Bearing nut DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1993, Model line: TRUCK, Model: DODGE TRUCK 1993Pages: 1502, PDF Size: 80.97 MB
Page 123 of 1502
2
- 70
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
• Depth shims are available in O.OOl-ineh incre
ments from 0.020 inch to 0.038 inch. (8) Note the etched number on the face of the drive
pinion gear (e.g., -0, -1, -2, +1, +2, etc.). The num
bers represent thousands-of-an-inch deviation from
the standard. If the number is - (negative), add that
value to the required thickness of the depth shim(s).
If the number is + (positive), subtract that value
from the thickness of the depth shim(s). If the num
ber is 0, no change is necessary.
(9) Remove the tools from the differential housing.
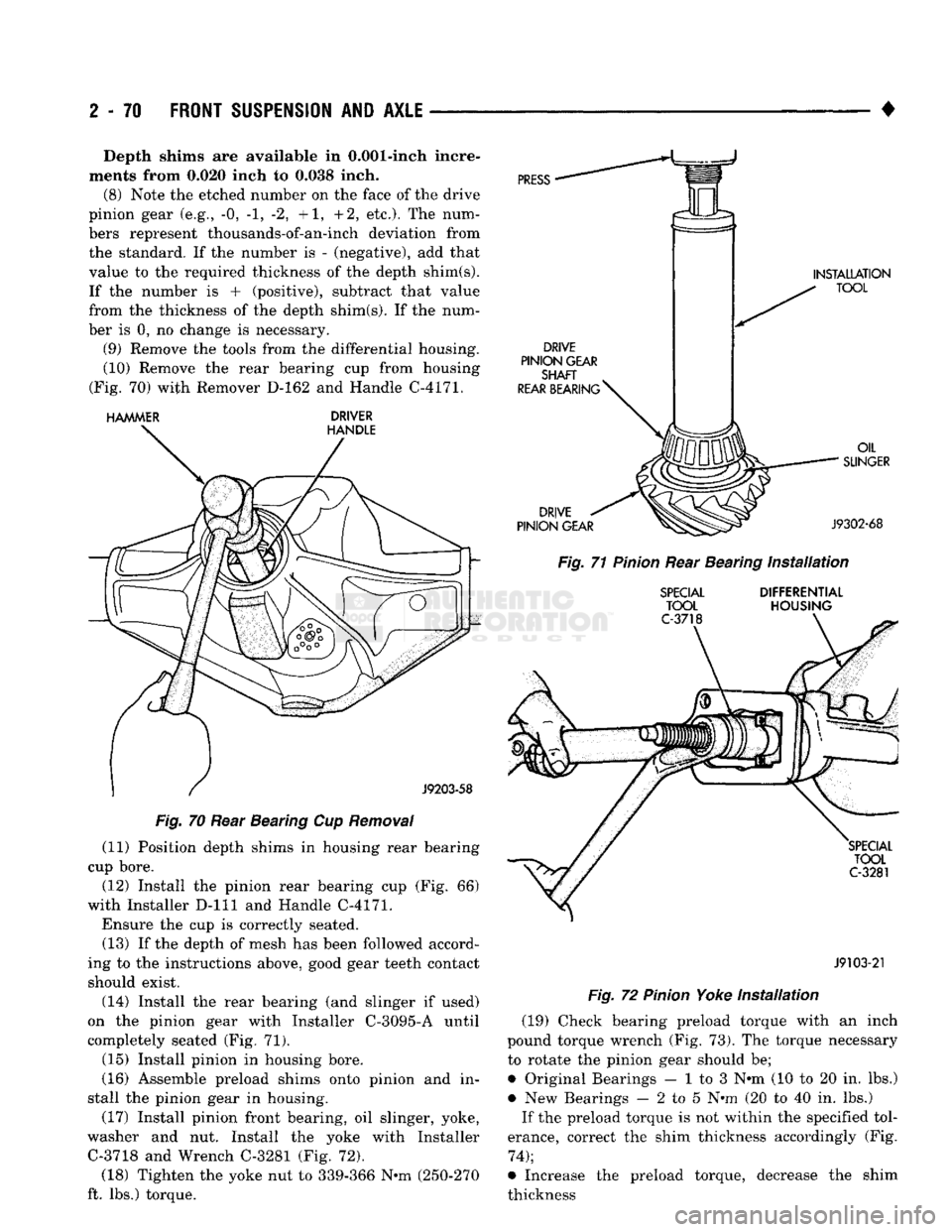
(10) Remove the rear bearing cup from housing
(Fig. 70) with Remover D-162 and Handle C-4171.
HAMMER
DRIVER
HANDLE
PRESS
DRIVE
PINION
GEAR SHAFT
REAR
BEARING' INSTALLATION
TOOL
DRIVE
PINION
GEAR OIL
SUNGER
J9302-68
Fig.
71
Pinion
Rear Bearing
Installation
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-3718
DIFFERENTIAL
HOUSING
J9203-58
Fig.
70 Rear Bearing Cup
Removal
(11) Position depth shims in housing rear bearing
cup bore.
(12) Install the pinion rear bearing cup (Fig. 66)
with Installer D-lll and Handle C-4171. Ensure the cup is correctly seated. (13) If the depth of mesh has been followed accord
ing to the instructions above, good gear teeth contact should exist.
(14) Install the rear bearing (and slinger if used)
on the pinion gear with Installer C-3095-A until
completely seated (Fig. 71).
(15) Install pinion in housing bore.
(16) Assemble preload shims onto pinion and in
stall the pinion gear in housing. (17) Install pinion front bearing, oil slinger, yoke,
washer and nut. Install the yoke with Installer C-3718 and Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 72).
(18) Tighten the yoke nut to 339-366 N-m (250-270
ft. lbs.) torque.
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-3281
J9103-21
Fig.
72
Pinion
Yoke
Installation
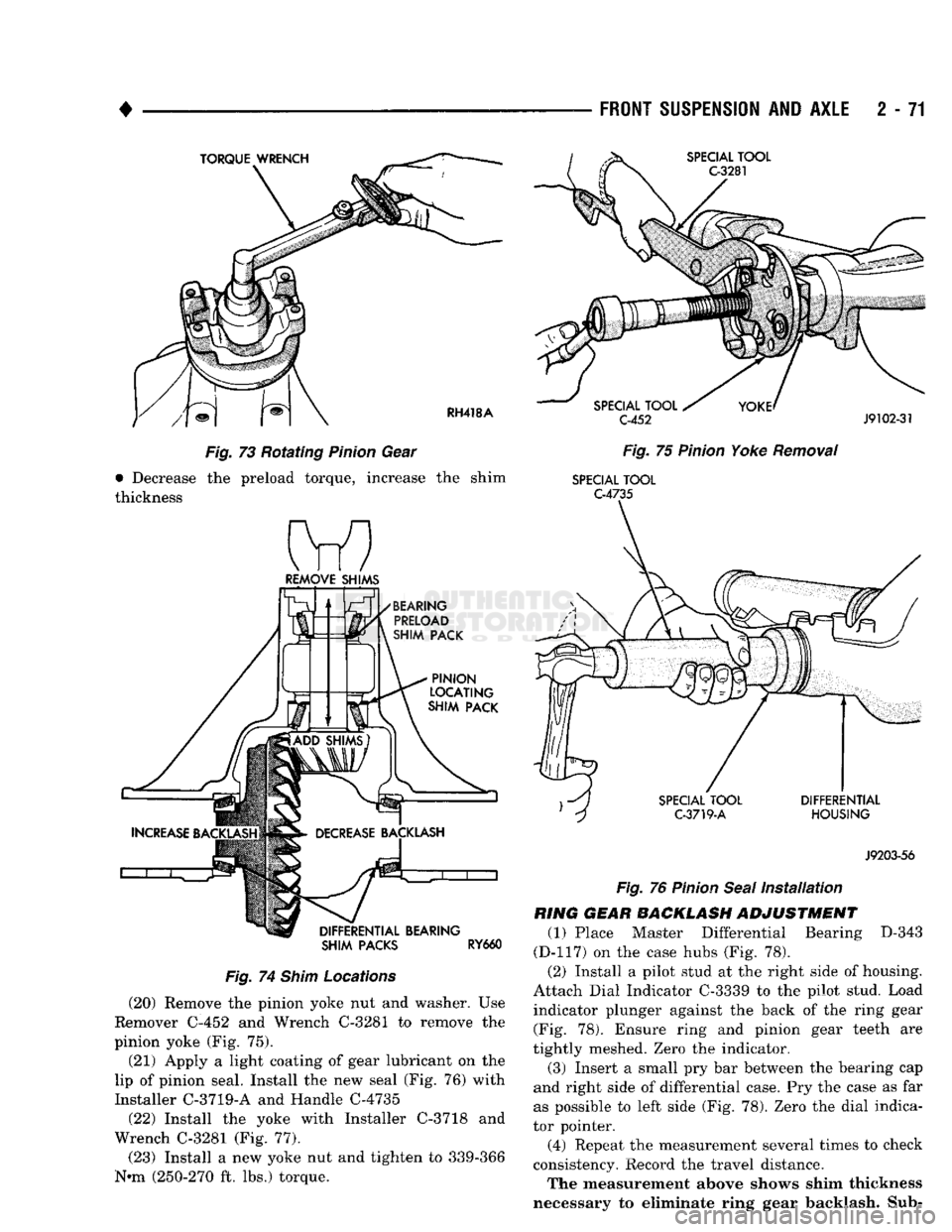
(19) Check bearing preload torque with an inch
pound torque wrench (Fig. 73). The torque necessary to rotate the pinion gear should be;
• Original Bearings — 1 to 3 N*m (10 to 20 in. lbs.) • New Bearings — 2 to 5 N»m (20 to 40 in. lbs.) If the preload torque is not within the specified tol
erance, correct the shim thickness accordingly (Fig.
74);
• Increase the preload torque, decrease the shim
thickness
Page 124 of 1502
•
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 71
TORQUE
WRENCH
SPECIAL
TOOL
G3281
RH418A
Fig.
73 Rotating
Pinion
Gear
• Decrease the preload torque, increase the shim
thickness
BEARING
PRELOAD
SHIM PACK
PINION
LOCATING
SHIM PACK
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM PACKS
RY660
Fig.
74
Shim
Locations
(20) Remove the pinion yoke nut and washer. Use
Remover C-452 and Wrench C-3281 to remove the
pinion yoke (Fig. 75).
(21) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal. Install the new seal (Fig. 76) with
Installer C-3719-A and Handle C-4735
(22) Install the yoke with Installer C-3718 and
Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 77).
(23) Install a new yoke nut and tighten to 339-366
N*m (250-270 ft. lbs.) torque.
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-452
J9102-31
Fig.
75
Pinion
Yoke
Removal
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-4735
SPECIAL
TOOL C-3719-A DIFFERENTIAL
HOUSING
J9203-56
Fig.
76
Pinion
Seal
Installation
RING
GEAR BACKLASH
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Place Master Differential Bearing D-343
(D-117) on the case hubs (Fig. 78).
(2) Install a pilot stud at the right side of housing.
Attach Dial Indicator C-3339 to the pilot stud. Load indicator plunger against the back of the ring gear (Fig. 78). Ensure ring and pinion gear teeth are
tightly meshed. Zero the indicator.
(3) Insert a small pry bar between the bearing cap
and right side of differential case. Pry the case as far
as possible to left side (Fig. 78). Zero the dial indica
tor pointer.
(4) Repeat the measurement several times to check
consistency. Record the travel distance.
The measurement above shows shim thickness
necessary to eliminate ring gear backlash. Sub-
Page 128 of 1502

FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 75
SPECIFICATIONS
MODEL
60
FRONT
AXLE
Axle Type........
Semi-floating,
hypoid
Application
D-TRK Ring Gear
Diameter
9.75
in.
(24.76 cm)
Lubricants
MOPAR
Gear
Lubricant
or
equivalent
SAE
75W-90,
API
Grade
GL-5,
MIL-L-2105C
Locking
Hubs Manual
type
Lubricant Capacity
6.5
pts. (3.1L)
Axle Model Dana
M60F
Axle Ratio.........
3.54
Tol
4.10
4.56
Track... 65.7
in.
GAWR....................
4500
lbs.
TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS
Differential
Bearing
Preload Shim 0.015
in.
0.38
mm
Differential
Side Gear-to-Case Clearance..
0.000-0.007
in.
0.00-0.18
mm
Ring
Gear Backlash 0.005-0,008
in.
0.12-0.20 mm
Drive Pinion Gearshaft Bearing Break-Away Preload Torque
Original
Bearings....
10-20
in. lbs. l-2N®m Replacement Bearings. 20-40
in.
lbs. 2-5 N®m
Drive Pinion Gear Depth Select shims Standard Setting.... 3.125
in.
79.37 mm
Side
Gear Clearance (max.) 0.006
in.
0.15
mm
Case
Runout (max.) 0.006
in.
0.15
mm
J9202-107
FRONT
SUSPENSION
COMPONENTS-
2WD
FRONT
SUSPENSION
COMPONENTS-
4WD
FRONT
SUSPENSION
COMPONENTS
%
WHEEL
DRIVE
FRONT
SUSPENSION
COMPONENTS
4
WHEEL
DRIVE
DESCRIPTION
TOROUE
Brake Rotor
Dust
Shield
Jounce Bumper to Bracket.... Lower
Suspension
Arm Pivot.
Lower Ball Stud
Nut
(11/16-18 Bolt)...............
Lower Ball Stud
Nut
(3/4-16 Bolt).....
Shock
Absorber Upper Nut..
Shock
Absorber Lower Bolt
..
Stabilizer Bar Retainer
Bolts
.
Stabilizer Bar Link Nut
Steering Arm to Knuckle 5/8-18 Bolt/Nut
.............
Steering Arm to Knuckle 3/4-16 Bolt/Nut . 20 N-m (180 in.
lbs.
....
41
N-m
(30
ft. lbs.
305
N-m (225
ft. lbs.
183
N-m (135
ft. lbs.
237 N-m (175
ft. lbs.
....
34
N-m
(25 ft.
lbs. .
23
N-m
(200
in. lbs.
.
23
N-m
(200
in. lbs.
. 11 N-m
(100
in. lbs.
Strut/Jounce Bumper to
Suspension
Arm Bolt/Nut.
Strut
Front
Nut Upper Ball Stud
Nut
290 N-m (215
ft. lbs.
330 N-m (225
ft.
lbs.
.. 129 N-m (95
ft.
lbs.
....
68
N-m
(50
ft.
lbs.
142
N-m
(105
ft.
lbs.
J9202-108
DESCRIPTION
TORQUE
Jounce Bumper to Bracket
....
Stabilizer Bar Retainer
Bolts..
Stabilizer Bar Link Nut
Shock
Absorber/Jounce Bracket to Frame
Shock
Absorber (Standard) Upper and Lower Nut
Shock
Absorber (Air Adjust) Upper Nut
Shock
Absorber (Air Adjust) Lower Nut
Spring
U-bolt/Stud Nuts (Model
44) ...
Spring
Front Pivot Nut (Model
44)
Spring
Rear Shackle
Nut
(Model
44)
Spring
U-bolt/Stud Nuts (Model
60)
Spring
Front
Pivot Nut (Model
60)
Spring
Rear Shackle Nut (Model
60)
...
41
N-m (30
ft.
lbs.)
23
N-m (200 in.
lbs.)
11
N-m
(100
in.
lbs.)
.. 101 N-m (75
ft.
lbs.)
.... 75 N-m (55
ft.
lbs.)
.... 75 N-m (55
ft.
lbs.)
271 N-m
(200
ft.
lbs.)
.. 115 N-m (85
ft.
lbs.)
135
N-m (100
ft.
lbs.)
.... 81 N-m
(60
ft.
lbs.)
..
129
N-m
(95
ft.
lbs.)
135
N-m (100
ft.
lbs.)
,.
108
N-m
(80
ft.
lbs.)
J9202-109
Page 129 of 1502
2
- 76
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
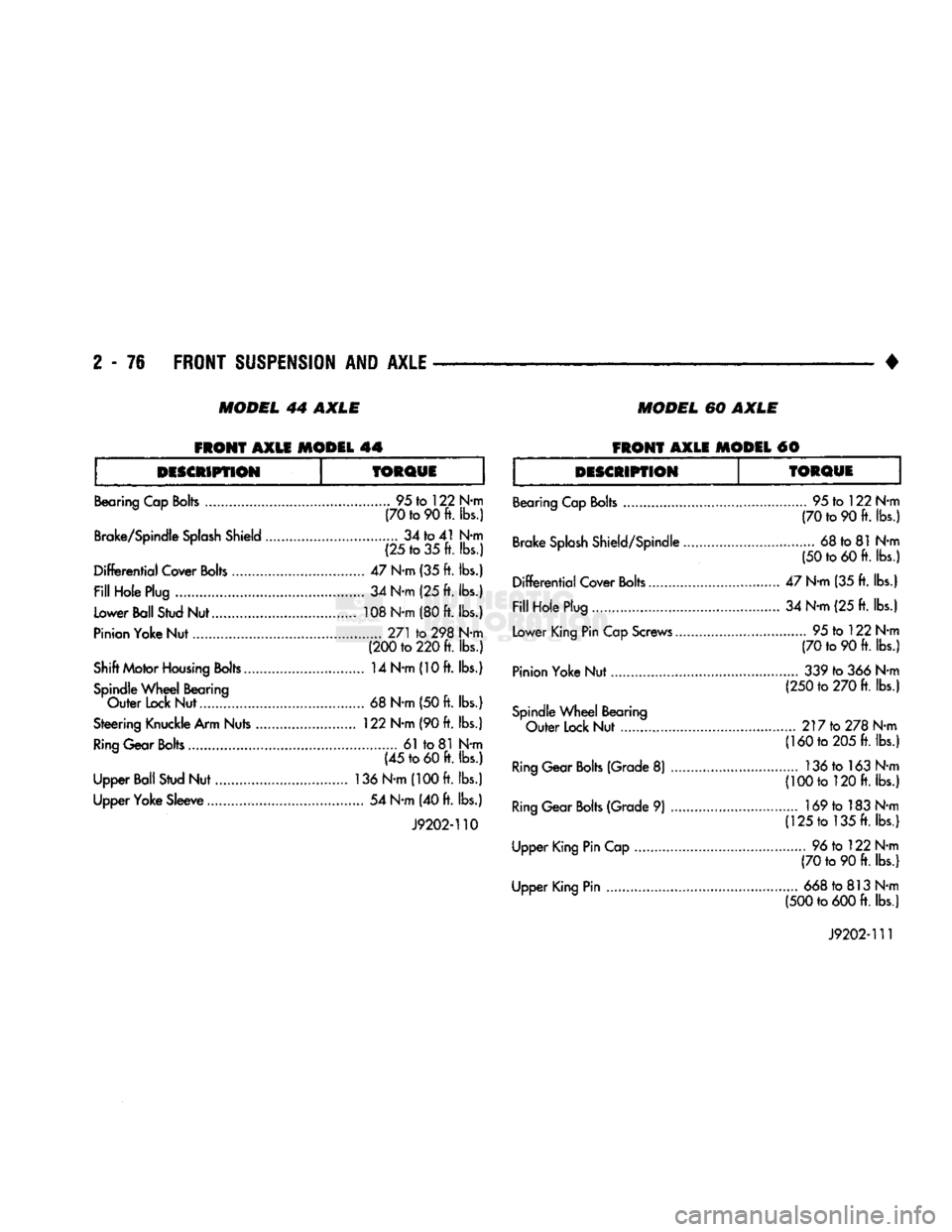
MODEL
44 AXLE
MODEL
60 AXLE
FRONT
AXLE MODEL 44
FRONT
AXLE MODEL #0
DESCRIPTION
TORQUE
Bearing Cap
Bolts
95 to 122 N-m (70 to 90 ft. lbs.)
Brake/Spindle
Splash
Shield 34 to 41 N-m
(25 to 35 ft. lbs.)
Differential
Cover
Bolts
47 N-m (35 ft. lbs.)
Fill
Hole Plug 34 N-m (25 ft. lbs.)
Lower Ball Stud Nut 108 N-m (80 ft. lbs.)
Pinion Yoke Nut 271 to 298 N-m (200 to 220 ft. lbs.)
Shift Motor
Housing
Bolts 14 N-m (10 ft. lbs.) Spindle
Wheel
Bearing
Outer
Lock Nut...... 68 N-m (50 ft. lbs.)
Steering Knuckle Arm Nuts 122 N-m (90 ft. lbs.)
Ring
Gear
Bolts
61 to 81 N-m (45 to 60 ft. lbs.)
Upper Ball Stud Nut 136 N-m (100 ft. lbs.)
Upper Yoke Sleeve 54 N-m (40 ft. lbs.)
J9202-110
DESCRIPTION
TORQUE
Bearing Cap Bolts
Brake
Splash
Shield/Spindle.
Differential
Cover Bolts
Fill
Hole Plug
Lower King Pin Cap Screws...
Pinion Yoke Nut.
Spindle
Wheel
Bearing
Outer
Lock Nut
Ring
Gear
Bolts
(Grade 8)
Ring
Gear
Bolts
(Grade 9)
Upper King Pin Cap
Upper King Pin 95 to 122 N-m
(70 to 90 ft. lbs.)
68 to 81 N-m
(50 to 60 ft. lbs.)
47 N-m (35 ft. lbs.) 34 N-m (25 ft. lbs.) 95 to 122 N-m
(70 to 90 ft. lbs.) 339 to 366 N-m
(250 to 270 ft. lbs.)
.... 217 to 278 N-m (160 to 205 ft. lbs.)
136tol63N-m
(100 to 120 ft. lbs.)
..... 169 to 183 N-m (125 to 135 ft. lbs.)
96 to 122 N-m
(70 to 90 ft. lbs.)
668 to 813 N-m
(500 to 600 ft. lbs.)
J9202-111
Page 135 of 1502
3
- 6
REAR SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
•
NUT PIPE
SOCKET
WRENCH
(DRIVER)
FLAT
THREADED
WASHER
ROD
J8917-20
Fig.
6
Spring
Eye
Bushing
Removal
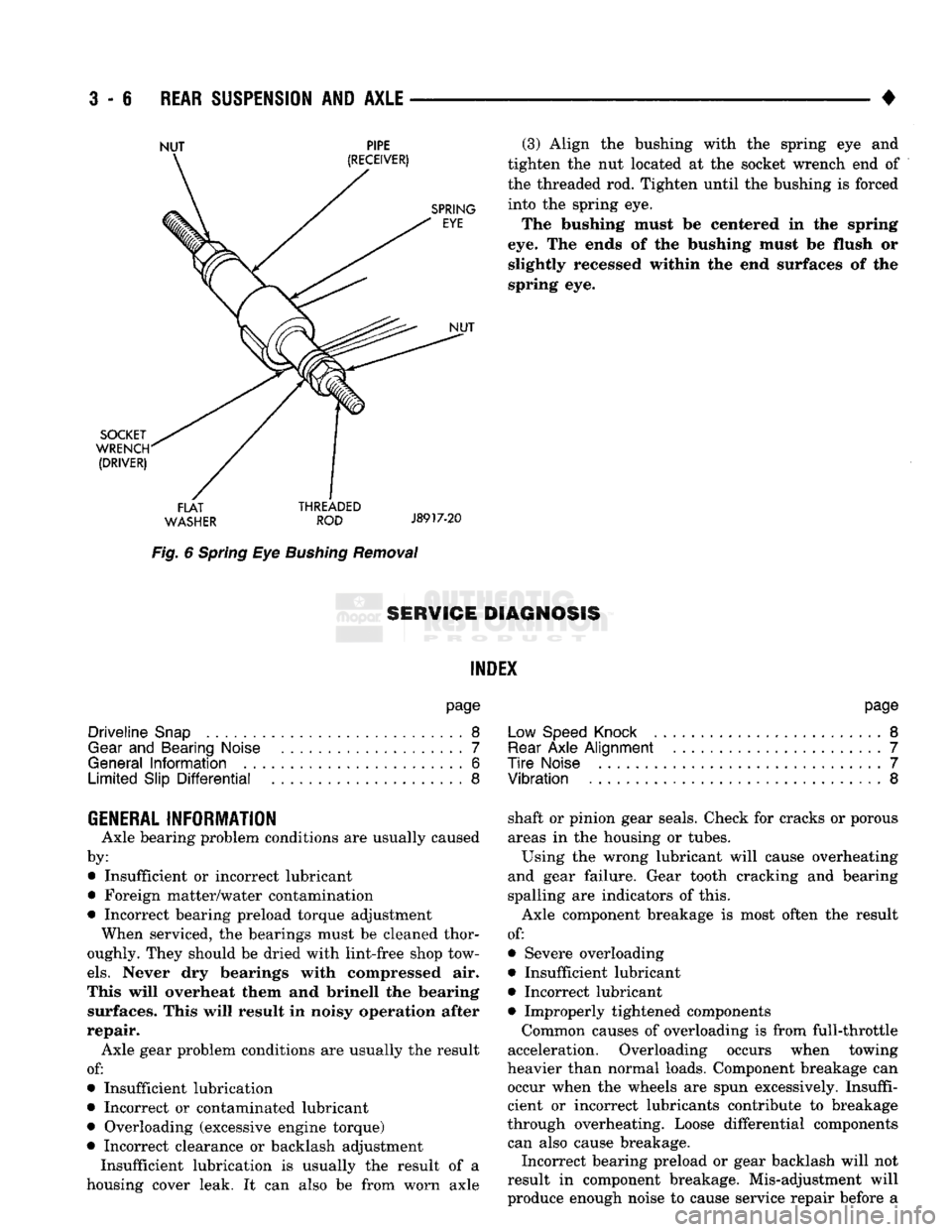
(3) Align
the
bushing with
the
spring
eye and
tighten
the nut
located
at the
socket wrench
end of
the threaded
rod.
Tighten until
the
bushing
is
forced into
the
spring
eye.
The bushing must
be
centered
in the
spring
eye.
The
ends
of the
bushing must
be
flush
or
slightly recessed within
the end
surfaces
of the
spring
eye.
8ERW1GE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page
Driveline
Snap
8
Gear
and
Bearing Noise
7
General
Information
6
Limited
Slip
Differential
8
page
Low Speed Knock
.........................
8
Rear
Axle
Alignment
.......................
7
Tire
Noise
7
Vibration
8
GENERAL INFORMATION
Axle bearing problem conditions
are
usually caused
by: • Insufficient
or
incorrect lubricant
• Foreign matter/water contamination
• Incorrect bearing preload torque adjustment When serviced,
the
bearings must
be
cleaned thor
oughly. They should
be
dried with lint-free shop tow
els.
Never
dry
bearings with compressed
air.
This will overheat them
and
brinell
the
bearing surfaces. This will result
in
noisy operation after
repair. Axle gear problem conditions
are
usually
the
result
of:
• Insufficient lubrication
• Incorrect
or
contaminated lubricant
• Overloading (excessive engine torque)
• Incorrect clearance
or
backlash adjustment Insufficient lubrication
is
usually
the
result
of a
housing cover leak.
It can
also
be
from worn axle shaft
or
pinion gear seals. Check
for
cracks
or
porous
areas
in the
housing
or
tubes.
Using
the
wrong lubricant will cause overheating
and gear failure. Gear tooth cracking
and
bearing
spalling
are
indicators
of
this.
Axle component breakage
is
most often
the
result
of:
• Severe overloading
• Insufficient lubricant
• Incorrect lubricant • Improperly tightened components
Common causes
of
overloading
is
from full-throttle
acceleration. Overloading occurs when towing
heavier than normal loads. Component breakage
can
occur when
the
wheels
are
spun excessively. Insuffi
cient
or
incorrect lubricants contribute
to
breakage
through overheating. Loose differential components can also cause breakage. Incorrect bearing preload
or
gear backlash will
not
result
in
component breakage. Mis-adjustment will
produce enough noise
to
cause service repair before
a
Page 137 of 1502

3
- 8
REAR SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
• level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion gear shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
• Damaged drive shaft
• Missing drive shaft balance weight
• Worn, out-of-balance wheel and tires
• Loose wheel lug nuts
• Worn U-joint • Loose spring U-bolts
• Loose/broken rear springs or shackles
• Damaged axle shaft bearings
• Loose pinion gear nut
• Excessive pinion yoke run out
• Bent axle shaft Check for loose or damaged front-end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear-end vi
bration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brackets and drive belts. All driveline components should be examined be
fore starting any repair. Refer to Group 22, Wheels and Tires for additional
information.
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by: • High engine idle speed
• Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts
9
Worn U-joints
• Loose spring shackles or U-bolts
• Loose pinion gear nut and yoke
• Excessive ring gear backlash
• Excessive differential side gear-to-case clearance A worn bushing in the transmission extension
housing can also cause noise. The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the ve
hicle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is
helpful in isolating the source of a noise.
LIMITED
SLIP DIFFERENTIAL
Under normal traction conditions, engine torque is
divided evenly. With low-traction surfaces, engine
torque is transferred to the wheel with the most tire
traction. When diagnosing a limited-slip differential
problem condition, the wheel with the least traction can continue spinning. The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Check for incorrect or contaminated lubricant. Replace the gear lubricant if necessary.
• With Sure-Grip differentials add a container of
MOPAR® Hypoid Gear Additive This will correct the condition in most instances. If
the chatter persists, clutch damage could have oc curred. After changing the lubricant, drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu
ver will pump lubricant through the clutches.
Page 138 of 1502
REAR
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
3 - 9
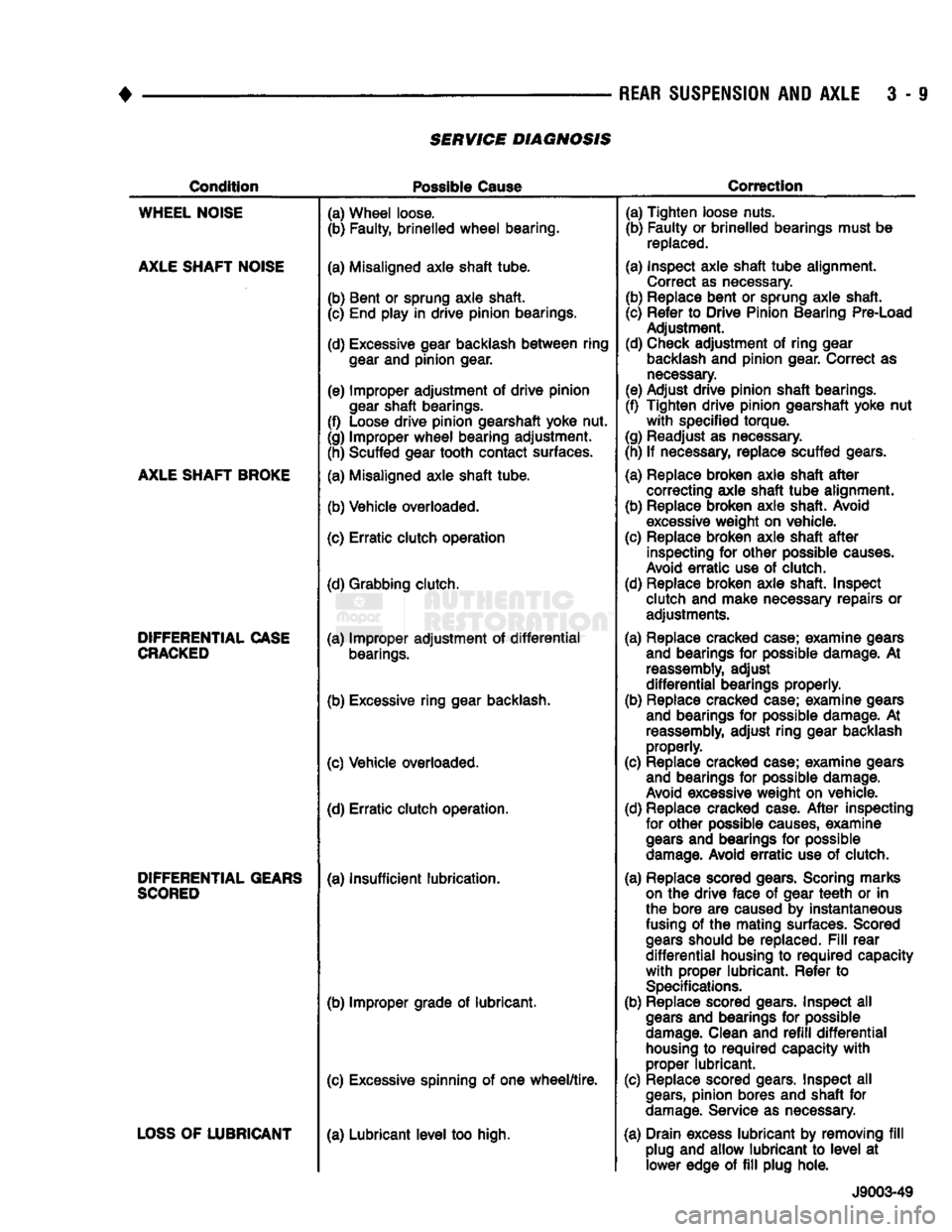
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
Condition
Possible
Cause
Correction
WHEEL
NOISE
AXLE
SHAFT
NOISE
AXLE
SHAFT
BROKE
DIFFERENTIAL
CASE
CRACKED
DIFFERENTIAL
GEARS
SCORED
LOSS
OF
LUBRICANT
(a) Wheel loose.
(b) Faulty, brinelled
wheel
bearing.
(a) Misaligned axle shaft tube.
(b) Bent or sprung axle shaft. (c) End play in drive pinion bearings.
(d) Excessive gear backlash
between
ring
gear
and pinion gear.
(e) Improper adjustment of drive pinion
gear
shaft bearings.
(f) Loose drive pinion gearshaft yoke nut.
(g) Improper
wheel
bearing adjustment. (h) Scuffed gear tooth contact surfaces.
(a) Misaligned axle shaft tube.
(b) Vehicle overloaded.
(c) Erratic clutch operation
(d) Grabbing clutch.
(a) Improper adjustment of
differential
bearings.
(b) Excessive ring gear backlash.
(c) Vehicle overloaded. (d) Erratic clutch operation.
(a) Insufficient lubrication.
(b) Improper grade of lubricant.
(c) Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.
(a) Lubricant
level
too high. (a) Tighten loose nuts.
(b) Faulty or brinelled bearings must be
replaced.
(a) Inspect axle shaft
tube
alignment. Correct as necessary.
(b) Replace bent or sprung axle shaft.
(c) Refer to Drive Pinion Bearing Pre-Load Adjustment.
(d) Check adjustment of ring gear
backlash
and pinion gear. Correct as
necessary.
(e) Adjust drive pinion shaft bearings.
(f) Tighten drive pinion gearshaft yoke nut
with
specified torque.
(g) Readjust as necessary.
(h) If necessary, replace scuffed gears.
(a) Replace broken axle shaft
after
correcting axle shaft
tube
alignment.
(b) Replace broken axle shaft. Avoid
excessive
weight on vehicle.
(c) Replace broken axle shaft
after
inspecting for other possible
causes.
Avoid
erratic
use of clutch.
(d) Replace broken axle shaft. Inspect clutch and make necessary repairs or adjustments.
(a) Replace cracked case; examine gears and bearings for possible damage. At
reassembly,
adjust
differential
bearings properly.
(b) Replace cracked case; examine gears and bearings for possible damage. At
reassembly,
adjust ring gear backlash properly.
(c) Replace cracked case; examine gears and bearings for possible damage.
Avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
(d) Replace cracked case.
After
inspecting for other possible
causes,
examine
gears
and bearings for possible
damage.
Avoid
erratic
use of clutch.
(a) Replace scored gears. Scoring marks
on
the drive face of gear
teeth
or in
the bore are caused by instantaneous
fusing
of the mating surfaces. Scored
gears
should be replaced.
Fill
rear
differential
housing to
required
capacity
with
proper lubricant. Refer to
Specifications.
(b) Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears
and bearings for possible
damage.
Clean and
refill
differential
housing
to
required
capacity
with
proper lubricant.
(c) Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears,
pinion bores and shaft for
damage.
Service as necessary.
(a) Drain excess lubricant by removing
fill
plug and allow lubricant to
level
at lower edge of
fill
plug hole.
J9003-49
Page 140 of 1502

•
REAR
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
3 - 11 8 3/8 and 9 1/4
AXLE
INDEX
page
Axle Shaft, Seal
and
Bearing Service
......... 11
Complete Axle Removal/Installation
16
Differential
Service
16
Information
11
INFORMATION
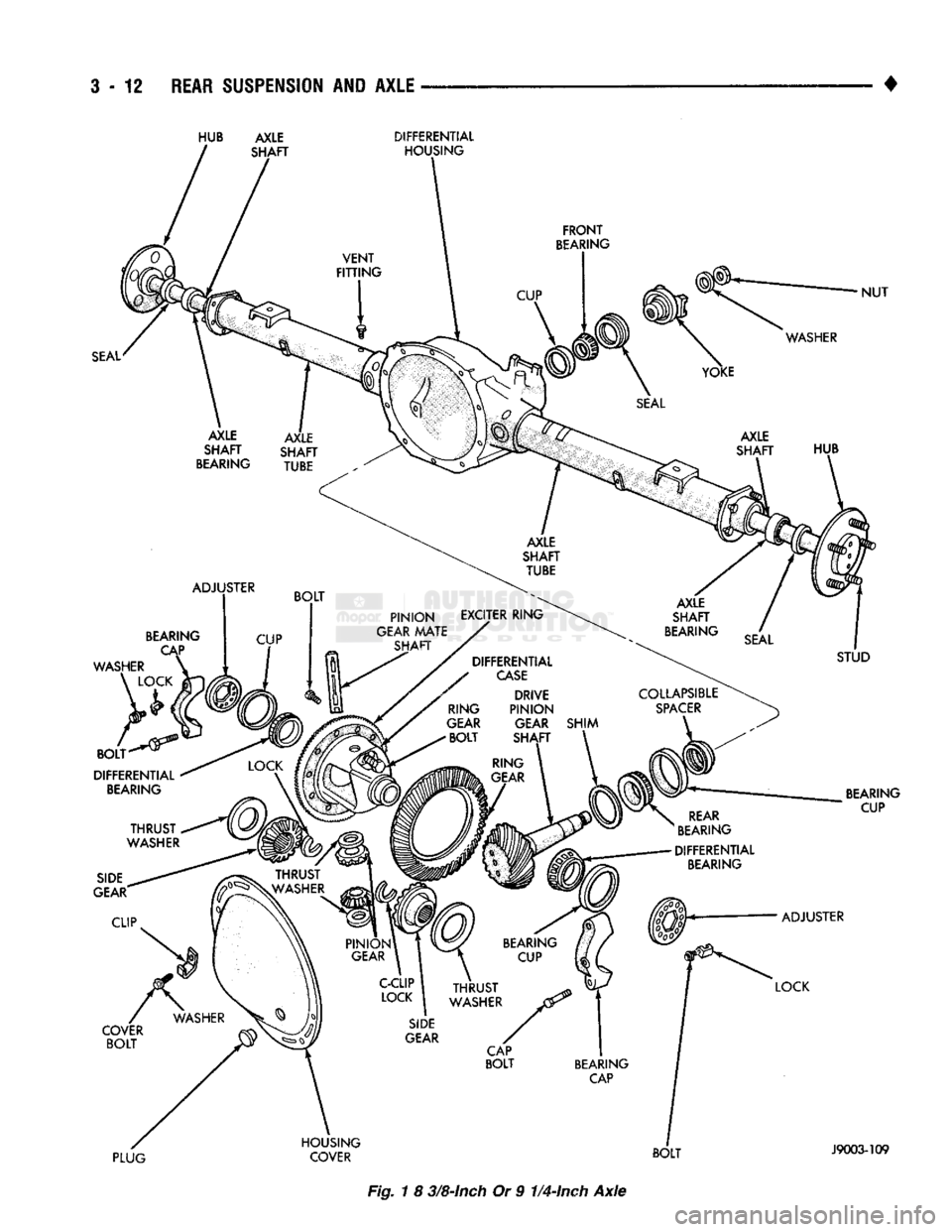
The 8 3/8 and 9 1/4 axle (Fig. 1) housing consist of
a cast iron center section. They also have two steel
axle shaft tubes that are pressed into and welded to
the differential housing. The removable, stamped steel cover provides a
means for inspection and service without removing
the complete axle from the vehicle.
LUBRICANT
Multi-purpose, hypoid gear lubricant should be
used for 8 3/8 and 9 1/4 axles. The lubricant should
have MIL-L-2105C and API GL 5 quality specifica
tions.
MOPAR® Hypoid Gear Lubricant conforms to
both of these specifications.
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
additional information.
CAUTION:
If a
rear axle
is
submerged
in
water,
the
axle lubricant must
be
replaced immediately.
DRAIN
AND
REFILL
(1) Drive the vehicle until the gear lubricant
reaches normal operating temperature.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the
differential housing cover.
(4) Remove the differential housing cover. Allow
the original lubricant to completely drain from the
housing and axle shaft tubes. (5) With standard differential, clean the differen
tial and the housing cavity with a flushing oil (or light engine oil). This will remove the residual lubri
cant and foreign matter.Do not use water, steam,
kerosene or gasoline for flushing.
CAUTION:
DO NOT
FLUSH
Sure-Grip differentials.
Sure-Grip
differentials
may be
cleaned only
by
wip
ing
with
clean,
lint-free
cloths.
(6)
Scrape the residual sealant from the housing
and cover mating surfaces. Clean the mating sur
faces with mineral spirits. Apply a bead of MOPAR® Silicone Rubber Sealant on the housing cover (Fig.
2).
Allow the sealant to cure for a few minutes.
page
Lubricant
11
Pinion Depth Measurement
and
Adjustment
with
Gauge
Set 20
Pinion
Seal
Replacement
14
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes af
ter applying the sealant. If not installed, the sealant must be removed and another bead ap
plied. (7) Install the cover on the differential. Install the
identification tag. Tighten the cover bolts to 47 N#m (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION:
Overfilling
the
differential
can
result
in
the lubricant foaming
and
overheating.
(8) Refill the differential with the specified quan
tity of MOPAR® Hypoid Gear Lubricant. With Sure- Grip differentials, add a container of MOPAR®
Hypoid Gear Lubricant Additive.
(9) Install the fill hole plug.
(10) Road test the vehicle.
AXLE
SHAFT, SEAL AND BEARING
SERVICE
CAUTION:
When rear axle service
is
necessary, both rear wheels must
be
raised
off the
surface
so
that
they
are
free
to
rotate.
Be
cautious when
the
tires
are
being rotated
by the
engine
or by
other
means.
CAUTION:
If
equipped
with
a
Sure-Grip
differential,
do
not
rotate
either
axle shaft unless both
are
prop
erly
in-place. Rotation
of one
axle shaft without
the
other being installed
can
result
in
misalignment
of
the side gears/splines. This
will
necessitate side
gear
re-alignment before
the
axle shaft
can be in
stalled.
AXLE SHAFT REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel.
(3) Remove the brake drum.
(4) Clean all the foreign material from housing
cover area.
(5) Loosen the housing cover bolts. Drain the lubri
cant from the housing. Remove the housing cover.
(6)
Rotate the differential case so the pinion mate
gear shaft lock screw is accessible. Remove the lock screw and the pinion mate gear shaft from the case (Fig. 3).
Page 141 of 1502
3
- 12
REAR
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
•
HUB
AXLE
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
HOUSING FRONT
BEARING
VENT
FITTING
SEAL
AXLE
AXLE
SHAFT SHAFT
BEARING
TUBE
BEARING
CAP
WASHER
LOCK
STUD
SIDE
GEAR
CLIP
NUT
BOLT
DIFFERENTIAL
BEARING BEARING
CUP
ADJUSTER
LOCK
COVER
BOLT
PLUG
HOUSING
COVER
BOLT
J9003-109
Fig. 1 8 3/8-Inch Or 9 1/4-Inch Axle
Page 143 of 1502
3
- 14
REAR SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
3
- 18
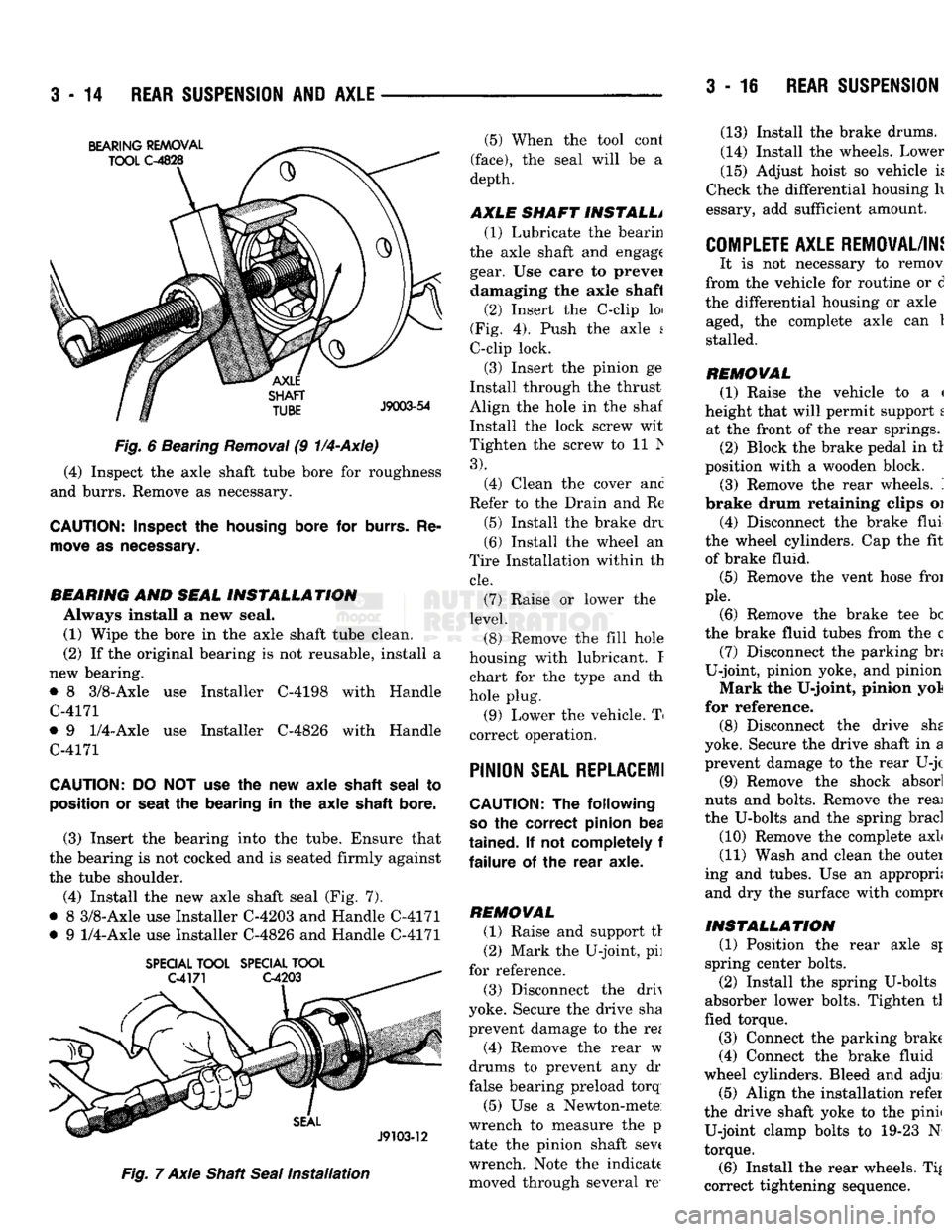
REAR SUSPENSION Fig.
6 Bearing
Removal
(9
1/4-Axle)
(4) Inspect the axle shaft tube bore for roughness
and burrs. Remove as necessary.
CAUTION:
Inspect
the
housing
bore for
burrs.
Re
move
as
necessary.
BEARING
AND
SEAL
INSTALLATION
Always install a new seal. (1) Wipe the bore in the axle shaft tube clean.
(2) If the original bearing is not reusable, install a
new bearing.
• 8 3/8-Axle use Installer C-4198 with Handle
C-4171
• 9
1/4-Axle
use Installer C-4826 with Handle
C-4171
CAUTION:
DO NOT use the new axle
shaft
seal
to
position
or
seat
the bearing in the axle
shaft
bore.
(3) Insert the bearing into the tube. Ensure that
the bearing is not cocked and is seated firmly against
the tube shoulder.
(4) Install the new axle shaft seal (Fig. 7).
• 8 3/8-Axle use Installer C-4203 and Handle C-4171
• 9
1/4-Axle
use Installer C-4826 and Handle C-4171
SPECIAL
TOOL
SPECIAL
TOOL
Fig.
7 Axle Shaft
Seal
Installation
(5) When the tool cont
(face),
the seal will be a
depth.
AXLE SHAFT INSTALL* (1) Lubricate the bearin
the axle shaft and engage gear. Use care to prevei damaging the axle shaft
(2) Insert the C-clip loi
(Fig. 4). Push the axle s
C-clip lock.
(3) Insert the pinion ge
Install through the thrust
Align the hole in the shaf
Install the lock screw wit
Tighten the screw to 11 Is
3).
(4) Clean the cover anc
Refer to the Drain and Re
(5) Install the brake drv
(6) Install the wheel an
Tire Installation within th
cle.
(7) Raise or lower the
level.
(8) Remove the fill hole
housing with lubricant. I chart for the type and th
hole plug.
(9) Lower the vehicle. T
correct operation.
PINION
SEAL REPLACE!!
CAUTION:
The following
so
the correct pinion bea
tained.
If not completely f
failure
of the rear axle.
REMOVAL (1) Raise and support tr
(2) Mark the U-joint, pi]
for reference.
(3) Disconnect the drh
yoke. Secure the drive sha
prevent damage to the re*
(4) Remove the rear w
drums to prevent any dr
false bearing preload torq
(5) Use a Newton-mete
wrench to measure the p
tate the pinion shaft sev( wrench. Note the indicate moved through several re' (13) Install the brake drums.
(14) Install the wheels. Lower
(15) Adjust hoist so vehicle k
Check the differential housing h
essary, add sufficient amount.
COMPLETE AXLE REMOVAL/IN!
It is not necessary to remov
from the vehicle for routine or d
the differential housing or axle aged, the complete axle can 1
stalled.
REMOVAL (1) Raise the vehicle to a <
height that will permit support t at the front of the rear springs. (2) Block the brake pedal in tl
position with a wooden block. (3) Remove the rear wheels. '.
brake drum retaining clips oi
(4) Disconnect the brake flui
the wheel cylinders. Cap the fit of brake fluid.
(5) Remove the vent hose froi
pie.
(6) Remove the brake tee be
the brake fluid tubes from the c (7) Disconnect the parking bn
U-joint, pinion yoke, and pinion
Mark the U-joint, pinion yol
for reference. (8) Disconnect the drive she
yoke. Secure the drive shaft in a prevent damage to the rear U-jc
(9) Remove the shock absorl
nuts and bolts. Remove the reai
the U-bolts and the spring brad
(10) Remove the complete axL
(11) Wash and clean the outei
ing and tubes. Use an appropri; and dry the surface with comprc
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the rear axle sj
spring center bolts.
(2) Install the spring U-bolts
absorber lower bolts. Tighten tl
fled torque.
(3) Connect the parking brake
(4) Connect the brake fluid
wheel cylinders. Bleed and adjui (5) Align the installation refer
the drive shaft yoke to the pinii U-joint clamp bolts to 19-23 N
torque.
(6) Install the rear wheels. Ti|
correct tightening sequence.