torque FORD GRANADA 1985 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: GRANADA, Model: FORD GRANADA 1985Pages: 255, PDF Size: 14.98 MB
Page 128 of 255

2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Drain the cooling system (Chapter 3). Save
the coolant if it is fit for re-use.
4Disconnect the multi-plug from the sensor.
Pull on the plug, not on the wiring (see
illustration).
5Unscrew the sensor and remove it.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Refill the cooling system.
Note: The manifold heater must not be
removed while it is hot.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead. 2Remove the air cleaner to improve access.
3Remove the three bolts which secure the
heater to the underside of the manifold.
4Disconnect the electrical feed from the heater.
5Remove the heater. Recover the gasket and
O-ring (see illustration).
6Use a new gasket and O-ring when refitting.
Offer the heater to the manifold, insert the
three bolts and tighten them evenly, making
sure that the heater does not tip or jam.
7Reconnect the electrical feed.
8Refit the air cleaner and reconnect the
battery.
All relays are located behind the facia panel.
Access is gained by removing the facia top
(see illustration).
Testing of a suspect relay is by substitution
of a known good unit.
1All models have a facility for retarding the
ignition timing by up to six degrees without
physically disturbing the distributor. The
adjustment is intended for use when the
correct grade of fuel is not available.
2Adjustment is made by earthing one or two
leads (sometimes called “octane adjustment”
leads) which terminate in a multi-plug next to
the ignition coil (see illustrations). Ideally a
service adjustment lead, available from a Ford
dealer, should be used. Cut and insulate the
wires in the adjustment lead which are not to
be earthed.
3The amount of ignition retardation is as
follows:
Wire(s) Degrees retard
earthed Carb. injection V6
Blue 2 4 6
Red 4 2 3
Blue and red 6 6 Forbidden
4Performance and efficiency will suffer as a
result of this adjustment. Normal timing should
be restored (by isolating the adjustment leads)
when the correct grade of fuel is available.
5If the yellow adjustment lead is earthed, thiswill raise the idle speed by 75 rpm (OHC) or 50
rpm (V6). It may be found that the yellow lead
has already been earthed in production, in
which case disconnecting it will lower the idle
speed by the same amount. This adjustment
does not apply to 1.8 litre carburettor models.
1.8 models from January 1987
6The effect of the “octane adjustment” leads
on these models fitted with the ESC Hybrid
Module is as follows.
Red lead earthed2°retarded
Blue lead earthed4°retarded
Red and blue leads earthed6°retarded
1Fitted to DOHC engines,the sensor is
located at the right-hand rear of the cylinder
block, behind the oil filter (see illustration).
2To remove the sensor, first disconnect the
battery negative lead.
3Access is most easily obtained from
underneath the vehicle. To improve access,
apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking”).
4Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor.
5Remove the securing screw and withdraw the
sensor from the location in the cylinder block.
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, using a
new sensor O-ring and tightening the retaining
screw to the specified torque setting.
24Crankshaft speed/position
sensor - removal and refitting
23Ignition timing and idle speed
adjustments
22Engine management system
relays - testing
21Manifold heater (carburettor
models) - removal and refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•11
5
20.4 Coolant temperature sensor multi-plug21.5 Removing the manifold heater22.1 Engine management system relays
A Power holdB Manifold heater
23.2a Octane adjustment lead multi-plug
23.2b Service adjustment lead for timing
and idle adjustment
A Earthing point (coil
screw)
B Multi-plugC Cut wires not to be
earthed
24.1 Crankshaft speed/position sensor
(viewed from underneath)
procarmanuals.com
Page 129 of 255

1The sensor is located in the upper section of
the inlet manifold (DOHC fuel-injection
engines) or the side of the plenum chamber
(V6 engines).
2To remove the sensor, first disconnect the
battery negative lead.
3Disconnect the sensor wiring plug by pulling
on the plug, not the wiring (see illustration).
4Unscrew the sensor from the inlet manifold
and remove it.
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, applying a
smear of sealant to the threads of the sensor
and tightening it to the specified torque.
1Fitted to 2.0 litre DOHC fuel-injected
engines,this sensor is located in the top of the
fuel rail.
2To remove the sensor, first disconnect the
battery negative lead, and to improve access,
disconnect the wiring plug from the air charge
temperature sensor (in the inlet manifold).
Disconnect the sensor wiring plug by pulling
on the plug, not the wiring.
3Disconnect the fuel temperature sensor
wiring plug, again pulling on the plug (see
illustration).
4Unscrew the sensor from the fuel rail and
remove it.
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, tightening
the sensor to the specified torque.1Fitted to DOHC fuel-injected engines and to
V6 engines with catalytic converters, this
sensor is located in the left-hand side of the
gearbox/transmission.
2To remove the sensor first disconnect the
battery negative lead.
3Firmly apply the handbrake then jack up the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands
(see “Jacking”).
4Detach the sensor wiring connector from
the bracket, and separate the two halves of
the connector (see illustration).
5Unscrew the securing bolt, and withdraw
the wiring connector bracket, noting the
orientation.
6Withdraw the sensor from the
gearbox/transmission casing.
7Before refitting the sensor, examine the O-
ring, and renew if damaged or worn.
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the wiring connector bracket is correctly
located.
1On DOHC fuel-injected engines, this sensor
is located on the right-hand side of the engine
compartment where it is mounted either on
the suspension turret or on the bulkhead (see
illustration). V6 engines have the sensormounted on the centre of the engine
compartment bulkhead.
2To remove the sensor first disconnect the
battery negative terminal.
3Remove the two sensor retaining screws
and carefully withdraw the sensor, taking care
not to strain the wiring.
4Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor,
pulling on the plug not the wiring, then
disconnect the vacuum hose and remove the
sensor.
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
28Manifold absolute pressure
(MAP) sensor - removal and
refitting
27Vehicle speed sensor -
removal and refitting
26Fuel temperature sensor -
removal and refitting
25Air charge temperature
sensor - removal and refitting
5•12Engine electrical systems
25.3 Disconnecting the air charge
temperature sensor wiring plug
28.1 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor location - models equipped with a
catalytic converter
26.3 Disconnecting the fuel temperature
sensor wiring plug27.4 Vehicle speed sensor wiring plug
(arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 131 of 255
Models covered in this Manual have disc
brakes fitted all round. The footbrake operates
hydraulically on all four wheels, and the
handbrake operates mechanically on the rear
wheels. Both footbrake and handbrake are
self-adjusting in use.
Ford’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) is
fitted to all models. The system monitors the
rotational speed of each roadwheel. When a
wheel begins to lock under heavy braking, the
ABS reduces the hydraulic pressure to that
wheel, so preventing it from locking. When this
happens a pulsating effect will be noticed at
the brake pedal. On some road surfaces the
tyres may squeal when braking hard even
though the wheels are not locked.
The main components of the system are the
hydraulic unit, the calipers, pads and discs,
the wheel sensors and the “brain” or control
module. The hydraulic unit contains the
elements of a traditional master cylinder, plus
an electric motor and pump, a pressure
accumulator and control valves. The pump is
the source of pressure for the system and
does away with the need for a vacuum servo.
The hydraulic circuit is split front and rear,
as is normal practice with rear-wheel drive
vehicles. In the event that the hydraulic pump
fails, unassisted braking effort is still available
on the front calipers only.
Warning lights inform the driver of low brake
fluid level, ABS failure and (on some models)
brake pad wear. The low fluid level light
doubles as a “handbrake on” light; if it
illuminates at the same time as the ABS
warning light, it warns of low hydraulic
pressure.
ABS cannot overturn the laws of physics:
stopping distances will inevitably be greater on
loose or slippery surfaces. However, the system
should allow even inexperienced drivers to
retain directional control under panic braking.
From August 1986 the following
modifications were made to the braking
system.
a)The relays differ from earlier versions.b)The hydraulic pump is constructed of iron
rather than alloy.
c)A new pressure warning switch is used.
d)The earlier high pressure rubber hose is
replaced by a steel pipe.
To overcome the problem of excessive rear
brake pad wear, Ford introduced a differential
valve which is screwed into the ABS valve
block.The valve limits the pressure applied to
the rear brake calipers and so reduces brake
pad wear. From 1988 onwards, the valve has
been fitted during production. The differential
valve can also be fitted to earlier models. Refer
to your Ford dealer for further information.
From April 1992 onwards, the models
covered in this Manual were equipped with a
new Teves MK IV anti-lock braking system
instead of the Teves MK II system fitted to the
earlier models.
The Teves MK IV system differs from the
earlier MK II system in the following ways.
a)The source of hydraulic pressure for the
system is a conventional master cylinder
and vacuum servo assembly.
b)A valve block and pump assembly is used
instead of the hydraulic control unit. The
block contains the inlet and outlet
solenoid valves that control the hydraulic
system. There are three pairs of valves,
one for each brake circuit (paragraph c).
c)The hydraulic braking system consists of
three separate circuits; one for each front
brake (which are totally independent of
each other), and a joint circuit which
operates both rear brakes.
d)A G (gravity) switch is incorporated in the
system. This is an inertia type switch and
informs the control module when the
vehicle is decelerating rapidly.
e)A Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) is fitted to the
vacuum servo unit. The PTS informs the
control module of the position of the brake
pedal when the anti-lock sequence starts
and ensures that a constant pedal height
is maintained during the sequence.
The MK IV system operates as follows.
During normal operation the system
functions in the same way as a non-ABS
system would. During this time the three inlet
valves in the valve block are open and theoutlet valves are closed, allowing full hydraulic
pressure present in the master cylinder to act
on the main braking circuit. If the control
module receives a signal from one of the
wheel sensors and senses that a wheel is
about to lock, it closes the relevant inlet valve
in the valve block which then isolates the
brake caliper on the wheel which is about to
lock from the master cylinder, effectively
sealing in the hydraulic pressure. If the speed
of rotation of the wheel continues to decrease
at an abnormal rate, the control module will
then open the relevant outlet valve in the valve
block; this allows the fluid from the relevant
hydraulic circuit to return to the master
cylinder reservoir, releasing pressure on the
brake caliper so that the brake is released. The
pump in the valve block also operates to assist
in the quick release of pressure. Once the
speed of rotation of the wheel returns to an
acceptable rate the pump stops, the outlet
valve closes and the inlet valve is opened,
allowing the hydraulic master cylinder
pressure to return to the caliper which then
reapplies the brake. This cycle can be carried
many times a second. The solenoid valves
connected to the front calipers operate
independently, but the valve connected to the
rear calipers operates both calipers
simultaneously.
The operation of the ABS system is entirely
dependent on electrical signals. To prevent
the system responding to any inaccurate
signals, a built-in safety circuit monitors all
signals received by the control module. If an
inaccurate signal or low battery voltage is
detected, the ABS system is automatically
shut down and the warning lamp on the
instrument cluster is illuminated to inform the
driver that the ABS system is not operational.
Whilst in this state the system functions in the
same way as a non-ABS system would. If a
fault does develop in the ABS system, the car
must be taken to a Ford dealer for fault
diagnosis and repair. The system is equipped
with a diagnostic plug into which a special
diagnostic (STAR) tester can be plugged. This
allows faults to be easily traced.
1General information
10•2Braking system
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Front caliper:
To stub axle carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Slide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Rear caliper:
Bracket to carrier plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Slide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31 to 3523 to 26
Hydraulic unit to bulkhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Accumulator to pump body . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Pump mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 95 to 7
High pressure hose banjo bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 to 2412 to 18
Reservoir mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 to 63 to 4
Wheel sensor fixing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Vacuum servo unit retaining nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Master cylinder retaining nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Valve block and pump assembly mounting nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . .21 to 2815 to 21
procarmanuals.com
Page 133 of 255

and bracket off the disc and tie them up out of
the way. Do not allow the caliper to hang on
the flexible hose.
3Remove the spring clip which secures the
disc (see illustration).
4Mark the relationship of the disc to the hub
if it is to be re-used, then remove the disc.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tighten the caliper bracket bolts to the
specified torque, and check that the brake
flexible hose is not kinked or fouling in any
position of the steering wheel.
6Pump the brake pedal to bring the pads up
to the disc.
1Chock the front wheels and release the
handbrake. Slacken the rear wheel nuts, raise
and support the vehicle and remove the
relevant rear wheel.
2Free the handbrake cable from its clip in the
suspension lower arm.
3Remove the two bolts which secure the
caliper bracket to the hub. Lift the caliper and
bracket off the disc and suspend it without
straining the flexible hose.
4Remove the spring clip from the wheel stud.
Mark the disc-to-hub relationship and remove
the disc.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
6Pump the brake pedal to bring the pads up
to the disc.1Disc pads can be inspected without
removing the front wheels, using a mirror and
a torch through the aperture in the rear face of
the caliper. If any one pad is worn down to the
minimum specified, all four pads (on both front
wheels) must be renewed.
2To renew the pads, first remove the front
wheels, then prise free the spring clip from the
outboard face of a caliper (see illustration).
3Disconnect the pad wear warning wires,
when fitted (see illustration).
4Unscrew the two caliper slide bolts, using
a 7 mm hexagon key, until the caliper is free
of the bracket (see illustration).
5Lift the caliper off the disc and remove the
pads (see illustration). Support the caliper so
that the flexible hose is not strained. Do not
press the brake pedal with the caliper removed.
6Clean the dust and dirt from the caliper,
bracket and disc, using a damp cloth or old
paintbrush which can be thrown away
afterwards. Take care not to disperse the dust
into the air, or to inhale it, since it may contain
asbestos. Scrape any scale or rust from the
disc. Investigate any hydraulic fluid leaks.
7Push the caliper piston back into its
housing, using the fingers or a blunt
instrument, to accommodate the extra
thickness of the new pads.
8Fit the new pads to the caliper, being careful
not to contaminate the friction surfaces with oilor grease. The inboard pad has a spring clip
which fits into the piston recess; the outboard
pad must have its backing paper peeled off,
after which the pad should be stuck to the
other side of the caliper (see illustrations).
9Fit the caliper and pads over the disc and
onto the caliper bracket. Tighten the slide
bolts to the specified torque.
10Reconnect the wear warning wires, if fitted.
11Refit the spring clip to the caliper.
12Repeat the operations on the other caliper,
then refit the wheels and lower the vehicle.
Tighten the wheel nuts.
13Pump the brake pedal several times to
bring the pads up to the disc, then check the
brake fluid level.
14Avoid heavy braking as far as possible for
the first hundred miles or so to allow the new
pads to bed in.7Front brake pads - inspection
and renewal
6Rear brake disc - removal and
refitting
10•4Braking system
5.3 Disc-securing spring clip
7.5 Lifting a front caliper off the disc7.8a Clipping the inboard front pad into the
piston
7.4 Undoing a caliper slide bolt
7.8b Both pads fitted to a front caliper
7.2 Spring clip fitted to outboard face of
front caliper7.3 Pad wear warning multi-plug (arrowed)
on front caliper
procarmanuals.com
Page 141 of 255

3Press the multi-plug locking lever,
disconnect the multi-plug and unhook it from
the module. Remove the module.
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the multi-plug is properly
engaged before refitting the module.
Front
1Ensure that the handbrake is applied. Raise
and support the front of the vehicle.
2From under the bonnet disconnect the
wheel sensor wiring multi-plug. Unclip the
wiring, working towards the sensor.
3Remove the securing bolt and withdraw the
sensor from the stub axle carrier (see
illustration).
4Unclip the wire from the bracket on the
strut. Remove the sensor and its wiring (see
illustration).
5Clean any rust or debris from the sensor
bore in the stub axle carrier. Pack the bore
with clean wheel bearing grease.
6Renew the O-ring on the sensor and smear
it with grease.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Rear
8Chock the front wheels and release the
handbrake. Slacken the rear wheel nuts, raiseand support the rear of the vehicle and remove
the rear wheel.
9Fold the rear seat cushion forwards, remove
the side kick panel and roll back the carpet to
gain access to the sensor multi-plug (see
illustration).
10Disconnect the multi-plug, release the
floor grommet and pass the cable through the
floor.
11Unclip the handbrake cable from the
suspension lower arm.
12Remove the caliper front slide bolt and
pivot the caliper rearwards to gain access to
the sensor.
13Remove the sensor securing bolt and
withdraw the sensor.
14Clean up the sensor bore, pack it with
grease and renew the sensor O-ring.
15Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2Disconnect the wiring plug then remove the
master cylinder reservoir cap; do not invert the
cap as hydraulic fluid could enter and damage
the reservoir level switch. Syphon the
hydraulic fluid from the reservoir. Note: Do not
syphon the fluid by mouth, as it is poisonous;
use a syringe or an old poultry baster.
Alternatively, open any convenient bleed
screw in the system and gently pump the
brake pedal to expel the fluid through a plastic
tube connected to the screw.
3Wipe clean the area around the brake pipe
unions on the right-hand side of the master
cylinder and place absorbent rags beneath the
pipe unions to catch any surplus fluid.
4To disconnect the plastic low pressure
hoses, use a small flat bladed screwdriver to
carefully press the flange of the collet into the
master cylinder then pull the hoses out from
the reservoir(see illustration).Unscrew the
two union nuts and disconnect the brake
pipes from master cylinder. Plug or tape over
the pipe/hose ends and master cylinder
orifices to minimise the loss of brake fluid and
to prevent the entry of dirt into the system.
Wash off any spilt fluid immediately with cold
water.5Slacken and remove the two nuts securing
the master cylinder to the vacuum servo unit
then withdraw the unit from the engine
compartment. Remove the O-ring from the
rear of master cylinder and discard it.
6If necessary remove the reservoir from the
master cylinder and withdraw the mounting
bush seals and O-rings. Note that the master
cylinder is a sealed unit with no spare parts
available separately. Therefore if it is faulty it
must be renewed as a unit.
7Fit new mounting bush seals and O-rings to
the master cylinder and refit the reservoir (if
removed). Remove all traces of dirt from the
master cylinder and servo unit mating surfaces
and fit a new O-ring onto the master cylinder
body.
8Fit the master cylinder to the servo unit
ensuring that the pushrod enters the servo unit
bore centrally. Refit the master cylinder
mounting nuts and tighten them to the
specified torque.
9Wipe clean the brake pipe/hose unions and
the master cylinder ports. Refit the pipes to
the master cylinder ports and tighten them
securely. Push the low pressure hoses into
position and check they are securely held by
their retaining collets.
10Refill the master cylinder reservoir with
new fluid and bleed the hydraulic system
1To test the operation of the servo unit
depress the footbrake several times to
exhaust the vacuum then start the engine
whilst keeping the pedal firmly depressed. As
the engine starts there should be a noticeable
“give” in the brake pedal as the vacuum builds
up. Allow the engine to run for at least two
minutes then switch it off. If the brake pedal is
now depressed it should feel normal, but
further applications should result in the pedal
feeling firmer, with the pedal stroke decreasing
with each application.
2If the servo does not operate as described,
inspect the servo unit check valve as
describedin paragraph 3 of Section 29.28Vacuum servo unit (April 1992
on) - testing, removal and
refitting
27Master cylinder (April 1992
on) - removal and refitting
26Wheel sensors - removal and
refitting
10•12Braking system
26.3 Removing a front sensor
27.4 Disconnecting the master cylinder low
pressure hoses (A) and brake pipes (B) -
models from April 1992
26.4 Unclipping the sensor wire from the
strut26.9 Rear wheel sensor multi-plug
(arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 142 of 255

3If the servo unit still fails to operate
satisfactorily the fault lies within the unit itself.
Repairs to the unit are not possible.
4Remove the master cylinder (Section 27).
5Disconnect the vacuum hose from the servo
unit taking care not to displace the rubber
sealing grommet. Disconnect the wiring plug
from the Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) which is
situated on the front of the servo.
6Working from inside the vehicle, remove the
servo pushrod retaining clip from the brake
pedal. If necessary, to improve access to the
brake pedal remove the right-hand lower facia
panel .
7Slacken and remove the four nuts securing
the servo unit to the bulkhead, then return to
the engine compartment and remove the
servo unit from the vehicle. Remove the
gasket from the rear of the unit and discard it.
8Note that the vacuum servo unit is a sealed
assembly with no spare parts available
separately. Therefore if it is faulty it must be
renewed as a unit. Inspect the vacuum servo
vacuum hose sealing grommet for damage or
deterioration and renew if necessary.
9Remove all traces of dirt from the servo unit
and bulkhead mating surfaces and fit a new
gasket onto the rear of the servo.
10Manoeuvre the servo unit into position,
ensuring that the servo unit pushrod is
correctly located with the hole in the pedal.
Refit the servo unit retaining nuts and tighten
them to the specified torque setting. Secure
the pushrod in position with the retaining clip
11Carefully refit the vacuum hose to the servo
unit taking great care not to damage or displace
the sealing grommet. Reconnect the wiring
connector to the Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS).
12Refit the master cylinder as described
above. On completion start the engine and
check the operation of the servo unit.
1Disconnect the vacuum hose from the servo
unit taking care not to displace the rubber
sealing grommet.
2To disconnect the hose from the inlet
manifold, use a small flat-bladed screwdriver
to carefully press the flange of the collet into
the manifold then pull the hose out and
remove it from the vehicle (see illustration).
3Examine the vacuum hose and sealing
grommet for damage, splits, cracks or general
deterioration and renew as necessary. Make
sure that the check valve is working correctly
by blowing through the hose from the servo
unit end. Air should flow in this direction, but
not when blown through from the inlet
manifold hose end. Renew the check valve if it
is at all suspect.
4Ensure that the check valve is fitted the
correct way around then push the connector
into the manifold and check that it is securely
held by the retaining collet.5Carefully refit the vacuum hose to the servo
unit taking great care not to damage or
displace the sealing grommet.
6On completion start the engine and check
the operation of the servo unit.
1Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2Carry out the operations described in
paragraphs 2 to 4 of Section 27.
3Remove all traces of dirt from the exterior of
the block then disconnect the motor and valve
block wiring plugs and free the diagnostic test
wiring plug from the mounting bracket.
4Position some absorbent rag beneath the
valve block then unscrew the three brake pipe
outlet unions whilst avoiding getting surplus
brake fluid in the wiring plugs. Plug the block
ports and pipe ends to minimise the loss of
fluid and prevent the entry of dirt into the
system. Wash off any spilt fluid immediately
with cold water.
5Slacken and remove the three valve block
and pump assembly mounting nuts and
remove the unit from the engine compartment.
6Note that the valve block and pump
assembly is a sealed unit and cannot be
overhauled. If it is faulty it must be renewed.
Note that if the low pressure hoses are
disconnected from the assembly, great care
must be taken when reconnecting them to
ensure that the valve block filter is not
damaged.
7Manoeuvre the assembly into position then
refit the mounting nuts and tighten them by
hand only. Taking into account the amount of
movement in the mounting rubbers, position
the assembly so that it will not contact the
mounting bracket then tighten the mounting
nuts to the specified torque setting.
8Remove the plugs then reconnect the outlet
pipes to the assembly and tighten the union
nuts securely.
9Ensure that the wiring is correctly routed
and reconnect the wiring plugs to the valve
block and pump assembly. Refit thediagnostic test wiring connector to the
mounting bracket.
10Wipe clean the brake pipe/hose unions
and the master cylinder ports. Refit the pipes
to the master cylinder ports and securely
tighten the union nuts. Push the low pressure
hoses into position and check they are
securely held by their retaining collets.
11Reconnect the battery negative terminal,
then fill the master cylinder and bleed the
complete hydraulic system using the
information given earlier in this Section.
1The anti-lock braking control module is
located behind the glovebox. To remove the
module first disconnect the battery negative
terminal.
2Open up the glovebox then, using a small
flat-bladed screwdriver, carefully prise up the
retaining clip and disconnect the glovebox
hinge arms. Withdraw the glovebox assembly
from the facia noting the plastic bushes which
are fitted to the glovebox pivot points.
3Lift the wiring plug retaining clip and
disconnect the plug to the control module. The
ABS module is the upper of the two control
modules mounted horizontally.
4Release the retaining clips and slide the
module out of the mounting bracket (see
illustration).
5Commence refitting by sliding the module
into the mounting bracket until it clips into
position.
6Connect the wiring connector to the
module, ensuring that the wiring is correctly
routed, and secure it in position with the
retaining clip.
7Ensure that the plastic bushes are correctly
fitted to the glovebox then refit the glovebox
assembly, locating the pivots in the correct
locations on the facia panel. Clip the hinge
arms onto the glovebox and check that it
opens and closes smoothly.
8Reconnect the battery negative terminal.
31Control module (April 1992
on) - removal and refitting
30Valve block and pump
assembly (April 1992 on) -
removal and refitting
29 Vacuum servo unit check
valve (April 1992 on) -
removal, testing and refitting
Braking system 10•13
10
29.2 Disconnecting brake servo vacuum
hose from the inlet manifold (DOHC engine
shown)31.4 Removing the ABS control module -
models from April 1992
procarmanuals.com
Page 145 of 255

11•2Steering and suspension
Front wheel alignment (continued)
Camber :
SOHC and 2.8 litre models:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0°23’ ±1°00’
Heavy duty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0°00’ ±1°00’
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0°17’
2.4 litre low series models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0°27’
2.4 litre high series and 2.9 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0°21’
Tolerance:
DOHC, 2.4 and 2.9 litre models: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°00’ to + 0°60’
Difference between left-hand and right-hand sides:
SOHC and 2.8 litre models:
Castor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°00’ maximum
Camber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°15’ maximum
DOHC, 2.4 and 2.9 litre models:
Castor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°00’
Camber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°15’
Steering gear
Make:
Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Cam Gears
Power-assisted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Cam Gears or ZF
Power steering fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ATF to Ford spec SQM-2C9010-A (Automatic Transmission
Fluid)
Tyres
Tyre sizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175 SR/TR/HR 14, 185/70 HR/TR/VR 14, 195/65 HR 15, 205/60
VR 15
Tyre pressures: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .FrontRear
Normal load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.8 bar (26 lbf/in
2)1.8 bar (26 lbf/in2)
Full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.1 bar (30 lbf/in2)2.9 bar (42 lbf/in2)
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Steering
Steering gear-to-crossmember bolts:
Stage 1 (clamping) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Slacken, then Stage 2 (snug) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Tighten further 90°Tighten further 90°
Track rod end balljoint nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25 to 3018 to 22
Track rod end locknut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57 to 6842 to 50
Track rod inner balljoint nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7555
Intermediate shaft coupling pinch-bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Pinion retaining nut (manual steering) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
Pinion shaft nut (power steering) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37 to 4727 to 34
Slipper yoke plug (see text):
Manual steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 to 53 to 4
Power steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 to 42 to 3
Steering wheel nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 to 5533 to 41
Steering column mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2413 to 18
Steering column adjuster pivot nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 to 137 to 10
Steering pump bracket to block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52 to 6438 to 47
Steering pump pulley hub bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 to 127 to 9
Pressure hose to steering pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26 to 3119 to 23
Steering pump bracket-to-engine mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5830 to 43
Steering pump to bracket (V6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22 to 2916 to 21
Front suspension
Hub nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .390 to 450288 to 332
Lower arm balljoint nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65 to 8548 to 63
Top mount retaining nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2415 to 18
Stub axle carrier pinch-bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 9059 to 66
Anti-roll bar clamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9052 to 66
Anti-roll bar to lower arms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 11052 to 81
Crossmember to frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9052 to 66
Suspension strut to turret . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 5230 to 38
Lower arm pivot:
Stage 1 (clamping) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Slacken. then Stage 2 (snug) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Tighten further 90°Tighten further 90°
procarmanuals.com
Page 146 of 255

The steering gear is of rack-and-pinion type.
Power assistance is standard on V6 models
and optional on others. The power-assisted
steering gear has a “variable ratio” effect
which increases the steering ratio about the
straight-ahead position: this provides quick
lock-to-lock action without the penalty of
over-responsiveness in open road driving.
The steering wheel is adjustable both up-
and-down and fore-and-aft. Both steering
column and shaft are designed to collapse
under impact. The steering shaft is connected
to the pinion by an intermediate shaft, which
has a universal joint at its upper end and a
flexible coupling at the lower end.
Front suspension is independent, of the
MacPherson strut type, with coil springs and
concentric telescopic shock absorbers. The
struts are attached to the tops of the stub axle
carriers, which are located at their lower ends
by balljoints incorporated in the lower
suspension arms. The lower suspension arms
pivot at their inner ends, where they are
attached to a central crossmember. The anti-
roll bar is attached to the rear of the arms and
serves to control fore-and-aft movement as
well as reducing roll.
Suspension geometry has been designed to
give good steering “feel”, resistance to pulling
caused by uneven braking effort or tyre
deflation, and (in the case of manual steering)
acceptably low steering wheel effort at parking
speeds. Only toe is adjustable in service.
The rear suspension is also independent. It
is of the semi-trailing arm type, with coil
springs and separate telescopic shock
absorbers. An optionally-available ride height
control system keeps the rear suspension
height constant, regardless of vehicle load.
Both front and rear wheel bearings are of a
special taper-roller type and require no
periodic adjustment in service.1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 35, to check the
power steering fluid level.
2If the fluid level falls so low that air enters
the pump, or after component renewal, the
system must be bled as follows.
3Remove the reservoir filler cap. Top-up with
clean fluid to the appropriate “cold” level. It is
important that the fluid is free of air bubbles,
so do not shake the container when topping-
up, and pour the fluid slowly.
4Disconnect the negative LT lead from the
ignition coil. Have an assistant crank the
engine on the starter in two second bursts, at
the same time turning the steering wheel from
lock to lock. Keep the reservoir topped up
whilst this is going on.
5When air bubbles no longer appear in the
fluid, stop the cranking. Reconnect the coil
negative lead and run the engine for a few
seconds, then stop it and check the level
again. Refit the filler cap.
6Run the vehicle for a few miles to warm up
the fluid and expel any remaining air, then stop
the engine and make a final fluid level check.
Manual steering
1Position the steering in the straight-ahead
position, then remove the ignition key so that
the steering is locked.
2Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheels.
3Remove the pinch-bolt and nut which
secure the intermediate shaft flexible coupling
to the pinion shaft (see illustration).
4Slacken the track rod end locknuts by half a
turn each (see illustration).
5Remove the split pin from the track rod
balljoint nuts. Unscrew the nuts, break the
balljoint tapers using a separator tool anddisengage the track rod ends from the
steering arms.
6Remove the two bolts which secure the
steering gear to the crossmember. Lift out the
steering gear.
7Mark the positions of the track rod ends on
the track rods, using paint or sticky tape, so
that they can be refitted in approximately the
same positions. Unscrew the track rod ends
and locknuts.
8Commence refitting by screwing on the
locknuts and track rod ends, observing the
previously made position marks when
applicable.
9Bring the rack to the straight-ahead
position. Do this by counting the number of
turns of the pinion needed to go from lock to
lock, then applying half that number of turns
from full lock on one side.
10Offer the steering gear to the vehicle,
engaging the flexible coupling and loosely
fitting the securing bolts. Note that the master
spline on the pinion shaft mates with the
corresponding groove in the flexible coupling.
11Tighten the two steering gear-to-
crossmember bolts to the specified Stage 1
torque. Slacken the bolts and retighten to the
Stage 2 torque. Finally tighten the bolts
through the angle specified for Stage 3.
12Make sure that the flexible coupling and
pinion shaft are properly engaged, then fit the
pinch-bolt and nut. Tighten the pinch-bolt to
the specified torque.
3Steering gear - removal and
refitting
2Power steering fluid - level
check and bleeding1General information
Steering and suspension 11•3
11
3.3 Master spline and groove on pinion
shaft and coupling
Torque wrench settings (continued)Nmlbf ft
Rear suspension
Driveshaft stub axle nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .250 to 290180 to 210
Final drive mounting to floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Final drive mounting to rear cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 5030 to 37
Guide plate-to-floor bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Guide plate insulator bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69 to 8851 to 65
Lower arm to crossmember . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 9559 to 70
Brake anchor plate to lower arm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52 to 6438 to 47
Anti-roll bar bracket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Shock absorber mountings:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73 to 9754 to 72
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68 to 9250 to 68
Rear hub bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 10059 to 74
Wheels
Wheel nuts (steel or alloy wheels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
procarmanuals.com
Page 147 of 255
13Refit the track rod ends to the steering
arms. Fit the balljoint nuts and tighten them to
the specified torque, then secure with new
split pins.
14Nip up the track rod end locknuts, but do
not tighten them fully yet.
15Refit the front wheels and wheel nuts.
Lower the vehicle and tighten the wheel nuts
to the specified torque.
16Check the toe setting as described in
Section 19. When toe is correct, tighten the
track rod end locknuts fully.
Power-assisted steering
17Proceed as described for manual steering
gear, but before removing the steering gear-
to-crossmember bolts, remove the clamp
plate bolt from the steering gear valve body
(see illustration).18Pull the fluid pipes out of the valve body.
Be prepared for fluid spillage. Plug or cap the
open pipes and orifices.
19The steering gear may now be removed.
20Refit in the reverse order to removal, using
new O-rings on the fluid pipes.
21Bleed the steering gear hydraulic system
on completion.
1Remove the track rod end on the side
concerned.Also remove the locknut.
2Remove the bellows retaining clips and slide
the bellows off the track rod (see illustration).
3On manual steering racks, apply a smear of
grease to the track rod 4Fit the new bellows and secure with new
clips. Make sure that the ends of the bellows
are located in their grooves. Do not tighten the
outer clip yet - leave it slack until toe has been
checked after refitting.
5Refit the track rod end locknut, followed by
the track rod end itself.
6Repeat on the other side of the vehicle if
necessary.
Models before April 1992
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Prise off the horn push pad from the centre
of the steering wheel.
3Remove the three screws which secure the
horn switch plate. Withdraw the plate,
disconnect its wires and remove it.
4Engage the steering lock, then undo and
remove the steering wheel nut. Unlock the
steering again.
5Mark the relationship of the wheel to the
shaft, then pull the wheel off the shaft. Use a
puller if it cannot be removed by hand. Do not
use hammer blows, which may damage the
collapsible parts of the column and shaft.
6Recover the spacer from below the steering
wheel (see illustration).
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tighten the steering wheel nut to the specified
torque.
Models from April 1992
8The steering wheel can be removed and
refitted as described above whilst ignoring the
5Steering wheel - removal and
refitting
4Steering rack bellows - renewal
in vehicle
11•4Steering and suspension
3.17 Clamp plate bolt (arrowed) is located
between two fluid pipes4.2 Steering rack bellows retaining clips
(arrowed)5.6 Spacer ring (arrowed) fits below
steering wheel
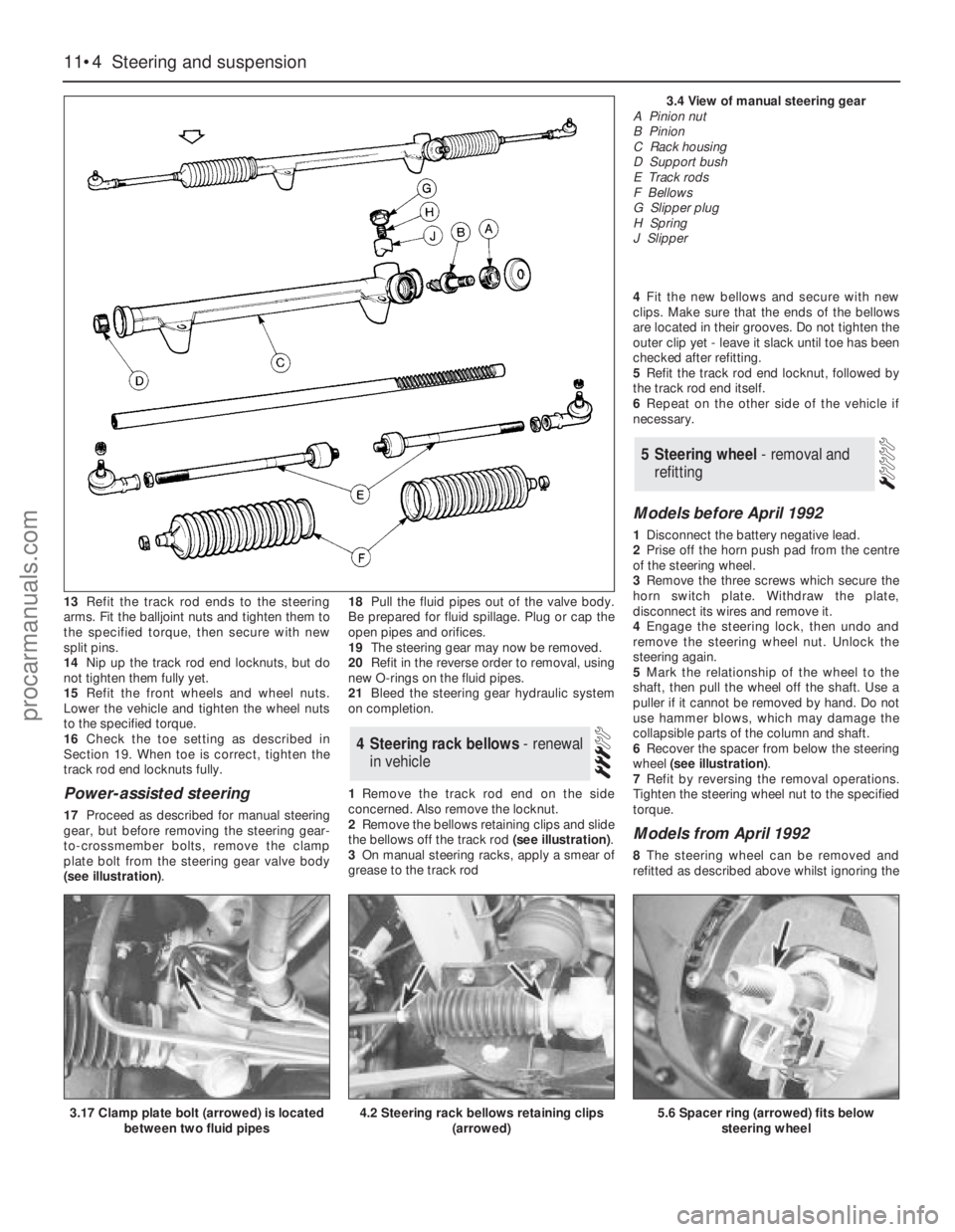
3.4 View of manual steering gearA Pinion nut
B Pinion
C Rack housing
D Support bush
E Track rods
F Bellows
G Slipper plug
H Spring
J Slipper
procarmanuals.com
Page 149 of 255

3Depress the locking button with a small
screwdriver. Draw the lock barrel out of its
housing using the key (see illustration).
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1The intermediate shaft and flexible coupling
are not available separately, and so must be
renewed as a unit.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Position the steering straight-ahead.
4Remove the pinch-bolts which secure the
upper and lower ends of the intermediate
shaft. Free the universal joint from the column
shaft, then pull the flexible coupling off the
pinion shaft.
5When refitting, engage the master spline on
the pinion shaft with the groove in the flexible
coupling.
6Tighten the pinch-bolts to the specified
torque.
7Reconnect the battery.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 21.
All engines except DOHC
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Wipe clean around the unions, then
disconnect the high pressure and return pipes
from the pump and the reservoir. Be prepared
for fluid spillage; take steps to keep fluid out of
the alternator.
3Remove the pump drivebelt(s).
4Remove the pump mounting, pivot and
adjustment bolts (as applicable) and lift the
pump from the engine (see illustration).
5If a new pump is to be fitted, recover the
pulley and mounting plate from the old pump.6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Adjust the drivebelt tension on completion and
bleed the steering hydraulic system.
DOHC engines
7The pump is mounted on a bracket on the
front right-hand side of the cylinder block. To
improve access to the pump, firmly apply the
handbrake then jack up the front of the car
and support it securely on axle stands (see
“Jacking”).
8Place a suitable container under the pump,
unscrew the fluid pipe unions, and drain the
fluid.
9Remove the drivebelt with reference to
Chapter 1.
10Prevent the pulley from rotating using a
strap wrench (which can be improvised using
an old drivebelt and a large socket and
wrench), and unscrew the three pulley
securing bolts (see illustration). Withdraw the
pulley.
11Unscrew the three pump securing bolts
from the front of the pump bracket, and the
single bolt from the rear of the bracket, and
withdraw the pump (see illustration).
12Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points:
a)Reconnect the fluid unions using new O-
rings.
b)On completion, top-up and bleed the
power steering fluid circuit.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Clean around the hose unions on the
steering gear. Remove the single securing
bolt, withdraw the hoses and catch the fluid
which will drain from the reservoir.
3Clean around the hose unions on the pump.
Disconnect the unions and remove the hoses.
4Refit in the reverse order to removal, using
new O-rings.
5Top-up the steering fluid and bleed the
system.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts, raise and
support the vehicle and remove the front
wheel on the side concerned.
2Slacken the track rod end locknut by half a
turn.
3Remove the split pin from the track rod end
balljoint nut. Unscrew the nut a few turns (see
illustration).
4Break the balljoint taper with a proprietary
balljoint separator (see illustration). Remove
the separator and the nut and disengage the
track rod end from the steering arm.
5Unscrew the track rod end from the track
rod, being careful not to disturb the locknut.
13Track rod end - removal and
refitting
12Power steering hoses -
removal and refitting
11Power steering pump -
removal and refitting
10Power steering pump
drivebelt - removal, refitting
and tensioning
9Steering intermediate shaft
and flexible coupling - removal
and refitting
11•6Steering and suspension
8.3 Depress the column lock locking button
11.11 . . . for access to the front pump
securing bolts (arrowed)13.3 Track rod end balljoint nut unscrewed
11.4 Steering pump pivot bolt (arrowed) -
V6 model shown11.10 Unbolt the power steering pump
pulley . . .
procarmanuals.com