engine DODGE RAM 2002 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 1560 of 2255

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BUZZING NOISE 1. Fluid Level Low 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Mis-assembled. 2. Route cable away from engine and bell
housing.
3. Valve Body Mis-assembled. 3. Remove, disassemble, inspect valve
body. Reassemble correctly if necessary.
Replace assembly if valves or springs are
damaged. Check for loose bolts or screws.
4. Pump Passages Leaking. 4. Check pump for porous casting, scores
on mating surfaces and excess rotor
clearance. Repair as required. Loose pump
bolts.
5. Cooling System Cooler Plugged. 5. Flow check cooler circuit. Repair as
needed.
6. Overrunning Clutch Damaged. 6. Replace clutch.
SLIPS IN REVERSE ONLY 1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust linkage.
3. Rear Band Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust band.
4. Rear Band Worn. 4. Replace as required.
5. Overdrive Direct Clutch Worn. 5. Disassemble overdrive. Repair as
needed.
6. Hydraulic Pressure Too Low. 6. Perform hydraulic pressure tests to
determine cause.
7. Rear Servo Leaking. 7. Air pressure check clutch-servo operation
and repair as required.
8. Band Linkage Binding. 8. Inspect and repair as required.
SLIPS IN FORWARD
DRIVE RANGES1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Fluid Foaming. 2. Check for high oil level, bad pump
gasket or seals, dirt between pump halves
and loose pump bolts. Replace pump if
necessary.
3. Throttle Linkage Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust linkage.
4. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 4. Adjust linkage.
5. Rear Clutch Worn. 5. Inspect and replace as needed.
6. Low Hydraulic Pressure Due to
Worn Pump, Incorrect Control
Pressure Adjustments, Valve Body
Warpage or Malfunction, Sticking,
Leaking Seal Rings, Clutch Seals
Leaking, Servo Leaks, Clogged Filter
or Cooler Lines.6. Perform hydraulic and air pressure tests
to determine cause.
7. Rear Clutch Malfunction, Leaking
Seals or Worn Plates.7. Air pressure check clutch-servo operation
and repair as required.
8. Overrunning Clutch Worn, Not
Holding (Slips in 1 Only).8. Replace Clutch.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 107
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1562 of 2255

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO 4-3 DOWNSHIFT
WHEN CONTROL SWITCH
IS TURNED OFF1. Control Switch Open/Shorted. 1. Test and replace switch if faulty.
2. Overdrive Solenoid Connector
Shorted.2. Test solenoids and replace if seized or
shorted.
3. PCM Malfunction. 3. Test with DRBTscan tool. Replace PCM
if faulty.
4. Valve Body Stuck Valves. 4. Repair stuck 3-4, lockup or lockup timing
valve.
CLUNK NOISE FROM
DRIVELINE ON CLOSED
THROTTLE 4-3
DOWNSHIFT1. Transmission Fluid Low. 1. Add Fluid.
2. Throttle Cable Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust cable.
3. Overdrive Clutch Select Spacer
Wrong Spacer.3. Replace overdrive piston thrust plate
spacer.
3-4 UPSHIFT OCCURS
IMMEDIATELY AFTER 2-3
SHIFT1. Overdrive Solenoid Connector or
Wiring Shorted.1. Test connector and wiring for loose
connections, shorts or ground and repair as
needed.
2. TPS Malfunction. 2. Test TPS and replace as necessary.
Check with DRBTscan tool.
3. PCM Malfunction. 3. Test PCM with DRBTscan tool and
replace controller if faulty.
4. Overdrive Solenoid Malfunction. 4. Replace solenoid.
5. Valve Body Malfunction. 5. Remove, disassemble, clean and inspect
valve body components. Make sure all
valves and plugs slide freely in bores.
Polish valves with crocus cloth if needed.
WHINE/NOISE RELATED
TO ENGINE SPEED1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Incorrect Routing. 2. Check shift cable for correct routing.
Should not touch engine or bell housing.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 109
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1563 of 2255

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO 3-4 UPSHIFT 1. O/D Switch In OFF Position. 1. Turn control switch to ON position.
2. Overdrive Circuit Fuse Blown. 2. Replace fuse. Determine why fuse failed
and repair as necessary (i.e., shorts or
grounds in circuit).
3. O/D Switch Wire Shorted/Open
Cut.3. Check wires/connections with 12V test
lamp and voltmeter. Repair damaged or
loose wire/connection as necessary.
4. Distance or Coolant Sensor
Malfunction.4. Check with DRBTscan tool and repair or
replace as necessary.
5. TPS Malfunction. 5. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace
if necessary.
6. Neutral Sense to PCM Wire
Shorted/Cut.6. Test switch/sensor as described in
service section and replace if necessary.
Engine no start.
7. PCM Malfunction. 7. Check with DRBTscan tool and replace
if necessary.
8. Overdrive Solenoid Shorted/Open. 8. Replace solenoid if shorted or open and
repair loose or damaged wires (DRBTscan
tool).
9. Solenoid Feed Orifice in Valve
Body Blocked.9. Remove, disassemble, and clean valve
body thoroughly. Check feed orifice.
10. Overdrive Clutch Failed. 10. Disassemble overdrive and repair as
needed.
11. Hydraulic Pressure Low. 11. Pressure test transmission to determine
cause.
12. Valve Body Valve Stuck. 12. Repair stuck 3-4 shift valve, 3-4 timing
valve.
13. O/D Piston Incorrect Spacer. 13. Remove unit, check end play and install
correct spacer.
14. Overdrive Piston Seal Failure. 14. Replace both seals.
15. O/D Check Valve/Orifice Failed. 15. Check for free movement and secure
assembly (in piston retainer). Check ball
bleed orifice.
21 - 110 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1567 of 2255

STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR
Damaged or worn threads in the aluminum trans-
mission case and valve body can be repaired by the
use of Heli-CoilsŸ, or equivalent. This repair con-
sists of drilling out the worn-out damaged threads.
Then tap the hole with a special Heli-CoilŸ tap, or
equivalent, and installing a Heli-CoilŸ insert, or
equivalent, into the hole. This brings the hole back to
its original thread size.
Heli-CoilŸ, or equivalent, tools and inserts are
readily available from most automotive parts suppli-
ers.
REMOVAL
The overdrive unit can be removed and serviced
separately. It is not necessary to remove the entire
transmission assembly to perform overdrive unit
repairs.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect and lower or remove necessary
exhaust components.
(3) Remove engine-to-transmission struts, if
equipped (Fig. 13).(4) Disconnect fluid cooler lines at transmission.
(5) Remove starter motor. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL)
(6) Disconnect and remove the crankshaft position
sensor. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJEC-
TION/CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
REMOVAL) Retain the sensor attaching bolts.
(7) Remove torque converter access cover.
(8) If transmission is being removed for overhaul,
remove transmission oil pan, drain fluid and reinstall
pan.
(9) Remove fill tube bracket bolts and pull tube
out of transmission. Retain fill tube seal (Fig. 13). On
4 x 4 models, it will also be necessary to remove bolt
attaching transfer case vent tube to converter hous-
ing (Fig. 14).
(10) Rotate crankshaft in clockwise direction until
converter bolts are accessible. Then remove bolts one
at a time. Rotate crankshaft with socket wrench on
dampener bolt.
(11) Mark propeller shaft and axle yokes for
assembly alignment. Then disconnect and remove
propeller shaft. On4x4models, remove both propel-
ler shafts. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(12) Disconnect wires from park/neutral position
switch and transmission solenoid.
Fig. 13 Transmission-To-Engine Strut Attachment
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - STRUT (PASSENGER SIDE)
3 - ENGINE MOUNT
4 - STRUT (DRIVER SIDE)
Fig. 14 Fill Tube Attachment
1 - TRANSFER CASE VENT TUBE
2 - FILL TUBE (V8)
3 - TUBE SEAL
4 - FILL TUBE (V6)
21 - 114 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1568 of 2255
(13) Disconnect gearshift rod and torque shaft
assembly from transmission.
(14) Disconnect throttle valve cable from transmis-
sion bracket and throttle valve lever.
(15) On4x4models, disconnect shift rod from
transfer case shift lever.
(16) Support rear of engine with safety stand or
jack.
(17) Raise transmission slightly with service jack
to relieve load on crossmember and supports.
(18) Remove bolts securing rear support and cush-
ion to transmission and crossmember. Raise trans-
mission slightly, slide exhaust hanger arm from
bracket (Fig. 15) and remove rear support.
(19) Remove bolts attaching crossmember to frame
and remove crossmember.
(20) On4x4models, remove transfer case with
transmission jack or aid of helper.
(21) Remove all converter housing bolts.
(22) Carefully work transmission and torque con-
verter assembly rearward off engine block dowels.
(23) Lower transmission and remove assembly
from under the vehicle.
(24) To remove torque converter, remove C-clamp
from edge of bell housing and carefully slide torque
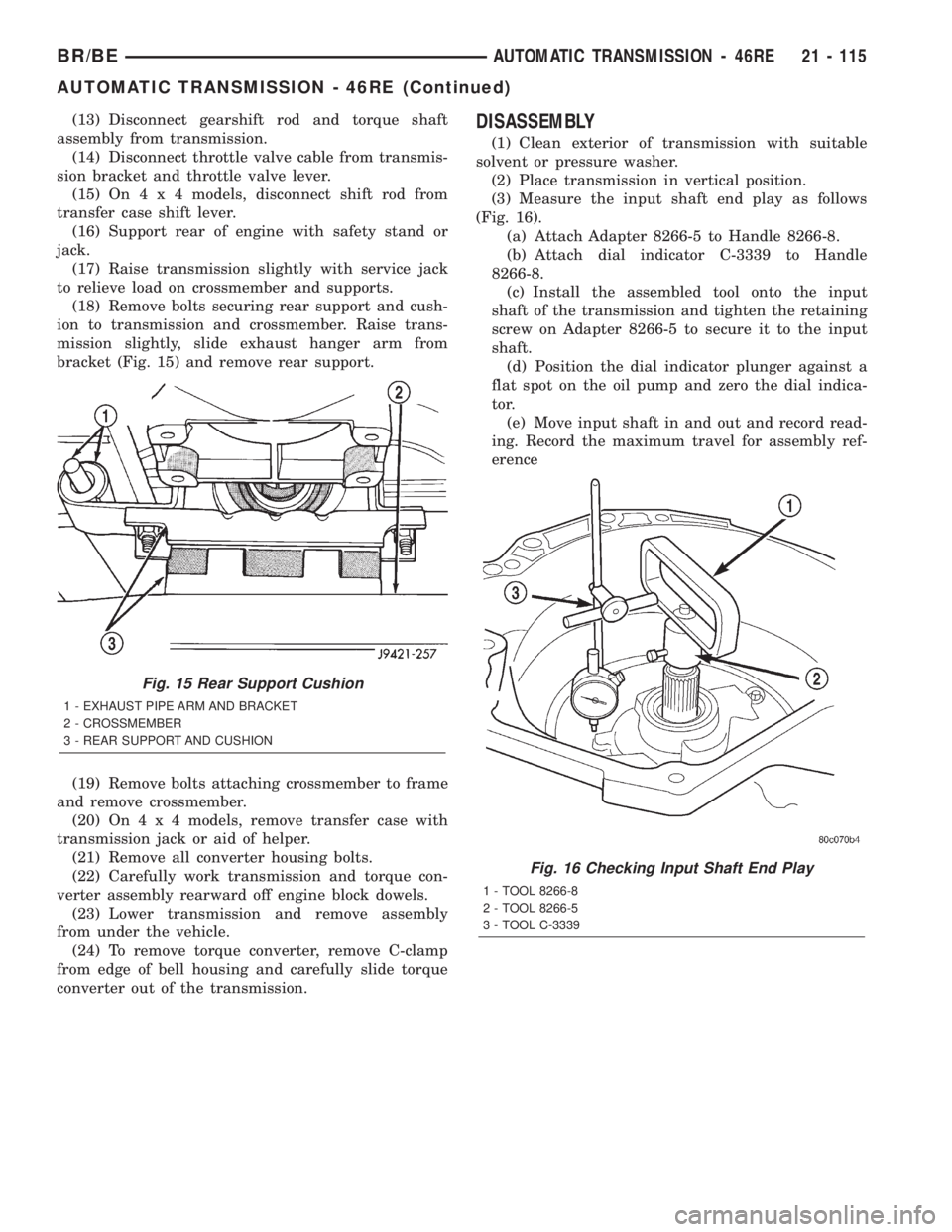
converter out of the transmission.DISASSEMBLY
(1) Clean exterior of transmission with suitable
solvent or pressure washer.
(2) Place transmission in vertical position.
(3) Measure the input shaft end play as follows
(Fig. 16).
(a) Attach Adapter 8266-5 to Handle 8266-8.
(b) Attach dial indicator C-3339 to Handle
8266-8.
(c) Install the assembled tool onto the input
shaft of the transmission and tighten the retaining
screw on Adapter 8266-5 to secure it to the input
shaft.
(d) Position the dial indicator plunger against a
flat spot on the oil pump and zero the dial indica-
tor.
(e) Move input shaft in and out and record read-
ing. Record the maximum travel for assembly ref-
erence
Fig. 15 Rear Support Cushion
1 - EXHAUST PIPE ARM AND BRACKET
2 - CROSSMEMBER
3 - REAR SUPPORT AND CUSHION
Fig. 16 Checking Input Shaft End Play
1 - TOOL 8266-8
2 - TOOL 8266-5
3 - TOOL C-3339
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 115
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1583 of 2255

(a) Loosen locknut on each band adjusting screw
4-5 turns.
(b) Tighten both adjusting screws to 8 N´m (72
in. lbs.).
(c) Back off front band adjusting screw 2-7/8
turns.
(d) Back off rear band adjusting screw 2 turns.
(e) Hold each adjusting screw in position and
tighten locknut to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install magnet in oil pan. Magnet seats on
small protrusion at corner of pan.
(3) Position new oil pan gasket on case and install
oil pan. Tighten pan bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in. lbs.).
(4) Install throttle valve and shift selector levers
on valve body manual lever shaft.
(5) Apply small quantity of dielectric grease to ter-
minal pins of solenoid case connector and neutral
switch.
(6) Fill transmission with recommended fluid.
Refer to Service Procedures section of this group.
INSTALLATION
(1) Check torque converter hub and hub drive
notches for sharp edges burrs, scratches, or nicks.
Polish the hub and notches with 320/400 grit paper
and crocus cloth if necessary. The hub must be
smooth to avoid damaging pump seal at installation.
(2) Lubricate pocket in the rear oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.(3) Lubricate converter pilot hub of the crankshaft
with a light coating of MopartHigh Temp Grease.
(4) Align and install converter in oil pump.
(5) Carefully insert converter in oil pump. Then
rotate converter back and forth until fully seated in
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with steel scale and
straightedge (Fig. 65). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) Temporarily secure converter with C-clamp.
(8) Position transmission on jack and secure it
with chains.
(9) Check condition of converter driveplate.
Replace the plate if cracked, distorted or damaged.
Also be sure transmission dowel pins are seated
in engine block and protrude far enough to
hold transmission in alignment.
(10) Raise transmission and align converter with
drive plate and converter housing with engine block.
(11) Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower
or tilt transmission to align converter housing with
engine block dowels.
(12) Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in
crankshaft.
(13) Install bolts attaching converter housing to
engine.
(14) Install rear support. Then lower transmission
onto crossmember and install bolts attaching trans-
mission mount to crossmember.
(15) Remove engine support fixture.
SOCKET 6984
Fig. 64 Manual Lever Shaft Seal
1 - 15/16©© SOCKET
2 - SEAL
Fig. 65 Checking Converter Seating - Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 130 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1599 of 2255
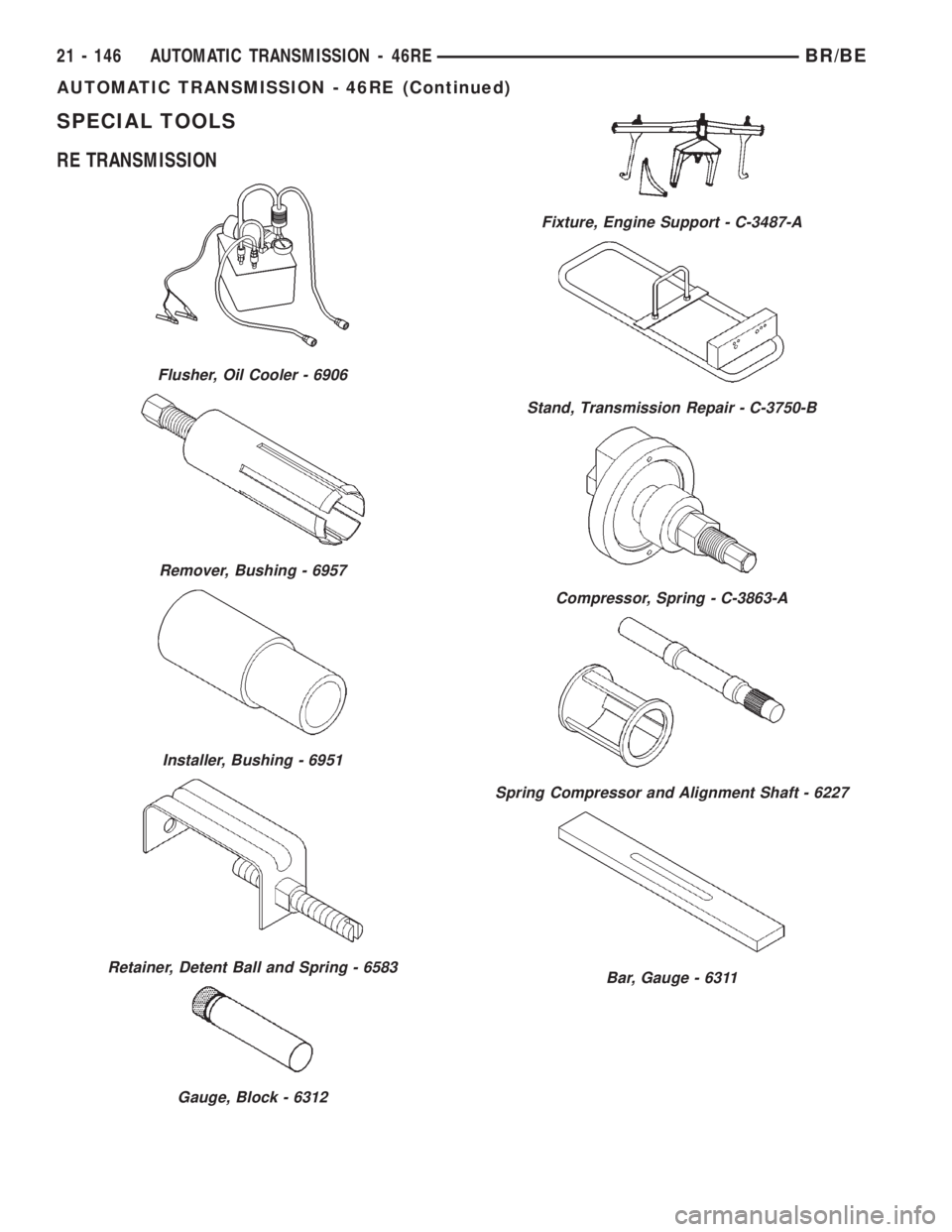
SPECIAL TOOLS
RE TRANSMISSION
Flusher, Oil Cooler - 6906
Remover, Bushing - 6957
Installer, Bushing - 6951
Retainer, Detent Ball and Spring - 6583
Gauge, Block - 6312
Fixture, Engine Support - C-3487-A
Stand, Transmission Repair - C-3750-B
Compressor, Spring - C-3863-A
Spring Compressor and Alignment Shaft - 6227
Bar, Gauge - 6311
21 - 146 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1606 of 2255

GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absence
of sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher
than normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
heavily loaded vehicle or on steep grades. When
hunting occurs, it is very objectionable because shifts
are frequent and accompanied by large changes in
noise and acceleration.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive mem-
ory in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the
preprogrammed optimum speed. WOT operation is
determined from the throttle position sensor, which
is also a part of the emission control system. The ini-
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 153
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1607 of 2255

tial setting for the WOT upshift is below the opti-
mum engine speed. As WOT shifts are repeated, the
PCM learns the time required to complete the shifts
by comparing the engine speed when the shifts occur
to the optimum speed. After each shift, the PCM
adjusts the shift point until the optimum speed is
reached. The PCM also considers vehicle loading,
grade and engine performance changes due to high
altitude in determining when to make WOT shifts. It
does this by measuring vehicle and engine accelera-
tion and then factoring in the shift time.
TRANSFER CASE LOW RANGE OPERATION
On four-wheel drive vehicles operating in low
range, the engine can accelerate to its peak more
rapidly than in Normal range, resulting in delayed
shifts and undesirable engine9flare.9The low range
governor pressure curve is also higher than normal
to initiate upshifts sooner. The PCM compares elec-
tronic vehicle speed signal used by the speedometer
to the transmission output shaft speed signal to
determine when the transfer case is in low range.
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Remove transmission fluid pan and filter.
(3) Disengage wire connectors from pressure sen-
sor and solenoid (Fig. 77).
(4) Remove screws holding pressure solenoid
retainer to governor body.
(5) Separate solenoid retainer from governor (Fig.
78).
(6) Pull solenoid from governor body (Fig. 79).
(7) Pull pressure sensor from governor body.(8) Remove bolts holding governor body to valve
body.
(9) Separate governor body from valve body (Fig.
80).
(10) Remove governor body gasket.
INSTALLATION
Before installing the pressure sensor and solenoid
in the governor body, replace o-ring seals, clean the
gasket surfaces and replace gasket.
(1) Place gasket in position on back of governor
body (Fig. 81).
(2) Place governor body in position on valve body.
(3) Install bolts to hold governor body to valve
body.
Fig. 77 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 78 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 79 Pressure Solenoid and O-ring
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
2 - O-RING
3 - GOVERNOR
21 - 154 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1610 of 2255

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary coolers
as well. The torque converter should also be replaced
whenever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing procedures
will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
Fig. 88 Installing Overdrive Housing Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A OR C-3972-A
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4471
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 157
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL (Continued)