air condition INFINITI QX56 2007 Factory Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: INFINITI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: QX56, Model: INFINITI QX56 2007Pages: 3061, PDF Size: 64.56 MB
Page 1736 of 3061

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
EI-7
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
EI
N
O
P
Most of these incidents can be repaired by adjusting, securing or insulating the item(s) or component(s) caus-
ing the noise.
SUNROOF/HEADLINING
Noises in the sunroof/headlining area can often be traced to one of the following:
1. Sunroof lid, rail, linkage or seals making a rattle or light knocking noise
2. Sun visor shaft shaking in the holder
3. Front or rear windshield touching headliner and squeaking
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicating the conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consist of insulating with felt cloth tape.
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (FRONT AND REAR)
Overhead console noises are often caused by the console panel clips not being engaged correctly. Most of
these incidents are repaired by pushing up on the console at the clip locations until the clips engage.
In addition look for:
1. Loose harness or harness connectors.
2. Front console map/reading lamp lens loose.
3. Loose screws at console attachment points.
SEATS
When isolating seat noise it's important to note the position the seat is in and the load placed on the seat when
the noise is present. These conditions should be duplicated when verifying and isolating the cause of the
noise.
Cause of seat noise include:
1. Headrest rods and holder
2. A squeak between the seat pad cushion and frame
3. The rear seatback lock and bracket
These noises can be isolated by moving or pressing on the suspected components while duplicating the con-
ditions under which the noise occurs. Most of these incidents can be repaired by repositioning the component
or applying urethane tape to the contact area.
UNDERHOOD
Some interior noise may be caused by components under the hood or on the engine wall. The noise is then
transmitted into the passenger compartment.
Causes of transmitted underhood noise include:
1. Any component installed to the engine wall
2. Components that pass through the engine wall
3. Engine wall mounts and connectors
4. Loose radiator installation pins
5. Hood bumpers out of adjustment
6. Hood striker out of adjustment
These noises can be difficult to isolate since they cannot be reached from the interior of the vehicle. The best
method is to secure, move or insulate one component at a time and test drive the vehicle. Also, engine RPM
or load can be changed to isolate the noise. Repairs can usually be made by moving, adjusting, securing, or
insulating the component causing the noise.
Page 1781 of 3061

NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTINGEM-11
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M A
EM
NP
O
Use the Chart Below to Help You
Find the Cause of the SymptomINFOID:0000000003531519
1. Locate the area where noise occurs.
2. Confirm the type of noise.
3. Specify the operating condition of engine.
4. Check specified noise source.
If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
A: Closely related B: Related C: Sometimes related —: Not relatedB. Tappet noise C. Camshaft bearing noise D. Valve mechanism
E. Rotation mechanism F. Piston pin noise G. Piston slap noise
H. Main bearing noise I. Connecting rod bearing noise J. Drive belt noise (slipping)
K. Drive belt noise (stick/slipping) L. Water pump noise M. Timing chain and chain tensioner noise
Location of noise Ty p e o f
noise Operating condition of engine
Source of noise Check item
Refer-
ence page
Be-
fore
warm- up After
warm-
up When
start-
ing When
idling When
racing While
driv-
ing
Top of en-
gine
Rocker cov-
er
Cylinder
head Ticking or
clicking
C A — A B — Tappet noise Valve clearance
EM-56
Rattle C A — A B CCamshaft
bearing noiseCamshaft journal clear-
ance
Camshaft runout EM-46EM-46
Crankshaft
pulley
Cylinder
block (Side
of engine)
Oil panSlap or
knock
—A—B B— Piston pin
noisePiston and piston pin
clearance
Connecting rod bushing
clearance EM-93
EM-93
Slap or
rap
A——B B A Piston slap
noisePiston-to-bore clear-
ance
Piston ring side clear-
ance
Piston ring end gap
Connecting rod bend
and torsion EM-93EM-93
EM-93
EM-93
Knock A B C B B B
Connecting
rod bearing
noiseConnecting rod bushing
oil clearance (Small
end)
Connecting rod bearing
clearance (Big end)
EM-93EM-93
Knock A B — A B C
Main bearing
noiseMain bearing oil clear-
ance
Crankshaft runout EM-93EM-93
Front of en-
gine
Chain case
cover
Front coverTapping
or ticking
AA—BBB Timing chain
and chain
tensioner
noiseTiming chain cracks
and wear
Timing chain tensioner
operation
EM-38
EM-38
Front of en-
gineSqueak-
ing or
fizzing
AB—B—C
Drive belts
(Sticking or
slipping)Drive belts deflection
EM-13Creaking A B A B A B Drive belts
(Slipping)Idler pulley bearing op-
eration
Squall
Creaking AB—BAB Water pump
noiseWater pump operation
EM-38
Rattle — — A — — — VTC VTC lockpin clearance EM-55
Page 1826 of 3061
EM-56
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
CAMSHAFT
2. Perform the following procedure so as to prevent the engine from being unintentionally started while
checking.
a. Release fuel pressure. Refer to EC-80, "
Fuel Pressure Check".
b. Disconnect ignition coil and injector harness connectors if practical.
3. Remove IVT control solenoid valve.
4. Crank engine, and then make sure that engine oil comes out from IVT control cover oil hole. End cranking
after checking.
WARNING:
Be careful not to touch rotating parts (drive be lts, idler pulley, and crankshaft pulley, etc.).
CAUTION:
• Engine oil may squirt from IVT control soleno id valve installation hole during cranking. Use a
shop cloth to prevent engine oil from splashin g on worker, engine components and vehicle.
• Do not allow engine oil to get on rubber compon ents such as drive belts or engine mount insula-
tors. Immediately wipe off any splashed engine oil.
5. Clean oil groove between oil strainer and IVT control solenoid valve if engine oil does not come out from IVT control valve cover oil hole. Refer to LU-7, "
Schematic".
6. Remove components between IVT control solenoid va lve and camshaft sprocket (INT), and then check
each oil groove for clogging.
• Clean oil groove if necessary.
7. After inspection, installation of the remaining components is in the reverse order of removal.
Valve ClearanceINFOID:0000000003531536
INSPECTION
NOTE:
Perform the following inspection after removal, installation or replacement of camshaft or valve-related parts,
or if there are unusual engine conditions due to changes in valve clearance over time (starting, idling, and/or
noise).
1. Warm up the engine. Then stop the engine.
2. Remove the engine cover and. Refer to EM-12, "
Removal and Installation".
3. Remove the battery cover. Refer to SC-8, "
Removal and Installation".
4. Remove the air cleaner and air duct assembly EM-15, "
Removal and Installation".
5. Remove the RH bank and LH bank rocker covers using power tool. Refer to EM-35, "
Removal and Instal-
lation".
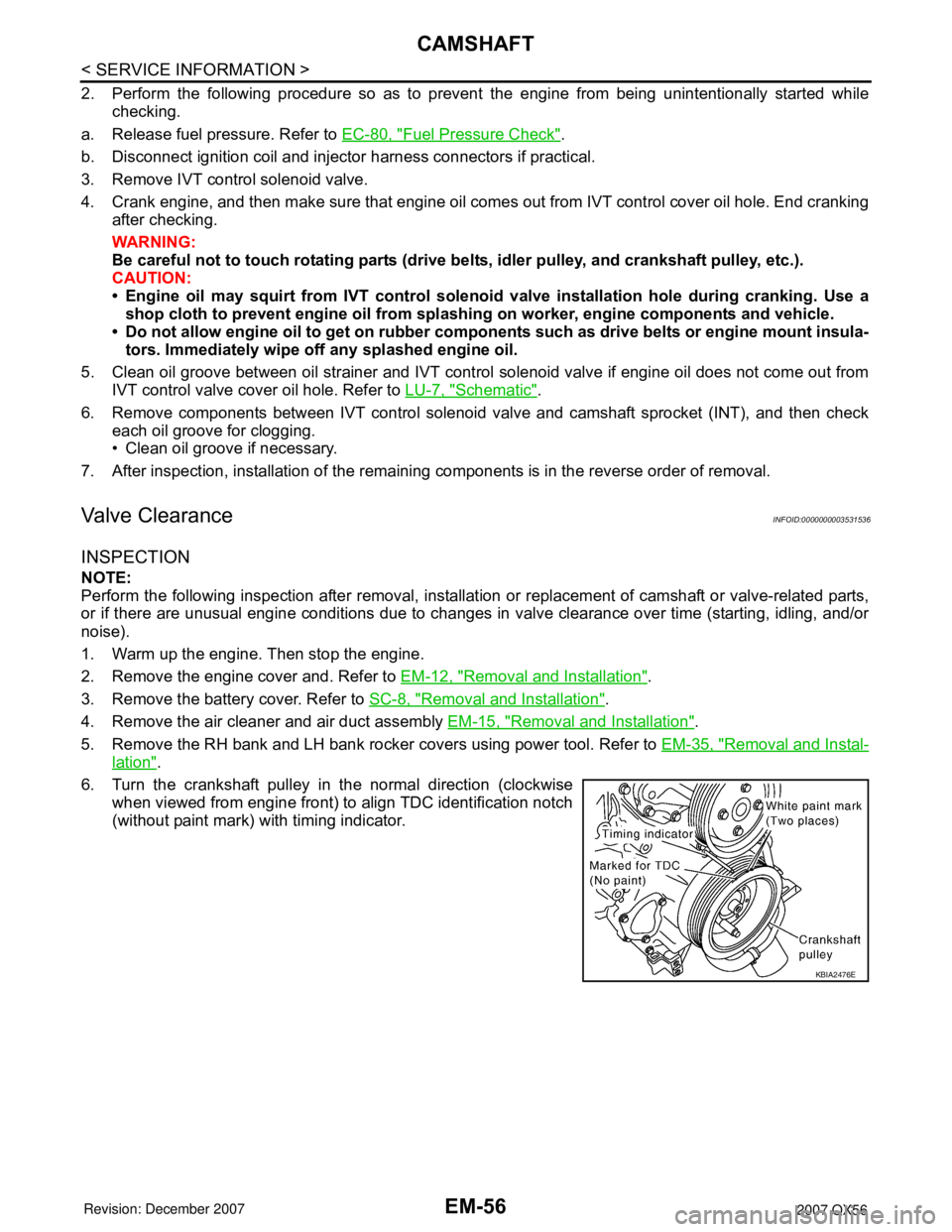
6. Turn the crankshaft pulley in the normal direction (clockwise when viewed from engine front) to align TDC identification notch
(without paint mark) with timing indicator.
KBIA2476E
Page 1857 of 3061

CYLINDER BLOCK
EM-87
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EM
N
P O
*For the service parts, the grade for fitting cannot be selected between a piston pin and a connecting rod.
(Only 0 grade is available.) The information at the shipment from the plant is described as a reference.
• The identification grade stamped on each part is the grade for the dimension measured in new condition.
This grade cannot apply to reused parts.
• For reused or repaired parts, measure the dimension accurately. Determine the grade by comparing the
measurement with the values of each selection table.
• For details of the measurement method of each part, the reuse standards, and the selection method of the
selective fitting parts, refer to the text.
HOW TO SELECT PISTON
Piston Selective Fitting When New Cylinder Block is Used:
• Check the cylinder bore grade on the bottom face of the cylinder
block, and select the piston of the same grade.
When Cylinder Block is Reused
1. Measure cylinder block bore diameter.
2. Determine the bore grade by comparing the measurement with the values under the “Cylinder bore diam-
eter” of the piston selection table.
Piston Selection Table
Connecting points Connecting parts Selection items Selection methods
Between cylinder block to
crankshaftMain bearingMain bearing grade (bearing
thickness)Determined by match of cylin-
der block bearing housing
grade (Housing inside diame-
ter) and crankshaft journal
grade (journal outside diameter)
Between crankshaft to connect-
ing rodConnecting rod bearingConnecting rod bearing grade
(bearing thickness)Connecting rod bearing grade =
crankshaft pin grade (pin diam-
eter). No grade exists for inside
diameter of connecting rod
large end.
Between cylinder block to pis-
tonPiston and piston pin assembly.
The piston is available together
with piston pin as an assembly.Piston grade (piston diameter)Piston grade = cylinder bore
grade (diameter of bore)
*Between piston to connecting
rod———
KBIA2495E
KBIA2496E
Page 1952 of 3061
FSU-6
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
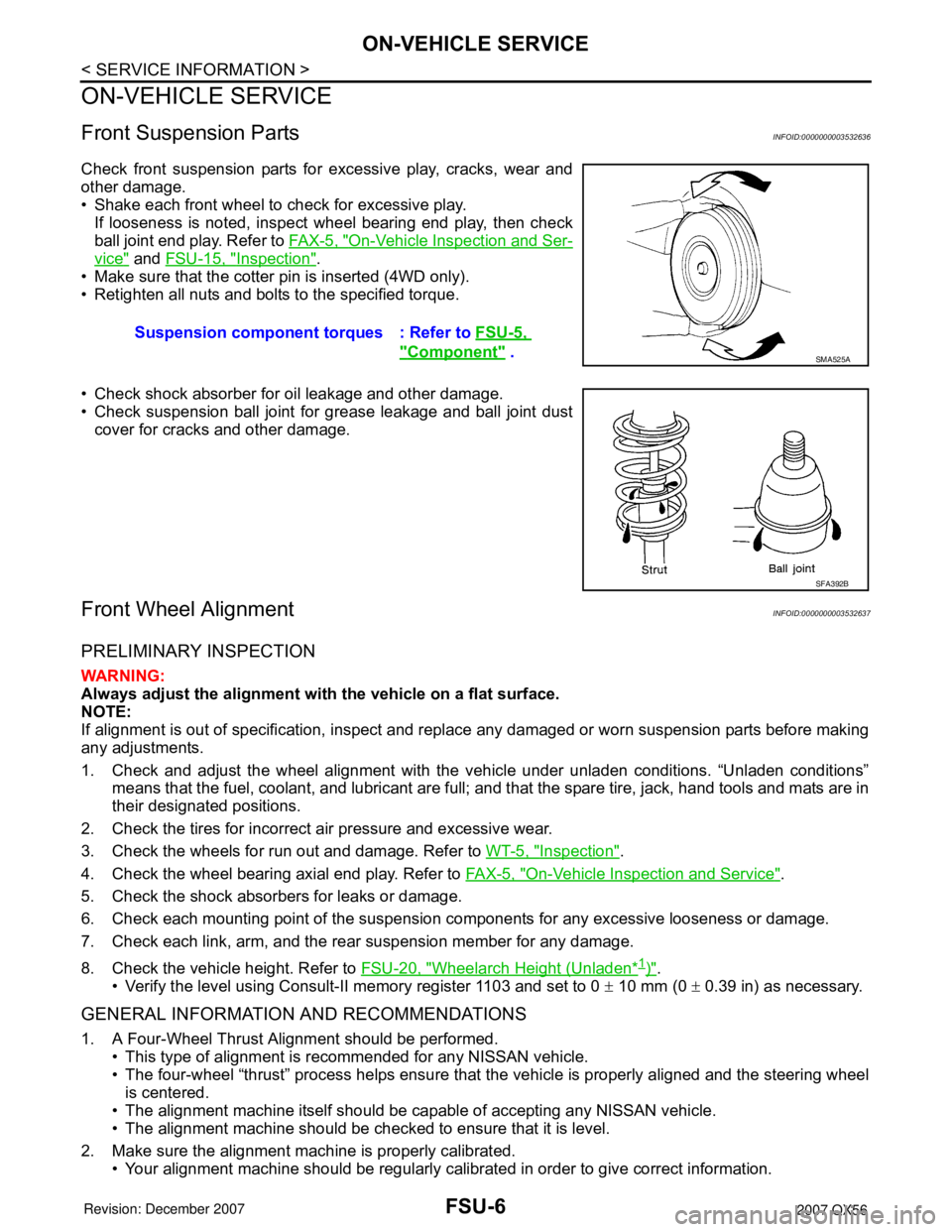
Front Suspension PartsINFOID:0000000003532636
Check front suspension parts for excessive play, cracks, wear and
other damage.
• Shake each front wheel to check for excessive play.
If looseness is noted, inspect wheel bearing end play, then check
ball joint end play. Refer to FA X - 5 , "
On-Vehicle Inspection and Ser-
vice" and FSU-15, "Inspection".
• Make sure that the cotter pin is inserted (4WD only).
• Retighten all nuts and bolts to the specified torque.
• Check shock absorber for oil leakage and other damage.
• Check suspension ball joint for grease leakage and ball joint dust
cover for cracks and other damage.
Front Wheel AlignmentINFOID:0000000003532637
PRELIMINARY INSPECTION
WARNING:
Always adjust the alignment with the vehicle on a flat surface.
NOTE:
If alignment is out of specification, inspect and replace any damaged or worn suspension parts before making
any adjustments.
1. Check and adjust the wheel alignment with the vehicle under unladen conditions. “Unladen conditions”
means that the fuel, coolant, and lubricant are full; and that the spare tire, jack, hand tools and mats are in
their designated positions.
2. Check the tires for incorrect air pressure and excessive wear.
3. Check the wheels for run out and damage. Refer to WT-5, "
Inspection".
4. Check the wheel bearing axial end play. Refer to FA X - 5 , "
On-Vehicle Inspection and Service".
5. Check the shock absorbers for leaks or damage.
6. Check each mounting point of the suspension components for any excessive looseness or damage.
7. Check each link, arm, and the rear suspension member for any damage.
8. Check the vehicle height. Refer to FSU-20, "
Wheelarch Height (Unladen*1)".
• Verify the level using Consult-II memory register 1103 and set to 0 ± 10 mm (0 ± 0.39 in) as necessary.
GENERAL INFORMATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
1. A Four-Wheel Thrust Alignment should be performed.
• This type of alignment is recommended for any NISSAN vehicle.
• The four-wheel “thrust” process helps ensure that the vehicle is properly aligned and the steering wheel
is centered.
• The alignment machine itself should be capable of accepting any NISSAN vehicle.
• The alignment machine should be checked to ensure that it is level.
2. Make sure the alignment machine is properly calibrated.
• Your alignment machine should be regularly calibrated in order to give correct information.Suspension component torques : Refer to FSU-5,
"Component" . SMA525A
SFA392B
Page 1967 of 3061

GI-1
GENERAL INFORMATION
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
SECTION GI
N
O
P
CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION
SERVICE INFORMATION ............................2
PRECAUTIONS ...................................................2
Description ................................................................2
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT PRE-TEN-
SIONER" ...................................................................
2
Precaution for NVIS/IVIS (NISSAN/INFINITI VE-
HICLE IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM - NATS) (If
Equipped) ..................................................................
2
General Precaution ...................................................3
Precaution for Three Way Catalyst ...........................4
Precaution for Fuel (Unleaded Premium Gasoline
Required) ..................................................................
4
Precaution for Multiport Fuel Injection System or
Engine Control System .............................................
5
Precaution for Hoses .................................................5
Precaution for Engine Oils ........................................6
Precaution for Air Conditioning .................................6
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL ............................7
Description ................................................................7
Terms ........................................................................7
Units ..........................................................................7
Relation between Illustrations and Descriptions .......7
Contents ....................................................................8
Component ................................................................8
How to Follow Trouble Diagnosis ..............................9
How to Read Wiring Diagram ..................................13
Abbreviations ..........................................................20
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL
INCIDENT ...........................................................
22
How to Check Terminal ...........................................22
How to Perform Efficient Diagnosis for an Electri-
cal Incident ..............................................................
25
Control Units and Electrical Parts ............................32
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM ..................35
Description ...............................................................35
Function and System Application ............................35
Nickel Metal Hydride Battery Replacement .............36
Checking Equipment ...............................................36
CONSULT-II Start Procedure ..................................36
CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit .....38
LIFTING POINT .................................................40
Pantograph Jack ......................................................40
Garage Jack and Safety Stand ................................40
2-Pole Lift ................................................................40
TOW TRUCK TOWING .....................................42
Tow Truck Towing ...................................................42
Vehicle Recovery (Freeing a stuck vehicle) ............43
TIGHTENING TORQUE OF STANDARD
BOLTS ...............................................................
44
Tightening Torque Table .........................................44
RECOMMENDED CHEMICAL PRODUCTS
AND SEALANTS ...............................................
45
Recommended Chemical Product and Sealant .......45
IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION ....................46
Model Variation ........................................................46
Identification Number ...............................................47
Dimensions ..............................................................48
Wheels & Tires ........................................................48
TERMINOLOGY ................................................50
SAE J1930 Terminology List ...................................50
Page 1972 of 3061
GI-6
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
PRECAUTIONS
• After installing leaf spring clamps, apply force to them in the direc-
tion of the arrow, tightening rubber hose equally all around.
Precaution for Engine OilsINFOID:0000000003531476
Prolonged and repeated contact with used engine oil may cause skin cancer. Try to avoid direct skin contact
with used oil.
If skin contact is made, wash thoroughly with soap or hand cleaner as soon as possible.
HEALTH PROTECTION PRECAUTIONS
• Avoid prolonged and repeated contact with oils, particularly used engine oils.
• Wear protective clothing, including impervious gloves where practicable.
• Do not put oily rags in pockets.
• Avoid contaminating clothes, particularly underpants, with oil.
• Heavily soiled clothing and oil-impregnated footwear should not be worn. Overalls must be cleaned regu-
larly.
• First aid treatment should be obtained immediately for open cuts and wounds.
• Use barrier creams, applying them before each work period, to help the removal of oil from the skin.
• Wash with soap and water to ensure all oil is removed (skin cleansers and nail brushes will help). Prepara-
tions containing lanolin replace the natural skin oils which have been removed.
• Do not use gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, gas oil, thinners or solvents for cleaning skin.
• If skin disorders develop, obtain medical advice without delay.
• Where practical, degrease components prior to handling.
• Where there is a risk of eye contact, eye protection should be worn, for example, chemical goggles or face
shields; in addition an eye wash facility should be provided.
Precaution for Air ConditioningINFOID:0000000003531477
Use an approved refrigerant recovery unit any time the air conditioning system must be discharged. Refer to
ATC-150, "
HFC-134a (R-134a) Service Procedure" for specific instructions.
SMA022D
Page 1986 of 3061
GI-20
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
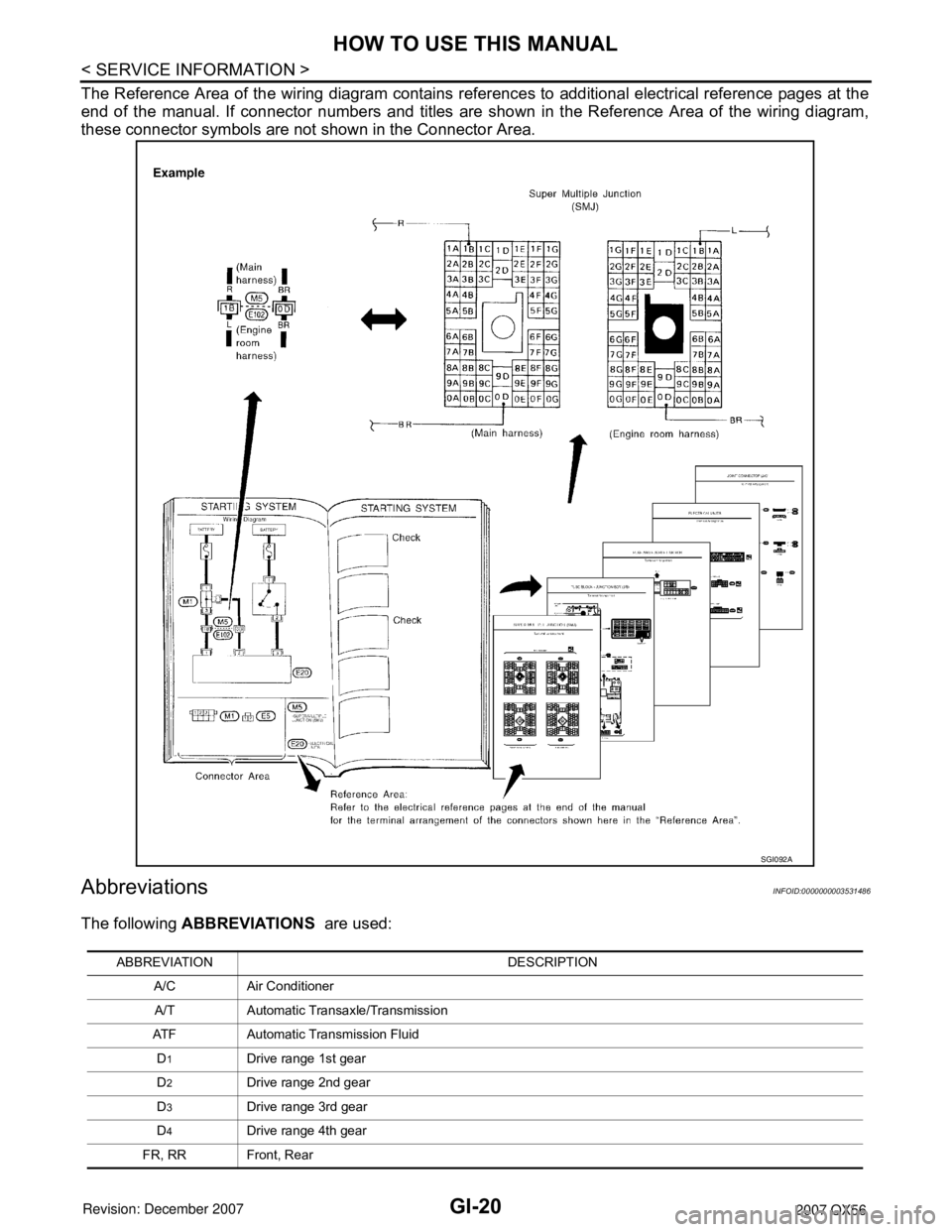
The Reference Area of the wiring diagram contains references to additional electrical reference pages at the
end of the manual. If connector numbers and titles are shown in the Reference Area of the wiring diagram,
these connector symbols are not shown in the Connector Area.
AbbreviationsINFOID:0000000003531486
The following ABBREVIATIONS are used:
SGI092A
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
A/C Air Conditioner
A/T Automatic Transaxle/Transmission
ATF Automatic Transmission Fluid
D
1Drive range 1st gear
D
2Drive range 2nd gear
D
3Drive range 3rd gear
D
4Drive range 4th gear
FR, RR Front, Rear
Page 1991 of 3061

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-25
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
How to Perform Efficient Diagnosis for an Electrical IncidentINFOID:0000000003531488
WORK FLOW
INCIDENT SIMULATION TESTS
Introduction
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The fol-
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
• Vehicle vibration
• Heat sensitive
• Freezing
• Water intrusion
• Electrical load
SGI838
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHATVehicle Model, Engine, Transmission/Transaxle and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHENDate, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERERoad Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOWSystem Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem cannot be duplicated, refer to “Incident Simulation Tests”.
STEP 3Get the proper diagnosis materials together including:
• Power Supply Routing
• System Operation Descriptions
• Applicable Service Manual Sections
• Check for any Service Bulletins
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the customer comments.
STEP 4Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing and Harness Lay-
outs.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you have not inad-
vertently created a new incident during your diagnosis or repair steps.
Page 1993 of 3061
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-27
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
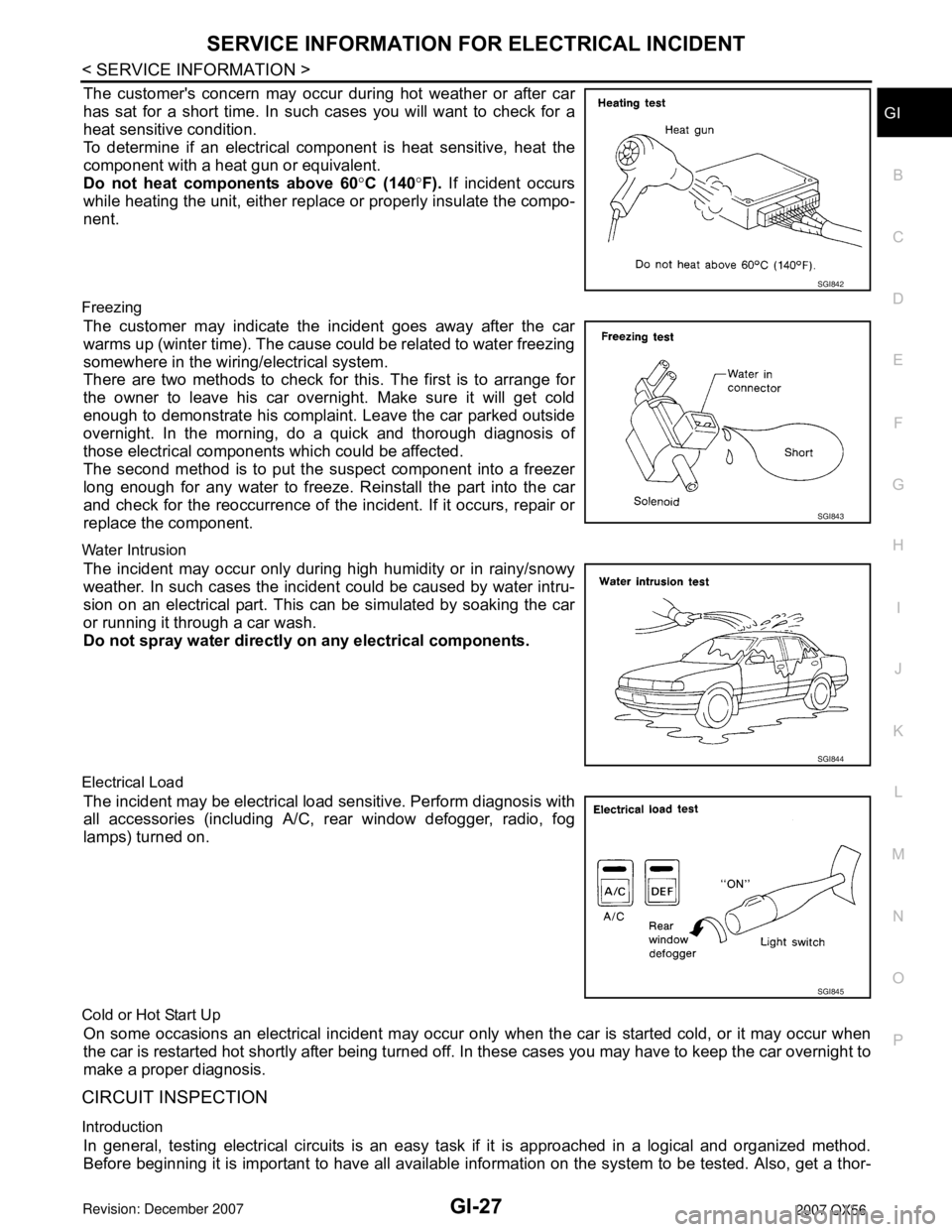
The customer's concern may occur during hot weather or after car
has sat for a short time. In such cases you will want to check for a
heat sensitive condition.
To determine if an electrical component is heat sensitive, heat the
component with a heat gun or equivalent.
Do not heat components above 60°C (140°F). If incident occurs
while heating the unit, either replace or properly insulate the compo-
nent.
Freezing
The customer may indicate the incident goes away after the car
warms up (winter time). The cause could be related to water freezing
somewhere in the wiring/electrical system.
There are two methods to check for this. The first is to arrange for
the owner to leave his car overnight. Make sure it will get cold
enough to demonstrate his complaint. Leave the car parked outside
overnight. In the morning, do a quick and thorough diagnosis of
those electrical components which could be affected.
The second method is to put the suspect component into a freezer
long enough for any water to freeze. Reinstall the part into the car
and check for the reoccurrence of the incident. If it occurs, repair or
replace the component.
Water Intrusion
The incident may occur only during high humidity or in rainy/snowy
weather. In such cases the incident could be caused by water intru-
sion on an electrical part. This can be simulated by soaking the car
or running it through a car wash.
Do not spray water directly on any electrical components.
Electrical Load
The incident may be electrical load sensitive. Perform diagnosis with
all accessories (including A/C, rear window defogger, radio, fog
lamps) turned on.
Cold or Hot Start Up
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the car is started cold, or it may occur when
the car is restarted hot shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep the car overnight to
make a proper diagnosis.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
Introduction
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is approached in a logical and organized method.
Before beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thor-
SGI842
SGI843
SGI844
SGI845