service INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: INFINITI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: M35, Model: INFINITI M35 2006Pages: 5621, PDF Size: 65.56 MB
Page 3496 of 5621
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-33
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check
for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
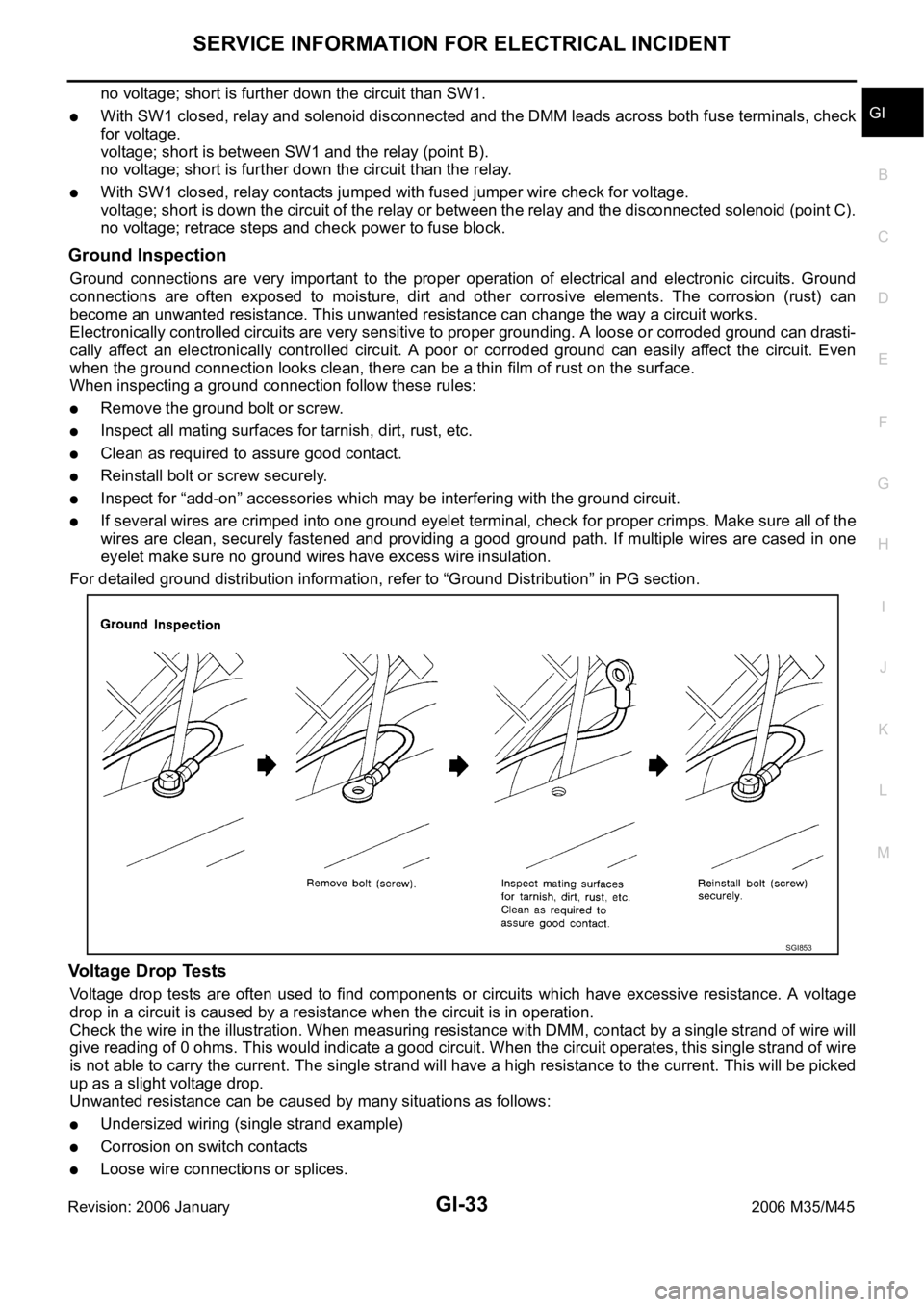
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
Remove the ground bolt or screw.
Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
Clean as required to assure good contact.
Reinstall bolt or screw securely.
Inspect for “add-on” accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
If several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the
wires are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are cased in one
eyelet make sure no ground wires have excess wire insulation.
For detailed ground distribution information, refer to “Ground Distribution” in PG section.
Voltage Drop Tests
Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage
drop in a circuit is caused by a resistance when the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with DMM, contact by a single strand of wire will
give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single strand of wire
is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
Undersized wiring (single strand example)
Corrosion on switch contacts
Loose wire connections or splices.
SGI853
Page 3497 of 5621

GI-34
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger gauge.
MEASURING VOLTAGE DROP — ACCUMULATED METHOD
Connect the DMM across the connector or part of the circuit you want to check. The positive lead of the
DMM should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to ground.
Operate the circuit.
The DMM will indicate how many volts are being used to “push” current through that part of the circuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop between the battery and the bulb.
MEASURING VOLTAGE DROP — STEP-BY-STEP
The step-by-step method is most useful for isolating excessive drops in low voltage systems (such as those in
“Computer Controlled Systems”).
Circuits in the “Computer Controlled System” operate on very low amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely affected by any variation in resistance in the
system. Such resistance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper installation, improper wire
gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire with too much resistance.
SGI974
SAIA0258E
Page 3498 of 5621

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-35
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Control Unit Circuit Test
System Description:When the switch is ON, the control unit lights up the lamp.
INPUT-OUTPUT VOLTAGE CHART
The voltage value is based on the body ground.
*:If high resistance exists in the switch side circuit (caused by a single strand), terminal 1 does not detect battery voltage. Control unit
does not detect the switch is ON even if the switch does not turn ON. Therefore, the control unit does not supply power to light up the
lamp.
INPUT-OUTPUT VOLTAGE CHART
The voltage value is based on the body ground.
*:If high resistance exists in the switch side circuit (caused by a single strand), terminal 2 does not detect approx. 0V. Control unit does
not detect the switch is ON even if the switch does not turn ON. Therefore, the control unit does not control ground to light up the lamp.
MGI034A
Pin
No.Item ConditionVoltage
value [V]In case of high resistance such as single strand [V] *
1 SwitchSwitch ON Battery voltage Lower than battery voltage Approx. 8 (Example)
Switch OFF Approx. 0 Approx. 0
2LampSwitch ON Battery voltage Approx. 0 (Inoperative lamp)
Switch OFF Approx. 0 Approx. 0
MGI035A
Pin
No.Item ConditionVoltage
value [V]In case of high resistance such as single strand [V] *
1 LampSwitch ON Approx. 0 Battery voltage (Inoperative lamp)
Switch OFF Battery voltage Battery voltage
2SwitchSwitch ON Approx. 0 Higher than 0 Approx. 4 (Example)
Switch OFF Approx. 5 Approx. 5
Page 3499 of 5621

GI-36
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Control Units and Electrical PartsNAS0008L
PRECAUTIONS
Never reverse polarity of battery terminals.
Install only parts specified for a vehicle.
Before replacing the control unit, check the input and output and
functions of the component parts.
Do not apply excessive force when disconnecting a connector.
If a connector is installed by tightening bolts, loosen bolt mount-
ing it, then take it out by hand.
Before installing a connector, make sure the terminal is not bent
or damaged, and then correctly connect it.
When installing a connector by tightening bolts, fix it by tighten-
ing the mounting bolt until the painted projection of the connec-
tor becomes even with the surface.
For removal of the lever type connector, pull the lever up to the
direction pointed to by the arrow A in the figure, and then
remove the connector.
For installation of the lever type connector, pull down the lever to
the direction pointed by the arrow B in the figure, and then push
the connector until a clicking noise is heard.
SAIA0251E
SAIA0252E
SAIA0253E
SAIA0254E
Page 3500 of 5621

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-37
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Do not apply excessive shock to the control unit by dropping or
hitting it.
Be careful to prevent condensation in the control unit due to
rapid temperature changes and do not let water or rain get on it.
If water is found in the control unit, dry it fully and then install it in
the vehicle.
Be careful not to let oil to get on the control unit connector.
Avoid cleaning the control unit with volatile oil.
Do not disassemble the control unit, and do not remove the
upper and lower covers.
When using a DMM, be careful not to let test probes get close to
each other to prevent the power transistor in the control unit
from damaging battery voltage because of short circuiting.
When checking input and output signals of the control unit, use
the specified check adapter.
SAIA0255E
SEF348N
Page 3505 of 5621
GI-42
LIFTING POINT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
LIFTING POINTPFP:00000
Special Service Tools NAS0007Y
The actual shapes of Kent-Moore tools may differ from those of special service tools illustrated here.
CAUTION:
Every time the vehicle is lifted up, maintain the complete vehicle curb condition.
Since the vehicle's center of gravity changes when removing main parts on the front side (engine,
transmission, suspension etc.), support a jack up point on the rear side garage jack with a mission
jack or equivalent.
Since the vehicle's center of gravity changes when removing main parts on the rear side (rear axle,
suspension, etc.), support a jack up point on the front side garage jack with a mission jack or
equivalent.
Be careful not to smash or do not do anything that would affect piping parts.
Garage Jack and Safety Stand and 2-Pole LiftNAS0007Z
WAR NING :
Park the vehicle on a level surface when using the jack. Make sure to avoid damaging pipes,
tubes, etc. under the vehicle.
Never get under the vehicle while it is supported only by the jack. Always use safety stands when
you have to get under the vehicle.
Place wheel chocks at both front and back of the wheels on the ground.
When lifting the vehicle, open the lift arms as wide as possible and ensure that the front and rear
of the vehicle are well balanced.
When setting the lift arm, do not allow the arm to contact the brake tubes, brake cable, fuel lines
and sill spoiler.
Tool number
(Kent-Moore No.)
Tool nameDescription
LM4086-0200
( - )
Board on attachment
LM4519-0000
( - )
Safety stand attachment
S-NT001
S-NT002
Page 3509 of 5621

GI-46
TOW TRUCK TOWING
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
To tow a vehicle equipped with an automatic transmission, an appropriate vehicle dolly MUST be placed
under the towed vehicle's drive wheels. Always follow the dolly manufacture's recommendations when using
their product.
If the vehicle is stuck in sand, snow, mud, etc., use the following procedure:
1. Turn off the Vehicle Dynamic Control System.
2. Make sure the area in front and behind the vehicle is clear of obstructions.
3. Turn the steering wheel right and left to clear an area around the front tires.
4. Slowly rock the vehicle forward and backward.
Shift back and forth between R (reverse) and D (drive).
Apply the accelerator as little as possible to maintain the rocking motion.
Release the accelerator pedal before shifting between R and D.
Do not spin the tires above 35 mph (55 km/h).
5. If the vehicle can not be freed after a few tries, contact a professional towing service to remove the vehi-
cle.
Page 3511 of 5621
GI-48
RECOMMENDED CHEMICAL PRODUCTS AND SEALANTS
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
RECOMMENDED CHEMICAL PRODUCTS AND SEALANTSPFP:00000
Recommended Chemical Products and SealantsNAS00084
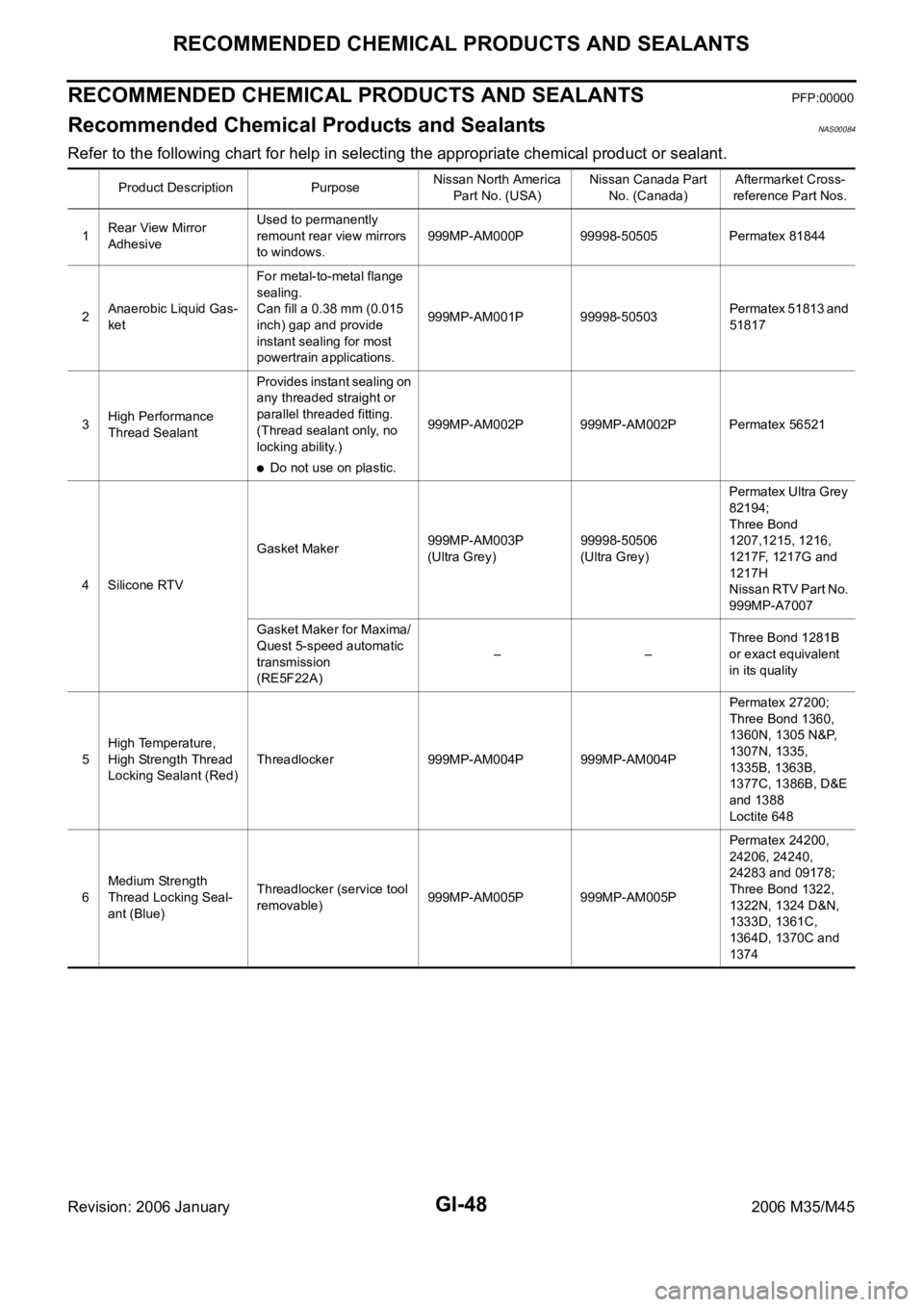
Refer to the following chart for help in selecting the appropriate chemical product or sealant.
Product Description PurposeNissan North America
Part No. (USA)Nissan Canada Part
No. (Canada)Aftermarket Cross-
reference Part Nos.
1Rear View Mirror
AdhesiveUsed to permanently
remount rear view mirrors
to windows.999MP-AM000P 99998-50505 Permatex 81844
2Anaerobic Liquid Gas-
ketFor metal-to-metal flange
sealing.
Can fill a 0.38 mm (0.015
inch) gap and provide
instant sealing for most
powertrain applications.999MP-AM001P 99998-50503Permatex 51813 and
51817
3High Performance
Thread SealantProvides instant sealing on
any threaded straight or
parallel threaded fitting.
(Thread sealant only, no
locking ability.)
Do not use on plastic.999MP-AM002P 999MP-AM002P Permatex 56521
4 Silicone RTVGasket Maker999MP-AM003P
(Ultra Grey)99998-50506
(Ultra Grey)Permatex Ultra Grey
82194;
Three Bond
1207,1215, 1216,
1217F, 1217G and
1217H
Nissan RTV Part No.
999MP-A7007
Gasket Maker for Maxima/
Quest 5-speed automatic
transmission
(RE5F22A)––Three Bond 1281B
or exact equivalent
in its quality
5High Temperature,
High Strength Thread
Locking Sealant (Red)Threadlocker 999MP-AM004P 999MP-AM004PPermatex 27200;
Three Bond 1360,
1360N, 1305 N&P,
1307N, 1335,
1335B, 1363B,
1377C, 1386B, D&E
and 1388
Loctite 648
6Medium Strength
Thread Locking Seal-
ant (Blue)Threadlocker (service tool
removable)999MP-AM005P 999MP-AM005PPermatex 24200,
24206, 24240,
24283 and 09178;
Three Bond 1322,
1322N, 1324 D&N,
1333D, 1361C,
1364D, 1370C and
1374
Page 3518 of 5621

TERMINOLOGY
GI-55
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
Nonvolatile random access memory NVRAM ***
On board diagnostic system OBD system Self-diagnosis
Open loop OL Open loop
Oxidation catalyst OC Catalyst
Oxidation catalytic converter system OC system ***
Oxygen sensor O2S Exhaust gas sensor
Park position switch *** Park switch
Park/neutral position switch PNP switchPark/neutral switch
Inhibitor switch
Neutral position switch
Periodic trap oxidizer system PTOX system ***
Positive crankcase ventilation PCV Positive crankcase ventilation
Positive crankcase ventilation valve PCV valve PCV valve
Powertrain control module PCM ***
Programmable read only memory PROM ***
Pulsed secondary air injection control sole-
noid valvePAIRC solenoid valve AIV control solenoid valve
Pulsed secondary air injection system PAIR system Air induction valve (AIV) control
Pulsed secondary air injection valve PAIR valve Air induction valve
Random access memory RAM ***
Read only memory ROM ***
Scan tool ST ***
Secondary air injection pump AIR pump ***
Secondary air injection system AIR system ***
Sequential multiport fuel injection system SFI system Sequential fuel injection
Service reminder indicator SRI ***
Simultaneous multiport fuel injection sys-
tem*** Simultaneous fuel injection
Smoke puff limiter system SPL system ***
Supercharger SC ***
Supercharger bypass SCB ***
System readiness test SRT ***
Thermal vacuum valve TVV Thermal vacuum valve
Three way catalyst TWC Catalyst
Three way catalytic converter system TWC system ***
Three way + oxidation catalyst TWC + OC Catalyst
Three way + oxidation catalytic converter
systemTWC + OC system ***
Throttle body TBThrottle chamber
SPI body
Throttle body fuel injection system TBI system Fuel injection control
Throttle position TP Throttle position
Throttle position sensor TPS Throttle sensor
Throttle position switch TP switch Throttle switch
Torque converter clutch solenoid valve TCC solenoid valveLock-up cancel solenoid
Lock-up solenoid NEW TERMNEW ACRONYM /
ABBREVIATIONOLD TERM
Page 3520 of 5621

GW-1
GLASSES, WINDOW SYSTEM & MIRRORS
I BODY
CONTENTS
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
SECTION GW
A
B
GW
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
GLASSES, WINDOW SYSTEM & MIRRORS
PRECAUTIONS .......................................................... 3
Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) “AIR BAG” and “SEAT BELT PRE-TEN-
SIONER” .................................................................. 3
Precautions for Procedures without Cowl Top Cover ..... 3
Handling for Adhesive and Primer ........................... 3
PREPARATION ........................................................... 4
Special Service Tools ............................................... 4
Commercial Service Tools ........................................ 4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES ..... 5
Work Flow ................................................................ 5
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW ..................................... 5
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE ....... 6
CHECK RELATED SERVICE BULLETINS ........... 6
LOCATE THE NOISE AND IDENTIFY THE
ROOT CAUSE ...................................................... 6
REPAIR THE CAUSE ........................................... 6
CONFIRM THE REPAIR ....................................... 7
Generic Squeak and Rattle Troubleshooting ........... 7
INSTRUMENT PANEL .......................................... 7
CENTER CONSOLE ............................................. 7
DOORS ................................................................. 7
TRUNK .................................................................. 8
SUNROOF/HEADLINING ..................................... 8
SEATS ................................................................... 8
UNDERHOOD ....................................................... 8
Diagnostic Worksheet .............................................. 9
WINDSHIELD GLASS ...............................................11
Removal and Installation ......................................... 11
REMOVAL ........................................................
.... 11
INSTALLATION ................................................... 12
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM .................................... 13
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location ... 13
System Description ................................................ 13
MANUAL OPERATION ....................................... 14
AUTO OPERATION ............................................ 16
POWER WINDOW SERIAL LINK ....................... 16
POWER WINDOW LOCK ................................... 16
RETAINED POWER OPERATION ...................... 16ANTI-PINCH SYSTEM ........................................ 17
INITIALIZATION .................................................. 17
FAIL-SAFE CONTROL ........................................ 18
POWER WINDOW CONTROL BY THE KEY
CYLINDER SWITCH ........................................... 18
CAN Communication System Description .............. 19
CAN Communication Unit ....................................... 19
Schematic ............................................................... 20
Wiring Diagram — WINDOW — ............................. 21
Terminal and Reference Value for BCM ................. 27
Terminal and Reference Value for Power Window
Main Switch ............................................................ 28
Terminal and Reference Value for (Front and Rear)
Power Window Sub-Switch .................................... 29
CONSULT-II Function (BCM) ................................. 30
WORK SUPPORT ............................................... 31
DATE MONITOR ................................................. 31
Work Flow ............................................................... 32
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart ......................... 32
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check ...... 34
Power Window Main Switch Power Supply Circuit
Check ..................................................................... 35
Power Window Sub-Switch (Front Passenger Side)
Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check ............... 36
Power Window Sub-Switch (Rear LH or RH) Power
Supply and Ground Circuit Check .......................... 37
Power Window Motor (Front Driver Side) Circuit
Check ..................................................................... 38
Power Window Motor (Front Passenger Side) Cir-
cuit Check ............................................................... 39
Power Window Motor (Rear LH or RH) Circuit Check ... 40
Encoder Circuit Check (Driver Side) ....................... 42
Encoder Circuit Check (Passenger Side) ............... 45
Encoder Circuit Check (Rear LH or RH) ................. 48
Door Switch Check ..............................................
... 52
Front Door Key Cylinder Switch Check .................. 54
Power Window Serial Link Check (Passenger Side) ... 56
Power Window Serial Link Check (Rear LH or RH) ... 58
Power Window Lock Switch Check ........................ 58