ect HONDA CIVIC 2000 6.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 2000, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 2000 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 691 of 2189
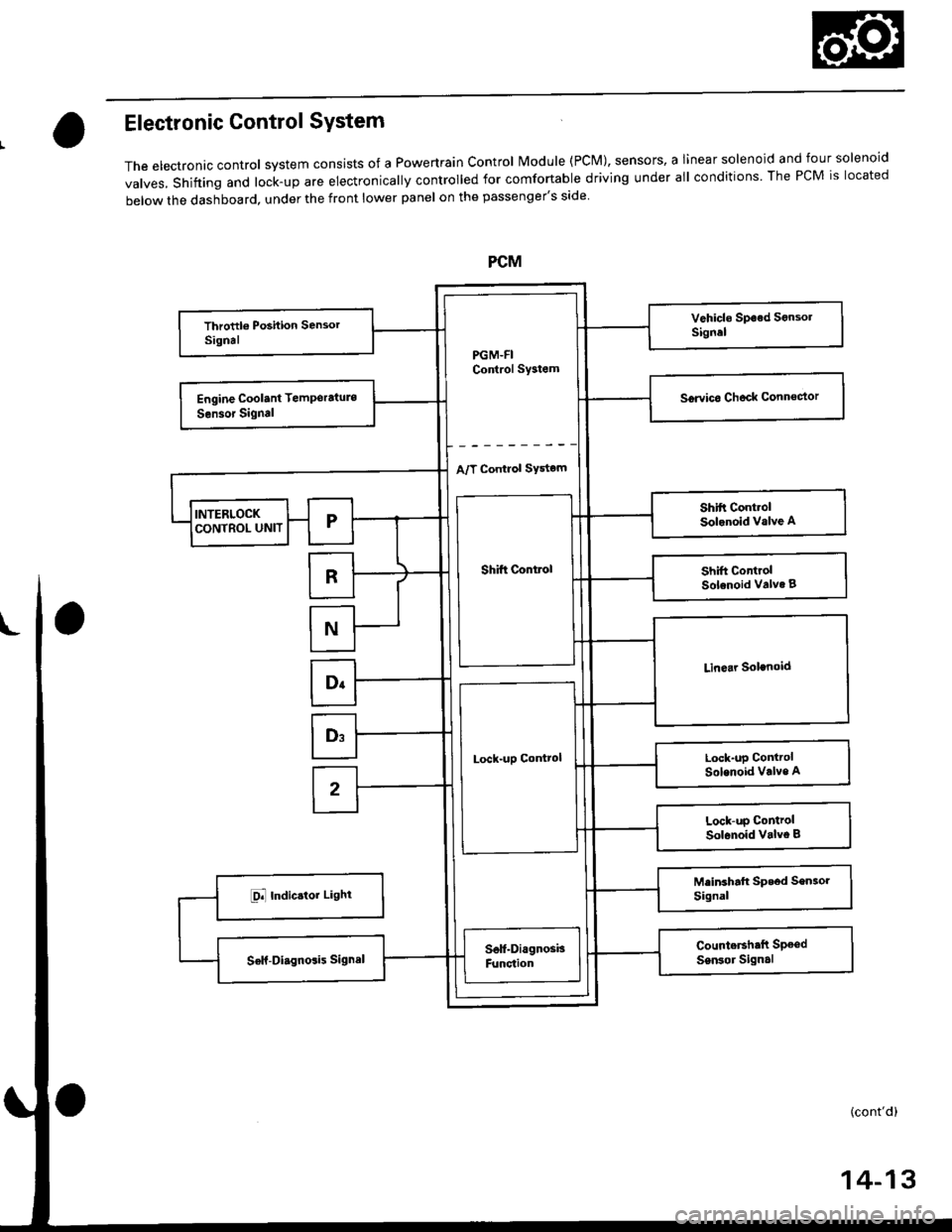
Electronic Control SYstem
The electronac controt system consrsts of a Powertrain control Module (PcM), sensors, a Iinear solenoid and four solenoid
valves, shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions The PCM is located
below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
PGM-FIControl Sy3tem
A/T Control SYstom
Shift Control
Lock-uD Control
14-13
Page 692 of 2189
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
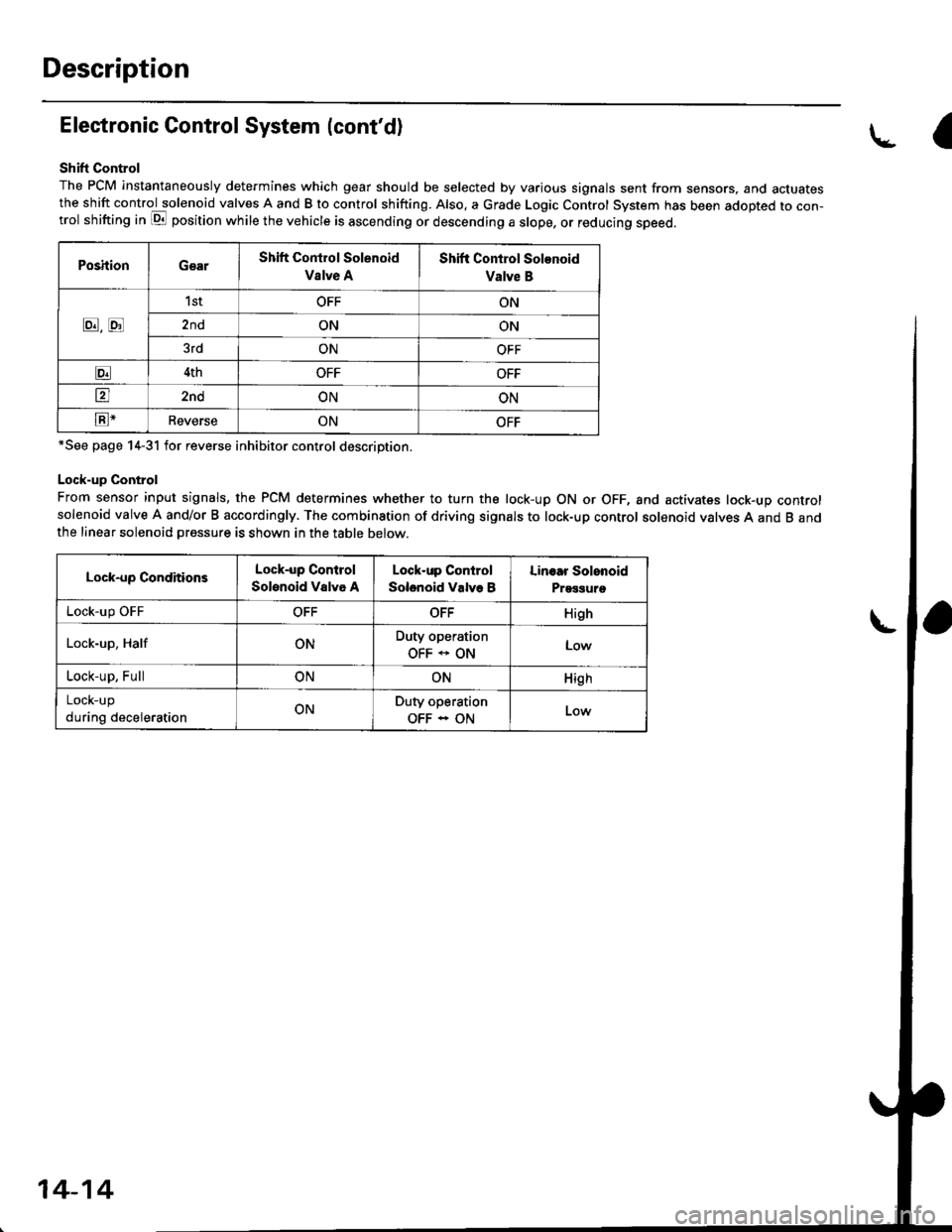
Shift Control
The PCM instantaneously determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuatesthe shift control solenoid valves A and B to control shifting. Also. a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to con-trol shifting in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speed.
PoshionGearShift Control Solenoid
Vslve A
Shift Control Solenoid
Valve B
8,tr
1stOFFON
2ndONON
3rdONOFF
E4thOFFOFF
tr2ndONON
E-ReverseONOFF
*See page 14-31 for reverse inhibitor control description.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the PCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up controlsolenoid valve A and/or B accordingly. The combination of driving signals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B andthe linear solenoid pressure is shown in the table below.
Lock-up ConditionsLock-up Control
Solenoid Valvo A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Linoar Solonoid
Prggguro
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF * ONLow
Lock-up, FullONONHigh
LOCK-Up
during decelerationONDuty operation
OFF - ON
a
14-14
Page 693 of 2189
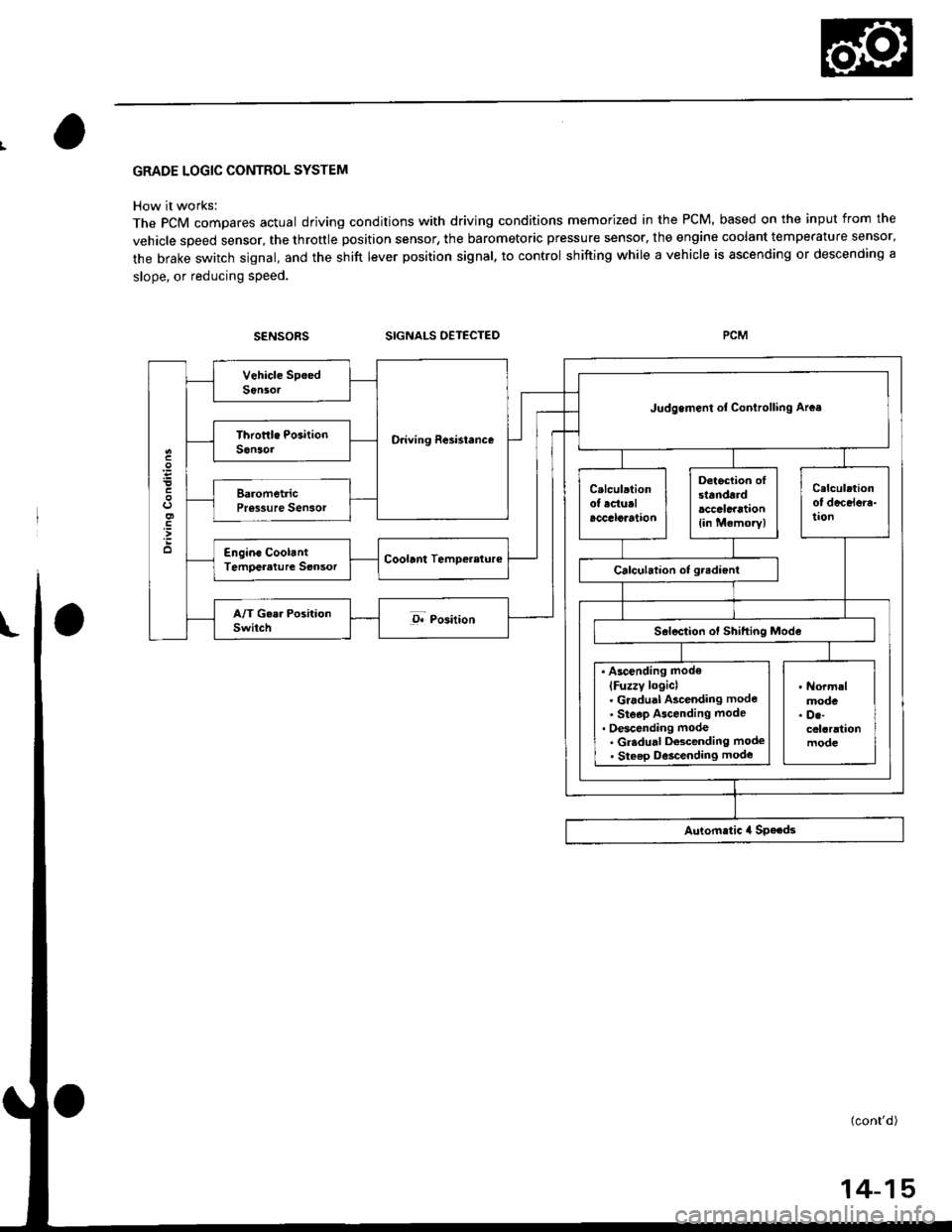
GRADE LOGIC CONTROL SYSTEM
How it works:
The pCM compares actual driving conditions with driving conditions memorized in the PCM, based on the input from the
vehicle speed sensor, the throttle position sensor, the barometoric pressure sensor, the engine coolant temperature sensor,
the brake switch signal, and the shift lever position signal, to control shifting while a vehicle is ascending or descending a
slope, or reducing speed.
SIGNALS OETECTED
O.iving Resi3lence
Judgemenl ot Conirolling Arca
. Ascending mod€
lFuzzy loqicl. Gradual Ascending mode' Ste€p Ascending mode. Oescending mode. Gr.du.l Descending mode. Steep D6cending mode
14-15
Page 694 of 2189
Description
Electronic Control System {cont'dl
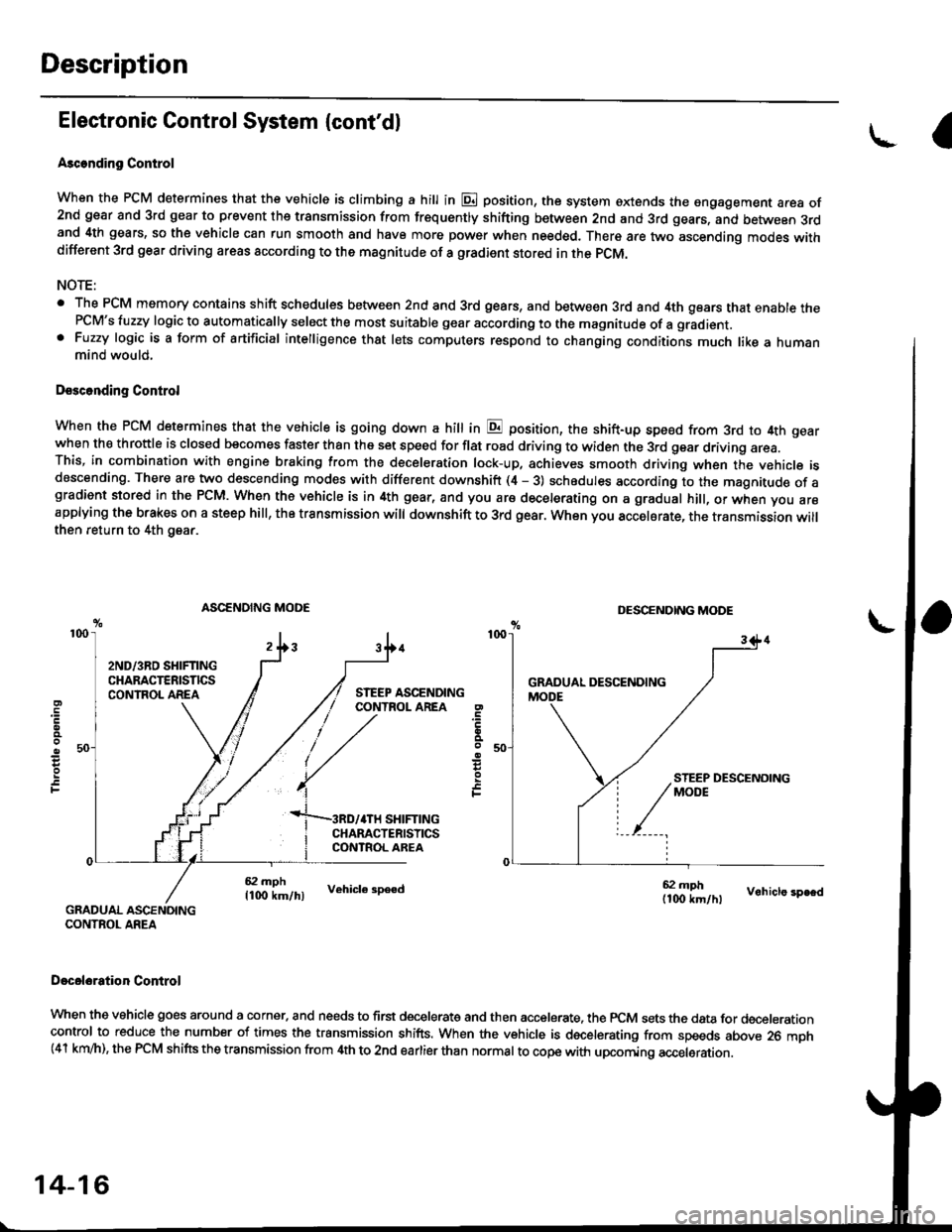
Ascending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E position, the system oxtends the sngagement area of2nd gear and 3rd gear to prevent ths transmission from fr€quently shifting between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rdand 4th gears, so the vehicle can run smooth and have more power when needed. There are two ascending modes withdifferent 3rd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradient stored in the pCM.
NOTE:
. The PCM memory contains shift schedules between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rd and 4th gears that enable thePCM's fuzzy logic to automatically select the most suitable gear according to the magnitude of a gradient. Fuzzy logic is a form of artificial intelligence that lets computers respond to changing conditions much like a humanmind would,
Dssconding Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hilt in E position, the shift-up speed from 3rd to 4th gearwhen th€ throftle is closed becomes faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear driving area.This, in combination with engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle isdescending. There are two descending modes with different downshift (4 - 3) schedules according to the magnitude of agradient stored in the PCM. When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating on a gradual hill, or when you areapplying the brakes on a steep hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear. When you accel6rate, the transmission willthen return to 4th gear.
ASCENDING MODEDESCENDING MODE
4TH SHIFTING
L.
F
CHARACTERISIICSCONTROL AREA
ff.1"11", vehicr. 3pe€dff;Tlr., vohicre speed
GRADUAL ASCENOINGCONTROL AREA
Docel6ration Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner. and needs to first decelerate and then accelerate. the rcM sets the data for decelerationcontrol to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 26 mph(41 km/h), the rcM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlier than normal to cope with upcoming acceleration.
14-16
Page 696 of 2189
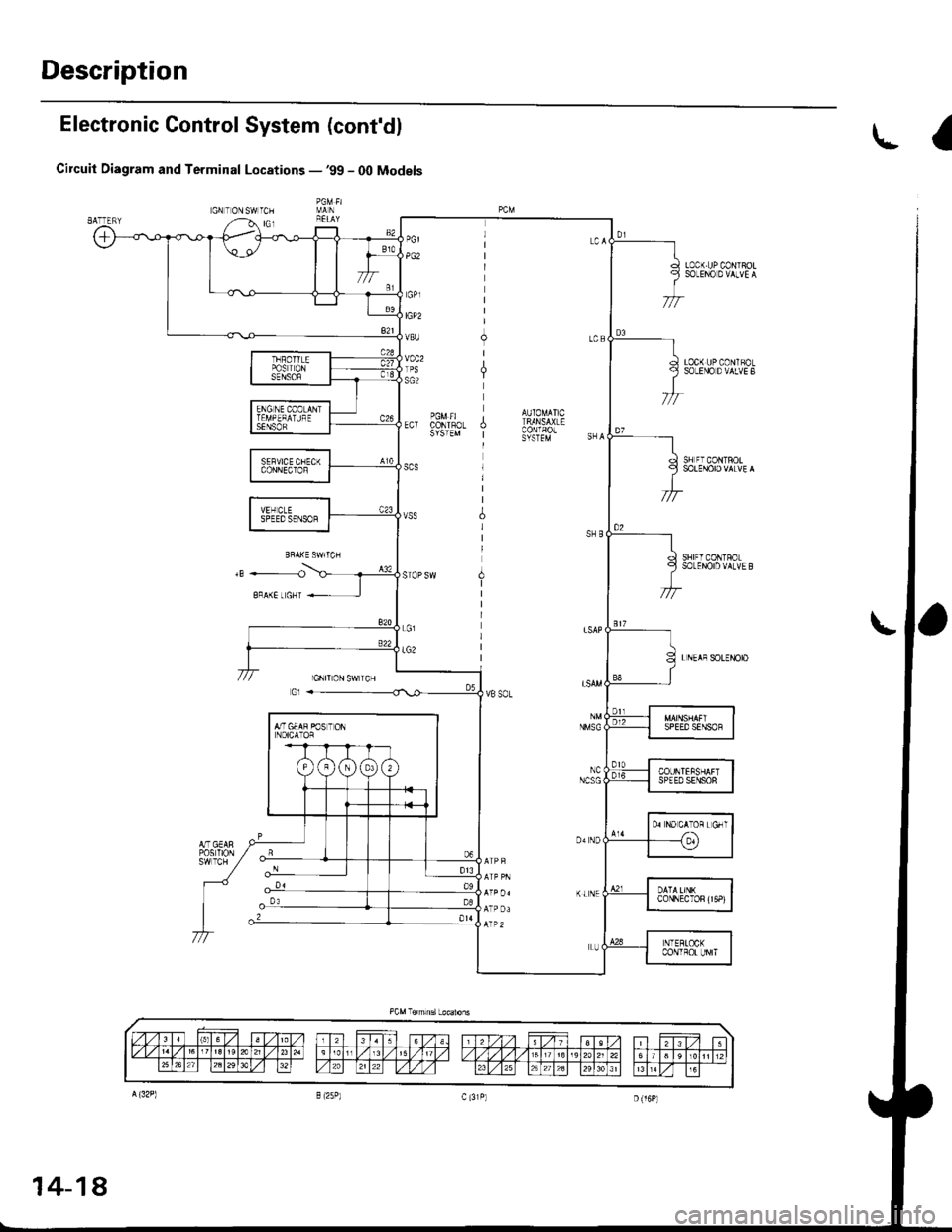
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'dl
Circuit Diagram and Terminal Locations -'99 - O0 Models
GNTONSWICH,,--b. rcj
LI
LOCK.UPCONIFOLSOLEI\Q D VALVE A
LOCK UP CON'IROLSOLENODVALVEB
SH FI CONTROL
SHIFTCONTFOLSOLENOIDVALVEE
L NEAF SOLEIOIO
PG2
IGP2
v3u
vcc2
sc2
6NII ON SWICH
14-18
Page 697 of 2189
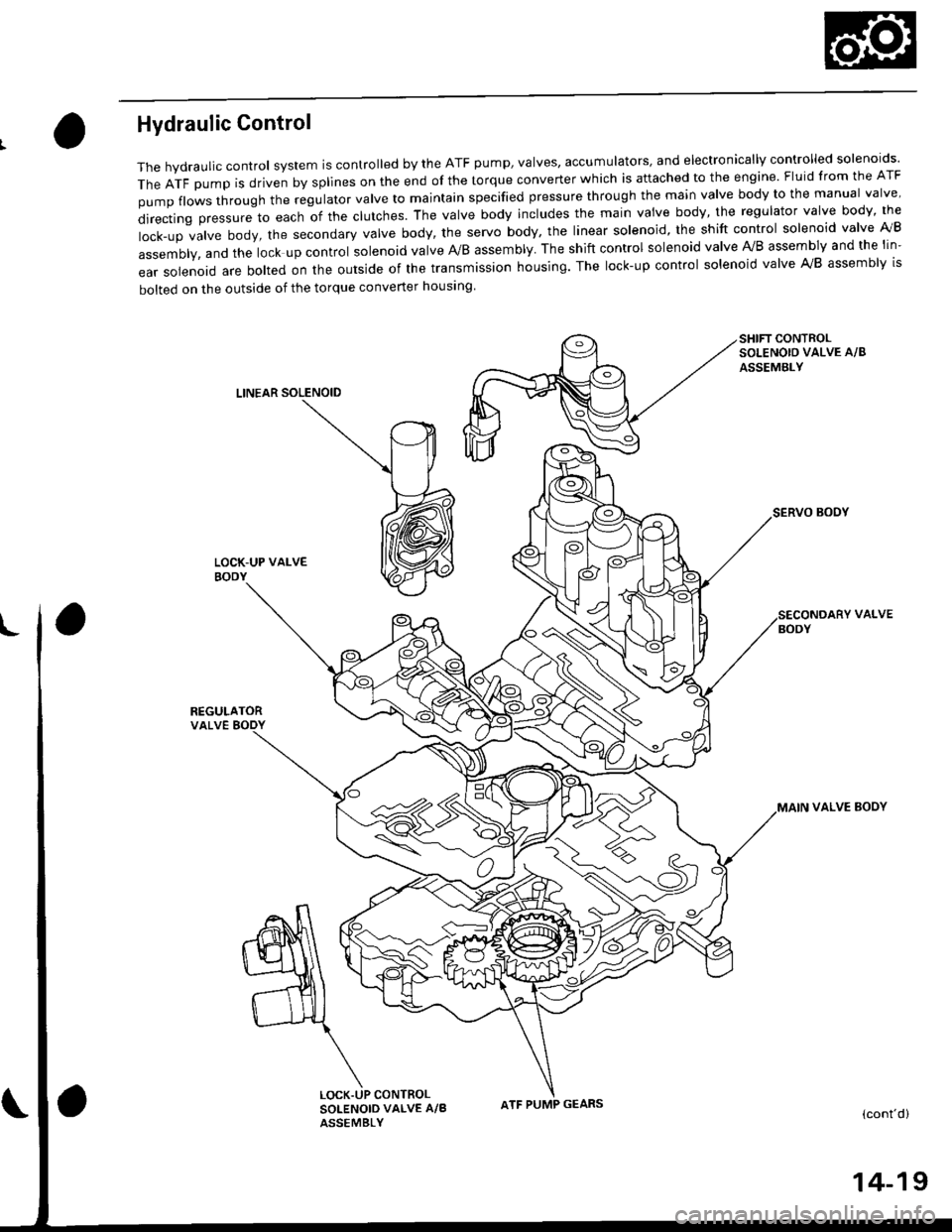
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids'
TheATFpUmpisdrivenbysp||nesontheendofthetorqueconverterWhichisattachedtotheengine.F|uidfromtheATF
pumpf|owsthroughtheregu|atorva|vetomajntainspecifiedpressurethroughthemainva|vebodytothemanuaIva|ve'
directingpressuretoeachofthec|utches.Theva|vebodyinc|udesthemainvaivebody,theregu|atorvalvebody,the
|ock-upva|vebody,thesecondaryVa|vebody,theservobody,theIinearso|enoid,theshiftcontro|so|enoidva|velVB
assembly, and the lock up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly and the lin-
ear solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is
bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOIO VALVE A/8
ASSEMBLY
LINEAR SOLENOID
SERVO BOOY
REGULATORVALVE BODY
VALVE
VALVE BOOY
(cont'd)
CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-19
Page 700 of 2189
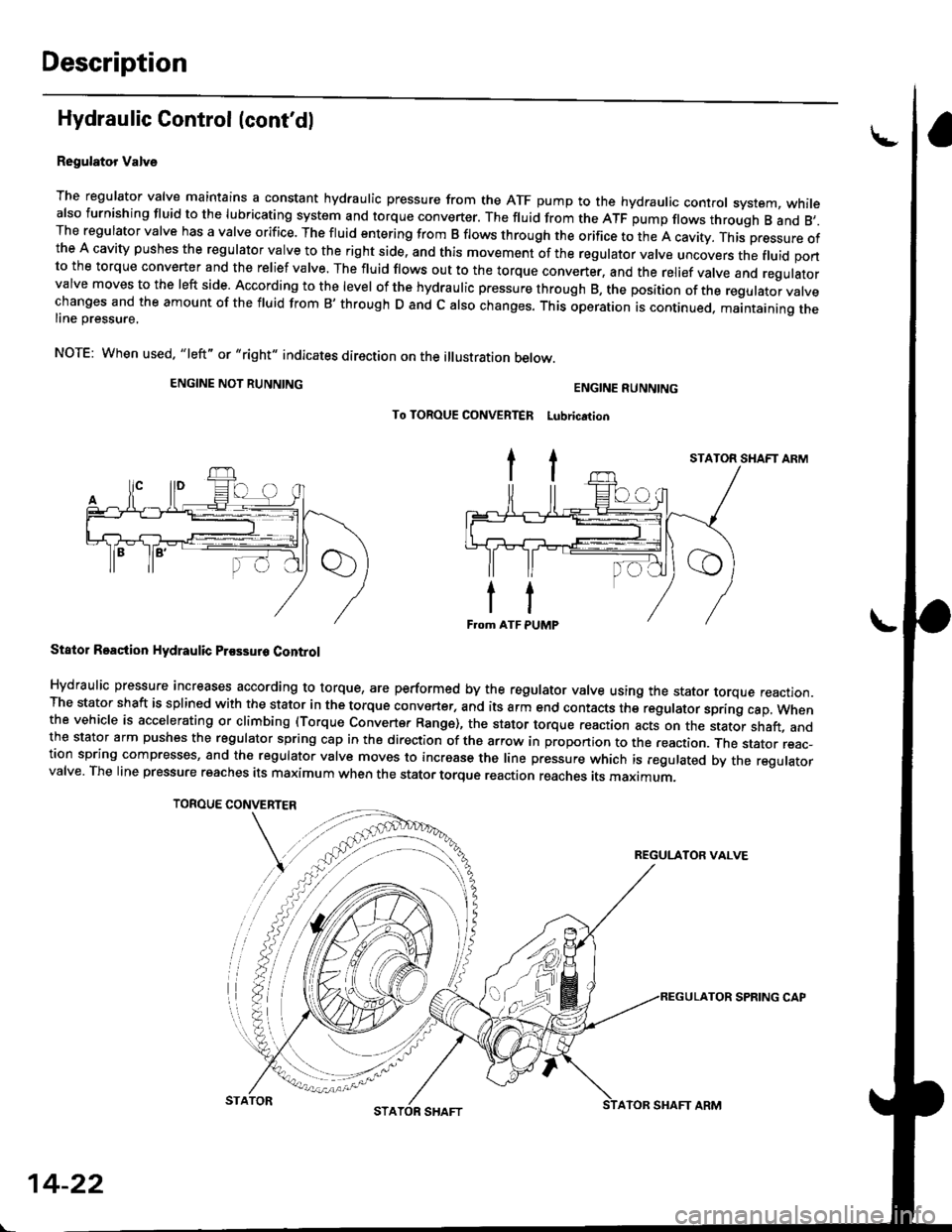
Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'dl
Regulator Valve
The regulator valve maintains a constant hydraulic pressure from the ATF pump to the hydraulic control system, whitealso furnishing fluid to the lubricating system and torque converter. The fluid from the ATF pump flows through B and 8,.The regulator valve has a valve orifice. The fluid entering from B flows through the orifice to the A cavity. This pressure ofthe A cavity pushes the regulator valve to the right side, and this movement of the regulator valve uncovers the fluid portto the torque converter and the relief valve. The fluid flows out to the torque converter, and the relief valve and regulatorvalve moves to the left side. According to the level of the hydraulic pressure through B, the position of the regutator vatvechanges and the amount of the fluid from B' through D and c also changes. This operation is continued. maantaining theline pressure,
NOTE: When used. "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the illustration betow.
ENGINE NOT RUNNING
TOROUE CONVERTER
ENGINE RUNNING
To TOROUE CONVERTER Lubrication
Stator Roaction Hydraulic Prossur6 Control
Hydraulic pressure increases according to torque, are performed by the regulator valve using the stator torque reaction.The stator shaft is splined with the stator in the torque converter, and its arm end contacts the regulator sprang cap. whenthe vehicle is accelerating or climbing (Torque Convert€r Range), the stator torque reaction acts on the stator shaft, andthe stator arm pushes the regulator spring cap in the direction of the arrow in proponion to the reaction. Jne stator reac-tion spring compresses, and th€ reoulator valve moves to increase the line pressure which is regulated by the regulatorvalve. The line pressure reaches its maximum when the stator torque reaction reaches its maximum.
STATOR SHAFT ARM
REGULATOR VALVE
14-22
STATORATOR SHAFT ARM
SPRING CAP
Page 702 of 2189
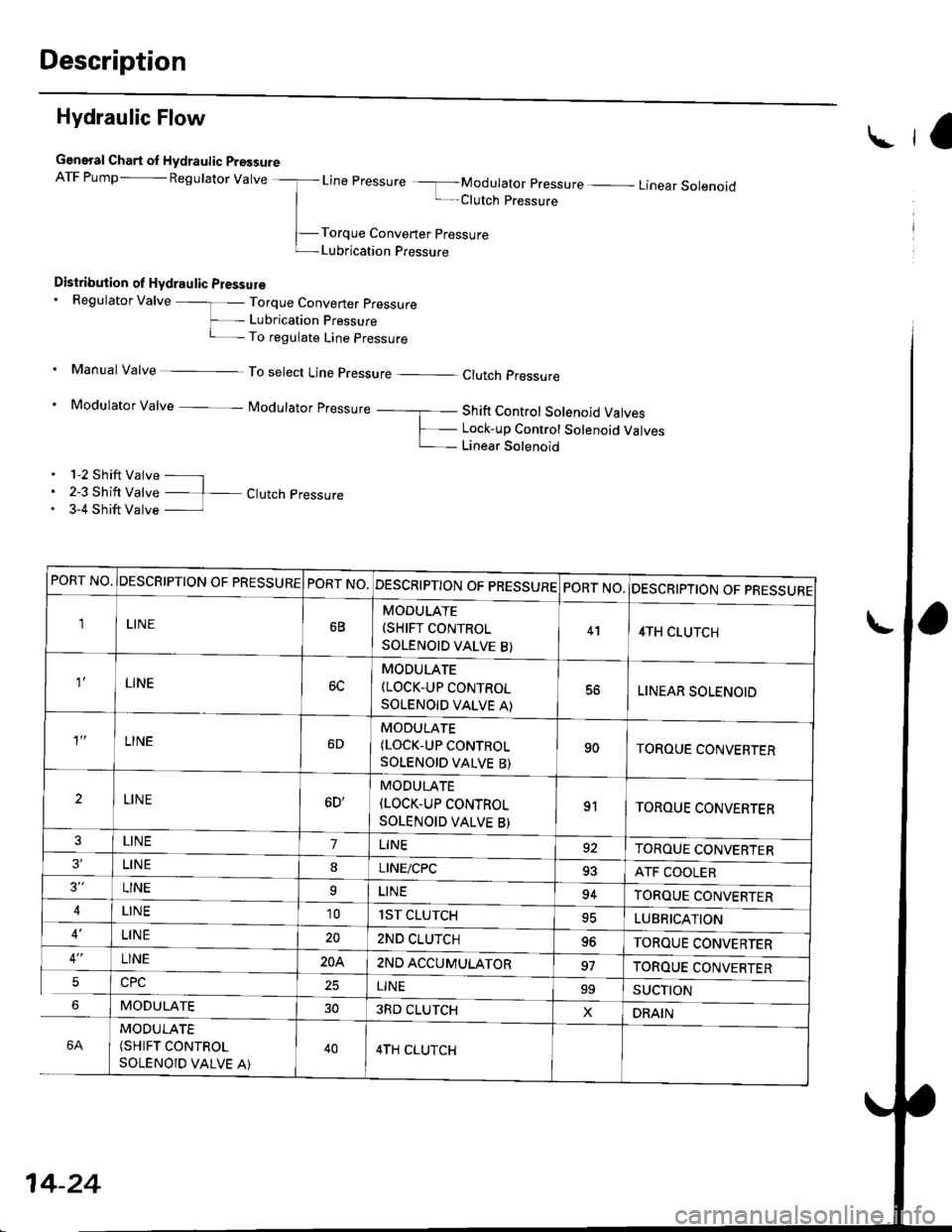
Description
Hydraulic Flow
General Chart ol Hydraulic PressureATF Pump- pegurator varve -_l- Line pressure -f- Modurator pressure - Linear sorenoid
| -Clutch pressure
-Torque Converter pressure
t-Lubrication Pressure
Distribution of Hydraulic Pressur€. Regulator Valve -]- Torque Converter pressure
F_ Lubrication pressure
i- To regulate Line pressure
. Manual valve _ To select Line pressure _ clutch pressure
' Modulator Valve i/odulator pressure _ ___f_ Shift Control Solenoid Valves
F_ Lock_up Control Solenoid ValvesL_ Linear Solenoid
. 1-2 Shift Valve - l. 2-3 Shift Valve - 1- Ctutch pressure. 3-4 Shift Valve
lra
PORT NO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSUREPORT NO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSUREPORT NO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSURE
1LINE6B
MODULATE(SHIFT CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE B)
414TH CLUTCH
LINEMODULATE(LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE A)
56LINEAR SOLENOID
LINE6D
MODULATE(LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE B)
90TOROUE CONVEBTER
2LINE6D'
MODULATE
(LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE B)
91TOROUE CONVERTER
LINE7LINE92TOROUE CONVERTERLINE8LINE/CPC93ATF COOLER3"LINE9LINE94TOROUE CONVERTER4LIN E'101ST CLUTCH95LUBRICATION
LINE202ND CLUTCHYOTOROUE CONVERTERLINE20A2ND ACCUMULATOR97TOROUE CONVERTER5LINE99SUCTION
MODULATE303RD CLUTCHXDRAIN
6A
MODULATE(SHIFT CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE A)
404TH CLUTCH
14-24
Page 703 of 2189
\
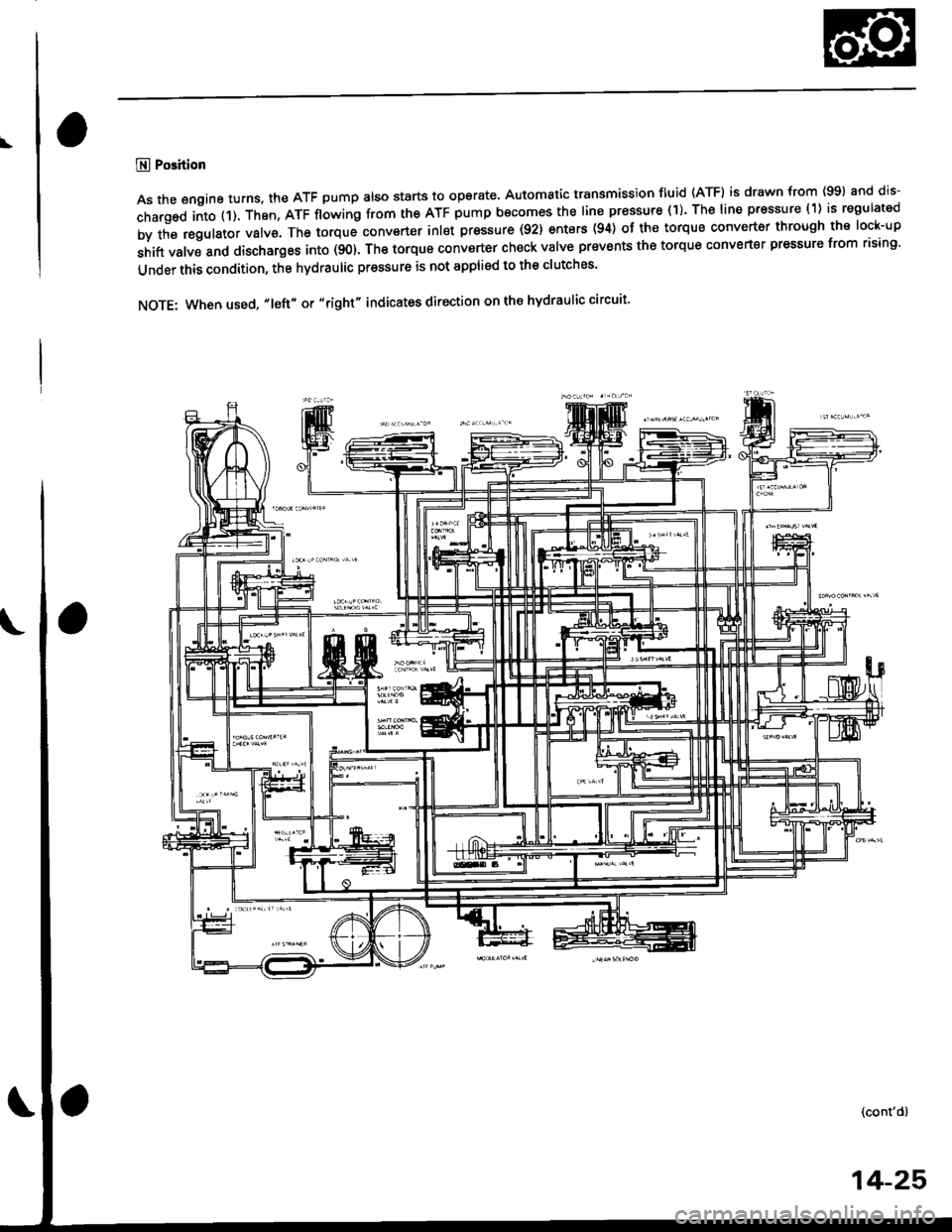
@ Position
As the engine turns, the ATF pump also starts to operate, Automatic transmission fluid (ATF) is drawn from (99) and dis-
charged into (1). Then, ATF flowing from the ATF pump becomes the line pressure (1). The line pressure (1) is regulated
by the regulator valve. The torque conv€rter inlet pressure (92) enters (94) of the torque converter through the lock-up
shift valve and discharges into (901. The torque converter ch€ck valve prevents the torque converter pressure from rising'
Under this condition, the hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches'
NOTE: When used, "1eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit'
14-25
Page 704 of 2189
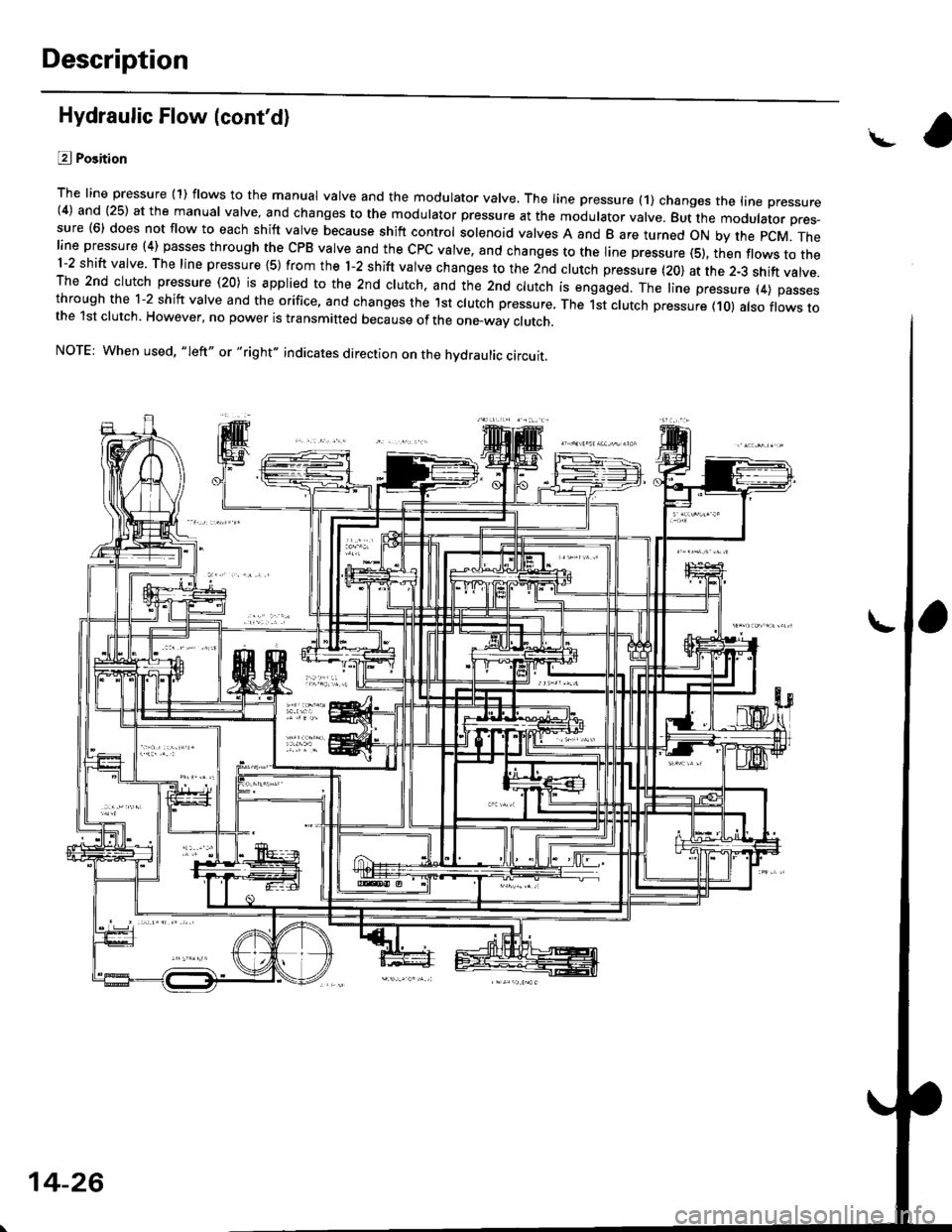
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'd)
L?j Position
The line pressure (1) flows to the manual valve and the modulator valve. The line pressure (1) changes the trne pressure(4) and (25) at the manual valve. and changes to the modulator pressure at the modulator valve. But the moourator pres-sure (6) does not flow to each shift valve because shift control solenoid valves A and B are turned oN by the pcM. Theline pressure (4) passes through the cPB valve and the cPc valve. and changes to the line pressure (s), th;n flows to the1-2 shift valve. The line pressure {S) from the l-2 shift valve changes to the 2nd clutch pressure (20) at the 2-3 shift valve.The 2nd clutch pressure (20) is applied to the 2nd clutch. and the 2nd clutch is engaged. The line pressure (4) passesthrough the 1-2 shift valve and the orifice, and changes the lst clutch pressure, The 1st clutch pressure (10) atso flows tothe 1st clutch. However, no power is transmitted because of the one_way clutch.
NOTE: When used, "Ieft" or "right" indicates direction on the hvdraulic circuit.
14-26