warning ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3205 of 6020

Fuel System – V6 Page 6C – 3
1 General Information
Description
Fuel is injected into the engine by separate fuel injectors that are mounted in the intake manifold (common chamber).
Fuel is supplied to the injectors under pressure from the fuel tank through the fuel lines and the fuel rail, which is
attached to the top of the common chamber.
A fuel pressure control valve is installed on the fuel rail to maintain fuel line pressure across the injectors under all
operating conditions. Fuel pressure is maintained by controlling the amount of fuel that is supplied from the fuel tank,
based on the demand of the engine via the engine control module (ECM).
Two interchangeable “O” rings are used on the fuel injector and must be replaced when the injectors are removed.
The Multiport Fuel Injection system utilizes an injection system where the injectors turn on at every crankshaft revolution.
The ECM controls the injector on time so that the correct amount of fuel is metered depending on driving conditions.
The V6 engine is designed to use only unleaded petrol.
Unleaded petrol must be used for correct emission control system operation and its use will also minimize spark plug
fouling and extend engine oil life.
Using leaded petrol can damage the emission control system and could void the vehicle warranty. All vehicles are
equipped with an Evaporative Emission Control System. The purpose of the system is to minimize the escape of fuel
vapours into the atmosphere.
Service Precautions
• Use extreme care when working on the fuel system and follow all safety precautions.
• W hen working on the fuel system, disconnect the battery ground cable except for tests where battery voltage is
required.
• Always keep a dry chemical (class B) fire extinguisher near the work area.
• Relace all fuel lines and fittings with the same type of line and fitting as those removed.
• Clean and inspect “O” rings carefully and replace if required.
• Always depressurize the fuel lines before servicing any fuel system components.
• Do not attempt any repairs on the fuel system until, all warnings and instructions, relating to that repair have been
read and ensure all notices and cautions are adhered to.
• Do not allow any naked frames or sparks near the work area when working on the fuel system.
• If draining of the fuel system is required, this should be done in a well ventilated area.
• Protect the fuel lines and associated parts from thermal damage, spattering when welding.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3206 of 6020

Fuel System – V6 Page 6C – 4
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
GM HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these
instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. GM HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to
diagnose and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard
to the technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
• Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with
greater ease.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3232 of 6020

Fuel System – V6 Page 6C – 30
4.7 Fuel Tank Siphon Procedure
• Fuel vapour remains in the modular fuel
pump and sender assembly and fuel lines
that can be spilled during service
operations. Ensure no naked flames or
other ignition sources are nearby. Ensure
all cellular phones (and transmission
devices that may cause any metal objects
to become unintentional receiving
antennas) are switched off.
• Place a dry chemical (Class B) fire
extinguisher nearby before performing any
on-vehicle service procedures. Failure to
follow these precautions may result in
personal injury.
For an exploded view of fuel tank components, refer Figure 6C – 17.
1 Depressurise the fuel system, refer to 3.4 Fuel System Depressurisation.
2 Reinstall the fuel pump relay, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
Disconnecting the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems. 1.1 WARNING,
CAUTION and NOTES.
3 Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
4 Remove the fuel filler cap.
NOTE
Lubricate the fuel siphon hose with J36850
TransJel Transmission Assembly Lubricant or
equivalent to aid hose insertion. Use only an
approved lubricant.
5 Install J44284–2 flapper door holder (2) into the fuel filler neck to hold the door open.
Do not siphon, drain or store fuel into an
open container, due to the possibility of fire
or explosion, or contamination. Always use
and approved fuel storage container.
6 Insert the J45004–1 fuel tank siphon hose (1) into the fuel tank filler neck and gradually twist it until the tip of
the hose meets the fuel tank check valve (3) and
continues to the bottom of the fuel tank.
7 Use a hand-operated or air-operated pump device to siphon as much fuel through the fuel fill pipe as
possible.
Figure 6C – 35
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3243 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–1
6C1-1 Engine Management – V6
General Information
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to 1.3 Warning
Caution and Notes for correct workshop practices with regard to safety and / or property damage.
1 General Information ............................................................................................................ ...................3
1.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................................................ 3
1.2 Emission Control ................................................................................................................................................... 3
ADR 79/01 Emissions Standards .......................................................................................................................... 3
1.3 Warning Caution and Notes .................................................................................................................................. 4
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements ............................................................................. .... 4
WARNING defined ............................................................................................................................................. 4
CAUTION defined .............................................................................................................................................. 4
NOTE defined..................................................................................................................................................... 4
2 Component Locations ............................................................................................................ ...............5
2.1 Cylinder Numbering............................................................................................................................................... 5
2.2 Engine Compartment............................................................................................................................................. 5
2.3 Engine ..................................................................................................................................................................... 6
2.4 Interior..................................................................................................................................................................... 8
3 System Operation ...................................................................................................................................9
3.1 Fuel Delivery System ............................................................................................................................................. 9
Fuel System Pressure ........................................................................................................... ................................ 9
Fuel Injection System .......................................................................................................................................... 10
Short Term Fuel Trim ....................................................................................................................................... 10
Long Term Fuel Trim ........................................................................................................................................ 10
3.2 Air / Fuel Control System ...................................................................................................... .............................. 11
Starting Mode ....................................................................................................................................................... 11
Run Mode.............................................................................................................................................................. 11
Open Loop Mode................................................................................................................. ............................. 11
Closed Loop Mode ............................................................................................................... ............................ 11
Acceleration Mode .............................................................................................................. ................................. 11
Deceleration Mode ............................................................................................................................................... 11
Fuel Shut-off Mode .............................................................................................................................................. 11
Battery Voltage Correction Mode ................................................................................................ ....................... 12
Limp Mode ............................................................................................................................................................ 12
Engine Protection Mode ......................................................................................................... ............................. 12
Clear Flood Mode ................................................................................................................................................. 12
3.3 Ignition Control System........................................................................................................ ............................... 12
3.4 Starter Motor Operation....................................................................................................................................... 12
3.5 Throttle Actuator Control System ............................................................................................... ....................... 12
Description ........................................................................................................................................................... 12
Throttle Body Relearn Procedure ....................................................................................................................... 14
TAC System Default Actions / Reduce Power Modes................................................................................ ....... 14
Forced Engine Shutdown .................................................................................................................................... 14
3.6 Cruise Control System ........................................................................................................................................ 14
3.7 Brake Torque Management ........................................................................................................ ......................... 15
3.8 Emission Control Systems.................................................................................................................................. 15
Evaporative Emission Control System ............................................................................................ .................. 15
Engine Ventilation System .................................................................................................................................. 16
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3246 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–4
ADR 37/01 (Petrol) 2.1 0.26 2 0.63 Not Applicable
ADR 79/01 (Petrol,
LPG, CNG) 2.3 0.2 2 0.15 0.05
1.3 Warning Caution and Notes
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
GM Holden LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these
instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. GM Holden LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
• Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with
greater ease.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3257 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–15
W hen the cruise control ON-OFF switch, located on the right hand side of the dash panel, is pressed, the PIM, on
receiving the input from the switch, turns on the cruise ON-OFF switch warning lamp to inform the user that the cruise
control has been engaged.
W hen the cruise control switch assembly is pressed to SET/COAST, the PIM on receiving the input, sends a signal via
the serial data bus to the ECM. Providing the pre-conditions for cruise control operation have been met, the ECM
activates cruise control and commands the PIM to turn on the instrument cluster cruise set warning lamp, to inform the
user that cruise control is active. The ECM receives all the various inputs required to maintain the correct speed and then
controls the throttle plate depending on the load on the engine (ascending or descending hills, etc).
The cruise control is deactivated by either pressing the brake pedal, clutch pedal, cruise CANCEL or by the cruise control
ON-OFF button. In each of these instances, the ECM receives an input when any of these switches are activated. For
further information on the cruise control system, refer to 8C Cruise Control – HFV6.
3.7 Brake Torque Management
Brake torque management places limits on engine torque when the brakes are applied, regardless of the accelerator
pedal position (APP). The conditions under which brake torque management occur are as follows:
• The accelerator has been depressed before the brakes are applied,
• The brakes are applied and the ECM receives an input from the stop lamp switch,
• Vehicle speed is greater than 5 km/h,
• Engine speed is greater than 1200 rpm and
• Conditions exist for greater than 2.5 seconds.
W hen brake torque management has been implemented, the torque is reduced by altering the throttle plate opening by
25%. The ECM will monitor the rate at which the vehicle is slowing and adjust the throttle plate opening accordingly.
3.8 Emission Control Systems
Evaporative Emission Control System
The evaporative emission control system used is the
activated carbon (charcoal) canister storage method. Fuel
vapour is drawn from the fuel tank into the canister where it
is held by the activated carbon until the ECM commands the
evaporative emission (EVAP) purge solenoid valve to open.
The ECM energises the EVAP purge solenoid valve by
applying a pulse width modulated (PW M) ground to the
EVAP purge solenoid valve control circuit.
Figure 6C1-1 – 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3267 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–25
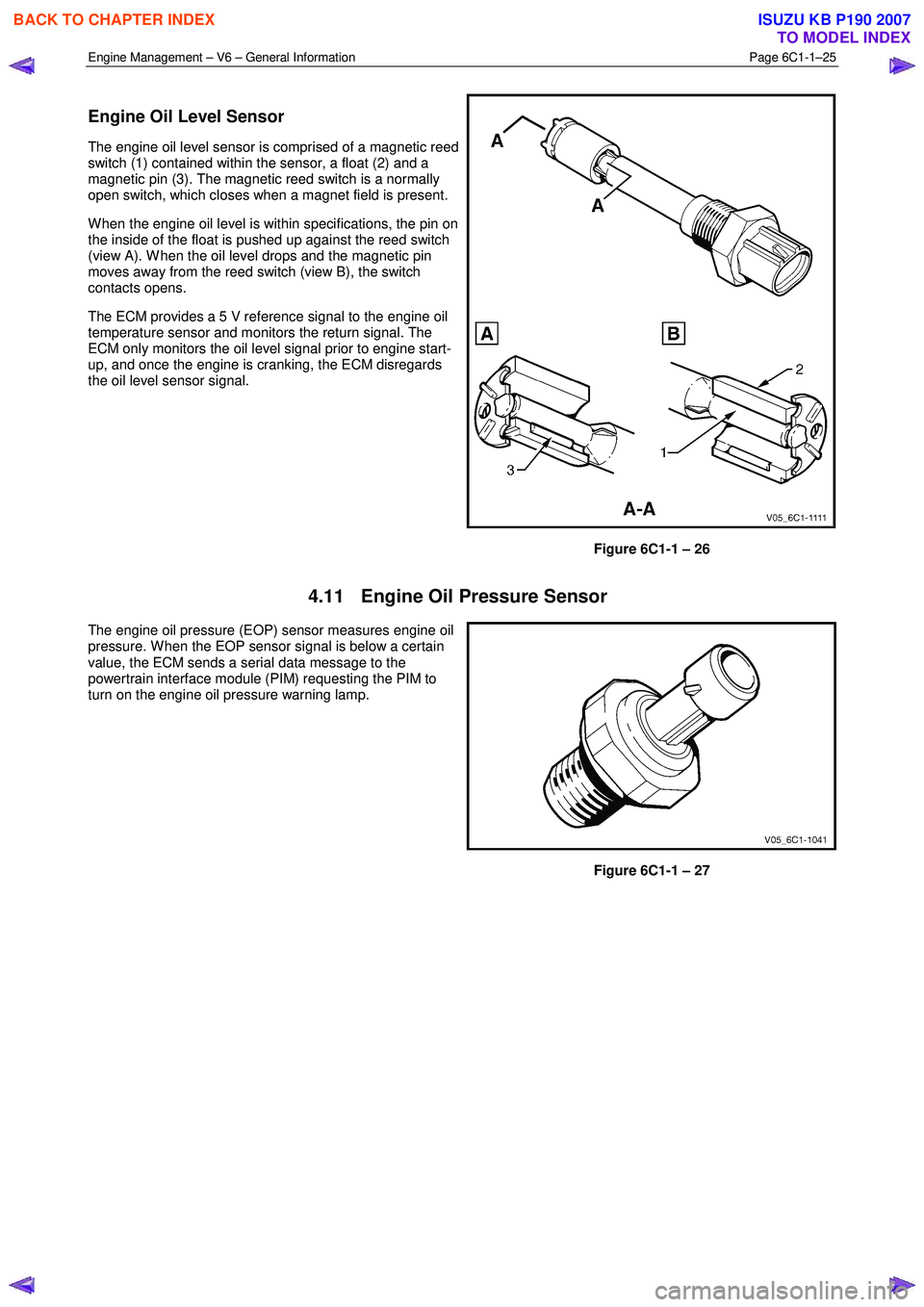
Engine Oil Level Sensor
The engine oil level sensor is comprised of a magnetic reed
switch (1) contained within the sensor, a float (2) and a
magnetic pin (3). The magnetic reed switch is a normally
open switch, which closes when a magnet field is present.
W hen the engine oil level is within specifications, the pin on
the inside of the float is pushed up against the reed switch
(view A). W hen the oil level drops and the magnetic pin
moves away from the reed switch (view B), the switch
contacts opens.
The ECM provides a 5 V reference signal to the engine oil
temperature sensor and monitors the return signal. The
ECM only monitors the oil level signal prior to engine start-
up, and once the engine is cranking, the ECM disregards
the oil level sensor signal.
Figure 6C1-1 – 26
4.11 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
The engine oil pressure (EOP) sensor measures engine oil
pressure. W hen the EOP sensor signal is below a certain
value, the ECM sends a serial data message to the
powertrain interface module (PIM) requesting the PIM to
turn on the engine oil pressure warning lamp.
Figure 6C1-1 – 27
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3279 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–1
6C1-2 Engine Management – V6
Diagnostics
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to 1.5 Warning
Caution and Notes for correct workshop practices with regard to safety and/or property damage.
1 General Information ............................................................................................................ ...................4
1.1 Diagnostic System Check ..................................................................................................................................... 4
1.2 Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables ................................................................................................. ......................... 4
1.3 Symptoms Diagnostics ......................................................................................................................................... 5
1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes .................................................................................................................................... 5
1.5 Warning Caution and Notes .................................................................................................................................. 6
2 GM LAN Serial Communication Circuit ............................................................................................ ....8
3 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts ........................................................................................... ...9
3.1 Wiring Diagrams .................................................................................................................................................... 9
3.2 ECM Connector End Views ................................................................................................................................. 12
3.2 Engine Control Connector End Views ............................................................................................. .................. 16
4 Diagnostics Starting Point...................................................................................................................18
4.1 Basic Requirements ............................................................................................................................................ 18
4.2 Diagnostic Precautions ......................................................................................................... .............................. 18
4.3 Preliminary Checks.............................................................................................................................................. 19
4.4 Diagnostic System Check ........................................................................................................ ........................... 20
5 Symptoms Diagnostics ........................................................................................................................22
5.1 Symptoms Diagnosis Table ....................................................................................................... ......................... 22
5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions .............................................................................................................................. 22
5.3 Backfire................................................................................................................................................................. 24
5.4 Cranks But Does Not Run ........................................................................................................ ........................... 26
5.5 Cuts Out, Misses.................................................................................................................................................. 27
5.6 Detonation / Spark Knock ....................................................................................................... ............................ 28
5.7 Dieseling, Run-on ................................................................................................................................................ 28
5.8 Hard Start ............................................................................................................................................................. 29
5.9 Hesitation, Sag and Stumble .................................................................................................... .......................... 30
5.10 Lack of Power, Sluggishness or Sponginess ...................................................................................... ............. 31
5.11 Poor Fuel Economy ............................................................................................................................................. 32
5.12 Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or Stalling .................................................................................... ................... 34
5.13 Surges / Chuggles ............................................................................................................................................... 35
6 Functional Checks................................................................................................................................37
6.1 General Information ............................................................................................................ ................................. 37
6.2 Fuel Injector Coil Test ......................................................................................................................................... 37
6.3 Fuel Injector Balance Test ..................................................................................................... ............................. 42
6.4 Fuel Injector Leak Down Test ................................................................................................... .......................... 44
6.5 Alcohol / Contaminants in Fuel Diagnosis ....................................................................................... ................. 46
6.6 Crankshaft Position (CKP) System Variation Learn Procedure..................................................................... .. 46
6.7 Throttle Body Relearn.......................................................................................................................................... 47
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3284 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–6
• Use Tech 2 to clear DTC/s.
Type C – Non-Emission Related DTCs
The ECM takes the following action when a Type A DTC runs and fails:
• sets a current Type C DTC that represents the fault condition, and
• records the operating conditions at the time the DTC is logged and stores this information in the Failure Record,
and:
NOTE
The instrument cluster malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) is not activated when a Type C DTC sets.
Conditions for Clearing Type C DTCs
• The current DTC clears when there is no fault condition in the current ECM self-diagnostics.
• Type C History DTC clears when there is no fault condition after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles.
• Use Tech 2 to clear DTCs.
Current DTCs
A DTC is a Current DTC if the fault condition that triggers that DTC is present during the last ECM self-diagnostics.
History DTCs
A DTC is a History DTC if the fault condition that triggers that DTC is not present during the last ECM self-diagnostics.
1.5 Warning Caution and Notes
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
GM Holden LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these
instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. GM Holden LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3420 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–142
Step Action Yes No
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
7.31 DTC P0521, P0522 or P0523
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0521 – Oil Pressure Sensor Range / Performance
• DTC P0522 – Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage Low
• DTC P0523 – Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage High
Circuit Description
The ECM applies a positive 5 V reference voltage to the engine oil pressure (EOP) sensor through the 5 V reference
circuit and the ground through the low reference circuit.
The EOP sensor provides signal voltage to the ECM that is proportional to the oil pressure generated by the engine oil
pump. The ECM monitors the EOP sensor signal voltage. If the ECM detects a low oil pressure condition, it sends a
serial data communication signal to the instrument cluster to illuminate the check oil warning icon.
The ECM monitors and compares the EOP sensor signal voltage against a specified range. An EOP sensor circuit DTC
sets if the ECM detects the EOP sensor signal voltage is outside the specified range.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0521, P0522 and P0523 run continuously when the engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
P0521
The ECM detects engine oil pressure is:
• greater than 800 kPa at idle, or
• engine rpm is greater than 2000 rpm and oil pressure is less than 8 kPa.
P0522
The oil pressure sensor signal voltage is less than 0.2 V for more than 10 seconds.
P0523
The oil pressure sensor signal voltage is more than 4.9 V for more than 10 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The EOP sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the EOP sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007