ignition DODGE RAM 2001 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 2407 of 2889
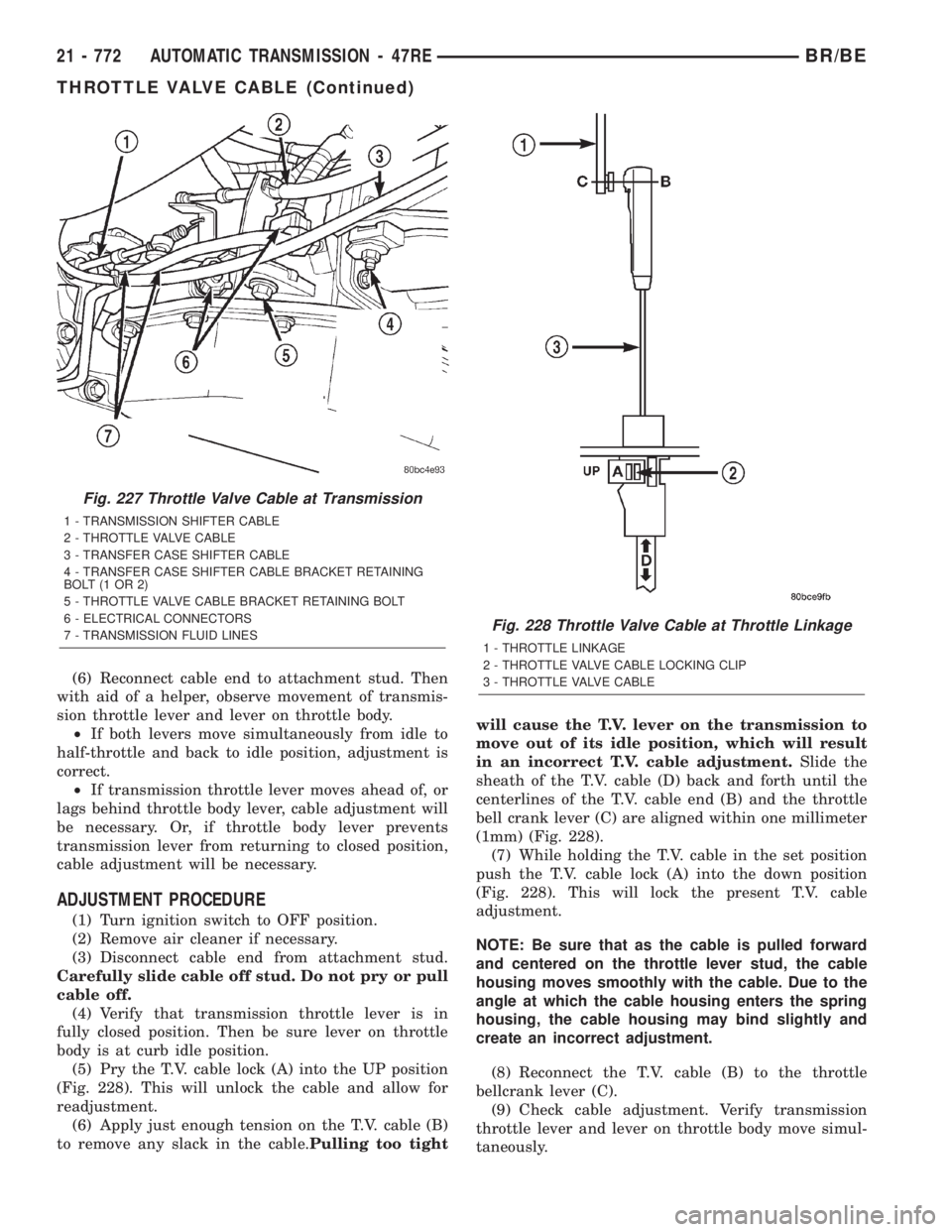
(6) Reconnect cable end to attachment stud. Then
with aid of a helper, observe movement of transmis-
sion throttle lever and lever on throttle body.
²If both levers move simultaneously from idle to
half-throttle and back to idle position, adjustment is
correct.
²If transmission throttle lever moves ahead of, or
lags behind throttle body lever, cable adjustment will
be necessary. Or, if throttle body lever prevents
transmission lever from returning to closed position,
cable adjustment will be necessary.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
(2) Remove air cleaner if necessary.
(3) Disconnect cable end from attachment stud.
Carefully slide cable off stud. Do not pry or pull
cable off.
(4) Verify that transmission throttle lever is in
fully closed position. Then be sure lever on throttle
body is at curb idle position.
(5) Pry the T.V. cable lock (A) into the UP position
(Fig. 228). This will unlock the cable and allow for
readjustment.
(6) Apply just enough tension on the T.V. cable (B)
to remove any slack in the cable.Pulling too tightwill cause the T.V. lever on the transmission to
move out of its idle position, which will result
in an incorrect T.V. cable adjustment.Slide the
sheath of the T.V. cable (D) back and forth until the
centerlines of the T.V. cable end (B) and the throttle
bell crank lever (C) are aligned within one millimeter
(1mm) (Fig. 228).
(7) While holding the T.V. cable in the set position
push the T.V. cable lock (A) into the down position
(Fig. 228). This will lock the present T.V. cable
adjustment.
NOTE: Be sure that as the cable is pulled forward
and centered on the throttle lever stud, the cable
housing moves smoothly with the cable. Due to the
angle at which the cable housing enters the spring
housing, the cable housing may bind slightly and
create an incorrect adjustment.
(8) Reconnect the T.V. cable (B) to the throttle
bellcrank lever (C).
(9) Check cable adjustment. Verify transmission
throttle lever and lever on throttle body move simul-
taneously.
Fig. 227 Throttle Valve Cable at Transmission
1 - TRANSMISSION SHIFTER CABLE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE
4 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE BRACKET RETAINING
BOLT(1OR2)
5 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE BRACKET RETAINING BOLT
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
7 - TRANSMISSION FLUID LINES
Fig. 228 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
21 - 772 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 47REBR/BE
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 2574 of 2889

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
DESCRIPTION............................1
WARNING...............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................2
WATER LEAKS..........................2
WIND NOISE...........................3
SPECIFICATIONS.........................4
DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE........62
DOOR - FRONT..........................67DOOR - CARGO.........................77
EXTERIOR..............................86
HOOD.................................99
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM.............104
INTERIOR.............................118
PAINT................................129
SEATS................................131
STATIONARY GLASS.....................145
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................152
BODY
DESCRIPTION ± PUSH-IN FASTENERS
DaimlerChrysler Corporation uses many different
types of push-in fasteners to secure the interior and
exterior trim to the body. Most of these fasteners can
be reused to assemble the trim during various repair
procedures. At times, a push-in fastener cannot be
removed without damaging the fastener or the com-
ponent it is holding. If it is not possible to remove a
fastener without damaging a component or body, cut
or break the fastener and use a new one when
installing the component. Never pry or pound on a
plastic or pressed-board trim component. Using a
suitable fork-type prying device, pry the fastener
from the retaining hole behind the component being
removed. When installing, verify fastener alignment
with the retaining hole by hand. Push directly on or
over the fastener until it seats. Apply a low-force pull
to the panel to verify that it is secure.
When it is necessary to remove components to ser-
vice another, it should not be necessary to apply
excessive force or bend a component to remove it.
Before damaging a trim component, verify hidden
fasteners or captured edges holding the component in
place.
DESCRIPTION ± LOCK CYLINDERS
Ignition, door, deck lid, and rear hatch lock cylin-
ders are all codable to the key. Lock barrels, tum-
blers, and tumbler springs are available to allow the
technician to change replacement locks cylinders to
match the customer's original key set. See the appro-
priate section in this manual for lock cylinder
removal. See the Moparž catalogue for part numbers
and lock coding procedures.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE A OSHA APPROVED BREATHING
FILTER WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN
A CONFINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH PETRO-
LEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEANING SOL-
VENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
DO NOT STAND UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE THAT
IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: When holes must be drilled or punched
in an inner body panel, verify depth of space to the
outer body panel, electrical wiring, or other compo-
nents. Damage to vehicle can result.
Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible
material on the interior of vehicle is removed from
the repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can
result.
Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use when
welding.
Disconnect the negative (-) cable clamp from the
battery when servicing electrical components that
are live when the ignition is OFF. Damage to electri-
cal system can result.
Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds on
painted surfaces. Damage to finish can result.
Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning solvents
on painted or upholstered surfaces. Damage to fin-
ish or color can result.
Do not hammer or pound on plastic trim panel
when servicing interior trim. Plastic panels can
break.
BR/BEBODY 23 - 1
Page 2682 of 2889

INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Position the ash receiver flame shield to the
instrument panel (Fig. 2).
(2) Squeeze the ash receiver lamp and hood
bracket and engage the unit to the mounting hole in
the flame shield.
(3) Insert the two retaining tabs on the top of the
ash receiver flame shield into the mounting holes in
the instrument panel, then push the shield forward
to engage the tabs with the instrument panel.
(4) Install and tighten the three screws that secure
the ash receiver flame shield to the instrument
panel. Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(5) Align the pivot receptacles on each side of the
ash receiver with the pivot pins in the lower instru-
ment panel.(6) Push the ash receiver forward onto the pivot
pins in the instrument panel until the open ash
receiver snaps into place.
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
CLUSTER BEZEL
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, turn the ignition switch to the Off posi-
tion (not Lock), set the parking brake, and place the
automatic transmission gear selector lever in the
Low position.
(3) If the vehicle is so equipped, set the tilt steer-
ing column in its lowest position.
(4) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry around the perimeter of
the cluster bezel to disengage the snap clips from
their receptacles in the instrument panel (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 Instrument Panel Ash Receiver Remove/
Install
1 - SCREW
2 - ASH RECEIVER
3 - FLAME SHIELD
Fig. 3 Cluster Bezel Remove/Install
1 - CLUSTER BEZEL
BR/BEINSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM 23 - 109
ASH RECEIVER (Continued)
Page 2747 of 2889

(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to fused battery feed. There should be bat-
tery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 30 at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the fuse in the PDC as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is not
used in this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal cavity (87) is
connected to the compressor clutch coil. There should
be continuity between this cavity and the A/C com-
pressor clutch relay output circuit cavity of the com-
pressor clutch coil wire harness connector. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit as
required.
(4) The relay coil battery terminal (86) is con-
nected to the fused ignition switch output (run/start)
circuit. There should be battery voltage at the cavity
for relay terminal 86 with the ignition switch in the
On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the
open circuit to the fuse in the junction block as
required.
(5) The coil ground terminal cavity (85) is switched
to ground through the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). There should be continuity between this cav-
ity and the A/C compressor clutch relay control cir-
cuit cavity of the PCM wire harness connector C
(gray) at all times. If not OK, repair the open circuit
as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 17).(3) Refer to the label on the PDC for compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch relay from the
PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the compressor clutch relay by aligning
the relay terminals with the cavities in the PDC and
pushing the relay firmly into place.
(2) Install the PDC cover.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Test the relay operation.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
Both the heater-only and a/c heater systems use a
combination of electrical and vacuum controls. These
controls provide the vehicle operator with a number
of setting options to help control the climate and
comfort within the vehicle. Refer to the owner's man-
ual in the vehicle glove box for more information on
the features, use, and suggested operation of these
controls.
OPERATION
The heater-only or a/c heater control panel is
located to the right of the instrument cluster on the
instrument panel. The control panel contains a rota-
ry-type temperature control knob, a rotary-type mode
control switch knob, and a rotary-type blower motor
speed switch knob. On models with the optional
heated mirror system, a momentary push button
switch and indicator lamp are located near the bot-
Fig. 16 COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 17 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
1 - COVER
2 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
24 - 18 CONTROLSBR/BE
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2751 of 2889

(2) Unplug the wire harness connector from the a/c
low pressure switch on the top of the accumulator
(Fig. 20).
(3) Unscrew the a/c low pressure switch from the
fitting on the top of the accumulator.
(4) Remove the O-ring seal from the accumulator
fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the accumulator fitting.
Use only the specified O-rings as they are made of a
special material for the R-134a system. Use only
refrigerant oil of the type recommended for the com-
pressor in the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT
OIL - DESCRIPTION)
(2) Install and tighten the a/c low pressure switch
on the accumulator fitting. The switch should be
hand-tightened onto the accumulator fitting.
(3) Plug the wire harness connector into the a/c
low pressure switch.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor relay is an International Stan-
dards Organization (ISO)-type relay. The relay is an
electromechanical device that switches battery cur-
rent from a fuse in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) directly to the blower motor. The relay is ener-
gized when the relay coil is provided a voltage signal
by the ignition switch. This arrangement reduces the
amount of battery current that must flow through
the ignition switch.
OPERATION
The blower motor relay control circuit is protected
by a fuse located in the junction block. When the
relay is de-energized, the blower motor receives no
battery current.
The blower motor relay is located in the PDC in
the engine compartment. Refer to the PDC label for
blower motor relay identification and location.
The blower motor relay cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
RELAY
RELAY TEST
The blower motor relay (Fig. 21) is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). Remove the blower
motor relay from the PDC to perform the following
tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 7565 ohms. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, see Relay Circuit Test below. If not
OK, replace the faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to fused battery feed directly from a fuse
in the Power Distribution Center (PDC), and should
be hot at all times. Check for battery voltage at the
PDC cavity for relay terminal 30. If OK, go to Step 2.
If not OK, repair the open circuit to the PDC fuse as
required.
Fig. 20 ACCUMULATOR AND A/C LOW PRESSURE
SWITCH
1 - CLIP
2 - BRACKET
3 - SCREW
4 - BAND
5 - ACCUMULATOR
6 - TO SUCTION LINE
7 - A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
8 - FROM EVAPORATOR OUTLET
24 - 22 CONTROLSBR/BE
A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2752 of 2889
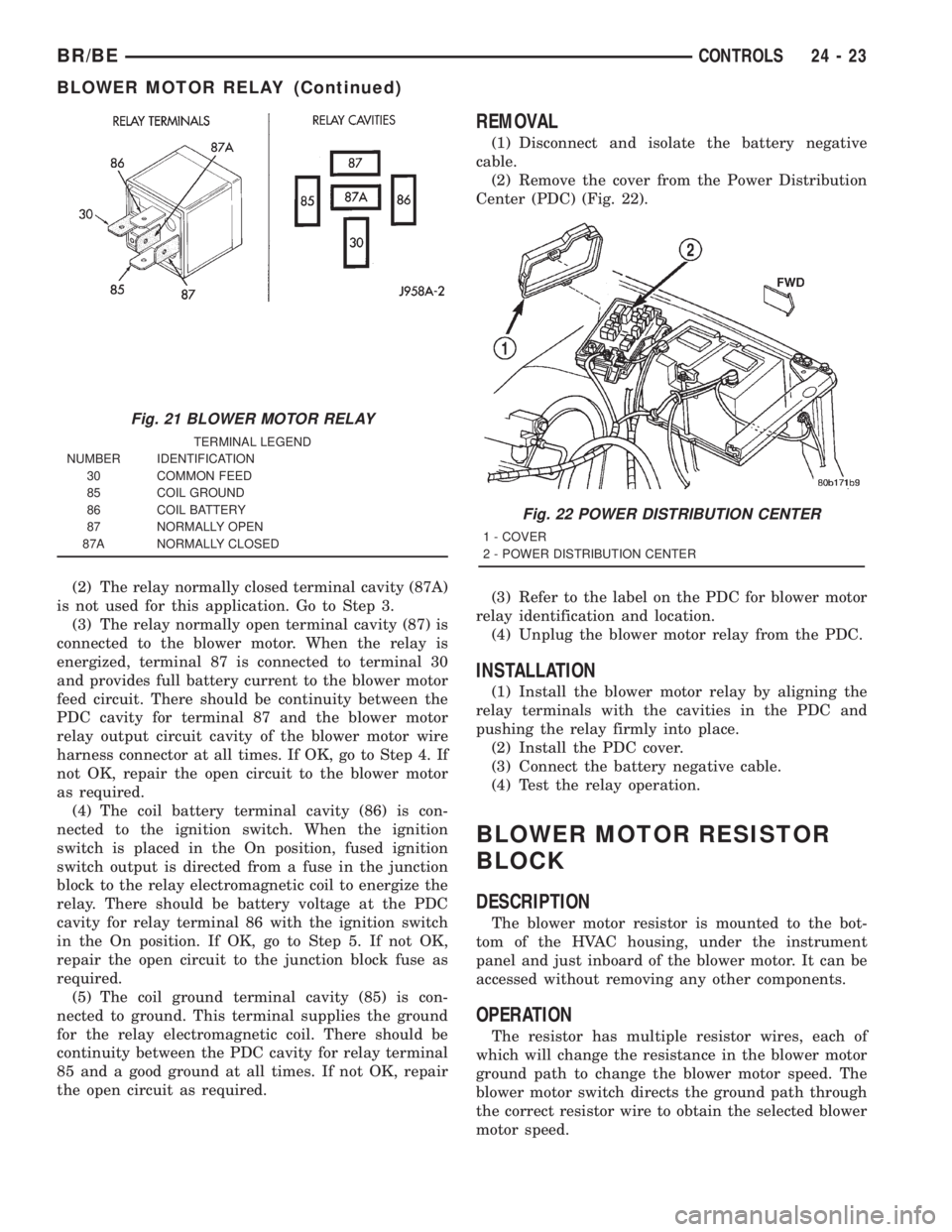
(2) The relay normally closed terminal cavity (87A)
is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal cavity (87) is
connected to the blower motor. When the relay is
energized, terminal 87 is connected to terminal 30
and provides full battery current to the blower motor
feed circuit. There should be continuity between the
PDC cavity for terminal 87 and the blower motor
relay output circuit cavity of the blower motor wire
harness connector at all times. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair the open circuit to the blower motor
as required.
(4) The coil battery terminal cavity (86) is con-
nected to the ignition switch. When the ignition
switch is placed in the On position, fused ignition
switch output is directed from a fuse in the junction
block to the relay electromagnetic coil to energize the
relay. There should be battery voltage at the PDC
cavity for relay terminal 86 with the ignition switch
in the On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK,
repair the open circuit to the junction block fuse as
required.
(5) The coil ground terminal cavity (85) is con-
nected to ground. This terminal supplies the ground
for the relay electromagnetic coil. There should be
continuity between the PDC cavity for relay terminal
85 and a good ground at all times. If not OK, repair
the open circuit as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 22).
(3) Refer to the label on the PDC for blower motor
relay identification and location.
(4) Unplug the blower motor relay from the PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the blower motor relay by aligning the
relay terminals with the cavities in the PDC and
pushing the relay firmly into place.
(2) Install the PDC cover.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Test the relay operation.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor resistor is mounted to the bot-
tom of the HVAC housing, under the instrument
panel and just inboard of the blower motor. It can be
accessed without removing any other components.
OPERATION
The resistor has multiple resistor wires, each of
which will change the resistance in the blower motor
ground path to change the blower motor speed. The
blower motor switch directs the ground path through
the correct resistor wire to obtain the selected blower
motor speed.
Fig. 21 BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 22 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
1 - COVER
2 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
BR/BECONTROLS 24 - 23
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)
Page 2754 of 2889

motor speeds, but can only be turned off by selecting
the Off position with the heater-only or a/c heater
control switch knob.
OPERATION
The blower motor switch directs the blower motor
ground path through the mode control switch to the
blower motor resistor, or directly to ground, as
required to achieve the selected blower motor speed.
The blower motor switch cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, the entire heater-only or a/c
heater control unit must be replaced. The blower
motor switch knob is serviced separately.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
SWITCH
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Check for battery voltage at the fuse in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Remove the a/c heater control from the instrument
panel. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CONTROLS/A/C HEATER CONTROL -
REMOVAL) Check for continuity between the ground
circuit cavity of the a/c heater control wire harness
connector and a good ground. There should be conti-
nuity. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to ground as required.
(3) With the a/c heater control wire harness con-
nector unplugged, place the a/c heater mode control
switch knob in any position except the Off position.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit ter-
minal and each of the blower motor driver circuit ter-
minals of the a/c heater control as you move the
blower motor switch knob to each of the four speed
positions. There should be continuity at each drivercircuit terminal in only one blower motor switch
speed position. If OK, test and repair the blower
driver circuits between the a/c heater control connec-
tor and the blower motor resistor as required. If not
OK, replace the faulty a/c heater control unit.
REMOVAL
The blower motor switch cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, the entire heater-only or a/c
heater control unit must be replaced. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C
HEATER CONTROL - REMOVAL) The blower motor
switch knob is serviced separately.
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the run position.
(2) Locate the temperature control knob in the mid
(12 o'clock) position.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the off position.
(4) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(5) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle.
Refer to Instrument Panel System for the procedures.
(6) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(7) Unplug the wire harness connector from the
blend door actuator (Fig. 24).
(8) Remove the two mounting screws which secure
the actuator to the housing.
(9) Slide the blend door actuator off the blend door
shaft.
NOTE: A black plastic coupler may be attached to
the blend door shaft. Remove the coupler and
inspect for damage. Reinstall if there is no damage
found.
BR/BECONTROLS 24 - 25
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2789 of 2889

DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.
Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0030 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Relay Circuit Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0036 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Relay Circuit Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0106 Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0121 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Low Throttle position sensor input below the acceptable
voltage range.
P0122 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2793 of 2889
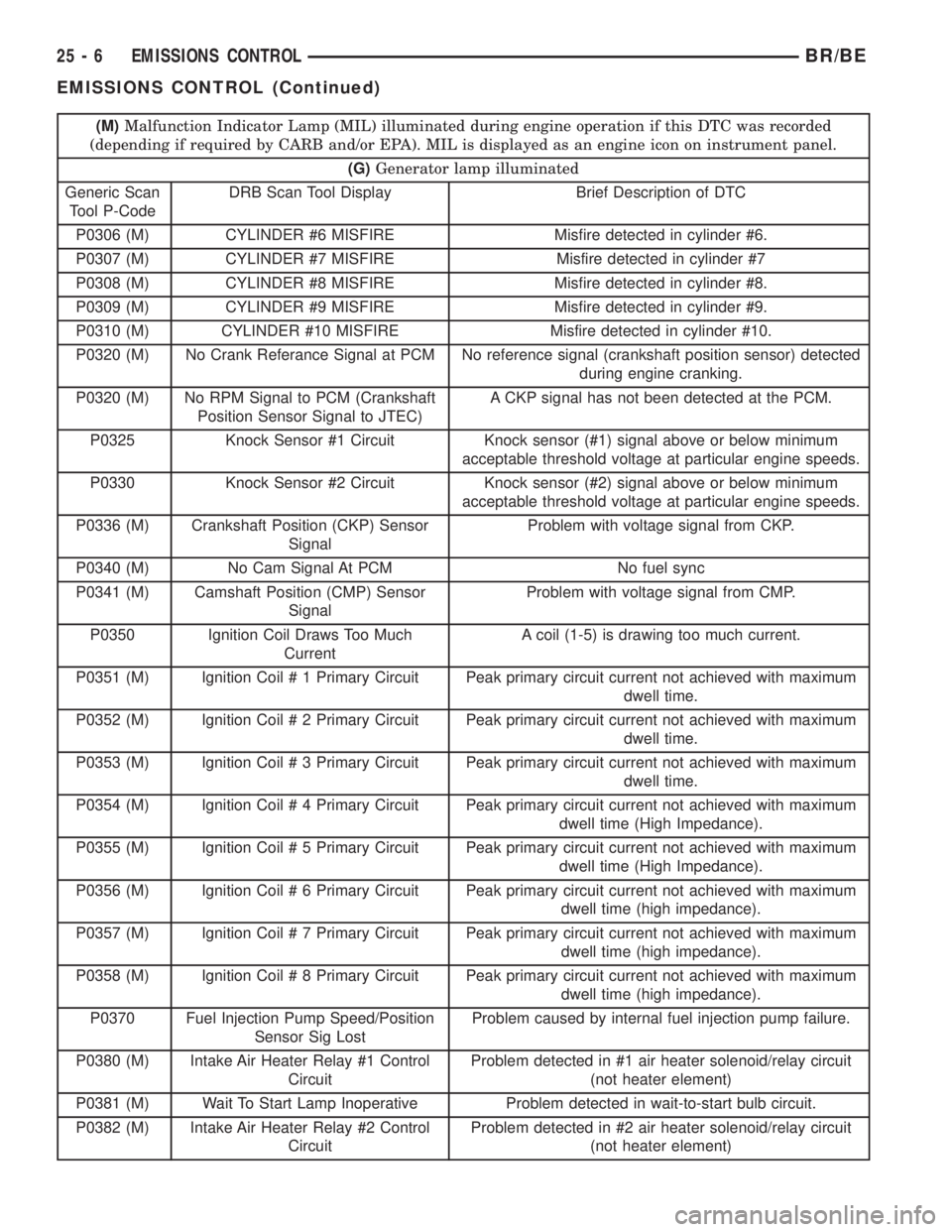
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0306 (M) CYLINDER #6 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #6.
P0307 (M) CYLINDER #7 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #7
P0308 (M) CYLINDER #8 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #8.
P0309 (M) CYLINDER #9 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #9.
P0310 (M) CYLINDER #10 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #10.
P0320 (M) No Crank Referance Signal at PCM No reference signal (crankshaft position sensor) detected
during engine cranking.
P0320 (M) No RPM Signal to PCM (Crankshaft
Position Sensor Signal to JTEC)A CKP signal has not been detected at the PCM.
P0325 Knock Sensor #1 Circuit Knock sensor (#1) signal above or below minimum
acceptable threshold voltage at particular engine speeds.
P0330 Knock Sensor #2 Circuit Knock sensor (#2) signal above or below minimum
acceptable threshold voltage at particular engine speeds.
P0336 (M) Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
SignalProblem with voltage signal from CKP.
P0340 (M) No Cam Signal At PCM No fuel sync
P0341 (M) Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
SignalProblem with voltage signal from CMP.
P0350 Ignition Coil Draws Too Much
CurrentA coil (1-5) is drawing too much current.
P0351 (M) Ignition Coil # 1 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0352 (M) Ignition Coil # 2 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0353 (M) Ignition Coil # 3 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0354 (M) Ignition Coil # 4 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0355 (M) Ignition Coil # 5 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0356 (M) Ignition Coil # 6 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0357 (M) Ignition Coil # 7 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0358 (M) Ignition Coil # 8 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0370 Fuel Injection Pump Speed/Position
Sensor Sig LostProblem caused by internal fuel injection pump failure.
P0380 (M) Intake Air Heater Relay #1 Control
CircuitProblem detected in #1 air heater solenoid/relay circuit
(not heater element)
P0381 (M) Wait To Start Lamp Inoperative Problem detected in wait-to-start bulb circuit.
P0382 (M) Intake Air Heater Relay #2 Control
CircuitProblem detected in #2 air heater solenoid/relay circuit
(not heater element)
25 - 6 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2802 of 2889

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1762 (M) Gov Press Sen Offset Volts Too Lo
or HighThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is greater than a
calibration limit or is less than a calibration limit for 3
consecutive park/neutral calibrations.
P1762 (M) Governor Press Sen Offset Volts Too
Low or HighSensor input greater or less than calibration for 3
consecutive Neutral/Park occurrences (4-speed auto.
trans. only).
P1763 Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
HiThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is above an
acceptable voltage level.
P1763 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
HIVoltage greater than 4.89 volts (4-speed auto. trans.
only).
P1764 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
LowThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is below an
acceptable voltage level.
P1764 (M) Governor Pressure Sensor Volts Too
LowVoltage less than .10 volts (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1765 (M) Trans 12 Volt Supply Relay CTRL
CircuitAn open or shorted condition is detected in the
Transmission Relay control circuit. This relay supplies
power to the TCC
P1765 (M) Trans 12 Volt Supply Relay Ctrl
CircuitCurrent state of solenoid output port is different than
expected (4-speed auto. trans. only).
P1899 (M) P/N Switch Stuck in Park or in Gear Incorrect input state detected for the Park/Neutral switch.
P1899 (M) P/N Switch Stuck in Park or in Gear Incorrect input state detected for the Park/Neutral switch
(3 or 4-speed auto. trans. only).
DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER
The PCM is responsible for efficiently coordinating
the operation of all the emissions-related compo-
nents. The PCM is also responsible for determining if
the diagnostic systems are operating properly. The
software designed to carry out these responsibilities
is call the 'Task Manager'.
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS
There are new electronic circuit monitors that
check fuel, emission, engine and ignition perfor-
mance. These monitors use information from various
sensor circuits to indicate the overall operation of the
fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems and thus
the emissions performance of the vehicle.
The fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems
monitors do not indicate a specific component prob-
lem. They do indicate that there is an implied prob-
lem within one of the systems and that a specific
problem must be diagnosed.
If any of these monitors detect a problem affecting
vehicle emissions, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated. These monitors generateDiagnostic Trouble Codes that can be displayed with
the MIL or a scan tool.
The following is a list of the system monitors:
²Misfire Monitor
²Fuel System Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
All these system monitors require two consecutive
trips with the malfunction present to set a fault.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnos-
tics Procedures manual for diagnostic proce-
dures.
The following is an operation and description of
each system monitor:
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 15
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)