bulb DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1993, Model line: TRUCK, Model: DODGE TRUCK 1993Pages: 1502, PDF Size: 80.97 MB
Page 190 of 1502

•
BRAKES
i - 3 BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page
Brake
Warning Lights
3
Diagnosing
Brake Problems .................
4
Diagnosis
Procedures
3
Low
Vacuum
Switch—Diesel
Models
3
page
Master
Cylinder/Power Booster Test
5
Power
Booster
Check
Valve Test .............
6
Power
Booster
Vacuum
Test .................
6
Testing Diesel
Engine
Vacuum
Pump
Output
.... 6
DIAGNOSIS
PROCEDURES
Brake diagnosis involves determining
if the
prob
lem
is
related
to a
mechanical, hydraulic
or
vacuum
operated component.
A
preliminary check, road test
ing
and
component inspection
can all be
used
to de
termine
a
problem cause. Road testing will either verify proper brake opera
tion
or
confirm
the
existence
of a
problem. Compo nent inspection will,
in
most cases, identify
the
actual part causing
a
problem. The first diagnosis step
is the
preliminary check. This
involves inspecting fluid level, parking brake action,
wheel
and
tire condition, checking
for
obvious leaks
or
component damage
and
testing brake pedal response. A road test will confirm
the
existence
of a
problem.
Final diagnosis procedure involves road test analysis and
a
visual inspection
of
brake components.
BRAKE
WARNING LIGHTS
The
red
brake warning light
is
connected
to the
parking brake switch
and to the
pressure differential switch
in the
combination valve. The
red
light will illuminate when
the
parking
brakes
are
applied
or
when
a
fluid pressure drop
oc
curs
in the
front
or
rear brake circuit.
The
light will
also illuminate
for
approximately
2-4
seconds
at en
gine start
up.
This
is a
self test feature designed
to
check bulb
and
circuit operation each time
the en
gine
is
started. The amber antilock light
is
connected
to the
anti-
lock rear brake hydraulic valve.
The
light will illu
minate
if a
fault occurs within
the
antilock system.
LOW VACUUM SWITCH-DIESEL MODELS
On diesel models,
the red
brake warning light
is
also
used
to
alert
the
driver
of a low
brake booster vacuum
condition.
The
warning light
is in
circuit with
a
vacuum
warning switch mounted
on the
driver side fender
panel.
The
vacuum side
of the
switch
is
connected
to the
power brake booster.
The
electrical side
of the
switch
is
connected
to the
brake warning light. The
low
vacuum switch monitors booster vacuum
level whenever
the
engine
is
running.
If
booster vac
uum falls below
8.5
inches vacuum
for a
minimum
of
10 seconds,
the
switch completes
the
circuit
to the
warning light causing
it to
illuminate.
The
warning light
is
designed
to
differentiate between
a low
vac
uum condition
and a
hydraulic circuit fault.
PRELIMINARY
BRAKE CHECK
(1) Check condition
of
tires
and
wheels. Damaged
wheels
and
worn, damaged,
or
underinflated tires
can
cause pull, shudder, tramp,
and a
condition similar
to
grab.
(2)
If
complaint
was
based
on
noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front
and
rear
of
vehicle
and
listen
for
noise that might
be
caused
by
loose, worn
or
damaged suspension
or
steering compo
nents.
(3) Inspect brake fluid level
and
condition. Note
that
the
front disc brake reservoir fluid level will drop
in
proportion
to
normal lining wear. Also note
that brake fluid tends
to
darken over time. This
is normal
and
should
not be
mistaken
for
con
tamination.
If the
fluid
is
still clear
and
free
of
foreign material,
it is OK.
(a)
If
fluid level
is
abnormally
low,
look
for
evi
dence
of
leaks
at
calipers, wheel cylinders, brake-
lines
and
master cylinder.
(b)
If
fluid appears contaminated, drain
out a
sample.
If
fluid
is
separated into layers,
or
obvi
ously contains
oil or a
substance other than brake
fluid,
the
system seals
and
cups will have
to be re
placed
and the
hydraulic system flushed.
(4) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement
and
full release
of
cables
and
pedal. Also
note
if
vehicle
was
being operated with parking
brake partially applied.
(5) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does
not
bind
and has
adequate free play.
If
pedal
lacks free play, check pedal
and
power booster
for be
ing loose
or for
bind condition.
Do not
road test until
condition
is
corrected.
(6)
If
components checked appear
OK,
road test
the
vehicle.
ROAD
TESTING (1)
If
complaint involved
low
brake pedal, pump
the pedal
and
note
if the
pedal comes back
up to
nor mal height.
(2) Check brake pedal response with transmission
in Neutral
and
engine running. Pedal should remain
firm under steady foot pressure.
Page 200 of 1502

•
BRAKES
5 - 13
COMBINATION VALVE OPERATION
METERING (HOLD-OFF) VALVE The metering valve is used to balance brake action
between the front disc and rear drum brakes. The
valve meters (holds-off) full apply pressure to the front disc brakes until the rear brakeshoes are in full
contact with the drums.
The valve is designed to maintain front brake fluid
pressure at 3-30 psi until the hold-off limit of 117 psi is reached. At this point, the metering valve opens completely permitting full fluid apply pressure to the
front disc brakes.
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL SWITCH AND VALVE The pressure differential switch is connected to the
brake warning light. The switch is triggered by movement of the switch valve. The purpose of the switch is to monitor fluid pressure in the separate
front/rear brake hydraulic circuits.
A decrease or loss of fluid pressure in either hy
draulic circuit will cause the switch valve to shuttle
forward or rearward in response to a pressure differ ential.
Movement of the switch valve will push the switch
plunger upward. This closes the switch internal con tacts completing the electrical circuit to the warning light. The switch valve will remain in an actuated
position until repair restores system pressures to nor mal levels.
COMBINATION VALVE TESTING
TESTING METERING VALVE Metering valve operation can be checked visually
and with the aid of a helper.
Observe the metering valve stem while a helper
applies and releases the brakes. If the valve is oper
ating correctly, the stem will extend slightly when
the brakes are applied and retract when the brakes are released.
If the valve is faulty, replace the entire combina
tion valve as an assembly.
TESTING PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL SWITCH (1) Have helper sit in drivers seat to observe brake
warning light and to operate brake pedal.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Connect bleed hose to left or right rear wheel
cylinder. Then immerse hose end in glass jar par
tially filled with brake fluid.
(4) Have helper press and hold brake pedal all the
way down and observe warning light.
(a) If warning light illuminates, switch is operat
ing correctly. (b) If light fails to illuminate, check circuit fuse,
bulb and wiring. Repair as necessary and repeat test steps (3) and (4). (5) If warning light still fails to illuminate, check
brakelight and park brake switches (and wiring) with test lamp. Repair or replace parts as necessary and test differential pressure switch operation again.
(6) If warning light still does not illuminate,
switch is faulty. Replace combination valve, bleed
brakes and verify proper switch and valve operation.
COMBINATION VALVE REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
VALVE REMOVAL (1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Mark or tag brake lines connected to valve for
assembly reference.
(3) Disconnect lines at valve (Fig. 8).
(4) Disconnect wires from differential pressure
switch.
(5) Remove bolts attaching valve to frame bracket
and remove valve.
VALVE INSTALLATION (1) Mount new valve on bracket and tighten valve
and bracket screws/nuts securely.
(2) Connect brakelines to valve. Tighten fittings to
16 N*m (145 in. lbs.)
(3) Connect wires to pressure differential switch
terminal. (4) Bleed brakes.
(5) Lower vehicle and verify proper brake opera
tion.
BRAKE
LINES AND
HOSES
BRAKE LINE AND HOSE INSPECTION Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes
and at the rear axle junction block. Inspect the hoses
whenever the brake system is serviced, at every en gine oil change, or whenever the vehicle is in for ser
vice.
Inspect the hoses for surface cracking, scuffing, or
worn spots. Replace any brake hose immediately if
the fabric casing of the hose is exposed by cracks or abrasion.
Also check brake hose installation. Faulty installa
tion can result in kinked, twisted hoses, or contact with the wheels and tires or other chassis compo
nents.
All of these conditions can lead to scuffing,
cracking and eventual failure.
The steel brake lines should be inspected periodi
cally for evidence of corrosion, twists, kinks, leaks, or
other damage. Heavily corroded lines will eventually
rust through causing leaks. In any case, corroded or damaged brake lines should be replaced.
Page 325 of 1502

8A
- 4
ELECTRICAL
•
IGNITION
OFF
DRAW
(IOD)
Ignition off draw refers to power being drained
from the battery with the ignition turned off. A nor
mal vehicle electrical system will draw from 5 to 20
milliamps. A vehicle that has not been operated for
an extended period of time (approximately 20 days)
may discharge the battery to an inadequate level.
Battery drain should not exceed approximately 20
MA (20 milliamps = 0.020 amps). The 20 MA are needed to supply PCM memory,
digital clock memory, and ETR (electronically tuned
radio) memory. Excessive battery drain is caused by items left
turned on, internally shorted generator, or intermit
tent short in wiring.
If the IOD is excessive (over 20 milliamperes), the
defect must be found and corrected before replacing a
battery. In most cases the battery can be charged and returned to service.
TEST PROCEDURE Testing for higher amperage IOD must be per
formed first to prevent damage to most milliamp
meters.
Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF. Turn
off all lights, remove ignition key, and close all
doors.
If the vehicle is equipped with electronic acces
sories (illuminated entry, high line radio), allow the
systems to automatically shut off (time out), up to 3
minutes.
(1) After determining that the underhood lamp is
operating properly then disconnect bulb. (2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Connect a typical 12 volt test light (low watt
age bulb) between the negative cable clamp and the
battery negative terminal. The test light may light brightly for up to 3 min
utes or may not light at all (depending on the elec
trical equipment). The term brightly being used
throughout the following tests, implies the bright ness of the test light will be the same as if it were
connected across the battery.
The test light must be securely clamped to the neg
ative cable and battery terminal. If the test light be
comes disconnected during any of the IOD test, the electronic timer function will be activated and all
tests must be repeated.
(4) After 3 minutes, the test light should turn OFF
or be DIMLY lit (depending on the electrical equip
ment).
If the test light remains brightly lit do not
disconnect it. Remove each fuse or circuit breaker (refer to Group 8 - Wiring Diagrams) until test light
is either OFF or DIMLY lit. This will eliminate the
higher amperage draw.
If test light is still bright after disconnecting each
fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect the wiring har ness from the generator. Refer to Generator Testing
in this group. Do not disconnect the test light. After higher amperage IOD has been corrected, low
amperage IOD may be checked.
It is now safe to install milliamp meter to check for
low amperage IOD.
(5) With test light still connected, securely clamp
an ammeter between battery negative terminal and
negative battery cable.
If the test light or the milliamp meter circuit is
broken the various timer circuits will start. Do
not open any doors or turn on any electrical ac cessories with the test light disconnected or the
meter may be damaged.
(6) Disconnect test light. The current draw should
not exceed 0.020 amp. If it exceeds 20 milliamps iso
late each circuit by removing circuit breakers and
fuses.
The meter reading drops once the high current
problem is found. Repair this section of the circuit,
whether it is a wiring short or component failure.
BATTERY
OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
A battery voltage (no load) test will indicate the
state of charge of a battery that will pass the Battery
Load Test described in this section. Before proceed
ing with this test or the Battery Load Test the
battery must be completely charged as de scribed in Battery Charging in this section. If a battery has a no load voltage reading of 12.4
volts or greater but will not endure a load test, it is
defective and should be replaced. Refer to Group 8B,
Battery/Starter Service for instructions. To test bat
tery no load voltage, perform the following operation: (1) Before measuring open circuit voltage, the sur
face charge must be removed from plates. Turn head lights on for 15 seconds then allow up to 5 minutes
for voltage to stabilize. (2) Remove both battery cables, negative first.
(3) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts,
see instructions provided with voltmeter, mea sure open circuit voltage (Fig. 6). This voltage reading will indicate state of charge,
but will not reveal cranking capacity. Refer to Bat
tery Open Circuit Voltage chart.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
Open
Circuit
Volts
Percent
Chang©
11.7
volts
or
less
0%
12.0 25%
12.2 50%
12.4 75%
12.6
or more 100%
918A-3
Page 334 of 1502

•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 13 GENERATOR TEST PROCEDURES ON
VEHICLE
INDEX
page
Current
Output
Test
......................
14
Diagnostic Procedures
13
General
Information
13
Generator
Output
Wire Resistance Test
.......
13
page
How
to
Use
Malfunction
Indicator
(Check Engine) Lamp
for
Fault
Codes
17
Operational Check
with
Voltmeter
............
13
Using
On-Board Diagnostic System
15
GENERAL
INFORMATION
The generator
is
belt-driven
by the
engine.
All en
gines
use
serpentine drive. The amount
of DC
current produced
by the
gener
ator
is
controlled
by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
All vehicles
are
equipped with
On
Board Diagnos
tics (OBD).
All OBD
sensing systems
are
monitored
by
the PCM. The PCM
will store
in
electronic mem ory
any
detectable failure within
the
monitored cir
cuits.
Refer
to
USING ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
in
this group
for
more information.
OPERATIONAL CHECK
WITH
VOLTMETER
When
the
ignition switch
is
turned
to the RUN po
sition, battery potential will register
on the
voltme
ter. During engine cranking
a
lower voltage will appear
on the
meter. With
the
engine running,
a
voltage reading higher than
the
first reading (igni
tion
in RUN)
should register.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
If
the
indicator does
not
operate properly,
or if an
undercharged
or
overcharged battery condition
oc
curs,
the
following procedures
may be
used
to
diag
nose
the
charging system. Remember that
an
undercharged battery
is
often
caused
by:
• accessories being left
on
overnight
•
or by a
defective switch which allows
a
bulb, such
as a
trunk
or
glove
box
light,
to
stay
on
(refer
to
Ignition
Off
Draw).
WISUAL
INSPECTION
• Inspect condition
of
battery cable terminals, bat
tery posts, connections
at
engine block, starter motor solenoid
and
relay. They should
be
clean
and
tight.
Repair
as
required.
• Inspect
all
fuses
in the
fuse block
for
tightness
in
receptacles. They should
be
properly installed
and
tight. Repair
or
replace
as
required.
• Inspect generator mounting bolts
for
tightness.
Re
place
or
torque bolt
as
required (refer
to
Torque Specifications).
• Inspect generator drive belt condition
and
tension.
Tension
or
replace belt
as
required. Refer
to
Belt
Tension Specifications. • Inspect connection
at
generator
B+
output.
It
should
be
clean
and
tight. Repair
as
required.
GENERATOR
OUTPUT
WIRE RESISTANCE TEST
(FIG.
1)
Generator output wire resistance test will show
amount
of
voltage drop across generator output wire
between generator
BAT
terminal
and
battery posi tive post.
PREPARATION
(1) Before starting test make sure vehicle
has a
fully charged battery. Test
and
procedures
on how to
check
for a
fully charged battery
are
shown
in
Bat
tery section
of
this Group.
(2) Turn
OFF
ignition switch.
(3)
Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4)
Disconnect generator output wire from genera
tor output Battery terminal. (5) Connect
a 0-150
ampere scale
D.C.
ammeter
in
series between generator
BAT
terminal
and
discon
nected generator output wire. Connect Positive lead
to generator
BAT
terminal
and
Negative lead
to
dis connected generator output wire. (6) Connect Positive lead
of a
test voltmeter
(Range
0-18
volts minimum)
to
disconnected genera
tor output wire. Connect negative lead
of
test voltme
ter
to
battery positive cable
at
positive post. (7) Connect
one end of a
Jumper Wire
to
ground
and with other
end
probe green
K20
lead wire
at
back
of
generator
(Fig. 1).
(This will generate
a
fault
code).
CAUTION:
Do not
connect blue
A142
lead
of
wiring
to ground. Refer
to
Group
8W
-
Wiring Diagrams
for
more information.
(8) Connect
an
engine tachometer
and
connect neg
ative cable
to
battery.
(9) Connect
a
variable carbon pile rheostat
be
tween battery terminals.
Be
sure carbon pile
is in
"Open"
or "Off
position before connecting leads.
See
Battery Section, Load Testing
for
instructions.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting,
re
duce engine speed
to
idle.
Page 387 of 1502

8E
- 6
INSTRUMENT PANEL
AND
GAUGES
•
(5)
Clip float arm of sending unit to its empty stop
(Fig. 2) and turn ignition key to ON position. The
gauge should read Empty, plus one pointer width, or
minus two pointer widths.
(6) Move and clip sending unit float arm to full
stop.
The gauge should read Full, or above.
Fig. 2 Fuel Tank Sending Unit Test
RESULTS (1) If fuel gauge does not meet specifications, check
following items as possible causes; (a) Wiring and connections between the gauge
sending unit and multiple connector. (b) Wiring and connections between multiple
connector and printed circuit board terminals.
(c) Circuit continuity between printed circuit
board terminals and gauge terminals.
If these items check okay, fuel gauge is defective
and must be replaced.
(2) If the fuel gauge meets specifications check fuel
tank and original installed fuel tank sending unit as follows:
(a) Carefully remove fuel tank sending unit from
tank.
(b) Connect sending unit wire and jumper wire
as described in the procedure.
(3) If fuel gauge now checks within specifications,
originally installed sending unit is electrically okay,
check following as possible cause:
(a) Ground strap from sending unit to fuel line
for continuity. (b) Sending unit deformed. Make sure sending
unit float arm moves freely and pick up tube is not
bent so that it contacts bottom of tank. Inspect float for any signs of damage or leaks. (c) Sending unit improperly installed. Install
properly.
(d) Mounting flange on fuel tank for sending
unit deformed. Feel for interference fit of sending
unit to bottom of tank. It is permissible to bend
pick up tube down a little near mounting flange to gain interference fit.
(e) Fuel tank bottom deformed causing improper
positioning of sending unit pick up tube. Replace or
repair tank and recheck sending unit. Refer to Fuel
Tank Section of Group 14 - Fuel System.
WARNING
LAMP
SYSTEM
TESTS
LOW
OH.
PRESSURE WARNING LAMP CIRCUIT
TEST
The low oil pressure warning lamp will illuminate
when the ignition key is turned to the ON position.
The lamp also illuminates if the engine oil pressure drops below a safe oil pressure level.
To test the system turn ignition key to the ON po
sition.
If the lamp fails to light, inspect for a broken or
disconnected wire at the oil pressure combination
unit. The combination unit is located at the rear of
the engine (Fig. 3). If the wire at the connector checks good, pull connector loose from the switch and
with a jumper wire ground connector to the engine (Fig. 4). With the ignition key turned to the ON po
sition check the warning lamp. If lamp still fails to
light, inspect for a burned out bulb or disconnected
socket in the cluster.
If light comes on, proceed and start engine. If the
lamp remains on, immediately turn engine off and
check engine oil pressure according to procedures as
outlined in Group 9 - Engine of this manual. If the
oil pressure meets specifications, check for a
grounded wire and/or replace the oil pressure send
ing unit (refer to combination oil unit test). Fig. 3 Oil Pressure Sending Unit—Gas Engine
Page 388 of 1502
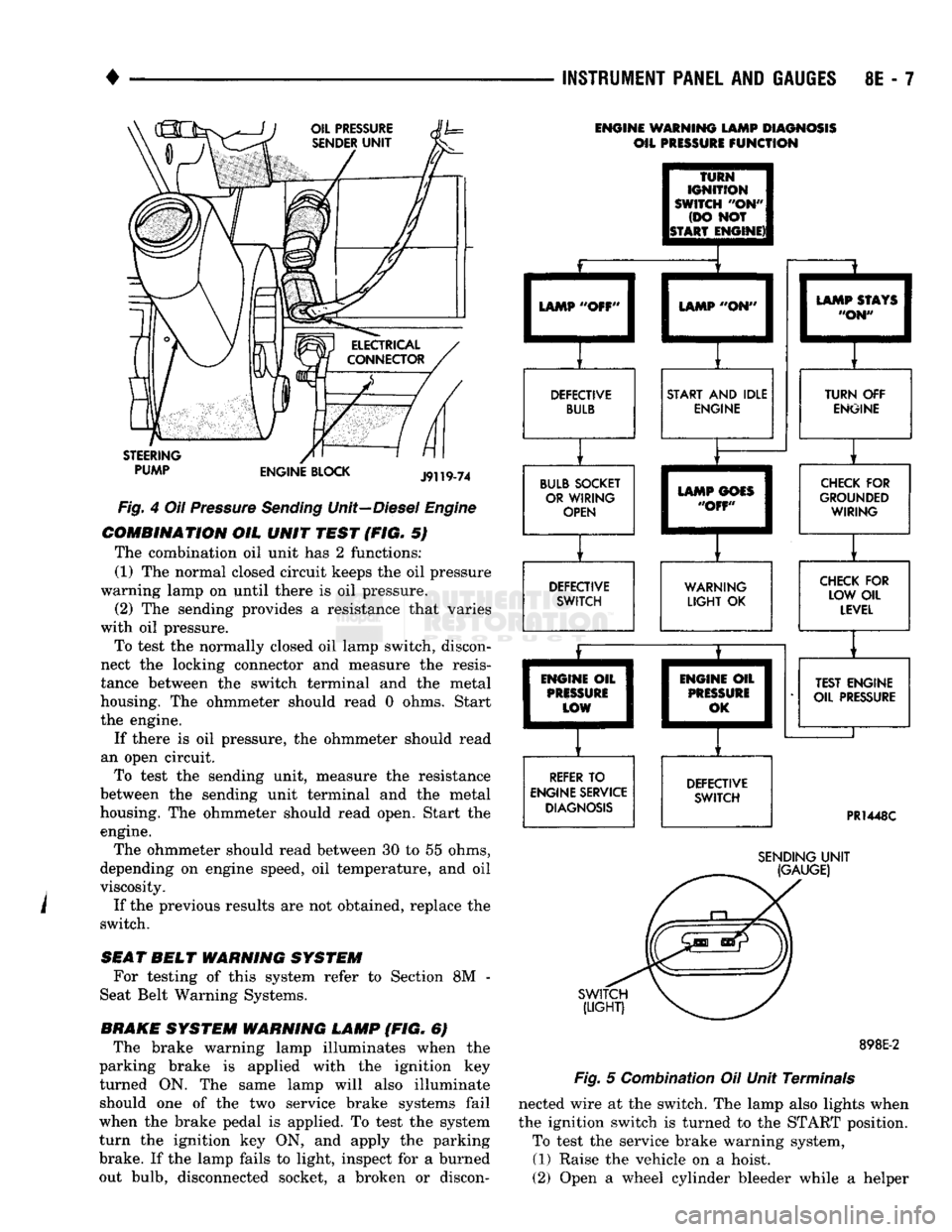
•
INSTRUMENT
PANEL
AND
GAUGES
8E - 7
STEERING PUMP
ENGINE
BLOCK
J9U9-74
Fig.
4 Oil
Pressure
Sending
Unit—Diesel
Engine
COMBINATION
OIL
UNIT
TEST
(FIG. 5)
The combination oil unit has 2 functions:
(1) The normal closed circuit keeps the oil pressure
warning lamp on until there is oil pressure. (2) The sending provides a resistance that varies
with oil pressure.
To test the normally closed oil lamp switch, discon
nect the locking connector and measure the resis
tance between the switch terminal and the metal
housing. The ohmmeter should read 0 ohms. Start
the engine.
If there is oil pressure, the ohmmeter should read
an open circuit. To test the sending unit, measure the resistance
between the sending unit terminal and the metal
housing. The ohmmeter should read open, Start the engine.
The ohmmeter should read between 30 to 55 ohms,
depending on engine speed, oil temperature, and oil
viscosity.
If the previous results are not obtained, replace the
switch.
SEAT
BELT
WARNING
SYSTEM
For testing of this system refer to Section 8M -
Seat Belt Warning Systems.
BRAKE
SYSTEM
WARNING
LAMP
(FIG. 6) The brake warning lamp illuminates when the
parking brake is applied with the ignition key
turned ON. The same lamp will also illuminate should one of the two service brake systems fail
when the brake pedal is applied. To test the system
turn the ignition key ON, and apply the parking
brake. If the lamp fails to light, inspect for a burned
out bulb, disconnected socket, a broken or discon-
ENGINE WARNING LAMP DIAGNOSIS
OIL PRESSURE
FUNCTION
TURN
IGNITION
SWITCH
"OH"
(DO NOT
ISTART ENGINE)! LAMP "OFF'
LAMP "ON"
DEFECTIVE BULB START AND IDLE
ENGINE
BULB SOCKET OR WIRING OPEN LAMP STAYS
"ON" TURN OFF
ENGINE LAMP GOES
"OFF" DEFECTIVE
SWITCH CHECK FOR
GROUNDED WIRING
WARNING
LIGHT
OK CHECK FOR
LOW OIL LEVEL
ENGINE OIL
PRISSURi
LOW
REFER TO
ENGINE SERVICE DIAGNOSIS ENGIM
PRES
0
IE OIL
1
SURE
1
,K I
DEFECTIVE SWITCH TEST ENGINE
OIL PRESSURE
PR1448C
SWITCH
(LIGHT)
SENDING
UNIT
(GAUGE)
898E-2
Fig.
5 Combination Oil Unit Terminals
nected wire at the switch. The lamp also lights when
the ignition switch is turned to the START position. To test the service brake warning system,
(1) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(2) Open a wheel cylinder bleeder while a helper
Page 389 of 1502
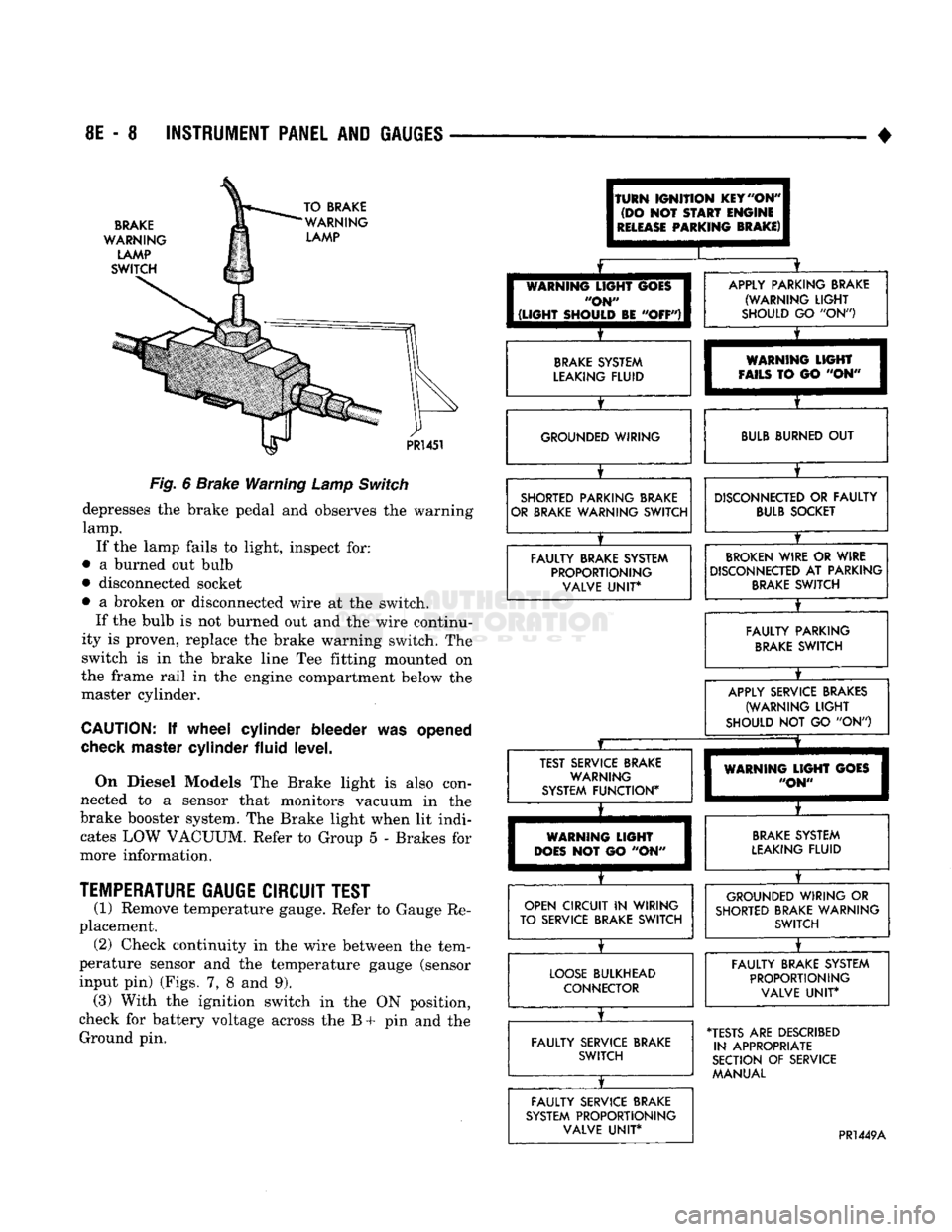
8E
- 8 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGES
•
BRAKE
WARNING
LAMP
SWITCH TO BRAKE
WARNING LAMP
PR!
451
Fig.
6
Brake Warning
Lamp
Switch
depresses
the
brake pedal
and
observes
the
warning
lamp.
If
the
lamp fails
to
light, inspect
for:
•
a
burned
out
bulb
• disconnected socket
•
a
broken
or
disconnected wire
at the
switch. If
the
bulb
is not
burned
out and the
wire continu
ity
is
proven, replace
the
brake warning switch.
The
switch
is in the
brake line
Tee
fitting mounted
on
the frame rail
in the
engine compartment below
the
master cylinder.
CAUTION:
If
wheel cylinder bleeder
was
opened
check
master cylinder fluid level.
On Diesel Models
The
Brake light
is
also con
nected
to a
sensor that monitors vacuum
in the
brake booster system.
The
Brake light when
lit
indi cates
LOW
VACUUM. Refer
to
Group
5 -
Brakes
for
more information.
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE CIRCUIT TEST
(1) Remove temperature gauge. Refer
to
Gauge
Re
placement. (2) Check continuity
in the
wire between
the
tem
perature sensor
and the
temperature gauge (sensor
input
pin)
(Figs.
7, 8 and 9).
(3) With
the
ignition switch
in the ON
position,
check
for
battery voltage across
the B + pin and the
Ground
pin.
(TURN
IGNITION
KEY
"ON"
(DO
NOT
START
ENGINE
I
RELEASE
PARKING
BRAKE)
I
I
[
WARNING
LIGHT
GOES
I
"ON"
I
1
(LIGHT
SHOULD
BE
"OFF")!
X
APPLY PARKING BRAKE (WARNING
LIGHT
SHOULD
GO "ON")
BRAKE
SYSTEM
LEAKING FLUID
X
WARNING
LIGHT
FAILS
TO GO "ON" GROUNDED WIRING
BULB
BURNED
OUT
SHORTED PARKING BRAKE
OR BRAKE WARNING SWITCH
X
DISCONNECTED
OR
FAULTY
BULB
SOCKET
FAULTY BRAKE SYSTEM PROPORTIONING VALVE
UNIT*
BROKEN
WIRE
OR
WIRE
DISCONNECTED
AT
PARKING
BRAKE
SWITCH
X
FAULTY PARKING
BRAKE
SWITCH
X
APPLY SERVICE BRAKES
(WARNING
LIGHT
SHOULD
NOT GO "ON")
JZ
X
TEST SERVICE BRAKE WARNING
SYSTEM FUNCTION*
X
WARNING
LIGHT
GOES
"ON"
WARNING
LIGHT
DOES
NOT GO "ON"
BRAKE
SYSTEM
LEAKING FLUID
OPEN CIRCUIT
IN
WIRING
TO SERVICE BRAKE SWITCH
X
GROUNDED WIRING
OR
SHORTED BRAKE WARNING SWITCH
LOOSE
BULKHEAD CONNECTOR
X
FAULTY BRAKE SYSTEM
PROPORTIONING VALVE
UNIT*
FAULTY SERVICE BRAKE SWITCH
X
•TESTS
ARE
DESCRIBED
IN APPROPRIATE
SECTION
OF
SERVICE MANUAL
FAULTY SERVICE BRAKE
SYSTEM PROPORTIONING VALVE
UNIT*
PR1449A
Page 393 of 1502

8E
- 12
INSTRUMENT PANEL
AND
GAUGES
•
CLUSTER AND GAUGE
SERVICE
PROCEDURES
INDEX
page
Cluster Bezel
12
Cluster
Mask
and
Lens
12
Fuel Gauge
13
Instrument
Cluster Assembly
12
Lamp Bulb Replacement—Message Center
..... 15
CLUSTER
BEZEL
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Tape
or
cover steering column
to
prevent dam
age
to
paint.
(3) Remove
2
screws and remove map lamp.
CAUTION:
Map
lamp must
be
removed
to
prevent
damage
to
instrument panel.
(4) Remove
6
screws which attach cluster bezel
to
base panel (Fig.
1).
Make sure
the
screw below
the
Heater-A/C control
is
removed.
(5)
Place column shift lever
in
Position
"1".
(6) Remove bezel
by
pulling
top
edge rearward
to
clear brow. Disengage attaching clips around bottom
of bezel
and
complete removal
of
bezel.
(7)
If
bezel
is
equipped with
a
four wheel drive
in
dicator, remove bulb socket
as
bezel
is
removed.
(8) Disconnect message center wires.
INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER BEZEL
J938E-51
Fig.
1 instrument
Cluster
Bezel
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect bulb socket
for
four wheel drive indi
cator
if
equipped.
(2)
Connect message center wires.
(3) Engage attaching clips around bottom
of
bezel,
roll bezel into position.
(4) Install
6
mounting screws. page
Lamp Bulbs
. . 15
Printed
Circuit
Board
13
PRND21
Indicator
. 15
Specifications
15
Speedometer/Odometer
14
(5)
Install map lamp.
(6) Remove tape from steering column.
(7) Connect negative cable
to
battery.
CLUSTER
MASK AND LENS REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove cluster bezel.
(3) Remove
8
screws holding mask
and
lens.
(4) Remove mask
and
lens.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position mask
and
lens.
(2) Install
8
screws.
(3) Install cluster bezel.
(4) Connect negative cable
to
battery.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER ASSEMBLY
(Fig.
2)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Tape
or
cover steering column
to
prevent dam
age
to
paint.
(3) Remove bezel.
(4) Remove lower steering column cover
4
screws.
(5)
Spread upper steering column cover
out of
the
locking tangs
and
slide downward. (6) Disconnect PRND21 actuator cable from steer
ing column
if
equipped.
(7) Loosen heater
and
A/C control. Pull rearward
to clear forward mount
on
cluster housing.
(8) Remove
6
screws that retain cluster. Pull clus
ter rearward
and
disconnect
2
large connectors.
(9) Remove cluster.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect
2
large connectors
to
cluster.
(2) Position cluster
to
instrument panel and install
6 retaining screws.
(3) Install heater A/C control.
(4) Connect PRND21 actuator
to
steering column
if
equipped.
(5)
Position upper steering column cover
and
slide
upward until tangs snap into place.
Page 396 of 1502

•
INSTRUMENT PANEL
AND
GAUGES
8E - 15
PRND21 INDICATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove bezel. Refer to Cluster Bezel Removal.
(2)
Remove cluster mask and lens. Refer to Cluster
Mask and Lens Removal. (3) Remove cluster assembly. Refer to Instrument
Cluster Removal. (4) Remove screws attaching PRND21 mechanism
to cluster housing.
(5)
Remove PRND21 mechanism.
INSTALLATION (1) Position PRND21 mechanism to cluster hous
ing. (2) Install mounting screws.
(3)
Install cluster assembly. (4) Install mask-lens.
(5)
Install bezel.
LAMP BULBS
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION LAMPS TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR LAMPS
LOW OIL PRESSURE INDICATOR LAMP
HIGH BEAM INDICATOR LAMP CHECK ENGINE LAMP
SEAT BELT WARNING LAMP
REMOVAL (1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove instrument cluster. See cluster re
moval.
(3)
Twist lamp socket assembly and remove from
printed circuit board. (4) Remove bulb from socket.
INSTALLATION (1) Install bulb into socket.
(2) Install socket assembly into printed circuit
board.
(3)
Position cluster into place in panel. See cluster
installation. (4) Connect battery negative cable.
LAMP BULB REPLACEMENT—MESSAGE CENTER
REMOVAL (1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument cluster bezel assembly. Re
fer to Instrument Cluster removal.
(3)
Twist lamp socket assembly and remove from
printed circuit board. (4) Remove bulb from socket.
INSTALLATION (1) Install bulb into socket assembly. (2) Install lamp socket assembly into printed cir
cuit board.
(3)
Install Instrument Cluster bezel assembly to
instrument panel. Refer to Instrument Cluster instal
lation.
(4) Connect negative cable from battery.
FOUR WHEEL DRIVE INDICATOR LAMP (1) Pull bulb and socket assembly from rear of
housing. (2) Remove bulb from socket.
(3)
Reverse removal procedures to install.
SPECIFICATIONS
Fuel
Gauge Calibration
Mntar Position Resistance
Empty Graduation 90
ohms
± 3
ohms
Empty Stop
Greater
than
96.5 ohms
Full
Graduation 12 ohm
± 3
ohms
Full
Stop
Less
than
8
ohms
1/2
45.3 ohms
± 3
ohms
Temperature
Gauge
Calibration
Pointer
Position Resistance
Cold Graduation 655 ohms
Hot Graduation 64 ohms
Oil Pressure Gauge Calibration
Pointer
Position Resistance
Low Graduation 100 ohms
High Graduation 12 ohms
J908E-58
Page 397 of 1502

8E - 16 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGES
• SWITCH AND
PANEL
COMPONENT
SERVICE
INDEX
page
Ash
Tray
20
Cigar
Lighter
........................ 20
Four
Wheel Drive
Indicator
19
Fuse
Block
and
Flashers
................... 19
Glove
Box 21
Heater A/C Control
17
page
Heater Control
16
Hood
Release
19
Illumination
Bulb Replacement
22
Message
Center Module
................... 18
Steering Column Lowering
and
Raising
16
Switches
17
DISCONNECT NEGATIVE CABLE FEOM
BATTERY IN ENGINE COMPAETMENT BE FORE SERVICING INSTRUMENT PANEL.
STEERING COLUMN LOWERING AND RAISING When servicing the instrument panel and the Low
ering and Raising of the steering column is required,
the following is the procedure for doing so: This procedure is not for removing and replac
ing the steering column. Refer to Group - 19 Steering of this manual for the removal and re
placement procedures.
LOWERING STEERING COLUMN
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2)
Remove 3 toe plate nuts and washers (Fig. 1).
(3) Remove 1 toe plate screw.
(4) Remove 4 screws attaching lower steering col
umn cover and remove cover. The fuse block is at
tached to this cover and should be supported when cover is removed.
(5) Spread upper steering column cover out of lock
ing tangs and slide downward.
(6)
Disconnect cable from shift indicator bracket.
(7)
Remove 2 nuts and washers attaching steering
column bracket to instrument panel steering column support bracket.
(8)
Allow column to lower and rest on seat.
STEERING
COLUMN SUPPORT
WASHER
AND NUT
Fig.
1 Steering
Column
Mounting
RAISING STEERING COLUMN
(1) Raise steering column assembly against the in
strument panel support bracket. (2) Install 2 steering column bracket washers and
nuts (Finger Tighten Only).
CAUTION:
Check that
all
wiring
is
clear
and not
pinched.
(3) Tighten the 2 bracket nuts to 12 Nnn-(110 in.
lbs.) torque. (4) Slide toe plate into position, install attaching
screw, tighten to 4 N®m (35 in. lbs.).
(5) Install toe plate nuts and washers and tighten
to 23 N*m (200 in. lbs.).
(6)
Connect cable to shift indicator bracket.
(7)
Position upper steering column cover and slide
upward until tangs snap into place.
(8) Install fuse block to cover.
(9)
Position lower steering column cover and in
stall 4 attaching screws.
HEATER CONTROL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove map lamp.
(2) Remove cluster bezel (refer to Cluster Bezel Re
moval). (3) Remove 2 control attaching screws. (4) Pull control rearward.
(5) Disconnect illumination lamp, and wire connec
tions.
(6)
Disconnect control cables.
(7)
Remove control.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position control near panel.
(2) Connect control cables to control (see Heater
A/C Section). (3) Connect illumination lamp, and wire connec
tors.
(4) Push control into panel.
(5) Install 2 control mounting screws.
(6)
Install bezel.
(7)
Install map lamp.