spark plugs ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2814 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–37
Page 6A1–37
2.7 Engine Misfire with Excessive Oil
Consumption
Cause Correction
Worn valves, valve guides and/or valve stem oil seals. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for coolant saturation, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Repair or replace components as required, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly.
Worn or broken piston rings.
Oil consumption may or may not cause an actual misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of
low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2819 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–42
Page 6A1–42
2.12 Engine Will Not Crank – Crankshaft Will
Not Rotate
Cause Correction
Seized accessory drive system component. 1 Remove the accessory drive belt, refer to
3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace accessory drive system components as required.
Hydraulically locked cylinder caused by:
• coolant in cylinder,
• oil in cylinder, or
• fuel in cylinder. 1 Remove the spark plugs and check for fluid, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect for broken head gasket/s.
3 Inspect for cracked engine block or cylinder head.
4 Inspect for sticking fuel injector.
5 Repair or replace components as required.
Seized torque converter. 1 Remove the torque converter bolts, refer to 7C1
Automatic – 4L60E – General Information – 4L60E –
General Information.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace torque converter as required.
Material in cylinder bore, caused by:
• broken valve,
• broken piston or ring, or
• dirt or foreign matter entry during engine assembly
procedure. 1 Clean and inspect the cylinder for damaged
components and or foreign matter, refer to 4.7
Cylinder Block.
2 Repair or replace components as required.
Seized crankshaft or connecting rod bearings. Inspect and repair or replace crankshaft, connecting rod
and bearings as required, refer to 4.5 Pistons, Pins, Rings,
Connecting Rods and Big-end Bearings and 4.6
Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Bent or broken connecting rod. Inspect and repair or replace connecting rod and bearings
as required, refer to 4.5 Pistons, Pins, Rings, Connecting
Rods and Big-end Bearings.
Bent or broken crankshaft. Inspect and repair or replace crankshaft and bearings as
required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Seized or broken camshaft. 1 Inspect and replace camshafts as required, refer to
3.19 Camshaft.
2 Inspect camshaft journals and cam caps on cylinder head and repair or replace components as required,
refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly.
Seized or broken camshaft timing components. 1 Inspect the crankshaft, idler, intake camshaft and
exhaust camshaft sprockets.
2 Inspect the timing chains.
3 Inspect the guides.
4 Inspect the tensioners.
5 Repair or replace components as required, refer to 3.16 Timing Chains, Tensioners, Shoes and Guides.
Seized or broken valve train components. 1 Inspect the stationary hydraulic lash adjusters, refer
to 3.21 Stationary Hydraulic Lash Adjuster.
2 Inspect the rocker arms, re fer to 3.20 Rocker Arm.
3 Inspect the Valves Refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly.
4 Inspect the valve springs, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly.
5 Repair or replace components as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2820 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–43
Page 6A1–43
2.13 Coolant in Combustion Chamber
Definition
Excessive white smoke and/or coolant type odour emitted from the exhaust pipe may indicate coolant in the combustion
chamber. Low coolant levels, an inoperativ e engine cooling fan or a faulty thermostat may lead to an over-temperature
condition which may cause internal engine component damage. A slower than normal cranking speed may indicate
coolant entering the combustion chamber.
1 Remove the spark plugs and inspect for spark plugs sa turated by coolant and coolant in the cylinder bore.
2 Inspect by performing a cylinder leakage test, refer to 2.16 Cylinder Leakage Test. During this test, excessive air
bubbles in the coolant may indicate a faulty head ga sket, cracked cylinder head or cracked cylinder block.
3 Inspect by performing a cylinder compression test. Two cylinders side-by-side on the cylinder block, with low
compression, may indicate a fa iled cylinder head gasket, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
Cause Correction
Cracked intake manifold or faulty gasket. Replace components as required, refer to 3.10 Intake
Manifold Assembly – Complete.
Faulty cylinder head gasket. Replace the cylinder head gasket, refer to 3.22 Cylinder
Head Assembly.
Warped cylinder head. Repair or replace the cylinder heads as required, refer to
3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly.
Cracked cylinder liner or block Repair or replace the cylinder block and components as
required, refer to 4.7 Cylinder Block.
Cylinder head or cylinder block porosity. Repair or replace the cylinder block or cylinder heads as
required, refer to 4.7 Cylinder Block or 3.22 Cylinder Head
Assembly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2822 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–45
Page 6A1–45
2.15 Engine Compression Test
A compression pressure test of the engine cylinders determines the condition of the rings, the valves and the head
gasket.
Preliminary Steps
1 Ensure the battery is fully charged.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
DTCs will set when the fuel system or the ignition
system is disabled and the engine is cranked.
Disregard DTCs that set under this condition.
3 Disable the fuel system by removi ng the fuel pump relay, refer to Section 8A Electrical Body & Chassis .
4 Start the engine to use any resi dual fuel from the fuel lines.
4 Disable the ignition coils by removing fuses 34 and 35, refer to Section 8A Electrical Body & Chassis .
5 Using Tech 2, command the throttle plate to wide open throttle.
Engine Cylinder Compression Test
1 Install the compression tester to cylinder number 1.
2 While observing the compression tester reading, turn t he ignition to the START position for several seconds and
then allow the ignition to return to the ON position.
3 Record the highest compression reading obtained.
4 Repeat the engine compression test for each cylinder.
Test Result Evaluation
Normal engine compression pressure builds quickly and evenly to over 965 kPa. In addition, the lowest reading of an
engine cylinder should not be less than 70 per cent of the highest reading. If any cylinder fails the compression test,
adding 15 ml of engine oil to the suspected cylinder may help isolate the following fault condition.
1 A fault condition in the piston rings will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression tends to build-up with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression improves with the addition of engine oil.
2 A fault condition in an intake or exhaus t valve will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
3 A fault condition in the cylinder head gasket will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
• The suspected cylinders are pos itioned adjacent to each other.
• The engine oil may be contaminated with engine coolant.
• The engine coolant may be cont aminated with engine oil.
Once the fault has been identified, refe r to the relevant service procedure and reinstall the removed components.
Using Tech 2, clear DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2823 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–46
Page 6A1–46
2.16 Cylinder Leakage Test
A leakage test may be performed to measure cylinder/combustion chamber leakage. High cylinder leakage may indicate
one or more of the following:
• worn or burnt valves,
• broken valve springs,
• stuck valve lifters,
• incorrect valve lash/adjustment,
• damaged piston,
• worn piston rings,
• worn or scored cylinder bore,
• damaged cylinder head gasket,
• cracked or damaged cylinder head, or
• cracked or damaged engine block.
1 Disconnect the battery ground negative cable.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
3 Rotate the crankshaft to place the piston in the cyli nder being tested at top dead centre (TDC) of the compression
stroke.
4 Install a commercially available cylinder head leak down tester into the spark plug hole.
NOTE
If required, hold the crankshaft balancer bolt to
prevent the engine from rotating.
5 Apply shop air pressure to the cylinder head leak dow n tester and adjust according to the manufacturers
instructions.
6 Record the cylinder leakage value. Cylinder leakage t hat exceeds 25 percent is considered excessive and may
require component service. In excessive leakage situations, inspect for the following conditions:
• air leakage sounds at the throttle body or air inlet duct that may indicate a worn or burnt intake valve or a
broken valve spring,
• air leakage sounds at the exhaust system tailpipe that may indicate a worn or burnt exhaust valve or a broken
valve spring,
• air leakage sounds from the crankcase, oil level indicator tube, or oil fill tube that may indicate worn piston
rings, a damaged piston, a worn or scored cylinder bore, a damaged engine block or a damaged cylinder
head, or
• air bubbles in the cooling system may indicate a damaged cylinder head or a damaged cylinder head gasket.
7 Perform the leakage test on the rema ining cylinders and record the values.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2891 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–114
Page 6A1–114
Remove
Right-hand Secondary Timing Chain
CAUTION
After removing the upper intake manifold, and
spark plugs, plug any openings to prevent dirt
and other contaminants from entering.
1 Remove the engine front cover assembly, refer to 3.15 Front Cover Assembly.
2 Remove the spark plugs to aid crankshaft/engine rotation, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations .
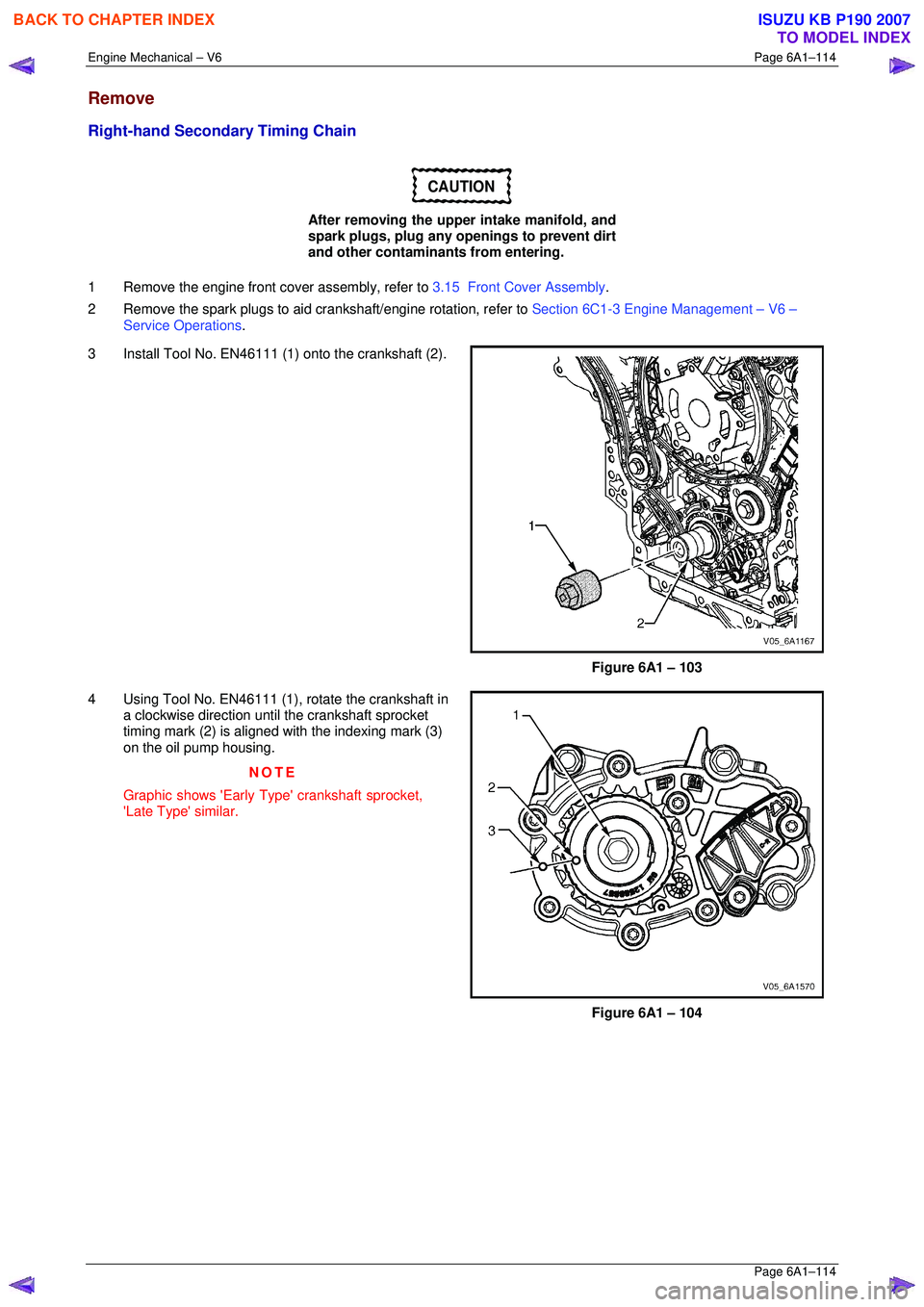
3 Install Tool No. EN46111 (1) onto the crankshaft (2).
Figure 6A1 – 103
4 Using Tool No. EN46111 (1), rotate the crankshaft in a clockwise direction until the crankshaft sprocket
timing mark (2) is aligned with the indexing mark (3)
on the oil pump housing.
NOTE
Graphic shows 'Early Type' crankshaft sprocket,
'Late Type' similar.
Figure 6A1 – 104
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2948 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–171
Page 6A1–171
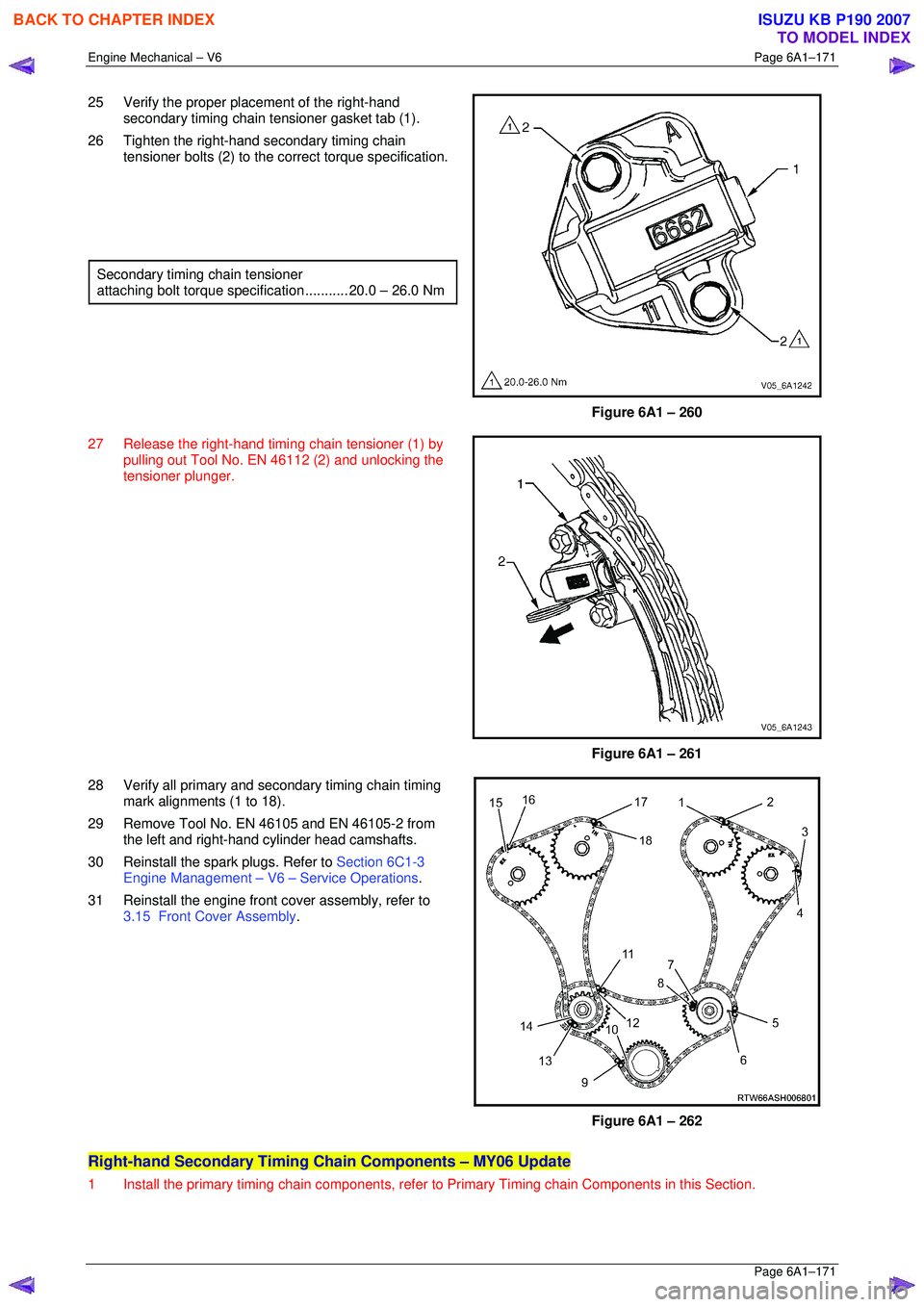
25 Verify the proper placement of the right-hand
secondary timing chain tensioner gasket tab (1).
26 Tighten the right-hand secondary timing chain tensioner bolts (2) to the co rrect torque specification.
Secondary timing chain tensioner
attaching bolt torque spec ification ........... 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Figure 6A1 – 260
27 Release the right-hand timi ng chain tensioner (1) by
pulling out Tool No. EN 46112 (2) and unlocking the
tensioner plunger.
Figure 6A1 – 261
28 Verify all primary and secondary timing chain timing mark alignments (1 to 18).
29 Remove Tool No. EN 46105 and EN 46105-2 from the left and right-hand cylinder head camshafts.
30 Reinstall the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
31 Reinstall the engine front cover assembly, refer to 3.15 Front Cover Assembly .
Figure 6A1 – 262
Right-hand Secondary Timing Chain Components – MY06 Update
1 Install the primary timing chain components, refer to Primary Timing chain Components in this Section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2956 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–179
Page 6A1–179
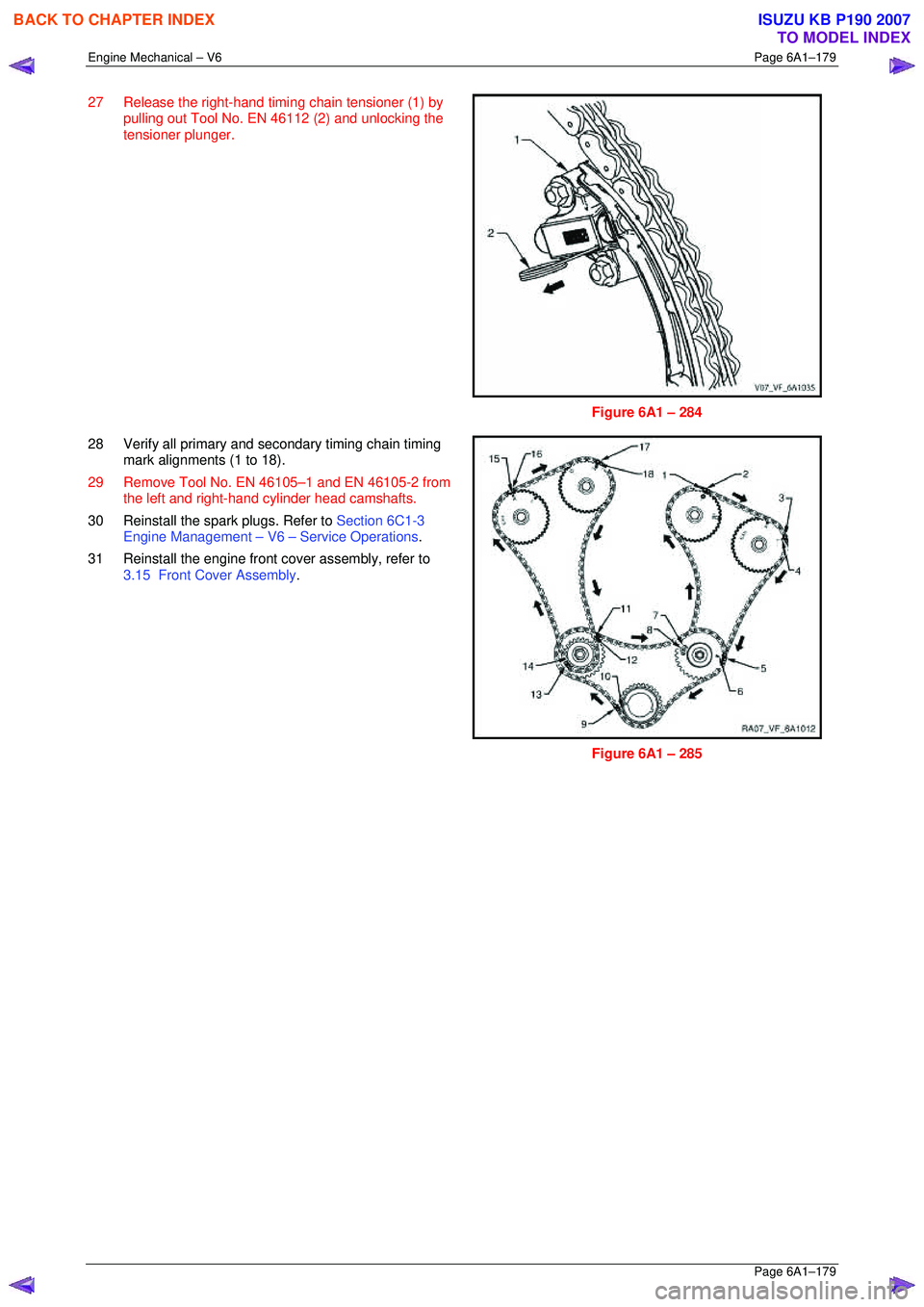
27 Release the right-hand timing chain tensioner (1) by
pulling out Tool No. EN 46112 (2) and unlocking the
tensioner plunger.
Figure 6A1 – 284
28 Verify all primary and secondary timing chain timing mark alignments (1 to 18).
29 Remove Tool No. EN 46105–1 and EN 46105-2 from the left and right-hand cylinder head camshafts.
30 Reinstall the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
31 Reinstall the engine front cover assembly, refer to 3.15 Front Cover Assembly .
Figure 6A1 – 285
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3273 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–31
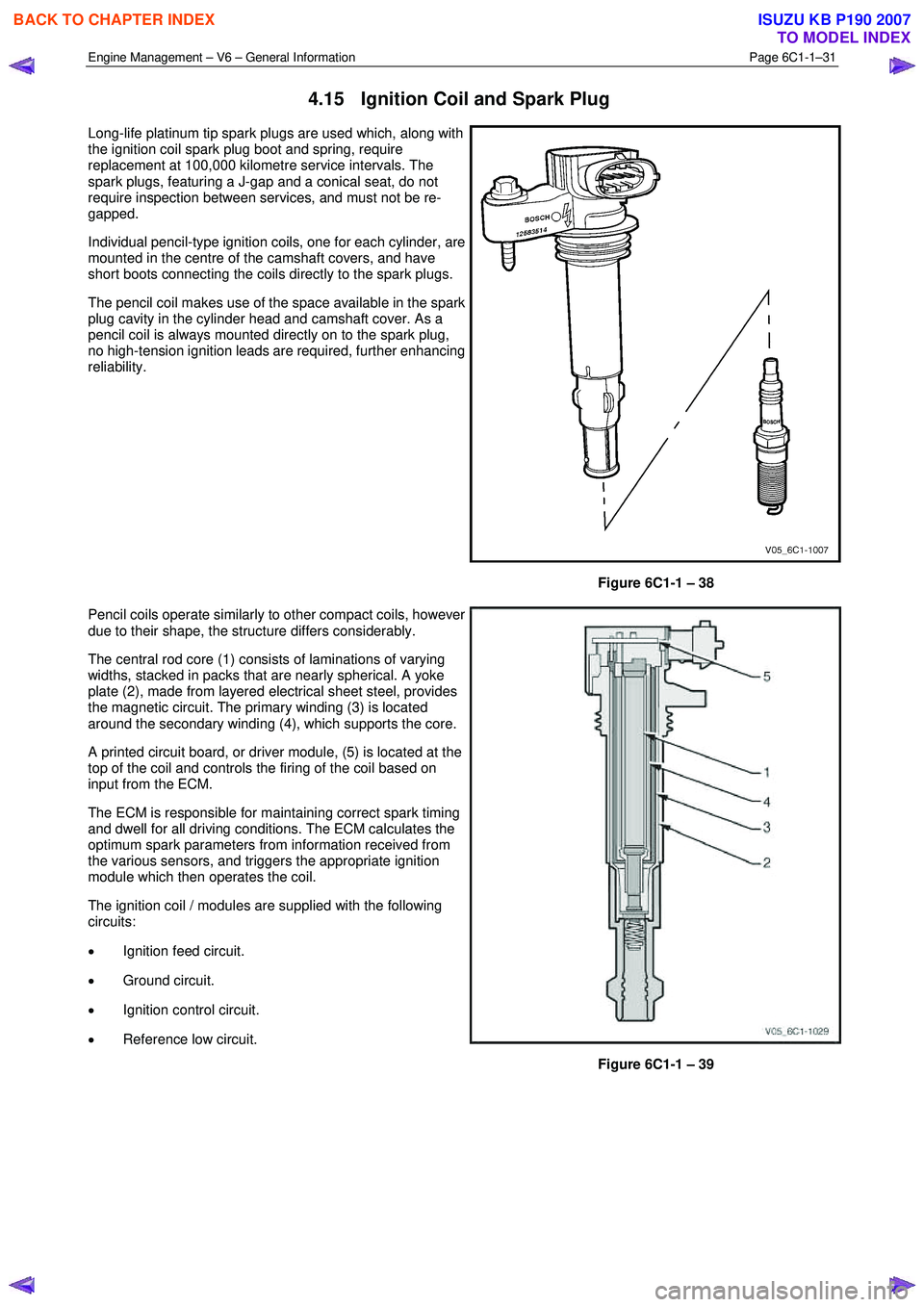
4.15 Ignition Coil and Spark Plug
Long-life platinum tip spark plugs are used which, along with
the ignition coil spark plug boot and spring, require
replacement at 100,000 kilometre service intervals. The
spark plugs, featuring a J-gap and a conical seat, do not
require inspection between services, and must not be re-
gapped.
Individual pencil-type ignition coils, one for each cylinder, are
mounted in the centre of the camshaft covers, and have
short boots connecting the coils directly to the spark plugs.
The pencil coil makes use of the space available in the spark
plug cavity in the cylinder head and camshaft cover. As a
pencil coil is always mounted directly on to the spark plug,
no high-tension ignition leads are required, further enhancing
reliability.
Figure 6C1-1 – 38
Pencil coils operate similarly to other compact coils, however
due to their shape, the structure differs considerably.
The central rod core (1) consists of laminations of varying
widths, stacked in packs that are nearly spherical. A yoke
plate (2), made from layered electrical sheet steel, provides
the magnetic circuit. The primary winding (3) is located
around the secondary winding (4), which supports the core.
A printed circuit board, or driver module, (5) is located at the
top of the coil and controls the firing of the coil based on
input from the ECM.
The ECM is responsible for maintaining correct spark timing
and dwell for all driving conditions. The ECM calculates the
optimum spark parameters from information received from
the various sensors, and triggers the appropriate ignition
module which then operates the coil.
The ignition coil / modules are supplied with the following
circuits:
• Ignition feed circuit.
• Ground circuit.
• Ignition control circuit.
• Reference low circuit.
Figure 6C1-1 – 39
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3303 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–25
Checks Actions
Fuel System
• Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6 – V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check the items that can cause an engine to run lean.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
Ignition System
• Check for an intermittent ignition circuit malfunction.
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System Check the engine for over-heating. Refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
W iring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
Dirty starter motor commutator or brushes can mask the crankshaft position sensor signal.
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to 7C1
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007