manual transmission FORD FIESTA 2007 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2007, Model line: FIESTA, Model: FORD FIESTA 2007Pages: 1226, PDF Size: 61.26 MB
Page 58 of 1226

100-04-2 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH)
Noise, vibration and harshness (NVH) is becoming
more important as vehicles become more '
Know the History of the Condition
sophisticated and passenger comfort levels
increase. This section is designed to aid in the
- Did it start suddenly or appear gradually?
diagnosis and testing and repair of NVH concerns.
- Was it related to some other occurrence such
- Noise is defined as sounds not associated with
as a collision or previous part replacement?
the operation of passenger compartment
- Know how the condition made itself known; it
equipment that interface with customer
may be an important clue to the cause.
satisfaction.
- Vibration is defined as impulses felt by the
customer that are not caused by road surface Know the Probability of Certain
changes. Conditions Develop~ng
- Harshness is a ride quality issue where the - Look for the simple rather than the complex.
customer feels that the vehicle response to the
road surface is sharply transmitted to the
- For example:
customer.
- Electrical conditions usually occur at
connections rather than components.
Diagnostic Theory - An engine no-start is more likely to be caused
by a loose wire or small adjustment rather
than a sheared-off
camshafi. Diagnosis is more than just following a series of
interrelated steps in order to find the solution to the - Know the difference between impossible and
specific condition. It is a way of looking at systems improbable. Certain failures
in a system can be
that are not functioning the way they should and improbable
but still happen.
finding out why. Also it is knowing how the system
- New parts are just that, new. It does not mean
should work and whether it is working correctly. they are always
good functioning parts.
There are basic rules for diagnosis. If these rules
are followed, the cause of the condition is usually
Do Not Cure the Symptom and Leave
found the first time through the system. the Cause
Know the System
- Know how the parts go together. Lowering
the pressure in a front tire may correct
the condition of a vehicle leaning to one side, but
it does not correct the original condition.
- Know how the system operates as well as its
limits and what happens when the system goes
Be Positive the Cause is Found
wrong.
- Sometimes this means checking the system - Double check findings.
against one that is known to be working
- What caused a worn component?
correctly.
- A loose transmission or engine mount could
indicate that other mounts are also loose.
Know the History of the System
Diagnostic Charts
A clue in any one of these areas may save time:
- How old or new is the system? Charts are a simple
way of expressing the
relationship between basic logic and a physical
- What kind of treatment has it had?
system of components. They help discover the ,.
- Has it been serviced in the past in such a
cause of a condition in the least time. Diagnostic (,-
manner that might relate to the present
charts combine many areas of diagnosis into one
condition? visual display:
- What is the service history?
2006.0 Fiesta 12/2006 G28448en
procarmanuals.com
Page 60 of 1226

100-04-4 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-0414
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH)
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern. Identify the Condition
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical NVH usually occur in four areas:
or electrical damage.
tires
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported
concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) engine accessories
before proceeding to the next step.
suspension
4. If the concern is not visually evident, verify the
symptom and REFER to the Symptom Chart.
How to Use this Diagnostic Procedure
Section
Noise, vibration and harshness (NVH) concerns
have become more important as
vehjcles have
become more sensitive to these vibrations. This
section is designed to aid in identifying these
concerns.
The section provides diagnostic procedures based on symptom. If the condition occurs at
high speed, for instance, the most likely place
to start is under Shake and Vibration While
Driving.
The road test procedure will tell how to sort the
conditions into categories and how to tell a
vibration from a shake.
A series of Road Test Quick Checks are
provided to make sure that a cause is either
pinpointed or eliminated.
Name the condition, proceed to the appropriate
section and locate the correct diagnosis. When
the condition is identified, the job is partly done.
Follow the diagnostic procedure as outlined.
Quick Checks are described within the step,
while more involved tests and adjustments are
outlined in General Procedures.
Always follow each step exactly and make notes
to recall important findings later.
driveline
It is important, therefore, that an NVH concern be
isolated into its specific
area(s) as soon as
possible. The easiest and quickest way to do this
is to carry out the Road Test as outlined. To assist
in the diagnosis and testing
procedure(s), use a
suitable approved NVH diagnosis tester.
Noise Diagnostic Procedure
Non-Axle Noise
The five most common sources of non-axle noise
are exhaust, tires, roof racks, trim panels and
( transmission.
Therefore, make sure that none of the following
conditions are the cause of the noise before
proceeding with a driveline
teardown and
diagnosis.
In certain conditions, the pitch of the exhaust
may sound very much like gear noise. At other
times, it can be mistaken for a wheel bearing
rumble.
Tires, especially snow tires, can have a high
pitched tread whine or roar, similar to gear
noise. Radial tires may have this characteristic.
Also, any non-standard tire with an unusual
tread construction may emit a roar or whine
noise.
Trim panels can also cause whistling or whining
noise.
Clunk may be a metallic noise heard when the
Customer Interview automatic transaxle is engaged in "R
(REVERSE) or "D" (DRIVE) or it may occur
The road test and customer interview (if available) when
the throttle is applied or released. It is
provide information that will help identify the caused
by backlash somewhere in the driveline.
,
concern and will provide direction to the correct Bearing rumble sounds like marbles being
starting point for diagnosis. (
tumbled. This condition is usually caused by a
damaged wheel bearing.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
procarmanuals.com
Page 61 of 1226

100-04-5 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Noise Conditions
Gear noise is typically a howling or whining due
to gear damage or incorrect bearing preload. It
can occur at various speeds and driving
conditions, or it can be continuous.
Chuckle is a particular rattling noise that sounds
like a stick against the spokes of a spinning
bicycle wheel. It occurs while decelerating from
64
kmlh (40 mph) and can usually be heard all
the way to a stop. The frequency varies with
vehicle speed.
Knock is very similar to chuckle, though it may
be louder and occurs on acceleration or
deceleration. The
teardown will disclose what
has to be corrected.
Clicking, popping or grinding noises may be caused
by the following:
worn, damaged or incorrectly installed wheel
bearing, suspension or brake component.
Check and rule out tires, exhaust and trim items
before disassembling the transmission to diagnose
and correct gear noise.
The noises described under Road Test usually
( have specific causes that can be diagnosed by
observation as the unit is disassembled. The initial
clues are the type of noise heard on the road test
and driving conditions.
Vibration Conditions
Vibration at highway speeds may be caused by
the following:
out-of-balance front or rear wheels.
out-of-round tires.
Shudder or vibration during acceleration may be
caused by the following:
damaged powertrainldrivetrain mounts.
excessively high constant velocity (CV) joint
operating angles caused by incorrect ride height.
Check ride height, verify correct spring rate and
check items under inoperative conditions.
Road Test
I A gear-driven unit will produce a certain amount
of noise. Some noise is acceptable and may be
audible at certain speeds or under various driving conditions,
as on a newly paved asphalt road. The
slight noise is in no way detrimental and must be
considered normal.
The road test and customer interview (if available)
provide information needed to identify the condition
-
and give direction to the correct starting point for
diagnosis.
1. Make notes throughout the diagnosis routine.
Make sure to write down even the smallest bit
of information, because it may turn out to be the
most important.
2. Do not touch anything until a road test and a
thorough visual inspection of the vehicle have been carried out. Leave the tire pressures and
vehicle load just where they were when the
condition was first observed. Adjusting tire
pressures, vehicle load or making other
adjustments may reduce the
condition(s)
intensity to a point where it cannot be identified
clearly. It may also inject something new into
the system, preventing correct diagnosis.
3. Make a visual inspection as part of the
preliminary diagnosis routine, writing down
anything that does not look right. Note tire
pressures, but do not adjust them yet. Note
leaking fluids, loose nuts and bolts, or bright
spots where components may be rubbing
against each other. Check the load space for
unusual loads.
4. Road test the vehicle and define the condition
by reproducing it several times during the road
test.
5. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks as soon
as the condition is reproduced. This will identify
the correct diagnostic procedure. Carry out the
Road Test Quick Checks more than once to
verify they are providing a valid result.
Remember, the Road Test Quick Checks may
not tell where the concern is, but they will tell
where it is not.
Road Test Quick Checks
1. 24-80 kmlh (1 5-50 mph): with light acceleration,
a moaning noise is heard and possibly a
vibration felt in the front floor panel. It is usually
worse at a particular engine speed and at a
particular throttle setting during acceleration at
that speed. It may also produce a moaning
sound, depending on what component is
causing it. REFER to Tip-in Moan in the
Driveline Noise and Vibration Symptom Chart.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
procarmanuals.com
Page 62 of 1226

100-04-6 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
2. AccelerationIDeceleration: With slow
acceleration and deceleration, a shake is
sometimes noticed in the steering
wheellcolumn,
seats, front floor panel, front door trim panel or
front end sheet metal. It is a low frequency
vibration (around
9-1 5 cycles per second). It
may or may not be increased by applying the
brakes lightly. REFER to
Idle
BoomIShakeNibration in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
High Speed: A vibration is felt in the front floor
panel or seats with no visible shake, but with
an accompanying sound or rumble, buzz, hum,
drone or booming noise. Coast with the clutch
pedal depressed (manual transmission) or shift
control selector lever in "N" (NEUTRAL)
(automatic transmission) and engine idling. If
vibration is still evident, it may be related to
wheels, tires, front brake discs, wheel hubs or
front wheel bearings. REFER to Shake and
Vibration While Driving in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
4. Engine rpm Sensitive: A vibration is felt
whenever the engine reaches a particular rpm.
It will disappear in neutral coasts. The vibration
can be duplicated by operating the engine at
the problem rpm while the vehicle is stationary.
It can be caused by any component, from the
accessory drive belt to the clutch or torque
converter which turns at engine speed when the
vehicle is stopped. REFER to Shake and
Vibration While Driving in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
5. Noise and Vibration While Turning: Clicking,
popping or grinding noises may be due to the
following:
worn, damaged or incorrectly installed front
wheel bearing.
damaged
powertrainldrivetrain mounts.
Road Conditions
An experienced technician will always establish a
route that will be used for all NVH diagnosis road
tests. The road selected should be reasonably
smooth, level and free of undulations (unless a
particular condition needs to be identified). A
smooth asphalt road that allows driving over a
range of speeds is best. Gravel or bumpy roads
are unsuitable because of the additional road noise produced.
Once the route is established and
consistently used, the road noise variable is
eliminated from the test results.
N0TE:Some concerns may be apparent only on
smooth asphalt roads.
If a customer complains of a noise or vibration on
a particular road and only on a particular road, the
source of the concern may be the road surface. If
possible, try to test the vehicle on the same type
of road.
Vehicle Preparation
Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the
vehicle before carrying out the road test. Note
anything which is unusual. Do not repair or adjust
any condition until the road test is carried out,
unless the vehicle is inoperative or the condition
could pose a hazard to the technician. After
verifying that the condition has been corrected,
make sure all components removed have been
installed.
Power Steering Conditions
c !
Check for the noise in the following conditions to
verify the customer concern.
Check for the noise in several temperature
conditions.
Is the noise from when the vehicle was new?
Can the noise be repeated constantly or is it
random?
Check the condition of the vehicle age, mileage
and service record.
Interview the customer to find the operating
condition in which the noise will occur. Test the
vehicle based on the
detail(s) from the customer
interview.
Follow the power steering operation noise
condition tables below, to find which condition
the noise will occur.
Power Steering Operation Noise Check
Step 1 : Check for NVH concerns from non-steering
components, which may sound like noises coming
from the steering system.
I:. ':
2006.0 Fiesta 121zoo6 G37349en
procarmanuals.com
Page 65 of 1226

100-04-9 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 1 00-04-9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Step 3: According to each identified operating
condition (Column A, B,
C, D, E, F), check each
possible Steering System
NVH concern with the
detail symptom charts below.
Before conducting a vehicle test to identify a
NVH
concern carry out the following checks.
1. Check the tire pressures and adjust to
specification, as necessary.
2. Make sure the steering system fluid is correct,
the system is free of leaks and is operating
correctly.
3. Make sure the vehicle steering system
temperature is the same as described at the
customer interview.
4. All evaluations must take place in a relatively
quiet location.
5. The heating
- air conditioning (AIC) fan and
radio must be turned off during evaluations and
the windows closed.
Symptom Chart
Power Steering Moan Noise
Test Condition
Listen for steering moan noise with the vehicle
parked, transmission in neutral and all windows
closed in the following test conditions.
1. Engine speed at idle with no steering action.
2. Engine speed at idle with slow 90 degrees per
second turning of the steering wheel.
3. Engine speed at 1250 +I- 50 rpm with no
steering action.
4. Engine speed at 1250 +I- 50 rpm with slow 90
degrees per second turning of the steering
wheel.
2006.0 Fiesta 12/2006 G37349en
procarmanuals.com
Page 66 of 1226
100-04-1 0 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Power Steering Whine Noise 2. Engine speed at 1800 +/- 50 rpm with slow 90
degrees turning of the steering wheel.
Test Condition 3. Engine speed at 3000 +I- 50 rpm with no
Listen for steering whine noise with the vehicle steering action.
parked, transmission in neutral and all windows
4. Engine speed at 3000
+I- 50 rpm with slow 90
closed in the following test conditions. degrees turning of the steering wheel.
1. Engine speed at 1800
+I- 50 rpm with no
steering action. Symptom
Power steering system moan
noise
- A continuous low pitched
humming noise occurs when the
steering wheel is turned and the
steering system is loaded. Noise
frequency changes with engine
rpm changes. Particularly
annoying at lower engine speed.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
Possible Sources
Power steering lines.
Incorrect power steering fluid.
Power steering pump. Action
CHECK
the routing of the
power steering lines.
CHECK the power steering line
clamps are secure.
CHECK the power steering
lines for clearance from the
vehicle body, front axle cross-
member and steering gear.
FLUSH the power steering
system. REFER to: (21 1-00
)
Power Steering System
Flushing
- I .8L Duratec-HE
(M14)/1.8L Duratec-SCi
(M14)/2.OL Duratec-HE (M14)
(General Procedures),
Power Steering System
Flushing
- 3.OL Duratec-SE
(VE6)/2.5L Duratec-VE
(VE6)/3.OL Duratec-ST (VE6)
(General Procedures),
Power Steering System
Flushing
- 2.OL Duratorq-
DirrDDi (Puma) Diesel12.0L
Duratorq-TDCi (Puma)
Diesell2.2L Duratorq-TDCi
(Puma) Diesel (General
Procedures).
Pressure pulses from the power
steering pump. Certain amount of
noise level acceptable, not a
safety critical item.
procarmanuals.com
Page 68 of 1226
I 00-04-1 2 Noise, Vibration and Harshness I 00=04m12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Power Steering Hiss Noise
Test Condition
Listen for steering hiss noise with the vehicle
parked, transmission in neutral and all windows
-
closed in the following test conditions.
Power Steering Lock Stop Impact Knock 1. Turn the steering wheel to the left-hand and
Noise right-hand steering locks and listen for the
impact noise.
Test Condition
Listen for steering knock noise with the engine
speed at idle in the following test conditions (noise
also apparent with engine off).
Action
CHECK the installation and
potential damage of the floor seal.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Symptom
N0TE:Engine speed at idle
turning the steering wheel slowly
lock to lock.
Power steering system hiss noise
- a high frequency, continuous
rush or swish noise like escaping
air from a balloon. Hiss occurs
while turning between the steering
lock stops, all steering angles.
Noise does not change with
engine rpm and is worse at high
operating temperatures.
N0TE:Engine speed at idle
holding the steering wheel against
a steering lock for three seconds.
Do not hold for more than five
seconds.
Power steering system hiss noise
- a continuous noise like escaping
air occurs while holding the
steering against a steering lock
stop.
Possible Sources
Floor seal.
Power steering gear valve design.
Power steering system hydraulic
design.
Power pump pressure
relief valve.
Power Steering Mechanical Knock Noise 1. Turn the steering wheel 90 degrees to the right,
(PAS off) hold and then quickly release.
2. Turn the steering wheel 90 degrees to the left, Test Condition hold and then quickly release.
Listen for steering knock noise with the engine off
in the following test conditions (no power assist).
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
Action
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Symptom
Power steering system knock
noise
- a heavy loud sound like a
knock on a door that occurs in
parking condition when hitting the
lock stop.
Possible Sources
Power steering gear mechanical
noise, metal to metal at end of
steering travel.
procarmanuals.com
Page 70 of 1226
100-04-14 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Power Steering Column Knock Noise I. Drive over cobbled stones at low speed 16-40
kmlh (1 0-25 mph) with and without steering
Test Condition input carefully listening for knock sounds.
Symptom
Power steering system knock1
clonk noise - sounds almost
identical to column knock that
occurs when driving and cornering
over cobbled stones or rough
roads. Noise may appear to
emanate from a location closer to
the floor than that for column
knock (Sounds like metallic noise
but is created by pressure impulse
in gear and return line
- similar to
a sound like quickly turning off a
water tap).
Listen for steering knock noise in the following test 2. Drive over straight tar strips, road rails or 25 mm
conditions with windows closed. tall
harshness strips at low speed 16-40
kmlh
(10-25 mph) both driving straight and with
moderate cornering.
Possible Sources
Power steering return lines.
High power assist gain of power
steering gear valve (steering gear
design
- no quality issue).
High power steering pump
flow
rate (by design).
Power Steering Toc-Toc Noise 1. Turn the steering wheel from left to right abruptly
changing direction.
Test Condition 2. Drive the vehicle for low speed parking
Listen for steering
toc-toc noise with the engine manoeuvres constantly changing steering
speed at idle and the vehicle parked, automatic direction.
transmission in "P" (PARK) or manual transmission
in neutral and the windows closed.
Action
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Symptom
Power steering system column
knock noise
- a loose sounding
rattle or vibration coming from the
column. Noticeable by hearing
and touch.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
Possible Sources
Steering column or steering
column
Action
CHECK the steering column
retaining bolts and attachments
to the steering column and secure
if necessary.
REFER to: Specifications (21 1
-
04, Specifications).
Check steering column and inter- mediate shaft for free play or
loose components.
REFER to: Steering System (2 11
-
00, Diagnosis and Testing).
procarmanuals.com
Page 71 of 1226
100-04-15 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Power Steering Grinding Noise 1. Slowly turn the steering wheel from lock to lock.
Test Condition
Action
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Symptom
Power steering system toc-toc
noise - a metallic noise created
when changing direction of
steering wheel rotation during
parking manoeuvre or at stand-
still.
2. Tilt and extend the steering column in various
positions and slowly turn the steering wheel
Possible Sources
gear (design tolerance
in steering rack).
Listen for steering grinding noise with the engine from lock to lock.
speed at idle and the vehicle parked, automatic
transmission in "P" (PARK) or manual transmission
in neutral and the windows closed.
Power Steering Zip Noise
Symptom Possible Sources Action
Power steering system grinding
noise
- an abrasive noise (like
sand paper rubbing against wood)
occurs between moving compon-
ents such as steering wheel and
the steering column shroud.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
Steering wheel to shroud interfer-
ence.
Steering column bearing.
Foreign material in contact with
the steering column
shaft.
Clockspring.
Action
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical item.
BLEED the power steering
system.
REFER
to: Power Steering
System Bleeding
(21 1-00
Steering System
- General
Information, General Proced-
ures).
Symptom
Power steering system zip noise
- occurs when hydraulic fluid
does not flow freely through the
power steering pump supply hose
from steering fluid reservoir to
power steering
pump causing
cavitation
at the pump. Zip is
primarily a cold weather start-up
phenomenon (below -1 0°C). Certain amount
of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
Certain amount of noise level
acceptable, not a safety critical
item.
CHECK if floor covering is
obstructing the steering gear
pinion.
CHECK the installation of the floor
seal.
CHECK the clockspring and
secure if necessary.
REFER to: Clockspring (501
-208,
Removal and Installation).
Possible Sources
steering
Aeration of the power steering
fluid.
procarmanuals.com
Page 72 of 1226
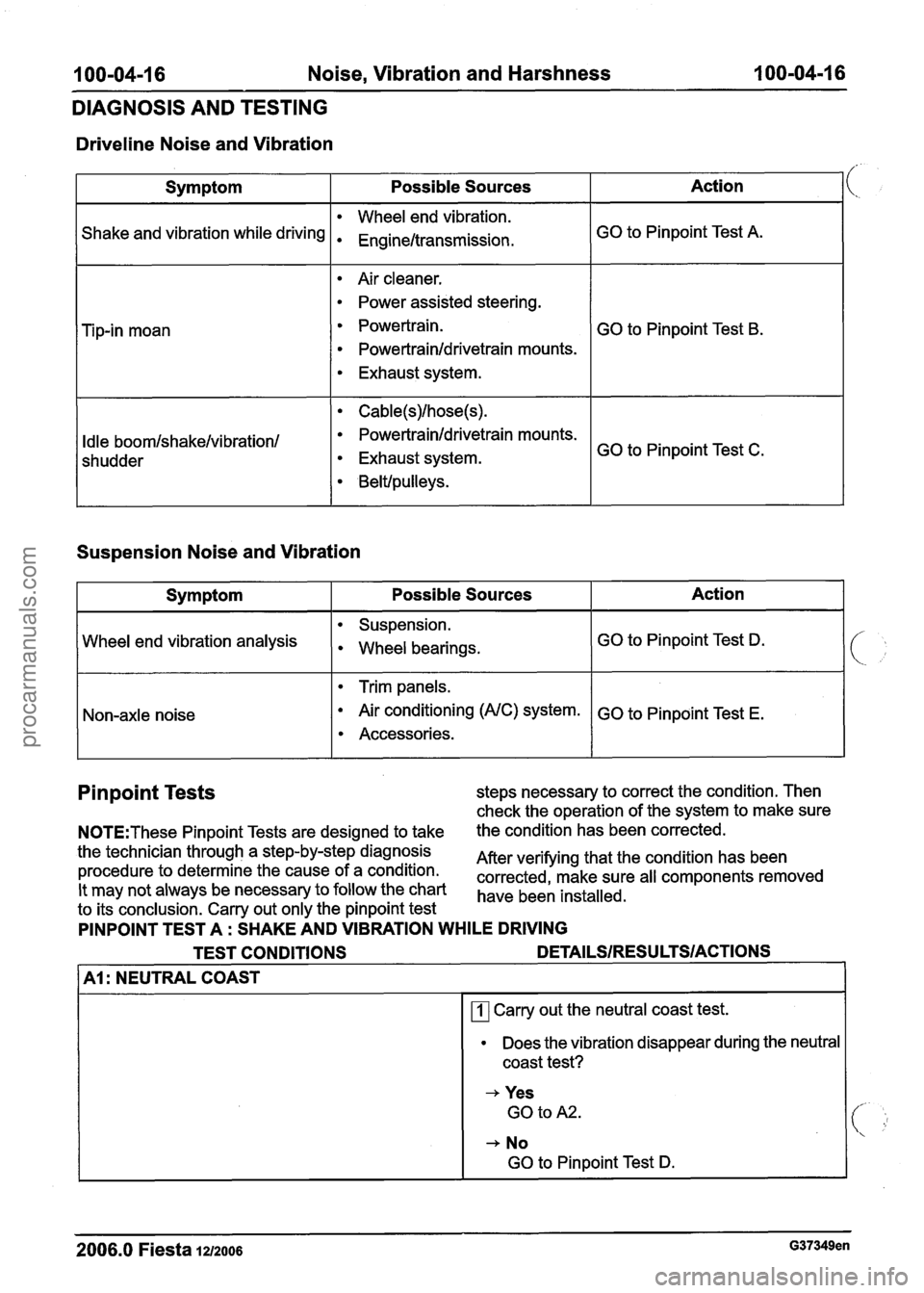
100-04-16 Noise, Vibration and Harshness 100-04-1 6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Driveline Noise and Vibration
Suspension Noise and Vibration
Action
GO to Pinpoint Test A.
GO to Pinpoint Test
B.
GO to Pinpoint Test C.
Symptom
Shake and vibration while driving
Tip-in moan
Idle boomlshake/vibration/
shudder
Pinpoint Tests steps necessary to correct the condition. Then
check the operation of the system to make sure
N0TE:These Pinpoint Tests are designed to take the
condition has been corrected.
the technician through
a step-by-step diagnosis ~fi~~ verifying that the condition has been procedure to determine the cause of a condition. corrected, make sure all components removed It may not always be necessary to follow the chart have been installed. to its conclusion. Carry out only the pinpoint test
PINPOINT TEST A : SHAKE AND VIBRATION WHILE DRIVING
TEST CONDITIONS
DETAILSIRESU LTSIACTIONS 1
Possible Sources
Wheel end vibration.
. Engine/transmissiOnm
Air cleaner.
Power assisted steering.
Powertrain.
Powertrainldrivetrain mounts.
Exhaust system.
Cable(s)lhose(s).
Powertrainldrivetrain mounts.
Exhaust system.
Belt/ pulleys.
I A1 : NEUTRAL COAST I
Action
GO to Pinpoint Test D.
GO to Pinpoint Test E,
Symptom
Wheel end vibration analysis
Nan-axle noise
Carry out the neutral coast test.
Does the vibration disappear during the neutral
coast test?
+ Yes
GO to A2.
+ No
GO to Pinpoint Test D.
Possible Sources
Suspension.
. Wheel bearings,
Trim panels.
Air conditioning (A/C) system.
Accessories.
- --
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G37349en
procarmanuals.com