ECO mode HONDA CR-V 2000 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 2000, Model line: CR-V, Model: HONDA CR-V 2000 RD1-RD3 / 1.GPages: 1395, PDF Size: 35.62 MB
Page 406 of 1395
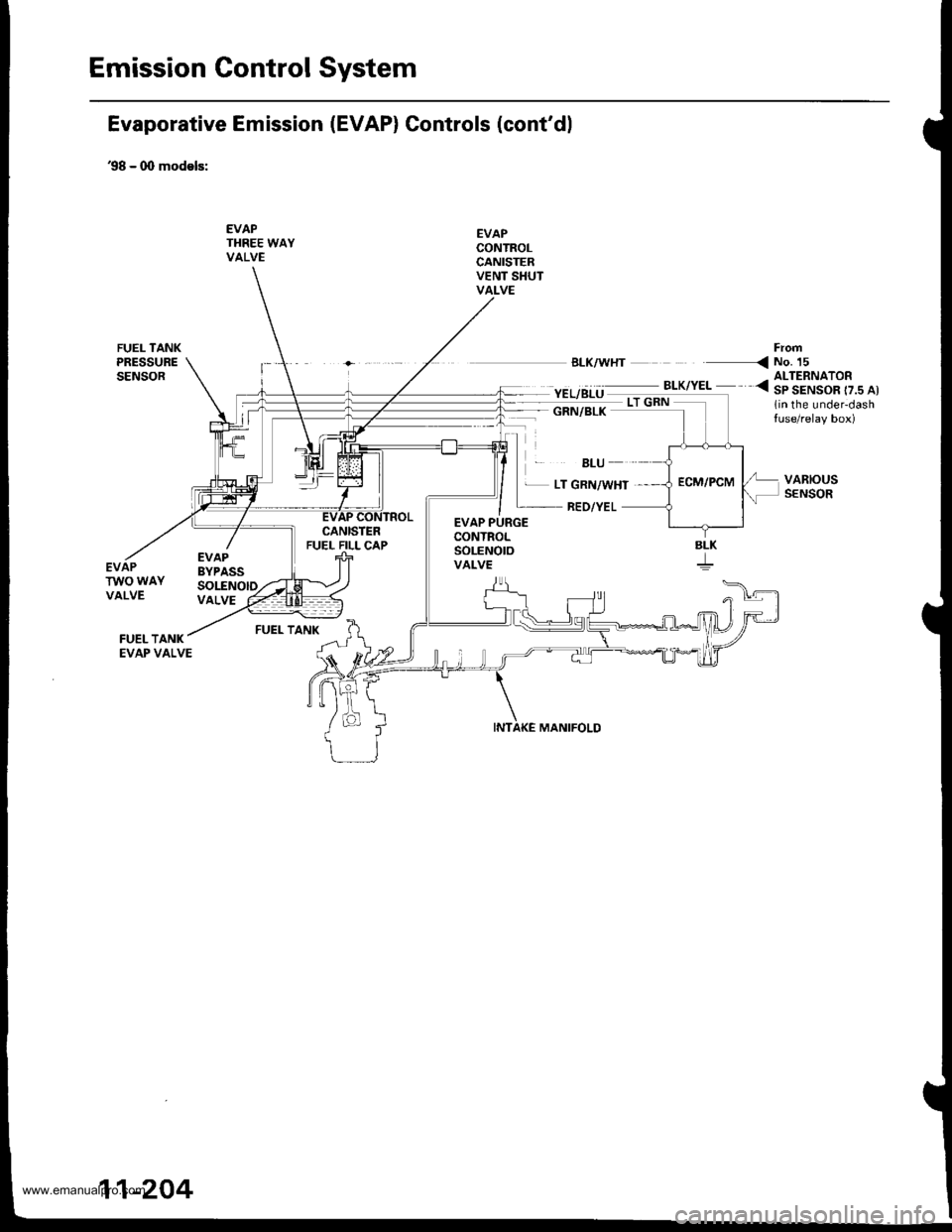
Emission Gontrol System
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls (cont'dl
'98 - 0O models:
EVAPTHREE WAYVALVE
EVAPCONTROLCANISTERVENT SHUTVALVE
'EL/BLU ._^_-:.*,".. <3|ltAIS"o[..^,
1in the under-dashtuse/relay box)
FrofiBLK/WHT < NO. 15
GRN/BLK
BLU
EVAPBYPASSSOLENOID
EVAP PURGECONTROLSoLENOtOVALVE
L LT GRN/WHT ,
RED/YEL
MANIFOLD
VARIOUSSENSOR
EVAPTWO WAYVALVEVALVE
FUEL TANK
SLK
11-204
www.emanualpro.com
Page 422 of 1395
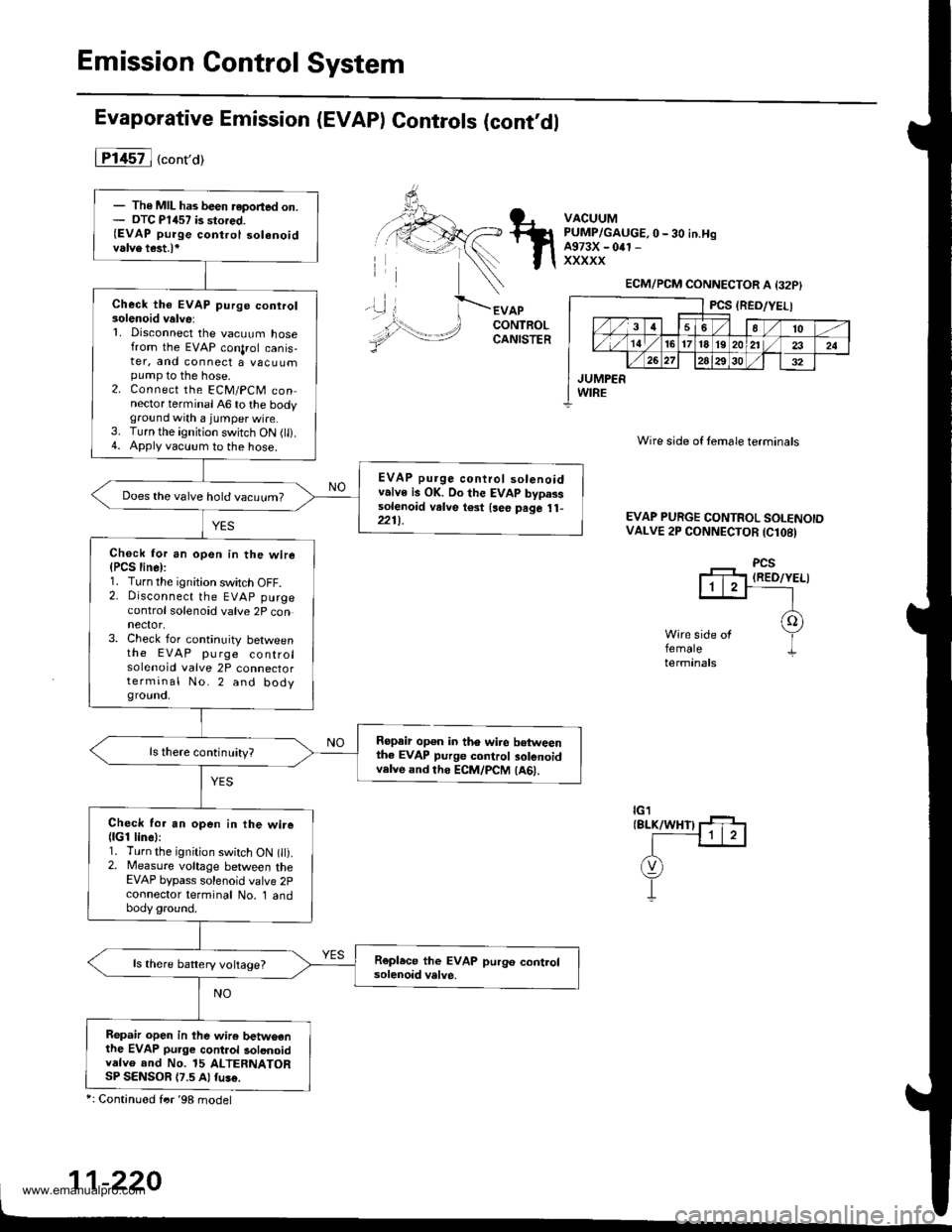
Emission Control System
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls (cont,dl
iTl457l ("ont'or
APCONTROLCANISTER
Ropair op€n in th6 wire betweenthe EVAP purge control 3olenoidvelve and ths ECM/PCM (A61.
VACUUMPUMP/GAUGE, O-30 iN.HgA973X - 0rl -
xxxxx
'\)
Wire side of lemale terminals
EVAP PURGE CONTROL SOI.ENOIDVALVE 2P CONNECTOR (Cl08)
PCSIRED/YELI
femaletermanals
ECM/PCM CONNECTOR A {32P}
PCS (RED/YELI
,/3 458/'t0
,,/ 14 ,/'t61718l92024
,/ 262930
JUMPERWIRE
- The MIL has been reported on.- DTC P1457 is stored.{EVAP purge control solenoidvalve test.l*
Check the EVAP purge conrrol30lenoid velve:L Disconnect the vacuum hosefrom the EVAP conlrol canis,ter, and connect a vacuumpump to the hose.2. Connect the ECM/PCM connector terminal A6 to the bodyground with a jumper wire.3. Turn the ignition switch ON (tl).4. Apply vacuum to the hose.
EVAP purge control solenoidvalve is OK. Oo the EVAP bypasssolenoid valve t€3t {see psge 1l-221t.
Does the valve hold vacuum?
Check for an open in the wire(PCS line):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the EVAP purgecontrol solenoid valve 2P connector,3. Check for continuity betweenthe EVAP pu rge controlsolenoid valve 2P connectorterminal No.2 and bodygrouno,
ls there continuity?
Check for an open in the wire(lGl line):1. Turn the ignition switch ON t).2. Measure voltage between theEVAP bypass solenoid valve 2pcoonector terminal No. 1 andbody ground.
ls there battery voltage?
Repah open in lhe wir6 betwoenthe EVAP pu.ge cont.ol solonoidvdlvo and No. 15 ALTERNATORSP SENSOR {7.5 Al fu!€.
*: Continued frr '98 model
1-220
www.emanualpro.com
Page 517 of 1395

Automatic Transmission
Special Tools . 14'2OescriptionGeneral Operation . .... 14 3Power Flow . . .. '14_6
Electronic Control System .. .. . . .. .14_15Hydraulic Control .. 14 24Hydraulic Flow....-....... .. . .... .. .. . 14_29Lock'up Syslem .. .'t4'39Electrical SystemComponenl Locdlrons 14 45
PCM Circuil Dragram (A/T Control Svstem)'97 Model ....................... . . .. - . ... .14-46'98Model ................. . ... .. .. .1450'99 00Models.... . .... . . . 1452
PCM Terminal Voltage/Measuring ConditionsA"/T Control System-'97Model ...... ..14'48A,/T Control System -'98 00 Models . . .. . . 14 54
Troubleshooting Procedures .. ..... ... - 14_56Svmotom to comoonent CharlEiectr,cal Syslem -'97 Model . . 14 60Electrical System -'98 - OO Models . .. . . 14_62Electrical Troubleshooting ('97 Model)Troubleshooting Flowaharts .... ..... . .. . . 14_64
Electrical Troubleshooting ('98 - 00 Models)Troubleshootinq Flowclt"n" .... . ....- . .14-93ElectricalTroublesliooting('99 00Models)Troubleshootino FlowchartO/D OFF Indicator Light Does Not Come On 14 131
O/D OFF Indicator Liaht On ConstantlY . . . .1!-132O/D OFF Indicator Light Does Not Come OnEven Though O/D Switch ls Pressed . .... - 14_133
Lock up Control Solenoid Valve A,/B AssemblyTest....................-......... . .14-135Replacement . .ll_135Shifr ControlSolenoid Valve Ay'B Assembl,Test .............................. . .. 14-136
Replacement..............- . .14'136Linear Solenoid AssemblYTest.............................................. .. .... . 14_137Replacement .. . 14138Marnshaftlcountershafl Speed SensorsReplacement ...-... 14_138A/T Gear Position SwitchTest ..........................-... . .. 14-139ReplacementA/T Gear Positionlndicator.................. 14-140
Valve Eodynepair ............................... ..... . . .. - . .. ... 14 192
Assembly .................... .. 1{_193
Valve CapsDesciiption....-........................ .. ...... 14194
tnspeition ................... .. 14' 195
N4ain Valve BodyDisassembly/lnspection/Reassemblv - ...... .. 14_196
Secondarv Valve BodYDisassemblv4nspectron/ReassemblY .. . 14 198
Reoulator Valve Bodvbisassembtv,lnspiction/Reassemblv . 14199
Servo EodvDisassembly/lnspection/Reassembly ... ....14'200
Lock'uo Valve BodYDis;ssembly/lnspection/Reassembly .... . 14_201
MainshaftDisassembly/lnspection/Reassembly .. .. .. ..14'202
Inspection ....-.............. ..11_203
Sealing RingsReilaceient ...... ..... . 14'204
CountershaftDisassembly/lnspection/Reassembly .. . . . . . 11-205
Disassembly/Reassemb|y . . ........ ...... . .. 14_206Inspedron ................ . .... . 14 207
One wav ClutchDisassembly/lnspection/ReassemblY ... 11_209
Sub-shaftDisassembly/lnspection/Reassembly ... . .. . 14-210
oisassembly/Re6ssembly . . ... .-...... . . ..14-211
Sub-shaft BearingsReplacement .......14'212
Clutchllfustrated Index .......... . . .14-213
Disassembly .... .. .....14-216Reassembfy .... . .. .. . 14'218
Differentialllfustrated Index " 14-222Backlash Inspection . .... . .14'223
Bearing Repiacement .. 11-223
Differe-ntial Carrier Replacement .. .. . . . .. ..11-2?4
OifSeal Replacement. . .. 14'225
Side Clearance lnspection . . - .. ... . - ...... . .. 11'226
Transmission Housing BearingsMainshaJVCountershaft EearingsRepfacement .......14221Sub'siralt Eearing Replacement . . . . . . . . . ..11'224
Toroue Converter Housing BearingsMainshattEearing/OilSe6lReplacement . .. l4229
Countershaft Bea;ing Replacement.. .... .. ..14-230
Input Test - '97 - 98 ModelsInput Test '99 - 00 Models
Symptom to-Component ChartHydraulic System ...............
Checking
Removal ...,lllustrated Index (4WD)
Interlock SystemInterlock ControlUnit lnputTest. -..... -.. .... . - 14 144* Key Interlock Solenoid Test .- .. . . . - . . . ..... 14_146* Shift Lock Solenoid Test ..............-.-. . .. . ... .... 14 147*Shift LockSolenoidReplacement...... .. . .. .. 14 148* park pin Switch Test ......... 14 119' Park Pin Switch Replacement- '97 - 98 Models ....... 14-150* Park Pin Swirch/Over Drive (O/Di SwitchReplacemenl '99-00Models . .. 14_151over-Drive (O/D) Switch {'99 00 [4odels]Test........_..................... .......14-152Hydr.ulic System
..............._............... t4 142.................................. 14-143
Control Lever AssemblyR6placement ......,.,Reverse ldler Gear
lllustrated lndex
.......... 14-230
14 231
11-231
1nsta1|ation ..................Park StopInspeclion/AdjustmenlTransfer AssemblY.......14.232
RoadTest.............-.... ........ .StallSpeedTest ....._........................ ....... 14-159Fluid Level......_................... 14'160
Disessembly .................... 14-235Transfer Drive Gear BearingReplacementTrans{er Driven Gesf Shaft BearingReplacementTransfer Housing Roller BearingReplacementTransfer Cov€r A Bearing Outer RaceReplacementTransfer Housing Bearing Outer RaceReplacement ......-..,,,,,.....ReassemblvTransmassaonBeassembly ... -.. .... .14 250
Torque Converier/Drive Plate . .-. .... .. . ... .....14_258
Transmissionlnstatlation .................. ....... 14'259
Cooler Flushing . . ......11-261ATF Cooler HosesConnection.................. ....... 14-266I Shift LeverRemoval/lnstallation . .. 14'261
Disassemblv/Reassemblv - '97 - 98 Models . . 14_264
Disassembli/Reassemblv -'99 - 00 Models . 14-269
Over'Orive (O/D) Switch WireClearanceAdjustment. - ... . . . .. .. . 14'270
Detent Spring Replscement . . -.. ... .14'271*Shift CableAdiustment ....... 14'272
Repfacement.............. . 11'273
14 15711-237
11-237
14-238
$-234
11-23914-240
Transmigrion
Inspeclron ....., ...........Transfer AssemblyRemova1,.,,,..............,lnstallalion ........... .. ...Transmission
14 164
14-16514,167
14-169
End Cover/Transmissio . 14'174Transmission Housing .... ... .. . . .... .. 14-176Torque Converter Housingly'alve Body.. - ... -. 14 178
lllustrated lndex (2WD)End Cover/Transmissio ....... 14 180Transmission Housing . . ... . .. .... ... 14'182Torque Convener Housing/r'alve Body ......- 14-184
End CovefRemovat ...................... ....... 14'186Transmission HousingRemoval ...................... .. 14_188Torque Convener HousingA/alve BodYRemovat ................-..... .-..... 14-190
www.emanualpro.com
Page 519 of 1395

Description
General Operation
The Automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and triple-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides 4
speeds forward and 1 reverse speed The unit is positioned in line with the engine'
There are two tvoes of automatic transmission on CR-V; the four-wheel drive (4WD) model ('97 - 00)' and the front-wheel
drive (2WD) model ('98 - 00).
Toroue Converter, G€ars, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump. turbine. and stator assembly in a single unit. The torque converter is connected to
the engine crankshatt. These parts turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is
a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is started. The torque converter assembly serves as a fly-
wheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has three parallel shafts: the mainshaft. the countershaft, and the sub-shaft. The mainshaft is in line with
the engine crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd. and 4th clutches, and gears lor 3rd,2nd,4th. reverse and 1st
(3rd gear is integral with the mainshaft, while reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd
clutch and gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse, 1st, and park. Reverse and 4th gears can be locked to the countershaft at its cen-
ter, providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on which way the selector is moved. The sub-shaft includes the lst-hold
clutch and gears for lst and 4th.
The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the countershaft and sub-shaft. When certain combinations
of gears are engaged by the ctutches, power is transmitted from the mainshaft to the countershaft to provide E, D!, tr, tr,
and E position ('97 - 98 models). and E. E, E, and E position ('99 - 00 models)'
Electlonic Control
The electronic controt system consists of the Powenrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid, and four
solenoid valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body, and
the lock up valve body. They are bolted to the torque converter housing. The main valve body contains the manual valve,
the 1-2 shift valve, the 2nd orifice control valve. the CPB {Clutch Pressure Back-up) valve, the modulator valve, the servo
control valve. the relief valve, and ATF pump gears. The secondary valve body contains the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4 shift
valve, the 3,4 orifice control valve. the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch Pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve
bodv contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve, the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up con-
trol valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the reverse shift tork, and the accumulators
The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing valve. The linear solenoid and the shift con-
trol solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted to the outside of the transmission housing, and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is
bolted to the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid trom the regulator passes through the manual valve to the
various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective feed pipes or internal hydraulic circuit
ShiftControl Mechanism
input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will acti-
vate. Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes
a line to one of the clutches. engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear. The shift control solenoid valves A and B are
controlled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
tn E! position (,97 - 98 modets) and in E position ('99 - O0 models), in 3rd and 4th, and in Del position in 3rd ('97 - 98
models) and in El position with Over,Drive (O/D) is OFF (by pressing rhe O/D switchl in 3rd ('99 - 00 models), pressurized
fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held
against the torque converter cover, As this takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft.
Together with hydraulic control, the PcM optimizes the timing of the lock-up mechanism The lock-up valves control the
range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and the linear solenoid. When lock-up control
solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes. The lock-up control solenoid valves A and B and the
linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
{cont'd)
14-3
www.emanualpro.com
Page 520 of 1395

Description
General Operation (cont'dl
Gsar Selection'97 - 98 Models
The shift lever has seven positions; El PARK, ts REVERSE, N NEUTRAL, Ell 1st through 4th ranges, lpq 1st th.ough 3rdranges, P 2nd gear, and [ 1st gear
'99 - 00 Models
The shitt lever has six positions; El PARK, E REVERSE, E NEUTRAL. E ,lst through 4th ranges, and 1st through 3rd(when Over-Drive (O/D) is OFF) ranges. @ 2nd gear, and E 1st gear.
Starting is possible only in @ and @ positions. using a slide-type. neutral-safety switch.
Automatic Transaxle (A/T) Gear Position IndicatorThis indicator in the instrument panel shows which gear has been selected.
Transler Mochanism {4WD}
The transfer mechanism consists of the transfer shaft drive gear. the transfer shaft. the transfer drive gear, the transfer driv-en gear shaft, and the companion flange, The transfer mechanism assembly is on the rear side ot the transmission. besidethe differential. The transfer shaft drive gear on the final driven gear drives the transfer shaft driven qear. power is transmit-ted to the rear differential via the transfer shaft and the Drooeller shaft.
Clutches
The four-speed automatic transmission uses hydraulically-actuated clutches to engage or disengage the transmission gears.When the hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum, the clutch piston moves. This presses the friction discs andsteel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is then transmifted through the engaged clutch pack to its hu$mounted gear. When hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack, the piston releases the friction discs and steel plates, andthey are free to slide past each other. This allows the gearto spin independently on its shaft, transmitting no power.
lst Clutch
The 1st clutch engages/disengages lst gear, and is located at the end ofthe mainshaft, just behind the end cover.The 1st clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the mainshaft.
lst-hold Clutch
The 1st-hold clutch engages/disengages 1st-hold or E position, and is located at the middle of the sub-shaft. The 1st-holdclutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the sub-shaft.
2nd Clutch
The znd ciutch engages/disengages 2nd gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft. The 2nd clutch is joined back-to-back to the 4th clutch. The 2nd clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure through the mainshaft by a circuit connected to theinternal hydraulic circuit.
PositionDescription
Reverse; reverse selector engaged with countershaft reverse gear and 4th clutch locked.
Allclutches released.
General driving; starts off in 1st, shifts automatically to 2nd, 3rd, then 4th, depending on vehicle speedand throftle position. Downshifts through 3rd,2nd, and lst on deceleration to stop.The lock-up mechanism operates;n 3rd and 4th gear.
used for rapid €cceleration at highway speeds and general driving; stans off in 1st, shifts automatically to2nd_then 3rd, dejending on vehicle speed and throttle position. Downshifts through lower gears on decel-eration to stop. The lock-up mechanism comes into operation in 3rd gear.
Driving in 2nd_gear; stays in 2nd gear, does not shift up and down. For engine braking or better trac_tion starting off on loose or slippery surfaces.
Driving in 1st gear; stays in 1st gear, does not shift up. For engine braking.
tll PARK
t!!l l|EvEn>E
E NEUTRAL
Ell DRrvE ('97 - sB)E DRrvE ('ss - oo)(1st through 4th )
E DRrvE {'97 - s8)O DRTVE with over-Drive (O/D) is OFF('99 - 00)(1st through 3rd)
E SECOND
E FIRST
14-4
www.emanualpro.com
Page 536 of 1395
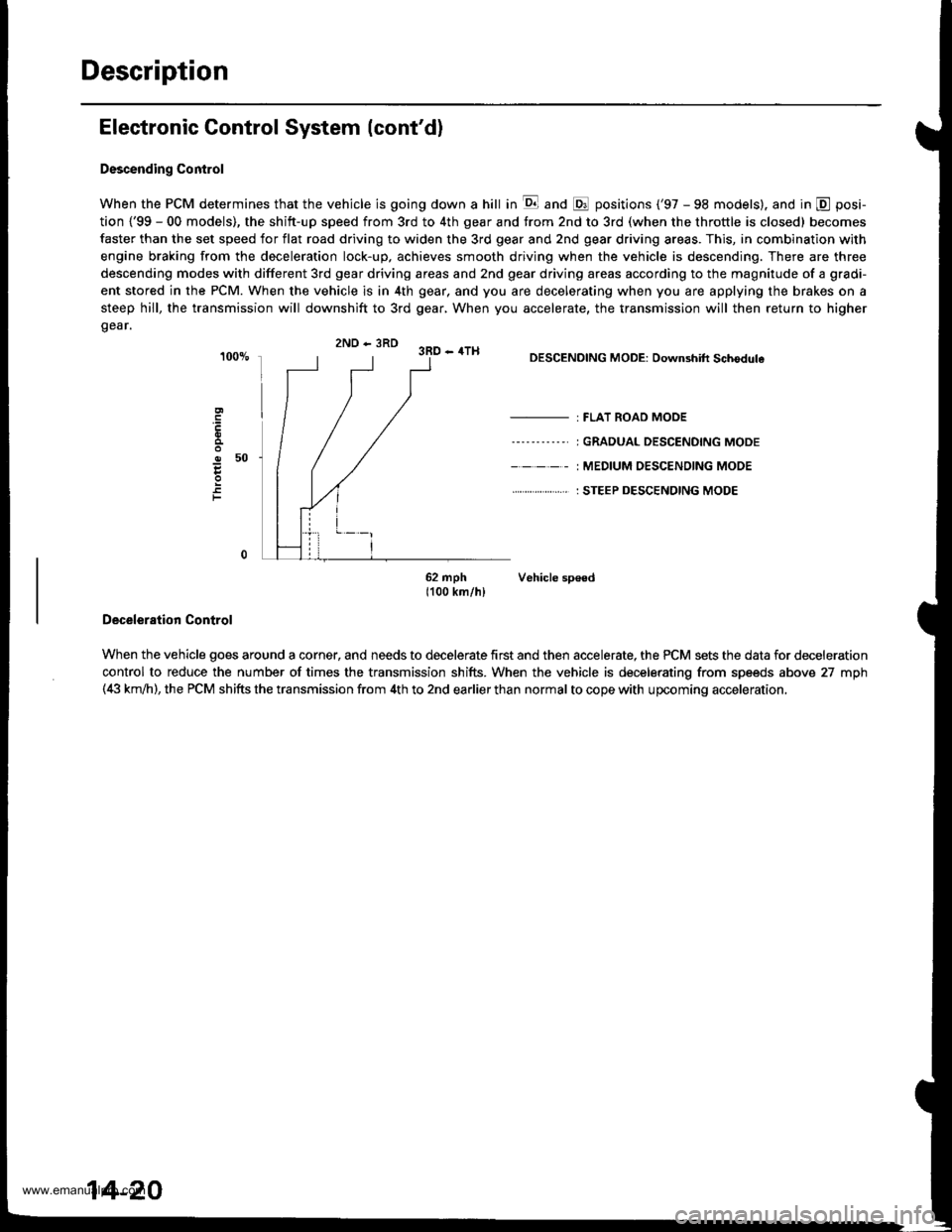
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
Descending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in E and @ positions ('97 - 98 models). and in @ posi-
tion {'99 - 00 models), the shitt-up speed from 3rd to 4th gear and from 2nd to 3rd (when the throttle is closed) becomes
faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear and 2nd gear driving areas. This, in combination with
engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle is descending. There are three
descending modes with different 3rd gear driving areas and 2nd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradi-
ent stored in the PCM. When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating when you are applying the brakes on a
steep hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear, When you accelerate, the transmission will then return to higher
gear.
2ND - 3RD 3RD - 4TH
o50
F
DESCENDING MODE: Downshift Schodule
- : FLAT ROAD MODE
----'-----' I GRADUAL DESCENDING MODE
- - - - - : MEDIUM OESC€NOING MODE
. . ... : STEEP DESCENDING MODE
62 mph Vehicle sp€ed1100 km/hl
Deceleration Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner, and needs to decelerate first and then accelerate, the PCM sets the data for deceleration
control to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 27 mph(4i| km,ih), the PCM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlier than normal to cope with upcoming acceleration,
14-20
www.emanualpro.com
Page 546 of 1395
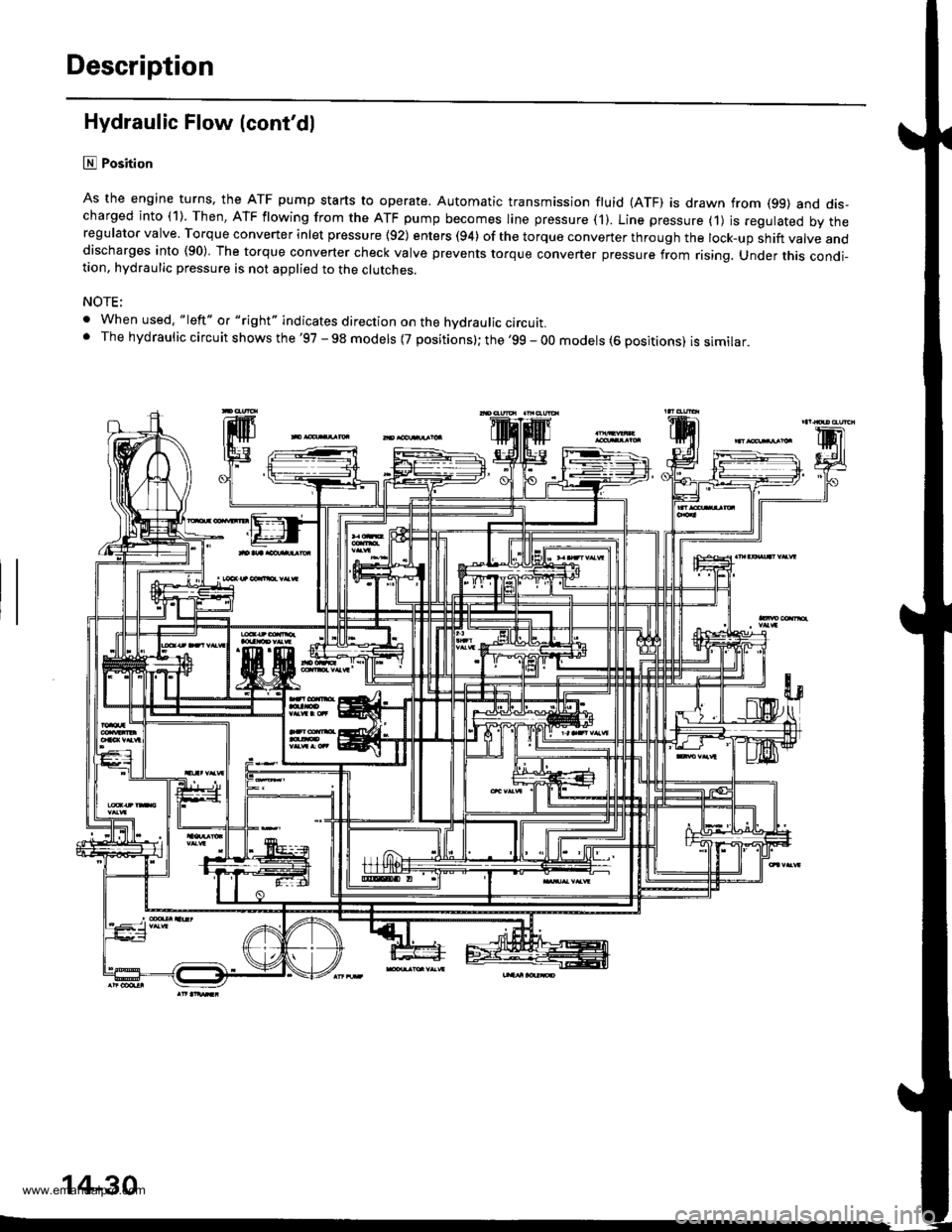
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'dl
lll Position
As the engine turns, the ATF pump starts to operate. Automatic transmission fluid (ATF) is drawn from (99) and dis-charged into (1). Then, ATF flowing from the ATF pump becomes line pressure ('l). Line pressure (1) js regulated by theregulator valve. Torque converter inlet pressure {92) enters (94) of the torque conveTter through the lock-up shift valve anddischarges into (90) The torque converter check valve prevents torque converter pressure from rising. Under this condi-tion, hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches.
NOTE;
. When used. "|eft" o. "right" indicates direction on the hvdraulic circutt.. The hydraulic circuit shows the '97 - 98 models {7 positions}; the '99 - 00 models (6 positions) is similar.
'lF'.j.l
14-30
www.emanualpro.com
Page 547 of 1395
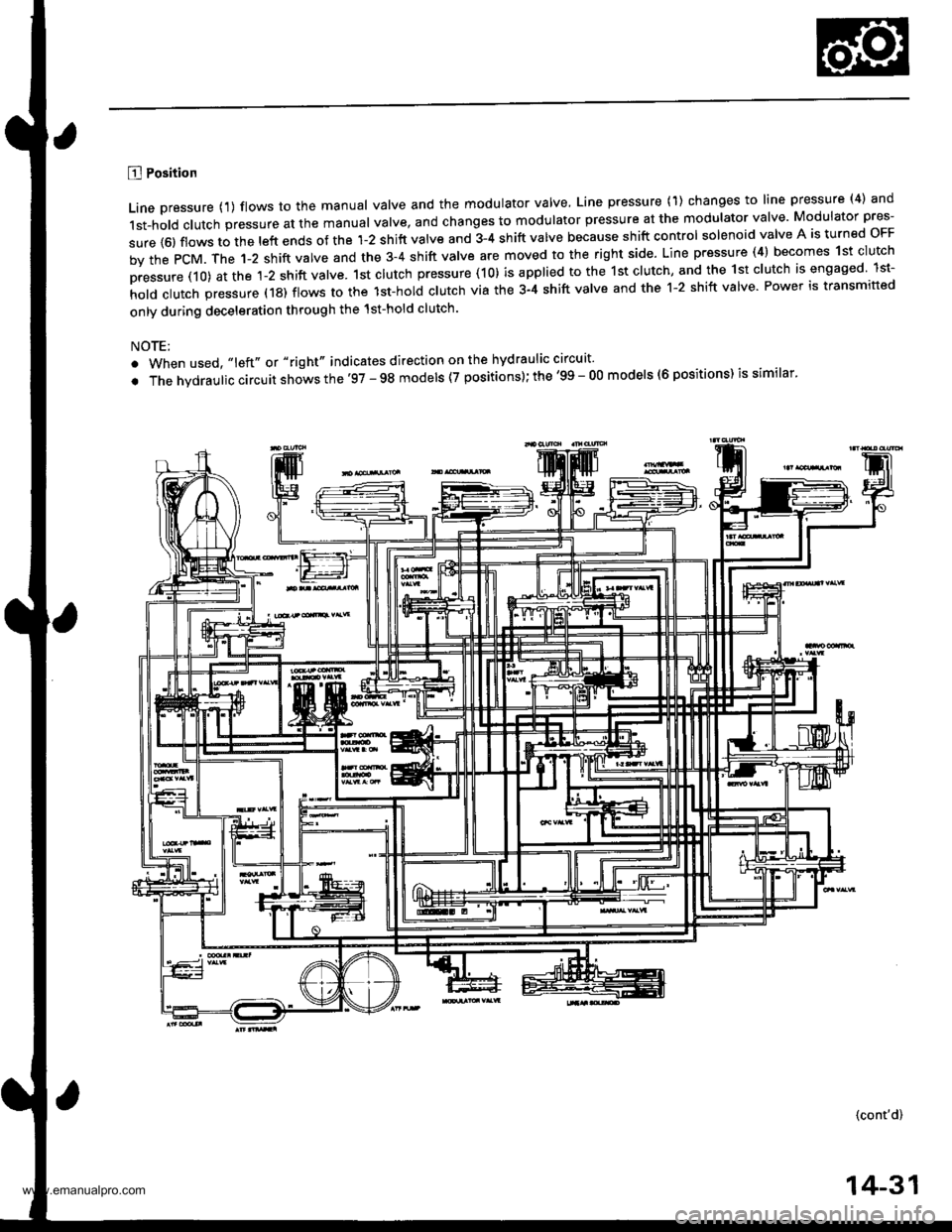
B Position
Line pressure {1) flows to the manual valve and the modulator valve, Line pressure (1) changes to line pressure (4) and
1st-hold clutch pressure at the manual valve, and changes to modulator pressure at the modulator valve Modulator pres-
sure {6) flows to the left ends of the 1-2 shift valve and 3-4 shift valve because shift control solenoid valve A is turned oFF
by the PcM. The 1-2 shift valve and the 3-4 shift valve are moved to the right side. Line pressure (4) becomes 1st clutch
pressure (10) at the 1-2 shift valve. 1st clutch pressure (10) is applied to the 1st clutch, and the 1st clutch is engaged lst-
hold clutch pressure (18) flows to the lst-hol; clutch via the 3-4 shift valve and the 1-2 shift valve Power is transmitted
only during deceleration through the 1st-hold clutch.
NOTE:
. When used, "left" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit'
. The hvdraulic circuit shows the'97 - 98 models (7 positions); the '99 - O0 models (6 positions) is similar'
(cont'd)
14-31
www.emanualpro.com
Page 551 of 1395
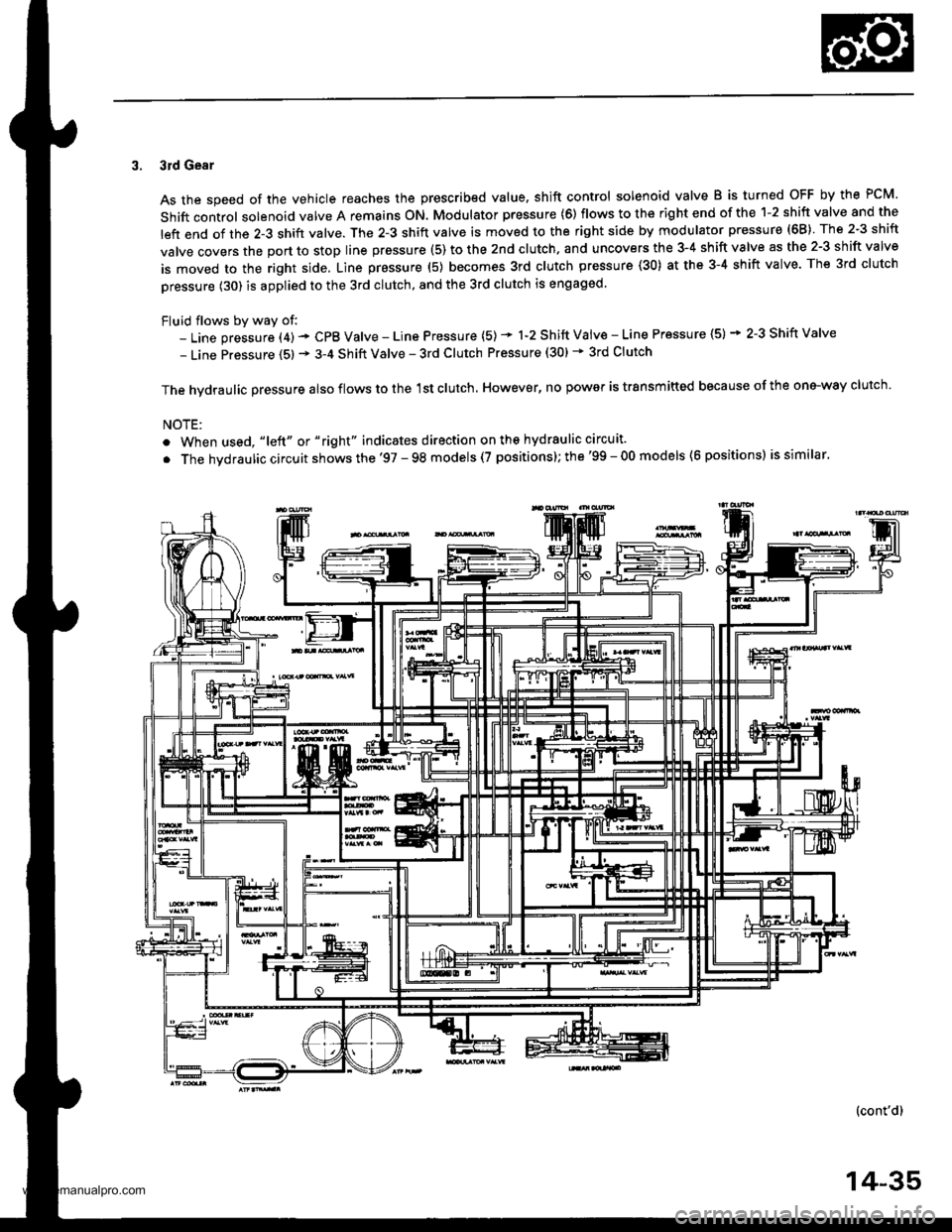
3. 3rd Gear
As the speed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value. shift control solenoid valve B is turned OFF by the PCM.
Shift control solenoid valve A remains ON. Modulator pressure (6) flows to the right end of the 1-2 shift valve and the
left end of the 2-3 shift valve. The 2-3 shift valve is moved to the right side by modulator pressure (68) The 2-3 shift
valve covers the port to stop line prsssure (5) to the 2nd clutch. and uncovers the 3-4 shift valve as the 2-3 shift valve
is moved to the right side, Line pressure (5) becomes 3rd clutch pressure (30) at the 3-4 shift valve. The 3rd clutch
pressure (30) is applied to the 3rd clutch, and the 3rd clutch is engaged.
Fluid flows by way of:- Line pressure (4) - CPB Valve - Line Pressure (5) * 1-2 Shift Vaiv€ - Line Pressure (5) * 2-3 Shift Valve
- Line Pressure (5) * 3-4 Shift Valve - 3rd Clutch Pressure (30) * 3rd Clutch
The hvdraulic Dressure also flows to the 1st clutch. However, no power is trsnsmitted because of the one-way clutch.
NOTE:
. When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on ths hydraulic circuit.
. The hvdraulic circuit shows the '97 - 98 models (7 positions); the'99 - 00 models (6 positions) is similar.
(cont'd)
14-35
www.emanualpro.com
Page 552 of 1395
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'd)
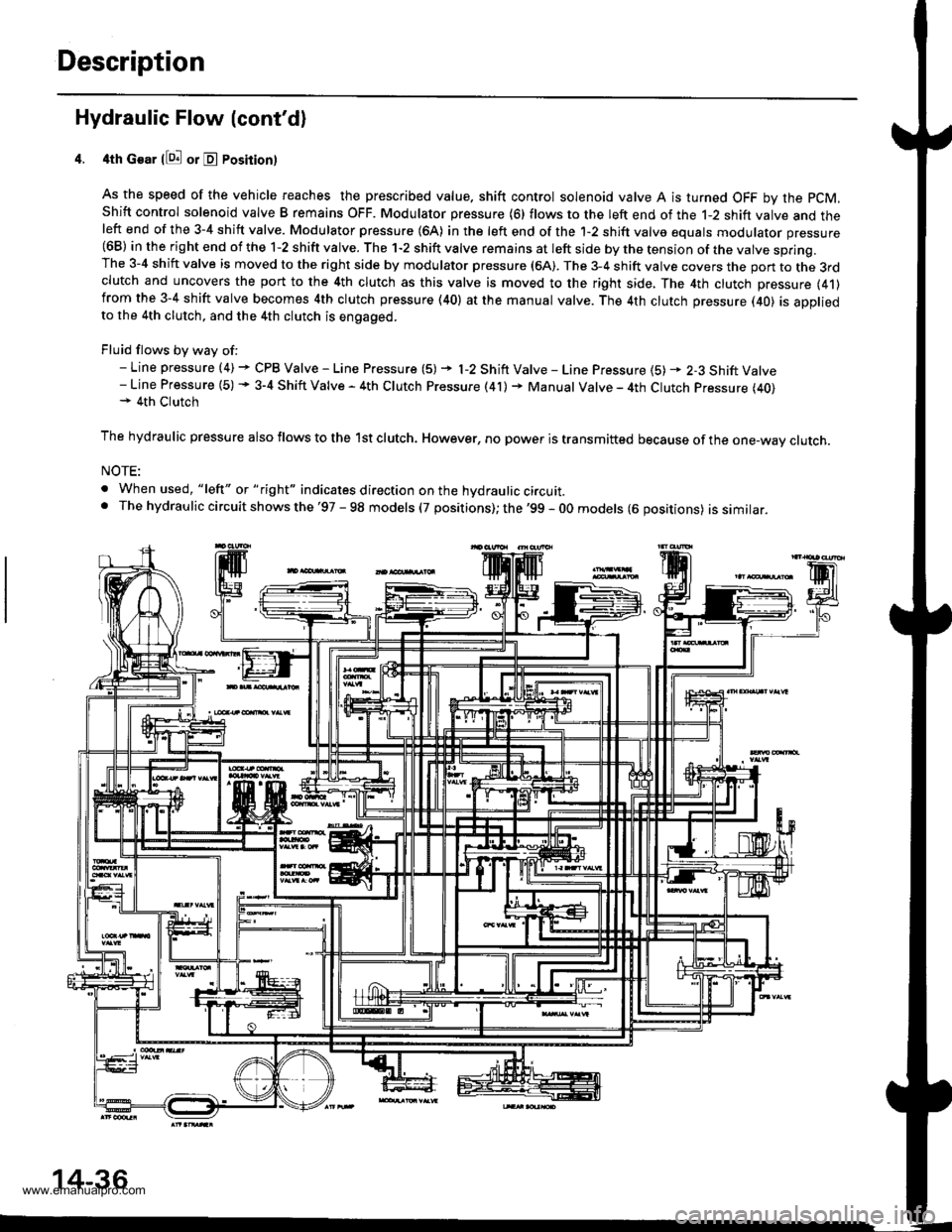
4th Gear llQ! or E Posirion)
As the speed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value. shift control solenoid valve A is turned OFF by the pCM,
Shift control solenoid valve B remains OFF. Modulator pressure (6) flows to the left end of the 1-2 shift valve and theleft end of the 3-4 shift valve. Modulator pressure (64) in the left end of the 1-2 shift valve equals modulator pressure(68) in the right end of the 1-2 shift valve. The 1-2 shift valve remains at left side by the tension of the valve spring.The 3-4 shift valve is moved to the right side by modulator pressure (6A). The 3-4 shift valve covers the pon to the 3rdclutch and uncovers the port to the 4th clutch as this valve is moved to the right side, The 4th clutch pressure (41)from the 3-4 shift valve becomes 4th clutch pressure (40) at the manual valve. The 4th clutch pressure (40) is appliedto the 4th clutch, and the 4th clutch is engaged.
Fluid flows by way of:- Line pressure (4) + CPB Valve - Line Pressure (5) + l-2 Shift Valve - Line Pressure {5) * 2-3 Shift Valve- Line Pressure (5) + 3-4 Shift Valve - 4th Clutch Pressure (41) + Manual Valve - 4th Clutch Pressure (40)+ 4th Clutch
The hydraulic pressure also flows to the lst clutch. However, no power is transmitted because of the one-wav clutch.
NOTE:
. When used, "lelt" or " tight" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.. The hydrau lic circuit shows the '97 - 98 models (7 positions); the '99 - 0O models (6 oositions) issimilar.
14-36
www.emanualpro.com