height adjustment DODGE RAM 2001 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 46 of 2889

down several times. Always release the bumper in
the down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications while the vehicle is in its NOR-
MALLY LOADED CONDITION.
Camber and caster angle adjustments involve
changing the position of the upper suspension arm
pivot bar (Fig. 3). Refer to the Alignment Specifica-
tion Chart for the correct setting.
CASTER:Move the rear position of the pivot bar
in or out. This will change the caster angle signifi-
cantly and camber angle only slightly. To retain cam-
ber move the forward pivot very slightly in the
opposite direction.
NOTE: For example, to increase a positive caster
angle, move the rear position of the pivot bar
inward (toward the engine). Move the front of pivot
bar outward (away from the engine) slightly until
the original camber angle is obtained.CAMBER:Move the forward position of the pivot
bar in or out. This will change the camber angle sig-
nificantly and caster angle only slightly. The camber
angle should be adjusted as close as possible to the
preferred service specification. After adjustment
is made tighten pivot bar nuts to specifications.
TOE POSITION:The wheel toe position adjust-
ment should be the final adjustment.
(1) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways
before straightening the wheels. Center and secure
the steering wheel and turn off engine.
(2) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts/nuts.
NOTE: Each front wheel should be adjusted for
one-half of the total toe position specification. This
will ensure the steering wheel will be centered
when the wheels are positioned straight-ahead.
(3) Adjust the wheel toe position by turning the tie
rod adjustment sleeves as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CASTER
CORRECTION MEASUREMENT
NOTE: To determine the correct caster alignment
angle for Cab-Chassis vehicles the following proce-
dure must be performed.
NOTE: 4x2 11000 GVW has a solid front axle and
uses a 4x4 frame.
(1) Take a height measurement to the center of the
front gauge hole in the frame. Take another measure-
ment to the center of the rear spring hanger bolt
(Fig. 4). Take these measurements on both sides of
the vehicle.
(2) Subtract the front measurement from the rear
measurement and use the average between the right
and left side. Use this number (caster correlation
valve) with the Corrected Caster Chart to obtain the
preferred caster angle.
Fig. 3 Caster Camber Adjustment Location
1 - PIVOT BAR
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - SUSPENSION ARM FRAME MOUNT
4 - ADJUSTMENT SLOTS
BR/BEWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 3
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 57 of 2889

FRONT - 4WD
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT - 4WD
DESCRIPTION...........................14
SPECIFICATIONS........................15
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................16
HUB / BEARING
REMOVAL..............................16
INSTALLATION...........................18
KNUCKLE
DESCRIPTION...........................20
OPERATION.............................20
REMOVAL..............................20
INSTALLATION...........................20
LOWER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL..............................20
INSTALLATION...........................20
SHOCK
DESCRIPTION...........................21
OPERATION.............................21
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................21
SHOCK..............................21
REMOVAL..............................21
INSTALLATION...........................21
SPRING
DESCRIPTION...........................22OPERATION.............................22
REMOVAL..............................22
INSTALLATION...........................22
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION...........................22
OPERATION.............................22
REMOVAL..............................22
INSTALLATION...........................23
TRACK BAR
DESCRIPTION...........................23
OPERATION.............................23
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................23
TRACK BAR...........................23
REMOVAL..............................23
INSTALLATION...........................23
UPPER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL..............................23
INSTALLATION...........................24
LOWER BALL JOINT
REMOVAL..............................24
INSTALLATION...........................25
UPPER BALL JOINT
REMOVAL..............................25
INSTALLATION...........................25
FRONT - 4WD
DESCRIPTION
The link/coil suspension allows each wheel to adapt
to different road surfaces. The suspension is com-
prised of (Fig. 1) :
²Shock absorbers
²Coil springs
²Upper and lower suspension arms
²Stabilizer bar
²Track bar
²Steering Knuckles
²Hub/Bearing
²Ball Joints
²Jounce Bumpers
CAUTION: Components attached with a nut and cot-
ter pin must be torqued to specification. Then if the
slot in the nut does not line up with the cotter pin
hole, tighten nut until it is aligned. Never loosen the
nut to align the cotter pin hole.CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings (except stabilizer bar) should be tightened
with the vehicle at normal height. It is important to
have the springs supporting the weight of the vehi-
cle when the fasteners are torqued. If springs are
not at their normal ride position, vehicle ride com-
fort could be affected and premature bushing wear
may occur.
DESCRIPTION
The upper and lower suspension arms use bush-
ings to isolate road noise. The suspension arms are
bolted to the frame and axle through the rubber
bushings. The lower suspension arm uses cam bolts
at the axle to allow for caster and pinion angle
adjustment.
2 - 14 FRONT - 4WDBR/BE
Page 90 of 2889

(8) Disconnect the stabilizer bar links at the axle
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
brackets.
(10) Disconnect the track bar from the axle
bracket.
(11) Disconnect the tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckles.
(12) Position the axle with a suitable lifting device
under the axle assembly.
(13) Secure axle to lifting device.
(14) Mark suspension alignment cams for installa-
tion reference.
(15) Disconnect the upper and lower suspension
arms from the axle bracket.
(16) Lower the axle. The coil springs will drop
with the axle.
(17) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the weight of the
vehicle on the suspension, at normal height. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur. Rubber bushings must never
be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a suitable lifting device.
(2) Secure axle to lifting device.
(3) Position the axle under the vehicle.
(4) Install the springs, retainer clip and bolts.
(5) Raise the axle and align it with the spring
pads.
(6) Position the upper and lower suspension arms
in the axle brackets. Install bolts, nuts and align the
suspension alignment cams to the reference marks.
Do not tighten at this time.
(7) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
(8) Install the shock absorber and tighten bolts to
121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the stabilizer bar link to the axle
bracket. Tighten the nut to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(10) Install the drag link and tie rod to the steer-
ing knuckles and tighten the nuts to 88 N´m (65 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(11) Install the ABS wheel speed sensors, if
equipped. Refer to group 5, Brakes, for proper proce-
dures.
(12) Install the brake calipers and rotors. Refer to
Group 5, Brakes, for proper procedures.
(13) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(14) Connect vacuum hose and electrical connector
to disconnect housing.(15) Install front propeller shaft.
(16) Check and add differential lubricant, if neces-
sary. Refer to Lubricant Specifications in this section
for lubricant requirements.
(17) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(18) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(19) Tighten the upper suspension arm nuts at
axle to 121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the
upper suspension arm nuts at frame to 84 N´m (62 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(20) Tighten the lower suspension arm nuts at
axle to 84 N´m (62 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the lower
suspension arm nuts at frame to 119 N´m (88 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(21) Tighten the track bar bolt at the axle bracket
to 176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.) torque.
(22) Check the front wheel alignment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig.
4). A plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
ter line of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 109.5 mm (4.312 in.). The standard depth provides
the best gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to Back-
lash and Contact Pattern in this section for addi-
tional information.
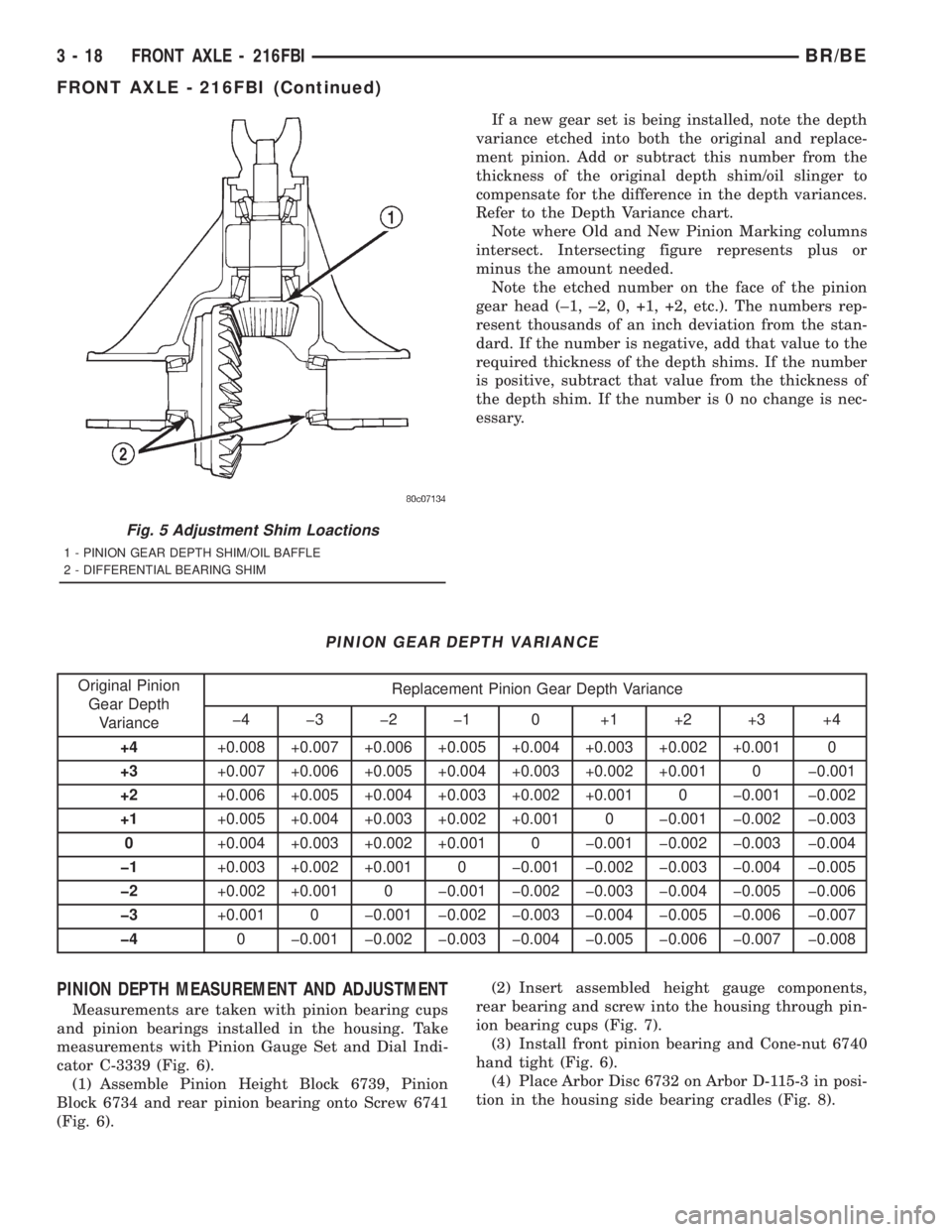
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim/oil baffle. The shims are
placed between the rear pinion bearing and the pin-
ion gear head (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 17
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 91 of 2889
If a new gear set is being installed, note the depth
variance etched into both the original and replace-
ment pinion. Add or subtract this number from the
thickness of the original depth shim/oil slinger to
compensate for the difference in the depth variances.
Refer to the Depth Variance chart.
Note where Old and New Pinion Marking columns
intersect. Intersecting figure represents plus or
minus the amount needed.
Note the etched number on the face of the pinion
gear head (±1, ±2, 0, +1, +2, etc.). The numbers rep-
resent thousands of an inch deviation from the stan-
dard. If the number is negative, add that value to the
required thickness of the depth shims. If the number
is positive, subtract that value from the thickness of
the depth shim. If the number is 0 no change is nec-
essary.
PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
þ4 þ3 þ2 þ1 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004
þ1+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005
þ2+0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006
þ3+0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007
þ40 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007 þ0.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 6).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6734 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
Fig. 5 Adjustment Shim Loactions
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM/OIL BAFFLE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
3 - 18 FRONT AXLE - 216FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 123 of 2889

REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheels and tires.
(3) Remove the brake calipers and rotors. Refer to
Group 5, Brakes, for proper procedures.
(4) Remove ABS wheel speed sensors, if equipped.
Refer to Group 5, Brakes, for proper procedures.
(5) Disconnect the axle vent hose.
(6) Disconnect vacuum hose and electrical connec-
tor at disconnect housing.
(7) Remove the front propeller shaft.
(8) Disconnect the stabilizer bar links at the axle
brackets.
(9) Disconnect the shock absorbers from axle
brackets.
(10) Disconnect the track bar from the axle
bracket.
(11) Disconnect the tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckles.
(12) Position the axle with a suitable lifting device
under the axle assembly.
(13) Secure axle to lifting device.
(14) Mark suspension alignment cams for installa-
tion reference.
(15) Disconnect the upper and lower suspension
arms from the axle bracket.
(16) Lower the axle. The coil springs will drop
with the axle.
(17) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the weight of the
vehicle on the suspension, at normal height. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur. Rubber bushings must never
be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a suitable lifting device.
(2) Secure axle to lifting device.
(3) Position the axle under the vehicle.
(4) Install the springs, retainer clip and bolts.
(5) Raise the axle and align it with the spring
pads.
(6) Position the upper and lower suspension arms
in the axle brackets. Install bolts, nuts and align the
suspension alignment cams to the reference marks.
Do not tighten at this time.
(7) Connect the track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
(8) Install the shock absorber and tighten bolts to
121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.) torque.(9) Install the stabilizer bar link to the axle
bracket. Tighten the nut to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(10) Install the drag link and tie rod to the steer-
ing knuckles and tighten the nuts to 88 N´m (65 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(11) Install the ABS wheel speed sensors, if
equipped. Refer to group 5, Brakes, for proper proce-
dures.
(12) Install the brake calipers and rotors. Refer to
Group 5, Brakes, for proper procedures.
(13) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(14) Connect vacuum hose and electrical connector
to disconnect housing.
(15) Install front propeller shaft.
(16) Check and add differential lubricant, if neces-
sary. Refer to Lubricant Specifications in this section
for lubricant requirements.
(17) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(18) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(19) Tighten the upper suspension arm nuts at
axle to 121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the
upper suspension arm nuts at frame to 84 N´m (62 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(20) Tighten the lower suspension arm nuts at
axle to 84 N´m (62 ft. lbs.) torque. Tighten the lower
suspension arm nuts at frame to 119 N´m (88 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(21) Tighten the track bar bolt at the axle bracket
to 176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.) torque.
(22) Check the front wheel alignment.ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig.
4). A plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
ter line of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 127 mm (5.00 in.). The standard depth provides
the best gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to Back-
lash and Contact Pattern in this section for addi-
tional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim/oil baffle. The shims are
placed between the rear pinion bearing and the pin-
ion gear head (Fig. 5).
If a new gear set is being installed, note the depth
variance etched into both the original and replace-
ment pinion. Add or subtract this number from the
thickness of the original depth shim/oil slinger to
compensate for the difference in the depth variances.
Refer to the Depth Variance chart.
3 - 50 FRONT AXLE - 248FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 124 of 2889

Note where Old and New Pinion Marking columns
intersect. Intersecting figure represents plus or
minus the amount needed.
Note the etched number on the face of the pinion
gear head (±1, ±2, 0, +1, +2, etc.). The numbers rep-
resent thousands of an inch deviation from the stan-
dard. If the number is negative, add that value to the
required thickness of the depth shims. If the numberis positive, subtract that value from the thickness of
the depth shim. If the number is 0 no change is nec-
essary.
PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
þ4 þ3 þ2 þ1 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004
þ1+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005
þ2+0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006
þ3+0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007
þ40 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007 þ0.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 6).
(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6736 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
Fig. 5 Adjustment Shim Loactions
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM/OIL BAFFLE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
Fig. 4 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 51
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 159 of 2889

(5) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
(6) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in axle housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the rearward surface of the pinion
height block (Fig. 8). Hold scooter block in place and
zero the dial indicator. Tighten dial indicator face
lock screw.
(7) Slowly slide the dial indicator probe over the
edge of the pinion height block.
(8) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 11). When the dial probe contacts the arbor bar,
the dial pointer will turn clockwise. Continue moving
the dial probe to the crest of the arbor bar and record
the highest reading. If the dial indicator can not
achieve the zero reading, the rear bearing cup or the
pinion depth gauge set is not installed correctly.
(9) Select a shim equal to the dial indicator read-
ing plus the drive pinion gear depth variance number
marked on the shaft of the pinion. For example, if
the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD AND GEAR
BACKLASH
The following must be considered when adjusting
bearing preload and gear backlash:
²The maximum ring gear backlash variation is
0.003 inch (0.076 mm).
²Mark the gears so the same teeth are meshed
during all backlash measurements.²Maintain the torque while adjusting the bearing
preload and ring gear backlash.
²Excessive adjuster torque will introduce a high
bearing load and cause premature bearing failure.
Insufficient adjuster torque can result in excessive
differential case free-play and ring gear noise.
²Insufficient adjuster torque will not support the
ring gear correctly and can cause excessive differen-
tial case free-play and ring gear noise.
NOTE: The differential bearing cups will not always
immediately follow the threaded adjusters as they
are moved during adjustment. To ensure accurate
bearing cup responses to the adjustments:
²Maintain the gear teeth engaged (meshed) as
marked.
²The bearings must be seated by rapidly rotating
the drive pinion gear a half turn back and forth.
²Do this five to ten times each time the threaded
adjusters are adjusted.
(1) Use Wrench C-4164 to adjust each threaded
adjuster inward until the differential bearing free-
play is eliminated (Fig. 12). Allow some ring gear
backlash (approximately 0.25 mm / 0.01 inch)
between the ring and pinion gear. Seat the bearing
cups with the procedure described above.
(2) Install dial indicator and position the plunger
against the drive side of a ring gear tooth (Fig. 13).
Measure the backlash at 4 positions (90 degrees
apart) around the ring gear. Locate and mark the
area of minimum backlash.
(3) Rotate the ring gear to the position of the least
backlash. Mark the gear so that all future backlash
Fig. 10 Pinion Depth Tools
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCKFig. 11 Pinion Gear Depth Measurement
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - 86 REAR AXLE-91/4BR/BE
REAR AXLE - 9 1/4 (Continued)
Page 188 of 2889

PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
þ4 þ3 þ2 þ1 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004
þ1+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005
þ2+0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006
þ3+0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007
þ40 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007 þ0.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 6).(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6736 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
Fig. 6 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge Tools
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 115
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 219 of 2889

PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
þ4 þ3 þ2 þ1 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004
þ1+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005
þ2+0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006
þ3+0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007
þ40 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007 þ0.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion bearing cups
and pinion bearings installed in the housing. Take
measurements with Pinion Gauge Set and Dial Indi-
cator C-3339 (Fig. 6).(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6737 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-nut 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 has different step diame-
ters to fit other axles. Choose proper step for axle
being serviced.
Fig. 6 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge Tools
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
3 - 146 REAR AXLE - 267RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)
Page 248 of 2889

PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceReplacement Pinion Gear Depth Variance
þ4 þ3 þ2 þ1 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004
þ1+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005
þ2+0.002 +0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006
þ3+0.001 0 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007
þ40 þ0.001 þ0.002 þ0.003 þ0.004 þ0.005 þ0.006 þ0.007 þ0.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion cups and pin-
ion bearings installed in housing. Take measure-
ments with a Pinion Gauge Set 6730 and Dial
Indicator C-3339 (Fig. 6).(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 6738 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 6).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through pin-
ion bearing cups (Fig. 7).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone 6740
hand tight (Fig. 6).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 in posi-
tion in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 8).
Install differential bearing caps on Arbor Discs and
snug the bearing cap bolts. Then tighten cap bolts in
a criss-cross pattern to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
NOTE: Arbor Discs 6732 have different step diame-
ters to fit other axle sizes. Pick correct size step for
axle being serviced.
Fig. 6 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 7 Pinion Height Block
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 286RBI 3 - 175
REAR AXLE - 286RBI (Continued)