DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 961 of 1285

SHIFT CROSSOVER SHAFT BUSHING
REMOVAL
(1) Install slide hammer #3752 through the cross-
over bushing.
(2) Thread nut and washer onto slide hammer.
(3) Using the slide hammer, remove the crossover
shaft bushing (Fig. 155).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the replacement crossover shaft bush-
ing over the crossover shaft bushing bore.
(2) Using an appropriate size deep±well socket,
install the crossover shaft bushing into the bushing
bore.
REAR BEARING OIL FEED TROUGH
The bearing oil feed trough is retained in the case
by a pin that is molded into the case and clips that
are part of the trough (Fig. 156).
REMOVAL
(1) Using light plier pressure, squeeze the clips
together at the rear of the trough.
(2) Slide the trough over the retaining pin that
locates the trough in the case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Reverse removal procedure to install oil feed
trough.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
TRANSAXLE
Clean the gears, bearings, shafts, synchronizers,
thrust washers, oil feeder, shift mechanism, gear
case, and bellhousing with solvent. Dry all parts
except the bearings with compressed air. Allow the
bearings to either air dry or wipe them dry with
clean shop towels.
Inspect the gears, bearings, shafts and thrust wash-
ers. Replace the bearings and cups if the rollers are
worn, chipped, cracked, flat spotted, or brinnelled, or if
the bearing cage is damaged or distorted. Replace the
thrust washers if cracked, chipped, or worn. Replace
the gears if the teeth are chipped, cracked, or worn
thin. Inspect the synchronizers. Replace the sleeve if
worn or damaged in any way. Replace the stop rings if
the friction material is burned, flaking off, or worn.
Check the condition of the synchro keys and springs.
Replace these parts if worn, cracked, or distorted.
SYNCHRONIZER
CLEAN
Do not attempt to clean the blocking rings in sol-
vent. The friction material will become contaminated.
Place synchronizer components in a suitable holder
and clean with solvent. Air dry.
INSPECT
Proper inspection of components involve:
²Teeth, for wear, scuffed, nicked, burred, or bro-
ken teeth
²Keys, for wear or distortion
²Balls and springs, for distortion, cracks, or wear
If any of these conditions exist in these compo-
nents, replace as necessary.
Fig. 155 Crossover Shaft Bushing Removal
1 ± SLIDE HAMMER
2 ± SHIFTER SHAFT BUSHING
Fig. 156 Oil Feed Trough
1 ± OIL FEED TROUGH
21 - 48 TRANSAXLEPL
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 962 of 1285
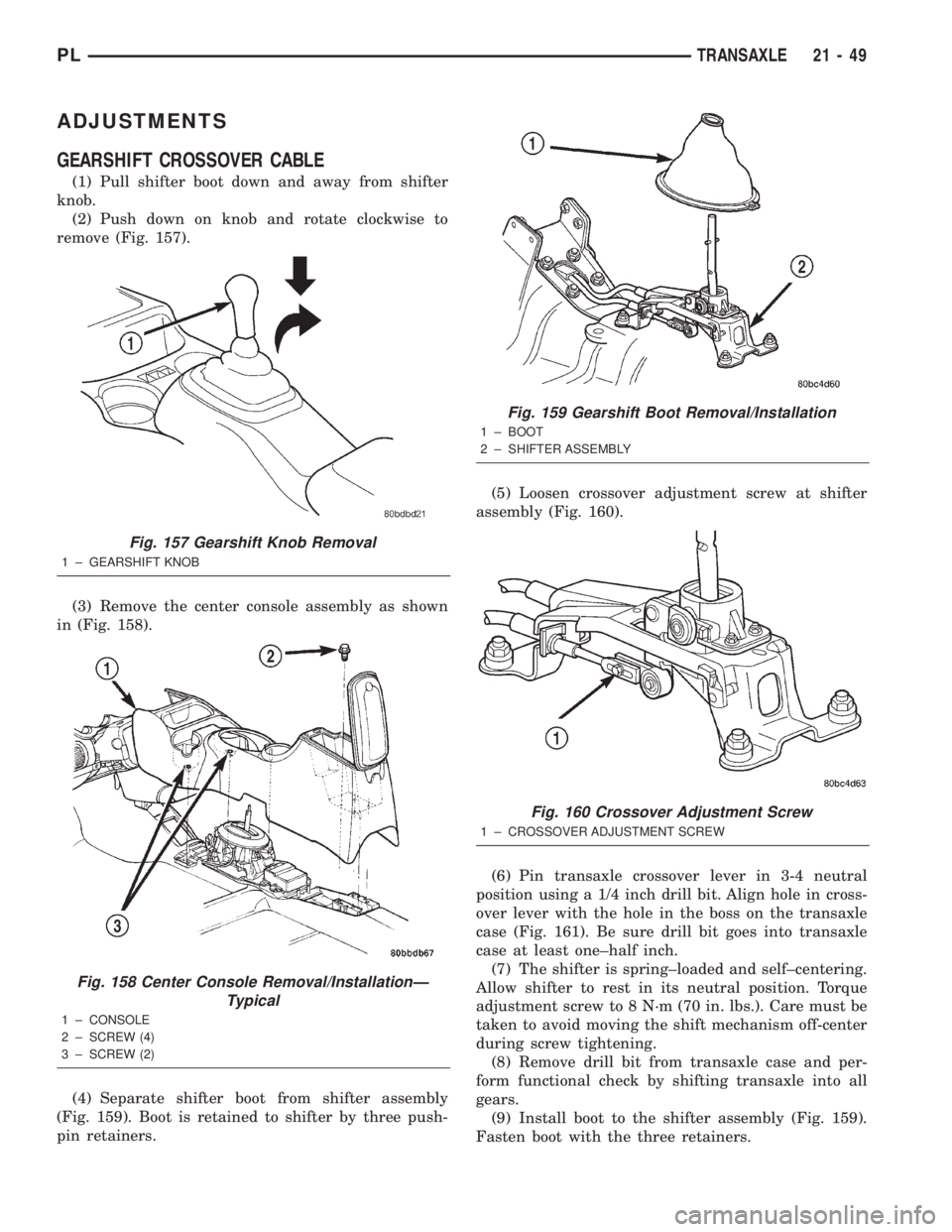
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CROSSOVER CABLE
(1) Pull shifter boot down and away from shifter
knob.
(2) Push down on knob and rotate clockwise to
remove (Fig. 157).
(3) Remove the center console assembly as shown
in (Fig. 158).
(4) Separate shifter boot from shifter assembly
(Fig. 159). Boot is retained to shifter by three push-
pin retainers.(5) Loosen crossover adjustment screw at shifter
assembly (Fig. 160).
(6) Pin transaxle crossover lever in 3-4 neutral
position using a 1/4 inch drill bit. Align hole in cross-
over lever with the hole in the boss on the transaxle
case (Fig. 161). Be sure drill bit goes into transaxle
case at least one±half inch.
(7) The shifter is spring±loaded and self±centering.
Allow shifter to rest in its neutral position. Torque
adjustment screw to 8 N´m (70 in. lbs.). Care must be
taken to avoid moving the shift mechanism off-center
during screw tightening.
(8) Remove drill bit from transaxle case and per-
form functional check by shifting transaxle into all
gears.
(9) Install boot to the shifter assembly (Fig. 159).
Fasten boot with the three retainers.
Fig. 157 Gearshift Knob Removal
1 ± GEARSHIFT KNOB
Fig. 158 Center Console Removal/InstallationÐ
Typical
1 ± CONSOLE
2 ± SCREW (4)
3 ± SCREW (2)
Fig. 159 Gearshift Boot Removal/Installation
1 ± BOOT
2 ± SHIFTER ASSEMBLY
Fig. 160 Crossover Adjustment Screw
1 ± CROSSOVER ADJUSTMENT SCREW
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 49
Page 963 of 1285

(10) Install center console assembly (Fig. 158). Ver-
ify that boot is not pinched at console opening before
tightening.
(11) Install knob to shifter lever, align knob to
three o'clock position, push knob down to engage
spring and rotate counter clockwise (Fig. 162).
(12) Return shifter boot to its original position
(seated around knob lip).
BEARING ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
GENERAL RULES ON SERVICING BEARINGS
(1) Use extreme care when removing and install-
ing bearing cups and cones. Use only an arbor pressfor installation, as a hammer may not properly align
the bearing cup or cone. Burrs or nicks on the bear-
ing seat will give a false end play reading while
gauging for proper shims. Improperly seated bearing
cups and cones are subject to low±mileage failure.
(2) Bearing cups and cones should be replaced if
they show signs of pitting or heat distress. If distress
is seen on either the cup or bearing rollers, both cup
and cone must be replaced.
(3) Bearing preload and drag torque specifications
must be maintained to avoid premature bearing fail-
ures. Used (original) bearings may lose up to 50% of
their original drag torque after break in. All bearing
adjustments must be made with no other component
interference or gear intermesh.
(4) Replace bearings as a pair: If one differential
bearing is defective, replace both differential bear-
ings, if one input shaft bearing is defective, replace
both input shaft bearings.
(5) Bearing cones must not be reused if removed.
(6) Turning torque readings should be obtained
while smoothly rotating in either direction.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD
ADJUSTMENT
NOTE: True bearing turning torque readings can be
obtained only with the geartrain removed from the
case.
(1) Remove bearing cup and existing shim from
clutch bellhousing case.
(2) Press in new bearing cup into bellhousing case
(or use a cup that has been ground down on the
outer edge for ease of measurement).
(3) Press in new bearing cup into gear case side.
(4) Oil differential bearings with Moparttype M.
S. 9417 Manual Transaxle Fluid. Install differential
assembly in transaxle gear case. Install clutch bell-
housing over gear case. Install and torque case bolts
to 29 N´m (21 ft. lbs.).
(5)
Position transaxle with bellhousing facing down
on workbench with C-clamps. Position dial indicator.
(6) Apply a medium load to differential with Tool
C-4995 and a T-handle, in the downward direction.
Roll differential assembly back and forth a number of
times. This will settle the bearings. Zero the dial
indicator. To obtain end play readings, apply a
medium load in an upward direction while rolling
differential assembly back and forth (Fig. 163).
Record end play.
(7) The shim required for proper bearing preload is
thetotal of end play, plus (constant) preload of
0.18mm (0.007 in.).Never combine shims to obtain
the required preload.
Fig. 161 Crossover Lever Pin Procedure
1±1¤488DRILL BIT
2 ± SELECTOR CABLE
3 ± CROSSOVER CABLE
Fig. 162 Gearshift Knob Installation
1 ± GEARSHIFT KNOB
2 ± SPRING
21 - 50 TRANSAXLEPL
ADJUSTMENTS (Continued)
Page 964 of 1285

(8) Remove case bolts. Remove clutch bellhousing
differential bearing cup. Install shim(s) selected in
Step 7. Then press the bearing cup into clutch bell-
housing.
(9) Install clutch bellhousing. Install and torque
case bolts to 26 N´m (19 ft. lbs.).
(10) Using Special Tool C-4995 and an inch-pound
torque wrench, check turning torque of the differen-
tial assembly (Fig. 164).The turning torque
should be 6 to 12 in. lbs. If the turning torque is
too high, install a 0.05mm (0.002 inch) thinner
shim. If the turning torque is too low, install a
0.05mm (0.002 inch) thicker shim.(11) Recheck turning torque. Repeat Step 10until
the proper turning torque is obtained.
SPECIFICATIONS
NV T350 (A-578) SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Back-up Lamp Switch........ 24N´m(18ft.lbs.)
Crossover Cable Adj. Screw.... 8N´m(70in.lbs.)
Drain Plug............... 28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Differential Ring Gear Bolts . . . 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.)
Dust Shield to Transaxle.... 12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
End Plate Cover Bolts........ 29N´m(21ft.lbs.)
Lateral Bending Strut to Engine......... 81N´m
(60 ft. lbs.)
Lateral Bending Strut to Trans.......... 81N´m
(60 ft. lbs.)
Left Mount Through Bolt.... 108N´m(80ft.lbs.)
Left Mount to Transaxle...... 68N´m(50ft.lbs.)
Output Bearing Race Ret. Strap......... 11N´m
(96 in. lbs.)
Reverse Fork Bracket........ 11N´m(96in.lbs.)
Reverse Idler Shaft Bolt...... 26N´m(19ft.lbs.)
Shift Cable Bracket to Transaxle........ 28N´m
(250 in. lbs.)
Transaxle Case Bolts......... 29N´m(21ft.lbs.)
Transaxle to Engine Bolt...... 95N´m(70ft.lbs.)
Trans. to Eng. Intake Bkt. Bolts......... 95N´m
(70 ft. lbs.)
Vehicle Speed Sensor......... 7N´m(60in.lbs.)
Vertical Bending Strut to Engine........ 81N´m
(60 ft. lbs.)
Vertical Bending Strut to Trans.......... 81N´m
(60 ft. lbs.)
NOTE: Bolts that have thread sealer or torque lock
patches should not be reused. Always install new
bolts in these applications.
Fig. 163 Checking Differential Bearing End Play to
Determine Shim Thickness
1 ± T-HANDLE
2 ± DIAL INDICATOR SET
3 ± SPECIAL TOOL C-4995
Fig. 164 Checking Differential Bearing Turning
Torque
1 ± INCH-POUND TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± SPECIAL TOOL C-4995
NV T350 (A-578) MANUAL TRANSAXLE FLUID
FILL
TRANSAXLE METRIC
MEASUREU. S.
MEASURE
NV T350 1.9-2.2 Liters 2.0-2.3 Quarts
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 51
ADJUSTMENTS (Continued)
Page 965 of 1285
SPECIAL TOOLS
NV T350 (A-578) MANUAL TRANSAXLE
Adapter Blocks C-293±45
Puller Press C-293±PA
Dial Indicator C-3339
Sleeve C-3717
Slide Hammer C-3752
Universal Handle C-4171
Bearing Installer C-4628
Seal Remover C-4680
Seal Installer C-4992
Torque Tool C-4995
21 - 52 TRANSAXLEPL
Page 966 of 1285
Adapter C-4996
Installer L-4410
Special Jaw Set L-4518
Bearing Splitter 1130
Driver 6342
Seal Installer 6709
Bearing Remover 6768
Bench Fixture 6785
Remover 6786
Remover 6787
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 53
SPECIAL TOOLS (Continued)
Page 967 of 1285

31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
IN VEHICLE SERVICE.....................55
FLUID REQUIREMENTS...................55
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
31TH GENERAL INFORMATION..............55
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION..............56
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH.............56
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM.............56
PRESSURE SUPPLY SYSTEM...............56
PRESSURE REGULATING VALVES...........56
FLOW CONTROL VALVES..................56
CLUTCHES, BAND SERVOS, AND
ACCUMULATOR........................57
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM..............................57
GEARSHIFT AND PARKING LOCK CONTROLS . . 57
COOLER BYPASS VALVE..................57
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID
WIRING CONNECTOR...................58
GOVERNOR.............................58
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TRANSAXLE PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS.......58
ROAD TEST.............................65
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS.............66
CLUTCH AND SERVO AIR PRESSURE TESTS . . 68
FLUID LEAKAGE-TRANSAXLE TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA.............70
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK....70
SERVICE PROCEDURES
TRANSAXLE FLUID AND FILTER SERVICE.....70
ALUMINUM THREAD REPAIR...............71
FLUSHING COOLERS AND TUBES...........72
OIL PUMP VOLUME CHECK................72
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
GEARSHIFT CABLE.......................73
GEARSHIFT MECHANISM..................76
THROTTLE VALVE (KICKDOWN) CABLE.......77
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
CABLE...............................79
INTERLOCK MECHANISM..................82
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR PINION GEAR......83
PARK/NEUTRAL STARTING AND BACK-UP
LAMP SWITCH.........................84TRANSAXLE AND TORQUE CONVERTER......84
PUMP OIL SEAL.........................88
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
TRANSAXLE............................89
VALVE BODY............................91
OIL PUMP.............................104
FRONT CLUTCH........................105
REAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY................108
FRONT PLANETARY AND ANNULUS
GEAR-RECONDITION...................110
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) SERVO-
RECONDITION........................112
ACCUMULATOR-RECONDITION............113
KICKDOWN SERVO (CONTROLLED LOAD)-
RECONDITION........................113
TRANSFER SHAFT REPAIR................114
PARKING PAWL.........................121
OUTPUT SHAFT REPAIR..................121
DIFFERENTIAL REPAIR...................129
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
VALVE BODY...........................135
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE......................135
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE ADJUSTMENT
PROCEDURE.........................136
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM.............................137
BAND ADJUSTMENT.....................138
HYDRAULIC CONTROL PRESSURE
ADJUSTMENTS.......................138
BEARING ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES......138
OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING................139
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING.................139
TRANSFER SHAFT BEARING..............140
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
31TH TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC SCHEMATIC . . 142
SPECIFICATIONS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.............150
31TH TRANSAXLE TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS . 150
SPECIAL TOOLS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.............151
21 - 54 TRANSAXLEPL
Page 968 of 1285

GENERAL INFORMATION
IN VEHICLE SERVICE
The following components are serviceable in the
vehicle without transaxle removal:
²Valve Body Assembly
²Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Governor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor & Pinion
²Park/Neutral & Back-up Lamp Switch
²Transfer Gears and Transfer Shaft
²Low/Reverse Servo
²Kickdown Servo
²Accumulator
FLUID REQUIREMENTS
NOTE: The transmission and differential have a
common oil sump with an opening between the
two.
TRANSMISSION/DIFFERENTIAL
MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid
Type 9602) is required in this transaxle. Substitute
fluids must meet fluid specification MS-9602.
FLUID ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation strongly recommends against
the addition of any fluids to the transmission, other
than those automatic transmission fluids listed
above. Exceptions to this policy are the use of special
dyes to aid in detecting fluid leaks.
Various ªspecialº additives and supplements exist
that claim to improve shift feel/quality and converter
clutch operation, inhibit overheating, oxidation, var-
nish and sludge. These claims have not been sup-
ported to Chrysler's satisfaction and these additives
must not be used. The use of transmission ªsealersº
should also be avoided, since they may adversely
affect the integrity of tranmission seals.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
31TH GENERAL INFORMATION
NOTE: Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on these transaxles.
This transaxle combines torque converter, three
speed transmission, final drive gearing, and differen-
tial into a front wheel drive system.
NOTE: Transaxle operation requirements are differ-
ent for each vehicle and engine combination. Some
internal parts will be different to provide for this.Therefore, when replacing parts, refer to the seven
digit part number stamped on rear of the transaxle
oil pan flange.
Within this transaxle, there are three primary
areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor
and parking sprag).
(3) Differential center line.
Center distances between the main rotating parts
in these three areas are held precise to maintain a
low noise level.
The torque converter, transaxle area, and differen-
tial are housed in an integral aluminum die casting.
The differential oil sump is common with the
transaxle sump. Separate filling of the differen-
tial is NOT necessary.
The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through a remote cooler. There are two types of
coolers used. An oil-to-water type cooler located in
the radiator side tank and/or an oil-to-air heat
exchanger. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assembly.
Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter and then through the input shaft to multiple-
disc clutches in the transaxle. The power flow
depends on the application of the clutches and bands.
Refer to Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and
Tests section.
The transaxle consists of:
²Two multiple-disc clutches
²An overrunning clutch
²Two servos
²A hydraulic accumulator
²Two bands
²Two planetary gear sets
This provides three forward ratios and a reverse
ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary gear
sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The driving shell is splined to the sun gear and
front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system consists
of an oil pump and a single valve body which con-
tains all of the valves except the governor valves.
The transaxle sump and differential sump are both
vented through the dipstick. Output torque from the
main center line is delivered through helical gears to
the transfer shaft. This gear set is a factor in the
transaxle final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also car-
ries the governor and parking sprag. An integral heli-
cal gear on the transfer shaft drives the differential
ring gear.
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 55
Page 969 of 1285

FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
NOTE: The transmission and differential sump have
a common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two.
The torque converter fills in both the P (Park) and
N (Neutral) positions. Place the selector lever in P
(Park) to be sure that the fluid level check is accu-
rate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground. This will ensure complete oil
level stabilization between differential and
transmission.The fluid should be at normal operat-
ing temperature (approximately 82É C. or 180É F.).
The fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT region
(cross-hatched area) on the dipstick (Fig. 1).
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions,
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy therefore, pressures will be
low and will build up slowly.
Improper filling also can raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
that occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, the air bubbles can cause overheat-
ing, fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and servo operation.
Foaming also can result in fluid escaping from the
transaxle dipstick, where it may be mistaken for a
leak.
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
or is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed.
Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely.
If there is any doubt about its condition, remove the
oil pan and inspect.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH
A torque converter clutch is standard on all vehi-
cles. The torque converter clutch is activated only in
direct drive and is controlled by the engine electron-
ics. A solenoid on the valve body, is powered by the
powertrain control module to activate the torque con-
verter clutch.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The hydraulic control system makes the transaxle
fully automatic, and has four important functions to
perform. The components of any automatic control
system may be grouped into the following basic
groups:
²Pressure supply system
²Pressure regulating valves
²Flow control valves
²Clutches
²Band servos
Taking each of these basic groups or systems in
turn, the control system may be described as follows:
PRESSURE SUPPLY SYSTEM
The pressure supply system consists of an oil pump
driven by the engine through the torque converter.
The single pump furnishes pressure for all hydraulic
and lubrication requirements.Oil pump housing
assemblies are available with preselected pump
gears.
PRESSURE REGULATING VALVES
The pressure regulating valve controls line pres-
sure dependent on throttle opening. The governor
valve transmits regulated pressure to the valve body
(in conjunction with vehicle speed) to control upshift
and downshift.
The throttle valve transmits regulated pressure to
the transaxle (dependent on throttle position) to con-
trol upshift and downshift.
FLOW CONTROL VALVES
The manual valve provides the different transaxle
drive ranges selected by the vehicle operator.
The 1-2 shift valve automatically shifts the tran-
saxle from first to second or from second to first,
depending on the vehicle operation.
The 2-3 shift valve automatically shifts the tran-
saxle from second to third or from third to second
depending on the vehicle operation.
Fig. 1 Transaxle Dipstick
1 ± TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
21 - 56 TRANSAXLEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 970 of 1285

The kickdown valve makes possible a forced down-
shift from third to second, second to first, or third to
first (depending on vehicle speed). This can be done
by depressing the accelerator pedal past the detent
feel near wide open throttle.
The shuttle valve has two separate functions and
performs each independently of the other. The first is
providing fast release of the kickdown band, and
smooth front clutch engagement when a lift-foot
upshift from second to third is made. The second
function is to regulate the application of the kick-
down servo and band when making third±to±second
kickdown.
The bypass valve provides for smooth application
of the kickdown band on 1-2 upshifts.
The torque converter clutch solenoid allows for the
electronic control of the torque converter clutch. It
also disengages the torque converter at closed throt-
tle. This is done during engine warm-up and part-
throttle acceleration.
The switch valve directs oil to apply the torque
converter clutch in one position. The switch valve
releases the torque converter clutch in the other posi-
tion.
CLUTCHES, BAND SERVOS, AND
ACCUMULATOR
The front and rear clutch pistons, and both servo
pistons, are moved hydraulically to engage the
clutches and apply the bands. The pistons are
released by spring tension when hydraulic pressure
is released. On the 2-3 upshift, the kickdown servo
piston is released by spring tension and hydraulic
pressure.
The accumulator controls the hydraulic pressure
on the apply±side of the kickdown servo during the
1-2 upshift; thereby cushioning the kickdown band
application at any throttle position.
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM
The Brake Transmission Shifter/Ignition Interlock
(BTSI) is a cable and solenoid operated system. It
interconnects the automatic transmission floor
mounted shifter to the steering column ignition
switch. The system locks the shifter into the PARK
position. The interlock system is engaged whenever
the ignition switch is in the LOCK or ACCESSORY
position. An additional electrically activated feature
will prevent shifting out of the PARK position unless
the brake pedal is depressed at least one-half inch. A
magnetic holding device integral to the interlock
cable is energized when the ignition is in the RUN
position. When the key is in the RUN position and
the brake pedal is depressed, the shifter is unlocked
and will move into any position. The interlock systemalso prevents the ignition switch from being turned
to the LOCK or ACCESSORY position, unless the
shifter is in the gated PARK position.
The following chart describes the normal operation
of the Brake Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI) sys-
tem. If the ªexpected responseº differs from the vehi-
cle's response, then system repair and/or adjustment
is necessary.
GEARSHIFT AND PARKING LOCK CONTROLS
The transaxle is controlled by alever typegear-
shift incorporated within the console. The control has
six selector lever positions: P (Park), R (Reverse), N
(Neutral), and D (Drive), 2 (Second), and 1 (First).
The parking lock is applied by moving the selector
lever past a gate to the (P) position.Do not apply
the parking lock until the vehicle has stopped;
otherwise, a severe banging noise will occur.
COOLER BYPASS VALVE
Some 31TH transaxles are equipped with a cooler
bypass valve (Fig. 2). The valve is designed to bypass
the transaxle oil cooler circuit in cold weather condi-
tions, or when circuit restriction exceeds 25±30 p.s.i.
The valve consists of an integrated check ball and
spring, and a return tube to carry bypassed oil back
to the pump. The bypass valve is mounted to the
valve body transfer plate and is sealed with a rubber
o-ring seal (Fig. 3).
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the ªOFFº
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUNº position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
ªON/RUNº position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the ªLOCKº or9ACCº
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the ªLOCKº or
ªACCº position.
5. Return shifter to
ªPARKº and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to ªLOCKº
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of ªPARKº.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of ªPARKº.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 57
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)