Start HONDA CR-V 2000 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 2000, Model line: CR-V, Model: HONDA CR-V 2000 RD1-RD3 / 1.GPages: 1395, PDF Size: 35.62 MB
Page 762 of 1395
Transfer Assembly
Reassembly (cont'd)
Secure the transfer housing in a bench vise with
soft jaws. To prevent damage, always use soft jaws
or equivalent materials between the transfer hous-
ing and the vise.
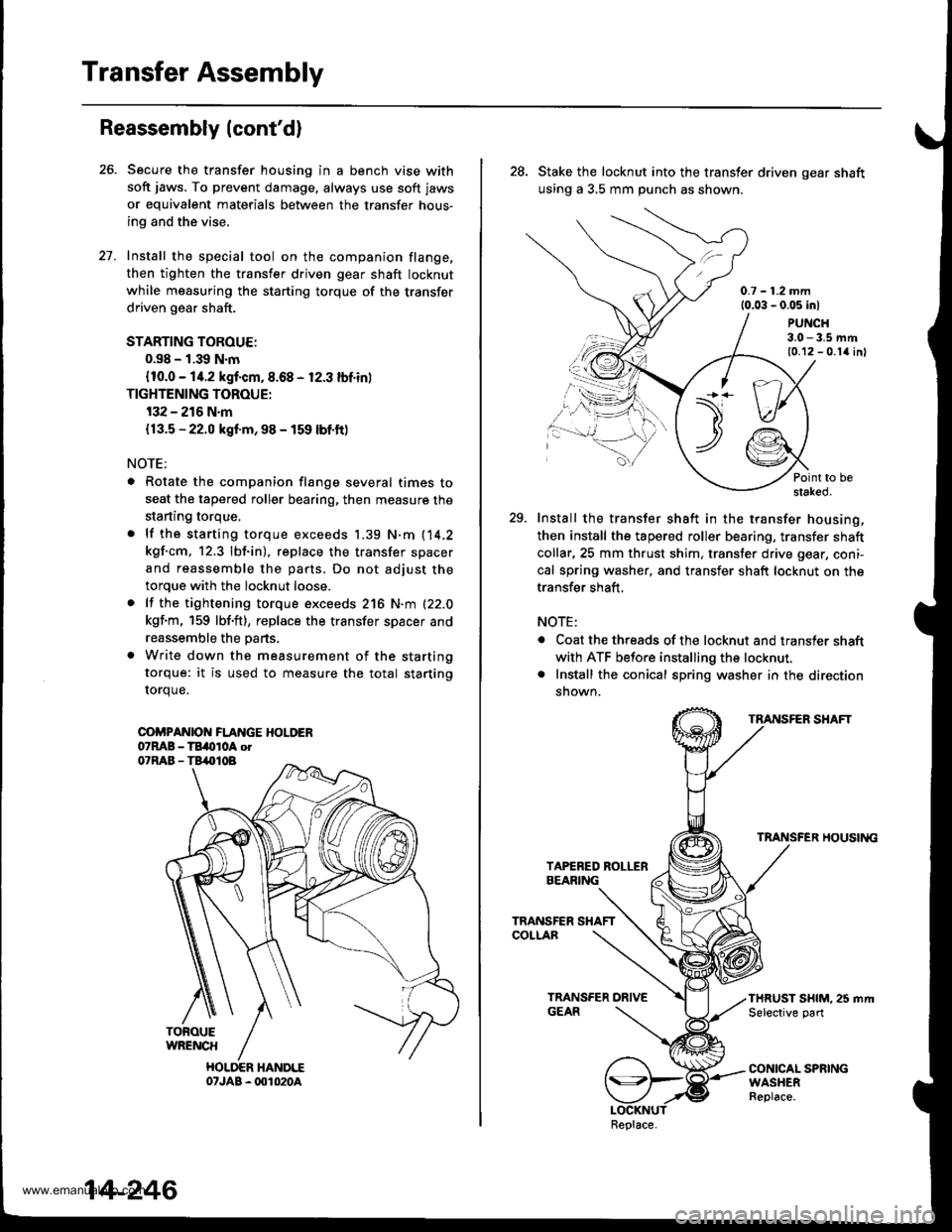
Install the special tool on the companion flange,
then tighten the transfer driven gear shaft locknut
while measuring the starting torque of the transfer
driven gear shaft.
STARTING TOROUE:
0.s8 - 1.39 N.m
{10.0 - 14.2 kgf.cm,8.68 - 12.3 lbf.in)
TIGHTENING TOROUE:
132 - 216 N.m
{13.5 - 22.0 kgf.m, 98 - 159 lbf.ft)
NOTE;
. Rotate the companion flange several times to
seat the tapered roller bearing, then measure the
starting torque,
. lf the starting torque exceeds 1.39 N.m (14,2
kgf.cm, 12.3 lbf.in), replace the transfer spacer
and reassemble the parts. Do not adjust the
torque with the locknut loose.
. lf the tightening torque exceeds 216 N.m (22.0
kgf.m, 159 lbf'ft), replace the transfer spacer and
reassemble the parts.
. Write down the measurement of the starting
torque: it is used to measure the total starting
rorque.
COi'PANIOI{ FLANGE HOLDER07MB - TBi(tloA otO'RAB - TB,.|}IOB
TOFOUEWRENCH
HOLDER HANDLE07JAB - 001020A
27.
14-246
28. Stake the locknut into the transfer driven gear shaft
using a 3,5 mm punch as shown.
0.7 - 1.2 mm{0.03 - 0.05 inl
PUNCH3.0 - 3.5 mm10.12 - 0.1{ inl
Point to bestaked.
29. Install the transfer shaft in the transfer housing,
then install the tapered roller bearing, transfer shaft
collar,25 mm thrust shim, transter drive gear, coni-
cal spring washer, and transfer shaft locknut on the
transfer shaft,
NOTE:
. Coat the threads of the locknut and transler shaft
with ATF before installing the locknut.. Install the conical spring washer in the direction
snown.
TRANSFER SHAFT
TRANSFER HOUSII{G
THRUST SHIM. 25 mrt|Selective part
CONICAL SPRINGWASHERReplace.
\t)t--/./
.,.-,.,\
Replace.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 763 of 1395
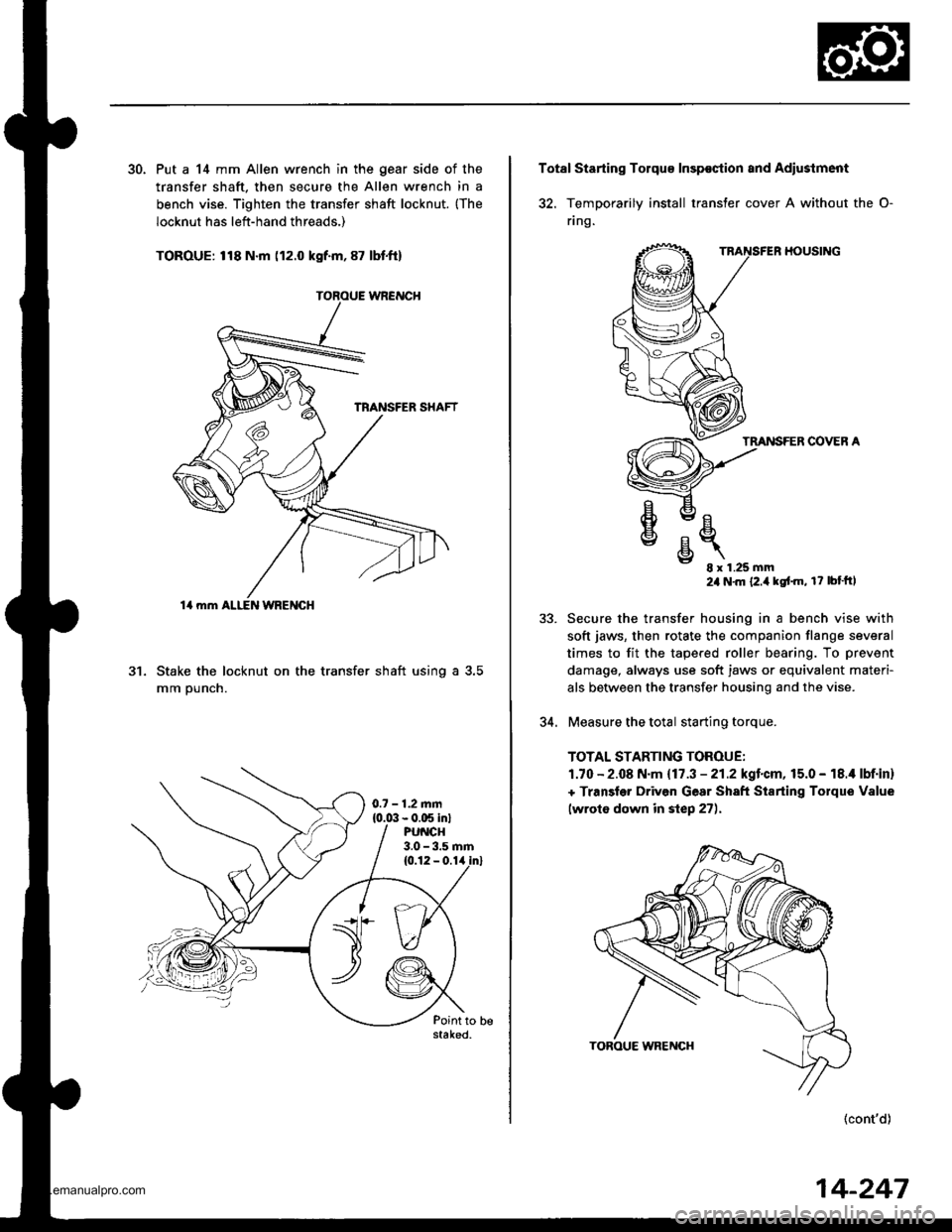
30. Put a 14 mm Allen wrench in the gear side of the
transfer shaft. then secure the Allen wrench in a
bench vise. Tighten the transfer shaft locknut. {The
locknut has left-hand threads,)
TOROUE: 118 N.m (12.0 kgf.m, 87 lbt.ft)
Stake the locknut on the transfer shaft using a 3.5
mm ounch.
al
14 mm ALI-EN WRENGH
0.7 - 1.2.nm{0.0:1- 0.C5 in}PU CH3.0 - 3.5 rnm
Total Starting Tolqu€ Insp€ction and Adiustment
32. TemDorarilv install transter cover A without the O-
flng.
HOUSING
TMNSFER COVER A
e
€
v
E- 8x1.25mm24 N'm {2.i1kgt'm, r? bt'ftl
Secure the transfer housing in a bench vise with
soft jaws, then rotate the companion flange several
times to fit the tapered roller bearing. To prevent
damage, always use soft jaws or equivalent materi-
als betlveen the transfer housing and the vise.
Measure the total starting torque.
TOTAL STARTING TOROUE:
1.70 - 2.08 N.m {17.3 - 21.2kgl.cm,15.0 - 18.i1 lbf.in}
+ Transler Driven Gear Sh8ft Starting Torque Value
lwroto down in step 27).
(cont'd)
5J.
34.
14-247
www.emanualpro.com
Page 764 of 1395
Transfer Assembly
35.
Reassembly (cont'dl
36.
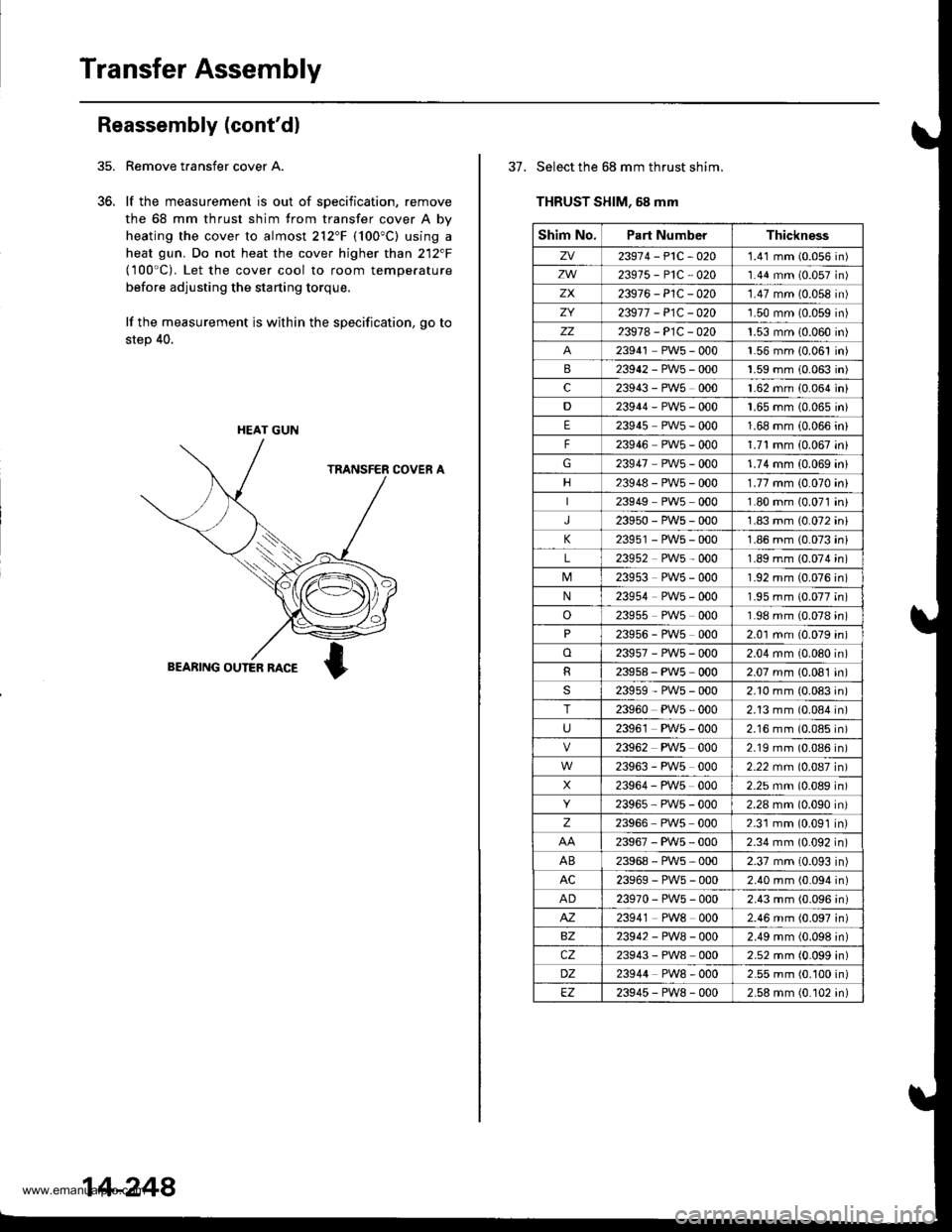
Remove taansfer cover A.
lf the measurement is out of specification, remove
the 68 mm thrust shim from transfer cover A by
heating the cover to almost 212"F (100"C) using a
heat gun. Do not heat the cover higher than 212"F(100'C). Let the cover cool to room temperature
before adjusting the starting torque,
lf the measurement is within the specification, go to
step 40.
HEAT GUN
14-248
37. Select the 68 mm thrust shim.
THRUST SHIM, 58 mm
Shim No.Part NumberThickness
zv23974-P1C-O201.41 mm (0.056 in)
zw23975-P1C-O201.44 mm (0.057 in)
zx23976-P1C-020'1.47 mm (0.058 in)
ZY23977 - P1C - O201.50 mm (0.059 in)
zz23978-P1C-0201.53 mm 10.060 in)
23941 PW5 - 000'1.56 mm {0.061 in)
B23942-PWs-0001.59 mm 10.063 in)
c23943 - PWs 0001.62 mm (0.064 in)
D23944-PW5-0001.65 mm {0.065 in}
E23945 PWs - 0001.68 mm (0.066 in)
F23946 PWs - 0001.71 mm (0.067 in)
G23947 PWs - 0001.74 mm (0.069 ini
23948-PW5-0001.77 mm (0.070 ini
23949 PW5 0001.80 mm (0.071 in,
J23950-PWs-0001.83 mm {0.072 ini
K23951 - PWs - 0001.86 mm (0.073 in
L23952 PW5 - 0001.89 mm (0.074 in
23953 PWs - 0001.92 mm (0.076 in
N23954 PW5 - 0001.95 mm (0.077 in
o23955 PW5 0001.98 mm (0.078 in
P23956 - PWs 0002.01 mm (0.079 in
o23957-PW5-0002.04 mm (0.080 in
R23958, PWs 0002.07 mm (0.081 in
s23959-PW5-0002.10 mm (0.083 in
T23960 PW5 - 0002.13 mm (0.084 in
U2396'1 PW5 - 0002.16 mm (0.085 in
23962 PWs 0002.19 mm (0.086 in
23963 - PW5 0002.22 mm (0.087 in
X23964 - PW5 0002.25 mm (0.089 in
23965 PW5 - 0002.28 mm (0.090 in
z23966 PWs 0002.31 mm (0.091 in
23967-PWs-0002.34 mm (0.092 in
AB23968-PWs-0002.37 mm (0.093 in)
AC23969-PWs-0002.40 mm (0.094 in)
AD23970-PW5-0002.43 mm (0.096 in)
M23941 PW8 0002.46 mm (0.097 in)
BZ23942-PW8-0002.49 mm (0.098 in)
cz23943 - PW8 0002.52 mm (0.099 in)
DZ23944 PW8 - 0002.55 mm (0.100 in)
EZ23945-PW8-0002.58 mm (0.102 in)
www.emanualpro.com
Page 765 of 1395
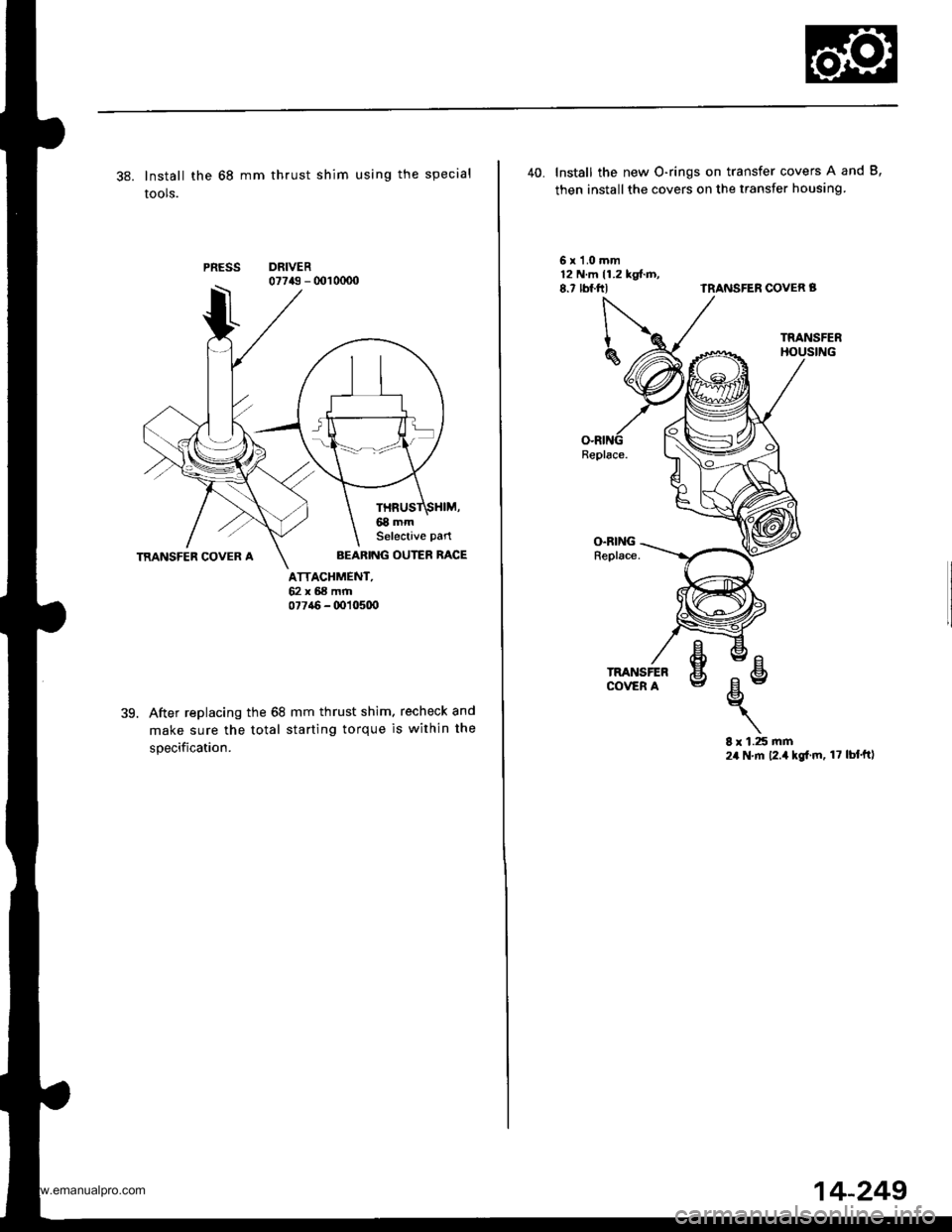
38. Install the 68 mm thrust shim using the special
tools.
PRESSDRIVER07743 - 001 0000
ATTACHMENT,62x68mrr|077a6 - (x)10500
39.After replacing the 68 mm thrust shim. recheck and
make sure the total starting torque is within the
specification.
AEARING OUTER RACE
40. Install the new O-rings on transfer covers A and B,
then installthe covers on the transfer housing
6x1.0mm12 N.m 11.2 kgt.D,8.7 rbf.ftlTRANSFEN COVER B
O.RINGReplace.
8 r 1.25 rnm24 N.m 12.4 kgl.m, 17 lbf'ftl
Replace.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 775 of 1395
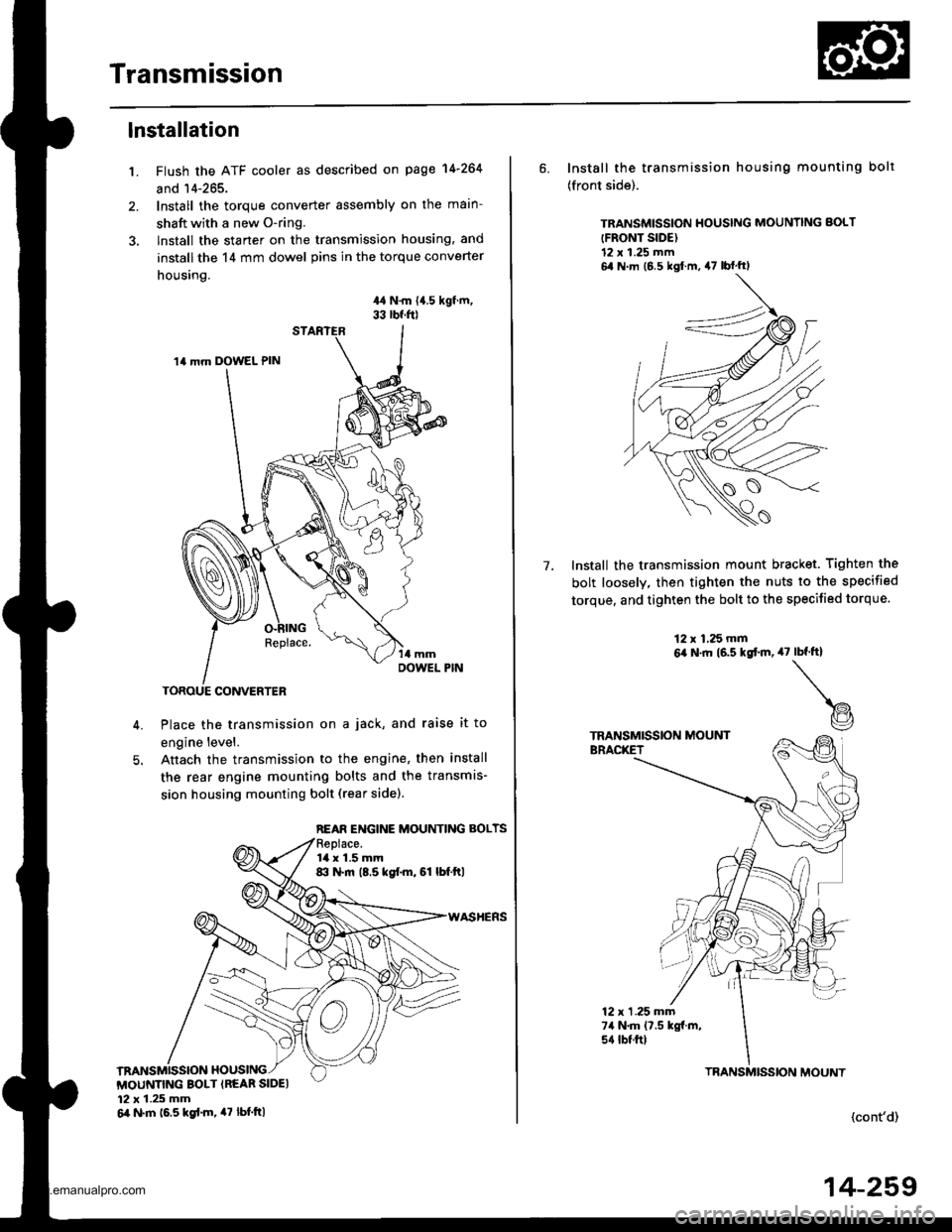
Transmission
1.
lnstallation
Flush the ATF cooler as described on page 14-264
and 14-265.
Install the torque converter assembly on the main-
shaft with a new O-ring.
lnstall the starter on the transmission housing, and
install the 14 mm dowel pins in the torque converter
housing.
44 N.m {{.5 kgf.m,33 rbf.f0
Place the transmission on a jack, and raise it to
engine level.
Anach the transmission to the engine, then install
the rear engine mounting bolts and the transmis-
sion housing mounting bolt (rear sidel.
14 mm DOWEL PIN
REAR ENGINE MOUNTING BOLTS
la x 1.5 mm8:l N.m (8.5 kgf.m, 61 lbf.ftl
MOUNTING BOLT {REAR SIDEI12 x 1.25 mm6il N.m 16.5 kgd.m, 47 tbt.ttl
6. Install the transmission housing mounting bolt
(front side).
TRANSMISSION HOUSING MOUNNNG BOLT
{FRONT SIDE)12 x 1.25 mm6,1 N m (6 5 kgl m, 47 lbf'ftl
Install the transmission mount bracket. Tighten the
bolt loosely, then tighten the nuts to the specified
torque, and tighten the bolt to the specified torque.
7.
12 x 1,25 mm6,a N.ft (6.5 kgtm,47rbf.ft)
t@
TRANSMISSION MOUNTBRACKET
12 x 1 .25 mm74 N.m (7.5 kgf.m,s{ tbtftl
(cont'd)
TBANSMISSION MOUNT
14-259
www.emanualpro.com
Page 779 of 1395
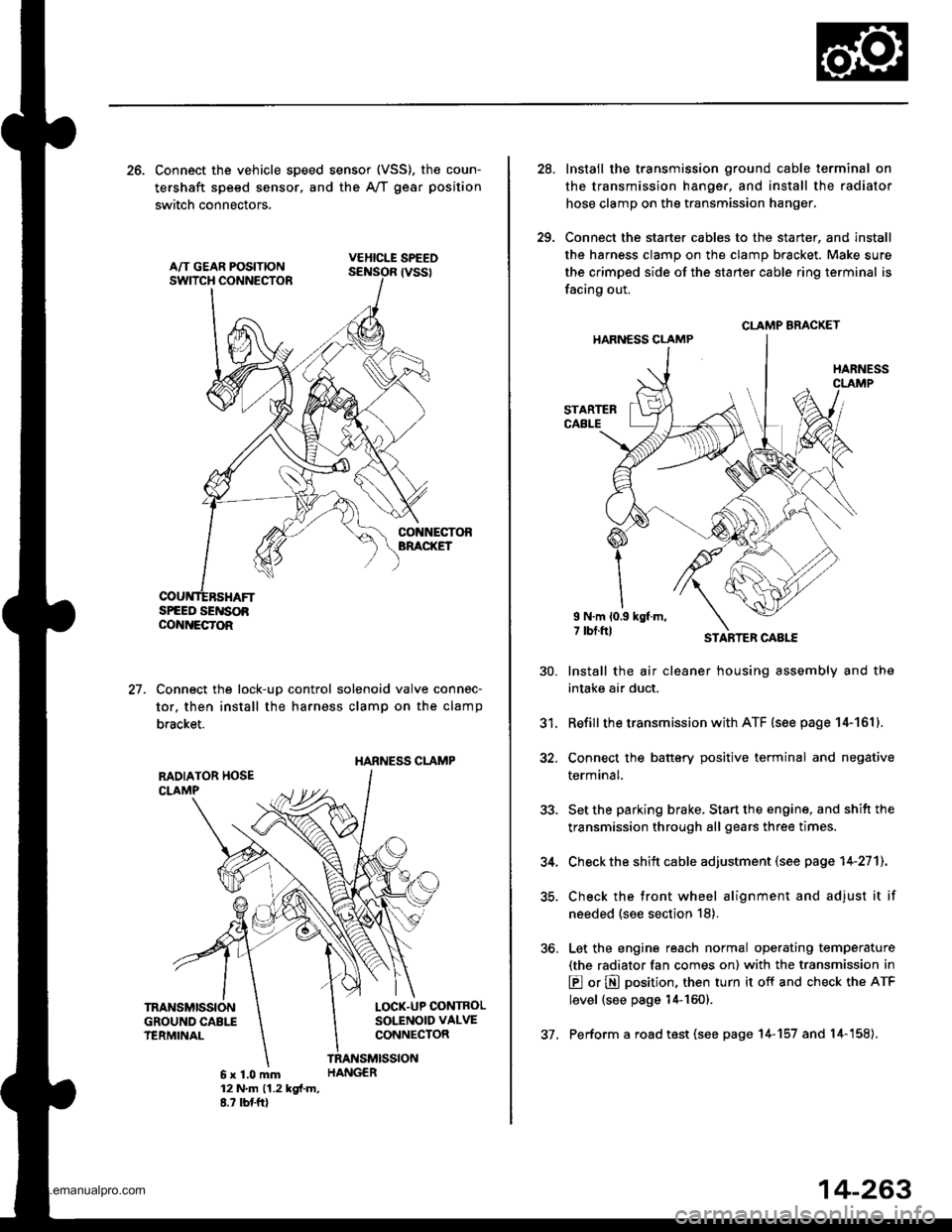
26. Connect the vehicle speed sensor (VSS). the coun-
tershaft speed sensor. and the A,/T gear position
switch connectors,
VEHICLE SPEEO
SPEED SENSOACO'{NECTOR
Connect the lock-up control solenoid valve connec-
tor, then install the harness clamp on the clamp
bracket.
HARNESS CI-AMP
27.
RADIATOR HOSECLAMP
TRANSMISSIONGROUND CAB1ITERMINAL
LOCK-UP OONTROLSOLENOID VALVECONNECTOR
6x1.0mm12 N'm (1.2 kgi.m,8.? tbtftl
28.
29.
Instail the transmission ground cable terminal on
the transmission hanger, and install the radiator
hose clamp on the transmission hanger,
Connect the starter cables to the starter, and install
the harness clamD on the clamD bracket. Make sure
the crimped side of the starter cable ring terminal is
facing out.
STARTEBCABLE
STARTER CAAtf,
Install the air cleaner housing assembly and the
intake air duct.
Refill the transmission with ATF (see page 14-161).
Connect the battery positive terminal and negative
terminal.
Set the parking brake, Start the engine, and shift the
transmission through all gears three times.
Check the shift cable adjustment (see page 14-271]-.
Check the tront wheel alignment and adjust it if
needed (see section 18).
Let the engine reach normal operating temperature
(the radiator fan comes on) with the transmission in
E or N position, then turn it off and check the ATF
level {see page 14-160).
Perform a road test (see page 14-157 and 14-158).
30.
31.
34.
CLAMP BRACKET
37.
14-263
www.emanualpro.com
Page 788 of 1395
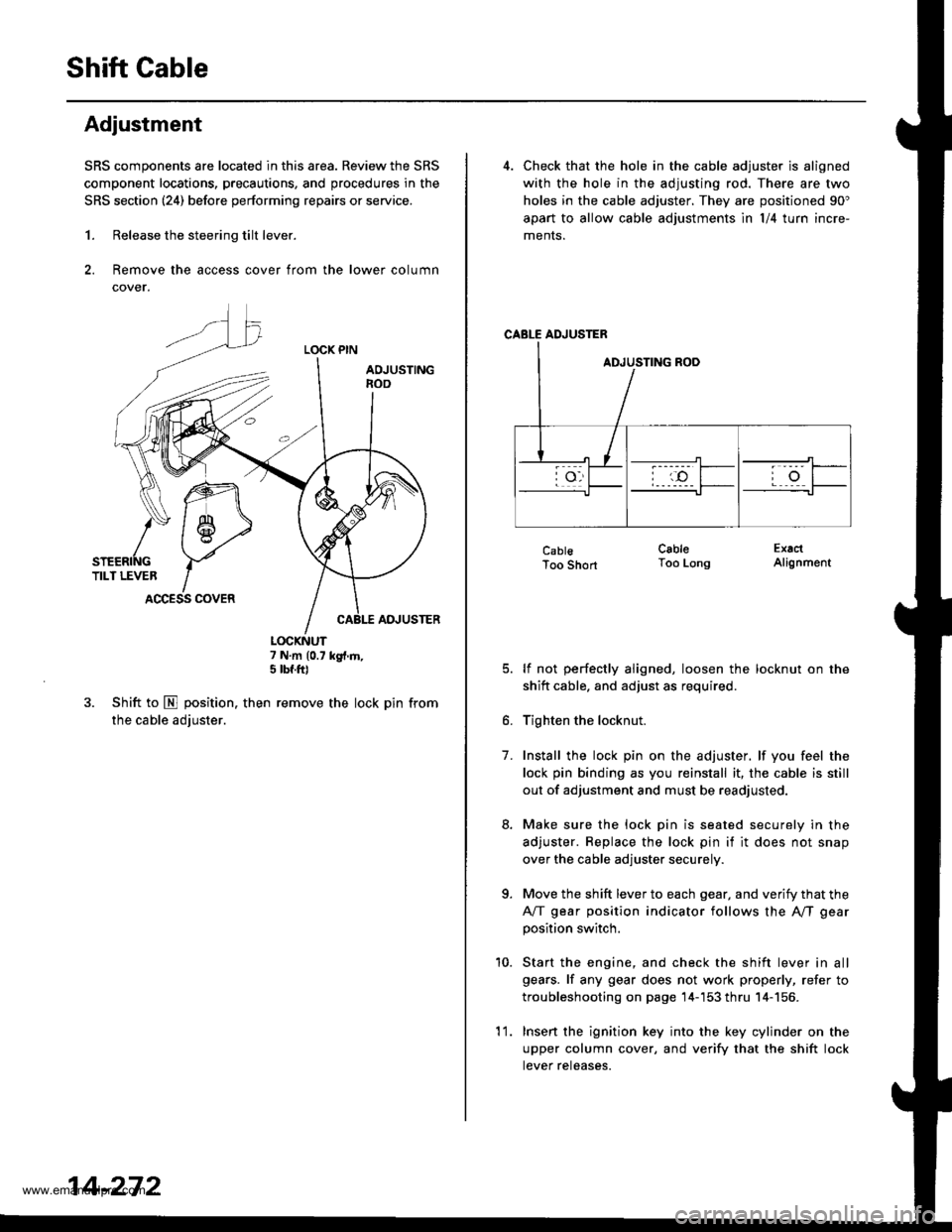
Shift Gable
Adjustment
SRS components are located in this area. Review the SRS
component locations, precautions, and procedures in the
SRS section (241 before performing repairs or service.
1. Release the steering tilt lever.
2. Remove the access cover from the lower column
cover.
LOCK PIN
AOJUSTINGnoo
ADJUSTER
7 N.m (0.7 kg{.m,5 tbf.ft)
3. Shift to E position. then remove the lock pin from
the cable adjuster.
K\ffi
/* 1 6-,>
snenrftc YTILT LEVER IACCESS COVER
14-272
'l 1.
4. Check that the hole in the cable adjuster is aligned
with the hole in the adjusting rod. There are two
holes in the cable adjuster. They are positioned 90"
apart to allow cable adjustments ln l/4 turn incre-
ments.
CABLE ADJUSTER
CablsToo Short
lf not perfectly aligned, loosen the locknut on the
shitt cable. and adjust as required.
Tighten the locknut.
Install the lock pin on the adjuster. lf you feel the
lock pin binding as you reinstall it, the cable is still
out of adjustment and must be readjusted.
Make sure the lock pin is seated securely in the
adjuster. Replace the lock pin if it does not snap
over the cable adjuster securely.
Move the shift lever to each gear, and verify that the
A/T gear position indicator follows the A"/T gear
position switch.
Start the engine, and check the shift lever in all
gears. lf any gear does not work properly, refer to
troubleshooting on page 14-'153 thru 14-156.
Insert the ignition key into the key cylinder on the
upper column cover, and verify that the shift lock
tever reteases.
CableToo LongExactAlignment
7.
a
10.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 794 of 1395

Description
Rear Differential
Outline
The Real-time 4WD-Dual Pump System model has a hydraulic clutch and a differential mechanism in the rear differential
assembly. Under normal conditions, the vehicle is driven by the front wheels. However, depending on to the driving force
of the front wheels and the road conditions. the system instantly transmits appropriate driving force to the rear wheels
without requiring the driver to switch between 2WD (tront wheel drive) and 4WD (four wheel drive). The switching mecha-
nism between 2WD and 4WD is integrated into the rear differential assembly to make the system light and compact.
ln addition, the dual-pump system switches off the rear-wheel-drive force when braking in a forward gear. This allows the
braking system to work properly on models equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
Construction
The rear differential assembly consists of the torque control differential case assembly and the rear differential carrier
assembly. The torque control differential case assembly consists of the differential clutch assembly, the companion
flange, and the oil pump body assembly. The rear differential carrier assembly consists of the differential mechanism. The
differential drive and driven gears are hypoid gears.
The oil pump body assembly consists of the front oil pump, the rear oil pump, the hydraulic control mechanism, and the
clutch piston. The clutch piston has a disc spring that constantly provides the differential clutch assembly with a preset
torque to Drevent abnormal sound.
The clutch guide in the differential clutch assembly is connected to the propeller shaft via the companion flange, and it
receives the driving force lrom the transfer assembly. The clutch guide rotates the clutch plate and the front oil pump in
the oil pump body.
The clutch hub in the differential clutch assembly has a clutch disc that is splined with the hypoid drive pinion gear. The
hypoid drive gear drives the rear oil pump.
The front and rear oil pumps are trochoidal pumps. The rear oil pump capacity is 2.5 percent larger that the front oil pump
to handle the rotation difference between the front and rear wheels caused by worn front tires and tight corner braking.
The oil pumps are designed so the fluid intake works as a fluid discharge when the oil pumps rotate in reverse. Genuine
Honda CVT fluid is used instead of differential fluid.
Operation
When there is a difference in rotation speed between the front wheels (clutch guide) and rear wheels (hypoid driven gear),
hydraulic pressure from the front and rear oil pumps engages the differential clutch, and drive force from the transler
assembly is applied to the rear wheels.
The hydraulic pressure control mechanism in the oil pump body selects 4WD mode when the vehicle is started abruptly,
or when accelerating in a forward or reverse gear (causing rotation difference between the front and rear wheels). or
when braking in reverse gear {when decelerating). lt switches to 2WD mode when the vehicle is driven at a constant speed
in forwar! or reverse gear (when there is no rotation difference between the front and rear wheels), or when braking in a
fo rwa rd gear (when decelerating).
To protect the system, the differential clutch assembly is lubricated by hydraulic pressure generated by the oil pumps in
both 4WD and 2WD modes. Also, the thermal switch relieves the hydraulic pressure on the clutch piston and cancels 4WD
mode if the temDerature of the differential fluid rises above normal.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 796 of 1395
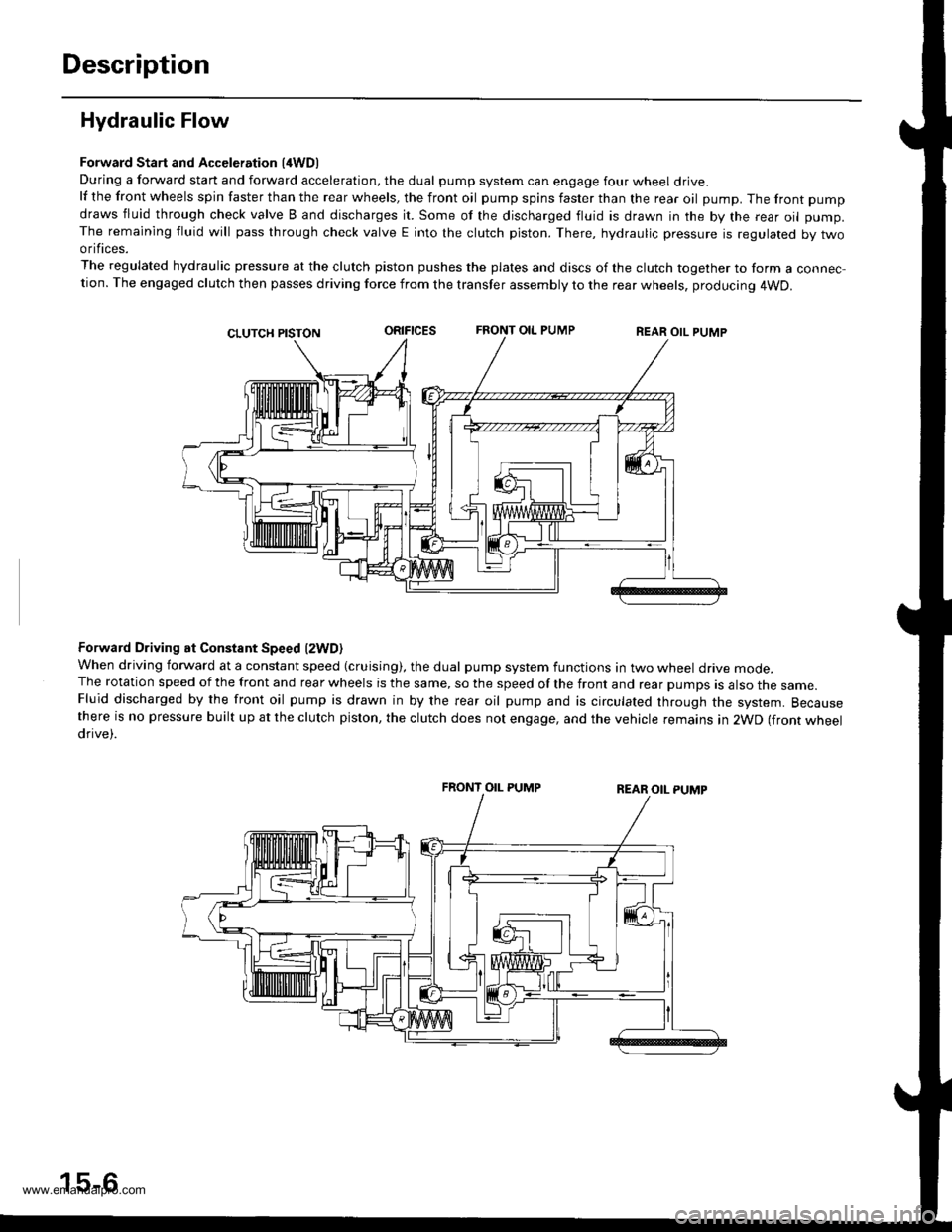
Description
Hydraulic Flow
Forward Start and Acceleration l4WD)During a forward start and forward acceleration, the dual pump system can engage four wheel drive.lf the front wheels spin faster than the rear wheels, the front oil pump spins faster than the rear oil pump. The front pump
draws fluid through check valve B and discharges it. Some of the discharged fluid is drawn in the by the rear oil pump.The remaining fluid will pass through check valve E into the clutch piston. There, hydraulic pressure is regulated by twoorifices.
The regulated hydraulic pressure at the clutch piston pushes the plates and discs of the clutch together to form a connec-tion. The engaged clutch then passes driving force from the transfer assembly to the rear wheels, producing 4WD.
oRrFtcEsFRONT OIL PUMPREAR OIL PUMP
Forward Driving at Constant Speed lzWD)When driving forward at a constant speed (cruising), the dual pump system functions in two wheel drive mode.The rotation speed of the front and rear wheels is the same, so the speed of the front and rear pumps is also the same.Fluid discharged by the front oil pump is drawn in by the rear oil pump and is circulated through the system. Becausethere is no pressure built up at the clutch piston, the clutch does not engage, and the vehicle remains in 2WD (front wheeldrive).
FRONT OIL PUMP
15-6
www.emanualpro.com
Page 797 of 1395
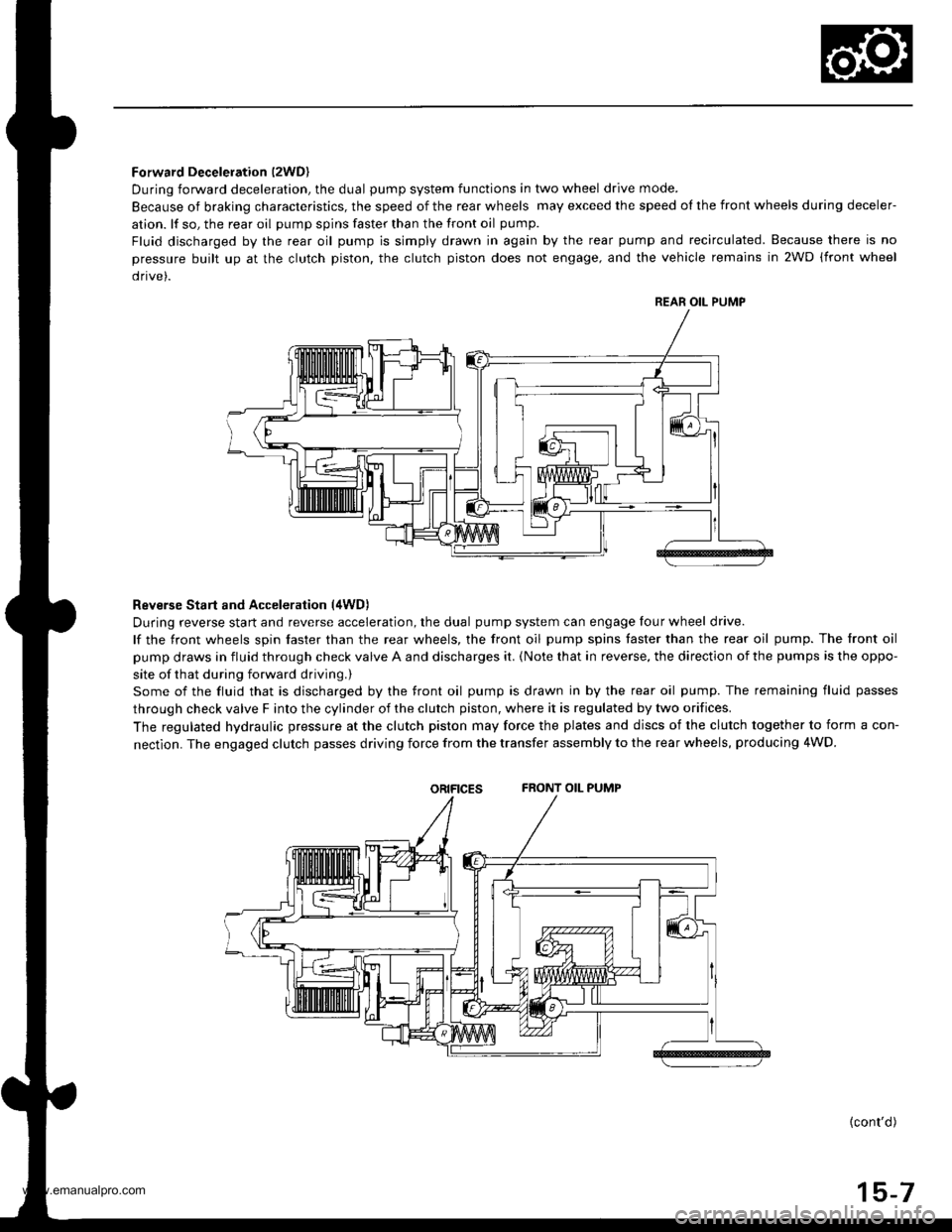
Forward Deceleration l2WDl
During forward deceleration, the dual pump system functions in two wheel drive mode.
Because of braking characteristics, the speed of the rear wheels may exceed the speed ol the front wheels during deceler-
ation. lf so, the rear oil pump spins faster than the front oil pump.
Fluid discharged by the rear oil pump is simply drawn in again by the rear pump and recirculated. Because there is no
pressure built up at the clutch piston. the clutch piston does not engage, and the vehicle remains in 2WD (front wheel
drive).
Reverse Start and Acceleration (4WD)
During reverse start and reverse acceleration, the dual pump system can engage four wheel drive.
lf the front wheels spin faster than the rear wheels, the front oil pump spins faster than the rear oil pump. The front oil
pump draws in fluid through check valve A and discharges it. {Note that in reverse, the direction of the pumps is the oppo-
site of that during forward driving.)
Some of the fluid that is discharged by the front oil pump is drawn in by the rear oil pump. The remaining fluid passes
through check valve F into the cylinder of the clutch piston, where it is regulated by two orifices.
The regulated hydraulic pressure at the clutch piston may force the plates and discs of the clutch together to form a con-
nectlon. The engaged clutch passes driving force from the transfer assembly to the rear wheels, producing 4WD.
oRtFtcEsFRONT OIL PUMP
{cont'd)
15-7
REAR OIL PUMP
www.emanualpro.com