warning ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2164 of 6020
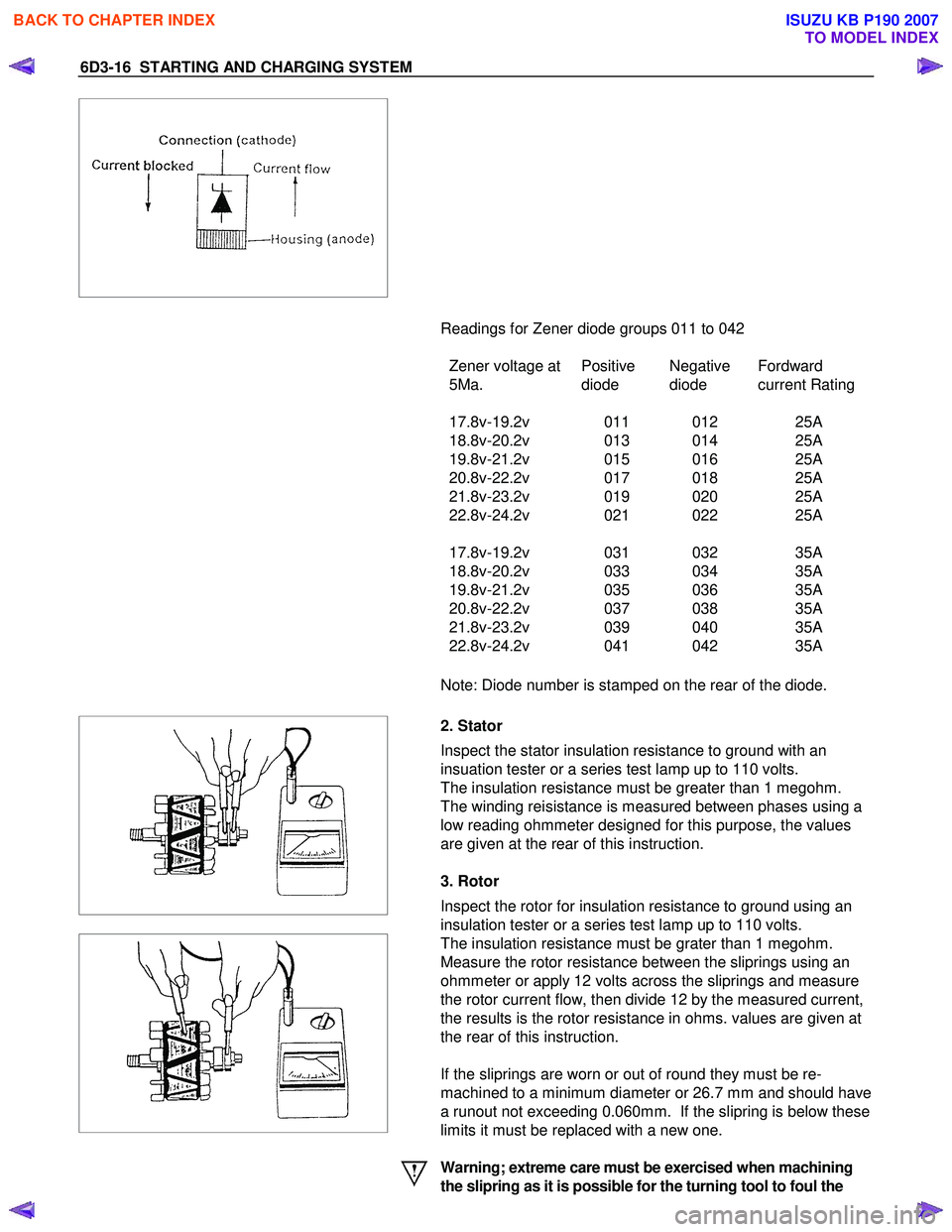
6D3-16 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Readings for Zener diode groups 011 to 042
Zener voltage at
5Ma. Positive
diode Negative
diode Fordward
current Rating
17.8v-19.2v 011 012 25A
18.8v-20.2v 013 014 25A
19.8v-21.2v 015 016 25A
20.8v-22.2v 017 018 25A
21.8v-23.2v 019 020 25A
22.8v-24.2v 021 022 25A
17.8v-19.2v 031 032 35A
18.8v-20.2v 033 034 35A
19.8v-21.2v 035 036 35A
20.8v-22.2v 037 038 35A
21.8v-23.2v 039 040 35A
22.8v-24.2v 041 042 35A
Note: Diode number is stamped on the rear of the diode.
2. Stator
Inspect the stator insulation resistance to ground with an
insuation tester or a series test lamp up to 110 volts.
The insulation resistance must be greater than 1 megohm.
The winding reisistance is measured between phases using a
low reading ohmmeter designed for this purpose, the values
are given at the rear of this instruction.
3. Rotor
Inspect the rotor for insulation resistance to ground using an
insulation tester or a series test lamp up to 110 volts.
The insulation resistance must be grater than 1 megohm.
Measure the rotor resistance between the sliprings using an
ohmmeter or apply 12 volts across the sliprings and measure
the rotor current flow, then divide 12 by the measured current,
the results is the rotor resistance in ohms. values are given at
the rear of this instruction.
If the sliprings are worn or out of round they must be re-
machined to a minimum diameter or 26.7 mm and should have
a runout not exceeding 0.060mm. If the slipring is below these
limits it must be replaced with a new one.
Warning; extreme care must be exercised when machining
the slipring as it is possible for the turning tool to foul the
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2165 of 6020

STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-17
fan.
4. Replacing the brushes (inbuilt regulator)
Check the brushes for length, this is measured from the brush
holder to the end of the brush along it's centre line. Also
inspect for any sideways wear. If worn replace both brushes.
The minimum length is 3.8mm. Inspect the brush springs for
signs of corrosion or loss of tension or uneven tension.
Replacing the brushes, using a soldering iron apply heat to the
soldered joints on the rear of the brush holder of the regulator,
using a small lever prise up the retaining tabs to release the
brush lead and spring. Thread the new brush lead up the
brush holder along with the spring, pull the lead through the
tabs until the brush is protruding 12mm from the holder.
Bend down the tabs and solder the brush lead taking care not
to allow the solder to run up the lead which will reduce
flexibility. Use 60/40 resin cored solder.
5. Ball bearing
Please note the bearings used in this KCA generator are a
high
tolerance type, only fully sealed bearings of the same
specification are to be used as replacements. It is
recommended that the bearings be replaced during the
reconditioning process to restore the unit to original
specification.
6. Regulator
The regulator can only be tested when fitted into an altenator.
Warning: do not reverse"S" and "L" connections or put 12
volt supply to "L" terminal, this connection must not be
used as a supply source other than to supply the
requirements of the warning lamp 2(watts).
Such action will destroy the regulator warning lamp
circuit.
For test voltages refer to Generator output testing section.
See also additional information on regulator function earlier in
this instruction.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2167 of 6020

STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-19
Inspection
Generator
Before any in field testing can be undertaken it is important
that the battery's conditions is established and the terminals
are clean and tight.
Check the condition of the generator drive belt and ensure that
it is adjusted in accordance with the engine manufacturer's
recommnedations.
Battery conditions:
Note: This assessment may be difficult with maintenance free
assemblies.
Test the specific gravity of the individual cells the readings
should be within 10 points of each other, it is recommended
that the average SG should be 1.260 or higher.
A load test should be carried out to determine the ability of the
battery to supply and accept current. This is a good indicator
as to the general condition of the battery.
A load equal to the normal starting current should be placed
across the battery, the duration of this load test should not
exceed 10 seconds, during this time the terminal voltage
across the battery should not drop below 9.6 volts. Observe
each cell for signs of excessive gas liberation, usuall an
indication of cell failure.
If the battery test is clear proceed with the Generator tests as
follows.
Care should be taken when making the following connections.
It is recommended that the battery negative terminal be
disconnected before the test meters are connected, and
reconnecting the negative terminal when the meters are
inserted into the circuit under test. The warning lamp in the D+
circuit should not exceed 2 watts.
Regulating voltage test on the vehicle.
Connect a voltmeter to the generator, the positive lead to the
B+ terminal and the nagative lead to the generator casing.
Select the voltage range to suit the system, i.e. 20v for 12 volt
sysytems or 40v for 24 volt systems. Connect an ammeter in
series with the main output cable from the B+ terminal on the
generator, the range selected must be capable of reading the
maximum output from the generator.
Note the voltmeter reading before starting the engine. This
reading should increase when the engine is running indicating
generator output, start the engine and increase the engine
speed until the generator is running at 4000 rpm, switch on
vehicle loads of 5-10 A is indcated on the ammeter, the
voltmeter shoud read 14.0-14.2 v for a 12 volt system, for a 24
volt system the readings should be 5-10 A and 27.7-28.5 volts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2241 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–71
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code
The purpose of the “Diagnostic Trouble Codes” mode is
to display stored trouble code in the ECM.
When “Clear DTC Information” is selected, a “Clear
DTC Information”, warning screen appears.
This screen informs you that by cleaning DTC's “all
stored DTC information in the ECM will be erased”.
After clearing codes, confirm system operation by test
driving the vehicle.
Use the “DTC Information” mode to search for a specific
type of stored DTC information.
History
This selection will display only DTCs that are stored in
the ECM's history memory. It will not display Type B
DTCs that have not requested the MIL (“Check Engine Lamp”). It will display all type A and B DTCs that
requested the MIL and have failed within the last 40
warm-up cycles. In addition, it will display all type C and
D DTCs that have failed within the last 40 warm-up
cycles.
MIL SVC or Message Request
This selection will display only DTCs that are requesting
the MIL. Type C and Type D DTCs cannot be displayed
using the MIL. Type C and D DTCs cannot be displayed
using this option.
This selection will report type B DTCs only after the MIL
has been requested.
Last Test Failed
This selection will display only DTCs that have failed the
last time the test run. The last test may have run during
a previous ignition cycle of a type A or type B DTC is
displayed. For type C and type D DTCs, the last failure
must have occurred during the current ignition cycle to
appear as last test fail.
Test Failed Since Code Cleared
The selection will display all active and history DTCs
that have reported a test failure since the last time
DTCs were cleared. DTCs that last failed more that 40
warm-up cycles before this option is selected will not be
displayed.
No Run Since Code Cleared
This selection will display up to DTCs that have not run
since the DTCs were last cleared. Since any displayed
DTCs have not run, their condition (passing or failing) is
unknown.
Failed This Ignition
This selection will display all DTCs that have failed
during the present ignition cycle.
F1: Data Display
The purpose of the “Data Display” mode is to
continuously monitor data parameters.
The current actual values of all important sensors and
signals in the system are display through F1 mode.
See the “Typical Scan Data” section.
F2: Snapshot
“Snapshot” allows you to focus on making the condition
occur, rather than trying to view all of the data in
anticipation of the fault.
The snapshot will collect parameter information around
a trigger point that you select.
F3: Miscellaneous Test:
The purpose of “Miscellaneous Test” mode is to check
for correct operation of electronic system actuators.
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code
F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority
F1: Clear DTC Information
F2: DTC Information
F0: History
F1: MIL SVS or Message Requested
F2: Last Test Failed
F3: Test Failed Since Code Cleared
F4: Not Run Since Code Cleared
F5: Failed This Ignition
F1: Data Display
F0: Engine Data
F1: O2 Sensor Data
F2: Snapshot
F3: Miscellaneous Test
F0: Lamps
F0: Malfunction Indicator Lamps
F1: Relays
F0: Fuel Pump Relay
F1: A/C Clutch Relay
F2: EVAP
F0: Purge Solenoid
F3: IAC System
F0: IAC Control
F1: IAC Reset
F4: Injector Balance Test
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2473 of 6020

E N G IN E SPEED C O NTR O L S Y STEM ( C 24SE) 6 H-1
Service Precaution
WARNING: THIS VEHICLE HAS A SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT S
YSTEM (SRS). REFER TO THE SRS
COMPONENT AND WIRING LOCATION VIEW IN
ORDER TO DETERMINE WHETHER YOU ARE
PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE SRS
COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING. WHEN YOU
ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE
SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING, REFER
TO THE SRS SERVICE INFORMATION. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW WARNINGS COULD RESULT IN
POSSIBLE AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL
INJURY, OR OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM
REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU will also call out
the fasteners that require thread lockers or thread
sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do not
use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, o
r
other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners or
fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener.
When you install fasteners, use the correct
tightening sequence and specifications. Following
these instructions can help you avoid damage to
parts and systems.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2480 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–1
6A1
Engine Mechanical – V6
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES for correct workshop practices with regard to safety and/or property
damage.
1 General Information ............................................................................................................ ...................8
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES .................................................................................................... ................... 8
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements ............................................................................. .... 8
WARNING defined ............................................................................................................................................. 8
CAUTION defined .............................................................................................................................................. 8
NOTE defined..................................................................................................................................................... 9
1.2 Engine Components .............................................................................................................................................. 9
Major Component Assemblies..................................................................................................... ......................... 9
Intake Manifold Assembly ................................................................................................................................... 10
Engine Front Cover.............................................................................................................................................. 12
Camshaft Timing Components ..................................................................................................... ...................... 13
Camshaft Cover Assembly.................................................................................................................................. 14
Cylinder Head Assembly ..................................................................................................................................... 15
Oil Pump ............................................................................................................................................................... 16
Engine Block Assembly .......................................................................................................... ............................ 17
Pistons, Rings, Bearing and Connecting Rod ..................................................................................... .............. 18
Oil Pan Assembly................................................................................................................................................. 19
Oil Filter Assembly .............................................................................................................................................. 20
1.3 Engine Serial Number........................................................................................................... ............................... 20
1.4 Engine Construction............................................................................................................................................ 21
Cylinder Block ...................................................................................................................................................... 21
Cylinder Heads ................................................................................................................. .................................... 21
Crankshaft ............................................................................................................................................................ 22
Pistons, Pins and Connecting Rods .............................................................................................. .................... 22
Camshaft Drive System ....................................................................................................................................... 22
1.5 Engine Lubrication System ...................................................................................................... ........................... 24
Lubrication Description....................................................................................................................................... 24
1.6 Service Notes ....................................................................................................................................................... 24
Cleanliness and Care........................................................................................................... ................................ 24
Replacing Engine Gaskets ....................................................................................................... ........................... 24
Re-Using Gaskets and Applying Sealants......................................................................................... ............... 24
Separating Components................................................................................................................................... 24
Cleaning Gasket Surfaces................................................................................................................................ 24
Assembling Components .......................................................................................................... ....................... 25
Use of Room Temperature Vulcanising and Anaerobic Sealer....................................................................... .25
Room Temperature Vulcanising Sealer............................................................................................................ 25
Anaerobic Sealer .............................................................................................................................................. 25
Pipe Joint Compound ............................................................................................................ ........................... 26
Separating Parts .................................................................................................................................................. 26
Tools and Equipment ............................................................................................................ .............................. 26
Fasteners .............................................................................................................................................................. 27
Clamp Load ..................................................................................................................... ................................. 27
Torque Angle and Torque to Yield Fasteners..................................................................................... .............. 27
2 Diagnosis ..............................................................................................................................................28
2.1 Engine Diagnosis ............................................................................................................... .................................. 28
2.2 Symptoms............................................................................................................................................................. 28
Strategy Based Diagnosis ....................................................................................................... ............................ 28
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2487 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–8
1 General Information
The HFV6 engine features a closed vee, deep skirt die cast aluminium cylinder block with cast iron cylinder liners,
internally balanced crankcase, full length water jackets and six bolt main bearing caps.
The cylinders are arranged in two banks of three with a 60 degree included angle between the two banks.
The right-hand bank of cylinders consists of number 1-3-5
cylinders and the left-hand bank of cylinders consists of
number 2-4-6.
The engine firing order is 1-2-3-4-5-6.
Each aluminium cylinder head is fitted with hardened valve
seats and four valves per cylinder: two intake and two
exhaust.
The valves are operated by two camshafts (DOHC) per
cylinder bank, one each for intake and exhaust valves.
The crankshaft is manufactured from forged steel. A reluctor
wheel is pressed in place onto the rear of the crankshaft for
the crankshaft position sensor.
The connecting rods are manufactured from powdered
metal and the rod cap is separated during the manufacturing
process using the fractured method. This creates a stronger,
visually seamless rod to cap union.
Figure 6A1 – 1
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2536 of 6020
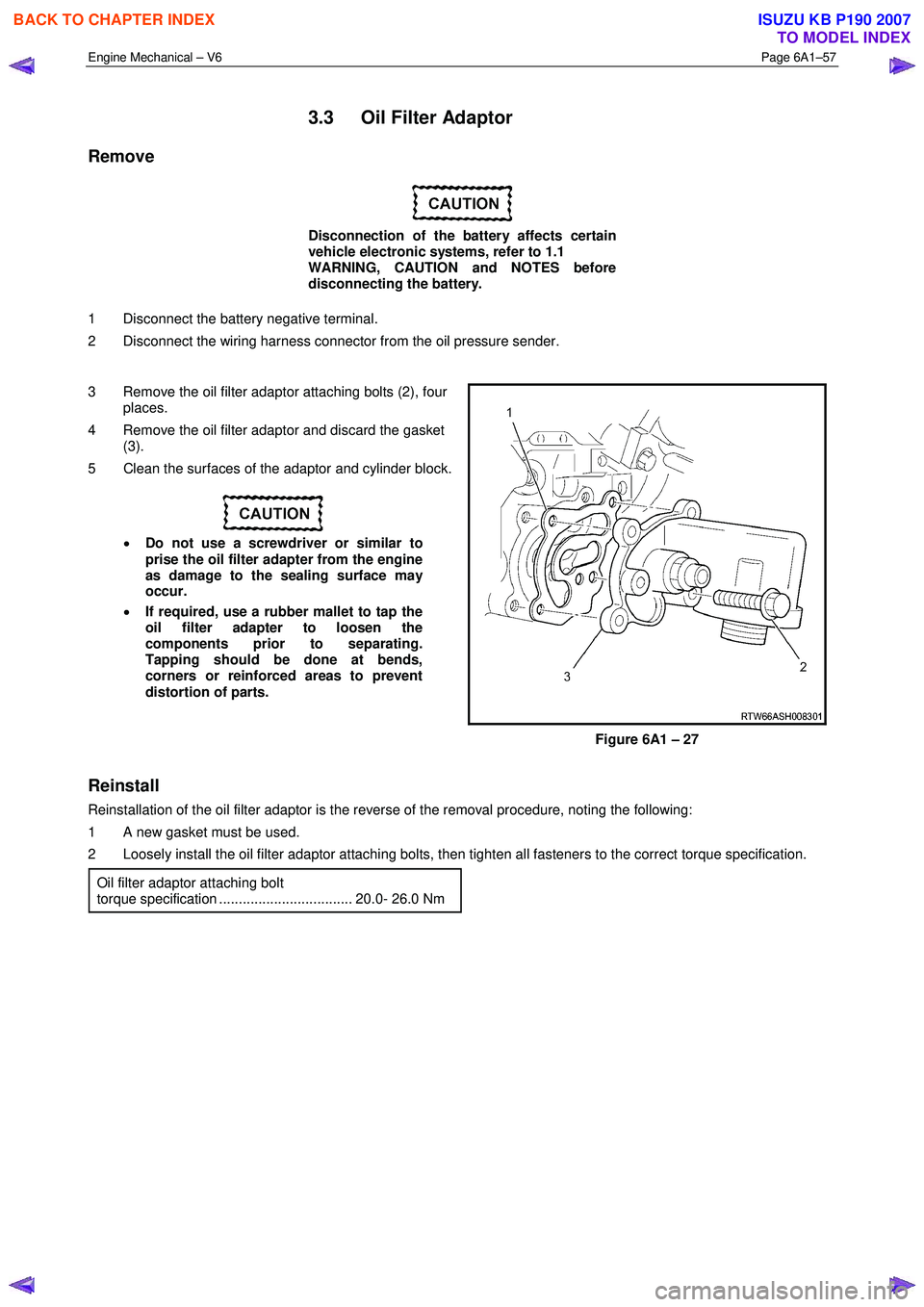
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–57
3.3 Oil Filter Adaptor
Remove
Disconnection of the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems, refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before
disconnecting the battery.
1 Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2 Disconnect the wiring harness connector from the oil pressure sender.
3 Remove the oil filter adaptor attaching bolts (2), four places.
4 Remove the oil filter adaptor and discard the gasket (3).
5 Clean the surfaces of the adaptor and cylinder block.
• Do not use a screwdriver or similar to
prise the oil filter adapter from the engine
as damage to the sealing surface may
occur.
• If required, use a rubber mallet to tap the
oil filter adapter to loosen the
components prior to separating.
Tapping should be done at bends,
corners or reinforced areas to prevent
distortion of parts.
Figure 6A1 – 27
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the oil filter adaptor is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 A new gasket must be used.
2 Loosely install the oil filter adaptor attaching bolts, then tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
Oil filter adaptor attaching bolt
torque specification .................................. 20.0- 26.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2542 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–63
Remove
Disconnection of the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems. Refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before
disconnecting the battery.
1 Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2 Remove the air intake duct (1) and hose (2), refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
Figure 6A1 – 34
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2547 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–68
CAUTION
Tighten the intake manifold bolts in a circular
pattern starting at the centre bolt and moving
outward.
2 Ensure that all fasteners are tightened to the correct torque specification. Upper intake manifold to lower
intake manifold attaching bolt
torque specification ............................................23.0 Nm
Upper intake manifold to
cylinder head attaching bolt
torque specification ............................................23.0 Nm
Incorrect wiring connector installation may
cause component malfunction or component
damage.
3 Ensure all wiring connectors are fully engaged and if applicable, locked in place.
4 Ensure all wiring harnesses are correctly routed and attached securely in their retaining clips.
5 Ensure that all hoses and pipes are routed correctly and that any retaining clips are correctly installed.
6 Start and run the engine to check for correct operation.
3.10 Intake Manifold Assembly – Complete
The intake manifold comprises of an upper and lower section. Some service procedures only require the removal of the
upper intake manifold (e.g. fuel injector/spark plug servicing), while other service procedures require the removal of both
the upper and lower manifold as a complete assembly (e.g. cylinder head/s). If only the upper intake manifold needs to
be removed, refer to 3.9 Upper Intake Manifold.
Remove
Disconnection of the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems. Refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before
disconnecting the battery.
1 Depressurise the fuel system.
2 Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007