ABS DODGE RAM 2003 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 203 of 2895

Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern. Adjust backlash or
pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a lifting device under the axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove wheels and tires assemblies.
(5) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing.
(6) Remove brake hose at the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(7) Disconnect parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(8) Remove brake calipers.
(9) Mark propeller shaft and companion flange for
installation alignment reference.
(10) Remove propeller shaft.
(11) Remove shock absorbers from axle.
(12) Remove U-bolets from axle.
(13) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lifting device and align to the
leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install axle U-bolts and tighten to 149 N´m
(110 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install shock absorbers to axle and tighten to
specification.
(4) Install the RWAL sensor to the differential
housing.
(5) Connect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(6) Connect brake hose to the axle junction block
and axle vent hose.
(7) Align propeller shaft and pinion companion
flange reference marks and tighten companion flange
bolts to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install the wheels and tires.
(9) Fill differential to specifications.
3 - 130 REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AADR
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA (Continued)
Page 228 of 2895

BRAKES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - BASE........................... 1BRAKES - ABS........................... 39
BRAKES - BASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - BASE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM.............................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANUAL
BLEEDING............................5
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PRESSURE
BLEEDING............................5
SPECIAL TOOLS
BASE BRAKES........................5
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE CHART.......6
BASE BRAKE.........................7
BRAKE LINES
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DOUBLE
INVERTED FLARING....................7
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ISO FLARING . . . 7
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - REAR BRAKE HOSE..........8
REMOVAL - REAR TUBE / HOSE
ASSEMBLY...........................8
REMOVAL - FRONT HOSE...............9
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - REAR BRAKE HOSE......9
INSTALLATION - REAR TUBE / HOSE
ASSEMBLY...........................9
INSTALLATION - FRONT BRAKE HOSE.....9
BRAKE PADS/SHOES
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS
DESCRIPTION.........................11OPERATION...........................12
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - REAR.....................12
REMOVAL - FRONT....................12
DISASSEMBLY.........................13
INSPECTION..........................14
ASSEMBLY............................15
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - REAR.................16
INSTALLATION - FRONT................16
DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - REAR.....................16
REMOVAL - FRONT....................16
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - REAR.................17
INSTALLATION - FRONT................17
DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER MOUNT
REMOVAL - REAR......................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
FLUID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE FLUID
CONTAMINATION.....................18
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL..............................18
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID........................18
FLUID RESERVOIR
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
BRAKE JUNCTION BLOCK
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................20
DRBRAKES 5 - 1
Page 230 of 2895

and cups will also have to be replaced after flush-
ing. Use clean brake fluid to flush the system.
(4) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and pedal. Also
note if vehicle was being operated with parking
brake partially applied.
(5) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does not bind and has adequate free play. If pedal
lacks free play, check pedal and power booster for
being loose or for bind condition. Do not road test
until condition is corrected.
(6) Check booster vacuum check valve and hose.
(7) If components checked appear OK, road test
the vehicle.
ROAD TESTING
(1) If complaint involved low brake pedal, pump
pedal and note if it comes back up to normal height.
(2) Check brake pedal response with transmission
in Neutral and engine running. Pedal should remain
firm under constant foot pressure.
(3) During road test, make normal and firm brake
stops in 25-40 mph range. Note faulty brake opera-
tion such as low pedal, hard pedal, fade, pedal pulsa-
tion, pull, grab, drag, noise, etc.
(4) Attempt to stop the vehicle with the parking
brake only and note grab, drag, noise, etc.
PEDAL FALLS AWAY
A brake pedal that falls away under steady foot
pressure is generally the result of a system leak. The
leak point could be at a brake line, fitting, hose, or
caliper/wheel cylinder. If leakage is severe, fluid will
be evident at or around the leaking component.
Internal leakage (seal by-pass) in the master cylin-
der caused by worn or damaged piston cups, may
also be the problem cause.
An internal leak in the ABS or RWAL system may
also be the problem with no physical evidence.
LOW PEDAL
If a low pedal is experienced, pump the pedal sev-
eral times. If the pedal comes back up worn linings,
rotors, drums, or rear brakes out of adjustment are
the most likely causes. The proper course of action is
to inspect and replace all worn component and make
the proper adjustments.
SPONGY PEDAL
A spongy pedal is most often caused by air in the
system. However, thin brake drums or substandard
brake lines and hoses can also cause a spongy pedal.
The proper course of action is to bleed the system,
and replace thin drums and substandard quality
brake hoses if suspected.HARD PEDAL OR HIGH PEDAL EFFORT
A hard pedal or high pedal effort may be due to
lining that is water soaked, contaminated, glazed, or
badly worn. The power booster or check valve could
also be faulty.
PEDAL PULSATION
Pedal pulsation is caused by components that are
loose, or beyond tolerance limits.
The primary cause of pulsation are disc brake
rotors with excessive lateral runout or thickness vari-
ation, or out of round brake drums. Other causes are
loose wheel bearings or calipers and worn, damaged
tires.
NOTE: Some pedal pulsation may be felt during
ABS activation.
BRAKE DRAG
Brake drag occurs when the lining is in constant
contact with the rotor or drum. Drag can occur at one
wheel, all wheels, fronts only, or rears only.
Drag is a product of incomplete brake shoe release.
Drag can be minor or severe enough to overheat the
linings, rotors and drums.
Minor drag will usually cause slight surface char-
ring of the lining. It can also generate hard spots in
rotors and drums from the overheat-cool down pro-
cess. In most cases, the rotors, drums, wheels and
tires are quite warm to the touch after the vehicle is
stopped.
Severe drag can char the brake lining all the way
through. It can also distort and score rotors and
drums to the point of replacement. The wheels, tires
and brake components will be extremely hot. In
severe cases, the lining may generate smoke as it
chars from overheating.
Common causes of brake drag are:
²Seized or improperly adjusted parking brake
cables.
²Loose/worn wheel bearing.
²Seized caliper or wheel cylinder piston.
²Caliper binding on corroded bushings or rusted
slide surfaces.
²Loose caliper mounting.
²Drum brake shoes binding on worn/damaged
support plates.
²Mis-assembled components.
²Long booster output rod.
If brake drag occurs at all wheels, the problem
may be related to a blocked master cylinder return
port, or faulty power booster (binds-does not release).
BRAKE FADE
Brake fade is usually a product of overheating
caused by brake drag. However, brake overheating
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 3
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 245 of 2895

(6) Adjust brake shoes to drum with brake gauge
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE/SHOES -
ADJUSTMENTS).
(7) Install the rotor (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS - INSTALLA-
TION).
(8) Install the caliper adapter (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the caliper (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC BRAKE CALIPERS
- INSTALLATION).
(10) Install wheel and tire assembly.
FLUID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brakes hydraulic unit and all hydraulic
fluid hoses.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL
Always clean the master cylinder reservoir and
caps before checking fluid level. If not cleaned, dirt
could enter the fluid.
The fluid fill level is indicated on the side of the
master cylinder reservoir (Fig. 33).
The correct fluid level is to the MAX indicator on
the side of the reservoir. If necessary, add fluid to the
proper level.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications and SAE J1703 standards.
No other type of brake fluid is recommended or
approved for usage in the vehicle brake system. Use
only Mopar brake fluid or an equivalent from a
tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
Fig. 32 CALIPER ADAPTER MOUNT - REAR
1 - CALIPER ADAPTER MOUNT
2 - AXLE TUBE
3 - MOUNTING STUDS
Fig. 33 FLUID LEVEL
1 - FLUID RESERVOIR
2 - MAX LEVEL MARK
5 - 18 BRAKES - BASEDR
DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER MOUNT (Continued)
Page 256 of 2895

(2) Install the caliper adapter (Fig. 50) (Refer to 5
- BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - INSTALLATION).
(3) Install the caliper adapter bolts (Fig. 50) and
tighten the mounting bolts to 135 N´m (100 ft.lbs).
(4) Install the disc brake caliper, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the tire and wheel assembly (Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(6) Lower the vehicle.
INSTALLATION - FRONT
(1) On models with all-wheel antilock system
(ABS), check condition of tone wheel on hub/bearing.
If teeth on wheel are damaged, hub/bearing assembly
will have to be replaced (tone wheel is not serviced
separately).
(2) Install the rotor onto the hub/bearing wheel
studs.
(3) Install the caliper adapter assembly,(Refer to 5
- BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION) and tighten
adapter bolts to:
(4) Install the wheel and tire assembly, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE) and lower the vehicle.
(5) Apply the brakes several times to seat brake
pads. Be sure to obtain firm pedal before moving
vehicle.
SUPPORT PLATE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(2) Remove the disc brake caliper (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the caliper adapter (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the rotor (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the axle shaft (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR AXLE - 9 1/4/AXLE
SHAFTS - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove the park brake shoes (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE/SHOES - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the parking brake cable from the
brake lever.
(8) Remove the bolts attaching the support plate to
the axle and remove the support plate (Fig. 54).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install support plate on axle flange (Fig. 55).
Tighten attaching bolts to 115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install parking brake cable in the brake lever.
(3) Install the park brake shoes (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE/SHOES - INSTALLA-
TION). (Fig. 55).
(4) Install axle shaft, (Refer to 3 - DIFFEREN-
TIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR AXLE - 9 1/4/AXLE
SHAFTS - INSTALLATION).
(5) Adjust brake shoes to drum with brake gauge
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE/SHOES -
ADJUSTMENTS).
Fig. 52 FRONT ROTOR
1 - ROTOR
2 - HUB/BEARING
Fig. 53 8 LUG ROTOR ASSEMBLY
1 - SPRING
2 - SHOCK
3 - UPPER AND LOWER SUSPENSION ARMS
4 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
5 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER
6 - ROTOR
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 29
ROTORS (Continued)
Page 258 of 2895

CABLES
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Lockout the parking brake cable (Fig. 58).
(3) Loosen adjusting nut to create slack in front
cable.
(4) Remove the front cable from the cable connec-
tor.
(5) Compress cable end fitting at underbody
bracket and remove the cable from the bracket.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Push ball end of cable out of pedal clevis with
small screwdriver.
(8) Compress cable end fitting at the pedal bracket
and remove the cable (Fig. 57).
(9) Remove the left cowl trim and sill plate.
(10) Pull up the carpet and remove the cable from
the body clip.
(11) Pull up on the cable and remove the cable
with the body grommet.
REMOVAL - REAR PARK BRAKE CABLE
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Lockout the parking brake cable (Fig. 58).
(3) Loosen cable adjuster nut.
(4) Remove the rear park brake cable from the
intermediate park brake cable.(5) Compress tabs on cable end fitting on the rear
park brake cable to the frame mount bracket. Then
pull the cable through the bracket.
(6) Disengage the park brake cable from behind
the rotor assembly. (Fig. 59).
(7) Compress cable tabs on each cable end fitting
at the brake cable support plate.
(8) Remove the cables from the brake cable sup-
port plates.
REMOVAL - RIGHT REAR CABLE
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Lockout the parking brake cable (Fig. 58).
(3) Loosen the brake cable at the equalizer and
adjuster nut.
(4) Remove the right cable from the front cable.
(5) Remove the right cable from the equalizer.
Fig. 57 Parking Brake Pedal
1 - PARK BRAKE PEDAL
2 - FRONT CABLE
Fig. 58 LOCK OUT PARKING CABLE
1 - LOCKING PLIERS
2 - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
Fig. 59 DISENGAGEMENT OF CABLE
1 - LEVER
2 - CABLE END
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 31
Page 259 of 2895

(6) Remove the cable from the frame bracket.
(7) Remove the cable from the axle bracket.
(8) Remove the cable bracket from the shock
bracket.
(9) Remove the brake cable from the brake lever.
(Fig. 60)
REMOVAL - LEFT REAR CABLE
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Lockout the parking brake cable (Fig. 58).
(3) Loosen the brake cable at the equalizer and
adjuster nut.
(4) Remove the left brake cable from the equalizer.
(5) Remove the brake cable from the frame
bracket.
(6) Remove the brake cable from the brake lever.
(Fig. 61)
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT PARKING BRAKE
CABLE
(1) From inside the vehicle, insert the cable end
fitting into the hole in the pedal assembly.
(2) Seat the cable retainer in the pedal assembly.
(3) Engage the cable ball end in clevis on the pedal
assembly.
(4) Route the cable through the floorpan and
install the body grommet.
(5) Place the carpet down and install the left cowl
trim and sill plate.
(6) Raise and support the vehicle.
(7) Route the cable through the underbody bracket
and seat the cable end fitting in the bracket.(8) Connect the cable to the cable connector.
(9) Perform the park brake adjustment procedure,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE/CABLE
TENSIONER - ADJUSTMENTS).
(10) Lower the vehicle.
INSTALLATION - REAR PARK BRAKE CABLE
(1) Push each cable end through the brake cable
support plate hole until the cable end fitting tabs
lock into place.
NOTE: Pull on the cable to ensure it is locked into
place.
(2) Push the cable through the frame bracket.
(3) Lock the left cable end fitting tabs into the
frame bracket hole.
(4) Install the rear cables into the tensioner rod
behind the rear of the brake assembly.
(5) Install the cable to the intermediate cable con-
nector.
(6) Release and remove the lock out device.
(7) Perform the park brake adjustment procedure,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE/CABLE
TENSIONER - ADJUSTMENTS).
(8) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
INSTALLATION - RIGHT REAR CABLE
(1) Install the brake cable to the brake lever. (Fig.
62)
(2) Install the cable bracket to the shock bracket.
(3) Install the cable to the axle bracket.
(4) Install the cable to the frame bracket.
(5) Install the right cable to the equalizer.
Fig. 60 CABLE MOUNT
1 - SUPPORT PLAT
2 - CABLE MOUNT
3 - PARK BRAKE LEVER
4 - CABLE
Fig. 61 REAR DISC BRAKE
1 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
2 - DISC BRAKE ROTOR
3 - DUST SHIELD
4 - REAR PARKING BRAKE CABLE
5 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - 32 BRAKES - BASEDR
CABLES (Continued)
Page 265 of 2895

RELEASE HANDLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Reach under the driver side outboard end of
the instrument panel to access and unsnap the plas-
tic retainer clip that secures the park brake release
linkage rod to the park brake mechanism on the left
cowl side inner panel.
(3) Disengage the park brake release linkage rod
end from the park brake mechanism.
(4) Lift the park brake release handle to access
and unsnap the plastic retainer clip that secures the
park brake release linkage rod to the lever on the
back of the park brake release handle.
(5) Lower the park brake release handle and reach
under the driver side outboard end of the instrument
panel to disengage the park brake release linkage
rod end from the lever on the back of the park brake
release handle.
(6) Lift the park brake release handle to access the
handle mounting bracket.
(7) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry each of the park brake
release handle mounting bracket latch tabs away
from the retaining notches in the instrument panel
receptacle (Fig. 74).
(8) With both of the park brake release handle
mounting bracket latches released, slide the handle
and bracket assembly down and out of the instru-
ment panel receptacle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the park brake release handle to the
instrument panel.
(2) Slide the handle and bracket assembly up into
the instrument panel receptacle until both of the
park brake release handle mounting bracket latches
are engaged with the notches in the instrument
panel receptacle.
(3) Lower the park brake release handle and reach
under the driver side outboard end of the instrument
panel to engage the park brake release linkage rodend with the lever on the back of the park brake
release handle.
(4) Lift the park brake release handle to access
and snap the plastic retainer clip that secures the
park brake release linkage rod to the lever on the
back of the park brake release handle over the link-
age rod.
(5) Reach under the driver side outboard end of
the instrument panel to access and engage the park
brake release linkage rod end to the park brake
mechanism.
(6) Snap the plastic retainer clip that secures the
park brake release linkage rod to the park brake
mechanism on the left cowl side inner panel over the
linkage rod.
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
Fig. 74 Park Brake Release Handle Remove/Install
1 - CLIP
2 - ROD
3 - MOUNTING BRACKET
4 - TRIM STICK
5 - LATCH TABS
6 - PARK BRAKE RELEASE HANDLE
5 - 38 BRAKES - BASEDR
Page 266 of 2895

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ABS BRAKE
BLEEDING...........................40
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................40
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................41
REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................42
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
ANTILOCK...........................42
REMOVAL.............................42
INSTALLATION.........................43
TONE WHEEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR......................43HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
DESCRIPTION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
BRAKE PROPORTIONING...............43
OPERATION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
BRAKE PROPORTIONING...............43
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
R WA L VA LV E
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................45
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
The antilock brake system (ABS) is an electroni-
cally operated, three channel brake control system.
The vehicle has Electronic Variable Brake Propor-
tioning (EVBP) designed into the system which elim-
inates the combination/proportioning valve.
The system is designed to prevent wheel lockup
and maintain steering control during braking. Pre-
venting lockup is accomplished by modulating fluid
pressure to the wheel brake units.
The hydraulic system is a three channel design.
The front wheel brakes are controlled individually
and the rear wheel brakes in tandem. The ABS elec-
trical system is separate from other electrical circuits
in the vehicle. A specially programmed controller
antilock brake unit operates the system components.
ABS system major components include:
²Controller Antilock Brakes (CAB)
²Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
²Wheel Speed Sensors (WSS)
²ABS Warning Light
OPERATION
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB. The CAB
performs a system initialization procedure at start
up. A check of the ABS motor is performed at 15
miles per hour. Initialization consists of a static and
dynamic self check of system electrical components.
The static and dynamic checks occurs at ignition
start up. During the dynamic check, the CAB briefly
cycles solenoids to verify operation. An audible noise
may be heard during this self check. This noise
should be considered normal. The ABS motor and
pump are then checked at a speed of 15 mile per
hour.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
The CAB monitors wheel speed sensor inputs con-
tinuously while the vehicle is in motion. However,
the CAB will not activate any ABS components as
long as sensor inputs indicate normal braking.
During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
DRBRAKES - ABS 5 - 39
Page 267 of 2895
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup. Preventing lockup helps maintain vehi-
cle braking action and steering control.
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of wheel slip.
The antilock system prevents lockup during a
wheel slip condition by modulating fluid apply pres-
sure to the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. Sensors at each front wheel convert wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the CAB for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a wheel slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program.
There are Two solenoid valves (Isolation and Dump
valve) which are used in each antilock control chan-
nel. The valves are all located within the HCU valve
body and work in pairs to either increase, hold, or
decrease apply pressure as needed in the individual
control channels.
During an ABS stop the ISO valve is energized
which acts to prevent further pressure build-up tothe calipers. Then the Dump valve dumps off pres-
sure until the wheel unlocks. This will continue until
the wheels quit slipping altogether.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ABS BRAKE
BLEEDING
ABS system bleeding requires conventional bleed-
ing methods plus use of the DRB scan tool. The pro-
cedure involves performing a base brake bleeding,
followed by use of the scan tool to cycle and bleed the
HCU pump and solenoids. A second base brake bleed-
ing procedure is then required to remove any air
remaining in the system.
(1) Perform base brake bleeding,(Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR (Refer to
5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Connect scan tool to the Data Link Connector.
(3) Select ANTILOCK BRAKES, followed by MIS-
CELLANEOUS, then ABS BRAKES. Follow the
instructions displayed. When scan tool displays TEST
COMPLETE, disconnect scan tool and proceed.
(4) Perform base brake bleeding a second time,(Re-
fer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
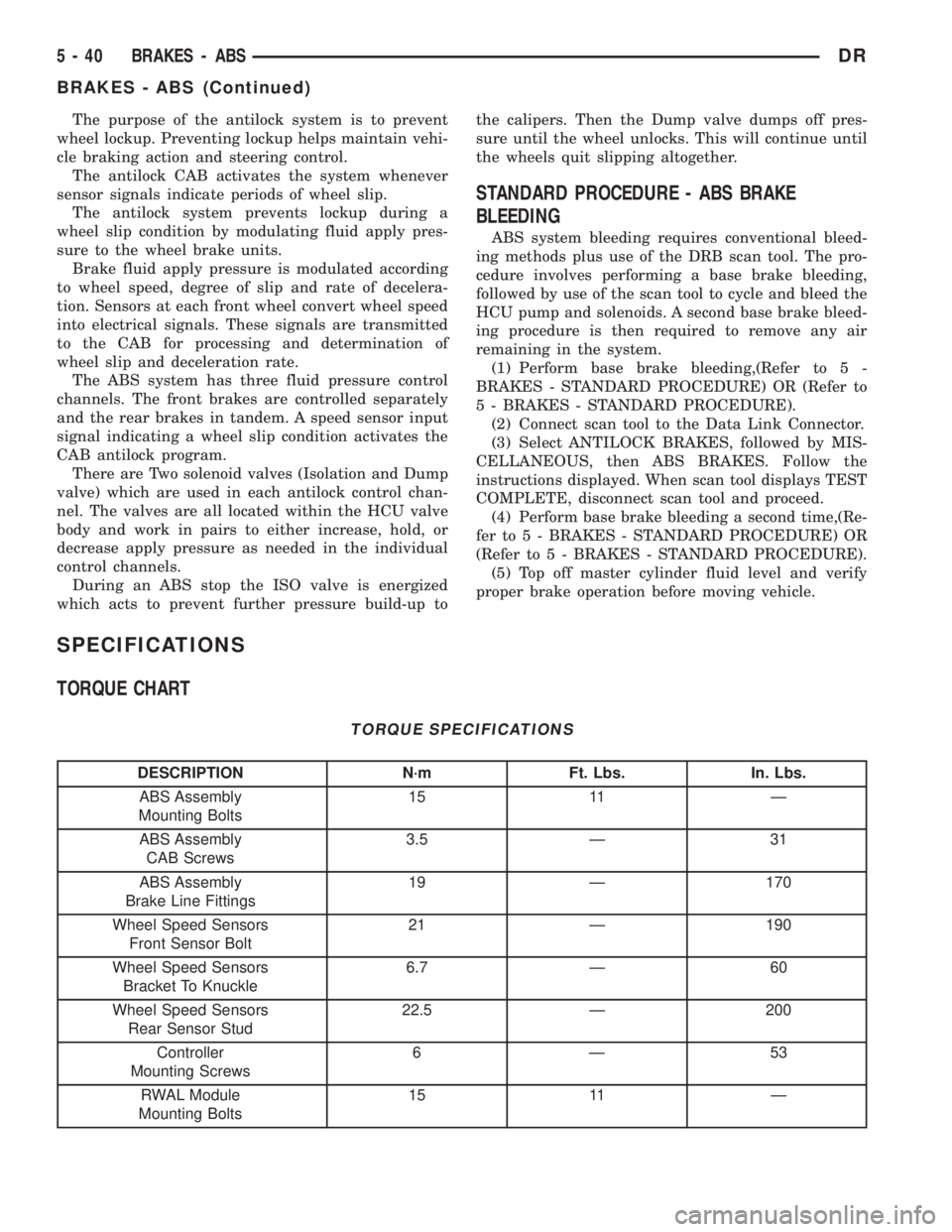
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
ABS Assembly
Mounting Bolts15 11 Ð
ABS Assembly
CAB Screws3.5 Ð 31
ABS Assembly
Brake Line Fittings19 Ð 170
Wheel Speed Sensors
Front Sensor Bolt21 Ð 190
Wheel Speed Sensors
Bracket To Knuckle6.7 Ð 60
Wheel Speed Sensors
Rear Sensor Stud22.5 Ð 200
Controller
Mounting Screws6Ð53
RWAL Module
Mounting Bolts15 11 Ð
5 - 40 BRAKES - ABSDR
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)