spark plugs ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3384 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–106
− Damaged accessory drive belt
• For an intermittent condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this
diagnostic procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305 or P0306 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2
W ere you sent here from DTC P0300? Go to Step 3 Go to 7.16
DTC P0300 in this Section
3 1 Ignition OFF.
2 Remove the ignition coil of the misfiring cylinder, but leave the electrical connector connected. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
3 Inspect the ignition coil boot for the following conditions:
− Holes.
− Tears.
− Carbon tracking.
− Oil contamination or water intrusion.
Did you find a condition with the ignition coil boot? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 4
4 1 Remove the fuel pump fuse from the under-hood fuse and relay
centre.
2 Install the J 26792 Spark Tester to the ignition coil boot and a good ground.
3 Crank the engine while observing J 26792.
Does the spark tester spark and is the spark consistent? Go to Step 5 Go to Electronic
Ignition System Diagnosis
5 1 Ignition OFF.
2 Remove the spark plug from the cylinder that indicated a misfire.
3 Inspect the spark plug. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Does the spark plug appear to be OK? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 6
6
Is the spark plug oil or coolant fouled? Inspect the spark
plugs. Go to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations Go to Step 7
7 Is the spark plug gas fouled? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
8 Does the spark plug show any signs of being cracked, worn, or
incorrectly gap? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3527 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–3
2.21 Schrader Valve – Fuel Pressure Gauge Connection Point............................................................................... 47
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 47
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 47
2.22 Spark Plugs .................................................................................................................... ...................................... 48
Service Precautions............................................................................................................ ................................. 48
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 48
Inspect .................................................................................................................................................................. 48
Spark Plug Inspection .......................................................................................................... ............................... 49
Poor Spark Plug Performance.................................................................................................... ...................... 49
Analysis of Spark Plug Condition ..................................................................................................................... 51
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 53
2.23 Throttle Body Assembly......................................................................................................... ............................. 53
Handling Precautions .......................................................................................................................................... 53
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 53
Inspect .................................................................................................................................................................. 55
Reinstall ................................................................................................................................................................ 55
3 Specifications ................................................................................................................. ......................57
4 Assembly Lubricants ............................................................................................................ ...............60
5 Torque Specifications ..........................................................................................................................61
6 Special Tools ........................................................................................................................................62
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3572 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–48
2.22 Spark Plugs
Service Precautions
1 Allow the engine to cool (to at least 50°C) before attempting to remove spark plugs. Attempting to remove spark
plugs from a hot engine may cause the plug / cylinder head threads to bind, resulting in tearing of the alloy cylinder
head threads.
2 Clean the spark plug recess area before removing any spark plug. Failure to do so could result in engine damage because of dirt or other foreign material entering the cylinder head or by the contamination of the cylinder head
threads. The contaminated threads may then prevent the correct seating of the new or replaced plug. If required,
use a thread chaser to clean the threads of any contamination where this is suspected.
3 Under no circumstances should the spark plug/s gap be adjusted. If the gap is not within specifications,
replace the spark plug.
Figure 6C1-3 – 66
Remove
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Remove the ignition coil/s, refer to 2.15 Ignition Coil.
3 Using a suitable spark plug socket, loosen the spark plug slightly and then re-tighten to break away any carbon deposits on the threads.
Wear eye protection to avoid injury.
4 Loosen the spark plug once again one or two turns, then use compressed air to remove any foreign material that may otherwise enter the combustion chamber.
5 Remove the spark plug (1).
6 Repeat as required for the remaining spark plugs.
NOTE
Place each spark plug in the same order as that
of removal. This will enable any abnormal spark
plug condition to be identified with the cylinder.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are removed for an indefinite
period before installation, plug the spark plug
openings to prevent foreign particle ingress.
7 Repeat steps 2 to 5 for the remaining spark plugs as required.
Figure 6C1-3 – 67
Inspect
The spark plugs must not be re-gapped. If the gap of a spark plug is outside the specified range, replace the spark plug.
In addition, replace spark plugs that shows excessive dirt deposit or broken insulators.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3573 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–49
1 Replace any plug that has cracked and / or broken insulation or loose electrodes.
2 Inspect the spark plugs for defects. Refer to Analysis of Spark Plug Condition in this Section for identification of the condition of spark plugs.
3 Ensure the threads are clean and in good order.
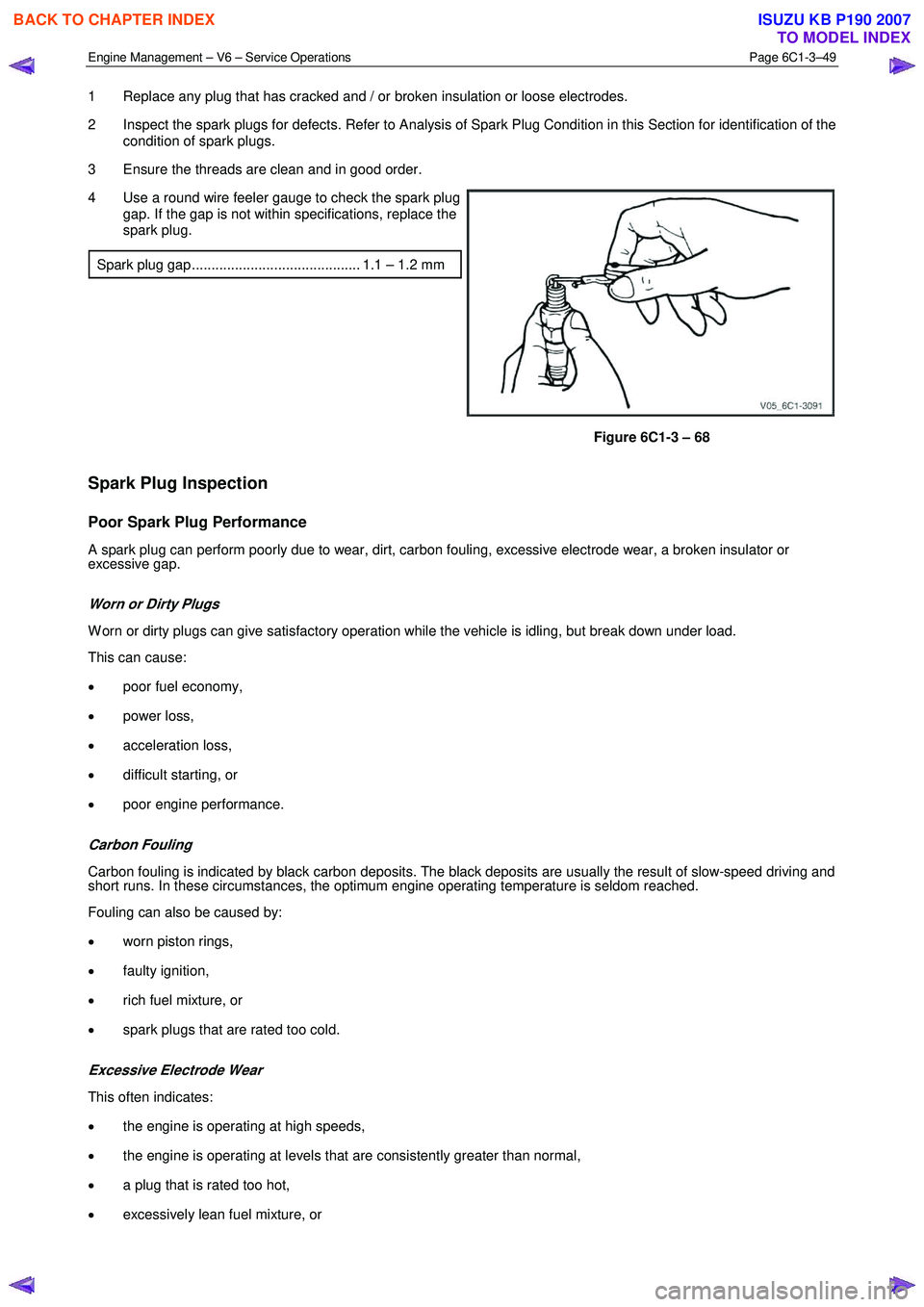
4 Use a round wire feeler gauge to check the spark plug gap. If the gap is not within specifications, replace the
spark plug.
Spark plug gap ........................................... 1.1 – 1.2 mm
Figure 6C1-3 – 68
Spark Plug Inspection
Poor Spark Plug Performance
A spark plug can perform poorly due to wear, dirt, carbon fouling, excessive electrode wear, a broken insulator or
excessive gap.
Worn or Dirty Plugs
W orn or dirty plugs can give satisfactory operation while the vehicle is idling, but break down under load.
This can cause:
• poor fuel economy,
• power loss,
• acceleration loss,
• difficult starting, or
• poor engine performance.
Carbon Fouling
Carbon fouling is indicated by black carbon deposits. The black deposits are usually the result of slow-speed driving and
short runs. In these circumstances, the optimum engine operating temperature is seldom reached.
Fouling can also be caused by:
• worn piston rings,
• faulty ignition,
• rich fuel mixture, or
• spark plugs that are rated too cold.
Excessive Electrode Wear
This often indicates:
• the engine is operating at high speeds,
• the engine is operating at levels that are consistently greater than normal,
• a plug that is rated too hot,
• excessively lean fuel mixture, or
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3576 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–52
Oil Fouled (3)
W et, oily deposits with minor electrode wear possibly due to oil leaking past worn piston rings.
Breaking in a new or recently overhauled engine before the rings are fully seated may also result in this condition.
Deposit Fouling A (4)
Red brown, yellow and white coloured coatings on the insulator tip which are by-products of combustion. They come
from fuel and lubricating oil which generally contain additives. Most powdery deposits have no adverse effect on spark
plug operation, however, they may cause intermittent missing under severe operating conditions.
Deposit Fouling B (5)
Deposits similar to those identified in deposit fouling A (4). These are also by-products of combustion from fuel and
lubricating oil. Excessive valve stem clearances and / or defective intake valve seals allow too much oil to enter the
combustion chamber. The deposits will accumulate on the portion of the spark plug that projects into the chamber and
will be heaviest on the side facing the intake valve. If this condition is only detected in one or two cylinders, check the
valve stem seals.
Deposit Fouling C (6)
Most powdery deposits identified in deposit fouling A (4) have no adverse effect on the operation of the spark plug as
long as they remain powdery.
Under certain conditions of operation however, these deposits melt and form a shiny glaze coating on the insulator.
W hen hot, this acts as a good electrical conductor allowing the current to flow along the deposit instead of sparking
across the gap.
Detonation (7)
Commonly referred to as engine knock or pinging, detonation causes severe shocks inside the combustion chamber
causing damage to parts.
Pre-ignition (8)
Burnt or blistered insulator tip and badly eroded electrodes probably due to the excessive heat.
This is often caused by a cooling system blockage, sticking valves, improperly installed spark plugs or plugs that are the
wrong heat rating (too hot).
Sustained high speed with a heavy load can produce temperatures high enough to cause pre-ignition.
Heat Shock Failure (9)
A rapid increase in spark plug tip temperature under severe operating conditions can cause heat shock and result in
fractured insulators. This is a common cause of broken and cracked insulator tips.
Insufficient Installation Torque (10)
Poor contact between the spark plug and the cylinder head seat.
The lack of proper heat transfer that results from poor seat contact causes overheating of the spark plug. In many cases,
severe damage occurs. Dirty threads in the cylinder head can cause the plug to seize before it is seated.
Ensure the cylinder head and spark plug threads are free of deposits, burrs and scale before installation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007