Gear HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: CR-V, Model: HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.GPages: 1395, PDF Size: 35.62 MB
Page 533 of 1395
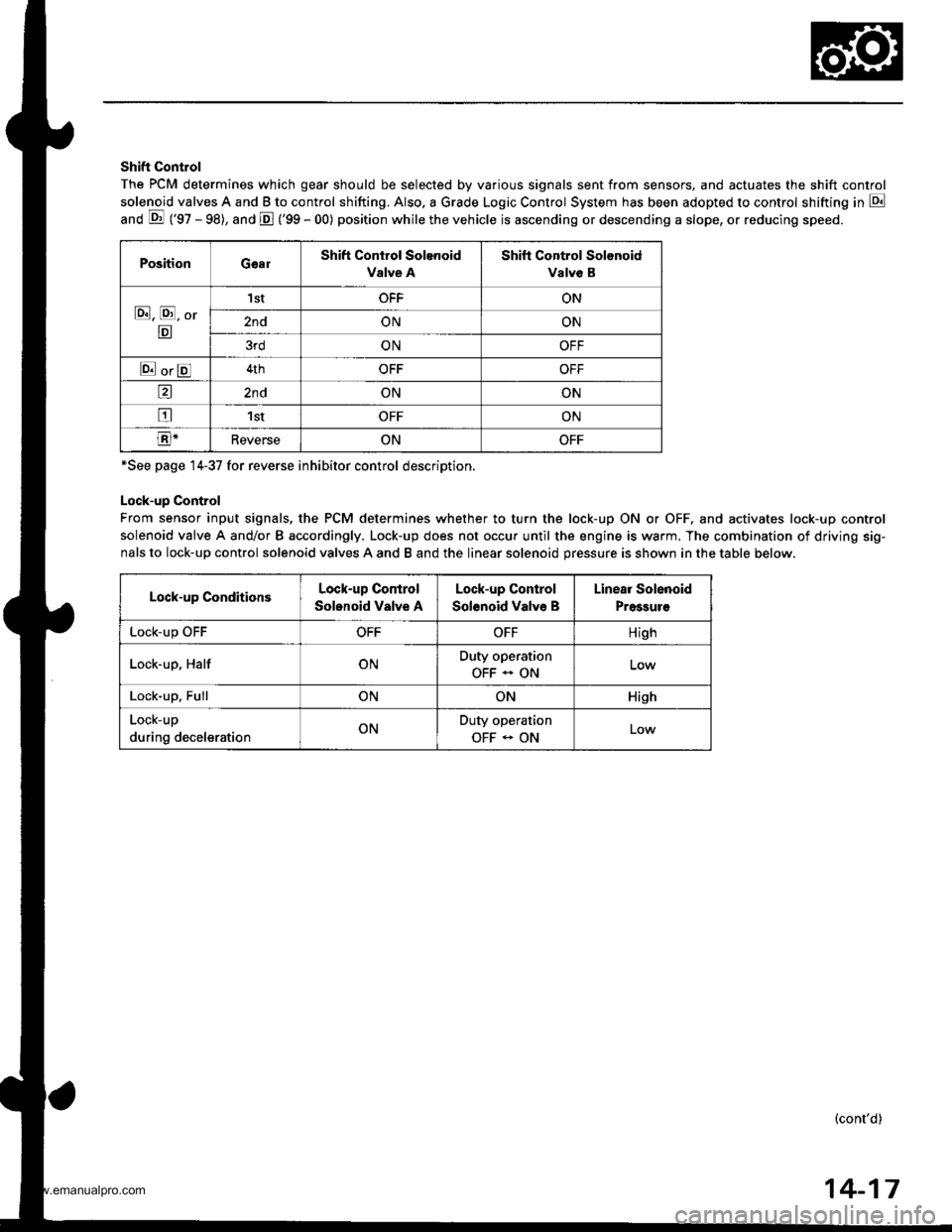
Shift Control
The PCM determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuates the shift control
solenoid valves A and B to control shifting. Also. a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to control shifting in E
anO E ('gZ - gg), and E ('99 - 00) position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speeo.
PositionGearShift Control Solenoid
Valve A
Shift Control Solonoid
Valve B
E, E, Or
E
'I stOFFON
2ndONON
3rdONOFF
E orE4thOFFOFF
a2ndONON
tr1stOFFON
E-ReverseONOFF
*See page 14-37 for reverse inhibitor control description.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the PCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up control
solenoid valve A and/or B accordingly. Lock-up does not occur until the engine is warm. The combination of driving sig-
nals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid pressure is shown in the table below.
Lock-up ConditionsLock-up Control
Solonoid Valve A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Linear Solenoid
Pressuro
LOCK-Up \JrrOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ON
Lock-up, FullONONHish
Lock-up
during decelerationONDuty operation
OFF - ONLow
(cont'd)
14-17
www.emanualpro.com
Page 535 of 1395
![HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
Ascending Control {37 Modol}
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E] and E positions, the system extends the engagement
area of 2nd g€ar and 3rd gear to prevent the transm HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
Ascending Control {37 Modol}
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E] and E positions, the system extends the engagement
area of 2nd g€ar and 3rd gear to prevent the transm](/img/13/5778/w960_5778-534.png)
Ascending Control {37 Modol}
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E] and E positions, the system extends the engagement
area of 2nd g€ar and 3rd gear to prevent the transmission from frequently shifting between 2nd and 3rd gears, and
between 3rd and 4th gears, so the vehicle can run smooth and have more power when needed.
NOTE:
. Shift schedules stored in ths PCM between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rd and 4th gears. enable the PCM's fuzzy
logic to automatically select the most suitable gear according to the magnitude of 8 gradient.
t Fuzzy logic is a form of artificial intslligence that lets computers respond to changing conditions much like a human
mind would.
3RD - tlTHASCENoING MODE: UFhift Sch.dulc
- . FLAT ROAD MODE
-----------. : GRADUAL ASCENDING MODE
- - - - - : STEEPASCENDING MODEo5l)
FFN1NS
7,.,.7a
: 2ND-3RD SHIFTING CHARACTERISTICSCONTROL AREA| 3RD-aTH SHIFTING CHARACTER|SnCSCONTROL AREA
62 mph
1100 km/h)Vehicle .o..d
Asconding Conirol ('98 - 00 Mod.ls)
When the PCM determines that the vohicle is climbing a hill in E] and E positions ('98 model), and in E] position ('99 -
00 models), the system extends the engagement srea of 2nd gear and 3rd gear to prevent the transmission from frequent-
ly shifting between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rd and 4th gears, so the vehicle can run smooth and have more
power when needed.
NOTE: Shift schedulss stored in the PCM between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rd and 4th gears, enable to selsct the
most suitable gear according to th6 magnitude of a gradi€nt.
ASCENDING MODE: Up.hift Sch.dul.
NN : 2ND-3RD SXImNG CHARACTERISTICS- GoNTRoLAREA
VVVVVZ:IRD-ITHSHIFnNGCHARACTERISTICS- cot{TRoL AREA
850
o
6:l mph11fl) km/hl
(cont'd)
2ND - 3RD
2ND + 3RD 3RD + 4TH
Vahicl. sDctd
14-19
www.emanualpro.com
Page 536 of 1395
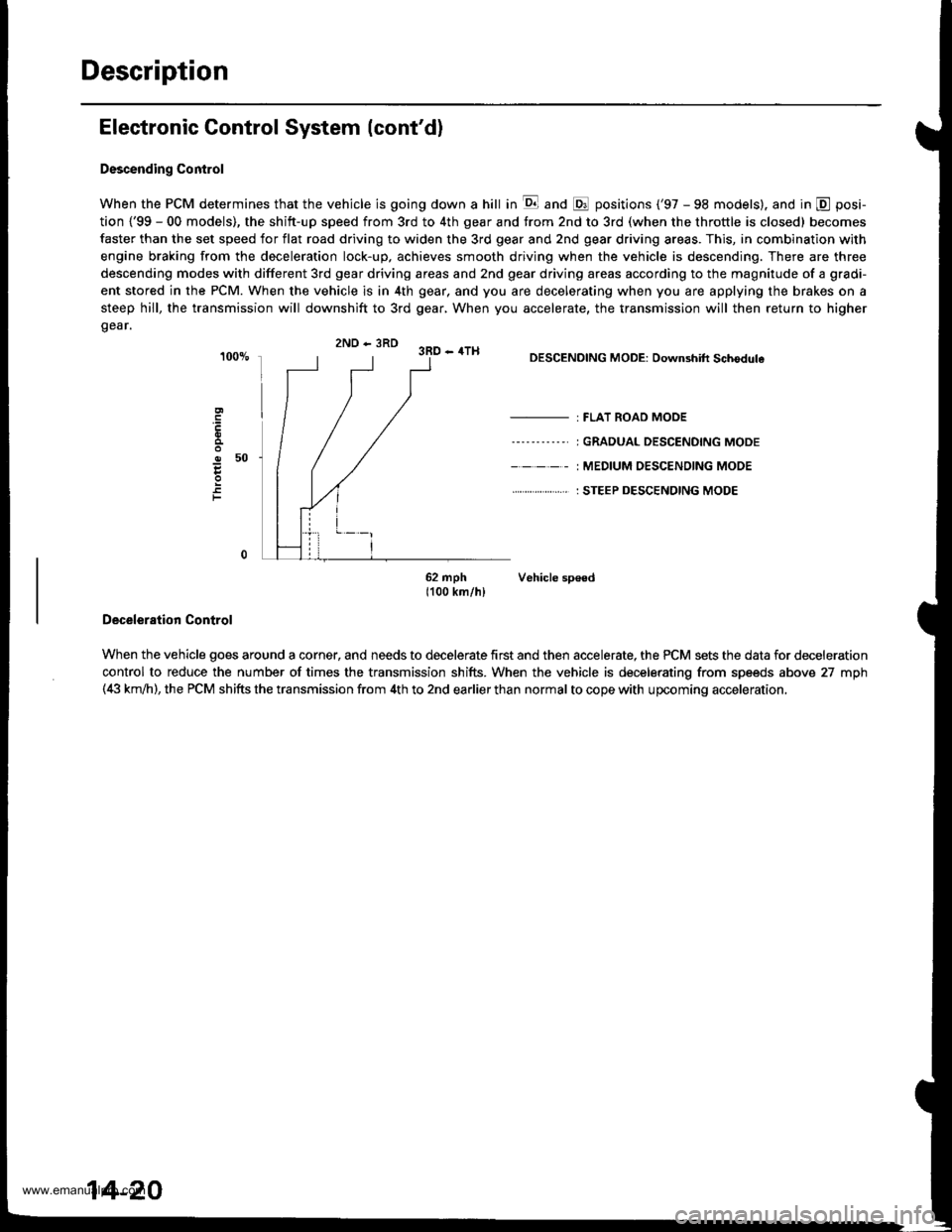
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
Descending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in E and @ positions ('97 - 98 models). and in @ posi-
tion {'99 - 00 models), the shitt-up speed from 3rd to 4th gear and from 2nd to 3rd (when the throttle is closed) becomes
faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear and 2nd gear driving areas. This, in combination with
engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle is descending. There are three
descending modes with different 3rd gear driving areas and 2nd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradi-
ent stored in the PCM. When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating when you are applying the brakes on a
steep hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear, When you accelerate, the transmission will then return to higher
gear.
2ND - 3RD 3RD - 4TH
o50
F
DESCENDING MODE: Downshift Schodule
- : FLAT ROAD MODE
----'-----' I GRADUAL DESCENDING MODE
- - - - - : MEDIUM OESC€NOING MODE
. . ... : STEEP DESCENDING MODE
62 mph Vehicle sp€ed1100 km/hl
Deceleration Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner, and needs to decelerate first and then accelerate, the PCM sets the data for deceleration
control to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 27 mph(4i| km,ih), the PCM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlier than normal to cope with upcoming acceleration,
14-20
www.emanualpro.com
Page 540 of 1395
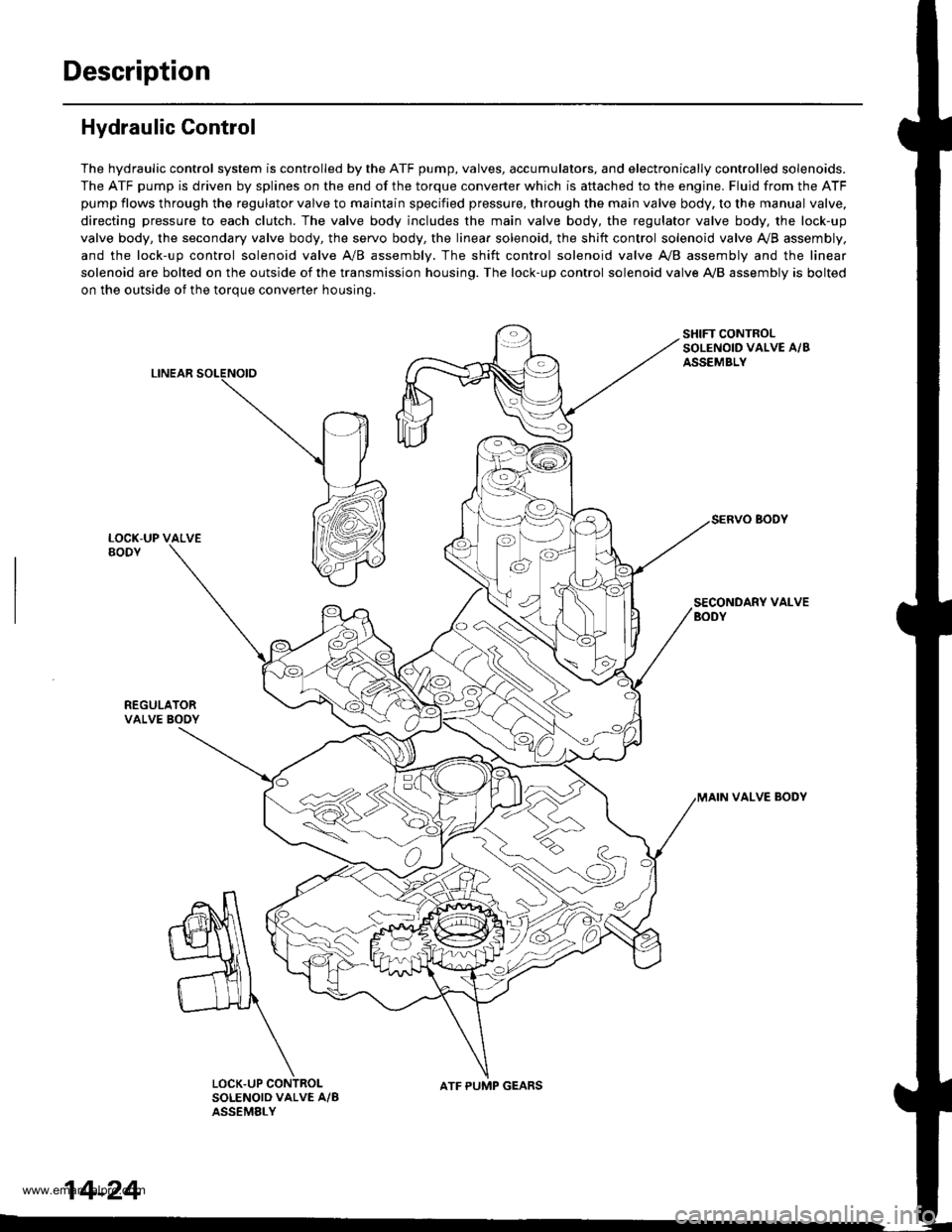
Description
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids.
The ATF pump is driven by splines on the end of the torque converter which is aftached to the engine. Fluid from the ATF
pump flows through the regulator valve to maintain specified pressure, through the main valve body, to the manual valve,
directing pressure to each clutch. The valve body includes the main valve body, the regulator valve body, the lock-up
valve body, the secondary valve body, the servo body, the linear solenoid, the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve A,/B assembly and the linear
solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is bolted
on the outside of the torque converter housing.
LINEAR
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
SECONDARY VALVEBODY
REGULATORVALVE BOOY
VALVE BODY
SOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMELY
N
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-24
www.emanualpro.com
Page 549 of 1395
![HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
E] or E Position (97 - 98 Models), and D Position (99 - 00 Modelsl
1. lst Gear
Fluid flow through the torque converter circuit is the same as in E] position. Line pressure flows to the manual valve HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
E] or E Position (97 - 98 Models), and D Position (99 - 00 Modelsl
1. lst Gear
Fluid flow through the torque converter circuit is the same as in E] position. Line pressure flows to the manual valve](/img/13/5778/w960_5778-548.png)
E] or E Position ('97 - 98 Models), and D Position ('99 - 00 Modelsl
1. lst Gear
Fluid flow through the torque converter circuit is the same as in E] position. Line pressure flows to the manual valve
and the modulator valve. Line pressure changes to modulator pressure (6) at the modulator valve and to line pressure
{4) at the manual valve. Modulator pressure (6) flows to the left end of the 1-2 shift valve and the 3-4 shift valve
because shift control solenoid valve A is turned oFF and B is turned oN by the PcM. The 1-2 shift valve is moved to
the right side. Line pressure {4) changes to 'lst clutch pressure (10} at the 1-2 shift valve and the orifice The 1st clutch
pressure (10) is applied to the 1st clutch and the 1st accumulator; the vehicle will move as the engine power is trans-
mitted.
NOTE:
. When used, "left" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
. The hvd rau lic circuit shows th e '97 - 98 models (7 positions); the '99 - 00 models {6 positions) issimilar.
(cont'dl
14-33
www.emanualpro.com
Page 551 of 1395
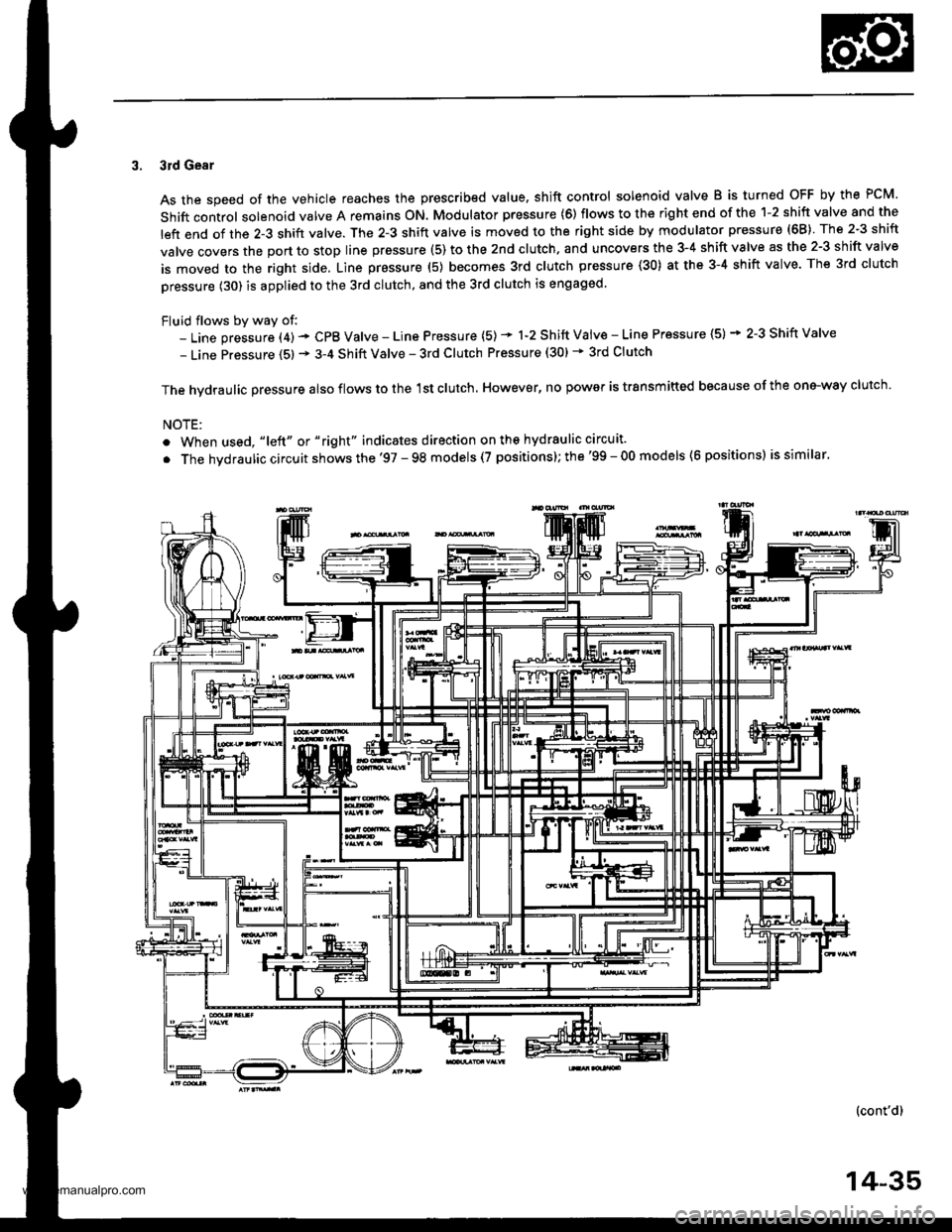
3. 3rd Gear
As the speed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value. shift control solenoid valve B is turned OFF by the PCM.
Shift control solenoid valve A remains ON. Modulator pressure (6) flows to the right end of the 1-2 shift valve and the
left end of the 2-3 shift valve. The 2-3 shift valve is moved to the right side by modulator pressure (68) The 2-3 shift
valve covers the port to stop line prsssure (5) to the 2nd clutch. and uncovers the 3-4 shift valve as the 2-3 shift valve
is moved to the right side, Line pressure (5) becomes 3rd clutch pressure (30) at the 3-4 shift valve. The 3rd clutch
pressure (30) is applied to the 3rd clutch, and the 3rd clutch is engaged.
Fluid flows by way of:- Line pressure (4) - CPB Valve - Line Pressure (5) * 1-2 Shift Vaiv€ - Line Pressure (5) * 2-3 Shift Valve
- Line Pressure (5) * 3-4 Shift Valve - 3rd Clutch Pressure (30) * 3rd Clutch
The hvdraulic Dressure also flows to the 1st clutch. However, no power is trsnsmitted because of the one-way clutch.
NOTE:
. When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on ths hydraulic circuit.
. The hvdraulic circuit shows the '97 - 98 models (7 positions); the'99 - 00 models (6 positions) is similar.
(cont'd)
14-35
www.emanualpro.com
Page 552 of 1395
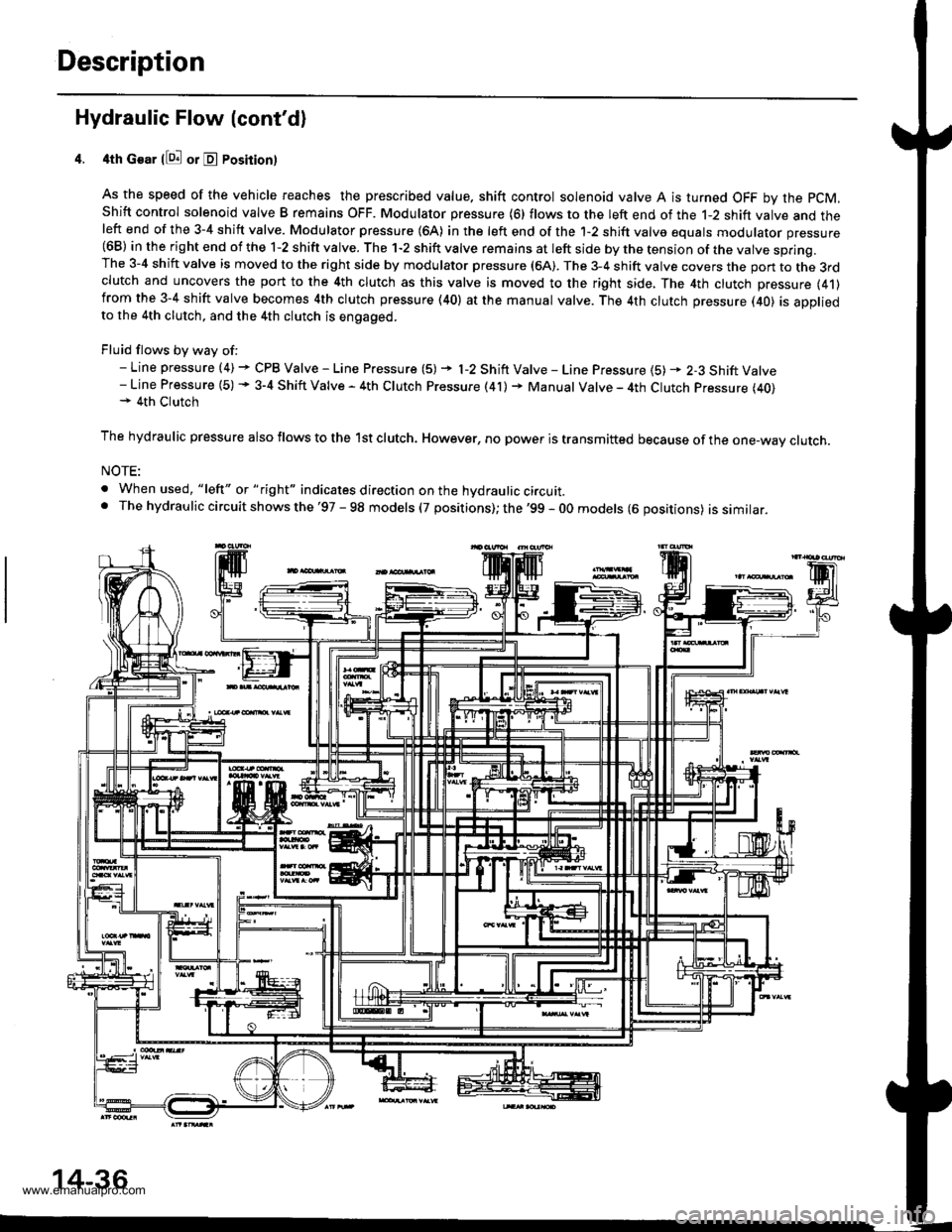
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'd)
4th Gear llQ! or E Posirion)
As the speed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value. shift control solenoid valve A is turned OFF by the pCM,
Shift control solenoid valve B remains OFF. Modulator pressure (6) flows to the left end of the 1-2 shift valve and theleft end of the 3-4 shift valve. Modulator pressure (64) in the left end of the 1-2 shift valve equals modulator pressure(68) in the right end of the 1-2 shift valve. The 1-2 shift valve remains at left side by the tension of the valve spring.The 3-4 shift valve is moved to the right side by modulator pressure (6A). The 3-4 shift valve covers the pon to the 3rdclutch and uncovers the port to the 4th clutch as this valve is moved to the right side, The 4th clutch pressure (41)from the 3-4 shift valve becomes 4th clutch pressure (40) at the manual valve. The 4th clutch pressure (40) is appliedto the 4th clutch, and the 4th clutch is engaged.
Fluid flows by way of:- Line pressure (4) + CPB Valve - Line Pressure (5) + l-2 Shift Valve - Line Pressure {5) * 2-3 Shift Valve- Line Pressure (5) + 3-4 Shift Valve - 4th Clutch Pressure (41) + Manual Valve - 4th Clutch Pressure (40)+ 4th Clutch
The hydraulic pressure also flows to the lst clutch. However, no power is transmitted because of the one-wav clutch.
NOTE:
. When used, "lelt" or " tight" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.. The hydrau lic circuit shows the '97 - 98 models (7 positions); the '99 - 0O models (6 oositions) issimilar.
14-36
www.emanualpro.com
Page 555 of 1395
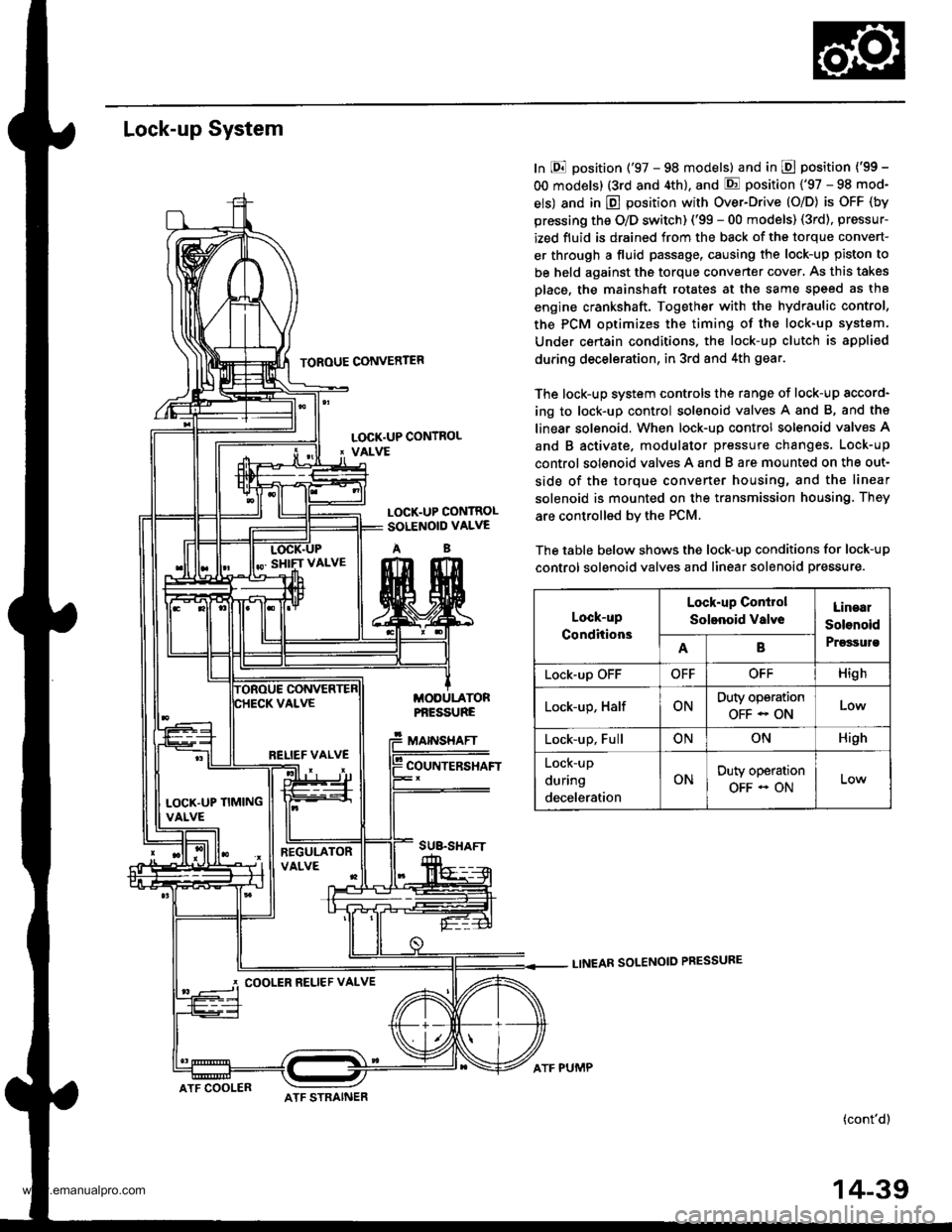
Lock-up System
TOROUE CONVERTER
In E position ('97 - 98 models) and in E position ('99 -
OO models) (3rd and 4th), and E position ('97 - 98 mod-
els) and in E position with Over-Drive (O/D) is OFF (by
pressing the O/D switch) ('99 - 00 models) (3rd), pressur-
ized fluid is drained from the back of the torque convert-
er through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to
be held against the torque converter cover, As this takes
Dlace, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as th8
engine crankshaft. Together with the hydraulic control,
the PCM optimizes the timing of the lock-up system.
Under certain condltions. the lock-up clutch is appli€d
during deceleration, in 3rd and 4th gear.
The lock-up system controls the range of lock-up sccord-
ing to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and ths
linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A
and B activate. modulator pressure changes. Lock-up
control solenoid valves A and B are mounted on the out-
side of the torque converter housing, and the linear
solenoid is mounted on the transmission housing. They
are controlled bv the PCM.
The table below shows the lock-up conditions for lock-up
control solenoid valves and linear solenoid pressure.
LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
(cont'd)
LOCK.UP CONTROL' VALVE
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE
AB
MODULATORPf,ESSURE
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
SUB.SHAFT
Lock-up
Conditions
Lock-up Conirol
Solenoid valveLinaal
Solenoid
PrgssulsAB
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ONLow
Lock-up, FullONONHigh
Lock-up
during
deceleration
ONDuty operation
OFF - ON
RELIEF VALVE
LOCK'UP TIMINGVALVE
COOLER RELIEF VALVE
ATF COOLERATF STRAINER
ATF PUMP
14-39
www.emanualpro.com
Page 561 of 1395
![HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
Component Locations
ASSEMBLY
POWERTRAIN CONTROLMODULE {PCMI
COUNTERSHAFTSPEED SENSOR
AUTOMAIIC TRANSAXI.E(A/T} GEAR POSITIONswtTcH
\
CONTBOL UN]T
SHIFT CONTROLSOLEM)ID VALVEASSEMBLY
SPEED SCNSOR
14-4 HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
Component Locations
ASSEMBLY
POWERTRAIN CONTROLMODULE {PCMI
COUNTERSHAFTSPEED SENSOR
AUTOMAIIC TRANSAXI.E(A/T} GEAR POSITIONswtTcH
\
CONTBOL UN]T
SHIFT CONTROLSOLEM)ID VALVEASSEMBLY
SPEED SCNSOR
14-4](/img/13/5778/w960_5778-560.png)
Component Locations
ASSEMBLY
POWERTRAIN CONTROLMODULE {PCMI
COUNTERSHAFTSPEED SENSOR
AUTOMAIIC TRANSAXI.E(A/T} GEAR POSITIONswtTcH
\
CONTBOL UN]T
SHIFT CONTROLSOLEM)ID VALVEASSEMBLY
SPEED SCNSOR
14-45
www.emanualpro.com
Page 562 of 1395
![HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
PCM Circuit Diagram (A/T Control System)
97 Model
UNDER.I]OOD FUSAFELAY BOXEATTEFY
_YEL_
T-l ,
TT-l
t_-:
G101
Fr-r.04
P- r.-or..u L_a TMEALOC(BrK€ru -<< calTFoL
P_ *+rr
F- onmrxCFUISECONTFOLUNITf HONDA CR-V 1998 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Manual Online
PCM Circuit Diagram (A/T Control System)
97 Model
UNDER.I]OOD FUSAFELAY BOXEATTEFY
_YEL_
T-l ,
TT-l
t_-:
G101
Fr-r.04
P- r.-or..u L_a TMEALOC(BrK€ru -<< calTFoL
P_ *+rr
F- onmrxCFUISECONTFOLUNITf](/img/13/5778/w960_5778-561.png)
PCM Circuit Diagram (A/T Control System)
'97 Model
UNDER.I]OOD FUSAFELAY BOXEATTEFY
_YEL_
T-l ,
TT-l
t_-:
G101
'Fr-r.04
P- r.-or..u L_a TMEALOC(BrK€ru -<< calTFoL
P_ *+rr
F- onmrxCFUISECONTFOLUNITf-"".>
| ["'"]
I l,[-l
III ;,
F_ pw
P_ eLu
F-- enN
UNDER DASN
M 25(7.54)
IGNITONSWITCH UNDEF OASNFUSAFELAYSOX
oowEa-qar. cor.lFo- MooLrE rpcMr F &*1 r*--'l_____O_=_ATP IO! ,ATP . ATD , A-P , A-P , A-PNP lrNo lR 101 103 12 ll
Ar'TGEAR POS]TIONswtcN
14-46
www.emanualpro.com