lubrication DODGE RAM 2002 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 23 of 2255

TOWING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TOWING
A vehicle equipped with SAE approved sling-type
towing equipment can be used to tow all vehicles.
When towing a 4WD vehicle using a wheel-lift towing
device, use tow dollies under the opposite end of the
vehicle. A vehicle with flat-bed device can also be
used to transport a disabled vehicle (Fig. 12).
A wooden crossbeam may be required for proper
connection when using the sling-type, front-end tow-
ing method.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION: The following safety precautions must be
observed when towing a vehicle:
²Secure loose and protruding parts.
²Always use a safety chain system that is inde-
pendent of the lifting and towing equipment.
²Do not allow towing equipment to contact the
disabled vehicle's fuel tank.
²Do not allow anyone under the disabled vehicle
while it is lifted by the towing device.
²Do not allow passengers to ride in a vehicle
being towed.
²Always observe state and local laws regarding
towing regulations.
²Do not tow a vehicle in a manner that could
jeopardize the safety of the operator, pedestrians or
other motorists.²Do not attach tow chains, T-hooks, J-hooks, or a
tow sling to a bumper, steering linkage, drive shafts
or a non-reinforced frame hole.
²Do not tow a heavily loaded vehicle. Damage to
the cab, cargo box or frame may result. Use a flatbed
device to transport a loaded vehicle.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels removed,
install lug nuts to retain brake drums or rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until lifted wheels
are a minimum 100 mm (4 in) from the ground. Be
sure there is adequate ground clearance at the oppo-
site end of the vehicle, especially when towing over
rough terrain or steep rises in the road. If necessary,
remove the wheels from the lifted end of the vehicle
and lower the vehicle closer to the ground, to
increase the ground clearance at the opposite end of
the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching studs
to retain brake drums or rotors.
RAMP ANGLE
If a vehicle with flat-bed towing equipment is used,
the approach ramp angle should not exceed 15
degrees.
Fig. 11 Front Lift Pad Location
1 - SHIPPING TIE DOWN SLOT
2 - CROSSMEMBER BOLT ACCESS HOLE
3 - LIFTARM
4 - LIFT PAD EXTENSION
5 - FRAME RAIL
Fig. 12 Tow Vehicles With Approved Equipment
1 - SLING TYPE
2 - WHEEL LIFT
3 - FLAT BED
0 - 10 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEBR/BE
HOISTING (Continued)
Page 24 of 2255

TOWING WHEN KEYS ARE NOT AVAILABLE
When the vehicle is locked and keys are not avail-
able, use a flat bed hauler. A Wheel-lift or Sling-type
device can be used on 4WD vehicles providedall the
wheels are lifted off the ground using tow dol-
lies.
FOUR-WHEEL-DRIVE VEHICLE TOWING
Chrysler Corporation recommends that a vehicle be
transported on a flat-bed device. A Wheel-lift or
Sling-type device can be used providedall the
wheels are lifted off the ground using tow dol-
lies.WARNING: WHEN TOWING A DISABLED VEHICLE
AND THE DRIVE WHEELS ARE SECURED IN A
WHEEL LIFT OR TOW DOLLIES, ENSURE THE
TRANSMISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION (AUTO-
MATIC TRANSMISSION) OR A FORWARD DRIVE
GEAR (MANUAL TRANSMISSION).
CAUTION: Many vehicles are equipped with air
dams, spoilers, and/or ground effect panels. To
avoid component damage, a wheel-lift towing vehi-
cle or a flat-bed hauling vehicle is recommended.
BR/BELUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 11
TOWING (Continued)
Page 26 of 2255

SUSPENSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WHEEL ALIGNMENT......................1
FRONT - 2WD............................7FRONT - 4WD...........................14
REAR.................................25
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRE-ALIGNMENT . 2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURES - ALIGNMENT
I.F.S. ................................3STANDARD PROCEDURE - CASTER
CORRECTION MEASUREMENT...........3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALIGNMENT
LINK/COIL SUSPENSION.................5
SPECIFICATIONS
ALIGNMENT..........................6
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION
Wheel alignment is the positioning of the wheels in
relation to the vehicle. This is accomplished through
suspension and steering linkage adjustments. An
alignment is essential for efficient steering, good
directional stability and to minimize tire wear. The
most important measurements of an alignment are
caster, camber and toe position (Fig. 1)and (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: Do not attempt to modify any suspen-
sion or steering components by heating and bend-
ing.
NOTE: Periodic lubrication of the front suspension/
steering system components may be required. Rub-
ber bushings must never be lubricated. Refer to
Lubrication And Maintenance for the recommended
maintenance schedule.
Fig. 1 Alignment Angles - Independent Front
Suspension
1 - FRONT OF VEHICLE
2 - STEERING AXIS INCLINATION
3 - PIVOT POINT
4 - TOE-IN
BR/BESUSPENSION 2 - 1
Page 36 of 2255

²136 N´m (110 ft. lbs.) Install the lower ball joint
cotter pin.
(6) Install the stabilizer bar link on the lower sus-
pension arm. Install the grommet, retainer and nut
and tighten to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install the tie rod end on the steering knuckle
and tighten nut to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.). Install cotter
pin.
(8) Install the brake rotor and caliper assembly,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTORS - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the tire and wheel assembly, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(10) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(11) Tighten the suspension arm crossmember
nuts to 169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
SHOCK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The shock absorber bushings do not require any
type of lubrication. Do not attempt to stop bushing
noise by lubricating them. Grease and mineral oil-
base lubricants will deteriorate the bushing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove shock upper nut and remove retainer
and grommet.
(3) Remove lower mounting bolt from suspension
arm and remove shock (Fig. 5).
INSTALLATION
(1) Extend shock fully, install retainer and grom-
met on top of shock absorber. Check grommets and
retainer for wear.(2) Guide shock up through upper suspension arm
bracket. Install top grommet, retainer and nut.
Tighten nut to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(3) Align bottom end of shock into lower suspen-
sion arm and install mounting bolt. Tighten bolt to
142 N´m (105 ft. lbs.).
(4) Remove support and lower vehicle.
SPRING
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the brake caliper assembly and rotor,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTORS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the tie rod.
Remove the tie rod end from the steering knuckle
with Puller C-3894-A.
(5) Remove the stabilizer bar link from the lower
suspension arm.
(6) Support the lower suspension arm outboard
end with a jack. Place a jack under the arm in front
of the shock mount.
(7) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the lower
ball joint. Separate the ball joint with Remover
C-4150A.
(8) Remove the lower shock bolt from the suspen-
sion arm.
(9) Lower the jack and suspension arm until
spring tension is relieved. Remove spring and rubber
isolator (Fig. 6).
Fig. 5 Shock
1 - SHOCK
2 - JOUNCE BUMPER
BR/BEFRONT - 2WD 2 - 11
LOWER CONTROL ARM (Continued)
Page 47 of 2255
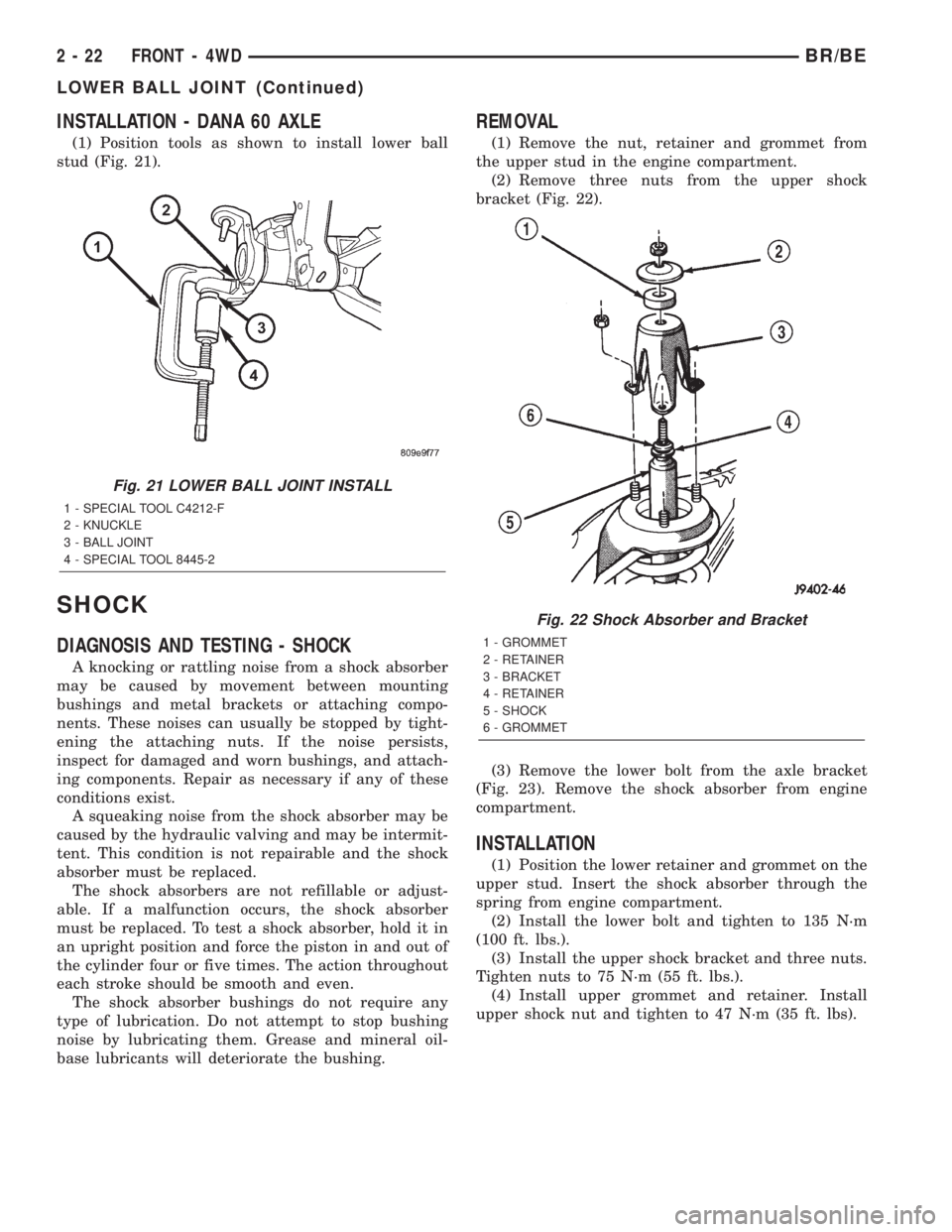
INSTALLATION - DANA 60 AXLE
(1) Position tools as shown to install lower ball
stud (Fig. 21).
SHOCK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The shock absorber bushings do not require any
type of lubrication. Do not attempt to stop bushing
noise by lubricating them. Grease and mineral oil-
base lubricants will deteriorate the bushing.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the nut, retainer and grommet from
the upper stud in the engine compartment.
(2) Remove three nuts from the upper shock
bracket (Fig. 22).
(3) Remove the lower bolt from the axle bracket
(Fig. 23). Remove the shock absorber from engine
compartment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the lower retainer and grommet on the
upper stud. Insert the shock absorber through the
spring from engine compartment.
(2) Install the lower bolt and tighten to 135 N´m
(100 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install the upper shock bracket and three nuts.
Tighten nuts to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install upper grommet and retainer. Install
upper shock nut and tighten to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs).
Fig. 21 LOWER BALL JOINT INSTALL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C4212-F
2 - KNUCKLE
3 - BALL JOINT
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8445-2
Fig. 22 Shock Absorber and Bracket
1 - GROMMET
2 - RETAINER
3 - BRACKET
4 - RETAINER
5 - SHOCK
6 - GROMMET
2 - 22 FRONT - 4WDBR/BE
LOWER BALL JOINT (Continued)
Page 50 of 2255

REAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR
DESCRIPTION.........................25
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPRING AND
SHOCK.............................25
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................26
SPECIAL TOOLS
SUSPENSION-REAR...................27
BUSHINGS
REMOVAL.............................27INSTALLATION.........................27
SHOCK
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................27
SPRING
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................28
STABILIZER BAR
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
REAR
DESCRIPTION
The rear suspension is comprised of:
²Shock Absorbers
²Jounce Bumpers
²Stabilizer Bar (optional)
²Leaf Springs
²Drive Axle
CAUTION: A vehicle should always be loaded so
the vehicle weight center-line is located immedi-
ately forward of the rear axle. Correct vehicle load-
ing provides proper front tire-to-road contact. This
results in maximum vehicle handling stability and
safety. Incorrect vehicle weight distribution can
cause excessive tire tread wear, spring fatigue or
failure, and erratic steering.
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber/ure-
thane bushings (except stabilizer bar) should be
tightened with the vehicle at normal ride height. It is
important to have the springs supporting the weight
of the vehicle when the fasteners are torqued. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPRING AND
SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The spring eye and shock absorber bushings do not
require any type of lubrication. Do not attempt to
stop spring bushing noise by lubricating them.
Grease and mineral oil-base lubricants will deterio-
rate the bushing rubber.
If the vehicle is used for severe, off-road operation,
the springs should be examined periodically. Check
for broken and shifted leafs, loose and missing clips,
and broken center bolts. Refer to Spring and Shock
Absorber Diagnosis chart for additional information.
BR/BEREAR 2 - 25
Page 57 of 2255

DRIVELINE VIBRATION
Drive Condition Possible Cause Correction
Propeller Shaft Noise 1) Undercoating or other foreign
material on shaft.1) Clean exterior of shaft and wash
with solvent.
2) Loose U-joint clamp screws. 2) Install new clamps and screws
and tighten to proper torque.
3) Loose or bent U-joint yoke or
excessive runout.3) Install new yoke.
4) Incorrect driveline angularity. 4) Measure and correct driveline
angles.
5) Rear spring center bolt not in
seat.5) Loosen spring u-bolts and seat
center bolt.
6) Worn U-joint bearings. 6) Install new U-joint.
7) Propeller shaft damaged or out
of balance.7) Installl new propeller shaft.
8) Broken rear spring. 8) Install new rear spring.
9) Excessive runout or unbalanced
condition.9) Re-index propeller shaft, test,
and evaluate.
10) Excessive drive pinion gear
shaft runout.10) Re-index propeller shaft and
evaluate.
11) Excessive axle yoke deflection. 11) Inspect and replace yoke if
necessary.
12) Excessive transfer case runout. 12) Inspect and repair as necessary.
Universal Joint Noise 1) Loose U-joint clamp screws. 1) Install new clamps and screws
and tighten to proper torque.
2) Lack of lubrication. 2) Replace as U-joints as
necessary.
BALANCE
NOTE: Removing and re-indexing the propeller
shaft 180É relative to the yoke may eliminate some
vibrations.
If propeller shaft is suspected of being unbalanced,
it can be verified with the following procedure:
(1) Raise the vehicle.
(2) Clean all the foreign material from the propel-
ler shaft and the universal joints.
(3) Inspect the propeller shaft for missing balance
weights, broken welds and bent areas.If the propel-
ler shaft is bent, it must be replaced.
(4) Inspect the universal joints to ensure that they
are not worn, properly installed and correctly aligned
with the shaft.
(5) Check the universal joint clamp screws torque.
(6) Remove the wheels and tires. Install the wheel
lug nuts to retain the brake drums or rotors.
(7) Mark and number the shaft six inches from the
yoke end at four positions 90É apart.(8) Run and accelerate the vehicle until vibration
occurs. Note the intensity and speed the vibration
occurred. Stop the engine.
(9) Install a screw clamp at position 1 (Fig. 1).
(10) Start the engine and re-check for vibration. If
there is little or no change in vibration, move the
clamp to one of the other three positions. Repeat the
vibration test.
(11) If there is no difference in vibration at the
other positions, the source of the vibration may not
be propeller shaft.
(12) If the vibration decreased, install a second
clamp (Fig. 2) and repeat the test.
(13) If the additional clamp causes an additional
vibration, separate the clamps (1/2 inch above and
below the mark). Repeat the vibration test (Fig. 3).
(14) Increase distance between the clamp screws
and repeat the test until the amount of vibration is
at the lowest level. Bend the slack end of the clamps
so the screws will not loosen.
3 - 2 PROPELLER SHAFTBR/BE
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 72 of 2255
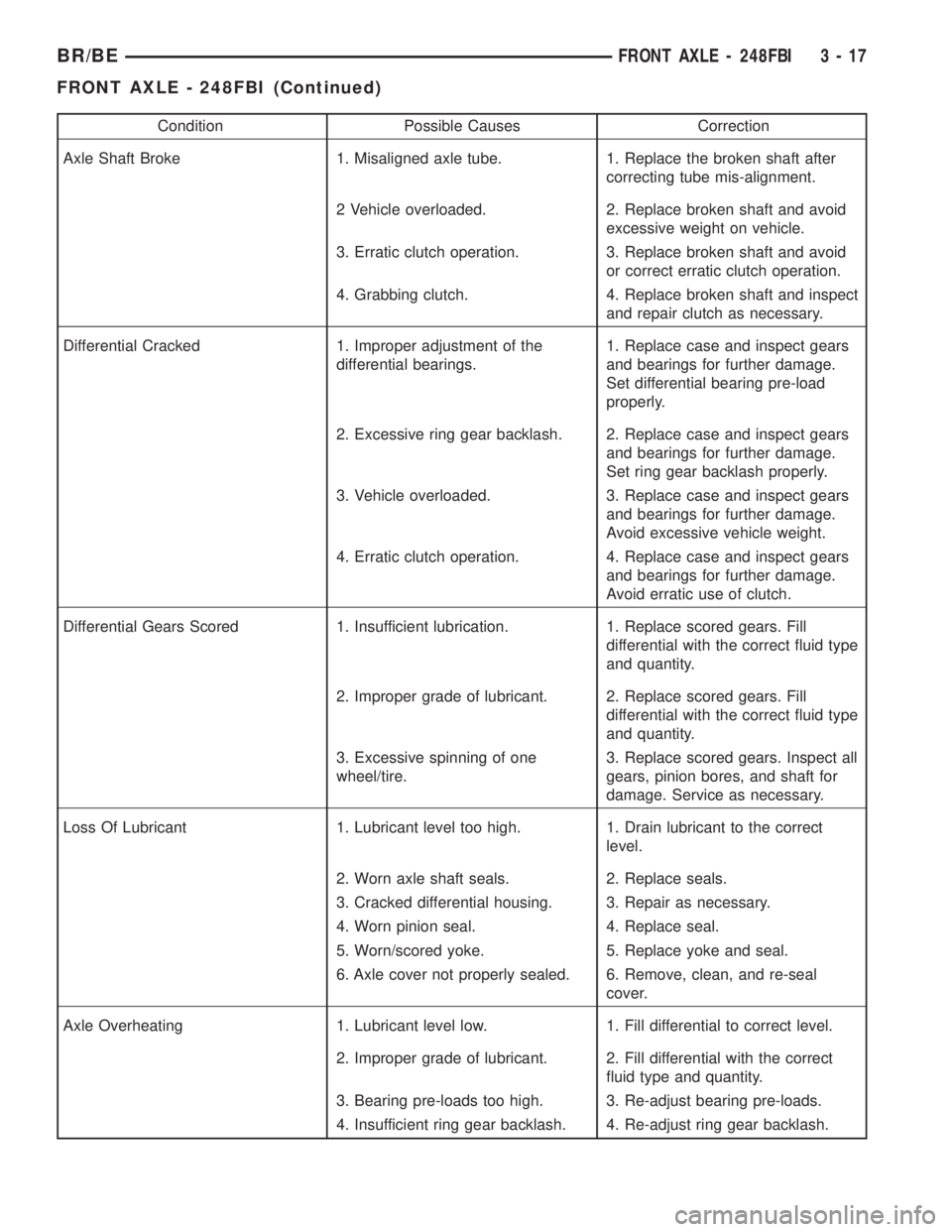
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 17
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 104 of 2255
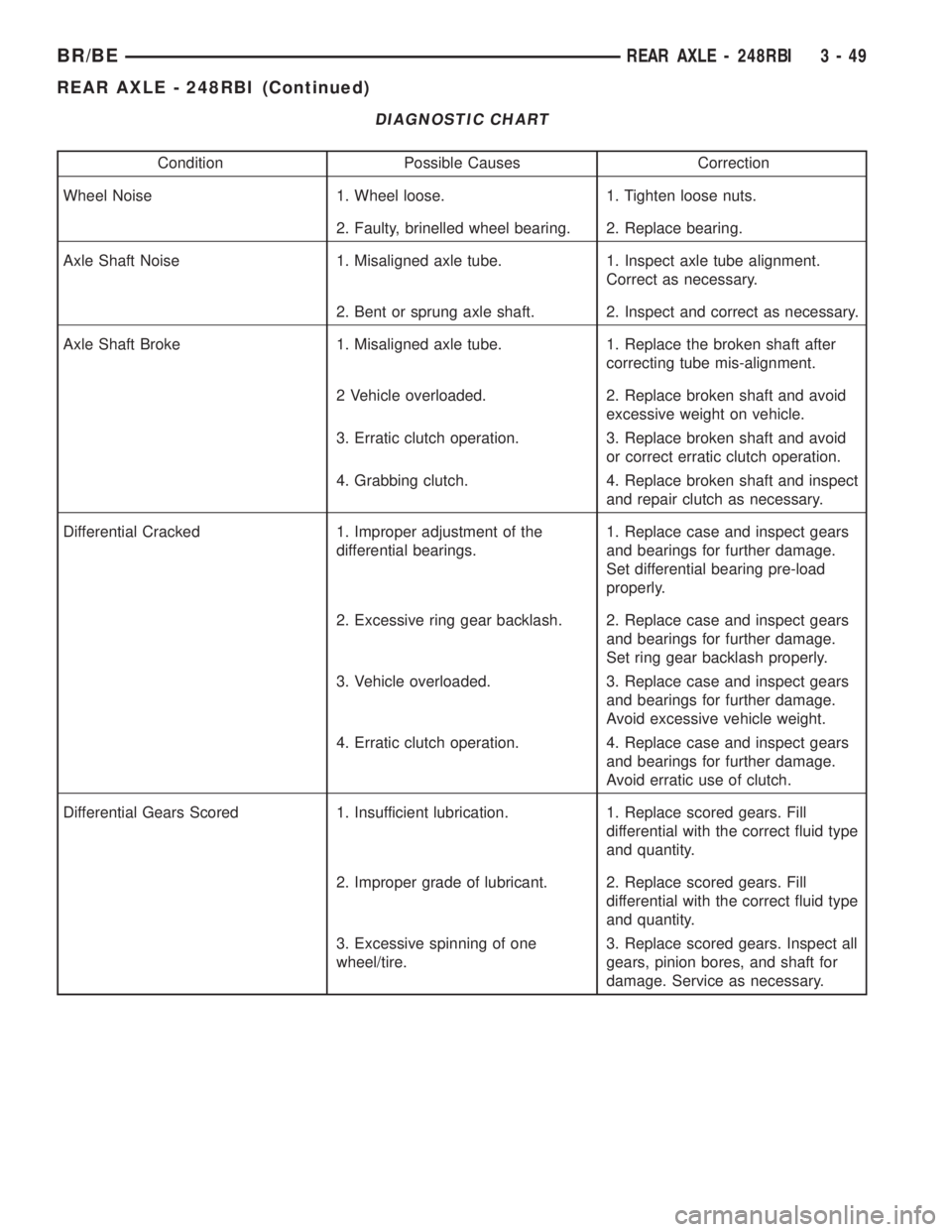
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 49
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 136 of 2255
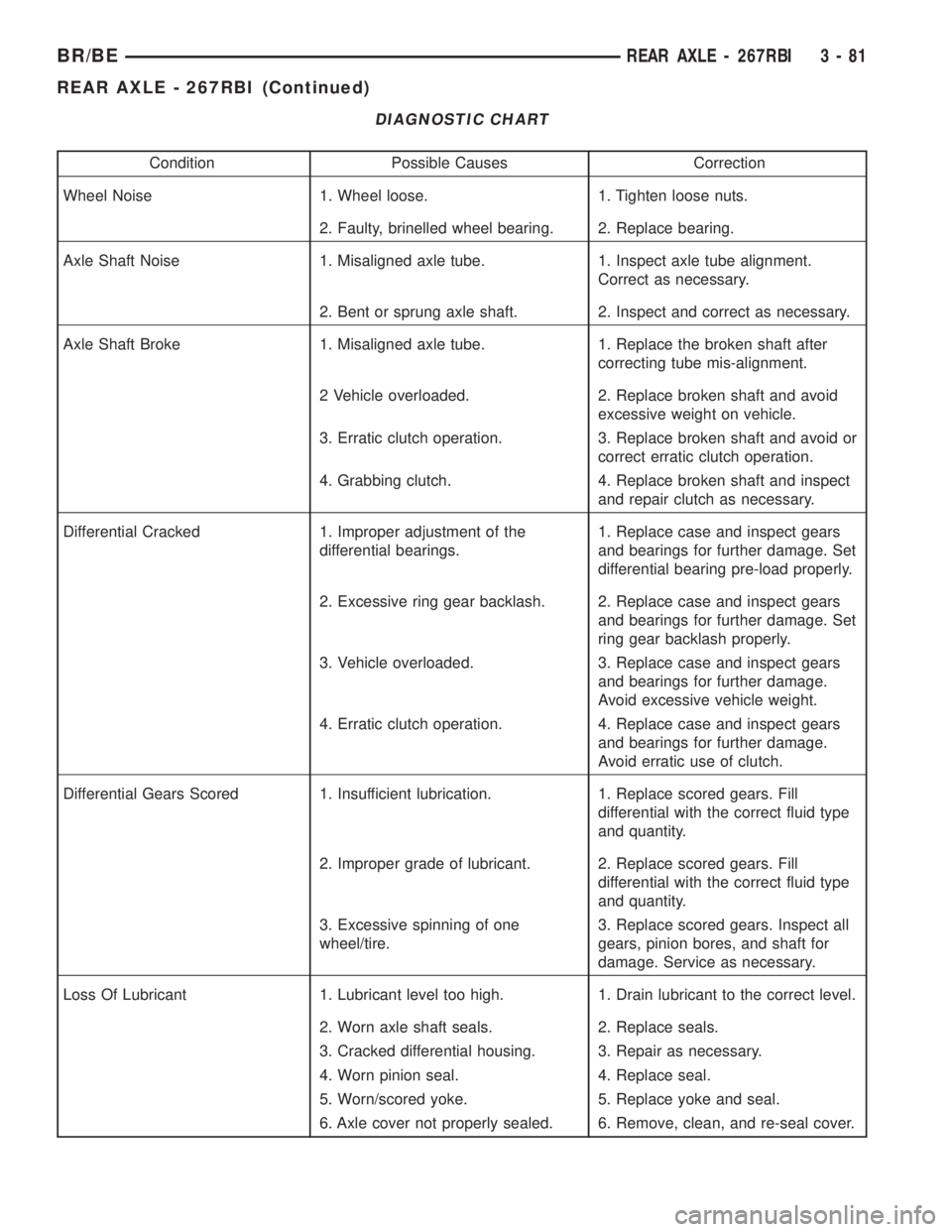
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid or
correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage. Set
differential bearing pre-load properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage. Set
ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal cover.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 267RBI 3 - 81
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)