key FORD GRANADA 1985 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: GRANADA, Model: FORD GRANADA 1985Pages: 255, PDF Size: 14.98 MB
Page 69 of 255

Other items
34Disconnect the throttle cable from the
operating lever and bracket.
35Disconnect the right-hand exhaust
downpipe from the manifold then remove the
starter motor, the oil filter, and disconnect the
left-hand exhaust downpipe, in that order.
Refer to Part A, Section 8, paragraphs 1 to 8
of this Chapter.
Cylinder head bolts on the V6 engine may
be conventional (hexagon-headed) or Torx
type. The appropriate Torx key will be needed
to deal with the latter.
Before dismantling the engine into its main
components, the following ancillaries can be
removed. The actual items removed, and the
sequence of removal, will depend on the work
to be done.
Distributor and bracket
Spark plugs
Inlet manifold and associated items
Exhaust manifolds
Clutch
Alternator and bracket
Oil pressure switch(see illustration) Temperature gauge sender
Engine bearer arms
Dipstick
If an oil cooler is fitted between the oil filter
and the block, remove it by disconnecting the
coolant hoses and unscrewing the central
sleeve. The cooler and seal can now be
removed. If the threaded bush is removed
from the block (it may come out with the
sleeve) it must be renewed.
The procedure is described for the engine in
the vehicle. With the engine removed, the
preliminary steps can be ignored.
2.8 litre engine
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the inlet manifold and associated
components.
3Unbolt the power steering pump, remove
the drivebelts and move the pump aside.
Support it by wiring it to adjacent
components.
4Remove the alternator and its bracket.
5Remove the three bolts which secure each
rocker shaft. Remove the shafts and
pushrods, keeping them in order so that they
can be refitted in the same locations.
6Unbolt the exhaust pipes from the
manifolds.
7Remove the spark plugs.8Slacken the cylinder head bolts half a turn at
a time, following the reverse sequence to that
used when tightening (see illustration 38.5).
Remove the bolts.
9Remove the cylinder heads. If they are
stuck, try to rock them free, or tap them with a
soft-faced hammer. Do nothit them directly
with a metal hammer, and do notlever in
between the joint faces.
10Recover the head gaskets.
2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
11Disconnect the battery and drain the
cooling system.
12Disconnect the radiator top hose and the
heater hose from the thermostat housing.
13Disconnect the air hoses from the throttle
valve housing (see illustration).
14Detach the two wiring plugs from the
airflow sensors (see illustrations).
15Pull the breather hose from the oil filler cap
(see illustration).
16Unclip the air cleaner cover and remove it
together with the airflow sensors and air hoses.
17Disconnect the hoses from the coolant
expansion tank.
18Disconnect the wiring from the following
components:
a)Alternator (right-hand cylinder head
removal only).
b)Coolant temperature sensors(see
illustration).
c)Idle speed control valve (see illustration).
d)Throttle valve potentiometer.
e)The fuel-injector wiring loom.8Cylinder heads - removal
7Ancillary components - removal
6Engine dismantling - general
2C•8V6 engines
7.1 The oil pressure switch is on the left-
hand side of the block
8.14b Throttle position sensor wiring plug
Vacuum nozzles arrowed
8.14a Front airflow sensor wiring plug
8.15 Oil filler breather hose (arrowed)8.18a Coolant temperature sensor location
8.13 Disconnecting the air hoses from the
throttle valve housing
procarmanuals.com
Page 71 of 255
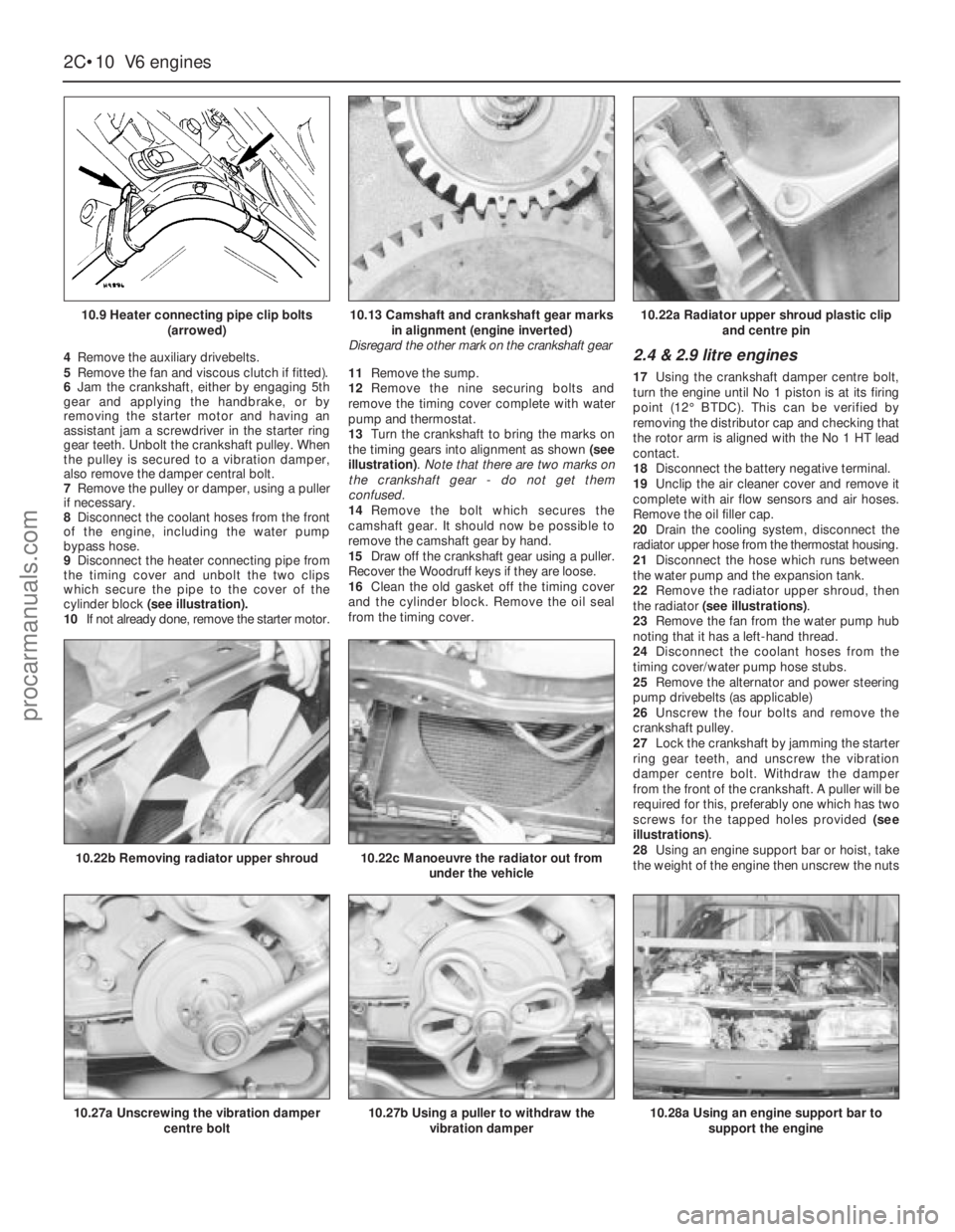
4Remove the auxiliary drivebelts.
5Remove the fan and viscous clutch if fitted).
6Jam the crankshaft, either by engaging 5th
gear and applying the handbrake, or by
removing the starter motor and having an
assistant jam a screwdriver in the starter ring
gear teeth. Unbolt the crankshaft pulley. When
the pulley is secured to a vibration damper,
also remove the damper central bolt.
7Remove the pulley or damper, using a puller
if necessary.
8Disconnect the coolant hoses from the front
of the engine, including the water pump
bypass hose.
9Disconnect the heater connecting pipe from
the timing cover and unbolt the two clips
which secure the pipe to the cover of the
cylinder block (see illustration).
10If not already done, remove the starter motor.11Remove the sump.
12Remove the nine securing bolts and
remove the timing cover complete with water
pump and thermostat.
13Turn the crankshaft to bring the marks on
the timing gears into alignment as shown (see
illustration). Note that there are two marks on
the crankshaft gear - do not get them
confused.
14Remove the bolt which secures the
camshaft gear. It should now be possible to
remove the camshaft gear by hand.
15Draw off the crankshaft gear using a puller.
Recover the Woodruff keys if they are loose.
16Clean the old gasket off the timing cover
and the cylinder block. Remove the oil seal
from the timing cover.2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
17Using the crankshaft damper centre bolt,
turn the engine until No 1 piston is at its firing
point (12°BTDC). This can be verified by
removing the distributor cap and checking that
the rotor arm is aligned with the No 1 HT lead
contact.
18Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
19Unclip the air cleaner cover and remove it
complete with air flow sensors and air hoses.
Remove the oil filler cap.
20Drain the cooling system, disconnect the
radiator upper hose from the thermostat housing.
21Disconnect the hose which runs between
the water pump and the expansion tank.
22Remove the radiator upper shroud, then
the radiator (see illustrations).
23Remove the fan from the water pump hub
noting that it has a left-hand thread.
24Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
timing cover/water pump hose stubs.
25Remove the alternator and power steering
pump drivebelts (as applicable)
26Unscrew the four bolts and remove the
crankshaft pulley.
27Lock the crankshaft by jamming the starter
ring gear teeth, and unscrew the vibration
damper centre bolt. Withdraw the damper
from the front of the crankshaft. A puller will be
required for this, preferably one which has two
screws for the tapped holes provided (see
illustrations).
28Using an engine support bar or hoist, take
the weight of the engine then unscrew the nuts
2C•10V6 engines
10.9 Heater connecting pipe clip bolts
(arrowed)
10.27a Unscrewing the vibration damper
centre bolt
10.22b Removing radiator upper shroud10.22c Manoeuvre the radiator out from
under the vehicle
10.27b Using a puller to withdraw the
vibration damper10.28a Using an engine support bar to
support the engine
10.13 Camshaft and crankshaft gear marks
in alignment (engine inverted)
Disregard the other mark on the crankshaft gear10.22a Radiator upper shroud plastic clip
and centre pin
procarmanuals.com
Page 72 of 255
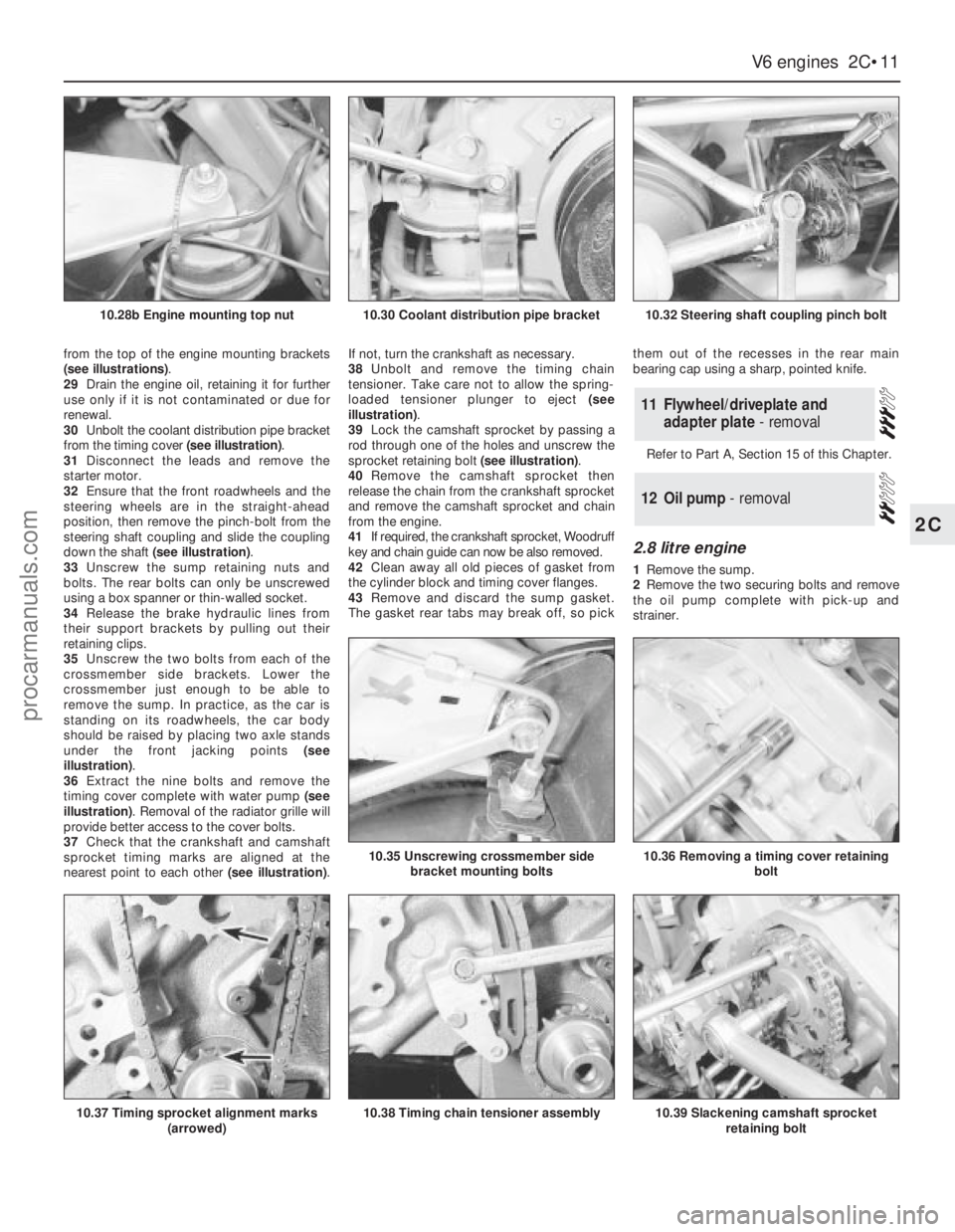
from the top of the engine mounting brackets
(see illustrations).
29Drain the engine oil, retaining it for further
use only if it is not contaminated or due for
renewal.
30Unbolt the coolant distribution pipe bracket
from the timing cover (see illustration).
31Disconnect the leads and remove the
starter motor.
32Ensure that the front roadwheels and the
steering wheels are in the straight-ahead
position, then remove the pinch-bolt from the
steering shaft coupling and slide the coupling
down the shaft (see illustration).
33Unscrew the sump retaining nuts and
bolts. The rear bolts can only be unscrewed
using a box spanner or thin-walled socket.
34Release the brake hydraulic lines from
their support brackets by pulling out their
retaining clips.
35Unscrew the two bolts from each of the
crossmember side brackets. Lower the
crossmember just enough to be able to
remove the sump. In practice, as the car is
standing on its roadwheels, the car body
should be raised by placing two axle stands
under the front jacking points (see
illustration).
36Extract the nine bolts and remove the
timing cover complete with water pump (see
illustration). Removal of the radiator grille will
provide better access to the cover bolts.
37Check that the crankshaft and camshaft
sprocket timing marks are aligned at the
nearest point to each other (see illustration).If not, turn the crankshaft as necessary.
38Unbolt and remove the timing chain
tensioner. Take care not to allow the spring-
loaded tensioner plunger to eject (see
illustration).
39Lock the camshaft sprocket by passing a
rod through one of the holes and unscrew the
sprocket retaining bolt (see illustration).
40Remove the camshaft sprocket then
release the chain from the crankshaft sprocket
and remove the camshaft sprocket and chain
from the engine.
41If required, the crankshaft sprocket, Woodruff
key and chain guide can now be also removed.
42Clean away all old pieces of gasket from
the cylinder block and timing cover flanges.
43Remove and discard the sump gasket.
The gasket rear tabs may break off, so pickthem out of the recesses in the rear main
bearing cap using a sharp, pointed knife.
Refer to Part A, Section 15 of this Chapter.
2.8 litre engine
1Remove the sump.
2Remove the two securing bolts and remove
the oil pump complete with pick-up and
strainer.
12Oil pump - removal
11Flywheel/driveplate and
adapter plate - removal
V6 engines 2C•11
2C
10.28b Engine mounting top nut10.30 Coolant distribution pipe bracket10.32 Steering shaft coupling pinch bolt
10.37 Timing sprocket alignment marks
(arrowed)
10.36 Removing a timing cover retaining
bolt10.35 Unscrewing crossmember side
bracket mounting bolts
10.38 Timing chain tensioner assembly10.39 Slackening camshaft sprocket
retaining bolt
procarmanuals.com
Page 76 of 255
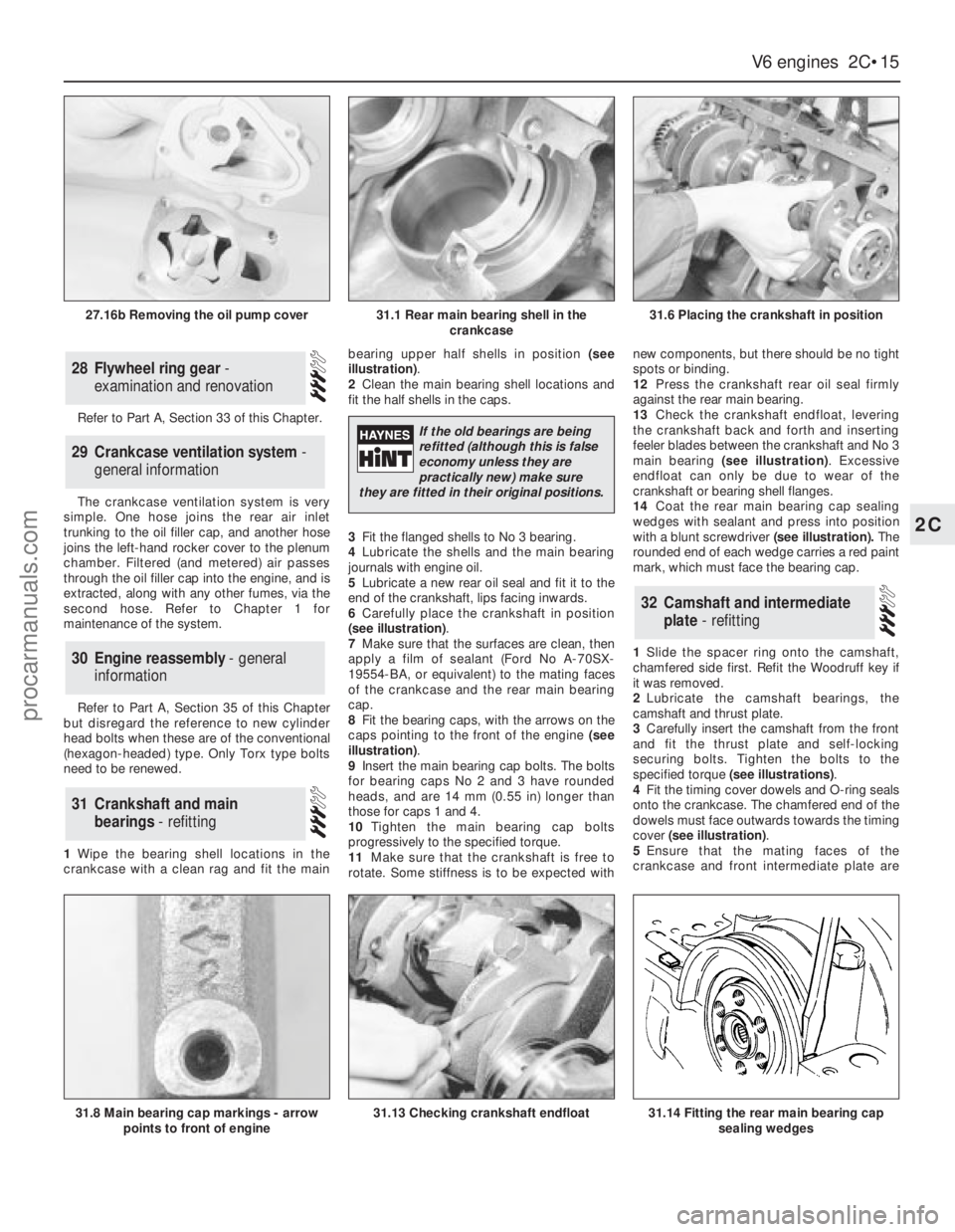
Refer to Part A, Section 33 of this Chapter.
The crankcase ventilation system is very
simple. One hose joins the rear air inlet
trunking to the oil filler cap, and another hose
joins the left-hand rocker cover to the plenum
chamber. Filtered (and metered) air passes
through the oil filler cap into the engine, and is
extracted, along with any other fumes, via the
second hose. Refer to Chapter 1 for
maintenance of the system.
Refer to Part A, Section 35 of this Chapter
but disregard the reference to new cylinder
head bolts when these are of the conventional
(hexagon-headed) type. Only Torx type bolts
need to be renewed.
1Wipe the bearing shell locations in the
crankcase with a clean rag and fit the mainbearing upper half shells in position (see
illustration).
2Clean the main bearing shell locations and
fit the half shells in the caps.
3Fit the flanged shells to No 3 bearing.
4Lubricate the shells and the main bearing
journals with engine oil.
5Lubricate a new rear oil seal and fit it to the
end of the crankshaft, lips facing inwards.
6Carefully place the crankshaft in position
(see illustration).
7Make sure that the surfaces are clean, then
apply a film of sealant (Ford No A-70SX-
19554-BA, or equivalent) to the mating faces
of the crankcase and the rear main bearing
cap.
8Fit the bearing caps, with the arrows on the
caps pointing to the front of the engine (see
illustration).
9Insert the main bearing cap bolts. The bolts
for bearing caps No 2 and 3 have rounded
heads, and are 14 mm (0.55 in) longer than
those for caps 1 and 4.
10Tighten the main bearing cap bolts
progressively to the specified torque.
11Make sure that the crankshaft is free to
rotate. Some stiffness is to be expected withnew components, but there should be no tight
spots or binding.
12Press the crankshaft rear oil seal firmly
against the rear main bearing.
13Check the crankshaft endfloat, levering
the crankshaft back and forth and inserting
feeler blades between the crankshaft and No 3
main bearing (see illustration). Excessive
endfloat can only be due to wear of the
crankshaft or bearing shell flanges.
14Coat the rear main bearing cap sealing
wedges with sealant and press into position
with a blunt screwdriver(see illustration).The
rounded end of each wedge carries a red paint
mark, which must face the bearing cap.
1Slide the spacer ring onto the camshaft,
chamfered side first. Refit the Woodruff key if
it was removed.
2Lubricate the camshaft bearings, the
camshaft and thrust plate.
3Carefully insert the camshaft from the front
and fit the thrust plate and self-locking
securing bolts. Tighten the bolts to the
specified torque (see illustrations).
4Fit the timing cover dowels and O-ring seals
onto the crankcase. The chamfered end of the
dowels must face outwards towards the timing
cover (see illustration).
5Ensure that the mating faces of the
crankcase and front intermediate plate are
32Camshaft and intermediate
plate - refitting
31Crankshaft and main
bearings - refitting
30Engine reassembly - general
information
29Crankcase ventilation system -
general information
28Flywheel ring gear -
examination and renovation
V6 engines 2C•15
2C
31.1 Rear main bearing shell in the
crankcase31.6 Placing the crankshaft in position
31.8 Main bearing cap markings - arrow
points to front of engine31.13 Checking crankshaft endfloat31.14 Fitting the rear main bearing cap
sealing wedges
27.16b Removing the oil pump cover
If the old bearings are being
refitted (although this is false
economy unless they are
practically new) make sure
they are fitted in their original positions.
procarmanuals.com
Page 78 of 255

1Make sure that the oil pump and crankcase
mating faces are clean.
2Check that the washer on the oil pump
driveshaft is located correctly (see illustration).
3If a new or overhauled pump is being fitted,
prime it by injecting oil into it and turning it by
hand.
4Insert the oil pump driveshaft into the block
with the pointed end towards the distributor
(see illustration).
5Fit the assembled oil pump, using a new
gasket. Insert the pump-to-block bolts and
tighten them to the specified torque (see
illustration).
6Refit the sump.Refer to Part A, Section 40 of this Chapter.
2.8 litre engines
1Lubricate a new oil seal and fit it to the
timing cover (see illustration).
2If the Woodruff keys were removed from the
camshaft and crankshaft, refit them.
3Refit the crankshaft gear, if removed, using
a length of tube to drive it home.
4Position the camshaft and crankshaft so
that their keyways are facing each other(seeillustration).Slide the camshaft gear onto the
camshaft, rotating the shafts slightly if
necessary so that the marks on the two gears
are aligned. Remember that there are two
marks on the crankshaft gear.
5Fit the camshaft gear retaining bolt and
washer(see illustration).Tighten the bolt to
the specified torque.
6Apply sealant to the mating faces of the
timing cover and the intermediate plate.
7Position a new gasket on the intermediate
plate and fit the timing cover to the cylinder
block (see illustrations).
8Fit the timing cover bolts, but do not tighten
them yet.
9Oil the sealing face of the crankshaft pulley
or damper. Fit the pulley/damper and the
central bolt and washer, applying sealant to
the inboard face of the washer (see
illustration). Draw the pulley/damper into
36Timing cover and drive -
refitting
35Flywheel/driveplate and
adapter plate - refitting34Oil pump - refitting
V6 engines 2C•17
2C
34.2 Oil pump driveshaft washer location34.4 Fitting the oil pump driveshaft34.5 Oil pump in position
36.7a Timing cover gasket in position
36.1 Timing cover oil seal36.5 Camshaft gear washer and bolt36.4 Crankshaft and camshaft gears
correctly aligned
36.7b Fitting the timing cover36.9 Fitting the crankshaft pulley
procarmanuals.com
Page 79 of 255

place by tightening the bolt; this will centralise
the timing cover.
10Tighten the timing cover bolts evenly to
the specified torque.
11Jam the crankshaft and tighten the pulley/
damper central bolt to the specified torque.
12Refit the sump.
13If the water pump was removed from the
timing cover, refit it using a new gasket.
14If the engine is still in the vehicle, reverse
the steps taken to gain access.
2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
15If the crankshaft sprocket was removed,
check that the key slots in the end of the
crankshaft and camshaft are in alignment at
the closest point to each other (see
illustration).16Fit the crankshaft sprocket and chain
guide.
17Engage the chain around the teeth of the
crankshaft sprocket.
18Engage the camshaft sprocket in the
upper loop of the chain in such a way so that
the camshaft sprocket will slip onto the key
slot when the timing mark is aligned with that
on the crankshaft sprocket (see illustration).
Some trial and error may be involved in
achieving this.
19Lock the camshaft sprocket and tighten
the retaining bolt to the specified torque.
20Retract the chain tensioner. To do this,
insert the plunger (bevelled side entering), then
release the pawl with a small screwdriver
pushed into the hole in the tensioner body
(see illustration).21Compress the plunger/slipper and retain it
in the retracted position using a cable-tie or
similar. New chain tensioners are supplied
complete with a retainer (see illustration).
22Bolt the tensioner in position, at the same
time removing the plunger retainer. Tighten the
bolts to the specified torque.
23Locate a new gasket on the front face of
the engine.
24Renew the timing cover oil seal and apply
grease to the lips.
25Fit the timing cover, centre it and align it
with the sump mounting flange.
26Although a special tool (21-137) is
available for centring the cover, a piece of
plastic pipe, or a socket of suitable thickness,
will serve as an adequate substitute.
Alternatively measure the space between the
crankshaft nose and the timing cover damper
recess at several different points and adjust
the position of the cover until all the
measurements are equal. A strip of metal 14.0
mm wide will serve as a gauge if calipers are
not available (see illustrations).
27Tighten the timing cover bolts (see
illustration)and fit the Woodruff key (where
removed) for the vibration damper.
28Apply jointing compound to the front and
rear sump flange areas on the timing
cover/cylinder block and rear main bearing
cap. Make sure that the bearing surfaces are
perfectly clean. Checking that the rear tabs of
the gasket enter the recesses in the main
bearing cap, locate a new sump gasket on the
crankcase (see illustration).
2C•18V6 engines
36.15 Crankshaft and camshaft key and
slot alignment
36.26b Using a socket to check the
crankshaft to timing cover gap
36.21 Timing chain tensioner retracted
using a cable-tie36.26a Measuring the crankshaft to timing
cover gap
36.27 Timing cover retaining bolts
(arrowed)36.28 Sump gasket at rear main bearing
cap
36.18 Fitting timing chain and sprockets36.20 Releasing timing chain tensioner
pawl
procarmanuals.com
Page 80 of 255

29Fit the sump and the retaining nuts and
bolts. Tighten them progressively in two stages.
30Oil the lip of the timing cover oil seal and
the contact surface of the crankshaft damper.
31Fit the damper to the crankshaft, being
careful not to dislodge the Woodruff key. Draw
the damper into position using the retaining
bolt and washer.
32Remove the bolt and apply sealant to the
faces of the washer. Refit the bolt and washer
then jam the starter gear ring teeth and tighten
the bolt to the specified torque.
33Refit the crankshaft pulley and tighten the
retaining bolts to the specified torque.
34Refit the crossmember side brackets and
brake pipes.
35Reconnect the engine mountings and
remove the engine hoist or axle stands (see
“Jacking”).36Connect the steering shaft coupling with
the steering wheel and front roadwheels in the
straight-ahead position. Fit the pinch-bolt and
tighten it to the specified torque.
37Fit the starter motor and connect the leads.
38Bolt the coolant distributor pipe to the
timing cover.
39Refit the alternator and power steering
pump drivebelts and tension them (see
illustrations).
40Fit the fan and radiator, connect all coolant
hoses, and fit the radiator upper shroud.
41Fit the air cleaner cover with attachments.
42Fill the engine with oil and coolant and
connect the battery.
2.8 litre engine
1Clean the mating faces of the crankcase
and sump. Ensure that the grooves in the seal
carriers are clean.
2Fit the rubber seals in the grooves.
3Apply sealing compound on the crankcase
and slide the tabs of the gasket under the cut-
outs in the rubber seals (see illustration).
4Ensure that the gasket hole lines up with the
holes in the gasket crankcase and fit the
sump. Take care not to dislodge the gasket.
5Fit the 24 securing bolts. Tighten them in
the sequence shown to the Stage 1 specified
torque starting at point A (see illustration),then to the Stage 2 torque starting at point B.
6Fit the sump drain plug, using a new
washer, and tighten it to the specified torque.
7If the engine is in the vehicle, reverse the
steps taken to gain access.
2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
8Refer to paragraphs 28 to 29, Section 36.
2.8 litre engine
1Lubricate the valve tappets with clean
engine oil and insert them in the cylinder
block. Ensure that they are fitted in their
original locations (see illustration).
2Ensure that the mating faces of the cylinder
block and the cylinder heads are clean.
3Position the new cylinder head gaskets over
the guide bushes on the cylinder block. Check
that they are correctly located. The right and
left-hand gaskets are different. The gaskets
are marked FRONT TOP (see illustration).
4Carefully lower the cylinder heads onto the
cylinder block. Oil the threads and contact
faces of the cylinder head bolts and insert
them into their holes.
5Tighten the cylinder head bolts, in the
correct order(see illustration),to the Stage 1
specified torque. Repeat in the same order for
Stages 2 and 3. Final tightening, when
required, is done after warm-up.
38Cylinder heads - refitting
37Sump - refitting
V6 engines 2C•19
2C
36.39a Alternator drivebelt tensioner strap
bolt36.39b Power steering pump drivebelt
tensioner bolt37.3 Slide the sump gasket tab into the seal
cut-out
38.1 Fitting a tappet in the block
37.5 Sump bolt tightening sequence
For A and B see text
38.3 Cylinder head gasket markings38.5 Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence
procarmanuals.com
Page 99 of 255
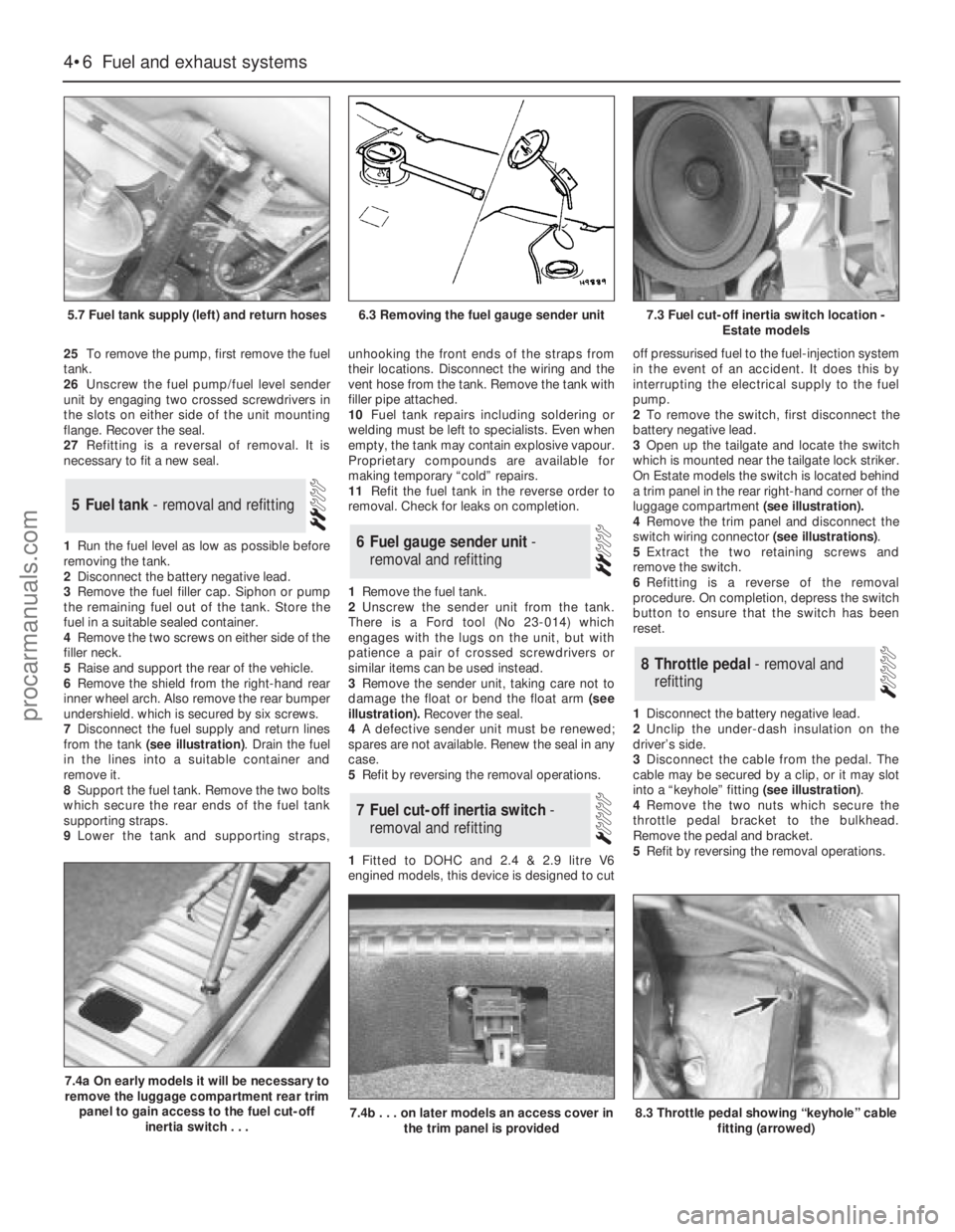
25To remove the pump, first remove the fuel
tank.
26Unscrew the fuel pump/fuel level sender
unit by engaging two crossed screwdrivers in
the slots on either side of the unit mounting
flange. Recover the seal.
27Refitting is a reversal of removal. It is
necessary to fit a new seal.
1Run the fuel level as low as possible before
removing the tank.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Remove the fuel filler cap. Siphon or pump
the remaining fuel out of the tank. Store the
fuel in a suitable sealed container.
4Remove the two screws on either side of the
filler neck.
5Raise and support the rear of the vehicle.
6Remove the shield from the right-hand rear
inner wheel arch. Also remove the rear bumper
undershield. which is secured by six screws.
7Disconnect the fuel supply and return lines
from the tank (see illustration). Drain the fuel
in the lines into a suitable container and
remove it.
8Support the fuel tank. Remove the two bolts
which secure the rear ends of the fuel tank
supporting straps.
9Lower the tank and supporting straps,unhooking the front ends of the straps from
their locations. Disconnect the wiring and the
vent hose from the tank. Remove the tank with
filler pipe attached.
10Fuel tank repairs including soldering or
welding must be left to specialists. Even when
empty, the tank may contain explosive vapour.
Proprietary compounds are available for
making temporary “cold” repairs.
11Refit the fuel tank in the reverse order to
removal. Check for leaks on completion.
1Remove the fuel tank.
2Unscrew the sender unit from the tank.
There is a Ford tool (No 23-014) which
engages with the lugs on the unit, but with
patience a pair of crossed screwdrivers or
similar items can be used instead.
3Remove the sender unit, taking care not to
damage the float or bend the float arm(see
illustration).Recover the seal.
4A defective sender unit must be renewed;
spares are not available. Renew the seal in any
case.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Fitted to DOHC and 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6
engined models, this device is designed to cutoff pressurised fuel to the fuel-injection system
in the event of an accident. It does this by
interrupting the electrical supply to the fuel
pump.
2To remove the switch, first disconnect the
battery negative lead.
3Open up the tailgate and locate the switch
which is mounted near the tailgate lock striker.
On Estate models the switch is located behind
a trim panel in the rear right-hand corner of the
luggage compartment (see illustration).
4Remove the trim panel and disconnect the
switch wiring connector (see illustrations).
5Extract the two retaining screws and
remove the switch.
6Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure. On completion, depress the switch
button to ensure that the switch has been
reset.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Unclip the under-dash insulation on the
driver’s side.
3Disconnect the cable from the pedal. The
cable may be secured by a clip, or it may slot
into a “keyhole” fitting (see illustration).
4Remove the two nuts which secure the
throttle pedal bracket to the bulkhead.
Remove the pedal and bracket.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
8Throttle pedal - removal and
refitting
7Fuel cut-off inertia switch -
removal and refitting
6Fuel gauge sender unit -
removal and refitting
5Fuel tank - removal and refitting
4•6Fuel and exhaust systems
5.7 Fuel tank supply (left) and return hoses
7.4a On early models it will be necessary to
remove the luggage compartment rear trim
panel to gain access to the fuel cut-off
inertia switch . . .
7.4b . . . on later models an access cover in
the trim panel is provided8.3 Throttle pedal showing “keyhole” cable
fitting (arrowed)
6.3 Removing the fuel gauge sender unit7.3 Fuel cut-off inertia switch location -
Estate models
procarmanuals.com
Page 102 of 255

1Check the cost and availability of spare parts
before deciding to dismantle the carburettor. If
the unit has seen much service, fitting a new or
reconditioned carburettor may prove more
satisfactory than any attempt at overhaul.
2Obtain a carburettor repair kit, which will
contain the necessary gaskets, diaphragms
and other renewable items.
3With the carburettor removed from the
vehicle, clean it thoroughly externally and
place it on a clean worksurface.
4 Referringto the exploded view of the
carburettor(see illustration),remove each
component part whilst making a note of its
fitted position. Make alignment marks on
linkages etc.
5Reassemble in the reverse order to
dismantling, using new gaskets, O-rings etc.
6To check the choke pull-down after
reassembly, position the fast idle screw on the
highest step of the cam. Press the pull-down
adjusting screw towards the pull-down
diaphragm and measure the choke valve
opening with a twist drill or gauge rod of the
specified diameter. Adjust if necessary using
a 2 mm Allen key (see illustration).
7After refitting the throttle damper, adjust its
position in the bracket so that with a 2 mm
(0.08 in) feeler blade inserted between the idle
speed adjusting screw and the throttle lever,
the damper plunger is just touching the
actuating lever(see illustration).
8Adjust the idle speed and mixture, and if
necessary the fast idle speed, after refitting the
carburettor.
9Recheck the throttle damper adjustment,
when applicable.
1This is not a routine operation. It should only
be necessary after overhaul, or when a new
carburettor is fitted.
2The idle speed and mixture must be
correctly set and the engine must be at
operating temperature.3Remove the air cleaner and plug the
manifold vacuum connection.
4With the engine running, position the fast
idle screw on the second highest step of the
fast idle cam(see illustration).Measure the
engine speed and compare it with that given in
the Specifications.
5If adjustment is necessary, remove the
tamperproof plug from the fast idle screw by
crushing it with pliers. Stop the engine and
open the throttle to gain access to the screw
with a small screwdriver. Turn the screw a
small amount clockwise to increase the speed,
anti-clockwise to reduce it, then reseat the
screw on the second highest step of the cam
and recheck the engine speed. Repeat as
necessary.
6Fit a new tamperproof cap where this is
required by law, then refit the air cleaner.
Idle speed cannot be adjusted in the usual
way on this carburettor, as it is controlled by
the ESC ll module.
If mixture adjustment is required, proceed
as described in Chapter 1, Section 16.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner.3Disconnect the choke and stepper motor
wiring. The stepper motor multi-plug locking
device must be depressed to release the plug
(seeillustration).
4Unclip the throttle arm from the throttle lever
and remove the throttle cable bracket.
5Disconnect the fuel hose from the
carburettor and plug it. If a crimped type hose
clip is fitted, cut it off and use a worm drive
clip when refitting.
6Disconnect the vacuum pipe(s) from the
carburettor, noting their connecting points if
there is any possibility of confusion.
7Remove the four carburettor-to-manifold
nuts. Check that nothing has been overlooked,
then lift off the carburettor. Recover the
gasket.
8Clean the carburettor and manifold mating
faces, being careful not to sweep dirt into the
manifold.
9Refit by reversing the removal operations. If
the stepper motor has been disturbed, refer to
Chapter 5, Section 19 for the initial
adjustment.
1Check the cost and availability of spare
parts before deciding to dismantle the
carburettor. If the unit has seen much service,
fitting a new or reconditioned carburettor may
prove more satisfactory than any attempt at
overhaul.
2Obtain a carburettor repair kit, which will
contain the necessary gaskets, diaphragms
and other renewable items.
3With the carburettor removed from the
vehicle, clean it thoroughly externally and
place it on a clean worksurface.
4 Referringto the exploded view of the
carburettor(see illustration),remove each
component part whilst making a note of its
fitted position. Make alignment marks on
linkages etc.
5Reassemble in the reverse order to
dismantling, using new gaskets, O-rings etc.
Be careful not to kink the diaphragms.
17Weber 2V carburettor -
dismantling and reassembly
16Weber 2V carburettor -
removal and refitting
15Weber 2V carburettor - idle
speed and mixture adjustments
14Pierburg 2V carburettor - fast
idle adjustment
13Pierburg 2V carburettor -
dismantling and reassembly
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•9
4
14.4 Fast idle adjustment - Pierburg 2V
Tip of fast idle screw is arrowed
13.6 Choke pull-down adjustment13.7 Throttle damper adjustment - Pierburg
2V carburettor
A Actuating lever
B Damper plungerC Damper locknut
D Feeler blade
16.3 Depress locking clip (arrowed) when
disconnecting stepper motor multi-plug
procarmanuals.com
Page 107 of 255

16Start the engine and note the engine
speed (rpm). The engine speed should
increase above the normal idle speed, and
should be as given in the Specifications.
17If the engine speed is not as specified,
remove the tamperproof plug from the top of
the throttle kicker housing, and turn the
adjustment screw to give the specified speed.
18On completion of adjustment, fit a new
tamperproof cap.
19Disconnect the tubing from the inlet
manifold, and reconnect the throttle kicker
vacuum hose.
20Refit the plastic shield and the air cleaner.
On 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 models especially,
residual pressure will remain in the fuel lines
long after the vehicle was last used therefore
the fuel system must be depressurised before
any hose is disconnected; the system is
depressurised via the vent valve on the fuel
rail, noting that it may be necessary to depress
the valve several times before the pressure is
fully released. As an added precaution place a
rag over the valve as it is depressed to catch
any fuel which is forcibly expelled. Before
carrying out any operation on the fuel system
refer to the precautions given in Safety first! at
the beginning of this Manual and follow them
implicitly. Petrol is a highly dangerous and
volatile liquid and the precautions necessary
when handling it cannot be overstressed.
Access to the relays is obtained by
removing the facia top cover (crash pad).
The relays are located on the passenger
side(see illustration). Also see Chapter 13,
Section 16.
See Chapter 1, Section 41.
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Idle speed is controlled by the EEC IV
module and no direct adjustment is possible.
2Idle mixture adjustment should not be
necessary on a routine basis. After component
renewal or a similar circumstance it may be
checked and adjusted as follows.
3The engine must be at operating temperature.
The valve clearances must be correct, the air
cleaner element must be clean and the ignition
system must be in good condition.
4Connect an exhaust gas analyser (CO
meter) and a tachometer (rev. counter) to the
engine as instructed by their makers.
5Run the engine at 3000 rpm for 15 seconds,
then allow it to idle. Repeat the procedure
every 60 seconds until adjustment is
complete.
6With the engine idling after the 3000 rpm
burst, record the CO level when the reading
has stabilised. The desired value is given in the
Specifications.
7If adjustment is necessary, remove the
tamperproof plug from the mixture adjusting
screw on the underside of the vane airflow
meter (see illustration).
8On V6 models, note that adjustment should
first be carried out on the front airflow meter.The rear meter should only be adjusted if the
range of adjustment on the front meter is
insufficient.
9Turn the mixture adjusting screw with a
hexagon key until the CO level is correct (see
illustration).
10Stop the engine and disconnect the test
gear.
11Fit a new tamperproof plug if required.
DOHC engine
Note: Before carrying out any adjustments
ensure that the ignition timing and spark plug
gaps are as specified. To carry out the
adjustments, an accurate tachometer and an
exhaust gas analyser (CO meter) will be
required.
12Idle speed is controlled by the EEC IV
module, and manual adjustment is not possible,
although the “base” idle speed can be adjusted
by a Ford dealer using special equipment.
13On models with a catalytic converter, the
mixture is controlled by the EEC IV module,
and no manual adjustment is possible.
14On models without a catalytic converter,
the idle mixture can be adjusted as follows.
15Run the engine until it is at normal
operating temperature.
16Stop the engine and connect a tachometer
and an exhaust gas analyser in accordance
with the manufacturer’s instructions.
17Start the engine and run it at 3000 rpm
for 15 seconds, ensuring that all electrical
loads (headlamps, heater blower, etc) are
switched off, then allow the engine to idle, and
check the CO content. Note that the reading
will initially rise, then fall and finally stabilise.
18If adjustment is necessary, remove the
cover from the mixture adjustment
potentiometer (located on the right-hand side
of the engine compartment, behind the MAP
sensor), and turn the screw to give the
specified CO content (see illustration).
19If adjustment does not produce a change
in reading, the potentiometer may be at the
extreme of the adjustment range. To centralise
the potentiometer, turn the adjustment screw
20 turns clockwise followed by 10 turns anti-
clockwise, then repeat the adjustment
procedure.
31Fuel-injection system - idle
speed and mixture adjustment
30Fuel filter - renewal
29Fuel-injection system relays -
location
28Fuel-injection system -
depressurisation
4•14Fuel and exhaust systems
31.18 Remove the cover from the mixture
adjustment potentiometer31.9 Idle mixture adjustment - fuel-injection
models
29.2 Fuel injection system relays - 2.4 and
2.9 litre V6 engines
A Power relayB Fuel pump relay
31.7 Tamperproof plug (arrowed) covering
mixture adjusting screw
Airflow meter is inverted for photo
procarmanuals.com