key ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 1967 of 6020

6E-350 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
• The hardware key is plugged into the computerport.
• Vehicle system voltage: - There are no charging system concerns. Allcharging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the ECM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts but less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the ECM.
- A battery charger is NOT connected to the vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage or
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or ECM damage.
- Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF or
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position of
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure: - The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
• DO NOT disturb the tool harnesses while programming. If an interruption occurs during the
programming procedure, programming failure or
ECM damage may occur.
• If you are performing the Pass-Thru programming procedure using a notebook computer without the
power cord, ensure that the internal battery is fully
charged.
Service Programming System (SPS)
(Remote Procedure)
Notice: Some module will not accept SPS remote
procedure using 10MB PCMCIA card. In such case,
use 32MB PCMCIA card or SPS pass-thru procedure.
The Remote SPS method is a three-step process that
involves the following procedures:
1. Connecting the scan tool to the vehicle and obtaining the information from the ECM.
2. Connecting the scan tool to the terminal and downloading a new calibration file from the
terminal into the scan tool memory.
3. Reconnecting the scan tool to the vehicle and uploading the new calibration file into the ECM. Performing the Remote Procedure
1. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and obtain the ECM information using the following procedure:
Notice: Ensure the ECM is installed in the vehicle and
the battery is fully charged before programming.
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Request Info.
d. If there is already stored in the scan tool, the existing data is displayed on the screen. The
scan tool asks user to keep existing data "Keep
Data" or "Continue" to request new vehicle
information from the ECM. If there is no data in
the scan tool, it will immediately start vehicle
identification.
e. Select the vehicle description by following the on-screen instructions based on stamped VIN
or affixed VIN plate on the vehicle.
f. During obtaining information, the scan tool is receiving information from all modules at the
same time. But only ECM information is
displayed on the screen.
g. Turn OFF all accessories and press "Okay".
h. Verify that the correct VIN is displayed on the scan tool. If the VIN is incorrect or no VIN,
record the correct VIN.
2. Turn OFF the ignition.
3. Turn OFF the scan tool and disconnect from the vehicle.
4. Transfer the data from the terminal to the scan tool using the following procedure:
Notice: The TIS supports service programming with
the Tech 2 scan tool only.
a. Connect the scan tool to the terminal.
b. Launch the TIS application.
c. Select the Service Programming System at the main screen.
d. Highlight the following information on the Select Diagnostic Tool and Programming Process
screen, then click "Next".
• Select Diagnostic Tool - Tech 2
• Select Programming Process - Identify whether an existing ECM is being
reprogrammed or an ECM is being replaced
with a new one
• Select ECU Location - Vehicle
e. Verify the connections on the Preparing for Communication screen, then click "Next".
f. Verify the VIN on the Validate Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) screen, then click
"Next".
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1981 of 6020

6E-364 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Fuel Injection System Description
Fuel Injection Quantity Control
This control determines the fuel injection quantity by
adding coolant temperature, fuel temperature, intake
air temperature, barometric pressure, mass air flow and
some switch inputs information corrections to the basic
injection quantity is calculated by the ECM based on
the engine operating conditions (engine speed,
accelerator pedal pressing amount and boost pressure
sensor). More fuel rate indicates if the engine load is
increased as the accelerator pedal is stepped on at
constant engine speed.
Combined with high pressure injection of atomized fuel,
this control improves exhaust gas and ensures proper
fuel consumption. Compared with conventional
mechanical governors, an electronic control system
provides higher degree of freedom of fuel injection
quantity control, thereby presenting high accelerator
response (acceleration feeling and pressing feeling).
Starting Injection Quantity Control
At the engine starting (after the key switch is turned to
the START position to start the engine, up to return of
key switch to the ON position), optimum fuel injection
quantity is controlled based on the information on the
engine speed and coolant temperature. At low
temperature, the fuel injection quantity increases.
When the engine started completely, this boosted
quantity mode at the starting is cancelled and normal
running mode is restored.
Idle Speed Control
A control is made so as to achieve stable idling speed
at all time regardless of engine secular changes or
engine condition variations. The ECM sets target idling
speed and controls the fuel injection quantity according
to the engine conditions (actual engine speed, coolant
temperature and engine load) to follow actual engine
speed to the target idling speed so as to ensure stable
idling speed.
Idle Vibration Control
A control is made so as to reduce the engine vibration
caused by torque variations between cylinders due to
variations in fuel injection quantity of each cylinder or
injector performance. The ECM corrects the injection
quantity between cylinders based on the revolution
signals from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
Normal range of correction quantity between cylinders
is within ±5 mm
3.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2129 of 6020
ENGINE FUEL (C24SE) 6C-11
140R100028
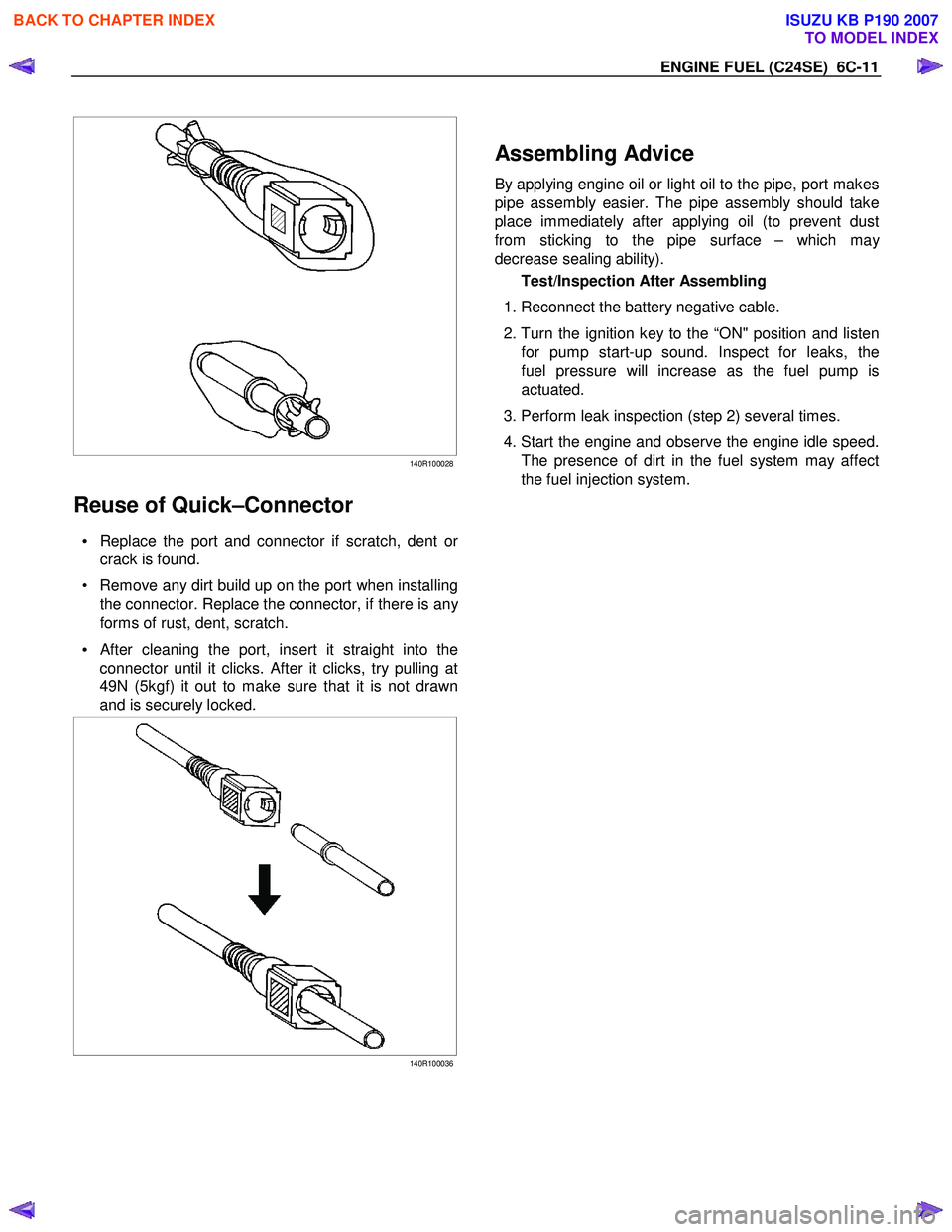
Reuse of Quick–Connector
• Replace the port and connector if scratch, dent or
crack is found.
• Remove any dirt build up on the port when installing the connector. Replace the connector, if there is an
y
forms of rust, dent, scratch.
•
After cleaning the port, insert it straight into the
connector until it clicks. After it clicks, try pulling at
49N (5kgf) it out to make sure that it is not drawn
and is securely locked.
140R100036
Assembling Advice
By applying engine oil or light oil to the pipe, port makes
pipe assembly easier. The pipe assembly should take
place immediately after applying oil (to prevent dust
from sticking to the pipe surface – which ma
y
decrease sealing ability).
Test/Inspection After Assembling
1. Reconnect the battery negative cable.
2. Turn the ignition key to the “ON" position and listen
for pump start-up sound. Inspect for leaks, the
fuel pressure will increase as the fuel pump is
actuated.
3. Perform leak inspection (step 2) several times.
4. Start the engine and observe the engine idle speed.
The presence of dirt in the fuel system may affect
the fuel injection system.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2162 of 6020

6D3-14 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
7. To remove the pulley, mount an 8mm Allen key in the vice
with the short end upwards, place a 24mm ring spanner on
the puley nut, position the internal hexagon of the roto
r
shaft onto the Allen ken, loosen the nut and remove the
pulley.
Note: the pulley has an integral boss which locks up against
the bearing,
therefore no thrust collar is provided.
8. Removing the rotor assembly. Remove the four retaining screws from the drive end housing, withdraw the roto
r
complete with the bearing.
Note: the rotor must not be pressed from the drive end housing
using a press as the bearing retaining plate and drive end
housing will be damaged or distorted. Parts removed in this
way must be replaced if the integrity of the generator is to be
maintained.
9. Remove the drive end bearing from the rotor shaft using a
chuck type puler, take care not to distort the fan assembl
y
during this process.
10. Remove the slipring end bearing using the same meghod as in 9.
Clean
Thoroughly clean all components except the rotor and stator
with an approved cleaning agent. Ensure that all traced of oil
and dirt are removed. If an abrasive cleaner is used to remove
scale and paint from the housings take care not to abrade the
bearing and mounting spigot surfaces. The rotor and stator
must be cleaned with compressed air only, the use of solvents
could cause damage to the insulating materials.
Inspection
1. Rectifier assembly
The following test equipment is required.
The recitifier assembly is not repairable and must be replaced
if a faulty diode is detected during inspection.
(a)
Adiode tester where the DC output at the test probes does
not exceed 14 volts or in the case of AC testers 12 volts
RMS. This is to ensue that when inspection rectifiers fitted
with zener power diodes the forward and reverse checks
are completer and are not masked by the diode turning on
due to the zener breakdown voltage.
(b) A zenere diode tester with a DC output in excess of 30 volts, the tester should also incorporate internal current
limiting set to 5 Ma. to prevent high currents during
inspection.
(c) Diodes can be destroyed during service due to high temperature and overload, open circuits are usually a result
of excessive voltage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2166 of 6020

6D3-18 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Reassembly
Generator
(a) Press new bearing onto slipring end of the rotor taking care to aplly the force to the bearing inner race only, otherwise
the bearing will be noisy and it's life will be shortened.
(b) Fit a new bearing to the drive end housing, fit the bearing plate, and four retaining screws, press the rotor into the
bearing, using a support tool to take the thrust against the
bearing inner.
The support is fitted from the pulley side of the bearing. In this way the thrust is not taken by the drive end housing.
(c) To fit pulley, mount an 8mm Allen key in the vice with the short end upwards, place a 24mm ring spanner on the shaft
nut, position the internal hexagon of the rotor shaft onto the
Allen key, tighten the nut to the required torque(See torque
chart)
(d) Inspect the bearing support ring for signs of damage, if in doubt replace the ring by pressing it into the housing b
y
hand, do not use excessive force.
(e) To refit the rectifier, fit new mica washers to the positive heatsink B+ bolt and retaining screw each washer must
have heatsink compound applied to both surfaces before
fitting.
Fit the three retaining screws to the rectifier then install into slipring end housing. Tighten the B+ bolt to the reuired
torque.
(f) To refit the stator, make sure the spigot surface are clean and free from damage, fit the stator into the slipring end
housing noting the correct lead connection positioning. Fit
the stator leads into the wire loops in the recrifier. Using a
pair of pliers squeeze the loop to retain the stator lead prior
to soldering. Repeat for each lead in turn, solder the leads
into position using 60/40 resin cored solder. Make sure the
leads will be clear of the internal fan when the rotor is
assmebled into the stator.
(g) Carefully install the rotor into the stator/slipring end housing assembly, noting the alignment of the housings and through
bolt holes. Fit the through bolts making sure the stator is
seated correctly, tighten the through bolts to the correct
torque setting (uneven torque can produce magnetic noise
levels above normal).
(h) Fitting the regulator. Compress the brushes into the brush holder by hand, slip the regulator through the opening in the
rear of the slipring end housing until the brushes come in
contact with the slipring. Press the regulator towards the
slipring until the holes are aligned then fit the retaining
screws and tighten.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2212 of 6020

6E–42 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ECM CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENT & OUTPUT SIGNAL
Connector J1 Port: View Looking Into ECM Case
1
17 16
32
PIN16
PIN1
PIN17 PIN32
Pin
No. B/
Box
No. Pin Function
Wire
Color Signal or Continuity
ECM
Connection Tester Position
Key SW Off Key SW
On Engine
Idle Engine
2000rpm Range (+) (-)
J1-1 J1-1 Ground BLK/
WHT Continuity
with
ground -
- - Disconnect ΩJ1-1 GND
J1-2 J1-2 Ground BLK/
WHT Continuity
with
ground -
- - Disconnect ΩJ1-2 GND
J1-3 J1-3 Knock Sensor Signal YEL Less than 1V--- ----
J1-4 J1-4 No Connection - --- - -- - -
J1-5 J1-5 Canister Purge Solenoid Valve RED/
YEL Less than
1V Wave form G or 12-14V
Connect DC V J1-5 GND
J1-6 J1-6 Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor (Ground) RED Approx.
0.58kΩ -
- - Disconnect ΩJ1-6 J1-21
J1-7 J1-7 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Output
Signal BLU Less than
1V Approx 0.7V Approx
0.8VConnect DC V J1-7 J1-32
J1-8 J1-8 No. 3 Injector GRN/
BLK Less than
1V Wave form E or 12-14V
Connect DC V J1-8 GND
J1-9 J1-9 No. 1 Injector GRN/
WHT Less than
1V Wave form E or 12-14V
Connect DC V J1-9 GND
J1-10 J1-10 No Connection - --- - -- - -
J1-11 J1-11 No. 4 Injector GRN Less than
1V Wave form E or 12-14V
Connect DC V J1-11 GND
J1-12 J1-12 No Connection - --- - -- - -
J1-13 J1-13 Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) Coil B High BLU/
RED Less than
1V Less than 1V / 10-14V
Connect DC V J1-13 GND
J1-14 J1-14 No Connection - --- - -- - -
J1-15 J1-15 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Power
Supply RED Less than
1V Approx. 5V
Connect DC V J1-15 J1-32
J1-16 J1-16 MAP Sensor Ground GRN Continuity with
ground -
- - Connect ΩJ1-16 GND
J1-17 J1-17 Ground BLK/
WHT Continuity
with
ground -
- - Connect ΩJ1-17 GND
J1-18 J1-18 Coil Module 2 (No. 2 & 3 Cylinder) BLU -
-Wave form F -- - -
J1-19 J1-19 Coil Module 1 (No. 1 & 4 Cylinder) GRN -
-Wave form F -- - -
J1-20 J1-20 No Connection - --- - -- - -
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2213 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–43
J1-21 J1-21 Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Signal WHT - - Wave form
or approx. 3.7V Wave form
A or
approx. 7.8V Connect AC V J1-21 J1-6
J1-22 J1-22 No.2 Injector GRN/
WHT Less than
1V Wave form E or 12-14V
Connect DC V J1-22 GND
J1-23 J1-23 No Connection - --- - -- - -
J1-24 J1-24 MAP Sensor Signal GRY Less than 1VApprox.
4.8V Approx.
1.3V Approx.
0.9V Connect DC V J1-24 J1-16
J1-25 J1-25 No Connection - --- - -- - -
J1-26 J1-26 No Connection - --- - -- J1-26 -
J1-27 J1-27 Engine Coolant Temp. (ECT) Sensor Signal GRY Less than
1V
20℃: Approx. 2.4V / 40 ℃: Approx. 1.4V or
4.1V / 60 ℃: Approx. 3.3V / 80 ℃: Approx.
2.5VConnect DC V J1-27 J1-32
J1-28 J1-28 Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) Coil A High BLU Less than
1V Less than 1V / 10-14V
Connect DC V J1-28 GND
J1-29 J1-29 Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) Coil B Low BLU/
BLK Less than
1V Less than 1V / 10-14V
Connect DC V J1-29 GND
J1-30 J1-30 Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) Coil A Low BLU/
WHT Less than
1V Less than 1V / 10-14V
Connect DC V J1-30 GND
J1-31 J1-31 MAP Sensor Power Supply RED Less than
1V Approx.. 5V
Connect DC V J1-31 J1-16
J1-32 J1-32 ECT Sensor, Knock Sensor, Throttle
Position Sensor Ground GRN Continuity
with
ground -
- - Connect ΩJ1-32 GND
Pin
No. B/
Box No. Pin Function
Wire
Color Signal or Continuity
ECM
Connection Tester Position
Key SW Off Key SW
On Engine
Idle Engine
2000rpm Range (+) (-)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2214 of 6020

6E–44 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Connector J2 Port: View Looking Into ECM Case
1
17 16
32
PIN32
PIN1
PIN17
PIN16
Pin
No. B/
Box No. Pin Function
Wire
Color Signal or Continuity
ECM
Connection Tester Position
Key SW Off Key SW
On Engine
Idle Engine
2000rpm Range (+) (-)
J2-1 J2-1 Intake Air Temp. (IAT) Sensor Ground GRN Continuity
with
ground -
- - Disconnect ΩJ2-1 GND
J2-2 J2-2 Battery Power Supply RED/ WHT10-14V
Connect DC V J2-2 GND
J2-3 J2-3 Ignition Power Supply BLU/ YELLess than
1V 10-14V
Connect DC V J2-3 GND
J2-4 J2-4 To Data Link Connector No. 6 BLU -
-- - -- - -
J2-5 J2-5 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-6 J2-6 Oxygen Sensor (Ground) PNK Continuity
with
ground -
- - Connect ΩJ2-6 GND
J2-7 J2-7 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-8 J2-8 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-9 J2-9 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-10 J2-10 CO Adjust Signal (W/O Catalystic
Converter) YEL -
-- - -- - -
J2-11 J2-11 Fuel Pump Relay GRN/ WHT10-14V
While relay
is activated; 10-14V
Relay is not
activated;
Less than 1V10-14V Connect DC V J2-11 GND
J2-12 J2-12 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-13 J2-13 A/C Compressor Relay GRY/
RED Less than
1V A/C comp. is operated: Less than 1V
A/C comp. is not operated: 10-14V Connect DC V J2-13 GND
J2-14 J2-14 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-15 J2-15 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-16 J2-16 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-17 J2-17 CO Adjust (W/O Catalystic Converter) RED -
-- - -- - -
J2-18 J2-18 Battery Power Supply RED/ WHT10-14V
Connect DC V J2-18 GND
J2-19 J2-19 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-20 J2-20 Power Steering Pressure Switch GRN/
YEL Less than
1V
Pressure switch is turned on: Less than 1VPressure switch is turned off: 10-14VConnect DC V J2-20 GND
J2-21 J2-21 Oxygen Sensor BLU Less than 1VApprox.
0.4V Wave form D or 0.1 -
0.9V Connect DC V J2-21 J2-6
J2-22 J2-22 Intake Air Temp. (IAT) Sensor (Signal) YEL/
GRN Less than
1V
20℃: Approx. 2.9V / 40 ℃: Approx. 1.8V V
/ 60 ℃: Approx. 1.1V / 80 ℃: Approx. 0.6VConnect DC V J2-22 33
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2215 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–45
J2-23 J2-23 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Signal
(Immobilizer Control
Unit Terminal B8) WHT -
- Wave form C or Approx.
6.5V at 20km/h Connect AC V J2-23 GND
J2-24 J2-24 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-25 J2-25 Tachometer Output Signal BLK/
RED -
- Wave form Wave form
B or
Approx.
4.5V Connect AC V J2-25 GND
J2-26 J2-26 Thermo Relay GRN/
BLK Less than
1V
A/C request is activated: 10-14V
A/C request is not activated: Less than 1VConnect DC V J2-26 GND
J2-27 J2-27 No Connection - - - - - - - - -
J2-28 J2-28 No Connection - - - - - - - - -
J2-29 J2-29 No Connection -- - - - -- - -
J2-30 J2-30 To Data Link Connector No. 2 GRN -
-- - -- - -
J2-31 J2-31 Oxygen Sensor Heater BLU/ WHTContinuity
with
ground - Wave
Form Wave
Form D Connect
ΩJ2-31 GND
J2-32 J2-32 Check Engine Lamp (Immobilizer Control
Unit Terminal B7) BRN/
YEL Less than
1V Less than
1V Lamp is turned on: Less
than 1V
Lamp is turned off: 10-
14V Connect DC V J2-32 GND
Pin
No. B/
Box No. Pin Function
Wire
Color Signal or Continuity
ECM
Connection Tester Position
Key SW Off Key SW
On Engine
Idle Engine
2000rpm Range (+) (-)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2219 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–49
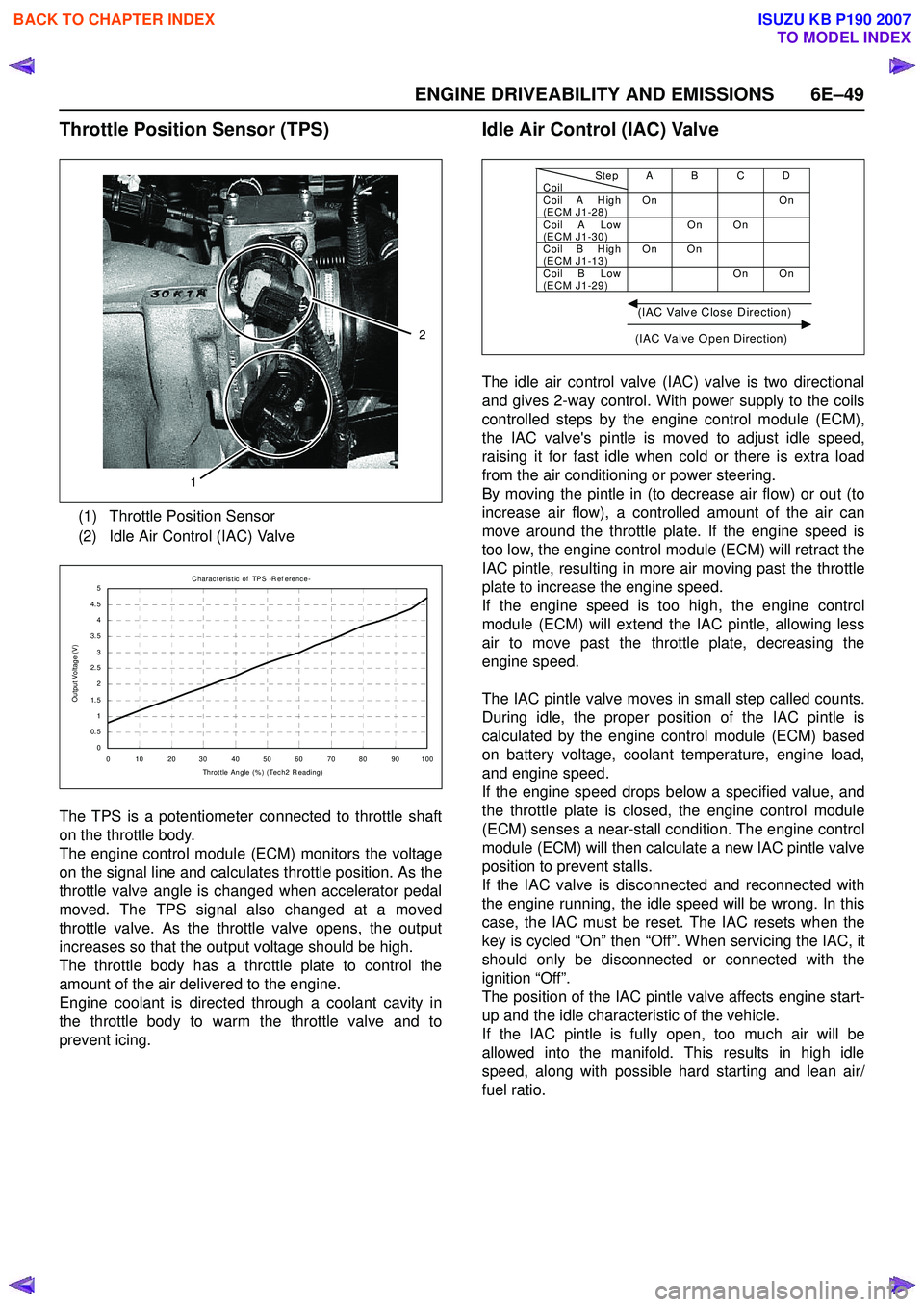
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
The TPS is a potentiometer connected to throttle shaft
on the throttle body.
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the voltage
on the signal line and calculates throttle position. As the
throttle valve angle is changed when accelerator pedal
moved. The TPS signal also changed at a moved
throttle valve. As the throttle valve opens, the output
increases so that the output voltage should be high.
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the
amount of the air delivered to the engine.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in
the throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to
prevent icing.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The idle air control valve (IAC) valve is two directional
and gives 2-way control. With power supply to the coils
controlled steps by the engine control module (ECM),
the IAC valve's pintle is moved to adjust idle speed,
raising it for fast idle when cold or there is extra load
from the air conditioning or power steering.
By moving the pintle in (to decrease air flow) or out (to
increase air flow), a controlled amount of the air can
move around the throttle plate. If the engine speed is
too low, the engine control module (ECM) will retract the
IAC pintle, resulting in more air moving past the throttle
plate to increase the engine speed.
If the engine speed is too high, the engine control
module (ECM) will extend the IAC pintle, allowing less
air to move past the throttle plate, decreasing the
engine speed.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small step called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the engine control module (ECM) based
on battery voltage, coolant temperature, engine load,
and engine speed.
If the engine speed drops below a specified value, and
the throttle plate is closed, the engine control module
(ECM) senses a near-stall condition. The engine control
module (ECM) will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve
position to prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with
the engine running, the idle speed will be wrong. In this
case, the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the
key is cycled “On” then “Off”. When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “Off”.
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-
up and the idle characteristic of the vehicle.
If the IAC pintle is fully open, too much air will be
allowed into the manifold. This results in high idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and lean air/
fuel ratio.
(1) Throttle Position Sensor
(2) Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
1
2
C harac teris t ic of TPS -R ef erenc e-
0
0.5
1
1.5 2
2.5
3
3.5 4
4.5 5
0 10 2030 405060 7080 90100 Throt t le Angle (% ) (Tec h2 R eading)
Output Voltage (V)
StepCoilAB CDCoil A H igh
(ECM J1-28) On On
Coil A Low
(ECM J1-30) On On
Coil B H igh
(ECM J1-13) On On
Coil B Low
(ECM J1-29) On On
(IAC Valve Close Direction)
(IAC Valve Open Direction)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007