Trans temp DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 2036 of 2627
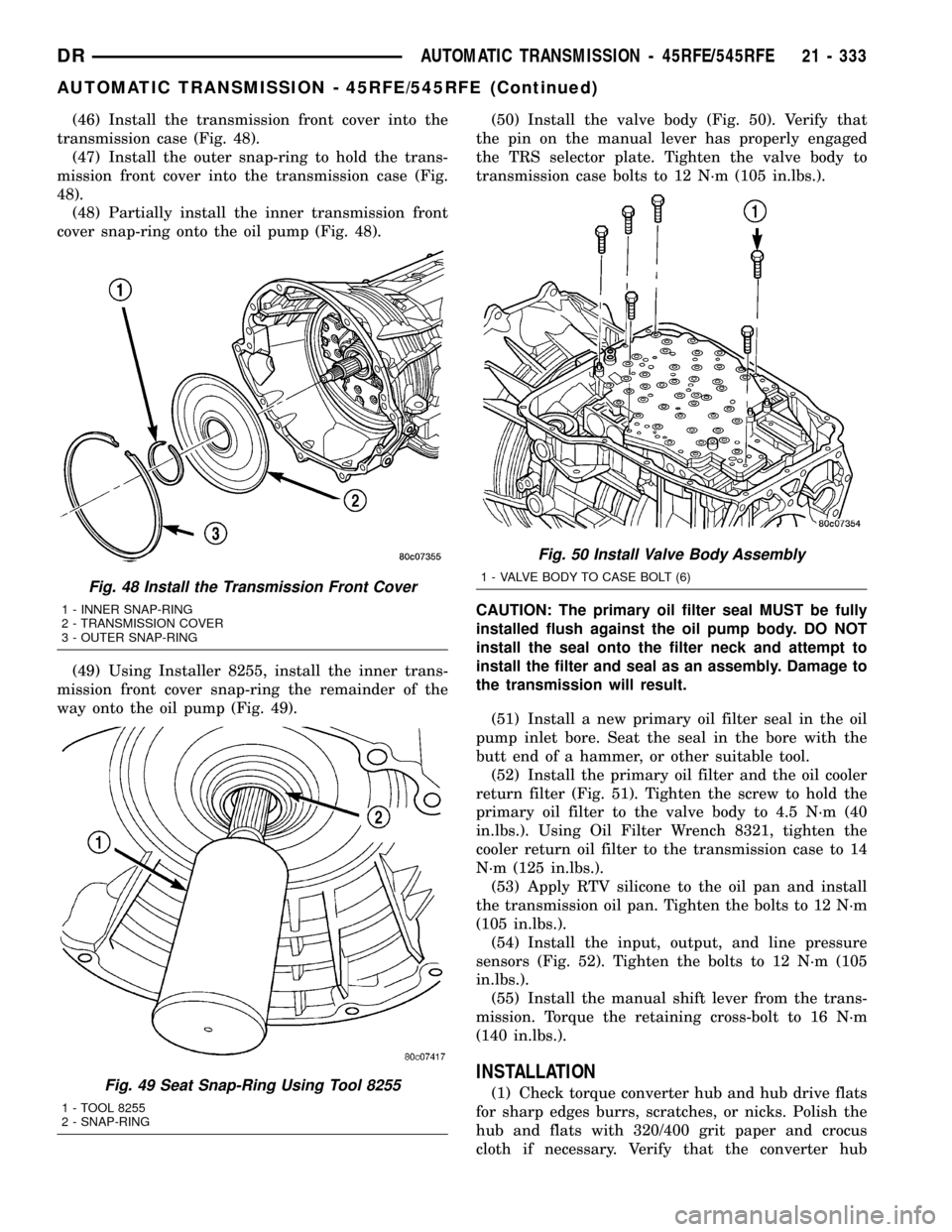

(46) Install the transmission front cover into the
transmission case (Fig. 48).
(47) Install the outer snap-ring to hold the trans-
mission front cover into the transmission case (Fig.
48).
(48) Partially install the inner transmission front
cover snap-ring onto the oil pump (Fig. 48).
(49) Using Installer 8255, install the inner trans-
mission front cover snap-ring the remainder of the
way onto the oil pump (Fig. 49).(50) Install the valve body (Fig. 50). Verify that
the pin on the manual lever has properly engaged
the TRS selector plate. Tighten the valve body to
transmission case bolts to 12 N´m (105 in.lbs.).
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(51) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
(52) Install the primary oil filter and the oil cooler
return filter (Fig. 51). Tighten the screw to hold the
primary oil filter to the valve body to 4.5 N´m (40
in.lbs.). Using Oil Filter Wrench 8321, tighten the
cooler return oil filter to the transmission case to 14
N´m (125 in.lbs.).
(53) Apply RTV silicone to the oil pan and install
the transmission oil pan. Tighten the bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in.lbs.).
(54) Install the input, output, and line pressure
sensors (Fig. 52). Tighten the bolts to 12 N´m (105
in.lbs.).
(55) Install the manual shift lever from the trans-
mission. Torque the retaining cross-bolt to 16 N´m
(140 in.lbs.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Check torque converter hub and hub drive flats
for sharp edges burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the
hub and flats with 320/400 grit paper and crocus
cloth if necessary. Verify that the converter hub
Fig. 48 Install the Transmission Front Cover
1 - INNER SNAP-RING
2 - TRANSMISSION COVER
3 - OUTER SNAP-RING
Fig. 49 Seat Snap-Ring Using Tool 8255
1 - TOOL 8255
2 - SNAP-RING
Fig. 50 Install Valve Body Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY TO CASE BOLT (6)
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 333
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2037 of 2627

o-ring is properly installed and is free of any debris.
The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging pump
seal at installation.
(2) If a replacement transmission is being
installed, transfer any components necessary, such as
the manual shift lever and shift cable bracket, from
the original transmission onto the replacement trans-
mission.
(3) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(4) Align converter and oil pump.(5) Carefully insert converter in oil pump. Then
rotate converter back and forth until fully seated in
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with steel scale and
straightedge (Fig. 53). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) Temporarily secure converter with C-clamp.
(8) Position transmission on jack and secure it
with chains.
(9) Check condition of converter driveplate.
Replace the plate if cracked, distorted or damaged.
Also be sure transmission dowel pins are seated
in engine block and protrude far enough to
hold transmission in alignment.
(10) Apply a light coating of MopartHigh Temp
Grease to the torque converter hub pocket in the rear
pocket of the engine's crankshaft.
(11) Raise transmission (Fig. 54) and align the
torque converter with the drive plate and transmis-
sion converter housing with the engine block.
(12) Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower
or tilt transmission to align the converter housing
with engine block dowels.
(13) Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in
crankshaft. Verify that no wires, or the transmission
vent hose, have become trapped between the engine
block and the transmission.
(14) Install two bolts to attach the transmission to
the engine.
(15) Install remaining torque converter housing to
engine bolts. Tighten to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
Fig. 51 Install Primary Oil and Cooler Filters
1 - PRIMARY OIL FILTER
2 - COOLER RETURN FILTER
3 - COOLER RETURN FILTER BYPASS VALVE
4 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 52 Install Input, Output, and Line Pressure
Sensors
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 53 Checking Torque Converter Seating - Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 334 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2068 of 2627

ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK
Correct cable adjustment is important to proper
interlock operation. The gearshift cable must be cor-
rectly adjusted in order to shift out of PARK.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Remove the steering column trim as necessary
for access to the brake transmission shift interlock.
(2) Shift the transmission into the PARK position.
(3) Pull upward on both the BTSI lock tab and the
gearshift cable lock tab (Fig. 65).
(4) Verify that the shift lever is in the PARK posi-
tion.
(5) Verify positive engagement of the transmission
park lock by attempting to rotate the propeller shaft.
The shaft will not rotate when the park lock is
engaged.
(6) Turn ignition switch to LOCK position.Be
sure ignition key cylinder is in the LOCK posi-
tion. Cable will not adjust correctly in any
other position.
(7) Ensure that the cable is free to self-adjust by
pushing cable rearward and releasing.
(8) Push the gearshift cable lock tab down until it
snaps in place.
(9) Locate the BTSI alignment hole in the bottom
of the BTSI mechanism between the BTSI lock tab
and the BTSI connector.(10) Move the BTSI assembly up or down on the
gearshift cable until an appropriate size drill bit can
be inserted into the alignment hole and through the
assembly.
(11) Push the BTSI lock tab down until it snaps
into place and remove the drill bit.
(12) Install any steering column trim previously
removed.
BTSI FUNCTION CHECK
(1) Verify removal of ignition key allowed in PARK
position only.
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK, the ignition
key cylinder should rotate freely from off to lock.
When the shifter is in any other position, the ignition
key should not rotate from off to lock.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should be possible when
the ignition key cylinder is in the off position.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal force, and ignition key cylin-
der is in the run or start positions, unless the foot
brake pedal is depressed approximately 1/2 inch
(12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the accessory or
lock position.
(6) Shifting between any gear and NEUTRAL, or
PARK, may be done without depressing foot brake
with ignition switch in run or start positions.
(7) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL positions only. Engine
starts must not be possible in any position other than
PARK or NEUTRAL.
(8) With shifter lever in the:
²PARK position - Apply upward force on the shift
arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must be
possible.
²PARK position - Apply downward force on the
shift arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must
be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Normal position. Engine
starts must be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Engine running and brakes
applied, apply upward force on the shift arm. Trans-
mission shall not be able to shift from neutral to
reverse.
Fig. 65 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 365
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 2069 of 2627

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repairThe use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P (PARK)
and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever
in P (PARK) to be sure that the fluid level check is
accurate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.At normal operating temperature
(approximately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is cor-
rect if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on
the oil level indicator. The fluid level will be approx-
21 - 366 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2070 of 2627
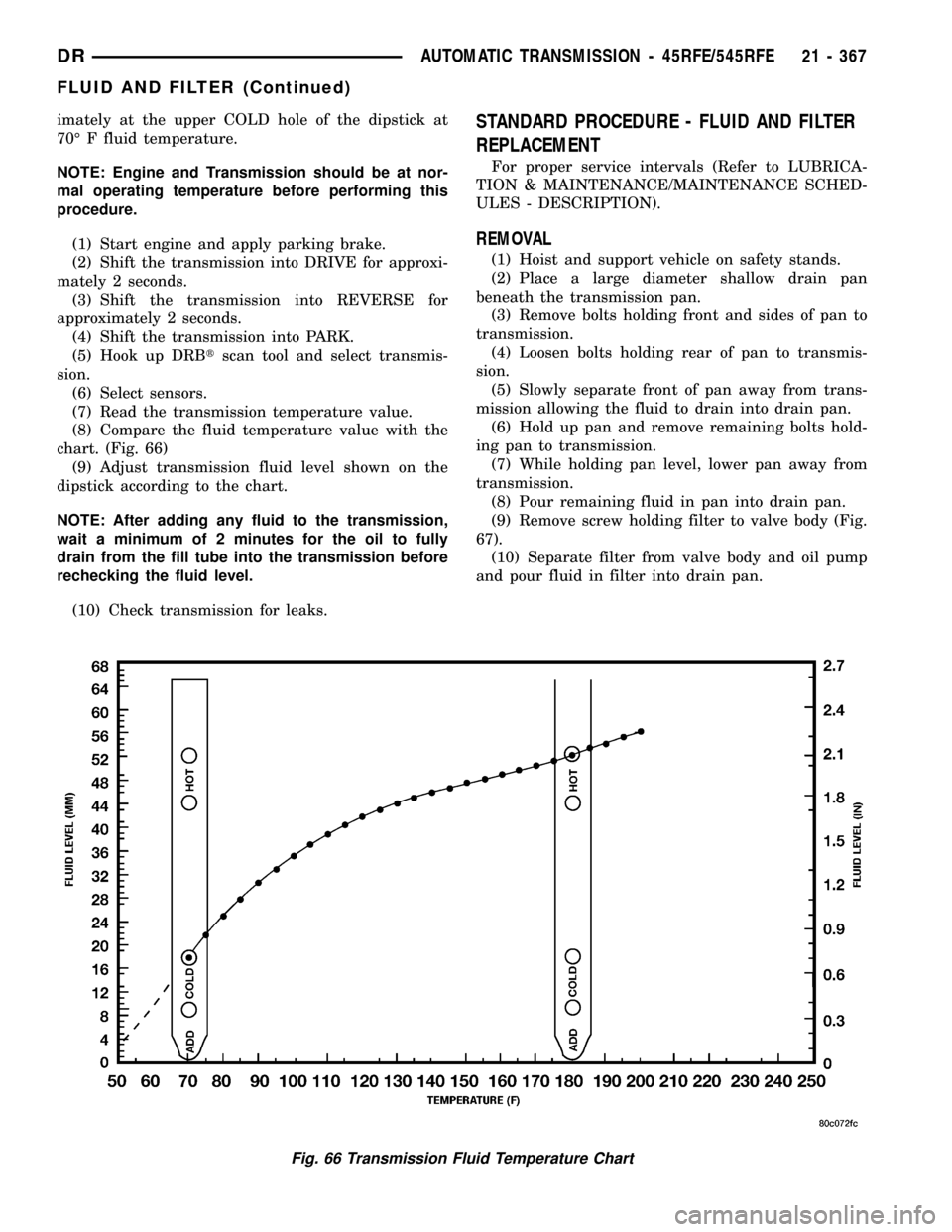
imately at the upper COLD hole of the dipstick at
70É F fluid temperature.
NOTE: Engine and Transmission should be at nor-
mal operating temperature before performing this
procedure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select transmis-
sion.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart. (Fig. 66)
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart.
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission.
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
(5) Slowly separate front of pan away from trans-
mission allowing the fluid to drain into drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolts hold-
ing pan to transmission.
(7) While holding pan level, lower pan away from
transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9) Remove screw holding filter to valve body (Fig.
67).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and oil pump
and pour fluid in filter into drain pan.
Fig. 66 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 367
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 2071 of 2627

(11) Remove and discard the oil filter seal from the
bottom of the oil pump.
(12) If replacing the cooler return filter, use Oil
Filter Wrench 8321 to remove the filter from the
transmission.
(13) Dispose of used trans fluid and filter(s) prop-
erly.
INSPECTION
Inspect bottom of pan and magnet for excessive
amounts of metal. A light coating of clutch material
on the bottom of the pan does not indicate a problem
unless accompanied by a slipping condition or shift
lag. If fluid and pan are contaminated with excessive
amounts of debris, refer to the diagnosis section of
this group.
CLEANING
(1) Using a suitable solvent, clean pan and mag-
net.
(2) Using a suitable gasket scraper, clean original
sealing material from surface of transmission case
and the transmission pan.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(1) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.(2) Place replacement filter in position on valve
body and into the oil pump.
(3) Install screw to hold filter to valve body (Fig.
67). Tighten screw to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install new cooler return filter onto the trans-
mission, if necessary. Torque the filter to 14.12 N´m
(125 in.lbs.).
(5) Place bead of MopartRTV sealant onto the
transmission case sealing surface.
(6) Place pan in position on transmission.
(7) Install bolts to hold pan to transmission.
Tighten bolts to 11.8 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4 to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add10
pints (5 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled
and the torque converter was replaced or drained,
add24 pints (12 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmis-
sion.
(3) Check the transmission fluid (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC - RFE/FLUID -
STANDARD PROCEDURE) and adjust as required.
GEARSHIFT CABLE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GEARSHIFT
CABLE
(1) Engine starts must be possible with shift lever
in PARK or NEUTRAL positions only. Engine starts
must not be possible in any other gear position.
(2) With the shift lever in the:
(a) PARK position - Apply upward force on the
shift arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must
be possible.
(b) PARK position - Apply downward force on
the shift arm and remove pressure. Engine starts
must be possible.
(c) NEUTRAL position - Normal position. Engine
starts must be possible.
(d) NEUTRAL position - Engine running and
brakes applied, apply upward force on the shift
arm. Transmission shall not be able to shift from
neutral to reverse.
Fig. 67 Transmission Filters - 4X4 Shown
1 - PRIMARY OIL FILTER
2 - COOLER RETURN FILTER
3 - COOLER RETURN FILTER BYPASS VALVE
4 - VALVE BODY
21 - 368 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 2073 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Route the transmission end of the gearshift
cable through the opening in the dash panel (Fig.
72).
(2) Seat the cable grommet into the dash panel
opening.
(3) Snap the cable into the steering column
bracket so the retaining ears (Fig. 73) are engaged
and snap the cable eyelet onto the shift lever ball
stud.(4) Raise the vehicle.
(5) Place the transmission manual shift lever in
the ªPARKº detent (rearmost) position and rotate
prop shaft to ensure transmission is in PARK.
(6) Route the gearshift cable through the transmis-
sion mounting bracket and secure the cable by snap-
ping the cable retaining ears into the transmission
bracket and snapping the cable eyelet on the manual
shift lever ball stud.
(7) Lower vehicle.
(8) Lock the shift cable adjustment by pressing the
cable adjuster lock tab downward until it snaps into
place.
(9) Check for proper operation of the transmission
range sensor.
(10) Adjust the gearshift cable (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/GEAR SHIFT
CABLE - ADJUSTMENTS) and BTSI mechanism
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SYS-
TEM - ADJUSTMENTS) as necessary.
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE
Check adjustment by starting the engine in PARK
and NEUTRAL. Adjustment is CORRECT if the
engine starts only in these positions. Adjustment is
INCORRECT if the engine starts in one but not both
positions. If the engine starts in any position other
than PARK or NEUTRAL, or if the engine will not
start at all, the transmission range sensor may be
faulty.
Gearshift Adjustment Procedure
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Release cable adjuster lock tab (underneath the
steering column) (Fig. 74) to unlock cable.
(3) Raise vehicle.
(4) Disengage the cable eyelet from the transmis-
sion manual shift lever.
(5) Verify transmission shift lever is in PARK
detent by moving lever fully rearward. Last rearward
detent is PARK position.
(6) Verify positive engagement of transmission
park lock by attempting to rotate propeller shaft.
Shaft will not rotate when park lock is engaged.
(7) Snap the cable eyelet onto the transmission
manual shift lever.
Fig. 72 Gearshift Cable at the Dash Panel
1 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
2 - GROMMET
Fig. 73 Gearshift Cable at Steering Column
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
21 - 370 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
GEARSHIFT CABLE (Continued)
Page 2079 of 2627

(15) Using Spring Compressor 8251, compress the
UD/OD balance piston and remove the snap-ring
from the input clutch hub (Fig. 80).(16) Remove the UD/OD balance piston and piston
return spring from the input clutch retainer (Fig. 81).
(17) Remove the underdrive piston from the input
clutch retainer (Fig. 81).
NOTE: Both the UD/OD balance piston and the
underdrive piston have seals molded onto them. If
the seal is damaged, do not attempt to install a new
seal onto the piston. The piston/seal must be
replaced as an assembly.
(18) Remove the input clutch retainer tapered
snap-ring.
(19) Separate input clutch retainer from input
clutch hub.
(20) Separate OD/reverse piston from input clutch
hub retainer (Fig. 81).
(21) Remove all seals and o-rings from the input
shaft and input hub. The o-rings on the input hub
are color coded. Be sure to make note of which o-ring
belongs in which location.
Fig. 80 Compressing UD/OD Balance Piston Using
Tool 8251
1 - PRESS
2 - TOOL 8251
3 - BALANCE PISTON
21 - 376 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 2090 of 2627

CONVERTER CLUTCH REGULATOR VALVE
The converter clutch regulator valve is used to con-
trol the hydraulic pressure supplied to the back (ON)
side of the torque converter clutch.
TORQUE CONVERTER LIMIT VALVE
The torque converter limit valve serves to limit the
available line pressure to the torque converter clutch.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP VOLUME
CHECK
Measuring the oil pump output volume will deter-
mine if sufficient oil flow to the transmission oil
cooler exists, and whether or not an internal trans-
mission failure is present.Verify that the transmission fluid is at the proper
level. Refer to the Fluid Level Check procedure in
this section. If necessary, fill the transmission to the
proper level with MopartATF +4, Automatic Trans-
mission Fluid.
(1) Disconnect theTo coolerline at the cooler
inlet and place a collecting container under the dis-
connected line.
CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(2) Run the engineat 1800 rpm, with the shift
selector in neutral. Verify that the transmission fluid
temperature is below 104.5É C (220É F) for this test.
Fig. 99 Oil Pump Reaction Shaft
1 - PUMP HOUSING 4 - SEAL RING (5)
2 - SEAL 5 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - OIL FILTER SEAL 6 - PUMP VALVE BODY
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 387
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2101 of 2627

SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION
The gear shift mechanism provides six shift posi-
tions which are:
²Park (P)
²Reverse (R)
²Neutral (N)
²Drive (D)
²Manual second (2)
²Manual low (1)
OPERATION
MANUAL LOW (1) range provides first gear only.
Overrun braking is also provided in this range.
MANUAL SECOND (2) range provides first and sec-
ond gear only.
DRIVE range provides FIRST, SECOND, THIRD,
OVERDRIVE FOURTH, and OVERDRIVE FIFTH (if
applicable) gear ranges. The shift into OVERDRIVE
FOURTH and FIFTH (if applicable) gear ranges
occurs only after the transmission has completed the
shift into D THIRD gear range. No further movement
of the shift mechanism is required to complete the
3-4 or 4-5 (if applicable) shifts.
The FOURTH and FIFTH (if applicable) gear
upshifts occur automatically when the overdrive
selector switch is in the ON position. No upshift to
FOURTH or FIFTH (if applicable) gears will occur if
any of the following are true:
²The transmission fluid temperature is below 10É
C (50É F) or above 121É C (250É F).
²The shift to THIRD is not yet complete.
²Vehicle speed is too low for the 3-4 or 4-5 (if
applicable) shifts to occur.
Upshifts into FOURTH or FIFTH (if applicable)
will be delayed when the transmission fluid temper-
ature is below 4.5É C (40É F) or above 115.5É C (240É
F).
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) is located in the
valve body and controls the direction of the transmis-
sion fluid when the L/R-TCC solenoid is energized.
OPERATION
The Solenoid Switch Valve controls line pressure
from the LR-TCC solenoid. In 1st gear, the SSV will
be in the downshifted position, thus directing fluid to
the L/R clutch circuit. In 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th (if
applicable) gears, the solenoid switch valve will be in
the upshifted position and directs the fluid into the
torque converter clutch (TCC) circuit.When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
1. Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
2. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
21 - 398 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR