 16
S107 Near Brake Warning
Indicator Switch T/O16
S108 In Controller Anti-Lock
Brake T/O16
S109 Near Power Distribution
Center16
S110 Near Radiator Fan Motor
T/O16
S111 Near Left Headlamp T/O 15
S112 Near Left Strut Tower 16
S113 Near Throttle Position
Sensor T/O16
S114 Near Idle Air Control
Motor T/O16
S116 Near C110 T/O 16
S117 Near Repeater Lamp T/O 15
S118 Near Powertrain Control
Module - C2 T/O16
S119 Near A/C High Pressure
Switch T/O16
S120 Near Siren T/O 14
S121 Near Fuel Injector NO. 4
T/O17
S122 Near Engine Oil Pressure
Switch T/O18
S123 Near Crankshaft Position
Sensor T/O18
S125 Near Manifold Absolute
Pressure Sensor T/O17
S129 (2.0L) Near Noise Suppressor
T/O18
S130 Near Ignition Coil T/O 18
S131 Right Front of Engine
Compartment15
S132 Near Left Strut Tower 16Spllice Location Fig.
S141 Near High Note Horn T/O N/S
S142 Near High Note Horn T/O N/S
S201 Near Left Instrument
Panel Speaker20
S202 Left Side of Instrument
Panel20
S203 Left Side of Instrument
Panel20
S204 Near C202 T/O 20
S205 Left Side of Instrument
Panel20
S206 Left Side of Instrument
Panel20
S207 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O20
S208 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O20
S209 Near Brake Shift
Interlock Solenoid T/ON/S
S211 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S212 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O20
S213 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O20
S214 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O20
S215 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S216 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S217 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S218 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S219 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S220 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S221 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 711 of 1285
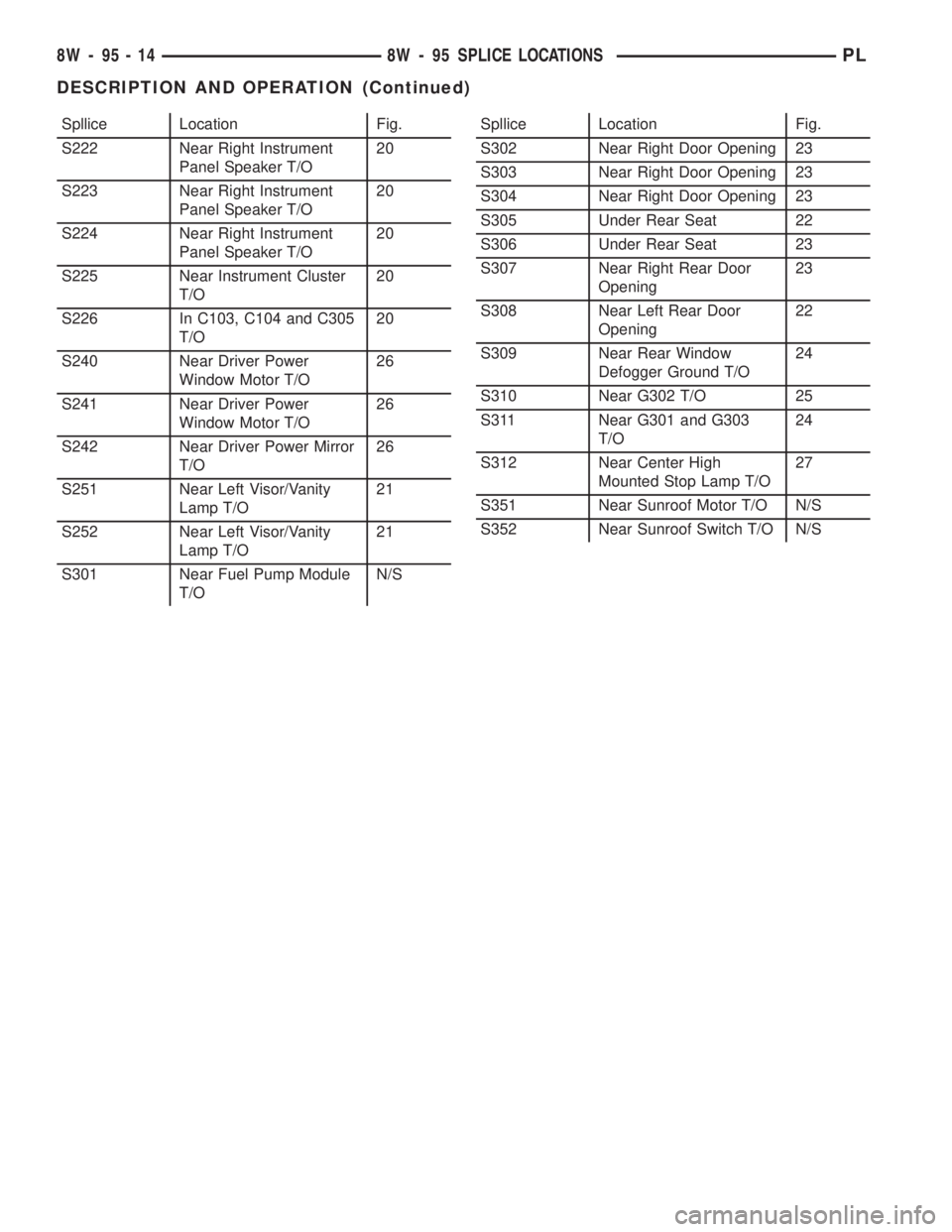
Spllice Location Fig.
S222 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S223 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S224 Near Right Instrument
Panel Speaker T/O20
S225 Near Instrument Cluster
T/O20
S226 In C103, C104 and C305
T/O20
S240 Near Driver Power
Window Motor T/O26
S241 Near Driver Power
Window Motor T/O26
S242 Near Driver Power Mirror
T/O26
S251 Near Left Visor/Vanity
Lamp T/O21
S252 Near Left Visor/Vanity
Lamp T/O21
S301 Near Fuel Pump Module
T/ON/SSpllice Location Fig.
S302 Near Right Door Opening 23
S303 Near Right Door Opening 23
S304 Near Right Door Opening 23
S305 Under Rear Seat 22
S306 Under Rear Seat 23
S307 Near Right Rear Door
Opening23
S308 Near Left Rear Door
Opening22
S309 Near Rear Window
Defogger Ground T/O24
S310 Near G302 T/O 25
S311 Near G301 and G303
T/O24
S312 Near Center High
Mounted Stop Lamp T/O27
S351 Near Sunroof Motor T/O N/S
S352 Near Sunroof Switch T/O N/S
8W - 95 - 14 8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 725 of 1285

MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4 oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
ENGINE GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
Neveruse the following to clean gasket surfaces:
²Metal scraper
²Abrasive pad or paper to clean cylinder block
and head
²High speed power tool with an abrasive pad or a
wire brush (Fig. 1)NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets
require a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:
²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 1)
²Drill motor with 3M RolocyBristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 1)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM can
damage the sealing surfaces. The mild (white, 120
grit) bristle disc is recommended. If necessary, the
medium (yellow, 80 grit) bristle disc may be used
on cast iron surfaces with care.
CRANKSHAFT DAMPER BOLT ACCESS PLUG
An access plug is located in the right splash shield
(Fig. 2). Remove the plug and insert the proper size
socket, extension and ratchet, when crankshaft rota-
tion is necessary.
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup
plug (Fig. 3). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmly
with pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug
(Fig. 3).
Fig. 1 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 ± ABRASIVE PAD
2 ± 3M ROLOCYBRISTLE DISC
3 ± PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
9 - 2 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 727 of 1285

will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done
using a cylinder surfacing hone, recommended tool
C-3501 or equivalent, equipped with 280 grit stones,
if the cylinder bore is straight and round. 20±60
strokes depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Inspect cyl-
inder walls after each 20 strokes, using a light
honing oil.Do not use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a cross-hatch pattern.
When hone marksintersectat 50-60 degrees, the
cross hatch angle is most satisfactory for proper seat-
ing of rings (Fig. 4).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200±300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50±60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.
CAUTION: Ensure all abrasives are removed from
engine parts after honing. It is recommended that a
solution of soap and hot water be used with a
brush and the parts then thoroughly dried. The bore
can be considered clean when it can be wiped
clean with a white cloth and cloth remains clean.
Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.MEASURING WITH PLASTIGAGE
PLASTIGAGE METHOD
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:
NOTE: The total clearance of the main bearings can
only be determined by removing the weight of the
crankshaft. This can be accomplished by either of
two methods:
PREFERRED METHOD
Shim the bearings adjacent to the bearing to be
checked in order to remove the clearance between
upper bearing shell and the crankshaft. This can be
accomplished by placing a minimum of 0.254 mm
(0.010 in.) shim (e. g. cardboard, matchbook cover,
etc.) between the bearing shell and the bearing cap
on the adjacent bearings and tightening bolts to
14-20 N´m (10-15 ft. lbs.). The number of main bear-
ing will vary from engine to engine.
ENGINE WITH 5 MAIN BEARINGS
²When checking #1 main bearing shim #2 main
bearing.
²When checking #2 main bearing shim #1 & 3
main bearing.
²When checking #3 main bearing shim #2 & 4
main bearing.
²When checking #4 main bearing shim #3 & 5
main bearing.
²When checking #5 main bearing shim #4 main
bearing.
ENGINE WITH 4 MAIN BEARING
²When checking #1 main bearing shim # 2 main
bearing.
Fig. 4 Cylinder Bore Cross-Hatch Pattern
1 ± CROSS-HATCH PATTERN
Fig. 5 Plastigage Placed in Lower Shell
1 ± PLASTIGAGE
9 - 4 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 728 of 1285

²When checking #2 main bearing shim #1 & #3
main bearing.
²When checking #3 main bearing shim #2 & #4
main bearing.
²When checking #4 main bearing shim #3 main
bearing.
NOTE: REMOVE ALL SHIMS BEFORE REASSEM-
BLING ENGINE
ALTERNATIVE METHOD
The weight of the crankshaft can be supported by a
jack under the counterweight adjacent to the bearing
being checked.
PLASTIGAGE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 5). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 6) with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Refer to Engine Specifications.Plastigage gener-
ally is accompanied by two scales. One scale is
in inches, the other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine connecting rod bearing clearances can be
determined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. Thefollowing is the recommended procedure for the use
of Plastigage:
(1) Rotate the crankshaft until the connecting rod
to be checked is at the bottom of its stroke.
(2) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the bearing cap approx-
imately 6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from
the oil hole (Fig. 5). In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing plastigage in that area.
(4) Assemble the rod cap with Plastigage in place.
Tighten the rod cap to the specified torque.Do not
rotate the crankshaft while assembling the cap
or the Plastigage may be smeared, giving inac-
curate results.
(5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 6) with the scale pro-
vided on the package. Locate the band closest to the
same width. This band indicates the amount of oil
clearance. Differences in readings between the ends
indicate the amount of taper present. Record all
readings taken. Refer to Engine Specifications.Plas-
tigage generally is accompanied by two scales.
One scale is in inches, the other is a metric
scale. If the bearing clearance exceeds wear
limit specification, replace the bearing.
REPAIR OF DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (including aluminum
head spark plug threads) can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of drilling out worn or
damaged threads, tapping the hole with a special
Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing an insert
into the tapped hole. This brings the hole back to its
original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original centerline.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
Fig. 6 Clearance Measurement
PLENGINE 9 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 731 of 1285

ENGINE DIAGNOSIS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION...................8
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS......8
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST . . . 8
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE
LEAKAGE TEST.........................9LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE
DIAGNOSIS............................9
ENGINE OIL LEAK INSPECTION..............9
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE........11
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL.........12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Service DiagnosisÐMechanical Chart
and the Service DiagnosisÐPerformance Chart, for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. Refer
to Group 14, Fuel System, for the fuel system diag-
nosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If engine RPM'S change, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.
(4) Disconnect coil wire from distributor and
secure to good ground to prevent a spark from start-
ing a fire (Conventional Ignition System). For Direct
Ignition System DIS disconnect the coil connector.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gage adaptor into the #1
spark plug hole in cylinder head. Crank engine until
maximum pressure is reached on gage. Record this
pressure as #1 cylinder pressure.
(7) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(8) Compression should not be less than (689 kPa)
100 psi and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(9) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(10) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
9 - 8 ENGINEPL
Page 752 of 1285

(2) Install intake manifold to lower support
bracket bolts (Fig. 31). Tighten bolts to 11 N´m (95
in. lbs.).
(3) Remove covering from fuel injector holes and
insure the holes are clean. Install fuel rail assembly
to intake manifold. Tighten screws to 23 N´m (200 in.
lbs.).
(4) Connect PCV and brake booster hoses.
(5) Inspect quick connect fittings for damage,
replace if necessary Refer to Group 14, Fuel System
for procedure. Apply a light amount of clean engine
oil to fuel inlet tube. Connect fuel supply hose to fuel
rail assembly. Check connection by pulling on connec-
tor to insure it locked into position.
(6) Connect Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Sensor wiring connector (Fig. 29).(7) Connect knock sensor connector, and wiring at
starter.
(8) Install inlet air duct to intake manifold and
throttle body. Tighten clamp to 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
(9) Connect negative cable to battery.
(10) With the DRB scan tool use ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize system to check for leaks.
Fig. 29 MAP Sensor
Fig. 30 Knock Sensor
1 ± KNOCK SENSOR
2 ± STARTER MOTOR
Fig. 31 Intake Manifold Lower Supports
1 ± BOLT
2 ± BRACKET
3 ± BRACKET
4 ± BOLT
Fig. 32 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 29
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)