clutch HONDA INTEGRA 1998 4.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: INTEGRA, Model: HONDA INTEGRA 1998 4.GPages: 1681, PDF Size: 54.22 MB
Page 432 of 1681
I
I
I
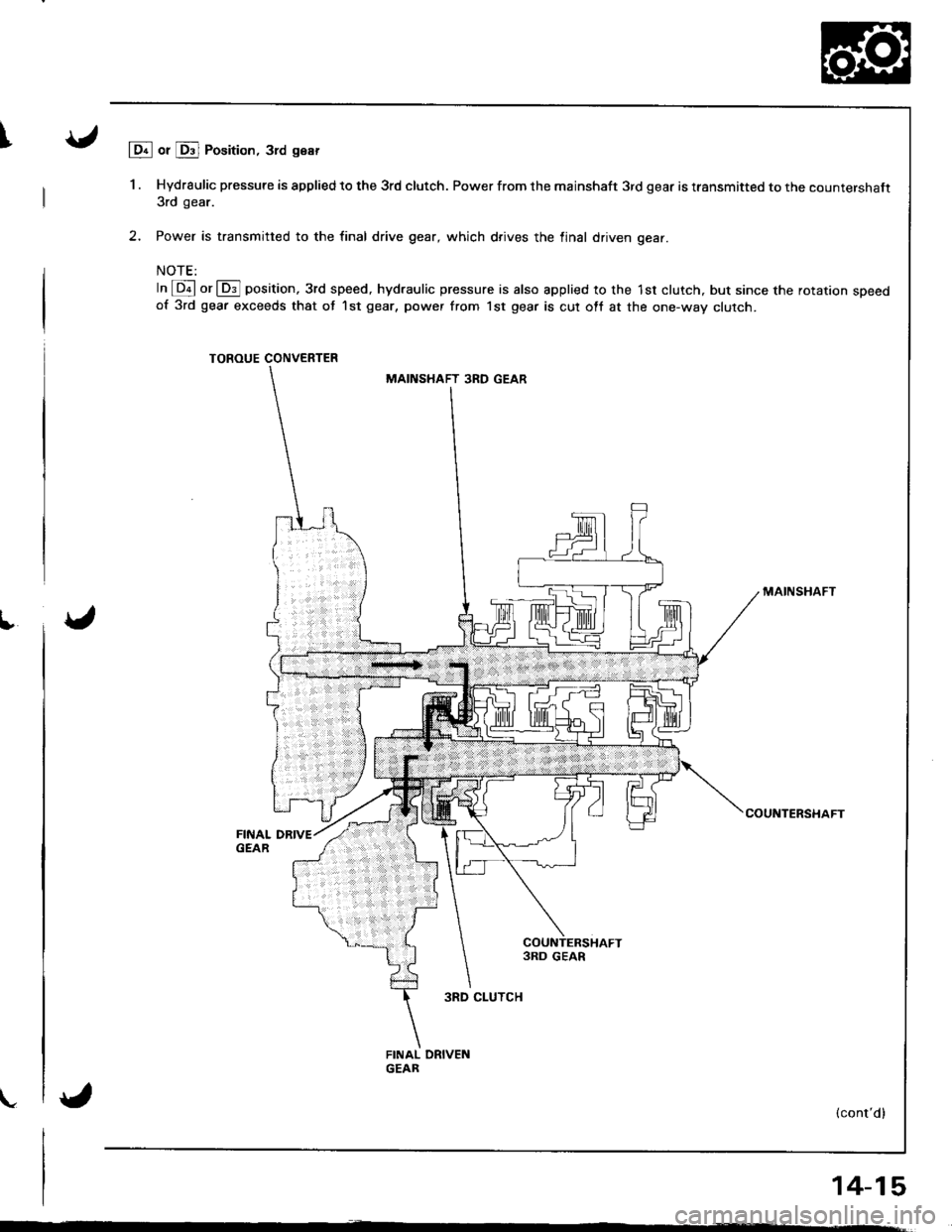
lDr or Drl Position, 3rd gear
1 . Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 3rd clutch. Power from the mainshaft 3rd gear is transmitted to the countershaft3rd gear.
2, Power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which d.ives the linal driven gear.
NOTE:
In @ or @] position, 3rd speed, hydraulic pressure is also applied 10 the 1st clutch, but since the rotarron speedof 3rd gear exceeds that ot 1st gear, power from lst gear is cut ott at the one-way clutch.
TOROUE CONVERTER
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
{cont'd}
14-15
MAINSHAFT 3RD GEAR
3RD CLUTCH
Page 433 of 1681
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
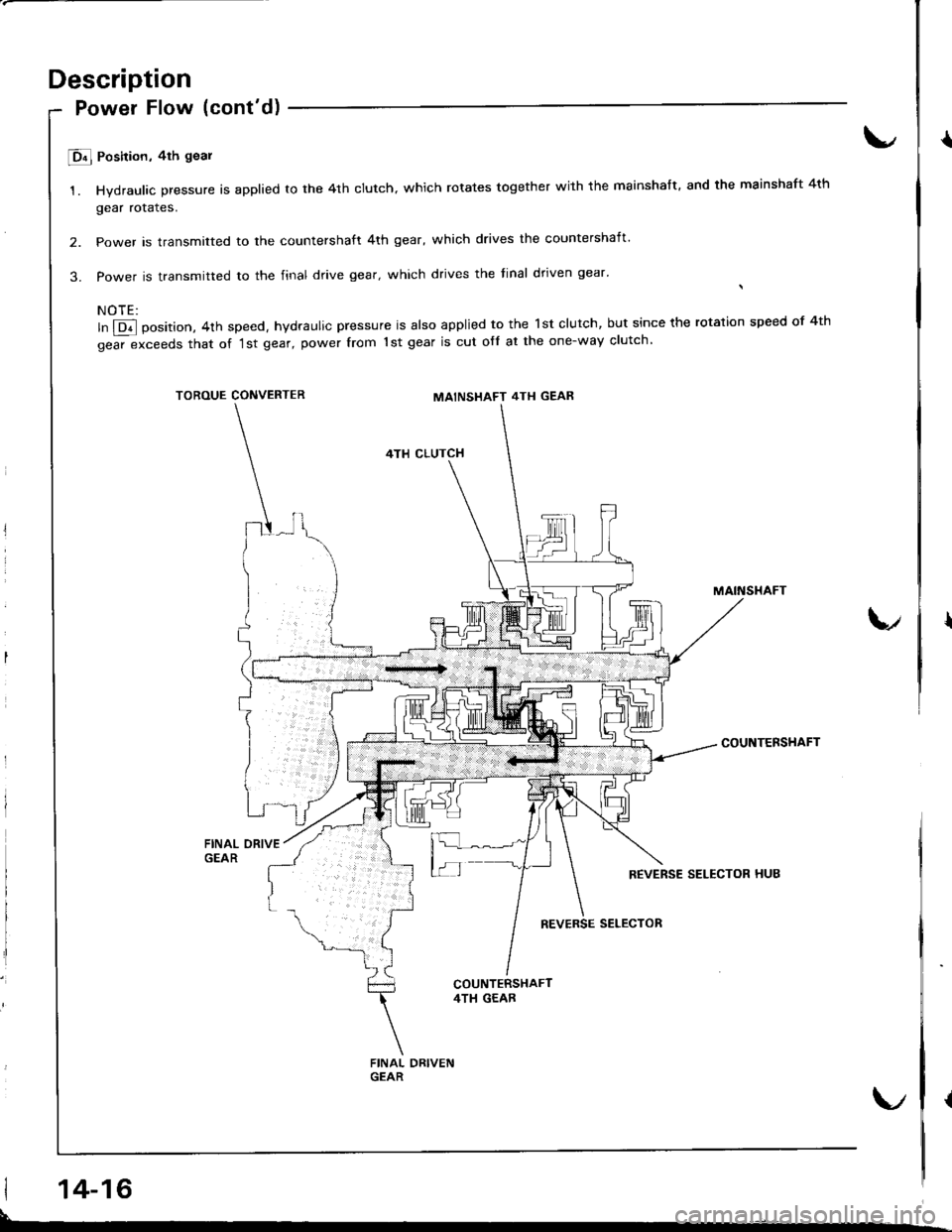
E Position, 4th goal
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 4th clutch. which rotates together with the mainshaft. and the mainshaft 4th
gear rotales.
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 4th gear, which drives the countershaft'
3. Power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which drives the tinal dtiven gear'
NOTE:
ln @ position, 4th speed, hydraulic pressure is also applied to the lst clutch, but since the rotation speed of 4th
gear exceeds that of '1st gear, power from 1st gear is cut ofl at the one-way clutch
TOROUE CONVERTERMAINSHAFT 4TH GEAR
4TH CLUTCH
MAINSTIAFT
COUNTENSHAFT
{
14-16
L
Page 434 of 1681
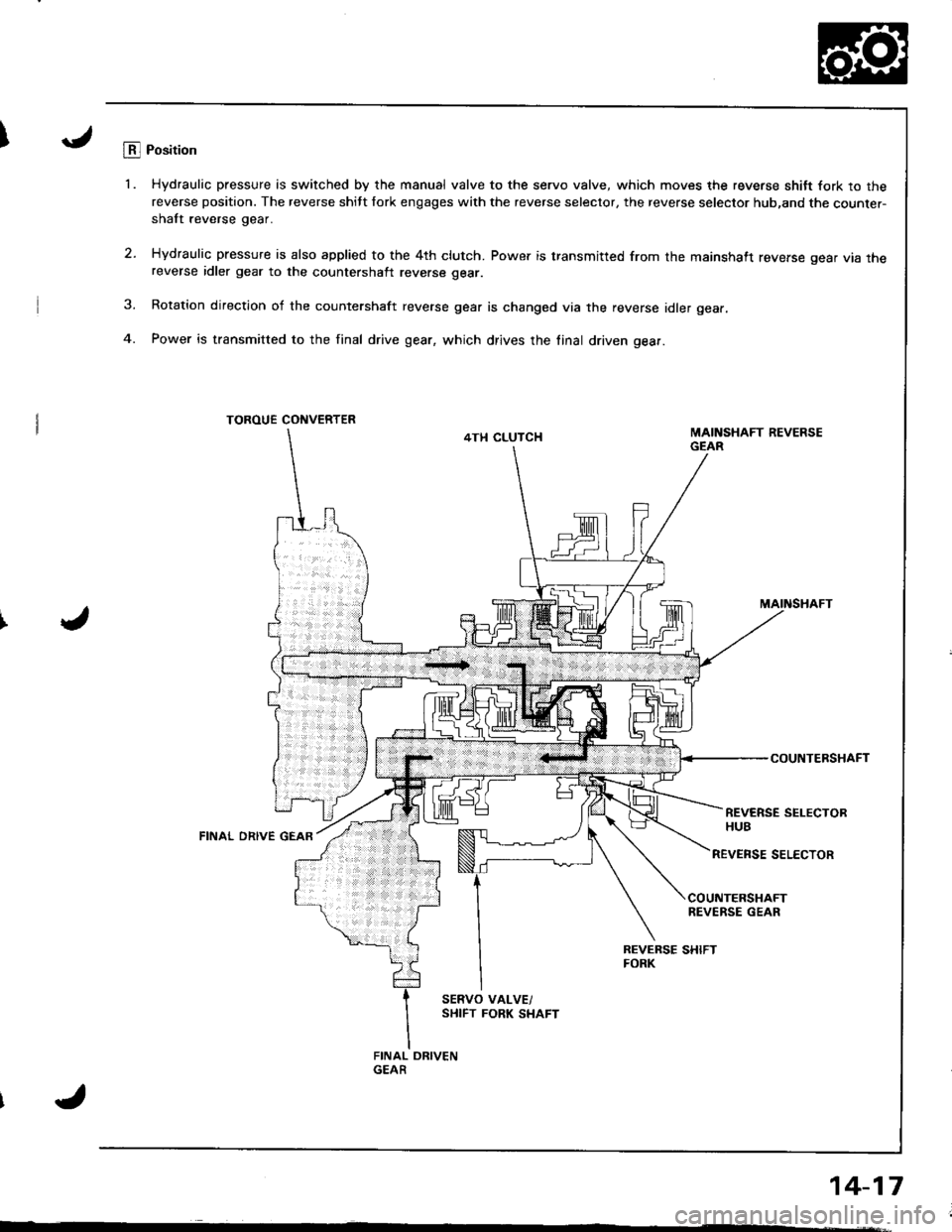
ILB.l Position
'1. Hydraulic pressure is switched by the manual valve to the servo valve, which moves the reverse shitt fork to thereverse position. The reverse shitt fork engages with the reverse selector, the reverse selector hub,and the counter-shaft reverse gear.
2. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 4th clutch. Power is transmitted from the mainshaft reverse gear vta rnereverse idler gear to the countershalt reverse gear.
3. Rotation direction of the countershaft reverse gear is changed via the reverse idler gear.
4. Power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which drives the linal driven gear.
TOROUE CONVERTER
4TH CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
REVERSE SELECTORHUBFINAL ORIVE GEAR
REVENSE SELECTOR
COUNTERSHAFTREVERSE GEAR
Page 440 of 1681
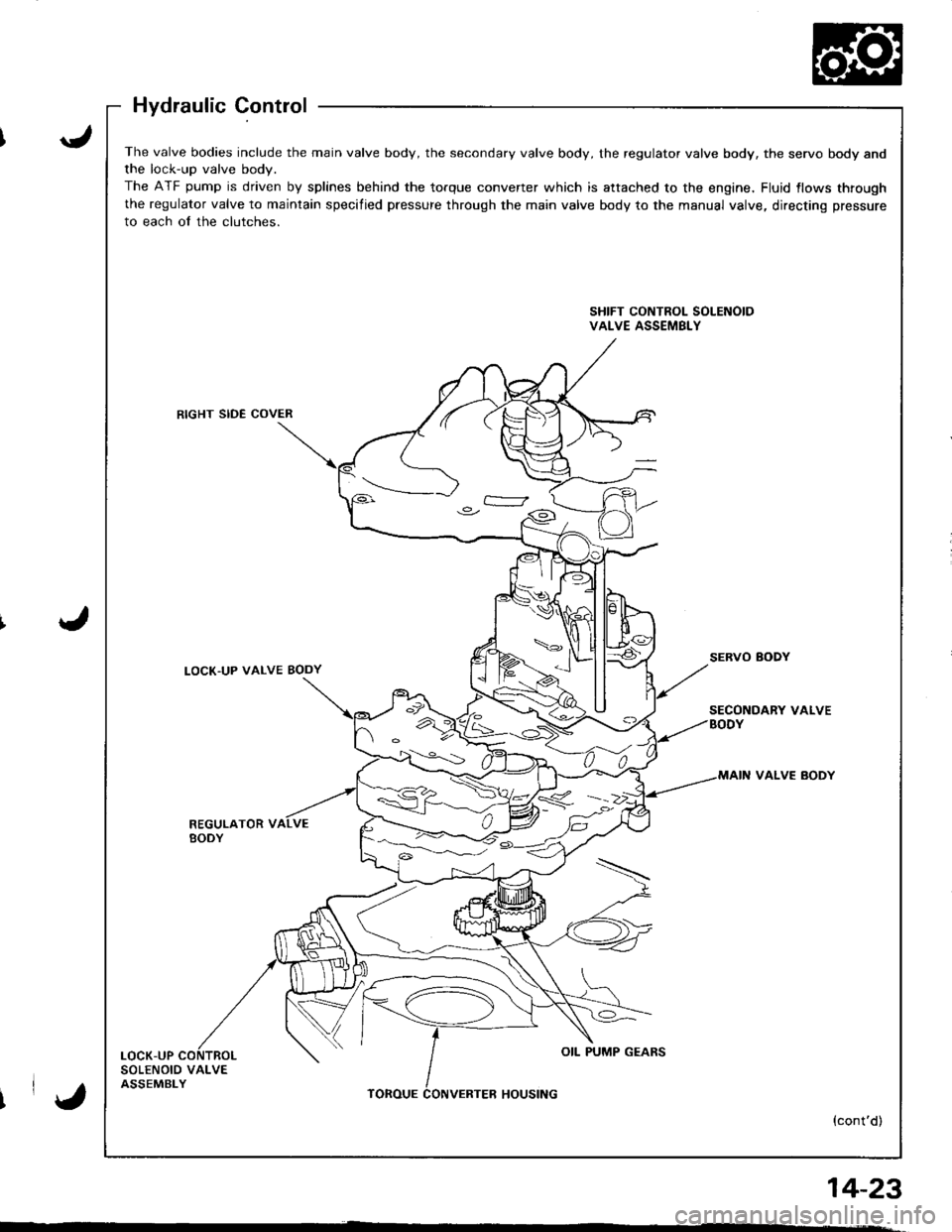
The valve bodies include the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body andthe lock-up valve bodv.
The ATF pump is driven by splines behind the torque converter which is attached to the engine, Fluid {lows through
the regulator valve to maintain specified pressure through the main valve body to the manual valve, directing pressure
to each of the clutches.
SHIFT CONTROL SOLENOIDVALVE ASSEMBLY
RIGHT SIDE COVER
LOCK'UP VALVE BODYSERVO BODY
SECONDARY VALVEBODY
VALVE BODY
REGULATOR VBODY
LOCK-UPOIL PUMP GEARS
SOLENOID VALVEASSEMBLYTOROUEHOUSING
{cont'd)
%<->--::/ )C)
IrY,
14_23
'
Page 444 of 1681
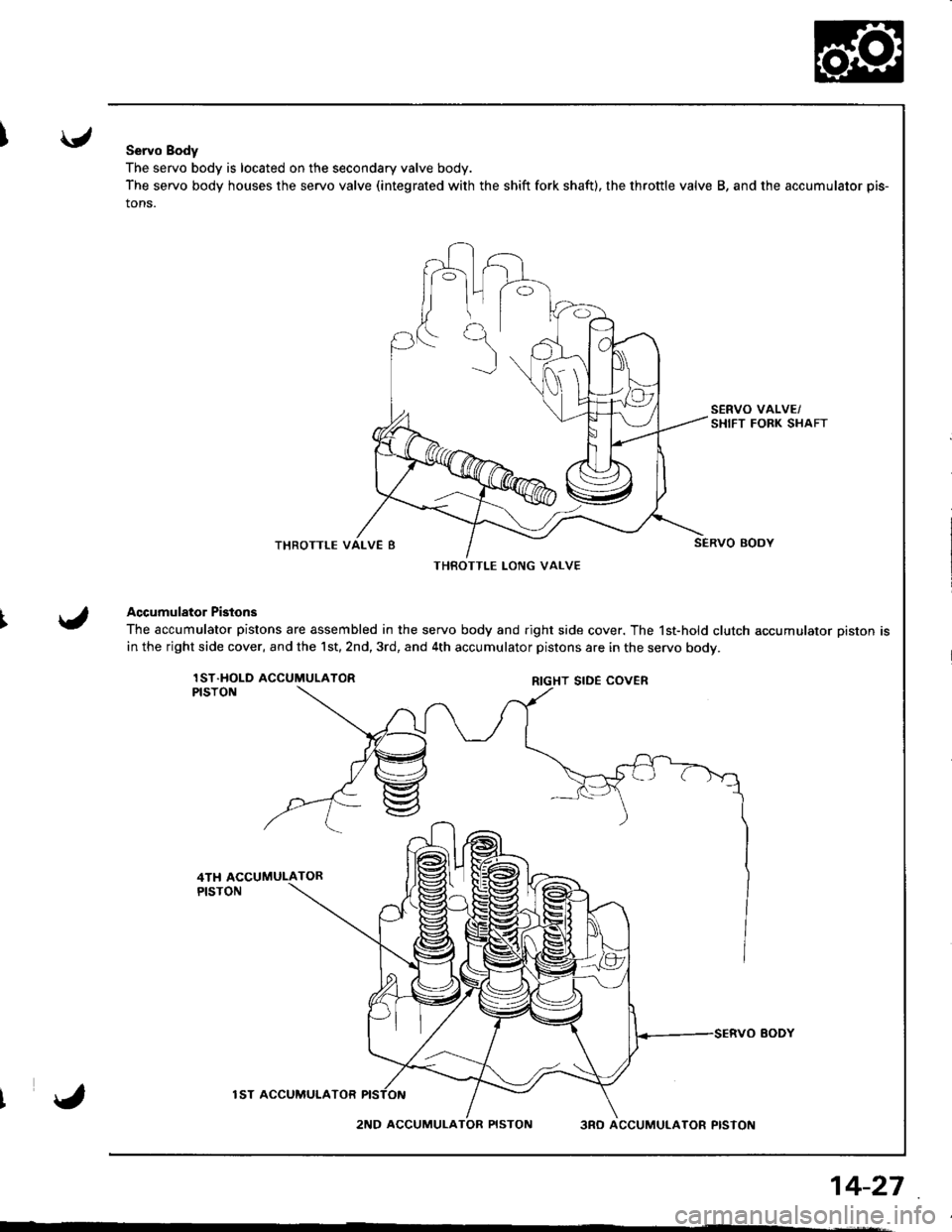
Servo Body
The servo body is located on the secondary valve body.
The servo body houses the servo valve (integrated with the shift fork shaft), the throttle valve B, and the accumulator pis-
tons.
THROTTLE
Accumulator Pistons
The accumulator pistons are assembled in the servo body and right side cover. The 1st-hold clutch accumulator piston is
in the right side cover, and the 1st,2nd,3rd, and 4th accumulator pistons are in the servo bodv.
lST.HOLD ACCUMULATORPISTON
lST ACCUMUI.ATOR
2ND ACCUMULA3RO ACCUMULATOR PISTON
THBOTTLE LONG VALVE
RIGHT SIDE COVER
14-27
Page 445 of 1681
Description
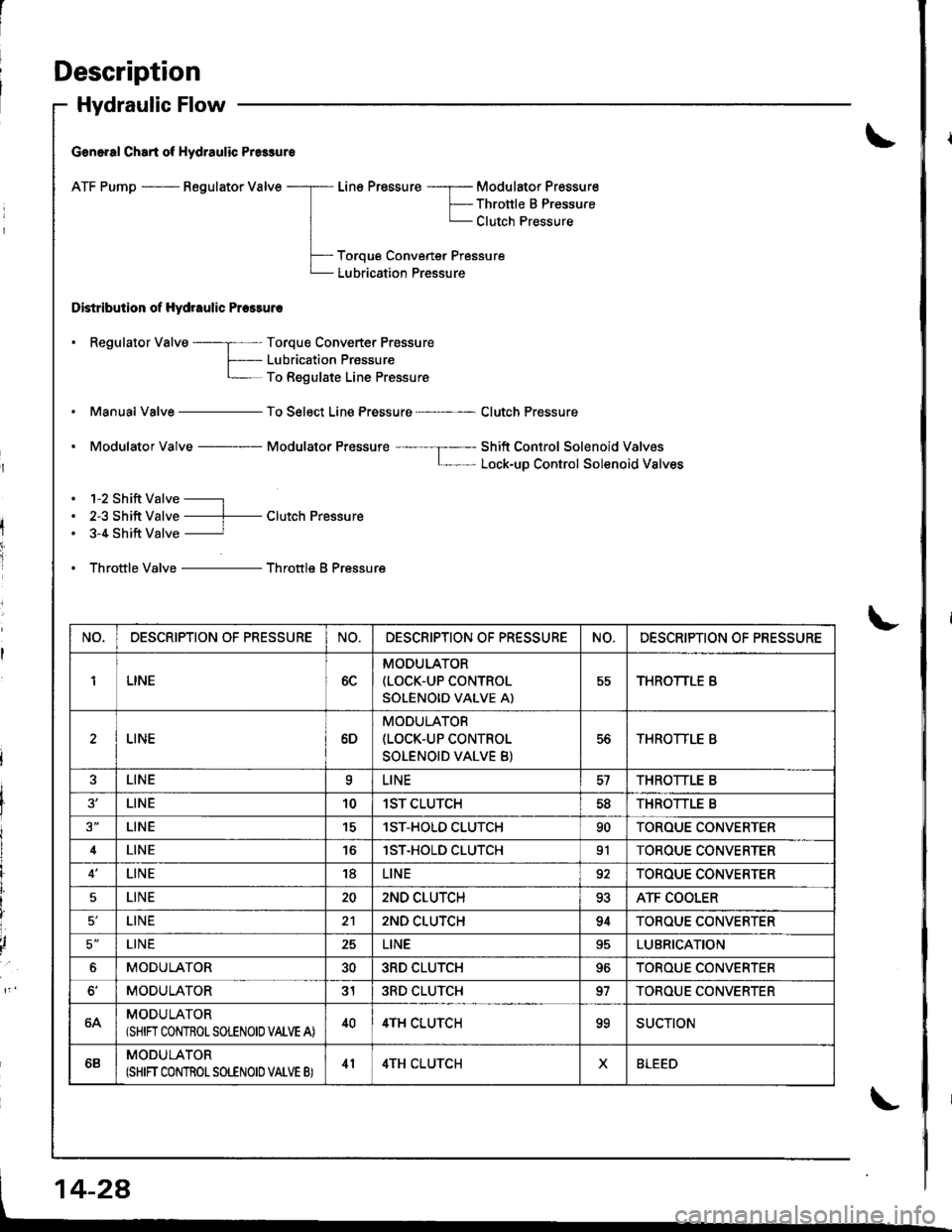
Hydraulic Flow
G€n6.al Chart of Hydraulic Pr6sure
ATF Pump - Regulator Valve
Distribution of Hydraulic Pressuro
Line Pressure -----r- Modulator Pressure
F-- Thronle B PressureL Clutch Pressure
Toroue Convener Pressure
Lubrication Pressure
. Regulator Valve ----; Torque Converter Prossure
f- Lubricaiion PrassureL To Regulate Line Pressure
Manual Valve - To Select Line Pressure - Clutch Pressure
. Modulator Valve Modulator Pressure ---- --I----- Shift Control Solenoid ValvosL- Lock-uD Control Solenoid Valves
. 1-2 Shift Valve -----l
. 2-3 Shift Valve ----f- Clutch Pressure. 3-4 Shift Valve ----------r
. Throttle Valve - Throttle B Pressure
NO,DESCRIPTION OF PRESSURENO.DESCRIPTION OF PR€SSURENO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSURE
1LINE6C
MODULATOR(LOCK.UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE A)
55THROTTLE B
LINE6D
MODULATOR(LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE B)
56THROTTLE B
LINEaLINETHROTTLE B
LINE101ST CLUTCH5dTHROTTLE B
LINE151ST-HOLD CLUTCH90TOROUE CONVERTER
4LINElST.HOLD CLUTCH91TOROUE CONVERTER
LINE18LINE92TOROUE CONVERTER
5LINE202ND CLUTCH93ATF COOLER
LINE212ND CLUTCH94TOROUE CONVERTER
5'LINE25LINELUBRICATION
6MODULATOR303RD CLUTCH96TOROUE CONVERTER
MODULATOR313RD CLUTCH97TOBOUE CONVERTER
64MODULATOR(SHIN CONTROLSOLENOIO VALVE A)404TH CLUTCHooSUCTION
6BMODULATOR(SHIFT CONTROT SOLENOID VATVE B)414TH CLUTCHXBLEED
Page 446 of 1681
I
I
I
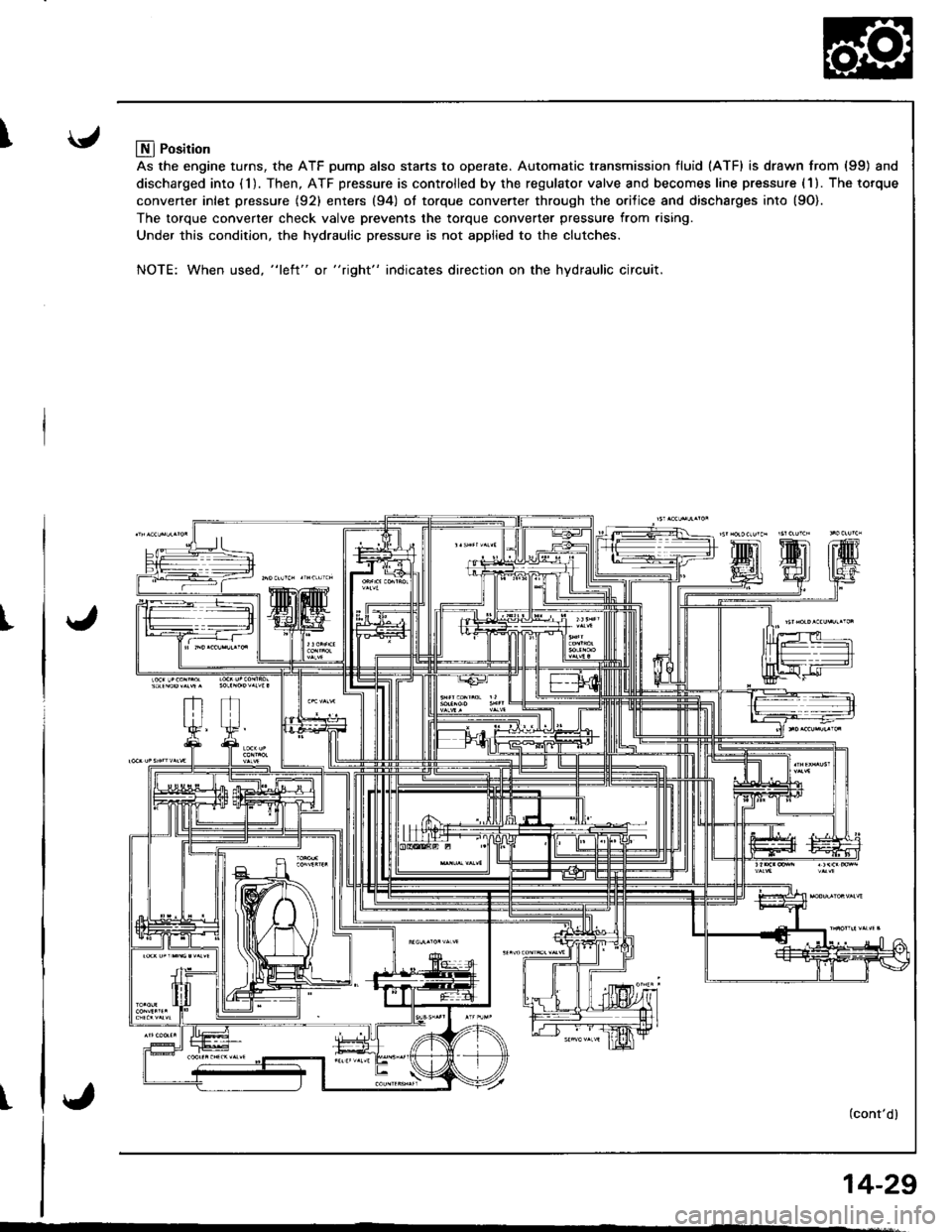
Llfl Position
As the engine turns, the ATF pump also starts to operate. Automatic transmission fluid (ATF) is drawn from (99) and
discharged into (1). Then, ATF pressure is controlled by the regulator valve and becomes line pressure (1). The torque
converter inlet pressure {92} enters (94) ol torque converter through the orilice and discharges into {9O).
The torque converter check valve prevents the torque converter pressure from rising.
Under this condition, the hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches.
NOTE: When used, "l€ft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
(cont'dl
14-29
Page 447 of 1681
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'dl
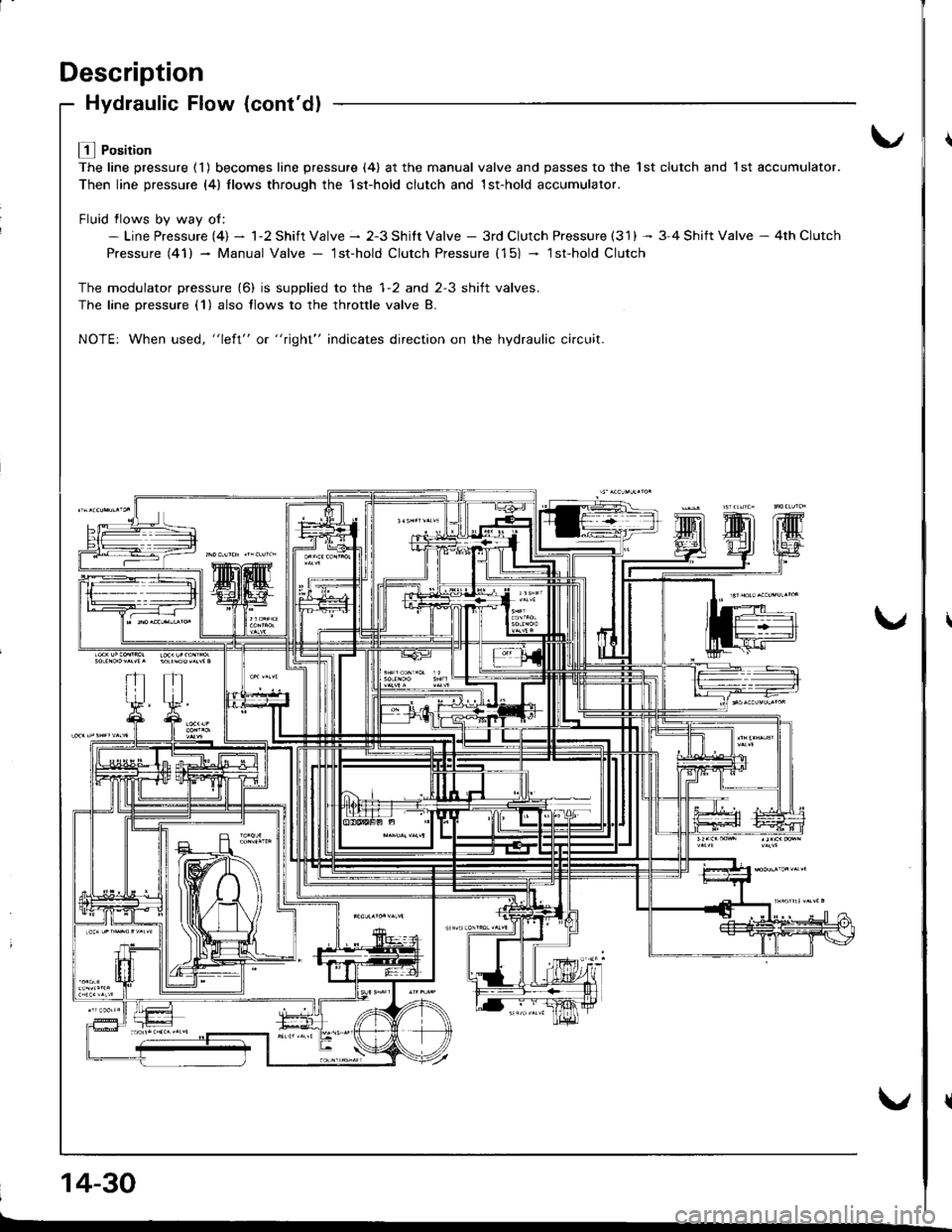
L! l Position
The line pressure ( 1 ) becomes line pressure (4) at the manual valve and passes to the 1st clutch and 1 st accumulator.
Then line pressure (4) llows through the 1st-hold clutch and 1st-hold accumulator.
Fluid flows bv wav of:- Line Pressure (4) - 1-2 Shift Valve - 2-3 Shitt Valve - 3rd Clutch Pressure (31) -- 3-4 Shift Valve - 4th Clutch
Pressure (41) - Manual Valve - lst-hold Clutch Pressure (15) - lsfhold Clutch
The modulator pressure (6) is supplied to the 1-2 and 2-3 shift valves.
The lane Dressure (1) also flows to the throttle valve B.
NOTE: When used, "left" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic ci.cuit.
14-30
Page 448 of 1681
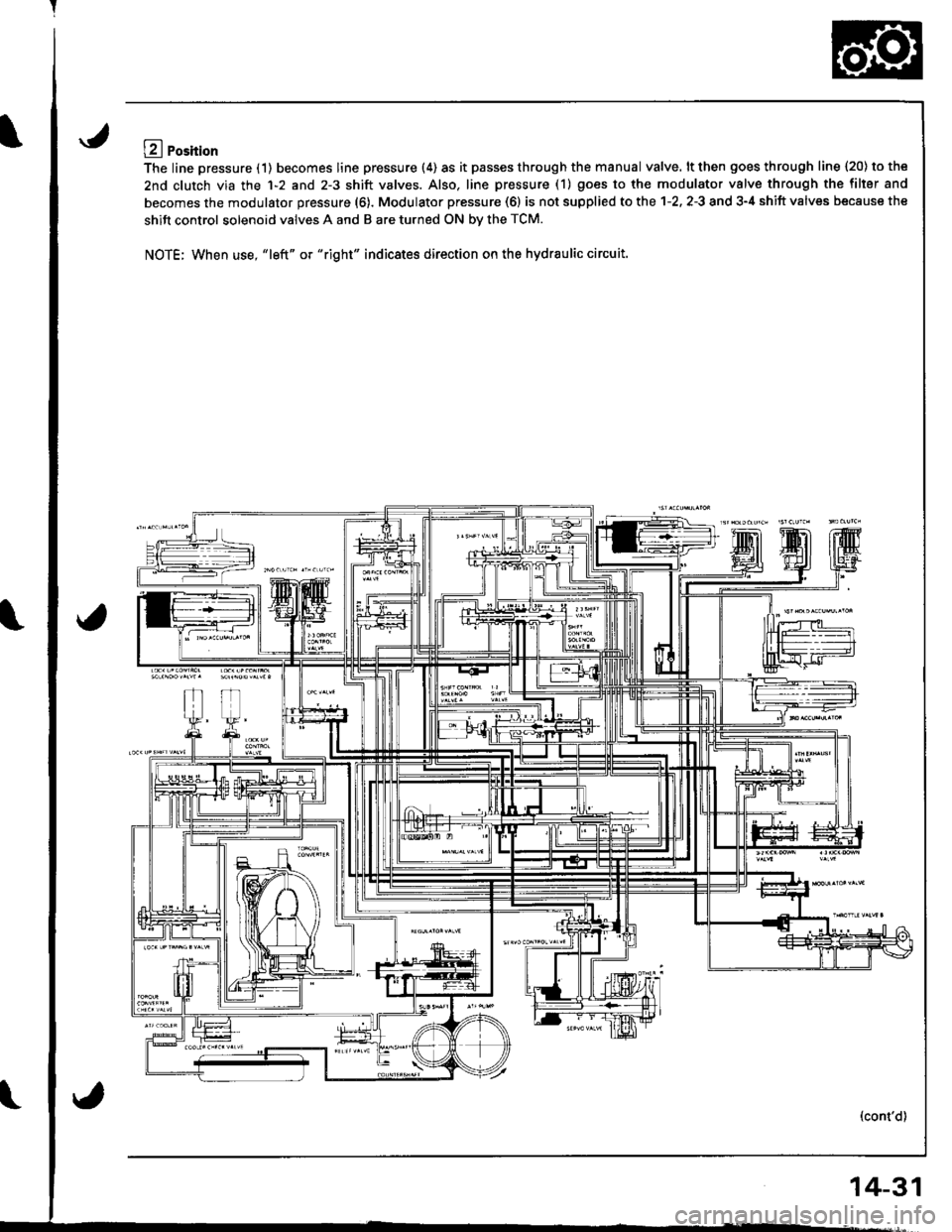
LA Position
The line pressure (1) becomes line pressure (4) as it passes through the manual valve. lt then goes through line 120) to the
2nd clutch via the 1-2 and 2-3 shift valves. Also. line pressure (1) goes to the modulator valve through the filler and
becomes the modulator pressure (6). Modulator pressure (6) is not supplied to the 1-2. 2-3 and 3-4 shift valves because the
shift control solenoid valves A and B are turned ON bv the TCM.
NOTE; When use, "left" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
(cont'd)
14-31
Page 449 of 1681
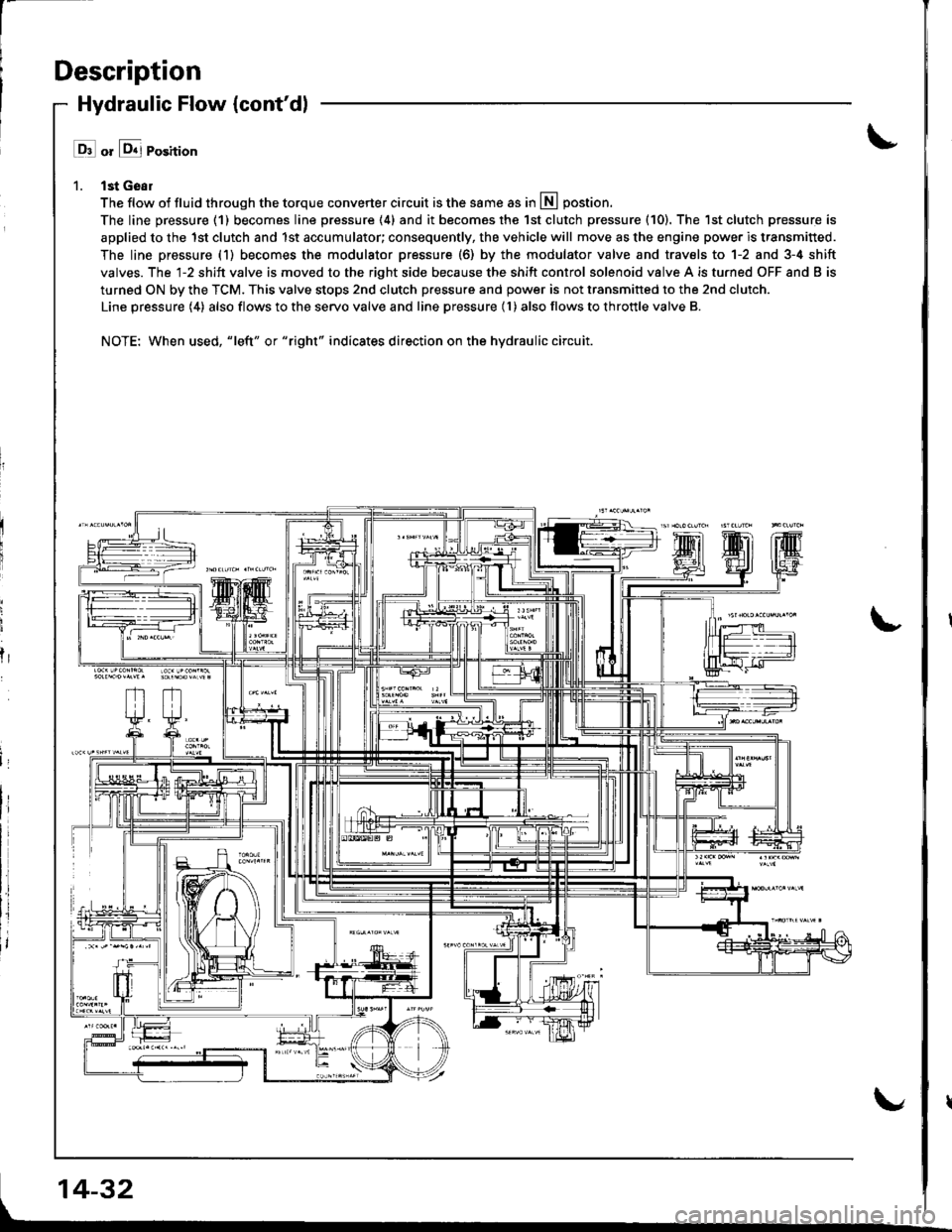
Description
Hydraulic Flow {cont'dl
l ll or &j Position
1. lst Geal
The flow of fluid through the torque converter circuit is the same as in lll postion.
The line pressure (1) becomes line pressure (4) and it becomes the 1st clutch pressure (10). The 1st clutch pressure is
applied to the 1st clutch and 1st accumulator; consequently, the vehicle will move as the engine power is transmitted.
The line pressure (1) becomes the modulator pressure (6) by the modulator valve and travels to 1-2 and 3-4 shift
valves. The l-2 shift valve is moved to the right side because the shift control solenoid valve A is turned OFF and B is
turned ON by the TCM. This valve stops 2nd clutch pressure and power is not transmitted to the 2nd clutch.
Line pressure (4) also flows to the servo valve and line pressure (l ) also flows to throttle valve B.
NOTE: When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
fr
14-32