lock FORD GRANADA 1985 Service Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1985, Model line: GRANADA, Model: FORD GRANADA 1985Pages: 255, PDF Size: 14.98 MB
Page 123 of 255
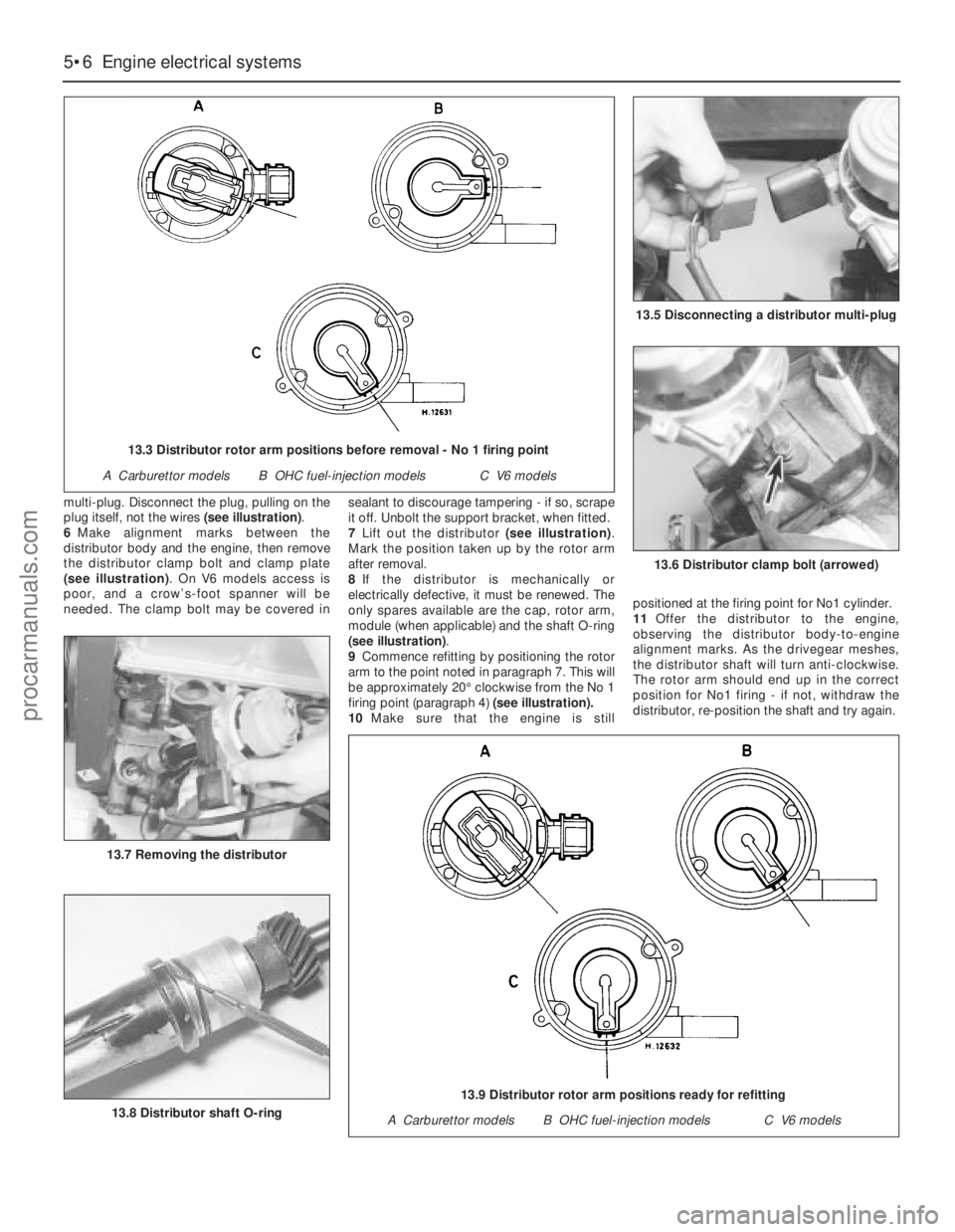
multi-plug. Disconnect the plug, pulling on the
plug itself, not the wires (see illustration).
6Make alignment marks between the
distributor body and the engine, then remove
the distributor clamp bolt and clamp plate
(see illustration). On V6 models access is
poor, and a crow’s-foot spanner will be
needed. The clamp bolt may be covered insealant to discourage tampering - if so, scrape
it off. Unbolt the support bracket, when fitted.
7Lift out the distributor (see illustration).
Mark the position taken up by the rotor arm
after removal.
8If the distributor is mechanically or
electrically defective, it must be renewed. The
only spares available are the cap, rotor arm,
module (when applicable) and the shaft O-ring
(see illustration).
9Commence refitting by positioning the rotor
arm to the point noted in paragraph 7. This will
be approximately 20°clockwise from the No 1
firing point (paragraph 4)(see illustration).
10Make sure that the engine is stillpositioned at the firing point for No1 cylinder.
11Offer the distributor to the engine,
observing the distributor body-to-engine
alignment marks. As the drivegear meshes,
the distributor shaft will turn anti-clockwise.
The rotor arm should end up in the correct
position for No1 firing - if not, withdraw the
distributor, re-position the shaft and try again.
5•6Engine electrical systems
13.6 Distributor clamp bolt (arrowed)
13.8 Distributor shaft O-ring
13.7 Removing the distributor
13.5 Disconnecting a distributor multi-plug
13.3 Distributor rotor arm positions before removal - No 1 firing point
A Carburettor modelsB OHC fuel-injection modelsC V6 models
13.9 Distributor rotor arm positions ready for refitting
A Carburettor modelsB OHC fuel-injection modelsC V6 models
procarmanuals.com
Page 124 of 255

12When the distributor is at the firing point,
the leading edge of one of the vanes should be
in line with the rib on the sensor (see
illustration). Turn the distributor body slightly
if necessary to achieve this.
13Refit the clamp plate and bolt. Just nip up
the bolt for the time being. Tighten it finally
after checking the timing. Also secure the
support bracket, when fitted.
14Refit the rotor arm, distributor cap and HT
leads.
15Reconnect the distributor multi-plug.
16Reconnect the battery. Run the engine
and check the ignition timing as described in
the next Section.
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
Note: The distributor should not be removed
or disturbed without good cause, since the
accuracy of timing achieved in production is
unlikely to be regained. If difficulty is
experienced in setting the timing after refitting,
or if a new distributor has been fitted, the
timing should be set by a Ford dealer using a
STAR (Self Test Automatic Readout) tester.
17Disconnect the battery negative lead.
18Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs noting the correct fitted locations.
19Release the distributor cap and place it to
one side, complete with the HT leads.
20Turn the engine by means of the vibration
damper centre bolt until No 1 piston is at its
firing point (12°BTDC) (see illustration).
21If there is no mark visible, mark the rim of
the distributor body to indicate the point of
alignment of the contact end of the rotor.
22Mark the position of the distributor
mounting plate in relation to the cylinder
block.
23Disconnect the distributor wiring
connector.
24Scrape the sealant from around the
distributor clamp bolt then unscrew the bolt
and withdraw the distributor.
25Prior to refitting the distributor check that
the crankshaft is still set in the 12°BTDC
position for the No 1 piston.
26Hold the distributor over the hole so that
the mounting plinth and cylinder head marks
are aligned then align the rotor arm contact
end with the mark on the distributor rim (see
illustration).
27As the distributor is inserted, the rotor will
turn due to the meshing of the drive gears.
When the distributor is fully inserted, rotate the
distributor body until the rotor arm aligns with
mark C on the distributor rim.
28Once the rotor arm, cylinder head and
distributor alignment marks are all correctly
aligned, fit the clamp bolt and tighten it
securely.
29Refit the distributor cap then connect the
HT leads, reconnect the vacuum pipe and
wiring plug.
30Run the engine to normal operating
temperature and check the ignition timing,
bearing in mind the note made at the start of
this sub-Section.
All engines except DOHC
1Ignition timing is set very accurately in
production. It does not need to be checked or
adjusted on a routine basis. Adjustment will
only be necessary if the distributor, or an
associated component such as the timing belt,
has been disturbed.
2Before checking the timing, the following
conditions must be met:
a)The engine must be warmed up
b)On carburettor models, the vacuum pipe
must be disconnected from the manifold
and the manifold hole be plugged
c)Idle speed must be below 900 rpm
d)Any earthed “octane adjustment” wires
must be temporarily isolated
3Locate the timing marks. On SOHC engines
the timing scale is on the crankshaft pulley,
and a pointer on the timing cover must be
aligned with the appropriate mark on the
pulley (see illustration). Note that two
alternative types of pulley may be fitted (see
illustration).On V6 engines there is a single
notch on the pulley and the timing scale is on
the timing cover (see illustration).The desiredvalues are given in the Specifications.
Highlight the appropriate marks with white
paint.
4Connect a timing light (strobe) to No 1 HT
lead, following the maker’s instructions. Some
lights require additional power connections to
be made, either to the mains or to the battery.
5Run the engine at idle and shine the timing
light onto the marks. Take care not to get the
timing light leads, clothing etc tangled in the
fan blades or other moving parts. The timing
marks will appear stationary and (if the timing
is correct) in alignment.
14Ignition timing - checking
Engine electrical systems 5•7
5
13.12 Vane leading edge and sensor rib
(arrowed) are aligned at firing point13.20 Crankshaft pulley notch set to the 12°
BTDC position
14.3a Timing marks and pointer
Cast pulley shown
13.26 Rotor arm position before (1) and after (2) refitting the distributor
X = XC Notch
procarmanuals.com
Page 125 of 255
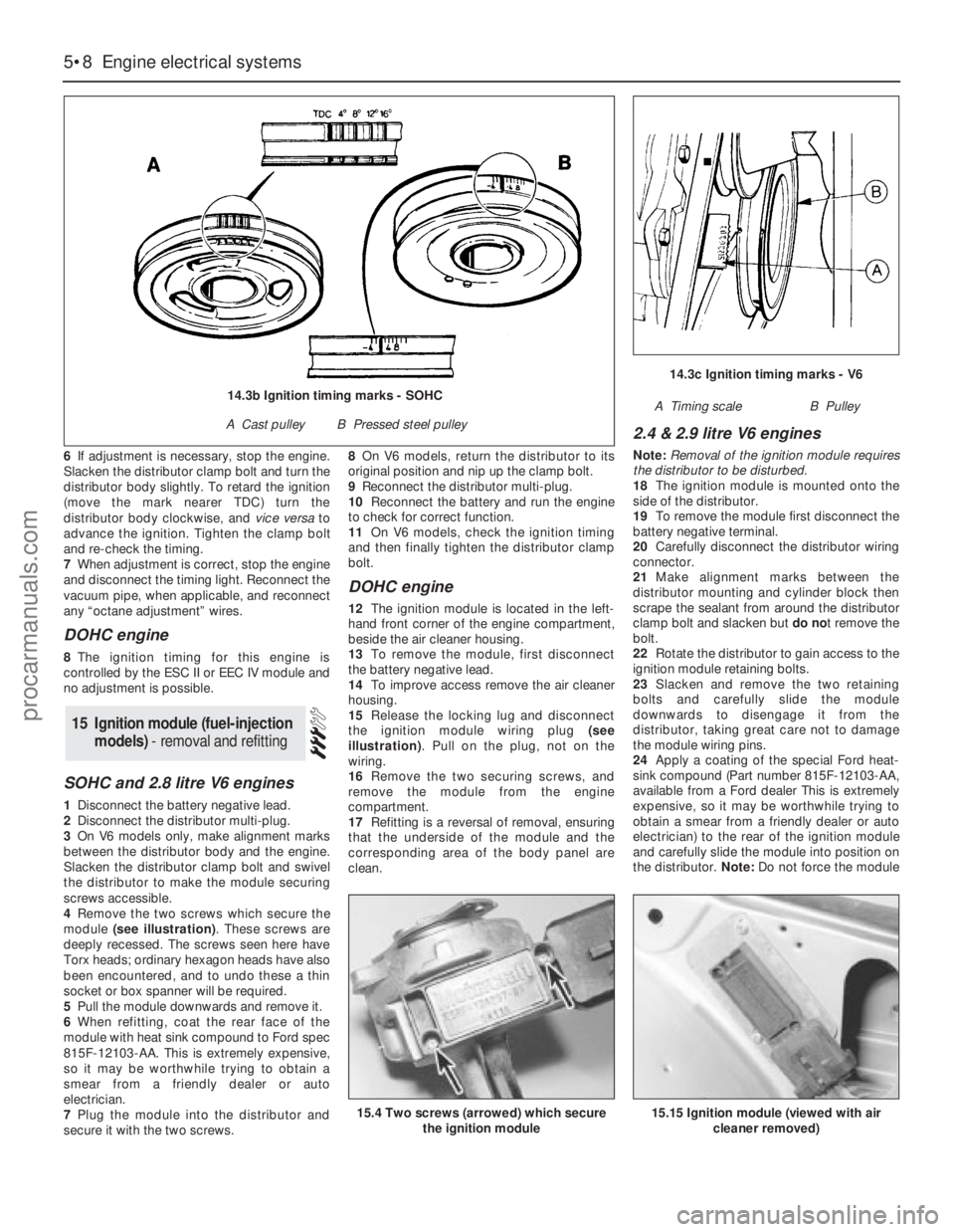
6If adjustment is necessary, stop the engine.
Slacken the distributor clamp bolt and turn the
distributor body slightly. To retard the ignition
(move the mark nearer TDC) turn the
distributor body clockwise, and vice versato
advance the ignition. Tighten the clamp bolt
and re-check the timing.
7When adjustment is correct, stop the engine
and disconnect the timing light. Reconnect the
vacuum pipe, when applicable, and reconnect
any “octane adjustment” wires.
DOHC engine
8The ignition timing for this engine is
controlled by the ESC II or EEC IV module and
no adjustment is possible.
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the distributor multi-plug.
3On V6 models only, make alignment marks
between the distributor body and the engine.
Slacken the distributor clamp bolt and swivel
the distributor to make the module securing
screws accessible.
4Remove the two screws which secure the
module (see illustration). These screws are
deeply recessed. The screws seen here have
Torx heads; ordinary hexagon heads have also
been encountered, and to undo these a thin
socket or box spanner will be required.
5Pull the module downwards and remove it.
6When refitting, coat the rear face of the
module with heat sink compound to Ford spec
815F-12103-AA. This is extremely expensive,
so it may be worthwhile trying to obtain a
smear from a friendly dealer or auto
electrician.
7Plug the module into the distributor and
secure it with the two screws.8On V6 models, return the distributor to its
original position and nip up the clamp bolt.
9Reconnect the distributor multi-plug.
10Reconnect the battery and run the engine
to check for correct function.
11On V6 models, check the ignition timing
and then finally tighten the distributor clamp
bolt.
DOHC engine
12The ignition module is located in the left-
hand front corner of the engine compartment,
beside the air cleaner housing.
13To remove the module, first disconnect
the battery negative lead.
14To improve access remove the air cleaner
housing.
15Release the locking lug and disconnect
the ignition module wiring plug (see
illustration). Pull on the plug, not on the
wiring.
16Remove the two securing screws, and
remove the module from the engine
compartment.
17Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the underside of the module and the
corresponding area of the body panel are
clean.
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
Note: Removal of the ignition module requires
the distributor to be disturbed.
18The ignition module is mounted onto the
side of the distributor.
19To remove the module first disconnect the
battery negative terminal.
20Carefully disconnect the distributor wiring
connector.
21Make alignment marks between the
distributor mounting and cylinder block then
scrape the sealant from around the distributor
clamp bolt and slacken but do not remove the
bolt.
22Rotate the distributor to gain access to the
ignition module retaining bolts.
23Slacken and remove the two retaining
bolts and carefully slide the module
downwards to disengage it from the
distributor, taking great care not to damage
the module wiring pins.
24Apply a coating of the special Ford heat-
sink compound (Part number 815F-12103-AA,
available from a Ford dealer This is extremely
expensive, so it may be worthwhile trying to
obtain a smear from a friendly dealer or auto
electrician) to the rear of the ignition module
and carefully slide the module into position on
the distributor. Note: Do not force the module
15Ignition module (fuel-injection
models) - removal and refitting
5•8Engine electrical systems
15.4 Two screws (arrowed) which secure
the ignition module15.15 Ignition module (viewed with air
cleaner removed)
14.3c Ignition timing marks - V6
A Timing scaleB Pulley14.3b Ignition timing marks - SOHC
A Cast pulleyB Pressed steel pulley
procarmanuals.com
Page 126 of 255

into position or the wiring pins will be
damaged.
25Refit the module retaining bolts and
tighten them securely.
26Rotate the distributor until the marks made
on removal are aligned then securely tighten
the clamp bolt.
27Reconnect the distributor wiring
connector and the battery negative terminal.
28Run the engine to normal operating
temperature and check the ignition timing.
All engines except DOHC fuel-
injection
1The ignition coil is mounted on the left-hand
side of the engine compartment (see
illustration). If it fails, there will be no spark
and the engine will stop.
2To test the coil an ohmmeter will be
required. Disconnect the LT and HT leads from
the coil and measure the resistance between
the two LT terminals (primary resistance), then
between the HT terminal and either LT
terminal (secondary resistance). Desired
values are given in the Specifications. In fact
most test gear will not be able to distinguish
between a normal primary resistance (which is
very low) and a short-circuit.
3In the absence of an ohmmeter, test the coil
by substitution of a known good unit.4To remove the coil, disconnect the LT and
HT leads, then remove the two screws which
secure the coil clamp. Lift out the coil.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
2.0 litre DOHC fuel-injection
engines
6Refer to the above paragraphs but note that
on some models the coil heat shield must be
removed for access to the coil securing bolts.
The heat shield is secured by two screws. An
earthing lead and/or a suppressor may also be
secured by one of the coil retaining screws
(see illustration).
1On carburettor models, a fuel trap is fitted in
the vacuum pipe between the inlet manifold
and the ESC II module.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Disconnect the vacuum pipes from the trap
and remove it. Dispose of it carefully, it may
contain fuel.
4When refitting, note that the end of the trap
marked CARB goes towards the manifold, and
the end marked DIST towards the module.
5Reconnect the battery.
ESC II module (carburettor
models)
SOHC engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the vacuum pipe from the
module (see illustration).
3Release the locking catch and disconnect
the multi-plug from the module (see
illustration).
4Remove the three securing screws and
detach the module and bracket from the left-
hand inner wing.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the multi-plug is securely fitted
and the locking catch engaged.Note: From January 1987, a new type of
module was fitted to the 1.8 litre engine. The
new module is smaller than the old unit and is
in the engine compartment mounted onto the
left-hand wing valance. The new module is
known as the ESC Hybrid Module.(see
illustration)
DOHC engine
6Removal and refitting is as above.
7The module is located on the left-hand side
of the engine compartment and is secured by
two screws.
EEC IV module (fuel-injection
models)
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
8Disconnect the battery negative lead.
9Remove the under-dash trim on the
passenger side.
10Unclip the module and lower it onto the
vehicle floor.
11Remove the control bolt from the multi-
plug and disconnect the plug from the module.
12Refit by reversing the removal operations.
DOHC and 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
13The module is situated behind the
passenger side of the facia and is accessible
from underneath the glovebox.
14To remove the module first disconnect the
battery negative terminal.
15Reach up behind the glovebox and unclip
the module from the mounting bracket (see
illustration).
18Engine management control
module - removal and refitting
17Fuel trap (carburettor
models) - removal and refitting
16Ignition coil - testing, removal
and refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•9
5
16.1 Ignition coil location16.6 Suppresser secured by one of the coil
retaining screws
18.2 Disconnecting the ESC II module
vacuum pipe18.5 Engine management module - 1.8 litre
engine from January 198718.3 ESC II module multi-plug
procarmanuals.com
Page 127 of 255

16Undo the wiring connector retaining bolt
then carefully disconnect the wiring plug and
remove the module from the car (see
illustration).
17Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure ensuring that the wiring plug bolt is
securely tightened. On completion start the
engine and check that it runs correctly.
Note: Irregular idle is not necessarily caused
by a faulty or badly adjusted stepper motor.
Good electrical contact between the stepper
motor plunger and the adjusting screw is
essential. Before attempting adjustment or
renewal of the motor, try the effect of cleaning
the plunger and adjusting screw contact faces
with abrasive paper followed by switch
cleaning fluid. Switch cleaning fluid is available
from electronic component shops.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner.
3Disconnect the multi-plug from the stepper
motor. Release the locking clip and pull on the
plug, not on the wires.
4Remove the four screws which secure the
stepper motor bracket to the carburettor.Remove the motor and bracket and separate
them (see illustration).
5Refit the motor and bracket to the
carburettor and secure with the four screws.
Reconnect the multi-plug.
6Make an initial adjustment to the throttle
lever adjusting screw if necessary so that it
protrudes from the lever by dimension X (see
illustration).
7Reconnect the air cleaner vacuum hose.
Position the air cleaner to one side so that
there is still access to the carburettor and
stepper motor.
8Connect a tachometer (rev. counter) to the
engine as instructed by the manufacturers.
Reconnect the battery.
9Run the engine. Check the idle mixture (CO
level) as described in Chapter 4 and adjust if
necessary.
10Switch off all electrical loads (headlights,
heater blower etc). If the idle speed adjustment
lead is earthed, temporarily isolate it. Make
sure that the automatic transmission selector is
in the N or P position (where applicable).
11Accelerate the engine to a speed greater
then 2500 rpm, allow it to return to idle, then
repeat. Insert a feeler blade of thickness 1.0
mm (0.04 in) between the stepper motor
plunger and the adjusting screw(see
illustration).With the feeler blade in place,
engine speed should be 875 ±25 rpm. 12If adjustment is necessary, remove the
tamperproof cap from the adjusting screw
locknut. Release the locknut, turn the
adjusting screw to achieve the correct speed
and tighten the locknut.
13Repeat paragraph 11 and check that the
speed is still correct. Readjust if necessary.
14Remove the feeler blade. Stop and restart
the engine, observing the stepper motor
plunger. Immediately after switching off, the
plunger should move to the “anti-dieseling”
position; after a few seconds it should extend
to the “vent manifold/start” position (see
illustration).
15Disconnect the test gear and refit the air
cleaner.
16Recheck the idle mixture.
17Fit new tamperproof plugs or caps if
necessary - see Chapter 4,
18Reconnect the idle speed adjustment lead
if it was earthed.
1The engine management system
temperature sensor is located on the underside
of the inlet manifold (SOHC engines), the side
of the manifold (DOHC engines) or on the front
face of the cylinder block (V6 engines).
20Coolant temperature sensor -
removal and refitting
19Carburettor stepper motor
(2.0 litre models) - removal,
refitting and adjustment
5•10Engine electrical systems
18.16 Disconnecting the EEC IV module
A Multi-plugB Securing bolt
19.6 Throttle lever initial adjustment
A Plunger
B Adjusting screw
C CapX 7.5 ±1.0 mm
(0.30 ±0.04 in)
19.11 Stepper motor adjustment
A LocknutB Feeler blade
19.14 Stepper motor plunger positions
A Vent manifold/start
B Anti-dieselingC Idle
19.4 Carburettor stepper motor and
mounting bracket18.15 Removing the engine management
modules (glovebox removed for clarity)
procarmanuals.com
Page 128 of 255

2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Drain the cooling system (Chapter 3). Save
the coolant if it is fit for re-use.
4Disconnect the multi-plug from the sensor.
Pull on the plug, not on the wiring (see
illustration).
5Unscrew the sensor and remove it.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Refill the cooling system.
Note: The manifold heater must not be
removed while it is hot.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead. 2Remove the air cleaner to improve access.
3Remove the three bolts which secure the
heater to the underside of the manifold.
4Disconnect the electrical feed from the heater.
5Remove the heater. Recover the gasket and
O-ring (see illustration).
6Use a new gasket and O-ring when refitting.
Offer the heater to the manifold, insert the
three bolts and tighten them evenly, making
sure that the heater does not tip or jam.
7Reconnect the electrical feed.
8Refit the air cleaner and reconnect the
battery.
All relays are located behind the facia panel.
Access is gained by removing the facia top
(see illustration).
Testing of a suspect relay is by substitution
of a known good unit.
1All models have a facility for retarding the
ignition timing by up to six degrees without
physically disturbing the distributor. The
adjustment is intended for use when the
correct grade of fuel is not available.
2Adjustment is made by earthing one or two
leads (sometimes called “octane adjustment”
leads) which terminate in a multi-plug next to
the ignition coil (see illustrations). Ideally a
service adjustment lead, available from a Ford
dealer, should be used. Cut and insulate the
wires in the adjustment lead which are not to
be earthed.
3The amount of ignition retardation is as
follows:
Wire(s) Degrees retard
earthed Carb. injection V6
Blue 2 4 6
Red 4 2 3
Blue and red 6 6 Forbidden
4Performance and efficiency will suffer as a
result of this adjustment. Normal timing should
be restored (by isolating the adjustment leads)
when the correct grade of fuel is available.
5If the yellow adjustment lead is earthed, thiswill raise the idle speed by 75 rpm (OHC) or 50
rpm (V6). It may be found that the yellow lead
has already been earthed in production, in
which case disconnecting it will lower the idle
speed by the same amount. This adjustment
does not apply to 1.8 litre carburettor models.
1.8 models from January 1987
6The effect of the “octane adjustment” leads
on these models fitted with the ESC Hybrid
Module is as follows.
Red lead earthed2°retarded
Blue lead earthed4°retarded
Red and blue leads earthed6°retarded
1Fitted to DOHC engines,the sensor is
located at the right-hand rear of the cylinder
block, behind the oil filter (see illustration).
2To remove the sensor, first disconnect the
battery negative lead.
3Access is most easily obtained from
underneath the vehicle. To improve access,
apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking”).
4Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor.
5Remove the securing screw and withdraw the
sensor from the location in the cylinder block.
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, using a
new sensor O-ring and tightening the retaining
screw to the specified torque setting.
24Crankshaft speed/position
sensor - removal and refitting
23Ignition timing and idle speed
adjustments
22Engine management system
relays - testing
21Manifold heater (carburettor
models) - removal and refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•11
5
20.4 Coolant temperature sensor multi-plug21.5 Removing the manifold heater22.1 Engine management system relays
A Power holdB Manifold heater
23.2a Octane adjustment lead multi-plug
23.2b Service adjustment lead for timing
and idle adjustment
A Earthing point (coil
screw)
B Multi-plugC Cut wires not to be
earthed
24.1 Crankshaft speed/position sensor
(viewed from underneath)
procarmanuals.com
Page 130 of 255

Chapter 10
Braking system
ABS module - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Brake discs - inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Brake hydraulic system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Brake hydraulic system - fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Brake pedal - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Brake pipes and hoses - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . .21
Control module (April 1992 on) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .31
Front brake disc - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Front brake pads - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Front caliper - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Front caliper - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
G (gravity) switch (April 1992 on) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .33
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Handbrake cable - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Handbrake cable - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Handbrake control lever - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Hydraulic unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Hydraulic unit accumulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .17Hydraulic unit fluid reservoir - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Hydraulic unit hoses - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Hydraulic unit pressure switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .19
Hydraulic unit pump and motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .18
Master cylinder (April 1992 on) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .27
Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) (April 1992 on) - removal and refitting . .32
Rear brake disc - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Rear brake pads - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Rear caliper - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Rear caliper - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Rear disc splash shield - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Vacuum servo unit (April 1992 on) - testing, removal and refitting .28
Vacuum servo unit check valve (April 1992 on) - removal, testing and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Valve block and pump assembly (April 1992 on) - removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Wheel sensors - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
General
System type: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Discs all round, hydraulic operation, anti-lock braking system
(ABS). Handbrake by mechanical operation of rear calipers
System make:
Models up to April 1992 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Teves MK II ABS
Models from April 1992 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Teves MK IV ABS
Hydraulic system
Fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hydraulic fluid to Ford spec SAM-6C9103-A
Operating pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130 to 190 bar (1885 to 2755 lbf/in2)
Pressure warning switch operates at . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 to 110 bar (1450 to 1595 lbf/in2)
Brake pads
Lining minimum thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm (0.06 in)
Brake discs
Run-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.15 mm (0.006 in) maximum
Thickness variation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.015 mm (0.0006 in) maximum
Minimum thickness:
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 mm (0.87 in)
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cast into outer rim (typically 8.9 mm/0.35 in)
Rear - Estate models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 mm (0.71 in)
10•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
10
procarmanuals.com
Page 131 of 255
Models covered in this Manual have disc
brakes fitted all round. The footbrake operates
hydraulically on all four wheels, and the
handbrake operates mechanically on the rear
wheels. Both footbrake and handbrake are
self-adjusting in use.
Ford’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) is
fitted to all models. The system monitors the
rotational speed of each roadwheel. When a
wheel begins to lock under heavy braking, the
ABS reduces the hydraulic pressure to that
wheel, so preventing it from locking. When this
happens a pulsating effect will be noticed at
the brake pedal. On some road surfaces the
tyres may squeal when braking hard even
though the wheels are not locked.
The main components of the system are the
hydraulic unit, the calipers, pads and discs,
the wheel sensors and the “brain” or control
module. The hydraulic unit contains the
elements of a traditional master cylinder, plus
an electric motor and pump, a pressure
accumulator and control valves. The pump is
the source of pressure for the system and
does away with the need for a vacuum servo.
The hydraulic circuit is split front and rear,
as is normal practice with rear-wheel drive
vehicles. In the event that the hydraulic pump
fails, unassisted braking effort is still available
on the front calipers only.
Warning lights inform the driver of low brake
fluid level, ABS failure and (on some models)
brake pad wear. The low fluid level light
doubles as a “handbrake on” light; if it
illuminates at the same time as the ABS
warning light, it warns of low hydraulic
pressure.
ABS cannot overturn the laws of physics:
stopping distances will inevitably be greater on
loose or slippery surfaces. However, the system
should allow even inexperienced drivers to
retain directional control under panic braking.
From August 1986 the following
modifications were made to the braking
system.
a)The relays differ from earlier versions.b)The hydraulic pump is constructed of iron
rather than alloy.
c)A new pressure warning switch is used.
d)The earlier high pressure rubber hose is
replaced by a steel pipe.
To overcome the problem of excessive rear
brake pad wear, Ford introduced a differential
valve which is screwed into the ABS valve
block.The valve limits the pressure applied to
the rear brake calipers and so reduces brake
pad wear. From 1988 onwards, the valve has
been fitted during production. The differential
valve can also be fitted to earlier models. Refer
to your Ford dealer for further information.
From April 1992 onwards, the models
covered in this Manual were equipped with a
new Teves MK IV anti-lock braking system
instead of the Teves MK II system fitted to the
earlier models.
The Teves MK IV system differs from the
earlier MK II system in the following ways.
a)The source of hydraulic pressure for the
system is a conventional master cylinder
and vacuum servo assembly.
b)A valve block and pump assembly is used
instead of the hydraulic control unit. The
block contains the inlet and outlet
solenoid valves that control the hydraulic
system. There are three pairs of valves,
one for each brake circuit (paragraph c).
c)The hydraulic braking system consists of
three separate circuits; one for each front
brake (which are totally independent of
each other), and a joint circuit which
operates both rear brakes.
d)A G (gravity) switch is incorporated in the
system. This is an inertia type switch and
informs the control module when the
vehicle is decelerating rapidly.
e)A Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) is fitted to the
vacuum servo unit. The PTS informs the
control module of the position of the brake
pedal when the anti-lock sequence starts
and ensures that a constant pedal height
is maintained during the sequence.
The MK IV system operates as follows.
During normal operation the system
functions in the same way as a non-ABS
system would. During this time the three inlet
valves in the valve block are open and theoutlet valves are closed, allowing full hydraulic
pressure present in the master cylinder to act
on the main braking circuit. If the control
module receives a signal from one of the
wheel sensors and senses that a wheel is
about to lock, it closes the relevant inlet valve
in the valve block which then isolates the
brake caliper on the wheel which is about to
lock from the master cylinder, effectively
sealing in the hydraulic pressure. If the speed
of rotation of the wheel continues to decrease
at an abnormal rate, the control module will
then open the relevant outlet valve in the valve
block; this allows the fluid from the relevant
hydraulic circuit to return to the master
cylinder reservoir, releasing pressure on the
brake caliper so that the brake is released. The
pump in the valve block also operates to assist
in the quick release of pressure. Once the
speed of rotation of the wheel returns to an
acceptable rate the pump stops, the outlet
valve closes and the inlet valve is opened,
allowing the hydraulic master cylinder
pressure to return to the caliper which then
reapplies the brake. This cycle can be carried
many times a second. The solenoid valves
connected to the front calipers operate
independently, but the valve connected to the
rear calipers operates both calipers
simultaneously.
The operation of the ABS system is entirely
dependent on electrical signals. To prevent
the system responding to any inaccurate
signals, a built-in safety circuit monitors all
signals received by the control module. If an
inaccurate signal or low battery voltage is
detected, the ABS system is automatically
shut down and the warning lamp on the
instrument cluster is illuminated to inform the
driver that the ABS system is not operational.
Whilst in this state the system functions in the
same way as a non-ABS system would. If a
fault does develop in the ABS system, the car
must be taken to a Ford dealer for fault
diagnosis and repair. The system is equipped
with a diagnostic plug into which a special
diagnostic (STAR) tester can be plugged. This
allows faults to be easily traced.
1General information
10•2Braking system
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Front caliper:
To stub axle carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Slide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Rear caliper:
Bracket to carrier plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Slide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31 to 3523 to 26
Hydraulic unit to bulkhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Accumulator to pump body . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Pump mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 95 to 7
High pressure hose banjo bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 to 2412 to 18
Reservoir mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 to 63 to 4
Wheel sensor fixing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Vacuum servo unit retaining nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Master cylinder retaining nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Valve block and pump assembly mounting nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . .21 to 2815 to 21
procarmanuals.com
Page 134 of 255

1It is necessary to remove the rear wheels in
order to inspect the rear pads. The pads can
be viewed through the top of the caliper after
removing the spring clip. If any one pad is
worn down to the minimum specified, all four
pads (on both rear wheels) must be renewed.
2Free the handbrake cable from its clip on
the suspension lower arm. Release the
handbrake.
3Remove the caliper slide bolt nearest the
front, counter-holding the slide pin with
another spanner (see illustration).
4Disconnect the pad wear warning wires,
when fitted (see illustration).
5Swing the caliper rearwards and remove the
pads (see illustration). Do not press the brake
pedal with the caliper removed.
6Clean the dust and dirt from the caliper,
bracket and disc, using a damp cloth or old
paintbrush which can be thrown away
afterwards. Take care not to disperse the dust
into the air, or to inhale it, since it may contain
asbestos. Scrape any scale or rust from the
disc. Investigate any hydraulic fluid leaks.
7Retract the caliper piston, by turning it
clockwise, to accommodate the extra
thickness of the new pads. There is a Ford tool
(No 12-006) for this purpose, but a pair of
circlip pliers or any similar tool can be used
instead (see illustration).
8Remove any backing paper from the newpads, then fit them to the caliper bracket. Be
careful not to contaminate the friction surfaces
with oil or grease.
9Swing the caliper over the pads. Refit and
tighten the slide bolt.
10Reconnect the wear warning wires, if fitted.
11Repeat the operations on the other rear
caliper.
12Secure the handbrake cable, refit the wheels
and lower the vehicle. Tighten the wheel nuts.
13Switch on the ignition and pump the brake
pedal several times to bring the pads up to the
discs. Switch off the ignition and check the
operation of the handbrake.
14Avoid heavy braking as far as possible for
the first hundred miles or so to allow the new
pads to bed in.
1With the ignition off, pump the brake pedal
at least 20 times (or until it becomes hard) to
depressurise the hydraulic system.
2Slacken the front wheel nuts, raise and
support the vehicle and remove the relevant
front wheel.
3Slacken the flexible hose hydraulic union at
the caliper by no more than a quarter turn.
4Remove the brake pads (Section 7).
5The caliper can now be removed by holding
the flexible hose stationary and rotating the
caliper to unscrew it. Be prepared for hydraulic
fluid spillage: plug or cap the caliper and hose.A brake hose clamp may be used if available
(see illustration). Take great care to keep dirt
out of the hydraulic system.
6The caliper bracket may be unbolted from
the stub axle carrier if wished.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations,
but before refitting the wheel, check the
positioning of the flexible hose. It must not be
kinked, nor foul adjacent components, in any
position of the steering wheel. Release the
other end of the hose from its bracket if
necessary and reposition it.
8Bleed both front brake calipers as described
in Section 2.
1It is possible to carry out these operations
without disconnecting the caliper hydraulic
hose, but this is not recommended because of
the risk of introducing dirt into the hydraulic
system. Scrupulous cleanliness is essential.
2Obtain a caliper repair kit, which will contain
a piston seal and a dust boot. (The piston itself
can also be renewed if necessary.)
3Remove the piston from the caliper. This is
best done with low air pressure (eg from a foot
pump) applied to the hydraulic inlet union.
Place a piece of wood opposite the piston to
prevent damage, and keep your fingers clear
as the piston may be ejected with some force.
4With the piston removed, pull off the dust
boot (see illustration).
10Front caliper - overhaul
9Front caliper - removal and
refitting
8Rear brake pads - inspection
and renewal
Braking system 10•5
10
8.3 Undoing a rear caliper front slide bolt8.4 Pad wear warning multi-plug (arrowed)
on rear caliper8.5 Removing a rear brake pad
8.7 Rotating the caliper piston to retract it9.5 Removing a front caliper - note clamp
on brake hose10.4 Removing the dust boot from a front
caliper
procarmanuals.com
Page 135 of 255

5Extract the piston seal from the groove in
the bore, using a blunt instrument (see
illustration). Discard the seal and dust boot.
6Clean the piston and bore with methylated
spirit and inspect them for scuffs, scores or
other damage. If the piston is corroded it must
be renewed. Slight imperfections in the bore
can be polished out with wire wool.
7Place the clean component on a clean
surface ready for reassembly. Lubricate the
caliper hose with clean hydraulic fluid.
8Fit the new piston seal to the groove in the
bore, using fingers only to work it into position.
9Lubricate the piston with clean hydraulic
fluid and fit the dust boot over the piston,
making sure it is the right way up. Insert the
piston into the bore and press it home,
engaging the dust boot lip with the groove on
the caliper (see illustration).
10This completes the overhaul of the hydraulic
components. Items such as slide bolts and
bracket can also be renewed if necessary.
11Remove the bleed screw while the caliper
is on the bench and apply a little anti-seize
compound to its threads, to avoid trouble in
undoing it later.
1With the ignition off, pump the brake pedal
at least 20 times (or until it becomes hard) to
depressurise the system.
2Chock the front wheels and release the
handbrake. Slacken the rear wheel nuts, raiseand support the vehicle and remove the
relevant wheel.
3Disconnect the pad wear warning wires,
when fitted.
4Disconnect the flexible hose from the brake
pipe. Plug or cap the open unions to reduce
spillage and to keep dirt out. Unscrew the
flexible hose from the caliper and remove it.
5Remove the two slide bolts. Lift the caliper
off the pads and bracket, at the same time
unhooking the handbrake cable (see
illustrations). Alternatively, the two bracket-
to-hub bolts can be removed and the caliper
and bracket separated on the bench.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations,
but before refitting the wheel, bleed both rear
calipers as described in Section 2.
7When bleeding is complete, pump the brake
pedal several times to bring the pads up to the
disc, then check the operation of the
handbrake.
Note: Complete dismantling of the rear caliper
should not be attempted unless Ford spring
compressor (tool No 12-007) is available. or
unless the problems likely to arise in the absence
of the tool are understood. Renewal of the piston
seal and dust boot requires no special tools.
1Clean the caliper externally and mount it in a
soft-jawed vice.
2Rotate the piston anti-clockwise until it isprotruding from the bore by about 20 mm (0.8 in).
Free the dust boot from the groove in the
piston, then carry on unscrewing the piston
and remove it. Remove and discard the dust
boot.
3The piston and bore may now be cleaned
and examined, and the piston seal and dust
boot renewed, as described for the front
caliper (Section 10).
4The piston adjuster nut seal should also be
renewed. Remove the circlip from the piston,
then extract the thrustwashers, wave washer
and thrust bearing. Note the fitted sequence of
these components. Finally remove the nut
(see illustrations).
5Remove the seal from the nut, noting which
way round it is fitted. Clean the nut with
methylated spirit. Lubricate the new seal with
clean hydraulic fluid and fit it to the nut.
12Rear caliper - overhaul
11Rear caliper - removal and
refitting
10•6Braking system
10.5 Removing the piston seal
12.4a Removing the circlip from a rear
caliper piston . . .12.4b . . . followed by a thrustwasher . . .
11.5b . . . and remove the rear caliper
10.9 Pressing the piston into the bore11.5a Unhook the handbrake cable . . .
12.4c . . . a wave washer and (not shown)
another thrustwasher . . .
procarmanuals.com