park assist DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 89 of 1285
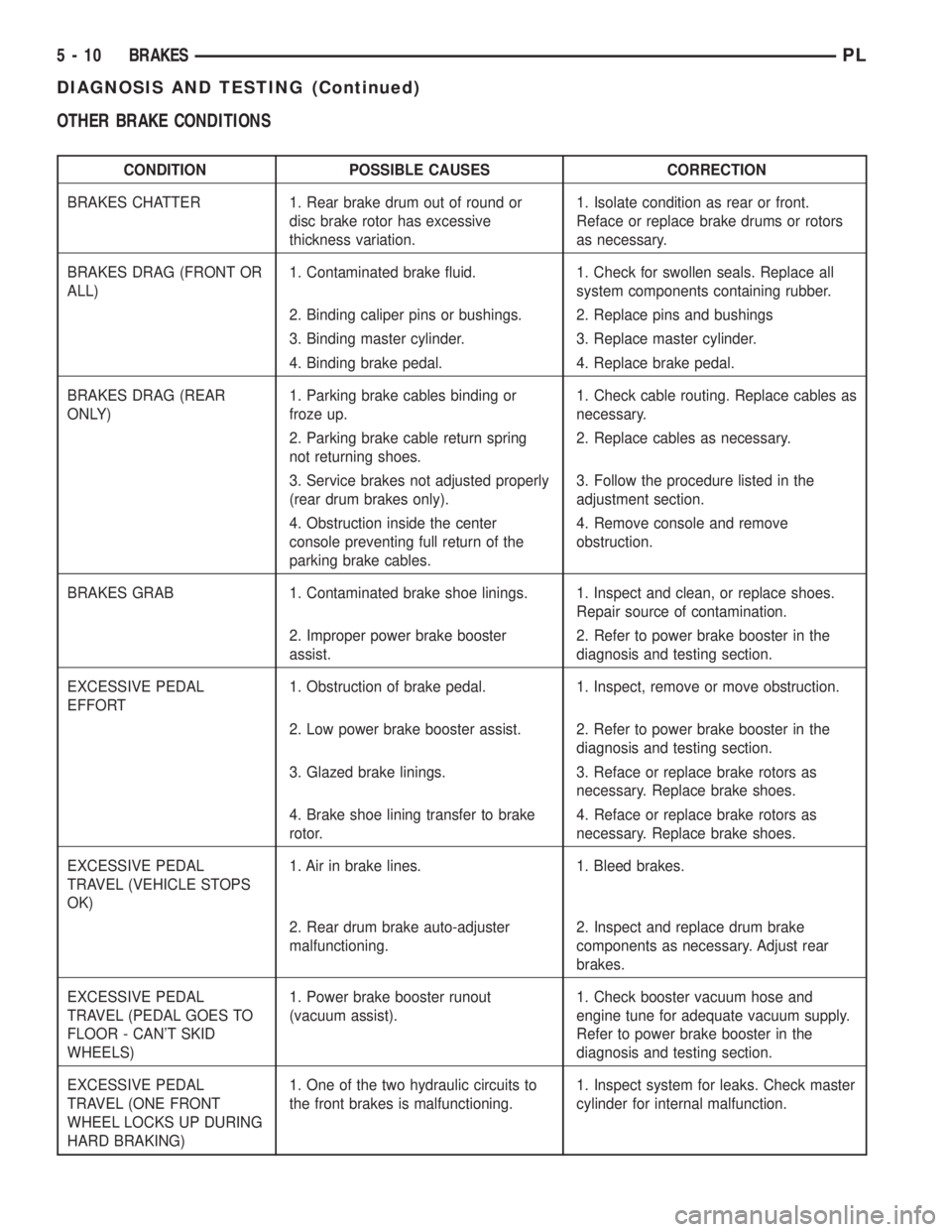
OTHER BRAKE CONDITIONS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BRAKES CHATTER 1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or rotors
as necessary.
BRAKES DRAG (FRONT OR
ALL)1. Contaminated brake fluid. 1. Check for swollen seals. Replace all
system components containing rubber.
2. Binding caliper pins or bushings. 2. Replace pins and bushings
3. Binding master cylinder. 3. Replace master cylinder.
4. Binding brake pedal. 4. Replace brake pedal.
BRAKES DRAG (REAR
ONLY)1. Parking brake cables binding or
froze up.1. Check cable routing. Replace cables as
necessary.
2. Parking brake cable return spring
not returning shoes.2. Replace cables as necessary.
3. Service brakes not adjusted properly
(rear drum brakes only).3. Follow the procedure listed in the
adjustment section.
4. Obstruction inside the center
console preventing full return of the
parking brake cables.4. Remove console and remove
obstruction.
BRAKES GRAB 1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Improper power brake booster
assist.2. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
EFFORT1. Obstruction of brake pedal. 1. Inspect, remove or move obstruction.
2. Low power brake booster assist. 2. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
3. Glazed brake linings. 3. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
4. Brake shoe lining transfer to brake
rotor.4. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (VEHICLE STOPS
OK)1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Rear drum brake auto-adjuster
malfunctioning.2. Inspect and replace drum brake
components as necessary. Adjust rear
brakes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (PEDAL GOES TO
FLOOR - CAN'T SKID
WHEELS)1. Power brake booster runout
(vacuum assist).1. Check booster vacuum hose and
engine tune for adequate vacuum supply.
Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (ONE FRONT
WHEEL LOCKS UP DURING
HARD BRAKING)1. One of the two hydraulic circuits to
the front brakes is malfunctioning.1. Inspect system for leaks. Check master
cylinder for internal malfunction.
5 - 10 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 90 of 1285

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
PEDAL PULSATES/SURGES
DURING BRAKING1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or rotors
as necessary.
PEDAL IS SPONGY 1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Power brake booster runout
(vacuum assist).2. Check booster vacuum hose and
engine tune for adequate vacuum supply.
Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
PREMATURE REAR WHEEL
LOCKUP1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Inoperative proportioning valve
(non-ABS vehicles only).2. Test proportioning valves folowing
procedure listed in diagnosis and testing
section. Replace valves as necessary.
3. ABS EBD not functioning. 3. Refer to the ABS section and Chassis
Diagnostic Procedures manual.
4. Improper power brake booster
assist.4. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
STOP LAMPS STAY ON 1. Brake lamp switch out of
adjustment.1. Adjust brake lamp switch.
2. Brake pedal binding. 2. Inspect and replace as necessary.
3. Obstruction in pedal linkage. 3. Remove obstruction.
4. Power Brake Booster not allowing
pedal to return completely.4. Replace power brake booster.
VEHICLE PULLS TO RIGHT
OR LEFT ON BRAKING1. Frozen brake caliper piston. 1. Replace frozen piston or caliper. Bleed
brakes.
2. Contaminated brake shoe lining. 2. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
3. Pinched brake lines. 3. Replace pinched line.
4. Leaking piston seal. 4. Replace piston seal or brake caliper.
5. Suspension problem. 5. Refer to the Suspension group.
PARKING BRAKE -
EXCESSIVE HANDLE
TRAVEL1. Rear brakes out of adjustment. 1. Adjust rear drum brake shoes, or rear
parking brake shoes on vehicles with rear
disc brakes.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
BASIC TEST
(1) With engine off, depress and release the brake
pedal several times to purge all vacuum from the
power brake booster.
(2) Depress and hold the pedal with light effort (15
to 25 lbs. pressure), then start the engine.
The pedal should fall slightly, then hold. Less effort
should be needed to apply the pedal at this time. If
the pedal fell as indicated, perform the VACUUM
LEAK TEST listed after the BASIC TEST. If thepedal did not fall, continue on with this BASIC
TEST.
(3) Disconnect the vacuum hose on the side of the
vacuum check valve that leads to the speed control,
then connect a vacuum gauge to the open vacuum
port on the valve.
(4) Start the engine.
(5) When the engine is at warm operating temper-
ature, allow it to idle and check the vacuum at the
gauge.
PLBRAKES 5 - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 217 of 1285

²It passes the 15 second load test. Refer to Bat-
tery Load Test.
²The built in test indicator dot is GREEN (Fig.
2).
NOTE: The battery cannot be refilled with water, it
must be replaced.
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE A BATTERY THAT
HAS EXCESSIVELY LOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL.
BATTERY MAY SPARK INTERNALLY AND
EXPLODE. EXPLOSIVE GASES FORM OVER THE
BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE, USE FLAME, OR CRE-
ATE SPARKS NEAR BATTERY. DO NOT ASSIST
BOOST OR CHARGE A FROZEN BATTERY. BAT-
TERY CASING MAY FRACTURE. BATTERY ACID IS
POISON, AND MAY CAUSE SEVERE BURNS. BAT-
TERIES CONTAIN SULFURIC ACID. AVOID CON-
TACT WITH SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING. IN THE
EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER AND
CALL PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT OF
REACH OF CHILDREN.
CAUTION: Disconnect the battery NEGATIVE cable
first, before charging battery to avoid damage to
electrical systems. Lift the red battery boot cover
from the positive cable clamp. Do not exceed 16.0
volts while charging battery. Refer to the instruc-
tions supplied with charging equipment
Battery electrolyte may bubble inside of battery
case while being charged properly. If the electrolyte
boils violently, or is discharged from the vent holes
while charging, immediately reduce charging rate or
turn off charger. Evaluate battery condition. Battery
damage may occur if charging is excessive.
Some battery chargers are equipped with polarity
sensing devices to protect the charger or battery from
being damaged if improperly connected. If the bat-
tery state of charge is too low for the polarity sensor
to detect, the sensor must be bypassed for charger to
operate. Refer to operating instructions provided
with battery charger being used.
CAUTION: Charge battery until test indicator
appears green. Do not overcharge.
It may be necessary to jiggle the battery or vehicle
to bring the green dot in the test indicator into view.
After the battery has been charged to 12.4 volts or
greater, perform a load test to determine cranking
capacity. Refer to Battery Load Test in this Group. If
the battery passes the load test, the battery is OK to
use. If battery will not pass the load test, it must be
replaced. Properly clean and inspect battery holddowns, tray, terminals, cables, posts, and top before
completing service.
CHARGING COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY
The following procedure should be used to recharge
a completely discharged battery. Unless procedure is
properly followed, a good battery may be needlessly
replaced. Refer to Battery Charging Rate Table for
proper charging time.
(1) Measure the voltage at battery posts with a
voltmeter accurate to 1/10 volt (Fig. 12). If below 10
volts, charge current will be low, and it could take
some time before it accepts a current in excess of a
few milliamperes. Such low current may not be
detectable on amp meters built into many chargers.
(2) Connect charger leads. Some chargers feature
polarity protection circuitry that prevents operation
unless charger is connected to battery posts correctly.
A completely discharged battery may not have
enough voltage to activate this circuitry. This may
happen even though the leads are connected properly.
(3) Battery chargers vary in the amount of voltage
and current they provide. For the time required for
the battery to accept measurable charger current at
various voltages, refer to the Battery Charging Rate
table. If charge current is still not measurable after
charging times, the battery should be replaced. If
charge current is measurable during charging time,
the battery may be good, and charging should be
completed in the normal manner.
BATTERY CHARGING RATE
Voltage Hours
16.0 volts maximum up to 4 hours
14.0 to 15.9 volts up to 8 hours
13.9 volts or less up to 16 hours
Fig. 12 Voltmeter Accurate to 1/10 Volt (Connected)
8A - 8 BATTERYPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 255 of 1285

(19) Disconnect one left side harness connector at
top left of instrument panel for vanity and rear view
mirrors.
(20) Pull off the hvac control head knobs.
(21) Remove two screws retaining the top front of
the center bezel.
(22) Using a trim stick, gently pry out on the
instrument panel center bezel and remove.
(23) Remove the two retaining screws to the hvac
control head.
(24) Disconnect the one instrument panel wire
harness connector.
(25) Disconnect the one vacuum harness connector.
(26) Pull hvac control head out of instrument
panel, twist 90É and push back through the opening
(Fig. 12). Do not disconnect the control cables.
(27) Disconnect the center console wiring:
²Airbag Control Module (ACM)
²Parking Brake Warning Lamp Switch
²Transmission Range Indicator Lamp
(28) With help on an assistant, pull rearward on
instrument panel assembly and remove from vehicle.
If replacing instrument panel, transfer parts as
necessary.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Fig. 12 HVAC Control Head
1 ± HVAC CONTROL HEAD
2 ± RADIO
3 ± HVAC CONTROL HEAD HARNESS CONNECTOR
8E - 8 INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMSPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 265 of 1285
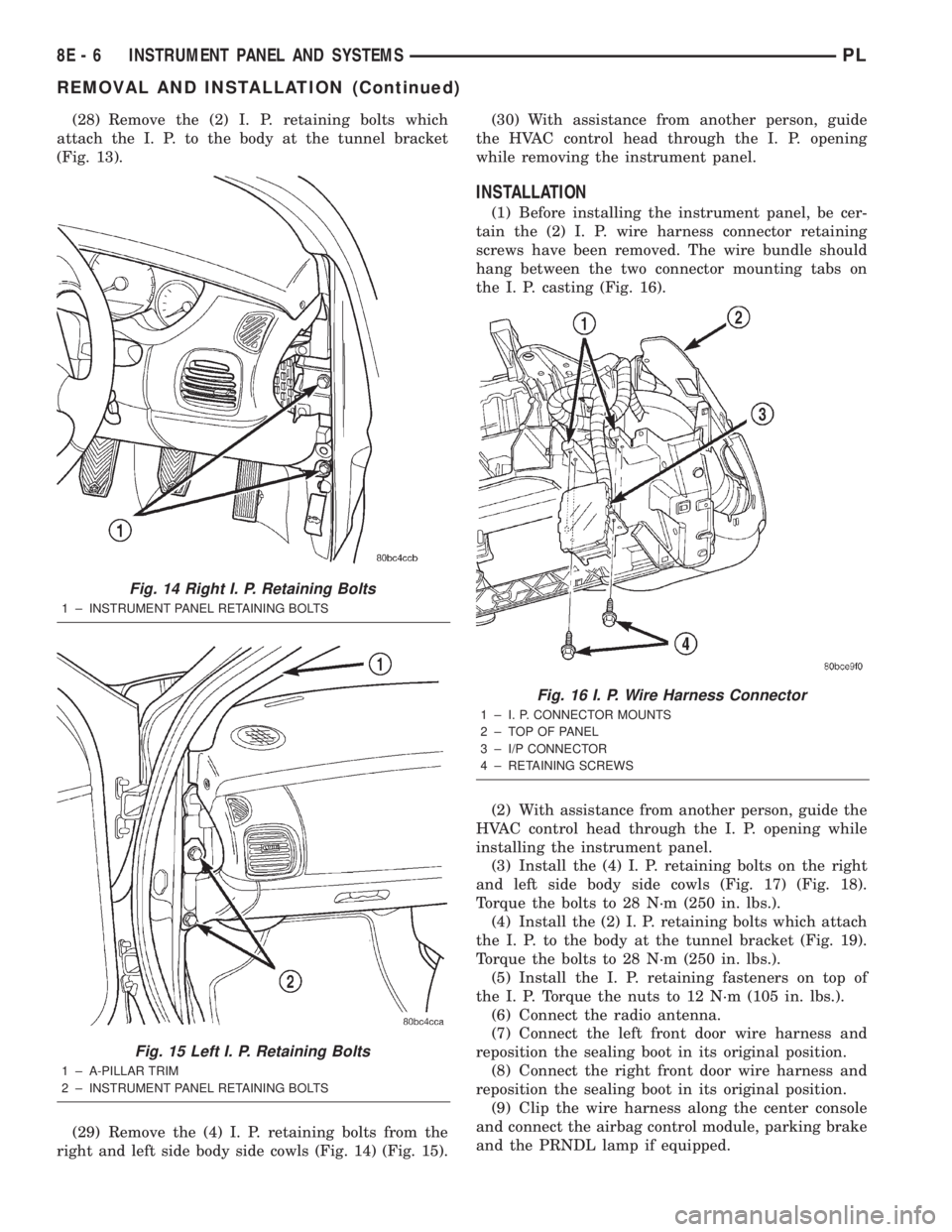
(28) Remove the (2) I. P. retaining bolts which
attach the I. P. to the body at the tunnel bracket
(Fig. 13).
(29) Remove the (4) I. P. retaining bolts from the
right and left side body side cowls (Fig. 14) (Fig. 15).(30) With assistance from another person, guide
the HVAC control head through the I. P. opening
while removing the instrument panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing the instrument panel, be cer-
tain the (2) I. P. wire harness connector retaining
screws have been removed. The wire bundle should
hang between the two connector mounting tabs on
the I. P. casting (Fig. 16).
(2) With assistance from another person, guide the
HVAC control head through the I. P. opening while
installing the instrument panel.
(3) Install the (4) I. P. retaining bolts on the right
and left side body side cowls (Fig. 17) (Fig. 18).
Torque the bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(4) Install the (2) I. P. retaining bolts which attach
the I. P. to the body at the tunnel bracket (Fig. 19).
Torque the bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the I. P. retaining fasteners on top of
the I. P. Torque the nuts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(6) Connect the radio antenna.
(7) Connect the left front door wire harness and
reposition the sealing boot in its original position.
(8) Connect the right front door wire harness and
reposition the sealing boot in its original position.
(9) Clip the wire harness along the center console
and connect the airbag control module, parking brake
and the PRNDL lamp if equipped.
Fig. 14 Right I. P. Retaining Bolts
1 ± INSTRUMENT PANEL RETAINING BOLTS
Fig. 15 Left I. P. Retaining Bolts
1 ± A-PILLAR TRIM
2 ± INSTRUMENT PANEL RETAINING BOLTS
Fig. 16 I. P. Wire Harness Connector
1 ± I. P. CONNECTOR MOUNTS
2 ± TOP OF PANEL
3 ± I/P CONNECTOR
4 ± RETAINING SCREWS
8E - 6 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND SYSTEMSPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 726 of 1285

CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly clean all debris/rust from inside of cup
plug hole in cylinder block or head. Be sure to
remove old sealer. Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole
with MopartStud and Bearing Mount Adhesive.
Make certain the new plug is cleaned of all oil or
grease. Using a proper driver, drive plug into hole so
that the sharp edge of the plug is at least 0.5 mm
(0.020 inch.) inside the lead in chamfer (Fig. 3).
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
If a loss of performance is noticed, timing belt or
chain may have skipped one or two teeth. Camshaft
and crankshaft timing should be checked. Refer to
Group 9, Engine Timing belt or chain installation.
It is important that the vehicle is operating to it's
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and lowest vehicle emissions. If vehicle is not operat-ing to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis in
this section. The following procedures can assist in
achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Group
8B, Starting.
(2) Check intake manifold for vacuum leaks.
(3) Perform cylinder compression pressure test.
Refer to Engine Diagnosis in this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8D, Ignition System.
Tighten to specifications.
(5) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8D, Ignition System.
(6) Test ignition coils primary and secondary resis-
tance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System.
(7) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and different
RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
specifications.
(8) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
(9) Inspect crankcase ventilation system. Refer to
Group 25, Emission Control Systems.
(10) Road test vehicle as a final test.HONING CYLINDER BORES
(1) Used carefully, the cylinder bore resizing hone,
recommended tool C-823 or equivalent, equipped
with 220 grit stones, is the best tool for this honing
procedure. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring or scratches. Usually a few strokes
Fig. 2 Access Plug
1 ± CRANKSHAFT BOLT ACCESS PLUG
2 ± RIGHT MOUNT BOLT ACCESS PLUG
3 ± FASCIA
4 ± SPLASH SHIELD
Fig. 3 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 ± CYLINDER BLOCK
2 ± REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 ± STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 ± DRIFT PUNCH
5 ± CUP PLUG
PLENGINE 9 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 823 of 1285

REFORMULATED GASOLINE
Many areas of the country require the use of
cleaner burning gasoline referred to as ªreformulat-
edº gasoline. Reformulated gasoline contain oxygen-
ates, and are specifically blended to reduce vehicle
emissions and improve air quality.
DaimlerChrysler Corporation strongly supports the
use of reformulated gasoline. Properly blended refor-
mulated gasoline will provide excellent performance
and durability for the engine and fuel system compo-
nents.
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
oxygenates such as 10% ethanol, MTBE, and ETBE.
Oxygenates are required in some areas of the country
during the winter months to reduce carbon monoxide
emissions. Fuels blended with these oxygenates may
be used in your vehicle.
CAUTION: DO NOT use gasoline containing METH-
ANOL. Gasoline containing methanol may damage
critical fuel system components.
MMT
MMT is a manganese-containing metallic additive
that is blended into some gasoline to increase octane.
Gasoline blended with MMT provide no performance
advantage beyond gasoline of the same octane num-
ber without MMT. Gasoline blended with MMT
reduce spark plug life and reduce emission system
performance in some vehicles. DaimlerChrysler rec-
ommends that gasoline without MMT be used in your
vehicle. The MMT content of gasoline may not be
indicated on the gasoline pump; therefore, you should
ask your gasoline retailer whether or not his/her gas-
oline contains MMT.
It is even more important to look for gasoline with-
out MMT in Canada because MMT can be used at
levels higher than allowed in the United States.
MMT is prohibited in Federal and California refor-
mulated gasoline.
SULFUR IN GASOLINE
If you live in the northeast United States, your
vehicle may have been designed to meet California
low emission standards with clean-burning, low-sul-
fur, California gasoline. Gasoline sold outside of Cal-
ifornia is permitted to have higher sulfur levels
which may affect the performance of the vehicle's cat-
alytic converter. This may cause the Check Engine or
Service Engine Soon light to illuminate.
Illumination of either light while operating on high
sulfur gasoline does not necessarily mean your emis-
sion control system is malfunctioning. DaimlerChrysler
recommends that you try a different brand of unleadedgasoline having lower sulfur to determine if the prob-
lem is fuel related prior to returning your vehicle to an
authorized dealer for service.
CAUTION: If the Check Engine or Service Engine
Soon light is flashing, immediate service is
required; see on-board diagnostics system section.
MATERIALS ADDED TO FUEL
All gasoline sold in the United States and Canada
are required to contain effective detergent additives.
Use of additional detergents or other additives is not
needed under normal conditions.
FUEL SYSTEM CAUTIONS
CAUTION: Follow these guidelines to maintain your
vehicle's performance:
²The use of leaded gas is prohibited by Federal
law. Using leaded gasoline can impair engine perfor-
mance, damage the emission control system, and
could result in loss of warranty coverage.
²An out-of-tune engine, or certain fuel or ignition
malfunctions, can cause the catalytic converter to
overheat. If you notice a pungent burning odor or
some light smoke, your engine may be out of tune or
malfunctioning and may require immediate service.
Contact your dealer for service assistance.
²When pulling a heavy load or driving a fully
loaded vehicle when the humidity is low and the tem-
perature is high, use a premium unleaded fuel to
help prevent spark knock. If spark knock persists,
lighten the load, or engine piston damage may result.
²The use of fuel additives which are now being
sold as octane enhancers is not recommended. Most
of these products contain high concentrations of
methanol. Fuel system damage or vehicle perfor-
mance problems resulting from the use of such fuels
or additives is not the responsibility of
DaimlerChrysler Corporation and may not be covered
under the new vehicle warranty.
NOTE: Intentional tampering with emissions control
systems can result in civil penalties being assessed
against you.
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
OPERATION
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
materials that contain oxygen such as alcohol, MTBE
(Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) and ETBE (Ethyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether). Oxygenates are required in some
areas of the country during winter months to reduce
14 - 2 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1110 of 1285

Pending ConditionsÐ
²Misfire DTC
²Front Oxygen Sensor Response
²Front Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Front Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Rationality (middle check)
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Fuel System Monitor
²All TPS faults
²All MAP faults
²All ECT sensor faults
²Purge flow solenoid functionality
²Purge flow solenoid electrical
²All PCM self test faults
²All CMP and CKP sensor faults
²All injector and ignition electrical faults
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor functionality
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Brake switch
²Intake air temperature
ConflictÐThe catalyst monitor does not run if
any of the following are conditions are present:
²EGR Monitor in progress
²Fuel system rich intrusive test in progress
²EVAP Monitor in progress
²Time since start is less than 60 seconds
²Low fuel level
²Low ambient air temperature
SuspendÐThe Task Manager does not mature a
catalyst fault if any of the following are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Priority 1
²Upstream Oxygen Sensor Heater, Priority 1
²EGR Monitor, Priority 1
²EVAP Monitor, Priority 1
²Fuel System Monitor, Priority 2
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
OPERATION
The PCM does not monitor all circuits, systems
and conditions that could have malfunctions causing
driveability problems. However, problems with these
systems may cause the PCM to store diagnostic trou-
ble codes for other systems or components. For exam-
ple, a fuel pressure problem will not register a fault
directly, but could cause a rich/lean condition or mis-
fire. This could cause the PCM to store an oxygen
sensor or misfire diagnostic trouble code.
The major non-monitored circuits are listed below
along with examples of failures modes that do not
directly cause the PCM to set a DTC, but for a sys-
tem that is monitored.FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system. It may set a EGR or Fuel
system fault or O2S.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injector
is installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIR FLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
VACUUM ASSIST
The PCM cannot detect leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices. However, these could cause the PCM
to store a MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code and
cause a high idle condition.
PCM SYSTEM GROUND
The PCM cannot determine a poor system ground.
However, one or more diagnostic trouble codes may
be generated as a result of this condition. The mod-
ule should be mounted to the body at all times, also
during diagnostic.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 23
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1135 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water-test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.
Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the lowest point of the water track or
drop. After leak point has been found, repair the leak
and water test to verify that the leak has stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.
MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
23 - 18 BODYPL